Improved Trimming Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm for Mobile Robot Path Planning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Traditional Ant Colony Optimization (ACO) Algorithm
2.1. State Transition Probability
2.2. Pheromone Update
3. Improved Trimming Ant Colony Optimization (ITACO) Algorithm
3.1. Improved State Transition Probability Formula
3.2. Improved Pheromone Increment Update Strategy
- is the pheromone intensity coefficient;
- is the length of the best path in the current iteration;
- is the average path length of successful ants;
- , , are positive constants satisfying >>> 0. In this paper, = 2, = 1.5, and = 0.5.
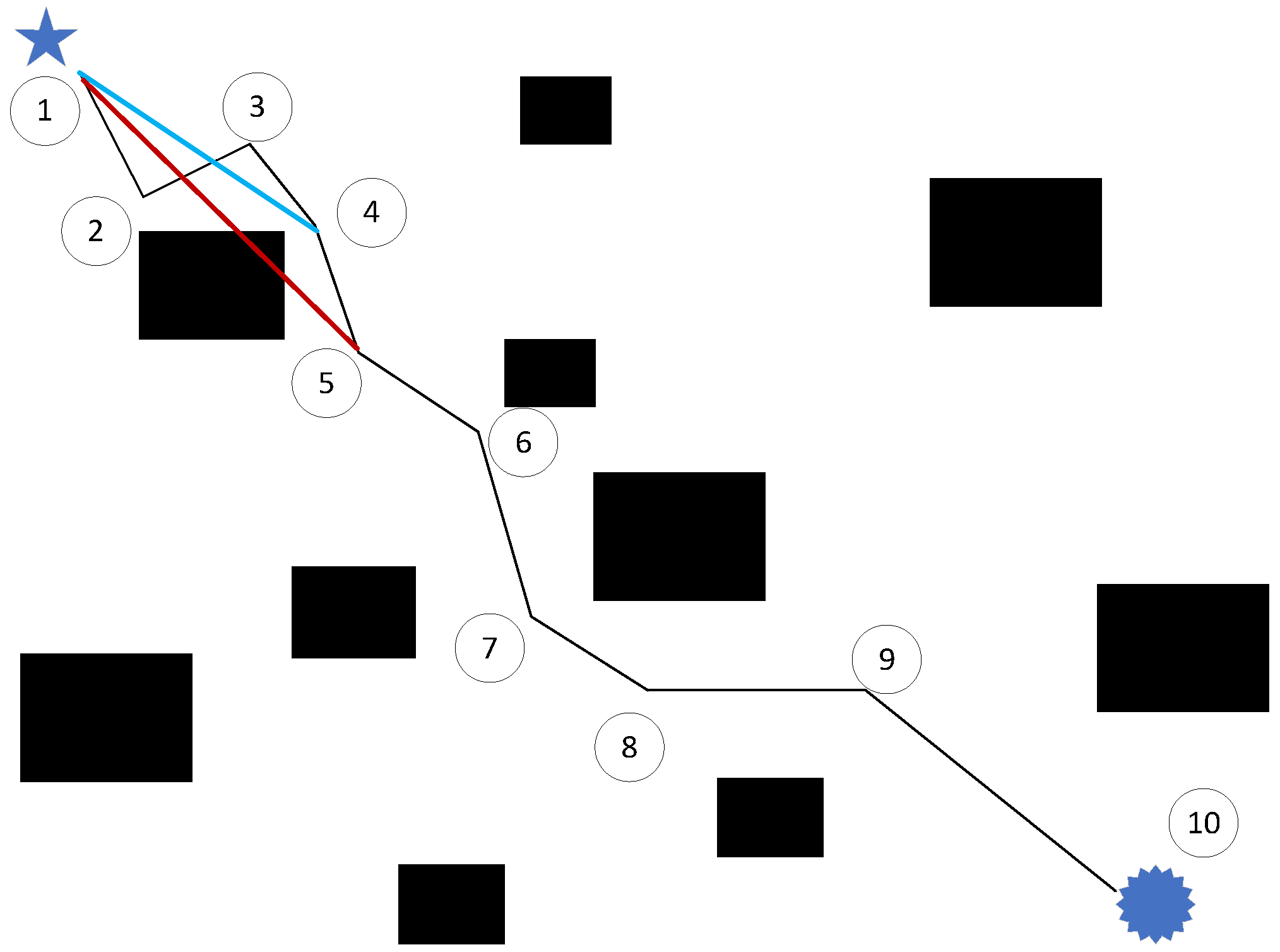
3.3. Triangular Trimming Path Optimization
- Black squares: Obstacle locations
- Circled numbers: Path nodes (1, 2, 3,…)
- Black solid line: Initial candidate path
- Blue bold line: Optimized path after pruning
- Red dashed line: Invalid obstacle-crossing paths
- The algorithm begins by connecting nodes sequentially (1→2→3→4→5…)
- When the direct connection between nodes 1→5 fails due to obstacle interference:
- (a)
- The system backtracks to the last viable node (node 4)
- (b)
- Establishes new valid segment (1→4)
- (c)
- Continues connection from node 4 onward
- This pruning process iterates until reaching the final node
4. Implementation of the Improved Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm
5. Experimental Simulation and Results
5.1. Simulation Setup
- ITACO: improved ant colony optimization algorithm proposed in this paper;
- IACO: improved algorithm without triangular pruning;
- ACO: classic ant colony algorithm.
5.2. Algorithm Performance Testing
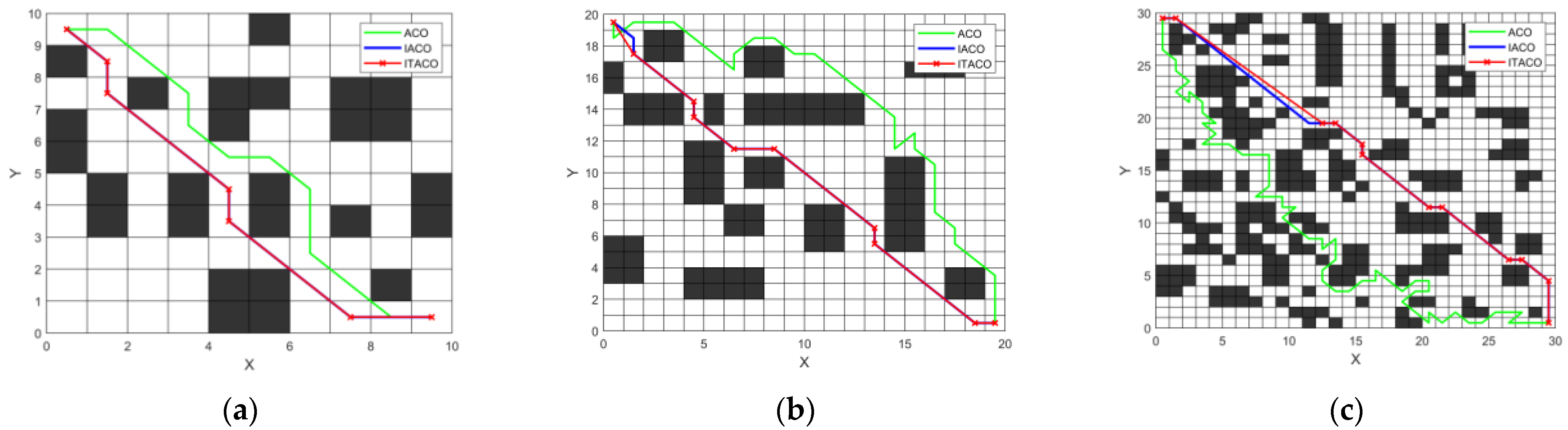
5.3. Verification of the Effectiveness of the ITACO Algorithm
- In the 10 × 10 grid map, the path lengths of the ITACO algorithm and the ACO algorithm are 13.8995 and 14.4853, respectively. Compared to the ACO algorithm, the ITACO algorithm reduces the path length by 4.04% and the computational time by 13.42%.
- In the 20 × 20 grid map, the path lengths of the ITACO algorithm and the ACO algorithm are 28.2711 and 33.5563, respectively. The ITACO algorithm reduces the path length by 15.75% and the computational time by 19.23% compared to the ACO algorithm.
- In the 30 × 30 grid map, the path lengths of the ITACO algorithm and the ACO algorithm are 43.3499 and 116.7107, respectively. The ITACO algorithm reduces the path length by 62.86% and the computational time by 22.1% compared to the ACO algorithm.
5.4. Verification of the Superiority of the ITACO Algorithm
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; Liu, C.; Zhao, Z.; Han, W.; Yin, L.; Guo, A. Design and Analysis of Small Fallen Leaf Collection, Crushing, and Recycling Vehicle. Processes 2024, 12, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Granda, I.D.; Cadena-Echeverría, J.; León-Jácome, J.C.; Herrera-Granda, E.P.; Chavez Garcia, D.; Rosales, A. A Heuristic Procedure for Improving the Routing of Urban Waste Collection Vehicles Using ArcGIS. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanushka, S.; Hasaranga, C.; Kahatapitiya, N.S.; Wijesinghe, R.E.; Wijethunge, A. Efficient Battery Management and Workflow Optimization in Warehouse Robotics Through Advanced Localization and Communication Systems. Eng. Proc. 2024, 82, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Tian, F.; Qiu, Z.; Yang, Z.; Zhan, R.; Zhan, J. Research on Machine Vision-Based Control System for Cold Storage Warehouse Robots. Actuators 2023, 12, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Ge, S.; He, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhang, S. Research on the Intelligent System Architecture and Control Strategy of Mining Robot Crowds. Energies 2024, 17, 1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, M.; Zhang, X.; Yang, W.; Wan, J.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, G. High-Precision Drilling by Anchor-Drilling Robot Based on Hybrid Visual Servo Control in Coal Mine. Mathematics 2024, 12, 2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayajneh, M.R.; Garibeh, M.H.; Younes, A.B.; Garratt, M.A. Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Path Planning Using Acceleration-Based Potential Field Methods. Electronics 2025, 14, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, S.; Wang, Z.; Xia, X.; Duan, Y. An Improved Human Evolution Optimization Algorithm for Unmanned Aerial Vehicle 3D Trajectory Planning. Biomimetics 2025, 10, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yang, Z.; Zhen, L.; Li, W.; Ren, Y. Joint optimization of order picking and replenishment in robotic mobile fulfillment systems. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2025, 194, 103930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baniasadi, P.; Foumani, M.; Smith-Miles, K.; Ejov, V. A transformation technique for the clustered generalized traveling salesman problem with applications to logistics. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2020, 285, 444–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Hou, X.R.; Yang, J. Surface optimal path planning using an extended Dijkstra algorithm. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 147827–147838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, R.; Watanobe, Y.; Islam, M.R.; Naruse, K. Enhanced Robot Motion Block of A-Star Algorithm for Robotic Path Planning. Sensors 2024, 24, 1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, T.; Chen, F.; Wu, Y.; Zeng, H.; Ouyang, S.; Guan, J. Research on Path Planning with the Integration of Adaptive A-Star Algorithm and Improved Dynamic Window Approach. Electronics 2024, 13, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Wu, H.; Wei, Y. Mobile Robot Path Planning Based on Kinematically Constrained A-Star Algorithm and DWA Fusion Algorithm. Mathematics 2023, 11, 4552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T. Recent advances in Rapidly-exploring random tree: A review. Heliyon 2024, 10, e32451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Yan, X.; Wang, Y.; Niu, Y. 3D real-time dynamic path planning for UAV based on improved interfered fluid dynamical system and artificial neural network. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2024, 59, 102306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, T.; Wang, X.; Ding, K.; Ni, K.; Zhou, Q. Improved Artificial Potential Field Algorithm Assisted by Multisource Data for AUV Path Planning. Sensors 2023, 23, 6680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awadallah, M.A.; Makhadmeh, S.N.; Al-Betar, M.A.; Dalbah, L.M.; Al-Redhaei, A.; Kouka, S.; Enshassi, O.S. Multi-objective Ant Colony Optimization: Review. Arch. Computat. Methods Eng. 2024, 32, 995–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonakis, A.; Nikolaidis, T.; Pilidis, P. Multi-Objective Climb Path Optimization for Aircraft/Engine Integration Using Particle Swarm Optimization. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faris, H.; Aljarah, I.; Al-Betar, M.A.; Mirjalili, S. Grey wolf optimizer: A review of recent variants and applications. Neural. Comput. Applic. 2018, 30, 413–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Q.; Liu, P.; Du, H.; Wang, H.; Ma, X. Improved multi-objective artificial bee colony algorithm-based path planning for mobile robots. Front. Neurorobot. 2023, 17, 1196683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Dai, Y.; Liu, H. Improvement of Dung Beetle Optimization Algorithm Application to Robot Path Planning. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorigo, M.; Birattari, M.; Stutzle, T. Ant colony optimization. IEEE Comput. Intell. Mag. 2006, 1, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.L.; Mei, H. Mobile robot global path planning based on improved ant colony system algorithm with potential field. J. Mech. Eng. 2021, 57, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Chen, S.; Zhang, K.; Qiu, G.; Li, Q.; Chen, X. A jump point search improved ant colony hybrid optimization algorithm for path planning of mobile robot. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2022, 19, 17298806221127953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, Y. Robot path planning based on improved ant colony algorithm with potential field heuristic. Control Decis. 2018, 33, 1775–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhan, J.; Huang, Y. Mobile Robot Path Planning Based on Adaptive Obstacle Avoidance Ant Colony Algorithm. J. Anhui Polytech. Univ. 2021, 36, 27–33. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, W.; Li, S.; Xie, X.; Yang, X.; Nie, J. Global path planning of mobile robot based on adaptive mechanism improved ant colony algorithm. Control Decis. 2023, 38, 2520–2528. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Li, Q.; Cui, B. Improved ant colony optimization algorithm based on islands type for mobile robot path planning. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2024, 21, 17298806241278170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, C.; Chen, G.; Yan, C.; Wu, Y. Path planning optimization of indoor mobile robot based on adaptive ant colony algorithm. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2021, 156, 107230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, F.; Zhu, S.; Dong, H.; Ren, W. A new approach to smooth path planning of Ackerman mobile robot based on improved ACO algorithm and B-spline curve. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2024, 175, 104655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Wei, W. Mobile robot path planning based on an improved ACO algorithm and path optimization. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takimi, T. A Study On Ant Colony Optimization. J. Photopolym. Sci. Technol. 2021, 3, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Q.; Liu, S.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, H. Application of Hybrid Algorithm Based on Ant Colony Optimization and Sparrow Search in UAV Path Planning. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 2024, 17, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Shao, S.; Wang, T.; Yu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Cao, Z. Review of Autonomous Path Planning Algorithms for Mobile Robots. Drones 2023, 7, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Yang, D.; Mei, Z.; Zheng, W. Progress in Construction Robot Path-Planning Algorithms: Review. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvitko, D.; Rybin, V.; Bayazitov, O.; Karimov, A.; Karimov, T.; Butusov, D. Chaotic Path-Planning Algorithm Based on Courbage–Nekorkin Artificial Neuron Model. Mathematics 2024, 12, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Liu, L.; Wang, L.; Yu, G. Energy-optimal adaptive artificial potential field method for path planning of free-flying space robots. J. Frankl. Inst. 2024, 361, 978–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Map Scale | Path Endpoint Index | Number of Ants | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 × 10 | 100 | 50 | 0.5 | 10 |
| 20 × 20 | 400 | 50 | 0.5 | 10 |
| 30 × 30 | 625 | 50 | 0.5 | 10 |
| Serial Number | Function Name | Search Range | Dimension | Theoretical Minimum Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | Shifted and Rotated Bent Cigar Function | [−100, 100]D | 30 | 100 |
| F3 | Shifted and Rotated Zakharov Function | [−100, 100]D | 30 | 300 |
| F4 | Shifted and Rotated Rosenbrock’s Function | [−100, 100]D | 30 | 400 |
| F5 | Shifted and Rotated Rastrigin’s Function | [−100, 100]D | 30 | 500 |
| F6 | Shifted and Rotated Expanded Scaffer’s F6 Function | [−100, 100]D | 30 | 600 |
| F7 | Shifted and Rotated Lunacek Bi_Rastrigin Function | [−100, 100]D | 30 | 700 |
| F8 | Shifted and Rotated Non-Continuous Rastrigin’s Function | [−100, 100]D | 30 | 800 |
| F9 | Shifted and Rotated Levy Function | [−100, 100]D | 30 | 900 |
| F10 | Shifted and Rotated Schwefel’s Function | [−100, 100]D | 30 | 1000 |
| F11 | Hybrid Function 1 (N = 3) | [−100, 100]D | 30 | 1100 |
| F12 | Hybrid Function 2 (N = 3) | [−100, 100]D | 30 | 1200 |
| F13 | Hybrid Function 3 (N = 3) | [−100, 100]D | 30 | 1300 |
| F14 | Hybrid Function 4 (N = 4) | [−100, 100]D | 30 | 1400 |
| F15 | Hybrid Function 5 (N = 4) | [−100, 100]D | 30 | 1500 |
| F16 | Hybrid Function 6 (N = 4) | [−100, 100]D | 30 | 1600 |
| F17 | Hybrid Function 6 (N = 5) | [−100, 100]D | 30 | 1700 |
| F18 | Hybrid Function 6 (N = 5) | [−100, 100]D | 30 | 1800 |
| F19 | Hybrid Function 6 (N = 5) | [−100, 100]D | 30 | 1900 |
| F20 | Hybrid Function 6 (N = 6) | [−100, 100]D | 30 | 2000 |
| F21 | Composition Function 1 (N = 3) | [−100, 100]D | 30 | 2100 |
| F22 | Composition Function 2 (N = 3) | [−100, 100]D | 30 | 2200 |
| F23 | Composition Function 3 (N = 4) | [−100, 100]D | 30 | 2300 |
| F24 | Composition Function 4 (N = 4) | [−100, 100]D | 30 | 2400 |
| F25 | Composition Function 5 (N = 5) | [−100, 100]D | 30 | 2500 |
| F26 | Composition Function 6 (N = 5) | [−100, 100]D | 30 | 2600 |
| F27 | Composition Function 7 (N = 6) | [−100, 100]D | 30 | 2700 |
| F28 | Composition Function 8 (N = 6) | [−100, 100]D | 30 | 2800 |
| F29 | Composition Function 9 (N = 3) | [−100, 100]D | 30 | 2900 |
| F30 | Composition Function 10 (N = 3) | [−100, 100]D | 30 | 3000 |
| Function | ITACO (Mean, Std, Best) | ACO (Mean, Std, Best) | AOA (Mean, Std, Best) | AMACA (Mean, Std, Best) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 1.42 × 103, 5.49 × 102, 4.41 × 102 | 7.96 × 104, 7.87 × 103, 6.18 × 104 | 7.81 × 104, 6.93 × 103, 6.45 × 104 | 7.69 × 103, 1.06 × 103, 4.86 × 103 |
| F3 | 3.01 × 102, 2.92 × 100, 3.00 × 102 | 4.33 × 103, 2.87 × 102, 3.99 × 102 | 3.03 × 102, 4.09 × 100, 3.01 × 102 | 5.04 × 102, 3.43 × 100, 3.13 × 102 |
| F4 | 4.1 × 102, 6.04 × 101, 4.01 × 102 | 4.1 × 102, 6.45 × 101, 4.01 × 102 | 4.1 × 102, 6.08 × 101, 4.01 × 102 | 4.1 × 102, 7.92 × 101, 4.01 × 102 |
| F5 | 6.2 × 102, 5.44 × 101, 5.03 × 102 | 1.11 × 103, 8.8 × 101, 1.08 × 103 | 1.02 × 103, 9.34 × 101, 1.00 × 103 | 5.14 × 102, 5.74 × 101, 5.05 × 102 |
| F6 | 8.77 × 102, 7.01 × 101, 6.11 × 102 | 6.08 × 103, 1.01 × 102, 5.24 × 103 | 9.14 × 103, 8.41 × 101, 8.63 × 103 | 9.67 × 103, 9.99 × 101, 7.00 × 103 |
| F7 | 7.47 × 102, 4.15 × 101, 7.11 × 102 | 7.49 × 103, 1.32 × 102, 4.65 × 103 | 1.03 × 104, 4.6 × 102, 5.76 × 103 | 4.73 × 103, 9.89 × 102, 1.56 × 103 |
| F8 | 9.01 × 102, 1.19 × 101, 8.01 × 102 | 9.2 × 103, 2.02 × 101, 9.14 × 102 | 1.12 × 103, 2.1 × 101, 1.11 × 103 | 1.02 × 103, 2.09 × 101, 1.01 × 103 |
| F9 | 9.21 × 102, 5.82 × 101, 9.21 × 102 | 9.21 × 102, 5.83 × 101, 9.21 × 102 | 9.21 × 102, 5.36 × 101, 9.21 × 102 | 9.21 × 102, 6.24 × 101, 9.21 × 102 |
| F10 | 1.8 × 103, 6.9 × 101, 1.22 × 103 | 4.21 × 103, 5.43 × 101, 3.81 × 103 | 4.16 × 103, 4.99 × 101, 3.91 × 103 | 4.21 × 103, 3.18 × 101, 4.05 × 103 |
| F11 | 1.99 × 103, 3.01 × 101, 1.19 × 103 | 1.89 × 104, 6.55 × 102, 4.62 × 103 | 1.79 × 104, 5.62 × 102, 8.00 × 103 | 1.93 × 104, 4.5 × 102, 1.08 × 104 |
| F12 | 2.32 × 103, 5.6 × 101, 1.25 × 103 | 1.22 × 104, 6.92 × 102, 7.19 × 103 | 1.27 × 104, 5.26 × 102, 1.09 × 104 | 2.7 × 103, 9.61 × 101, 2.19 × 103 |
| F13 | 2.43 × 103, 6.55 × 101, 1.32 × 103 | 1.5 × 104, 9.74 × 101, 1.34 × 103 | 1.45 × 104, 5.9.1 × 101, 1.33 × 103 | 1.45 × 104, 6.16 × 101, 1.31 × 103 |
| F14 | 2.5× 103, 4.19 × 101, 1.49 × 103 | 1.04 × 104, 9.15 × 102, 5.00 × 103 | 1.3 × 104, 3.05 × 102, 4.39 × 103 | 1.17 × 104, 7.48 × 102, 3.99 × 103 |
| F15 | 2.73 × 103, 5.66 × 101, 1.52 × 103 | 5.88 × 103, 1.35 × 102, 1.55 × 103 | 1.92 × 103, 6.87 × 101, 1.54 × 103 | 3.62 × 103, 8.19 × 101, 1.52 × 103 |
| F16 | 2.99 × 103, 8.15 × 101, 1.67 × 103 | 8.73 × 103, 5.77 × 102, 5.58 × 103 | 5.97 × 103, 3.54 × 102, 4.1 × 103 | 7.1 × 103, 2.02 × 102, 5.78 × 103 |
| F17 | 2.76 × 103, 1.66 × 102, 1.75 × 103 | 8.67 × 103, 4.85 × 103, 6.88 × 103 | 7.88 × 103, 5.41 × 103, 2.92 × 103 | 7.72 × 103, 6.25 × 103, 2.31 × 103 |
| F18 | 3.27 × 103, 1.31 × 102, 1.84 × 103 | 4.06 × 103, 5.91 × 102, 2.96 × 103 | 5.27 × 103, 2.67 × 102, 4.04 × 103 | 3.84 × 103, 8.43 × 102, 2.19 × 103 |
| F19 | 3.08 × 103, 2.72 × 102, 1.92 × 103 | 1.22 × 104, 5.37 × 102, 8.16 × 103 | 1.13 × 104, 2.27 × 102, 1.05 × 104 | 1.37 × 104, 4.74 × 102, 6.32 × 103 |
| F20 | 2.11 × 103, 1.9 × 102, 2.04 × 103 | 6.61 × 103, 5.34 × 102, 4.37 × 103 | 6.23 × 103, 7.29 × 102, 3.25 × 103 | 6.51 × 103, 6.84 × 102, 4.13 × 103 |
| F21 | 4.25 × 103, 4.12 × 101, 2.18 × 103 | 6.48 × 103, 8.45 × 102, 4.36 × 103 | 6.66 × 103, 6.85 × 102, 4.91 × 103 | 6.6 × 103, 8.13 × 102, 4.75 × 103 |
| F22 | 6.6 × 103, 8.13 × 102, 2.75 × 103 | 6.24 × 103, 5.63 × 102, 4.37 × 103 | 6.14 × 103, 6.25 × 102, 4.57 × 103 | 6.31 × 103, 4.37 × 102, 5.52 × 103 |
| F23 | 3.75 × 103, 1.46 × 102, 2.5× 103 | 6.56 × 103, 6.07 × 102, 5.19 × 103 | 6.40 × 103, 6.74 × 102, 4.34 × 103 | 6.32 × 103, 7.44 × 102, 4.77 × 103 |
| F24 | 32.62 × 103, 1.54 × 102, 2.57 × 103 | 6.42 × 103, 7.57 × 102, 4.62 × 103 | 6.24 × 103, 6.78 × 102, 5.04 × 103 | 6.13 × 103, 6.56 × 102, 4.38 × 103 |
| F25 | 4.75 × 103, 2.12 × 102, 2.62 × 103 | 5.98 × 103, 5.41 × 102, 4.45 × 103 | 5.8 × 103, 5.78 × 102, 4.28 × 103 | 5.73 × 103, 6.62 × 102, 3.55 × 103 |
| F26 | 4.78 × 103, 3.18 × 102, 2.69 × 103 | 5.72 × 103, 6.65 × 102, 4.39 × 103 | 5.78 × 103, 5.57 × 102, 4.58 × 103 | 5.95 × 103, 5.47 × 102, 4.55 × 103 |
| F27 | 3.88 × 103, 2.94 × 102, 2.79 × 103 | 6.39 × 103, 6.42 × 102, 4.85 × 103 | 6.35 × 103, 6.7 × 102, 4.79 × 103 | 6.1 × 103, 8.32 × 102, 4.18 × 103 |
| F28 | 3.98 × 103, 2.69 × 102, 2.94 × 103 | 6.28 × 103, 5.48 × 102, 5.06 × 103 | 6.47 × 103, 7.72 × 102, 4.17 × 103 | 6.26 × 103, 5.01 × 102, 5.24 × 103 |
| F29 | 4.25 × 103, 3.58 × 102, 3.11 × 103 | 6.56 × 103, 7.05 × 102, 4.17 × 103 | 6.84 × 103, 7.41 × 102, 5.46 × 103 | 6.44 × 103, 8.15 × 102, 4.67 × 103 |
| F30 | 5.24 × 103, 5.94 × 102, 3.19 × 103 | 6.27 × 103, 6.25 × 102, 4.94 × 103 | 6.28 × 103, 7.47 × 102, 3.75 × 103 | 6.38 × 103, 7.25 × 102, 4.39 × 103 |
| Map Scale | Algorithm | Theoretical Shortest Path | Path Length | Trimmed Path Length | Iterations | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 × 10 | ACO | 13.4350 | 14.4853 | - | - | 0.4261 |
| ITACO | 13.4350 | 13.8995 | 13.8995 | 1 | 0.3689 | |
| 20 × 20 | ACO | 27.5772 | 33.5563 | - | - | 4.8569 |
| ITACO | 27.5772 | 28.6274 | 28.2711 | 3 | 3.9229 | |
| 30 × 30 | ACO | 41.7193 | 116.7107 | - | - | 19.4413 |
| ITACO | 41.7193 | 50.5269 | 43.3499 | 5 | 15.1451 |
| Algorithm | Path Length | Improvement (%) | Iterations |
|---|---|---|---|
| ITACO | 27.5471 | 2 | |
| AOA | 30.3848 | 9.34% | 21 |
| AMACA | 28.0416 | 1.76% | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, J.; Liu, Q.; Yang, Z.; Wang, B. Improved Trimming Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm for Mobile Robot Path Planning. Algorithms 2025, 18, 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18050240
Ma J, Liu Q, Yang Z, Wang B. Improved Trimming Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm for Mobile Robot Path Planning. Algorithms. 2025; 18(5):240. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18050240
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Junxia, Qilin Liu, Zixu Yang, and Bo Wang. 2025. "Improved Trimming Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm for Mobile Robot Path Planning" Algorithms 18, no. 5: 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18050240
APA StyleMa, J., Liu, Q., Yang, Z., & Wang, B. (2025). Improved Trimming Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm for Mobile Robot Path Planning. Algorithms, 18(5), 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18050240








