Visual and Textual Sentiment Analysis of a Microblog Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Methods
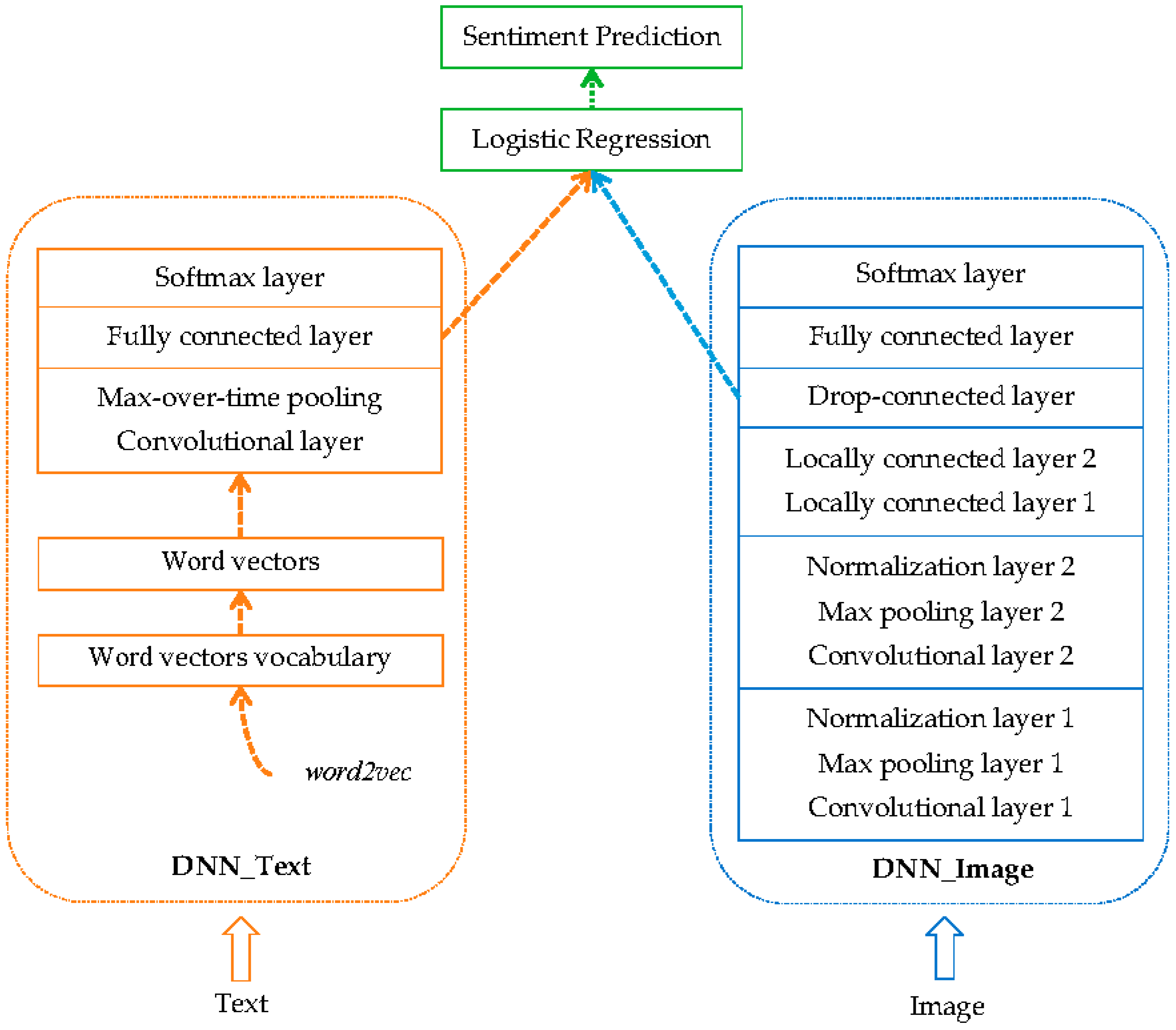
3.1. Textual Features
3.2. Visual Features
3.3. Fusion
4. Experiments
4.1. Dataset
4.2. Baselines
4.3. Experimental Results and Discussion
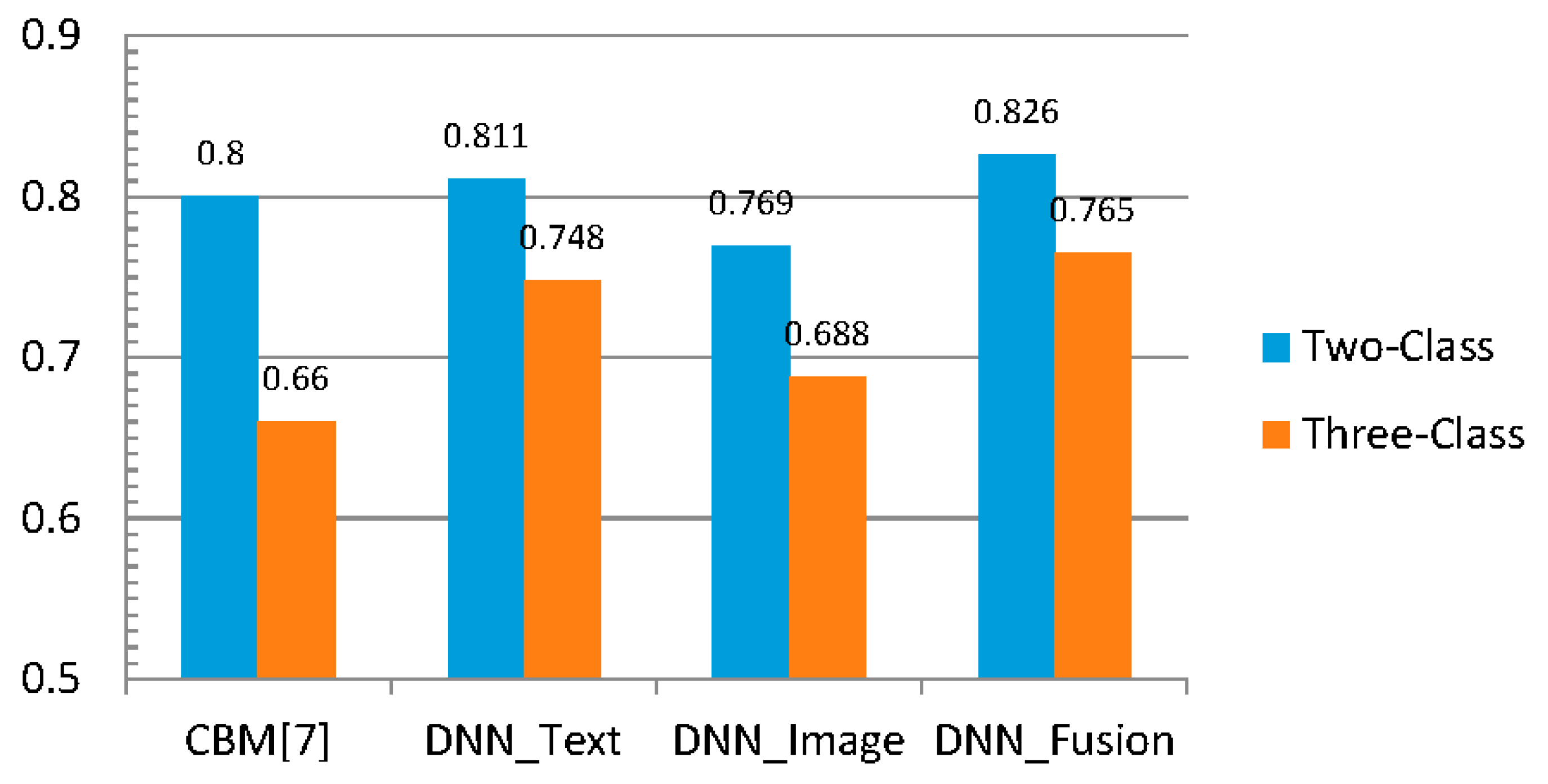
4.3.1. Textual Sentiment Analysis
4.3.2. Visual Sentiment Analysis
4.3.3. Multi-Modality Sentiment Analysis
4.4. Error Analysis
- First, emerging Chinese cyberspeak—the shorthand language used on the Internet, increases the difficulty of understanding text, especially when the intent of the symbols differs from their literal meaning.
- Second, film review fragments out of context make textual sentiment prediction more difficult.
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CNN | Convolutional neural network |
| DNN | Deep convolutional neural network |
| VSO | Visual Sentiment Ontology |
| ANPs | Adjective-Noun Pairs |
| NLP | Natural language processing |
References
- Cambria, E. Affective computing and sentiment analysis. IEEE Intell. Syst. 2016, 31, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strapparava, C.; Valitutti, A. WordNet Affect: An Affective Extension of WordNet. In Proceedings of the LREC, Lisbon, Portugal, 26–28 May 2004.
- Esuli, A.; Sebastiani, F. Sentiwordnet: A publicly available lexical resource for opinion mining. In Proceedings of the LREC; Citeseer: Genoa, Italy, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Cambria, E.; Olsher, D.; Rajagopal, D. SenticNet 3: A common and common-sense knowledge base for cognition-driven sentiment analysis. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Eighth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Québec, QC, Canada, 27–31 July 2014.
- Cambria, E.; Fu, J.; Bisio, F.; Poria, S. AffectiveSpace 2: Enabling Affective Intuition for Concept-Level Sentiment Analysis. In Proceedings of the AAAI, Austin, TX, USA, 25–30 January 2015.
- Cambria, E.; White, B. Jumping NLP curves: A review of natural language processing research [review article]. IEEE Comp. Intell. Mag. 2014, 9, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y. Convolutional neural networks for sentence classification. 2014; arXiv preprint. arXiv:1408.5882. [Google Scholar]
- dos Santos, C.N.; Gatti, M. Deep convolutional neural networks for sentiment analysis of short texts. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Computational Linguistics (COLING), Dublin, Ireland, 23–29 August 2014.
- Mesnil, G.; Mikolov, T.; Ranzato, M.; Bengio, Y. Ensemble of Generative and Discriminative Techniques for Sentiment Analysis of Movie Reviews. 2014; arXiv preprint. arXiv:1412.5335. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Cetintas, S.; Lee, K.-C.; Li, L.-J. Visual Sentiment Prediction with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. 2014; arXiv preprint. arXiv:1411.5731. [Google Scholar]
- Cambria, E.; Hussain, A. Sentic Computing: A Common-Sense-Based Framework For Concept-Level Sentiment Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Cambria, E.; Poria, S.; Bisio, F.; Bajpai, R.; Chaturvedi, L. The CLSA model: A novel framework for concept-level sentiment analysis. In Computational Linguistics and Intelligent Text Processing, Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Intelligent Text Processing and Computational Linguistics, Cairo, Egypt, 14–20 April 2015; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 3–22. [Google Scholar]
- Chikersal, P.; Poria, S.; Cambria, E. SeNTU: Sentiment analysis of tweets by combining a rule-based classifier with supervised learning. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation, (Semeval 2015), Denver, CO, USA, 31 May–5 June 2015.
- Chikersal, P.; Poria, S.; Cambria, E.; Gelbukh, A.; Siong, C.E. Modelling public sentiment in Twitter: Using linguistic patterns to enhance supervised learning. In Computational Linguistics and Intelligent Text Processing, Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Intelligent Text Processing and Computational Linguistics, Cairo, Egypt, 14–20 April 2015; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 49–65. [Google Scholar]
- Maynard, D.; Dupplaw, D.; Hare, J. Multimodal sentiment analysis of social media. In Proceedings of the BCS SGAI Workshop on Social Media Analysis, Cambridge, UK, 10 December 2013.
- Rosas, V.P.; Mihalcea, R.; Morency, L.-P. Multimodal sentiment analysis of spanish online videos. IEEE Intell. Syst. 2013, 28, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poria, S.; Cambria, E.; Howard, N.; Huang, G.-B.; Hussain, A. Fusing audio, visual and textual clues for sentiment analysis from multimodal content. Neurocomputing 2016, 174, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poria, S.; Cambria, E.; Hussain, A.; Huang, G.-B. Towards an intelligent framework for multimodal affective data analysis. Neural Net. 2015, 63, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poria, S.; Cambria, E.; Gelbukh, A. Deep convolutional neural network textual features and multiple kernel learning for utterance-level multimodal sentiment analysis. In Proceedings of the EMNLP, Lisbon, Portugal, 17–21 September 2015.
- Poria, S.; Huang, G.; Gelbukh, A.; Cambria, E.; Hussain, A.W.; Huang, B. EmoSenticSpace: A novel framework for affective common-sense reasoning. Knowl. Based Syst. 2014, 69, 108–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.H.; Pádua, F.L.; Pereira, A.; Benevenuto, F.; Dalip, D.H. Fusing Audio, Textual and Visual Features for Sentiment Analysis of News Videos. In Proceedings of the International AAAI Conference on Web and Social Media, Cologne, Germany, 17–20 May 2016.
- You, Q.; Luo, J.; Jin, H.; Yang, J. Joint Visual-Textual Sentiment Analysis with Deep Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 23rd Annual ACM Conference on Multimedia Conference, Brisbane, Australia, 26–30 Octorber 2015; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Cao, D.; Li, L.; Li, S.; Ji, R. Microblog Sentiment Analysis Based on Cross-media Bag-of-words Model. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Internet Multimedia Computing and Service, Xiamen, China, 10–12 July 2014; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, D.; Ji, R.; Lin, D.; Li, S. Visual sentiment topic model based microblog image sentiment analysis. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2014, 73, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Ji, R.; Lin, D.; Li, S. A cross-media public sentiment analysis system for microblog. Multimed. Syst. 2014, 71, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Zeiler, M.; Zhang, S.; Cun, Y.L.; Fergus, R. Regularization of neural networks using dropconnect. In Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML-13), Atlanta, GA, USA, 16–21 June 2013.
- Collobert, R.; Weston, J.; Bottou, L.; Karlen, M.; Kavukcuoglu, K.; Kuksa, P. Natural language processing (almost) from scratch. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2493–2537. [Google Scholar]
- Mikolov, T.; Chen, K.; Corrado, G.; Dean, J. Efficient estimation of word representations in vector space. 2013; arXiv preprint. arXiv:1301.3781. [Google Scholar]
- Mikolov, T.; Sutskever, I.; Chen, K.; Corrado, G.S.; Dean, J. Distributed representations of words and phrases and their compositionality. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 26, Carson, NV, USA, 5–10 December 2013.
- Mikolov, T.; Yih, W.-T.; Zweig, G. Linguistic Regularities in Continuous Space Word Representations. In Proceedings of the HLT-NAACL, Atlanta, GA, USA, 9–14 June 2013.
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 25, Carson, NV, USA, 3–6 December 2012.
- Borth, D.; Ji, R.; Chen, T.; Breuel, T.; Chang, S.F. Large-scale visual sentiment ontology and detectors using adjective noun pairs. In Proceedings of the 21st ACM international conference on Multimedia, Barcelona, Spain, 21–25 Octorber 2013; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Borth, D.; Darrell, T.; Chang, S.F. Deepsentibank: Visual sentiment concept classification with deep convolutional neural networks. 2014; arXiv preprint. arXiv:1410.8586. [Google Scholar]
- Zeiler, M.D. ADADELTA: An adaptive learning rate method. 2012; arXiv preprint. arXiv:1212.5701. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Lin, H.; Yu, Q.; Meng, J.; Zhao, Z.; Li, Y.; Zuo, L. Modality classification for medical images using multiple deep convolutional neural networks. J. Comput. Inf. Syst. 2015, 11, 5403–5413. [Google Scholar]

| Type | CBM_Text [23] | DNN_W2V_Phrase | DNN_W2V_Char | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 | |||
| Two-Class | 0.76 | 0.793 | 0.811 | 0.894 | 0.872 | 0.883 |
| Three-Class | 0.65 | 0.720 | 0.748 | - | - | - |
| Type | CBM_Image [23] | DNN_Image | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 | ||
| Two-Class | <0.725 | 0.763 | 0.955 | 0.747 | 0.838 |
| Three-Class | <0.66 | 0.688 | - | - | - |
| Type | CBM_Fusion [23] | DNN_Fusion | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 | ||
| Two-Class | 0.80 | 0.826 | 0.954 | 0.838 | 0.89 |
| Three-Class | 0.66 | 0.765 | - | - | - |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, Y.; Lin, H.; Meng, J.; Zhao, Z. Visual and Textual Sentiment Analysis of a Microblog Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Algorithms 2016, 9, 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/a9020041
Yu Y, Lin H, Meng J, Zhao Z. Visual and Textual Sentiment Analysis of a Microblog Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Algorithms. 2016; 9(2):41. https://doi.org/10.3390/a9020041
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Yuhai, Hongfei Lin, Jiana Meng, and Zhehuan Zhao. 2016. "Visual and Textual Sentiment Analysis of a Microblog Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks" Algorithms 9, no. 2: 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/a9020041
APA StyleYu, Y., Lin, H., Meng, J., & Zhao, Z. (2016). Visual and Textual Sentiment Analysis of a Microblog Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Algorithms, 9(2), 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/a9020041






