Pressure Model of Control Valve Based on LS-SVM with the Fruit Fly Algorithm
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. LS-SVM Upstream Pressure Model of Control Valve
2.1. Physical Model of the Upstream Pressure of Control Valve
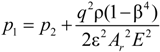
2.2. Introduction to LS-SVM



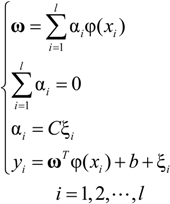


3. Influence of the LS-SVM Parameters on Identification Performance
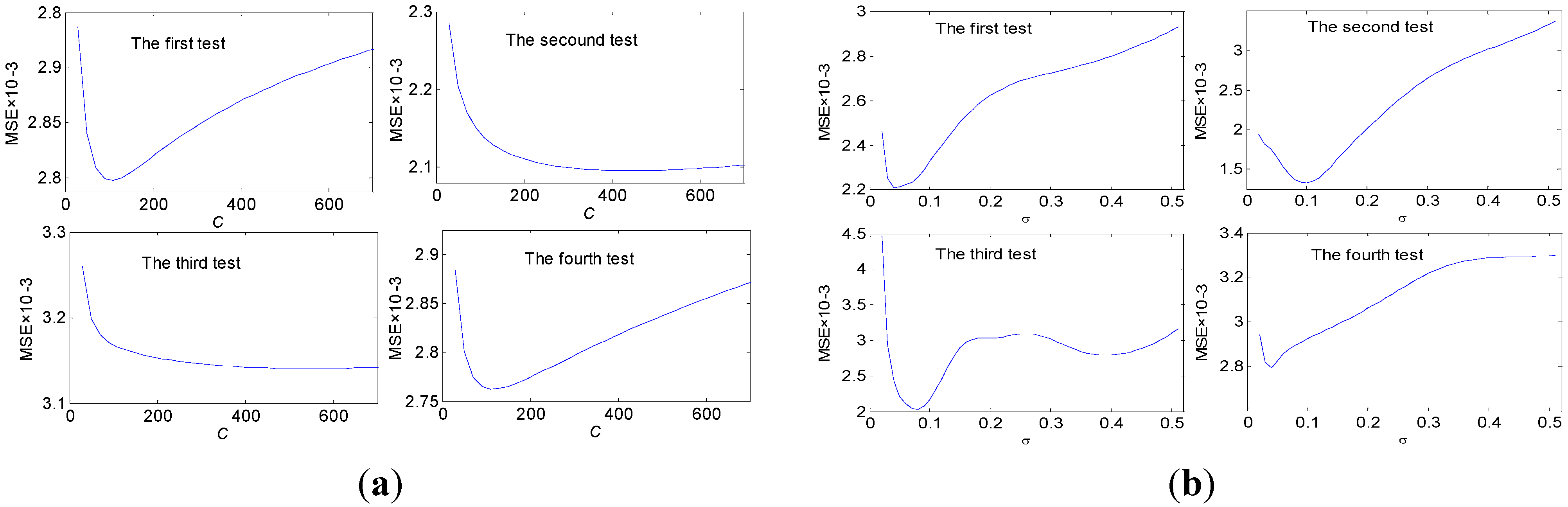
| Test Number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Optimal C (σ = 0.04) | 110 | 430 | 550 | 110 |
| Optimal σ (C = 200) | 0.04 | 0.10 | 0.8 | 0.04 |
4. Optimize Parameters of LS-SVM Employing Fruit Fly Optimization Algorithm
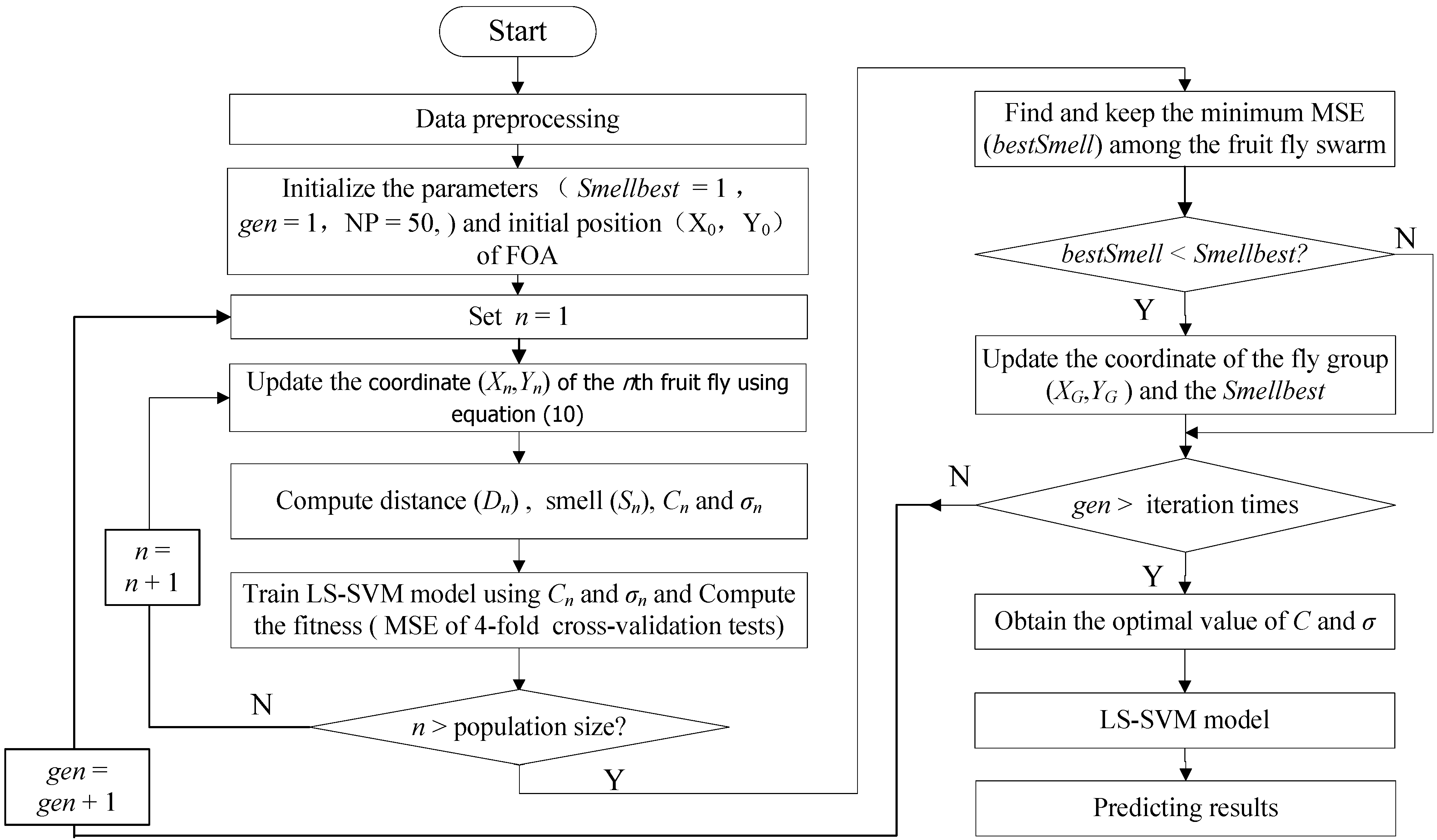


5. Modeling Design of LS-SVM Based on FOA and Simulation Test
5.1. Sampling Data
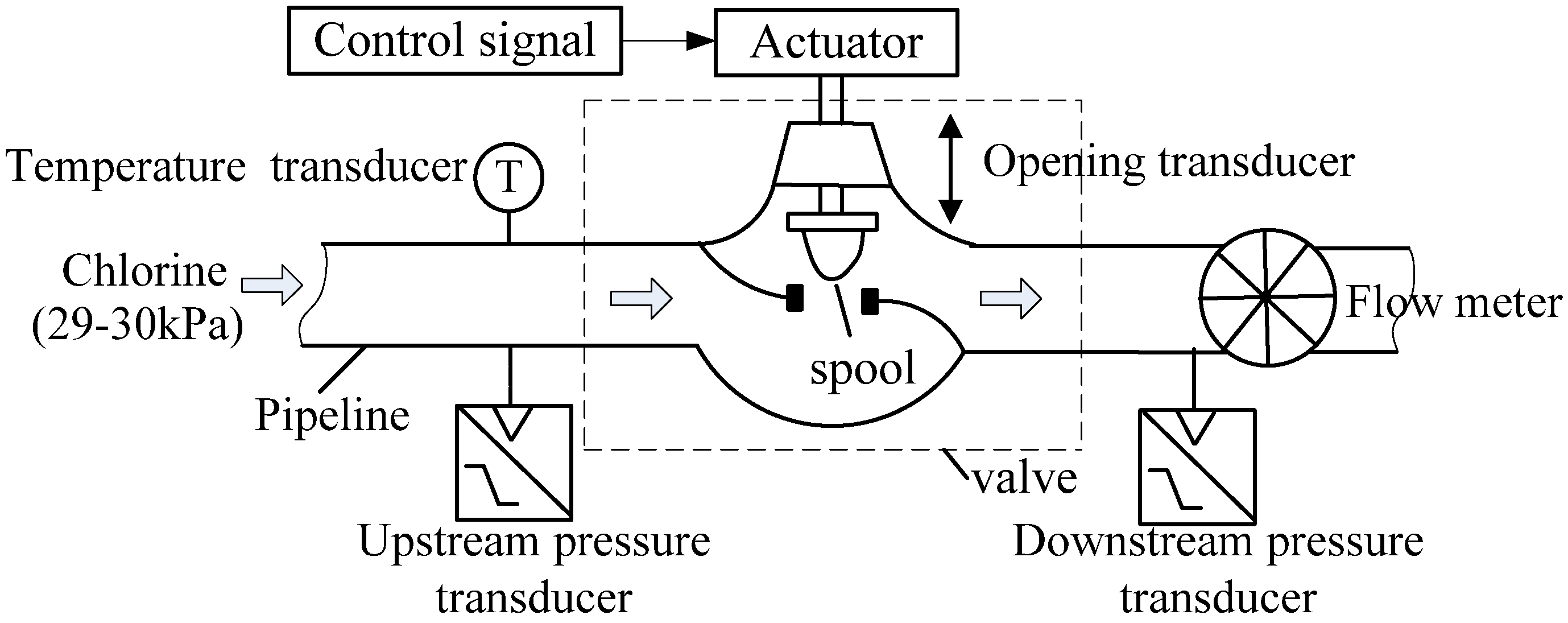
| Factor | Max | Min | Avg | Std |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| flow rate (Nm3/h) | 3666.3 | 1068.9 | 2256.3 | 920.6342 |
| Opening (%) | 61.9 | 36.2 | 48.2 | 8.6493 |
| upstream pressure(kPa) | 22.81 | 16.64 | 19.75 | 1.9464 |
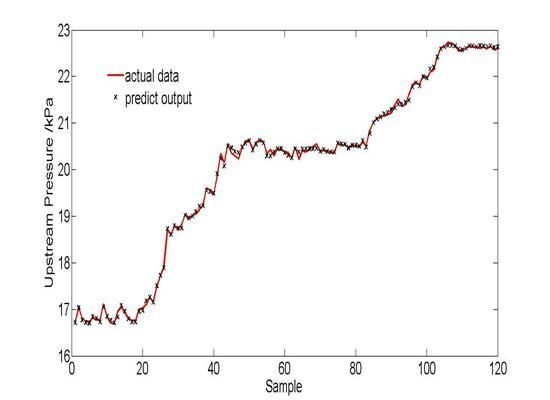
5.2. Simulation Result and Analysis
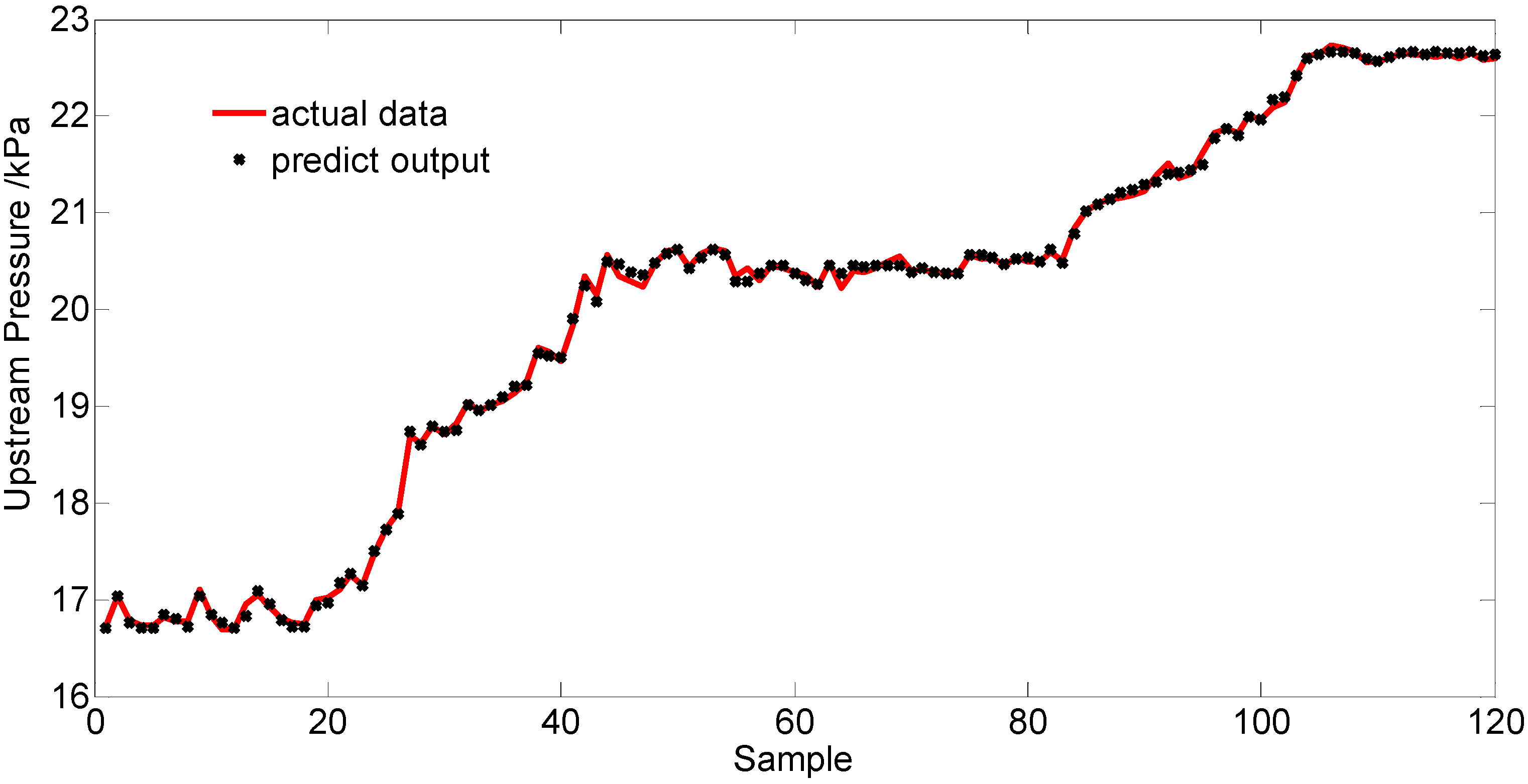
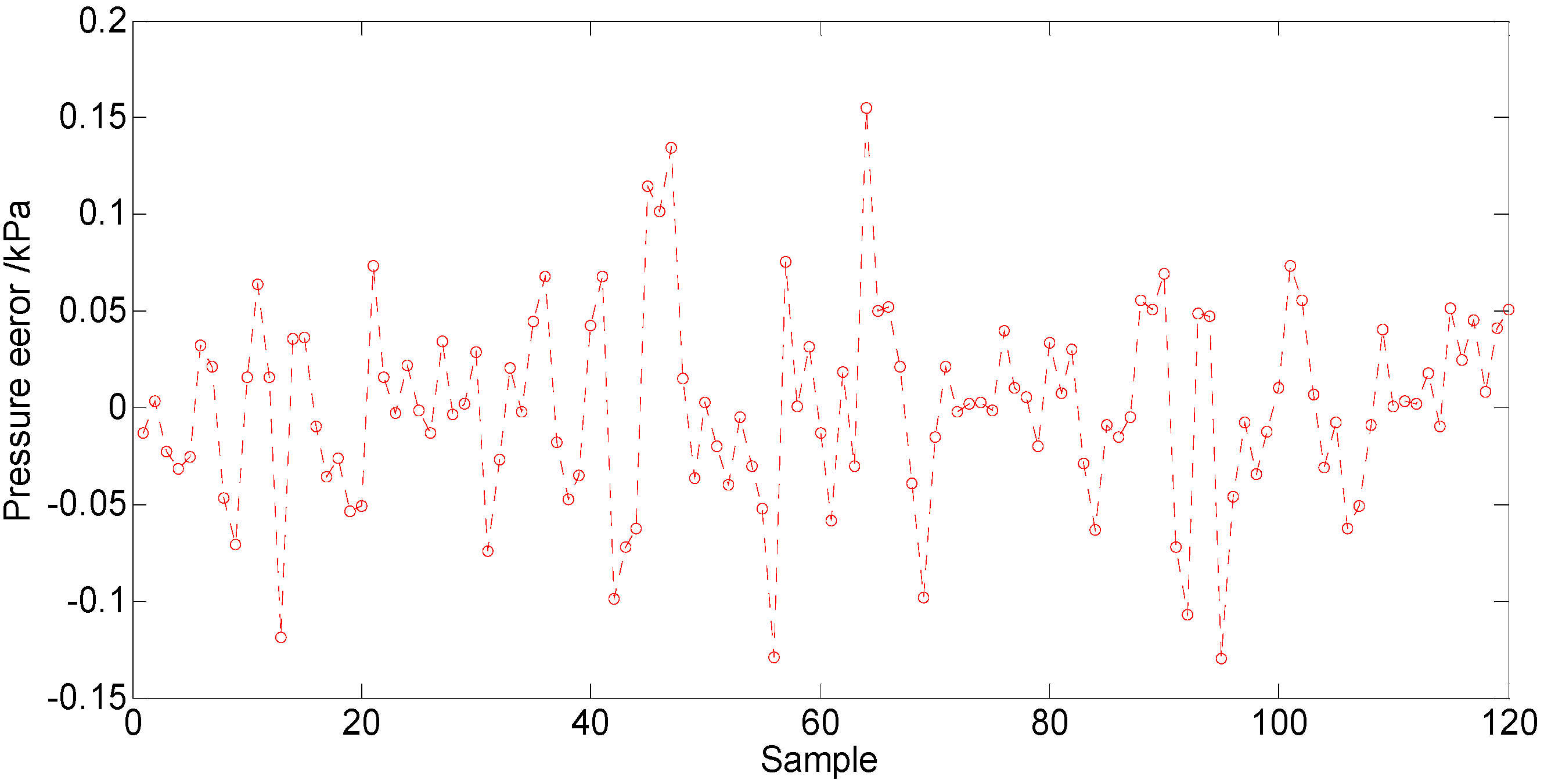
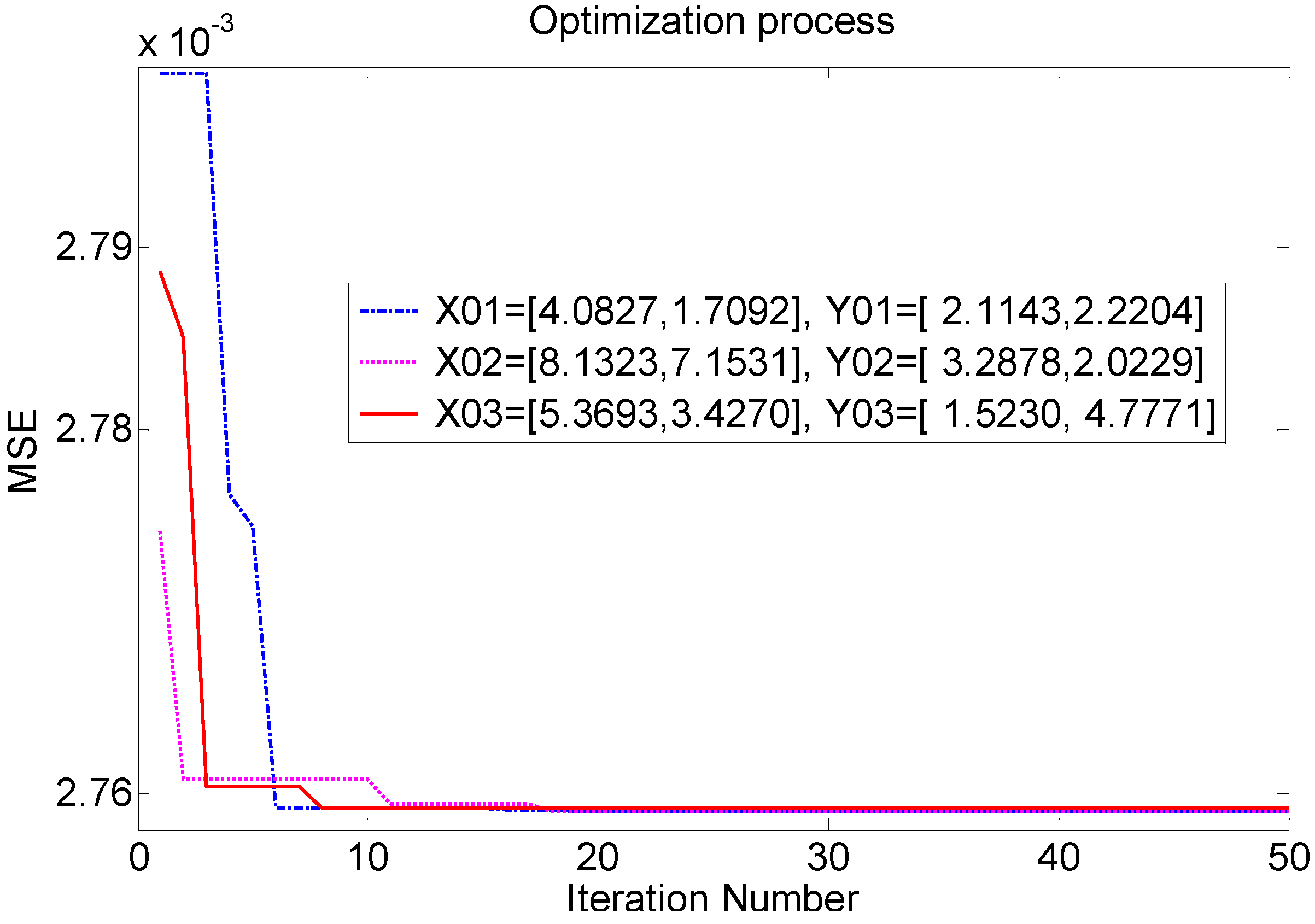
| No. | X0 | Y0 | C | σ | t/s | MSE/×10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | [4.0827,1.7092] | [2.1143,2.2204] | 91.6280 | 0.0367 | 37.6 | 2.8696 |
| 2 | [8.1323,7.1531] | [3.2878,2.0229] | 92.0664 | 0.0368 | 32.5 | 2.8696 |
| 3 | [5.3693,3.4270] | [1.5230,4.7771] | 93.1784 | 0.0373 | 33.0 | 2.8697 |
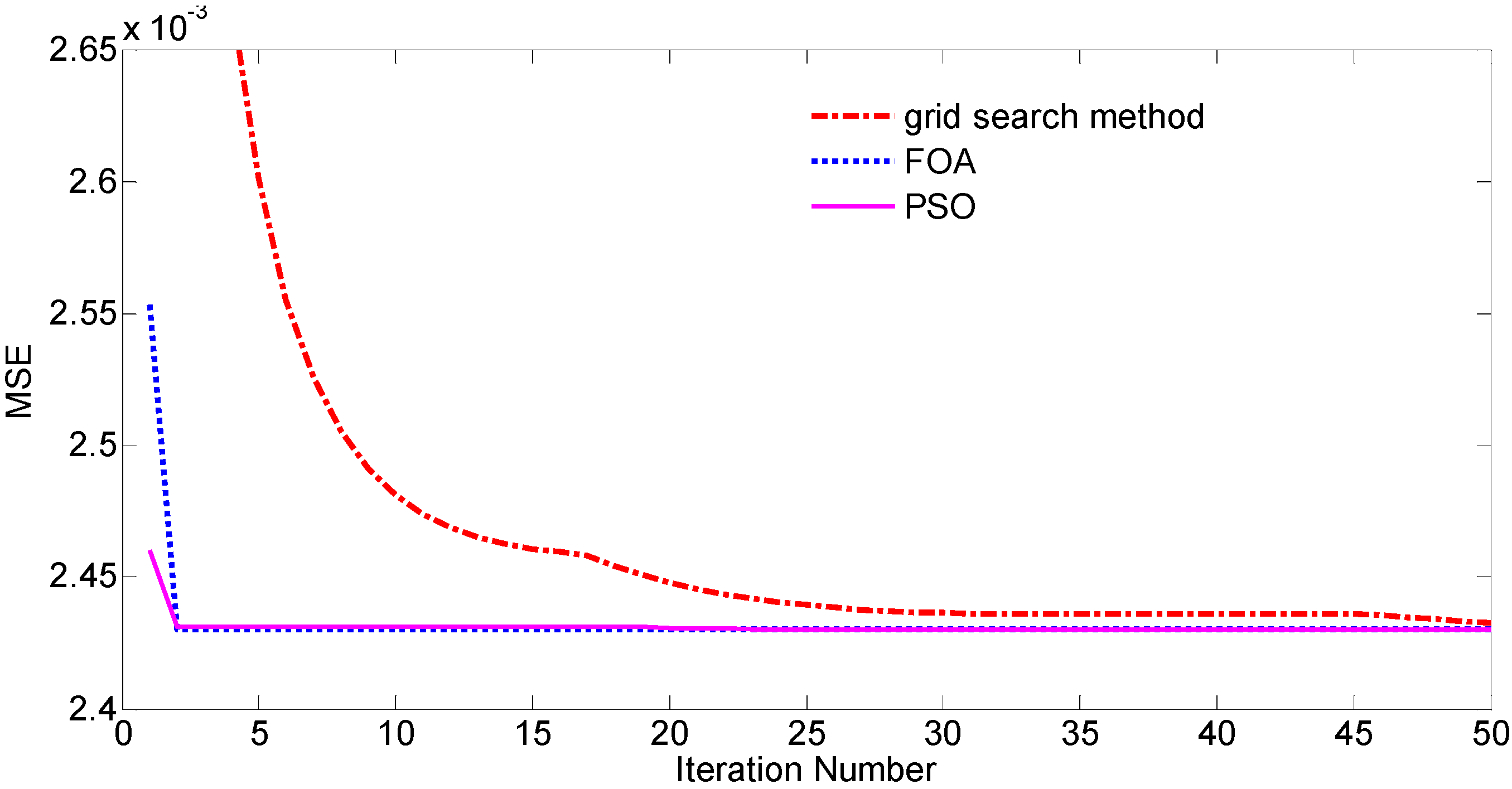
| Optimization Method | MSE/×10−3 | MAPE/% | MSE/×10−3kPa | Error Range/kPa | t/s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FOA | 2.474 | 0.1896 | 0.808 | [−0.69, 0.77] | 27.253 |
| PSO | 2.462 | 0.1888 | 1.043 | [−0.71, 0.76] | 43.649 |
| Grid Search | 2.497 | 0.1906 | 1.024 | [−0.71, 0.77] | 50.451 |
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Y.-S.; Lei, S.-X.; Wu, D.-F. Design and experimental research on a seawater hydraulic flow control valve with pressure compensation. China Mech. Eng. 2007, 12, 1448–1452. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.-G.; Tan, Y.-Q. Dynamic performance simulation and optimization of speed ratio control valve in continuously variable transmission. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2010, 3, 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta, K.; Watton, J. Modelling and dynamics of a two-stage pressure rate controllable relief valve: A bondgraph approach. Int. J. Model. Simul. 2008, 28, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.-W.; Wang, F.-J.; Jia, Z.-Y.; Wei, W.-L. Using support vector machine for characteristics prediction of hydraulic valve. Int. J. Comput. Appl. Technol. 2011, 41, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helling, A.; van Schoor, G.; Helberg, A. Data acquisition system for capturing dynamic transients in a control valve. In Proceedings of the 7th AFRICON Conference in Africa, Gaborone, Botswana, 15–17 September 2004; Volume 2, pp. 1059–1064.
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-vector networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gestel, T.; Suykens, J.A.K.; Baesens, B.; Viaene, S.; Vanthienen, J.; Dedene, G.; de Moor, B.; Vandewalle, J. Benchmarking least squares support vector machine classifiers. Mach. Learn. 2001, 54, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.-M.; Wong, P.-K.; Li, Y.-P. Prediction of automotive engine power and torque using least squares support vector machines and Bayesian inference. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2006, 19, 277–287. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.; Tao, J.-G.; Zhang, X.-X.; Liu, F. Multiple SVM-RFE for feature subset selection in partial sischarge pattern recognition. Int. Rev. Electr. Eng. 2012, 7, 5240–5246. [Google Scholar]
- Yeganeha, B.; Motlagh, S.P.M.; Rashidi, Y.; Kamalan, H. Prediction of CO concentrations based on a hybrid partial least square and support vector machine model. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 55, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, R.-J.; Zheng, H.-B.; Grzybowski, S.; Yang, L.-J. Particle swarm optimization-least squares support vector regression based forecasting model on dissolved gases in oil-filled power transformers. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2011, 81, 2074–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.-H.; Wang, G.; Zhao, K.-K.; Tan, D.-J. On-line least squares support vector machine algorithm in gas prediction. Mining Sci. Technol. 2009, 19, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q. Hybrid model based on wavelet support vector machine and modified genetic algorithm penalizing Gaussian noises for power load forecasts. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza, M.; Suykens, J.A.K.; de Moor, B. Fixed-size least squares support vector machines: A large Scale application in electrical load forecasting. Comput. Manag. Sci. 2006, 3, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza, M.; Suykens, J.A.K.; Belmans, R.; de Moor, B. Electric load forecasting-Using kernel based modeling for nonlinear system identification. IEEE Control Syst. 2007, 27, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.-P.; Pai, P.-F.; Lu, Y.-M.; Chang, P.T. Revenue forecasting using a least-squares support vector regression model in a fuzzy environment. Inf. Sci. 2013, 220, 196–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisi, O.; Cimen, M. Precipitation forecasting by using wavelet-support vector machine conjunction model. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2012, 25, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.-Y.; Shi, J.; Li, G. Fine tuning support vector machines for short-term wind speed forecasting, Energy Convers. Energy Convers. Manag. 2011, 52, 1990–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yu, L.; Tang, L.; Wang, S.-Y. A novel seasonal decomposition based least squares support vector regression ensemble learning approach for hydropower consumption forecasting in China. Energy 2011, 36, 6542–6554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santosa, G.S.; Justi Luvizottob, L.G.; Marianib, V.C.; Dos Santos, L.C. Least squares support vector machines with tuning based on chaotic differential evolution approach applied to the identification of a thermal process. Expert Syst. Appl. 2012, 39, 4805–4812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaimana, M.H.; Mustafab, M.W.; Shareefc, H. An application of artificial bee colony algorithm with least squares supports vector machine for real and reactive power tracing in deregulated power system. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2012, 37, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pa, P.-F.; Hong, W.-C. Support vector machines with simulated annealing algorithms in electricity load forecasting. Energy Convers. Manag. 2005, 46, 2669–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.-T. A new fruit fly optimization algorithm: Taking the financial distress model as an example. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2012, 26, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Wang, P.; Yang, X. Tuning of PID controller based on fruit fly optimization algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation (ICMA), Chengdu, China, 5–8 August 2012; pp. 409–413.
- Li, H.; Guo, S.; Zhao, H.-R.; Su, C.B.; Wang, B. Annual electric load forecasting by a least squares support vector machine with a fruit fly optimization algorithm. Energies 2012, 5, 4430–4445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Guo, S.; Li, C.; Sun, J. A hybrid annual power load forecasting model based on generalized regression neural network with fruit fly optimization algorithm. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2013, 37, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.-M. Analysis of service satisfaction in web auction logistics service using a combination of fruit fly optimization algorithm and general regression neural network. Neural Comput. Appl. 2013, 22, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.-Q.; Qiu, X.-Z.; Yang, J.; Yang, W.-G. Control Valve Engineering Design and Application; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2005; pp. 71–73. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.-L.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.-Y. A novel fruit fly optimization algorithm for the semiconductor final testing scheduling problem. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2014, 57, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.-F.; Dai, X.-S.; Zhao, J.-Y.; He, Q. On a novel multi-swarm fruit fly optimization algorithm and its application. Appl. Math. Comput. 2014, 233, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Aiqin, H.; Yong, W. Pressure Model of Control Valve Based on LS-SVM with the Fruit Fly Algorithm. Algorithms 2014, 7, 363-375. https://doi.org/10.3390/a7030363
Aiqin H, Yong W. Pressure Model of Control Valve Based on LS-SVM with the Fruit Fly Algorithm. Algorithms. 2014; 7(3):363-375. https://doi.org/10.3390/a7030363
Chicago/Turabian StyleAiqin, Huang, and Wang Yong. 2014. "Pressure Model of Control Valve Based on LS-SVM with the Fruit Fly Algorithm" Algorithms 7, no. 3: 363-375. https://doi.org/10.3390/a7030363
APA StyleAiqin, H., & Yong, W. (2014). Pressure Model of Control Valve Based on LS-SVM with the Fruit Fly Algorithm. Algorithms, 7(3), 363-375. https://doi.org/10.3390/a7030363