Abstract
The offshore oil engineering jacket is a giant super-heavy steel frame structure with dimensions in the hundreds of meters. A high-precision free station control network is usually arranged around it to ensure construction accuracy. However, as the jacket is gradually assembled, its extreme weight will cause the widespread deformation of the surrounding ground surface, and each control point may be affected to varying degrees, resulting in the non-uniform deformation of the entire network. For adjustments of control networks in the subsequent phases, if the same starting point as the first phase is chosen without careful analysis, the starting points’ non-uniform deformation will degrade the whole network’s accuracy. Considering the particularities of the free station control network, this paper proposes an adjustment algorithm consisting of a three-step analytical method. Firstly, the initial coordinates of the points of the current phase are obtained through classical free network adjustment; second, stable and unstable points are identified via coordinate similarity transformation between the current and the first phase; and finally, quasi-stable adjustment is conducted. The experimental data analysis of a jacket control network shows that this method can effectively identify stable and unstable points, thereby ensuring construction accuracy and jacket stability.
1. Introduction
A jacket platform is one of the main engineering facilities for offshore oil development [1], and the accuracy of its construction will directly affect the safety of operators and the economic benefits of the whole project. Due to the numerous components of the conductor frame and its complex spatial structure, the construction site observation conditions are exceptionally complicated, posing significant challenges in terms of precise measurement [2]. The line of sight between the control points will be blocked during construction (as shown in Figure 1), so it is necessary to lay a high-precision free station control network around the assembly site. However, as the jacket is assembled, its great weight will gradually deform the surrounding ground surface, and each control point may be affected to different degrees, resulting in non-uniform changes to the whole network [3]. The control network is the datum for subsequent construction, so judging the stability of the control network [4] and analyzing the deformation of each control point become the primary problems of data processing.

Figure 1.
Typical scenarios for complicated line-of-sight conditions during the construction of a jacket. (a) The inside of the jacket, (b) the outside of the jacket.
Selecting two or more control points to be constrained in adjustment is usually necessary [5], and this is called parameter adjustment with redundant known equations. Still, if the constrained points have undergone a large deformation, this forcible constraint will cause whole-network scale change and azimuthal distortion. The classical free network adjustment only constrains the necessary starting data, such as a point’s coordinates and a side’s azimuth. However, the problem of how to select reliable starting data remains. The rank loss of free network adjustment [6] (also known as the rank-deficient problem of least squares adjustment models [7]) considers all points as deformation points. It solves the rank loss problem by attaching the center-of-gravity data of all points as constraints, which is a feature that makes it widely used in the deformation monitoring of high-speed rail [8], embankment dams [9], and subways [10], and so forth. However, station location is also a pending parameter in a free station control network, which is inconsistent in each phase. Therefore, the assumption that the center-of-gravity datum remains unchanged is no longer tenable. In addition, if some relatively stable control points exist, disregarding such information will affect the accuracy of the deformation amount sought [11]. Quasi-stable free network adjustment (hereinafter referred to as “quasi-stable adjustment”) divides the control points into two categories, stable points and unstable points [12], and fits unknowns by attaching the center-of-gravity data of all stable points; that is, minimizing the sum of squares of parameter corrections and observation residuals [13]. Theory and practice have proved the necessity and superiority of the quasi-stable adjustment in the monitoring network [14]. However, selecting the stable points that meet reality is still a challenging problem [15]. A weighted quasi-stable adjustment method is proposed that uses posterior variance to determine the weight of the datum [16]. This method requires high-order control points, but jacket control networks often only have a primary control network.
In engineering practice, the commonly used methods for stability analysis include the t-test method [17], the average gap method [18], the block gap method [19], the weighted iteration method [20], the distance and azimuthal difference method [21], the supervised clustering method [22], etc. However, most of these methods involve complicated calculation steps and mathematical statistics, which are not easy to use in engineering practice; in addition, in the free station control network [23], there is usually no direct observation between the control points, and the location of the stations varies from phase to phase, so it is not possible to compare the distances and angles over multiple phases. Machine learning trains on input data and expected outputs to reveal the relationships between coordinate time series and various physical variables without having explicit mathematical equations [24]. However, machine learning requires a wealth of historical data to form training and test sets, as well as additional observed values like geological and temperature data. This makes it more suitable for control networks with long-term or continuous observation. It is less applicable to triangulation and trilateration control networks with few observation periods and a small number of points.
Because of this, this paper proposes a three-step analysis method of “classical free network adjustment to obtain the initial value-coordinate similarity transformation to identify the stable points-quasi-stable adjustment to get the final result”, which is analyzed and verified by two-phase observation data of an ultra-large jacket control network, and the results show that this method can more effectively identify the stable and unstable points in the network compared with the traditional method.
2. Materials and Method
2.1. Data Processing Flow
To identify stable points in a control network in the second and any subsequent phase, the following steps are proposed in this paper: (1) First, perform classical free network adjustment to arrive at the initial coordinates of the current phase; that is, only introduce the coordinates of one point and the azimuth of one side as the starting data to minimize the impact of starting data errors on the adjustment results. (2) Perform a coordinate similarity transformation between the coordinates of the current phase and the first phase, and absorb the overall parts of the changes between the two phases of data through four parameters, further eliminating the adverse impact of starting data errors on the adjustment results of the two phases, and dividing the control points into stable and unstable points based on the relative sizes of the residuals of the points after the similarity transformation. (3) Perform quasi-stable adjustment on the coordinate results of the points in the current phase. The technical route is shown in Figure 2.
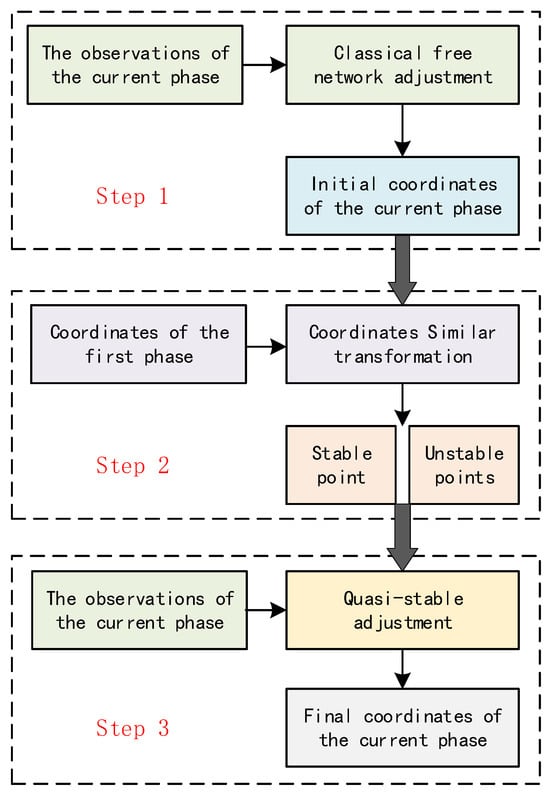
Figure 2.
Technical route of this paper.
2.2. Algorithmic Principle
2.2.1. Least Squares and Indirect Adjustment
The indirect adjustment based on the least squares principle is widely used in geodetic network adjustment. It involves estimating unknown parameters from a set of observations by minimizing the sum of the squares of the residuals [25].
For a linear model, the observation equation, namely, the mathematical model that relates the observations to the unknown parameters, can be expressed as:
where is the vector of observations, is the design matrix, is the vector of unknown parameters, and is the vector of residuals.
The error equation is:
where , , and are the initial values of .
The goal of least squares is to find the values of that minimize the sum of the residuals’ squares, , where P is the weight matrix of the observations. This leads to the normal equations:
where is the coefficient matrix of the normal equation, .
For the case of classic free network adjustment and constraint adjustment, the coefficient matrix is full-rank, and then the solution is:
Once the parameters of are determined, the residuals of can be calculated according to Equation (2). The unit weight variance can be calculated using the following formula:
where is the total number of observations, and is the number of necessary observations.
The variance–covariance matrix of the estimated parameters is given by:
2.2.2. Observation Equations of Free Station Control Network
Free station control networks differ from traditional traverse or triangulation and trilateral control networks in that the stations do not necessarily have to be set up at control points. Theoretically, any number of stations can be established at any location within and around the coverage area of the control network. This is of great significance for control networks where the line of sight between control points is obstructed. Typically, there are two or more common observed targets between stations to enable them to be connected to a network. Free station control network observations consist of horizontal directions and distances from the stations to their observed control points. Distances are usually derived from slope distances and vertical angles.
Let and be the measuring station and the target point to be determined, respectively, and the observation equation of the horizontal observation value between them is:
where is the observed value after adjustment; is the correction; and are the coordinate parameters of the station and the target point, respectively; and indicates the orientation angle parameter of the station, i.e., the coordinate azimuth of the zero direction of the horizontal circle of the total station, and , and is expanded to Taylor’s level:
where , , , and .
The observation equation for the horizontal distance observation is:
Expanding by the Taylor series, we obtain:
where , , , , , and .
2.2.3. Classic Free Network Adjustment and Constraint Adjustment
Classical free network adjustment means that the control network contains only the essential starting data. The essential starting data for a triangulation and trilateral control network is a known point and a known azimuth. It is called constraint adjustment if more starting data are employed, such as two known points. In both cases, the coefficient matrix of the normal equations is full-rank, so indirect adjustment can be used to solve the problem.
2.2.4. Quasi-Stable Adjustment
Let there be points in the control network, of which the first points are stable, and the remaining points are unstable, and let there be directional angle parameters in the network; then, the parameter solution of the quasi-stable adjustment is:
where
, , , , and .
2.2.5. Coordinate Similarity Transformation
The coordinate transformation equation for a four-parameter transformation between two coordinate systems is:
where , are the coordinate translation parameters, is the scale factor parameter, and is the rotation angle parameter. By applying and , this problem can be converted into a linear model.
It is known that there are common points in the old and new coordinate systems, the coordinates under the target coordinate system are set as the observed values, the coordinates in the source coordinate system are free of error, and the indirect adjustment solution can be further used to find out the adjustment values and the precision of each parameter.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. An Overview of the Control Network
A high-precision control network was laid around the construction site’s periphery to ensure the construction quality of an ultra-large jacket. Two observation phases were carried out using a Leica TS50 total station to adopt the free station method. Each station observed all of the visible control points for six observation sets, simultaneously observing the slope distance, horizontal direction, and vertical angle and measuring the dry and wet temperatures and atmospheric pressure at the site to impose ranging meteorological corrections.
3.1.1. The First Phase of Observation
The first observation phase was carried out in April 2022, when construction of the jacket had not yet started. The sight conditions were very good, with no obstructions between the survey stations and the control points at most locations. The total free station location is mainly located in the middle of the field, surrounded by the control points S1–S8, with a total of six stations, as shown in Figure 3.
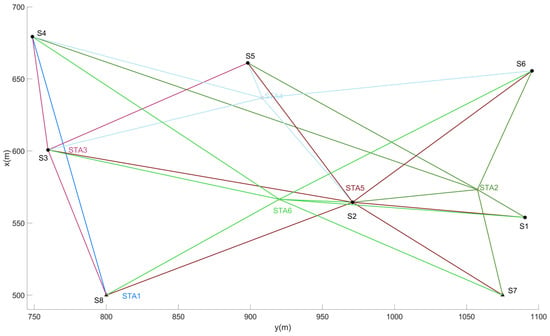
Figure 3.
Schematic diagram of the first free station observations. STA# indicates the station’s location, # represents the station number, and different colors distinguish the observation values of different stations.
3.1.2. The Second Phase of Observation
The second phase of observations was carried out in November 2023, and the monument of control point S2 was found to be damaged by the repeated rolling by large transport vehicles and heavy machinery during the construction of the jacket, so two new control points, S9 and S10, were added near it. By this time, the jacket had been constructed to a certain scale (as shown in Figure 4), and it was no longer possible to set up instruments in the center of the field, so a total of 12 stations were set up along the periphery of the field, as shown in Figure 5. The selection of the locations of these new stations was mainly based on the following considerations: firstly, they should be evenly distributed in the whole control network area; secondly, in the case of a serious line of sight occlusion, each station should be carefully selected to ensure visibility with at least three control points. In this way, reliable relatively geometric relationships between control points could be determined via adjustment by setting enough overlapping observations of common points between stations based on accurate angle and distance measurements obtained at each station.

Figure 4.
The construction scene of the jacket during the second phase of the observation of the control network.
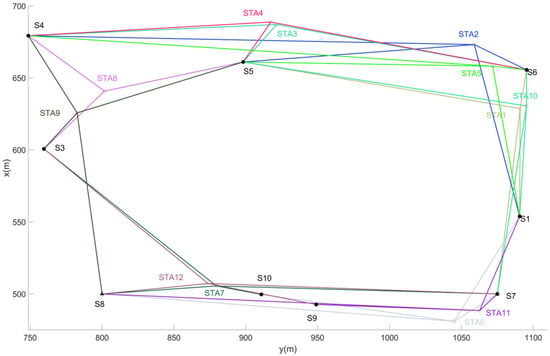
Figure 5.
A schematic diagram of the second phase of free station observations. STA# indicates the station’s location, # represents the station number, and different colors distinguish the observation values of different stations.
3.2. Comparison of Different Adjustment Schemes
Since there are no high-level control points in this control network, both the method of this paper and the traditional method use the classical free network adjustment method to calculate the coordinates of the first-phase control points, and the comparison with the conventional method is mainly reflected in the second-phase data processing.
3.2.1. Adjustment Results of the First Phase
Assuming that the coordinates of S8 are (500.000 m and 800.000 m), and the azimuth angle of S8–S7 is 90°00′00″, the classical free network adjustment method is used to calculate the adjustment coordinates of each point in the first phase and the root mean square error (RMSE), as shown in Table 1, in which mx and my denote the RMSE in the direction of x and y, respectively, and represents the RMSE of the whole point position. The table shows that the error of each point position is below 1.6 mm, and the average value is 1.2 mm, which indicates that the internal conformity accuracy of the first-phase control network observation is high.

Table 1.
The adjustment coordinates and RMSEs of the first phase.
3.2.2. Adjustment Results via Traditional Method
Constrain the coordinates of the S7 and S8 points in Table 1, and then implement adjustment for the second-phase observations, and calculate the coordinates of each point and their difference with the first coordinates as shown in Table 2 (the newly deployed S9 and S10 points are not involved in the comparison because there are no first coordinates, so they are not included in the table), in which dx and dy represent the deviation of the x and y directions, respectively, represents the deviation of the point position, and is the RMSE of the dp.

Table 2.
The adjustment coordinates (constraints S8 and S7) and their differences compared to the first results.
From the above table, it can be seen that except for the two starting points, S7 and S8, the coordinate deviations of the remaining five control points are a minimum of 0.9 cm (S3, S5) and a maximum of 1.5 cm (S6), with an average value of 1.1 cm. Their point deviations are greater than twice their mean square error, which can be considered a significant displacement.
In addition, we also compared the adjustment effect of constraining different control points. Figure 6 shows the point deviation of the coordinates of the points obtained when constraining S8 and any remaining control point (represented by S8 + S# in the figure, where # represents the station number) compared with the first-phase results. The RMSE of each point deviation is also plotted as error bars. To avoid overlapping between different error bars at the same point, we adjusted the ratio of the error bars to 30% of their original values.
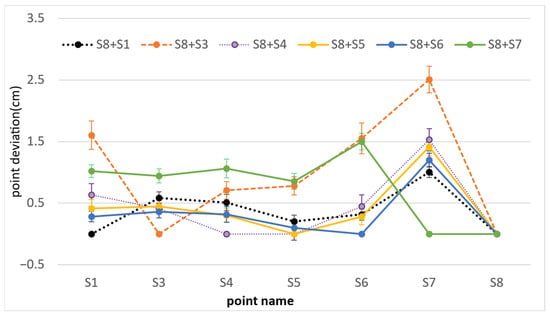
Figure 6.
The point deviation of different constraint adjustment schemes compared to the first phase.
Table 3 lists the statistical information on the point deviation of the various scenarios. It can be seen that the results vary considerably when different starting points are chosen for the constraints, making it challenging to determine which points are stable or unstable.

Table 3.
The statistics of point deviations between the adjustment coordinates with different constraints and the first results.
3.2.3. Adjustment Results via the Proposed Method
Firstly, the classical free network adjustment is carried out with the same starting data as that of the first phase to obtain the results of the coordinates of each control point and their differences from those of the first phase, which are listed in Table 4. It can be seen that the results are similar to those of Table 2, and the deviations of the points except S7 and S8 are large, with the smallest S5 being 9.8 mm, the largest S6 reaching 16.3 mm, and the mean value being 11.6 mm.

Table 4.
Classical free network adjustment coordinates of the second phase and their comparison with the first phase.
Then, the coordinate similarity transformation is carried out using the common points in Table 1 and Table 4. The unit-weighted RMSE is 3.3 mm after the transformation. The residuals of each point are shown in Table 5, in which Vx and Vy denote the residuals in the x and y directions, respectively, and denotes the point position deviation. Since the coordinate similarity transformation can absorb the rigid part of the deformation between the two control networks, the residual distribution after the coordinate transformation can effectively reflect the consistency of the deformation of each point.

Table 5.
Residuals of two phases of coordinate similarity transformations.
The maximum value of the point deviations is 7.7 mm, the minimum value is 1.5 mm, and the mean value is 3.5 mm, which is one order of magnitude lower than that of Table 4. Taking the value of two times the unit-weight RMSE of the coordinate similarity transformation as the tolerance, the control points whose point deviation is less than this value are regarded as stable points. Otherwise, they are considered to be unstable points. In this example, the tolerance is 6.6 mm, so all control points except S7 in Table 5 can be regarded as quasi-stable points.
Figure 7 shows the position deviations after applying multiple schemes for the classical free network adjustment and coordinate similarity transformation, which constrains the initial coordinates of S8 and the initial azimuths of different sides (denoted by S8–S#). It can be seen that the point deviations and unit-weight RMSE of each scheme show good consistency. This shows one of the significant advantages of this method over traditional methods—no matter how the starting data are selected, the final result will not be significantly different.
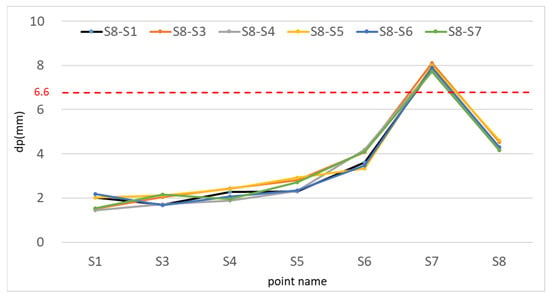
Figure 7.
The point deviations of the proposed adjustment method with different starting data compared to the first phase.
Finally, the quasi-stable adjustment is carried out, and the coordinates of each point after adjustment and the difference between them and the first adjustment result are listed in Table 6. It can be seen that the point deviation of S7 after adjustment reaches 1.1 cm and exceeds twice its mdp ( cm). In contrast, the deviations of the rest of the points do not exceed 3 mm, and these values are also less than twice their RMSE, indicating a significant inconsistent deformation of S7 compared to the other points. For the traditional method, if S7 and S8 are directly constrained, one cannot find this problem. They may even come to the opposite conclusion. Only by repeatedly transforming the constraint points for adjustment and comparing and analyzing the results of multiple schemes can S7 be identified as unstable. This method, however, effectively avoids differences in results due to different starting data by introducing coordinate similarity transformations and quasi-stable adjustments.

Table 6.
Quasi-stable adjustment coordinates for the second phase and their difference compared to the first-phase results.
4. Conclusions
For the second and consequent phases of a control network, if the first-phase coordinates of two or more control points are constrained to carry out the adjustment, the results would exhibit large differences due to the possible deformation. If there are large relative deformations between the constrained points, each point’s adjusted coordinates will be affected, leading to incorrect conclusions. The rank-deficient free network adjustment method effectively avoids the adverse effects of improper selection of starting data on adjustment. However, due to the characteristics of the jacket construction site, it is impossible to ensure that the location and number of stations are consistent in each phase relative to those in the first phase. Therefore, the center-of-gravity datum constraints do not apply to free station control networks. The quasi-stable adjustment is based on the rank-deficient free network adjustment while fully considering that some points in the network are stable and some points are unstable, which is more in line with the actual situation and can be applied to the free station control network. However, reasonably identifying the stable points is a major difficulty in the quasi-stable adjustment.
According to the special characteristics of the free station control network for deepwater ultra-large jackets, this paper proposes an effective three-step analysis method, i.e., firstly introducing only the necessary starting data to obtain the preliminary solution through the classical free network adjustment, then identifying the stable and unstable points by similarly transforming them with the first-phase coordinates and absorbing the rigid deformation of the two-phase control network, and then finally carrying out the quasi-stable adjustment to solve the coordinates of each point. The stable and unstable points can be identified accurately and efficiently without several adjustment attempts, which is advantageous in terms of accuracy and efficiency compared with the traditional method. The feasibility and accuracy of this methodology are validated through comparative analysis with conventional adjustment results, specifically applied to a real-world case study of ultra-large jacket structures in coastal offshore engineering. Notably, the proposed approach also provides a generalizable framework for various free station-type deformation monitoring scenarios.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.Z.; methodology, X.Y.; software, D.Z. and W.X.; validation, D.W.; formal analysis, W.S. and H.L.; investigation, H.W. and W.X.; resources, H.L.; data curation J.L. and W.X.; writing—original draft X.Y., W.S., H.W., Y.W. and D.W.; writing—review and editing, D.Z. and J.L.; visualization H.W. and H.L.; supervision, Y.W.; project administration W.S.; funding acquisition, D.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Xianyang Yang, Wei Shu, Haifeng Li and Yi Wang were employed by the company Offshore Oil Engineering Co., Ltd. Author Huoping Wang, Deyang Wang and Wangsui Xiao were employed by the company CNOOC (China) Limited Shenzhen Branch. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Liu, S.T.; Li, H.C.; Zhang, J.; Yang, S.T.; Zhang, T.Y. Shaking table test and numerical simulation of jacket offshore platform considering soil-water-structure interaction. Ocean Eng. 2024, 313, 119542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, Q.; Yang, X. A method to eliminate the influence of earth curvature on the elevation of very large jackets. Nat. Gas Oil 2022, 40, 132–138. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, G.; Jiao, F.; Zhao, P. Discussion on precision control method for 300 m class deepwater jacket assembly. Guangdong Shipbuild. 2024, 43, 82–84+48. [Google Scholar]
- Krawczyk, K. Influence of reference stations on the stability of the geodetic control network during deformation determination in the area of Kadzielnia in Kielce. Rep. Geod. Geoinformat. 2023, 115, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velsink, H. Testing Methods for Adjustment Models with Constraints. J. Surv. Eng. 2018, 144, 04018009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D. Compatibility test for known points of GNSS control network with rank-loss free network adjustment. Surv. Mapp. Sci. 2019, 44, 120–125. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y. A new iterative algorithm for a rank-deficient adjustment model with inequality constraints. J. Geod. 2019, 93, 2637–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Jiang, Y.; Tan, S. Research on Route Horizontal Control Network Retesting Update Index of High-Speed Railways. J. Geomat. 2021, 46, 75–78. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y. Study Some Theoretical Problems in Analyzing Dam Deformation Monitoring Data. Master’s Thesis, Tongji University, Shanghai, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Su, X.; Li, Z.; Huang, H. Application of rank-loss free network adjustment in metro tunnel protection zone. Mapp. Spat. Geogr. Inf. 2016, 39, 180–181+5. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, B.; Li, G.; Li, P.; Yang, Z. Quasi-Stable Adjustment of Laser Interferometer 3D Rank Defect Network. J. Geomat. Sci. Technol. 2014, 31, 459–462. [Google Scholar]
- Su, X.; Hu, H.; Ma, X. Key techniques for stability analysis and data maintenance of deformation monitoring network. Geospat. Inf. 2023, 21, 22–26. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, C.; Dang, Y.; Yang, Q. Research and Application of Quasi-Stable Adjustment Method in GNSS Time Series Restoration. J. Geod. Geodyn. 2024, 44, 16–20+26. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Xing, C.; Pan, X.; Zhou, X.; Shi, B. Microdeformation monitoring by permanent scatterer GB-SAR interferometry based on image subset series with short temporal baselines: The Geheyan Dam case study. Measurement 2021, 184, 109944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yang, G.; Zheng, Z.; Yin, H.; Jia, Y. Dynamic Adjustment of Re-measurement Leveling Network and Its Application in Vertical Crustal Deformation in Sichuan-Yunnan Region. J. Seismol. Res. 2020, 43, 87–94. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Li, Z. Weighted quasi-stable combined adjustment of two-order horizontal control network using posteriori variance to determine the weight. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2021, 32, 115027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Li, J.; Zhou, H. Retesting and Stability Analysis of Control Network of a Railway Project. Surv. Mapp. Spat. Geogr. Inf. 2013, 36, 189–191+193. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H. Research on the Key Technology of Construction Control Network Retesting and Settlement Observation During the Construction Period of Very Large Bridges. Master’s Thesis, Southeast University, Nanjing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Su, J. Stability analysis of control network. Urban Surv. 2000, 4, 14–16. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S. Stability analysis of monitoring network. Surv. Mapp. Inf. Eng. 2001, 1, 16–19. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, C.; Cao, C. Study a new method of stability analysis of high-speed railway CPI control network based on multi-limit difference. Railw. Surv. 2015, 41, 10–13. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, P.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, X.; Wu, S.; Xu, Y. Realization of an Optimal Dynamic Geodetic Reference Frame in China: Methodology and Applications. Engineering 2020, 6, 879–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de França, R.M.; Klein, I.; Veiga, L.A.K. Horizontal Reference Network Densification by Multiple Free Stations. J. Surv. Eng. 2023, 149, 116250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.Z.; Li, Z.; Chen, Q.S.; Jiang, W.P.; Feng, Y.M. Modelling and prediction of GNSS time series using GBDT, LSTM and SVM machine learning approaches. J. Geod. 2022, 96, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzao, T.; Weining, Q.; Yibin, Y. Error Theory ang Fundation of Surveying Adjustment; Wuhan University Press: Wuhan, China, 2019; p. 337. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).