Extraction and Segmentation of Sputum Cells for Lung Cancer Early Diagnosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Works
3. Cell Extraction
3.1. Sputum Cell Detection
3.1.1. Threshold Technique
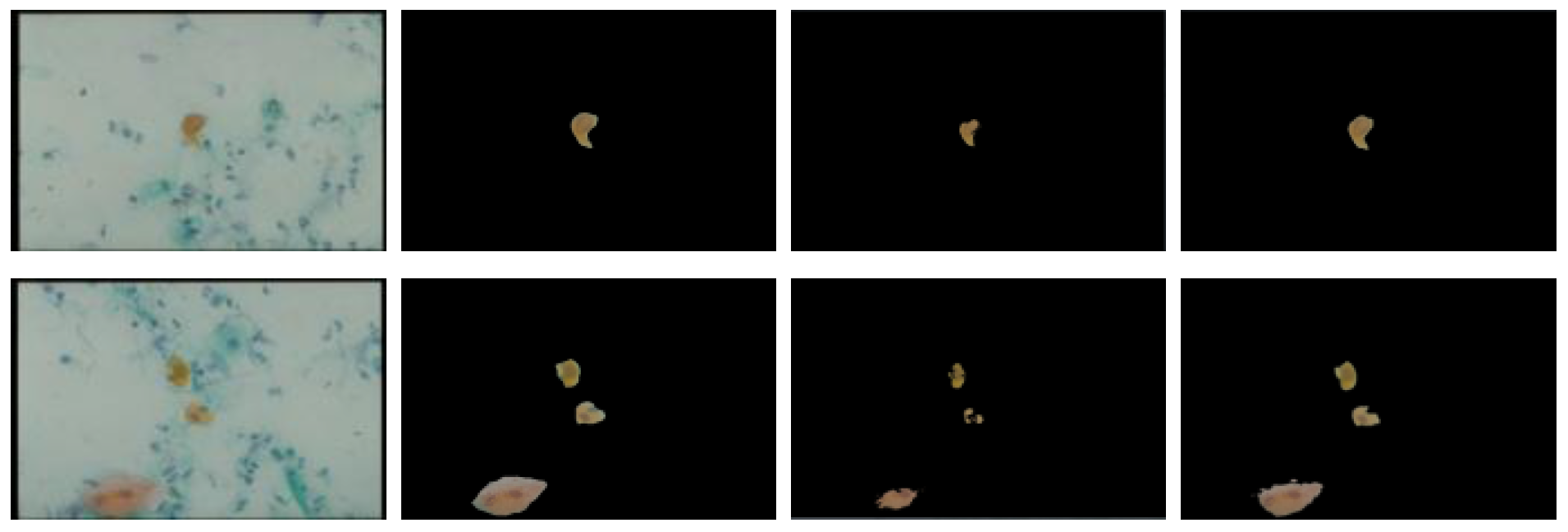
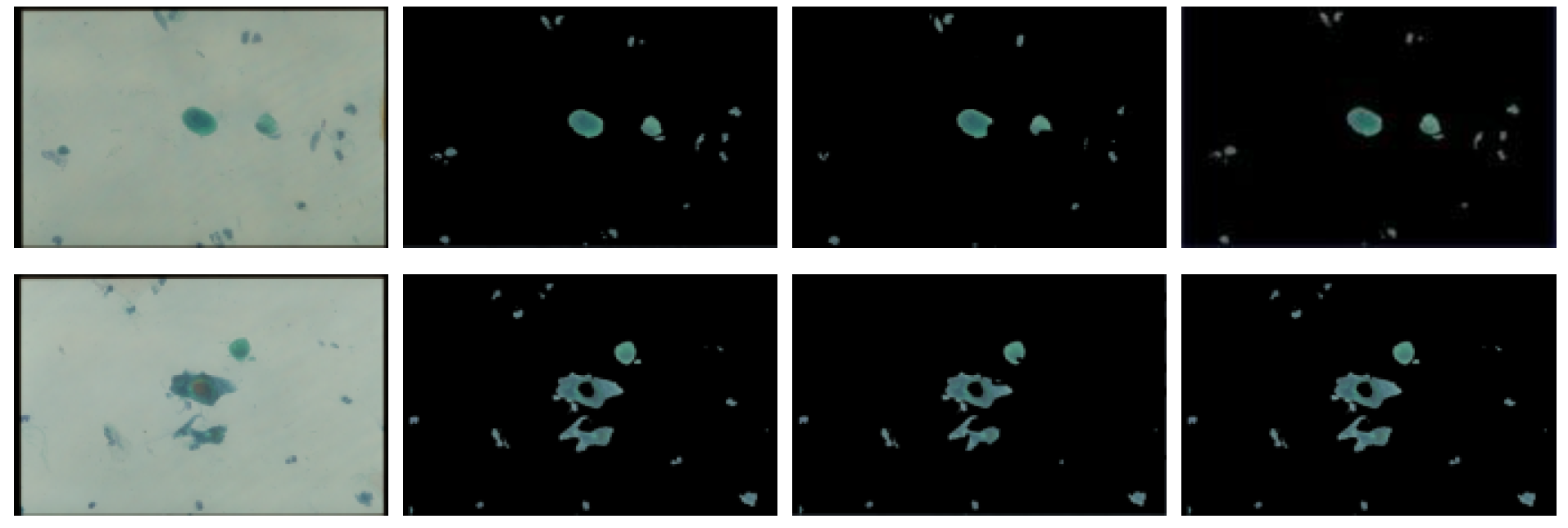

3.1.2. Bayesian Classification
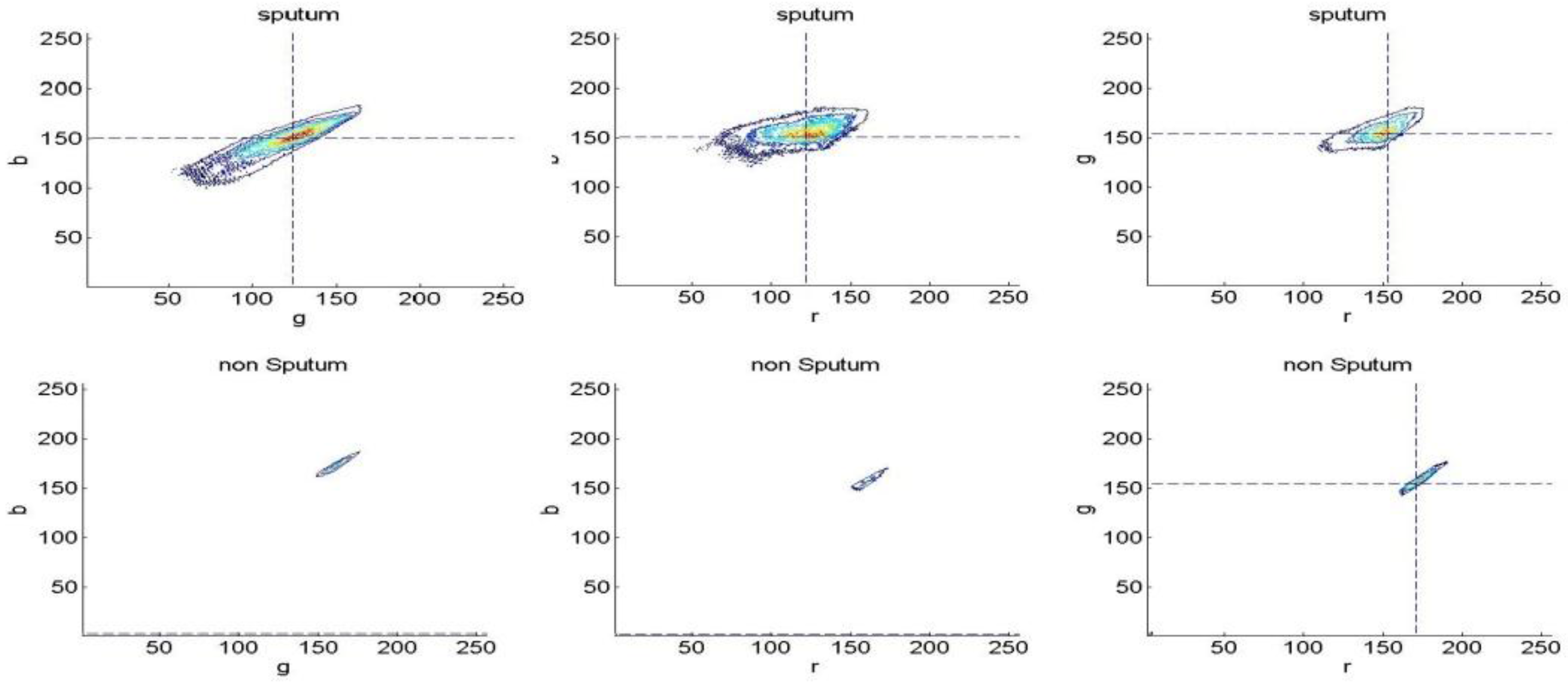
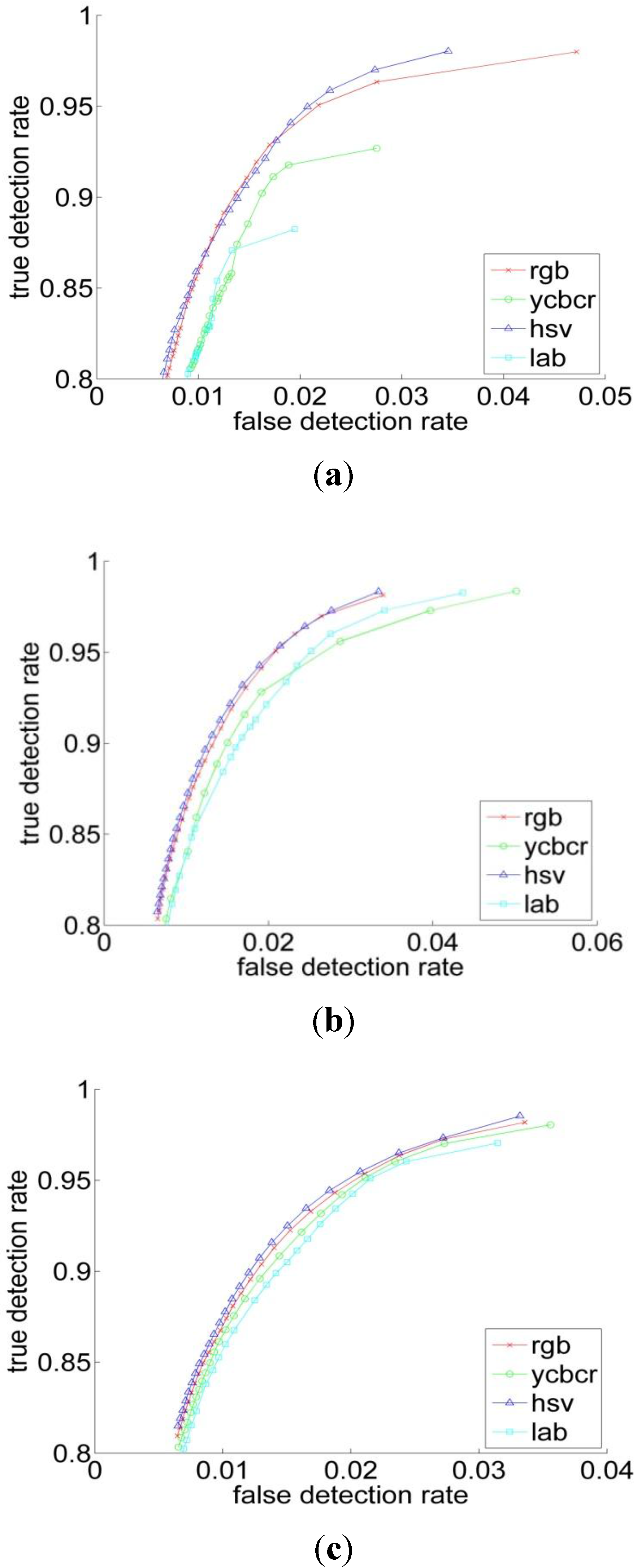
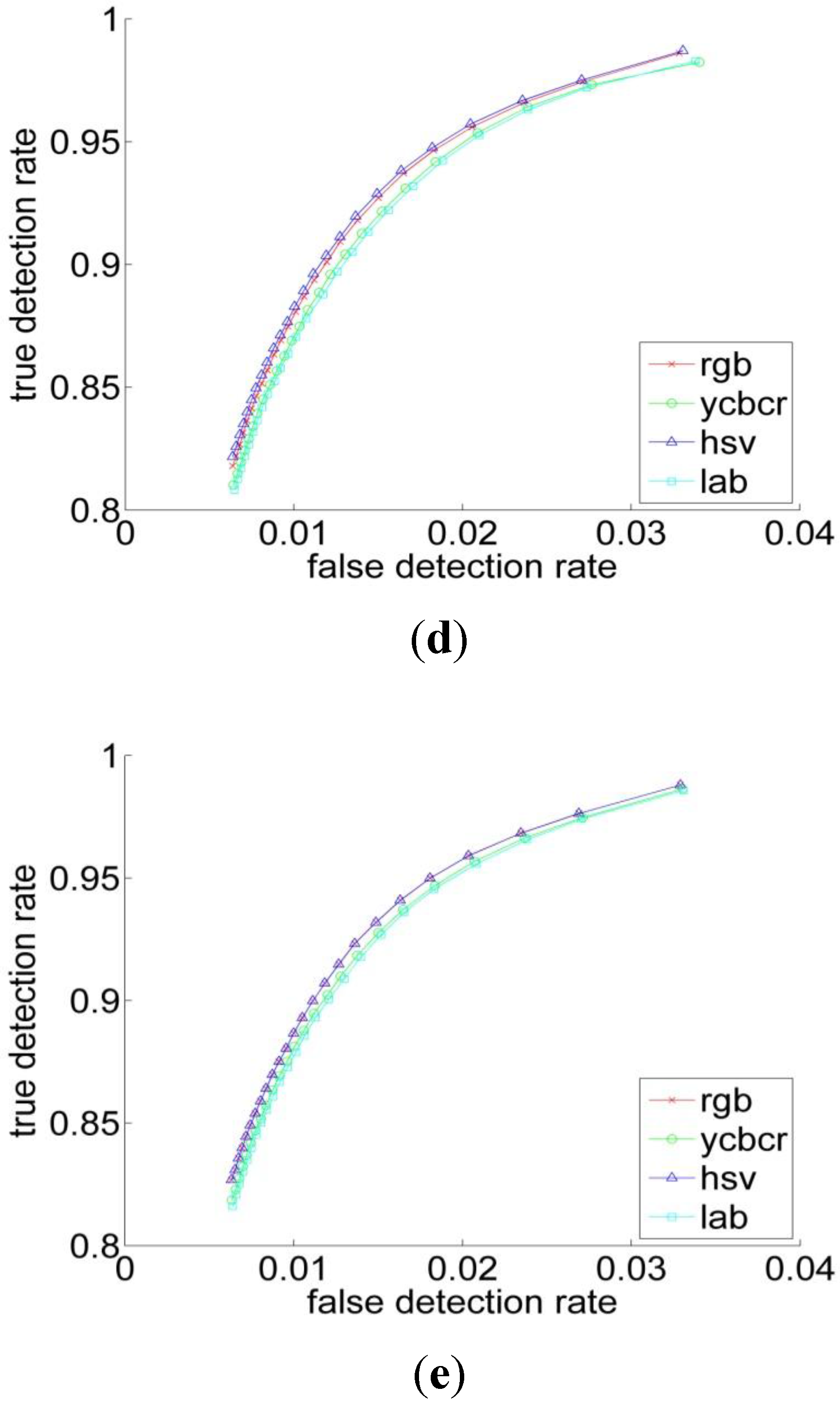
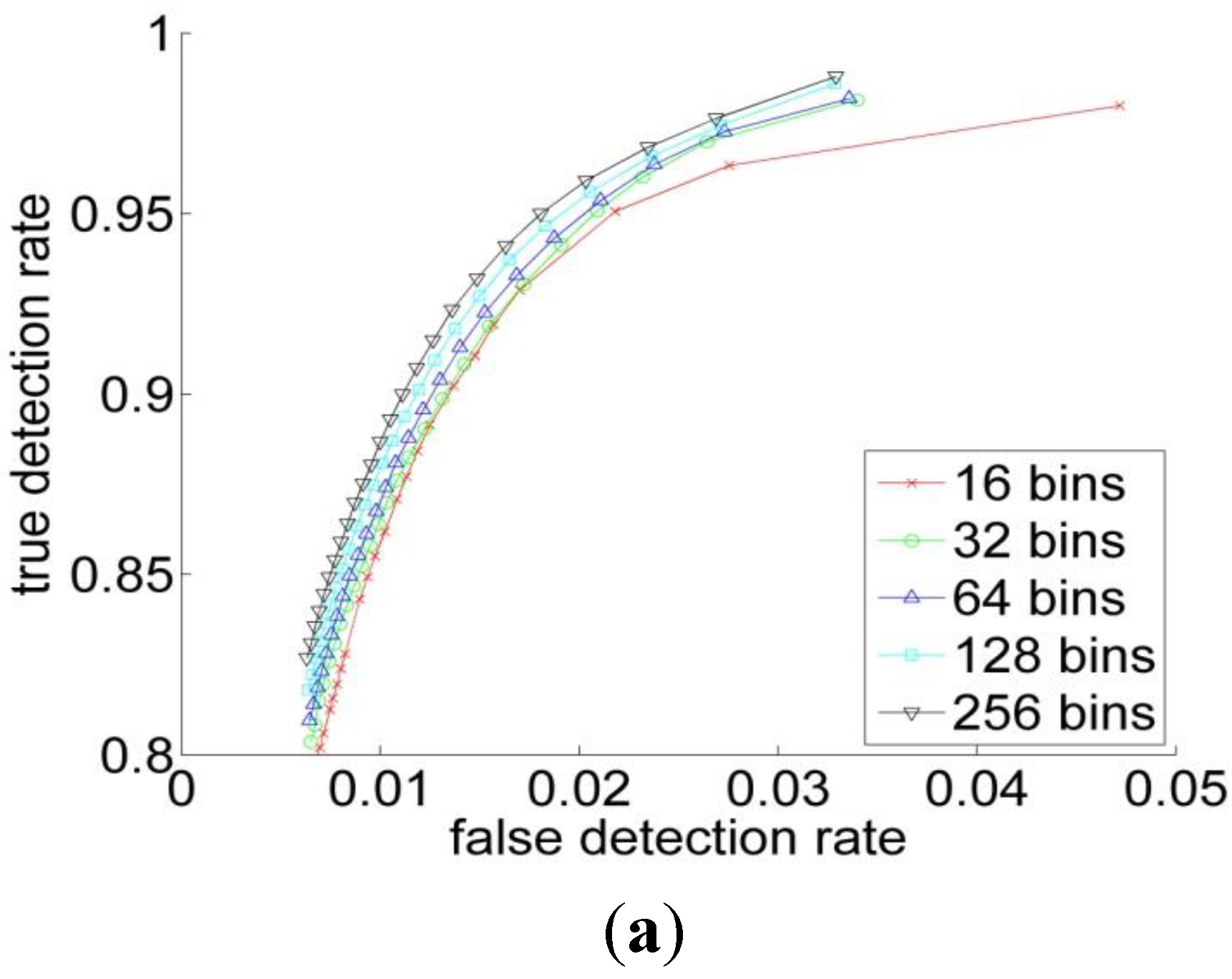
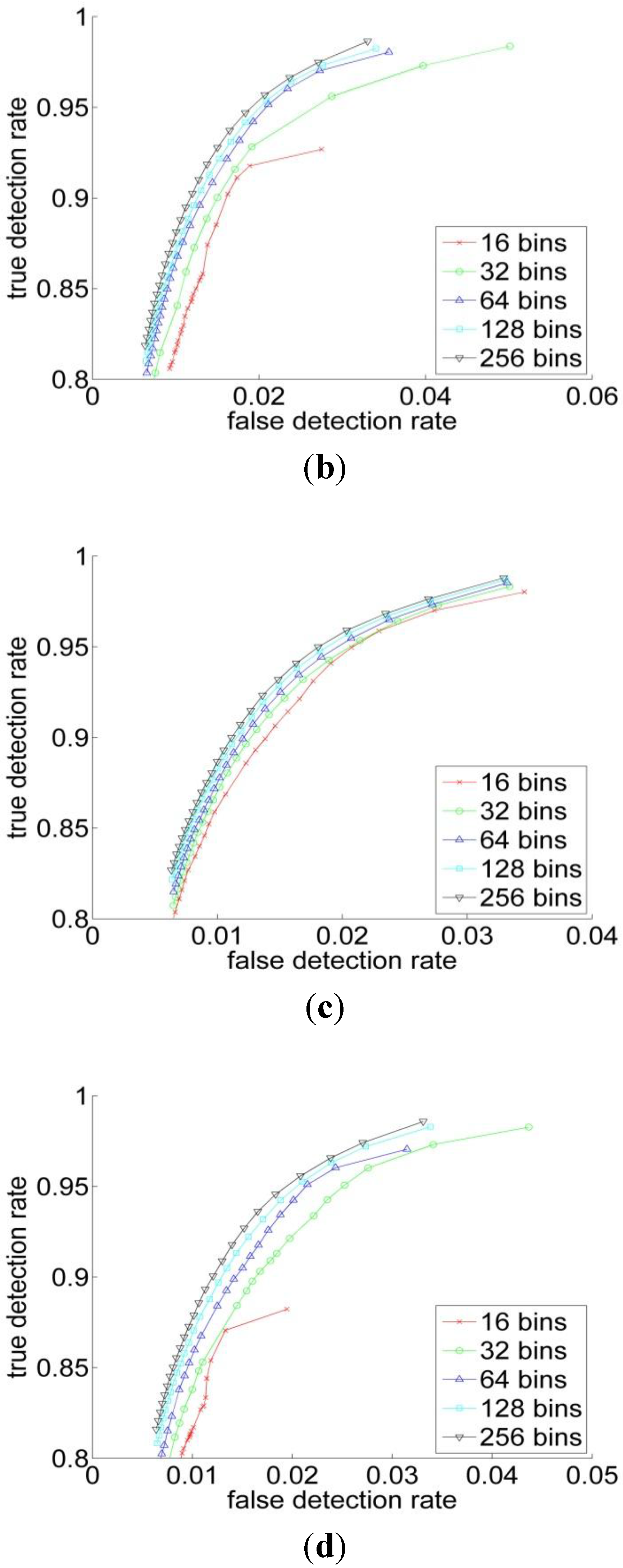
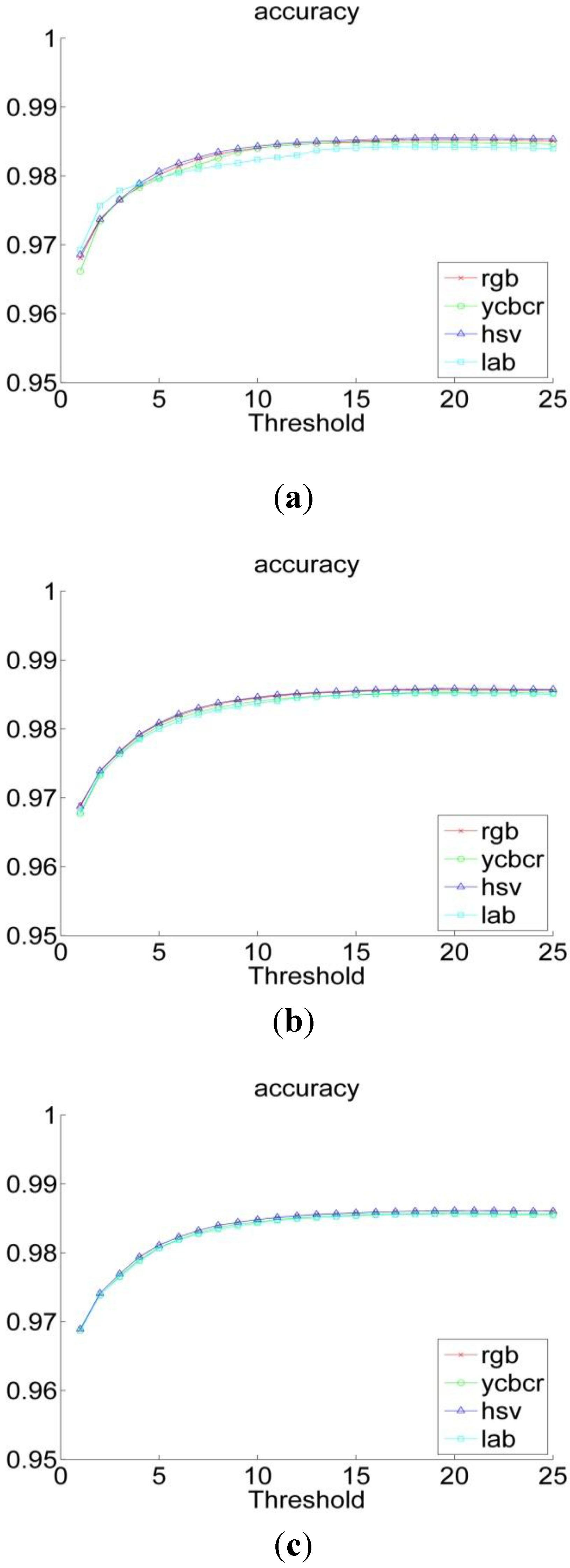
3.2. Experiments
| RGB | YCbCr | HSV | L*a*b | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Histogram Resolution | V | V | V | V |
| dev. | dev. | dev. | dev. | |
| 16 | 0.86 | 0.85 | 0.88 | 0.81 |
| 0.14 | 0.15 | 0.12 | 0.18 | |
| 32 | 0.88 | 0.82 | 0.88 | 0.87 |
| 0.12 | 0.17 | 0.12 | 0.13 | |
| 64 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.89 | 0.87 |
| 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.12 | |
| 128 | 0.89 | 0.88 | 0.89 | 0.88 |
| 0.11 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.11 | |
| 256 | 0.89 | 0.89 | 0.89 | 0.88 |
| 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.11 |
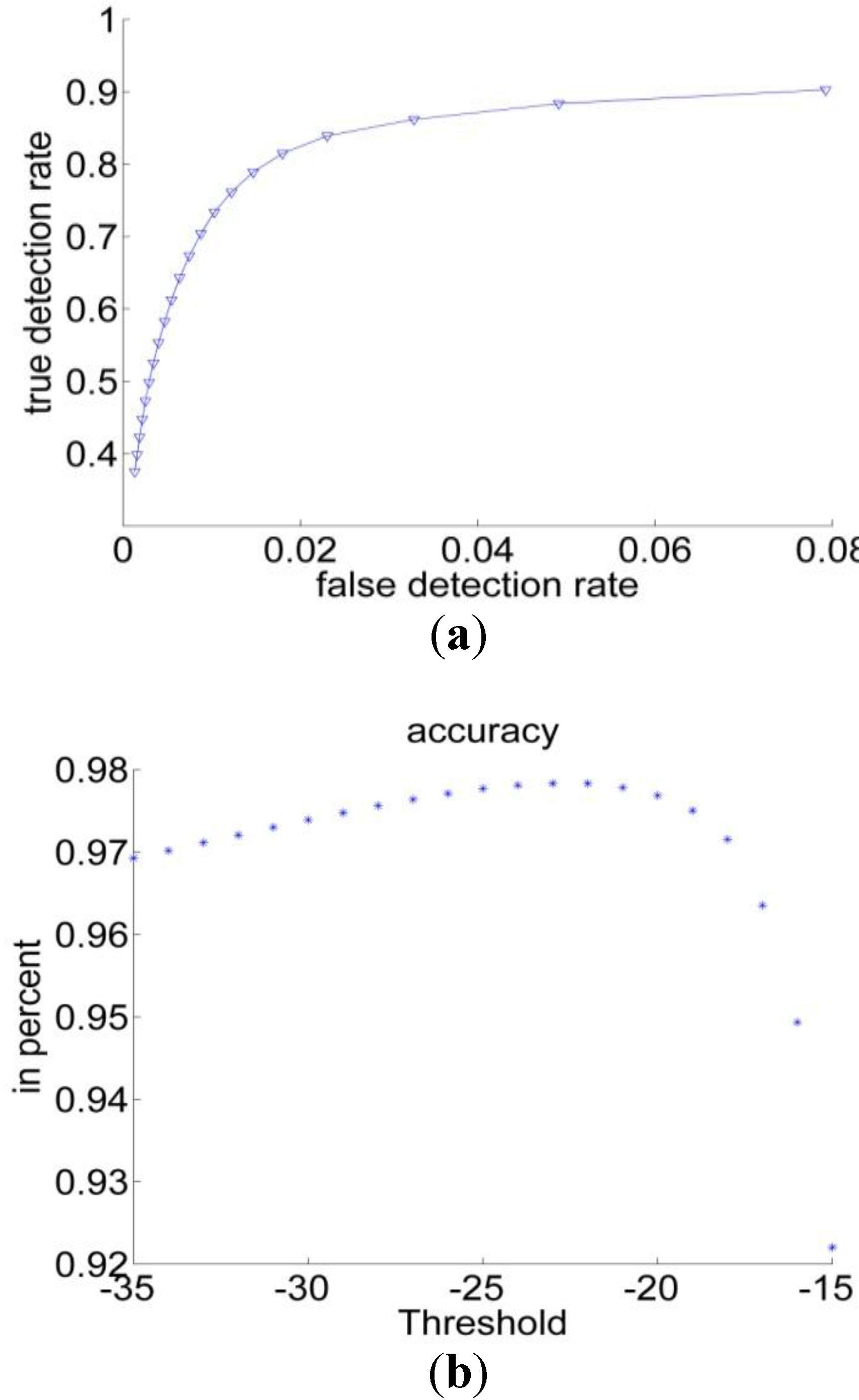
| Performance Measurements | Previous Threshold Method | Improved Threshold Method | Bayesian Classification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | 49% | 82% | 89% |
| Specificity | 97% | 99% | 99% |
| Accuracy | 96% | 98% | 98% |
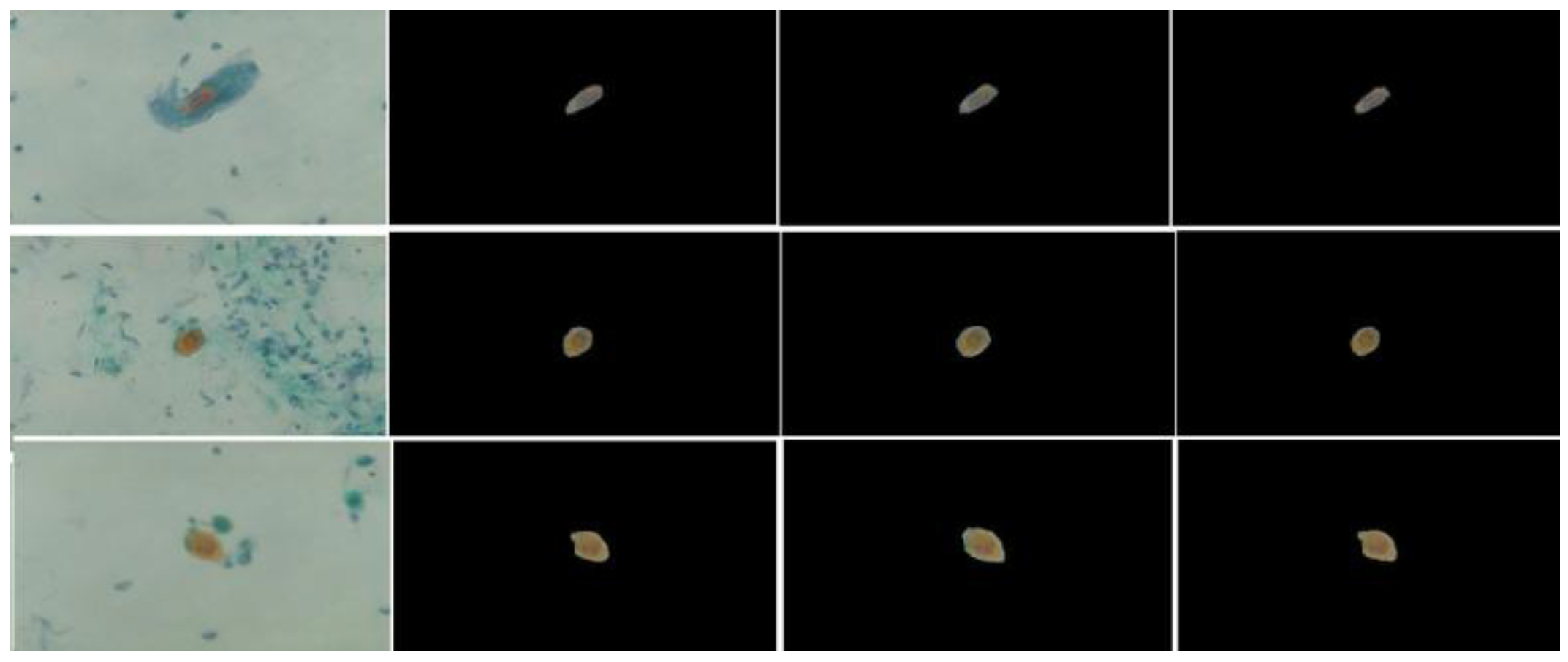
4. Cell Sgmentation

- Segment the feature space into a region.
- Choose the initial location of the mode in each region.
- Compute the new locations of the modes by updating them using the shift step.
- Repeat step 3 and 4 until convergence.
- Merge the neighboring modes and their associated pixels.
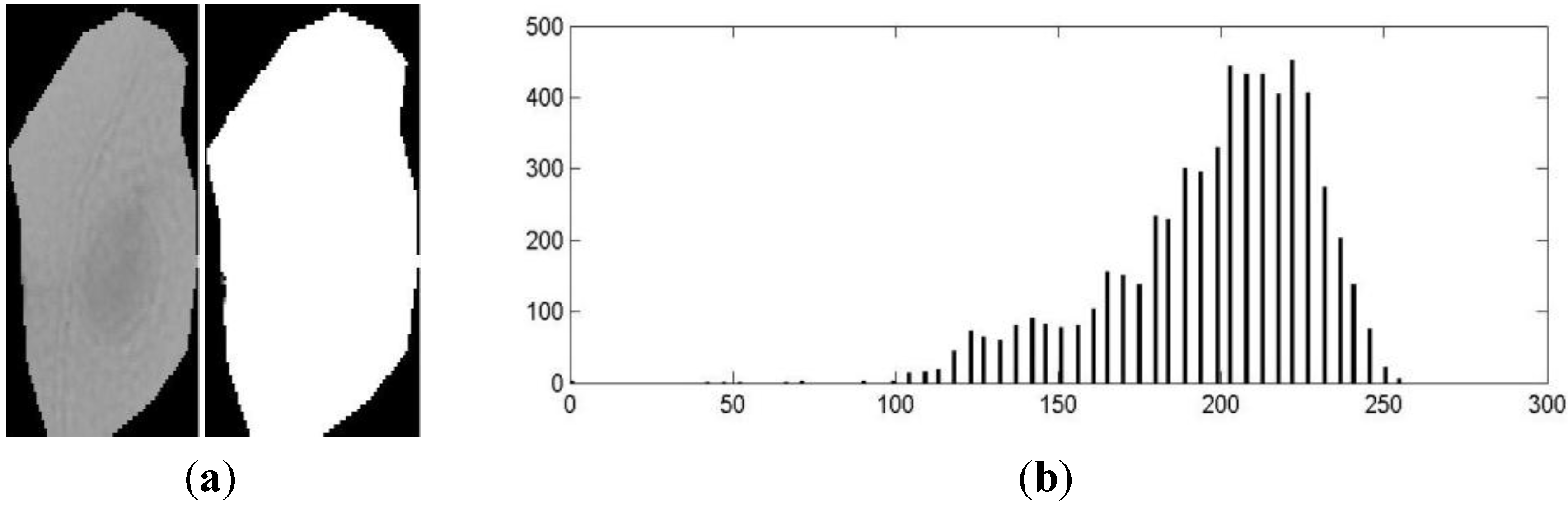
- a:
- The darkest region is part of the nucleus.
- b:
- The clearest region is part of the cytoplasm.
- c:
- Regions on the borders are part of the cytoplasm.
- d:
- The final number of regions must be equal to 2.
| Performance/Algorithm | HNN | Gray mean shift | Gray-Space mean shift |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | 73.77% | 92.7% | 93.40% |
| Specificity | 69.53% | 85.32% | 88.21% |
| Accuracy | 65.01% | 85.43% | 87.11% |
5. Conclusions
References
- Kennedy, T.C.; Miller, Y.; Prindiville, S. Screening for lung cancer revisited and the role of sputum cytology and fluorescence bronchoscopy in a high-risk group. Chest J. 2005, 10, 72–79. [Google Scholar]
- Dignam, J.; Huang, L.; Ries, L.; Reichman, M.; Mariotto, A.; Feuer, E. Estimating breast cancer-specific and other cause mortality in clinical trial and population-based cancer registry cohorts. J. Am. Cancer Soc. 2009, 115, 5272–5283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aravind, S.; Ramesh, J.; Vanathi, P.; Gunavathi, K. Roubust and Atomated lung Nodule Diagnosis from CT Images based on fuzzy Systems. In Proceeding in International Conference on Process Automation, Control and Computing (PACC), Tamilnadu, India, July 2011; pp. 1–6.
- Elbaz, A.; Gimel, G.; Falk, R.; Elghar, M. A new CAD System for Early Diagnosis of Detected Lung Nodules. In Proceeding in ICIP Conference, Louisville, KY, USA, May 2007; pp. 461–464.
- Gazdar, A.F.; Minna, J.D. Molecular detection of early lung cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1999, 91, 299–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiroo, Y. Usefulness of Papanicolaou stain by rehydration of airdried smears. J. Jpn. Soc. Clin. Cytol. 2003, 34, 107–110. [Google Scholar]
- Sammouda, R.; Niki, N.; Nishitani, H.; Nakamura, S.; Mori, S. Segmentation of sputum color image for lung cancer diagnosis based on neural network. IEICE Trans. Inf. Syst. 1998, E81, 862–870. [Google Scholar]
- El-Baz, A.; Farag, A.A.; Falk, R.; La Rocca, R. Detection, Visualization and Identification of Lung Abnormalities in Chest Spiral CT Scan: Phase-I. In Proceeding of the International Conference on Biomedical Engineering, Cairo, Egypt, 2003; Volume 12.
- Dougherty, G. Digital Image Processing for Medical Applications, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- El-Baz, A.; Beache, G.; Gimel’farb, G.; Suzuki, K.; Okada, K.; Elnakib, A.; Soliman, A.; Abdollahi, B. Computer-aided diagnosis systems for lung cancer: Challenges and methodologies. Int. J. Biomed. Imaging 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheila, A.; Ried, T. Interphase cytogenetics of sputum cells for the early detection of lung carcinogenesis. J. Cancer Prev. Res. 2010, 3, 416–419. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.; Chung, C.; Barnard, K. Relevance feedback using adaptive clustering for image similarity retrieval. J. Syst. Softw. 2005, 78, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forero, M.G.; Sroubek, F.; Cristobal, G. Identification of tuberculosis based on shape and color. J. Real Time Imaging 2004, 10, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forero, M.; Sroubek, F.; Alvarez, J.; Malpica, N.; Cristobal, G.; Santos, A.; Alcala, L.; Desco, M.; Cohen, L. Segmentation, autofocusing and signature extraction of tuberculosis sputum images. Proc. SPIE Photonic Devices Algorithms Comput. 2002, 4788, 341–352. [Google Scholar]
- Taher, F.; Sammouda, R. Identification of Lung Cancer based on Shape and Color. In Proceeding of the 4th International Conference on Innovation in Information Technology, Al Ain, UAE, November 2007; pp. 481–485.
- Taher, F.; Sammouda, R. Morphology Analysis of Sputum Color Images for Early Lung Cancer Diagnosis. In Proceeding of the 10th International Conference on Information Science, Signal Processing and their Applications (ISSPA 2010), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, May 2010; pp. 296–299.
- Kancherla, K.; Chilkapatti, R.; Mukkamal, S.; Cousins, J.; Dorian, C. Non Intrusive and Extremely Early Detection of Lung Cancer Using TCPP. In Proceedings of the 4th International conference on Computing in the Global Information Technology ICCGI, Games/La Bocca, Franch, 23–29 August 2009; pp. 104–108.
- Sluimer, I. Computer analysis of computer tomography scans of lung: A survey. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2006, 25, 385–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duda, R.; Hart, P. Pattern Classification, 2nd ed.; Wiley-Inter-Science: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Phung, S.; Bouzerdoum, A.; Chai, D. Skin segmentation using color pixel classification: Analysis and comparison. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2005, 27, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margaret, H. Dunham, Data Mining Introductory and Advanced Topics, 1st ed.; Prentice Hall: Now Jersey, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Abdollahi, B.; Soliman, A.; Civelek, A.; Li, X.-F.; Gimel’farb, G.; El-Baz, A. A Novel 3D Joint MGRF Framework for Precise Lung Segmentation. In Proceeding of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI) Conference, Nice, France, 1–5 October, 2012; pp. 86–93.
- El-Baz, A.; Gimelfarb, G.; Falk, R.; Abou El-Ghar, M.; Holland, T.; Shaffer, T. A New Stochastic Framework for Accurate Lung Segmentation. In Proceeding of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI'08), New York, NY, USA, 6–10 September 2008; pp. 322–330.
- Saleh, S.; Kalyankar, N.; Khamitkar, S. Image segmentation by using edge detection. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2010, 2, 804–807. [Google Scholar]
- Fussenegger, M.; Opelt, A.; Pinz, A.; Auer, P. Object Recognition Using Segmentation for Feature Detection. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Cambridge England, UK, 23–26, August, 2004; Volume 3, pp. 41–44.
- Comaniciu, D.; Meer, P. Mean shift: A robust approach towards feature space analysis. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2002, 24, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Taher, F.; Werghi, N.; Al-Ahmad, H.; Donner, C. Extraction and Segmentation of Sputum Cells for Lung Cancer Early Diagnosis. Algorithms 2013, 6, 512-531. https://doi.org/10.3390/a6030512
Taher F, Werghi N, Al-Ahmad H, Donner C. Extraction and Segmentation of Sputum Cells for Lung Cancer Early Diagnosis. Algorithms. 2013; 6(3):512-531. https://doi.org/10.3390/a6030512
Chicago/Turabian StyleTaher, Fatma, Naoufel Werghi, Hussain Al-Ahmad, and Christian Donner. 2013. "Extraction and Segmentation of Sputum Cells for Lung Cancer Early Diagnosis" Algorithms 6, no. 3: 512-531. https://doi.org/10.3390/a6030512
APA StyleTaher, F., Werghi, N., Al-Ahmad, H., & Donner, C. (2013). Extraction and Segmentation of Sputum Cells for Lung Cancer Early Diagnosis. Algorithms, 6(3), 512-531. https://doi.org/10.3390/a6030512





