Multiple Artificial Neural Networks with Interaction Noise for Estimation of Spatial Categorical Variables
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Method
3. Case Study
3.1. Synthetic Case Study
3.2. Real-World Case Study
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cao, G. Modeling uncertainty in categorical fields. In International Encyclopedia of Geography; Richardson, D., Ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Malden, MA, USA, 2016; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W. Markov chain random fields for estimation of categorical variables. Math. Geol. 2007, 39, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wang, Z.; Guo, J. Theoretical generalization of Markov chain random field from potential function perspective. J. Cent. South Univ. 2016, 23, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.; Kyriakidis, P.C.; Goodchild, M.F. A multinomial logistic mixed model for the prediction of categorical spatial data. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2011, 25, 2071–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Li, J.; Liang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Guo, J.; Jiao, P. Spatial hidden Markov chain models for estimation of petroleum reservoir categorical variables. J. Petrol. Explor. Prod. Technol. 2016, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wang, Z.; Guo, J. Prediction of categorical spatial data via Bayesian updating. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2016, 30, 1426–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y. Advances in artificial neural networks-methodological development and application. Algorithms 2009, 2, 973–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, M.M. Learning in neural spatial interaction models: a statistical perspective. J. Geogr. Syst. 2002, 4, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, M.M. Neural networks: A class of flexible non-linear models for regression and classification. In Handbook of Research Methods and Applications in Economic Geography; Karlsson, C., Andersson, M., Norman, T., Eds.; Edward Elgar: Cheltenham, UK, 2015; pp. 172–192. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, M.M.; Leung, Y. A genetic-algorithms based evolutionary computational neural network for modelling spatial interaction data. Ann. Reg. Sci. 1998, 32, 437–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, M.M.; Reismann, M.; Hlavackova-Schindler, K. Neural network modeling of constrained spatial interaction flows: Design, estimation, and performance issues. J. Reg. Sci. 2003, 43, 35–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Civco, D.L. Artificial neural networks for land-cover classification and mapping. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 1993, 7, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skabar, A. Modeling the spatial distribution of mineral deposits using neural networks. Nat. Resour. Model. 2007, 20, 435–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Openshaw, S.; Openshaw, C. Artificial Intelligence in Geography; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Haykin, S. Neural Networks: A Comprehensive Foundation; Macmillan: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson, P.M.; Tatnall, A.R.L. Introduction neural networks in remote sensing. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1997, 18, 699–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, C.M. Patter Recognition and Machine Learning; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberger, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnan, S. The Tau model for data redundancy and information combination in earth sciences: Theory and application. Math. Geosci. 2008, 40, 705–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyakova, E.I.; Journel, A.G. The Nu expression for probabilistic data integration. Math. Geol. 2007, 39, 715–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, D.; D’Or, D.; Froidevaux, R. An efficient maximum entropy approach for categorical variable prediction. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2011, 62, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, C. Application of transiograms to Markov chain simulation and spatial uncertainty assessment of land-cover classes. GISci. Remote Sens. 2005, 42, 297–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W. Transiogram: a spatial relationship measure for categorical data. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2006, 20, 693–699. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Zhang, C. Linear interpolation and joint model fitting of experimental transiograms for Markov chain simulation of categorical spatial variables. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 821–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goovaerts, P. Geostatistics for Natural Resources Evaluation; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Bel, L.; Allard, D.; Laurent, J.M.; Cheddadi, R.; Bar-Hen, A. CART algorithm for spatial data: Application to environmental and ecological data. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2009, 53, 3082–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strebelle, S. Conditional simulation of complex geological structures using multiple-point statistics. Math. Geol. 2002, 34, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

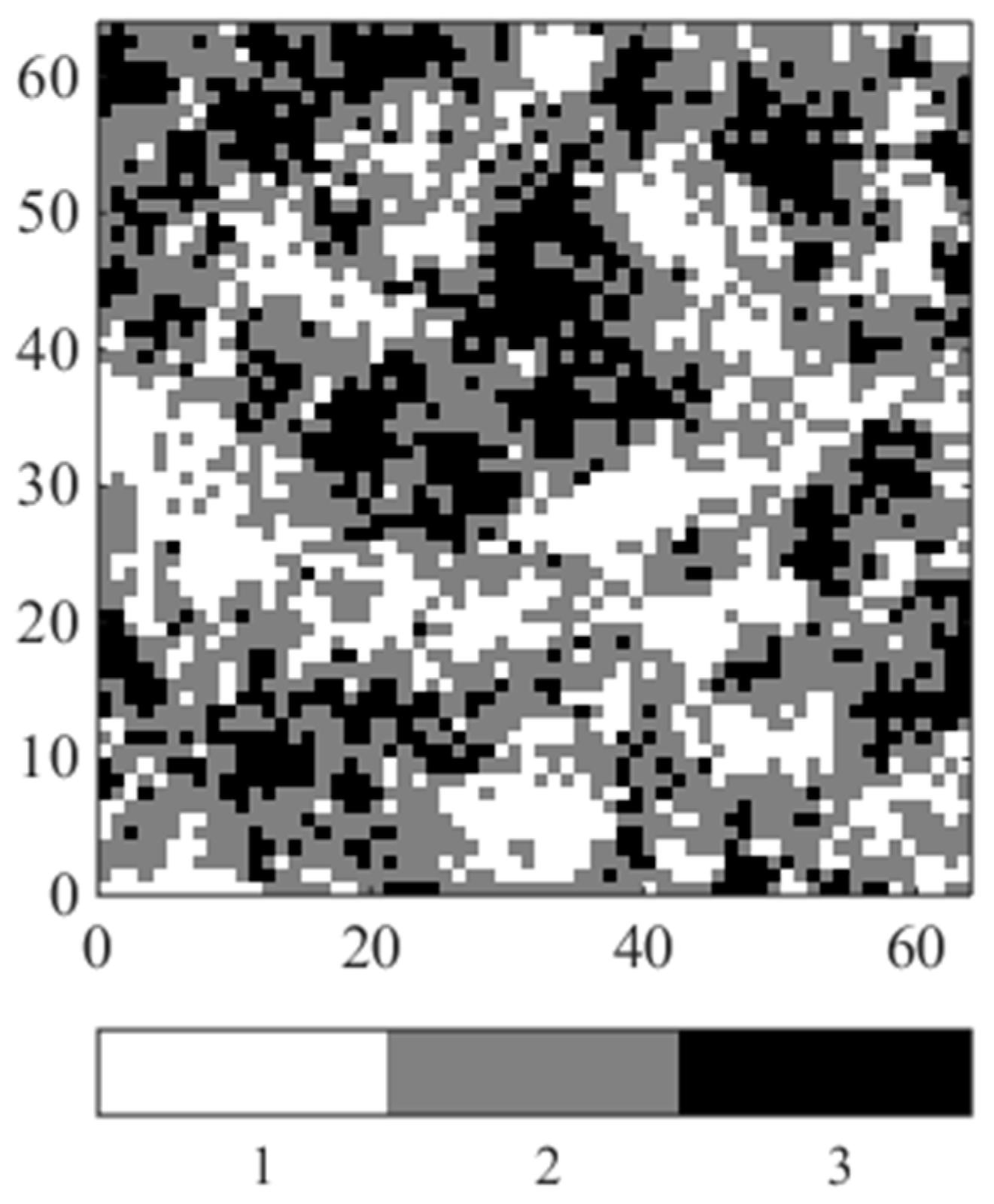
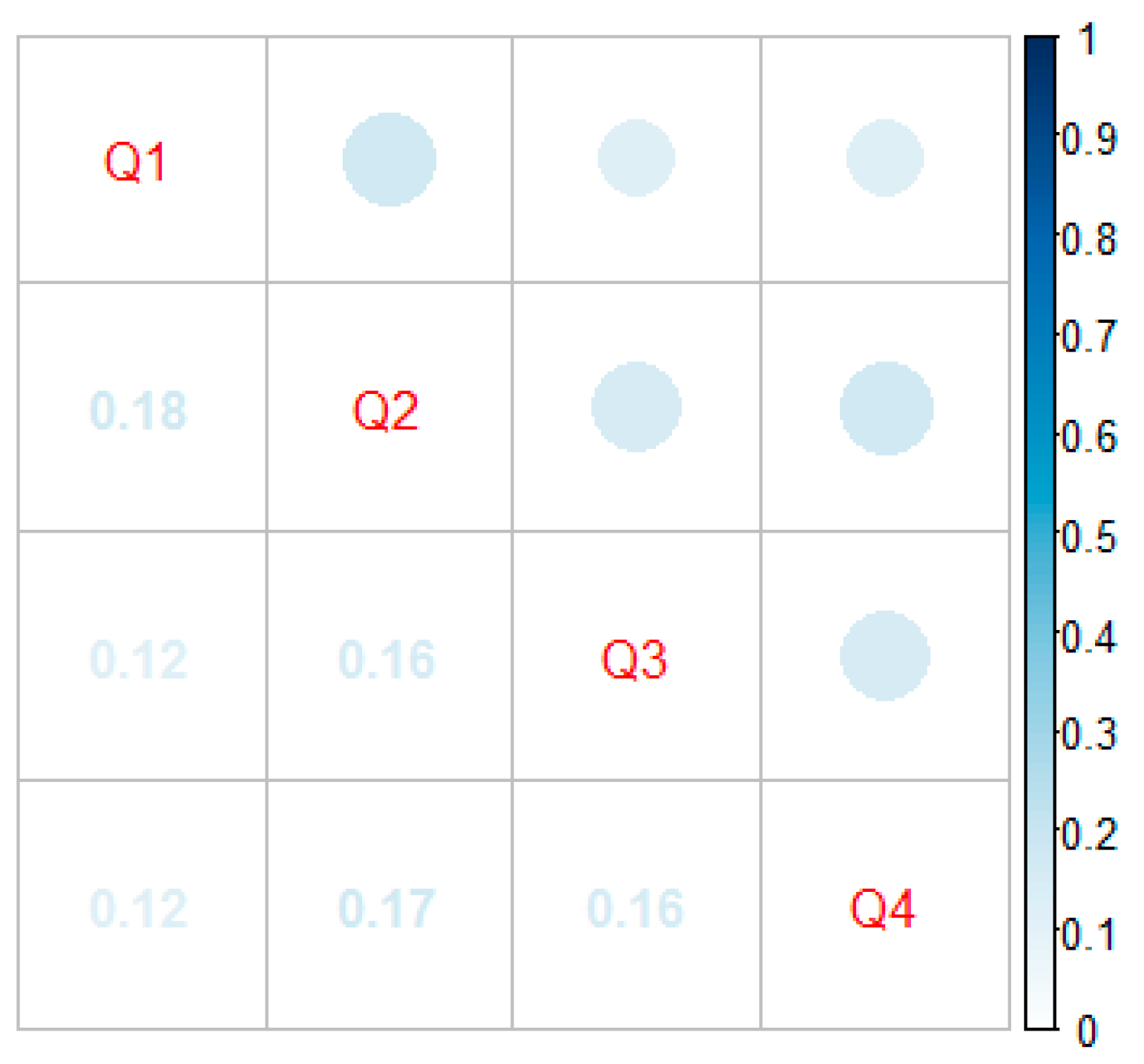
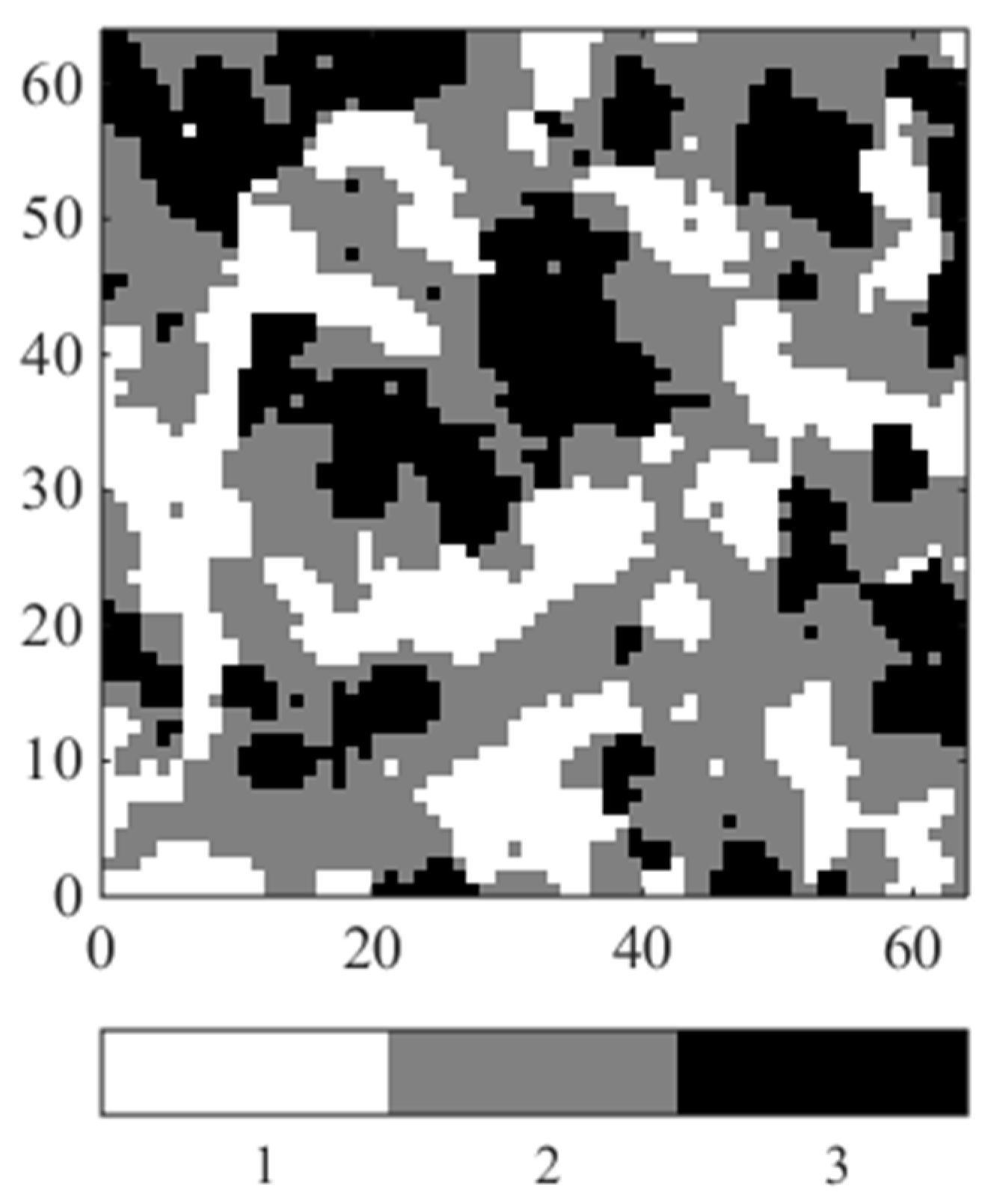
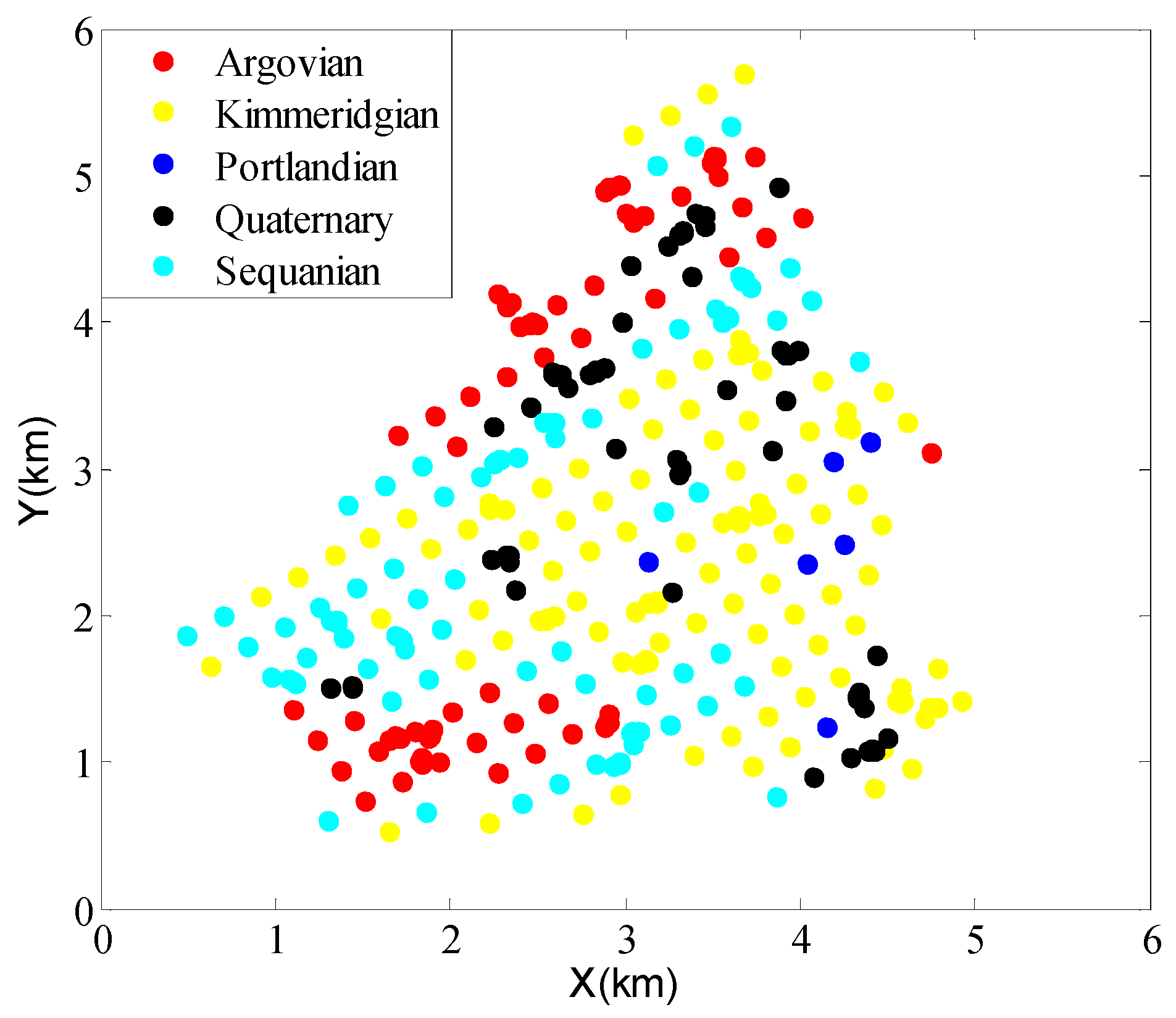
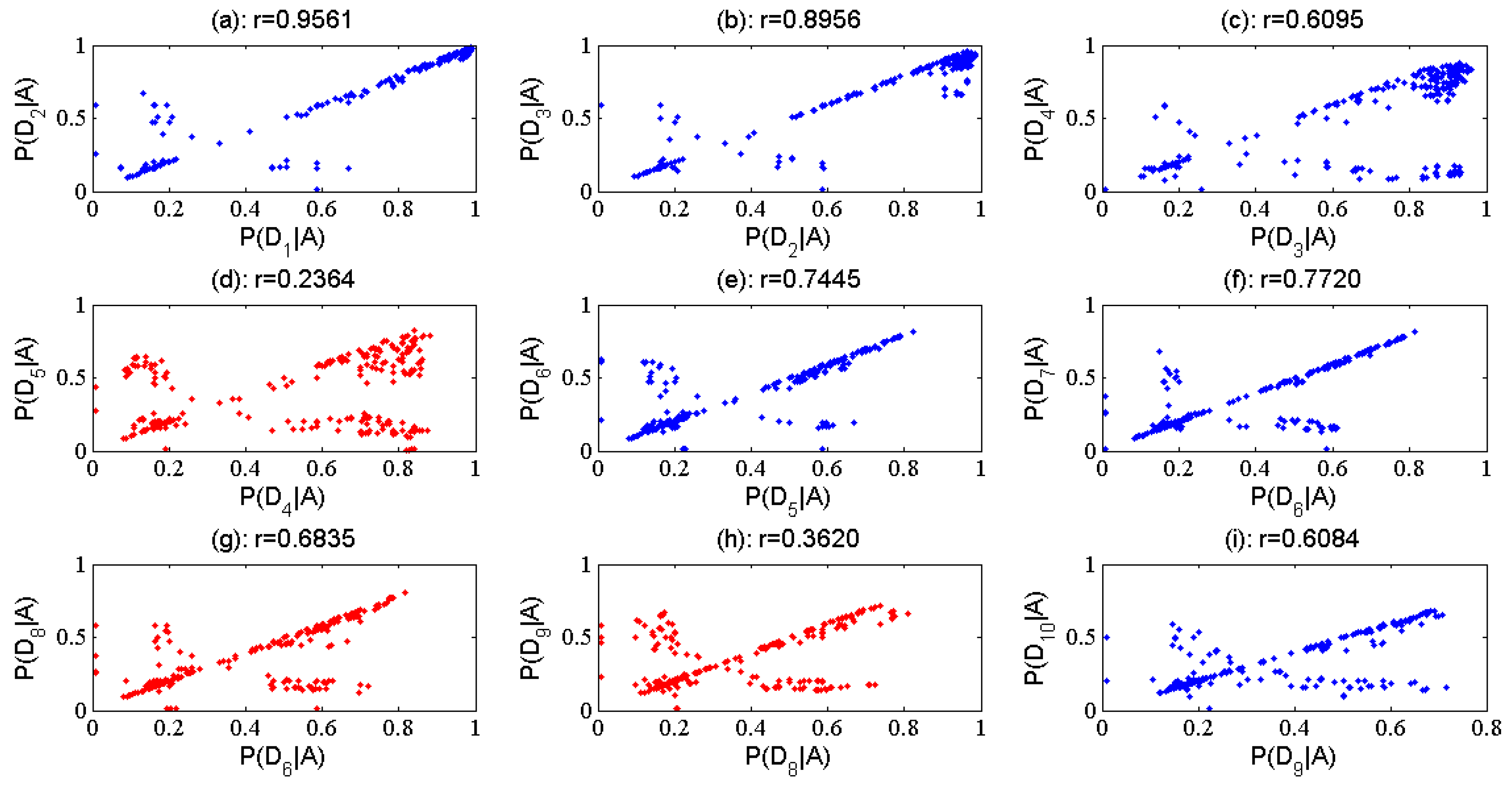
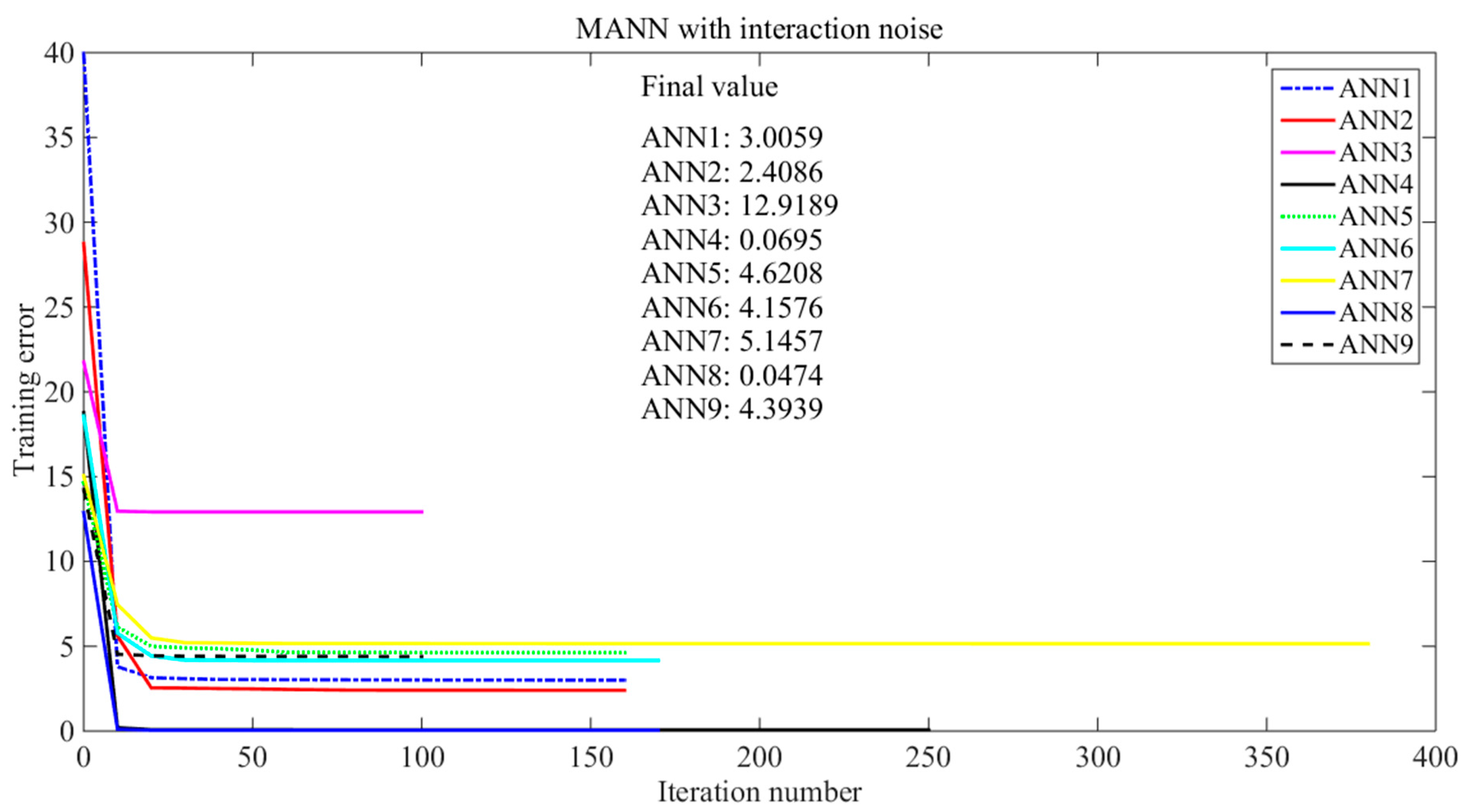

| Parameters | Class 1 | Class 2 | Class 3 | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ; | 58.02% (579/998) | 50.49% (830/1644) | 60.97% (517/848) | 55.19% (1926/3490) |
| ; | 58.62% (585/998) | 50.67% (833/1644) | 60.85% (516/848) | 55.42% (1934/3490) |
| ; | 58.82% (587/998) | 51.03% (839/1644) | 60.02% (509/848) | 55.44% (1935/3490) |
| ; | 57.72% (576/998) | 52.86% (869/1644) | 59.55% (505/848) | 55.87% (1950/3490) |
| ; | 54.91% (548/998) | 56.20% (924/1644) | 57.90% (491/848) | 56.25% (1963/3490) |
| ; | 55.71% (556/998) | 55.90% (919/1644) | 58.37% (495/848) | 56.45% (1970/3490) |
| ; | 52.30% (522/998) | 57.85% (951/1644) | 56.60% (480/848) | 55.96% (1953/3490) |
| ; | 53.51% (534/998) | 57.24% (941/1644) | 57.19% (485/848) | 56.16% (1960/3490) |
| ; | 53.51% (518/998) | 54.01% (888/1644) | 57.08% (484/848) | 54.15% (1890/3490) |
| ; | 50.00% (499/998) | 55.41% (911/1644) | 56.84% (482/848) | 54.21% (1892/3490) |
| MCRF | 57.21% (571/998) | 51.64% (849/1644) | 60.85% (516/848) | 55.47% (1936/3490) |
| Nodes | Weights | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANN1 | ANN2 | ANN3 | ANN4 | ANN5 | ANN6 | ANN7 | ANN8 | ANN9 | |
| b1->h1 | 0.11 | −3.74 | −2.15 | −0.15 | −0.11 | 5.61 | −0.05 | 0.23 | 0.03 |
| i->h1 | 0.66 | 5.64 | 2.54 | −6.28 | 2.04 | −7.38 | 1.97 | −2.48 | −0.54 |
| b1->h2 | 0.03 | 0.65 | −0.53 | 0.29 | 4.02 | 0.56 | 6.08 | 0.24 | 0.53 |
| i->h2 | 0.14 | 0.52 | 1.08 | −1.02 | −4.93 | 2.65 | −7.00 | −2.48 | −0.42 |
| b1->h3 | −5.43 | 0.66 | 1.04 | −3.16 | 0.60 | 0.09 | 0.28 | 0.24 | 2.73 |
| i->h3 | 6.00 | 10.09 | −1.58 | 3.85 | 12.06 | 0.13 | 0.80 | −2.48 | −5.02 |
| b2->o | −0.49 | 2.31 | −0.70 | −0.21 | 4.87 | 0.91 | 1.42 | 2.33 | 0.55 |
| h1->o | −0.75 | 4.81 | 3.05 | −4.61 | 4.83 | −4.12 | 2.18 | −2.87 | 0.62 |
| h2->o | −0.24 | 1.71 | 1.18 | −1.24 | −3.58 | 2.25 | −4.72 | −2.87 | 0.60 |
| h3->o | 6.76 | −5.56 | −2.32 | 4.12 | −5.68 | 0.47 | 1.30 | −2.87 | -2.91 |
| Method | Argovian | Kimmeridgian | Sequanian | Portlandian | Quaternary | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MANN with interaction noise | 75.78% (898/1185) | 78.19% (1592/2036) | 64.07% (1043/1628) | 0.00% (0/316) | 43.69% (346/792) | 65.12% (3879/5957) |
| MCRF | 72.07% (854/1185) | 74.17% (1510/2036) | 61.61% (1003/1628) | 0.00% (0/316) | 47.60% (377/792) | 62.85% (3744/5957) |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, X.; Wang, Z. Multiple Artificial Neural Networks with Interaction Noise for Estimation of Spatial Categorical Variables. Algorithms 2016, 9, 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/a9030056
Huang X, Wang Z. Multiple Artificial Neural Networks with Interaction Noise for Estimation of Spatial Categorical Variables. Algorithms. 2016; 9(3):56. https://doi.org/10.3390/a9030056
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Xiang, and Zhizhong Wang. 2016. "Multiple Artificial Neural Networks with Interaction Noise for Estimation of Spatial Categorical Variables" Algorithms 9, no. 3: 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/a9030056
APA StyleHuang, X., & Wang, Z. (2016). Multiple Artificial Neural Networks with Interaction Noise for Estimation of Spatial Categorical Variables. Algorithms, 9(3), 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/a9030056






