Knowledge Discovery in Predicting Martensite Start Temperature of Medium-Carbon Steels by Artificial Neural Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
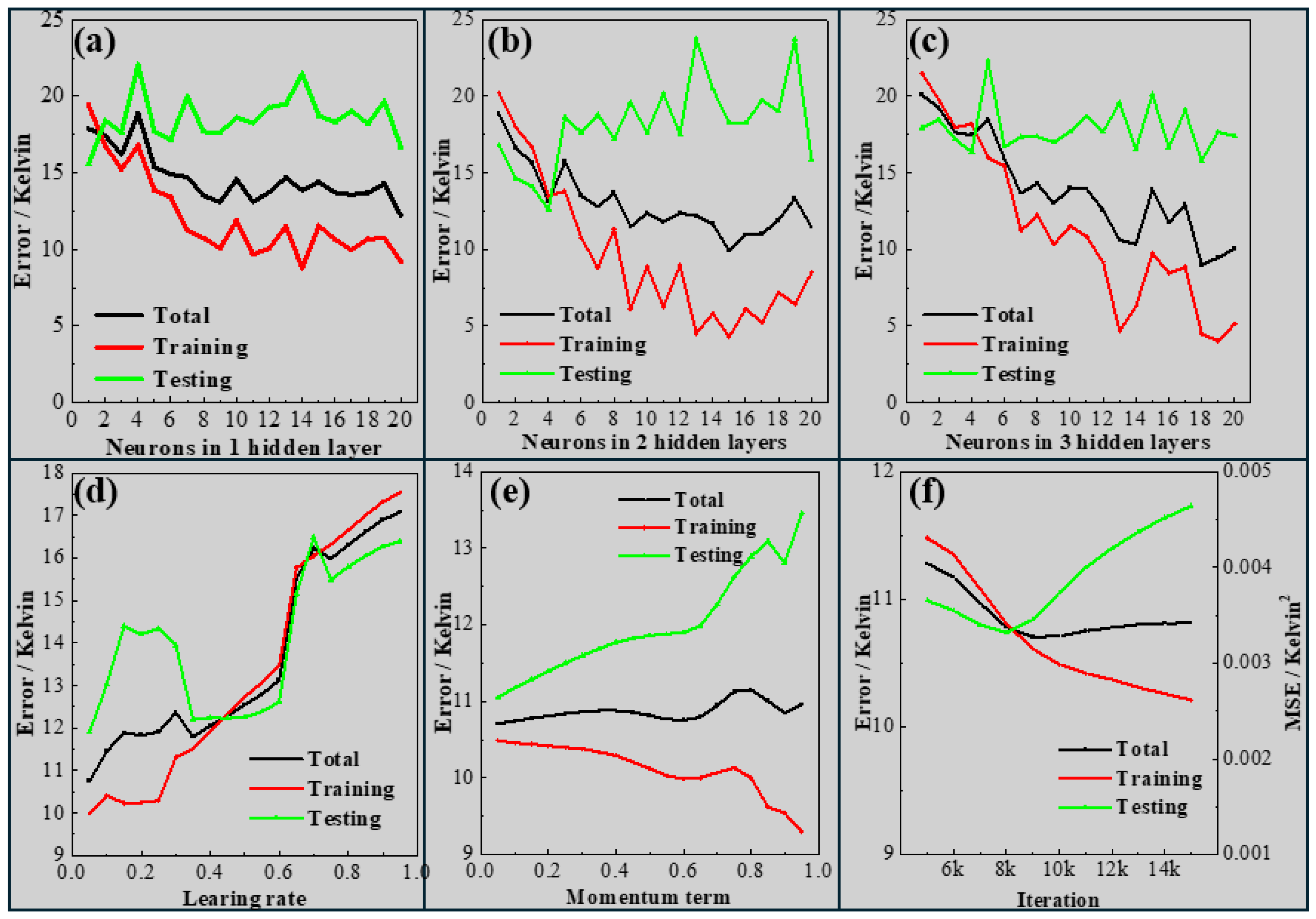
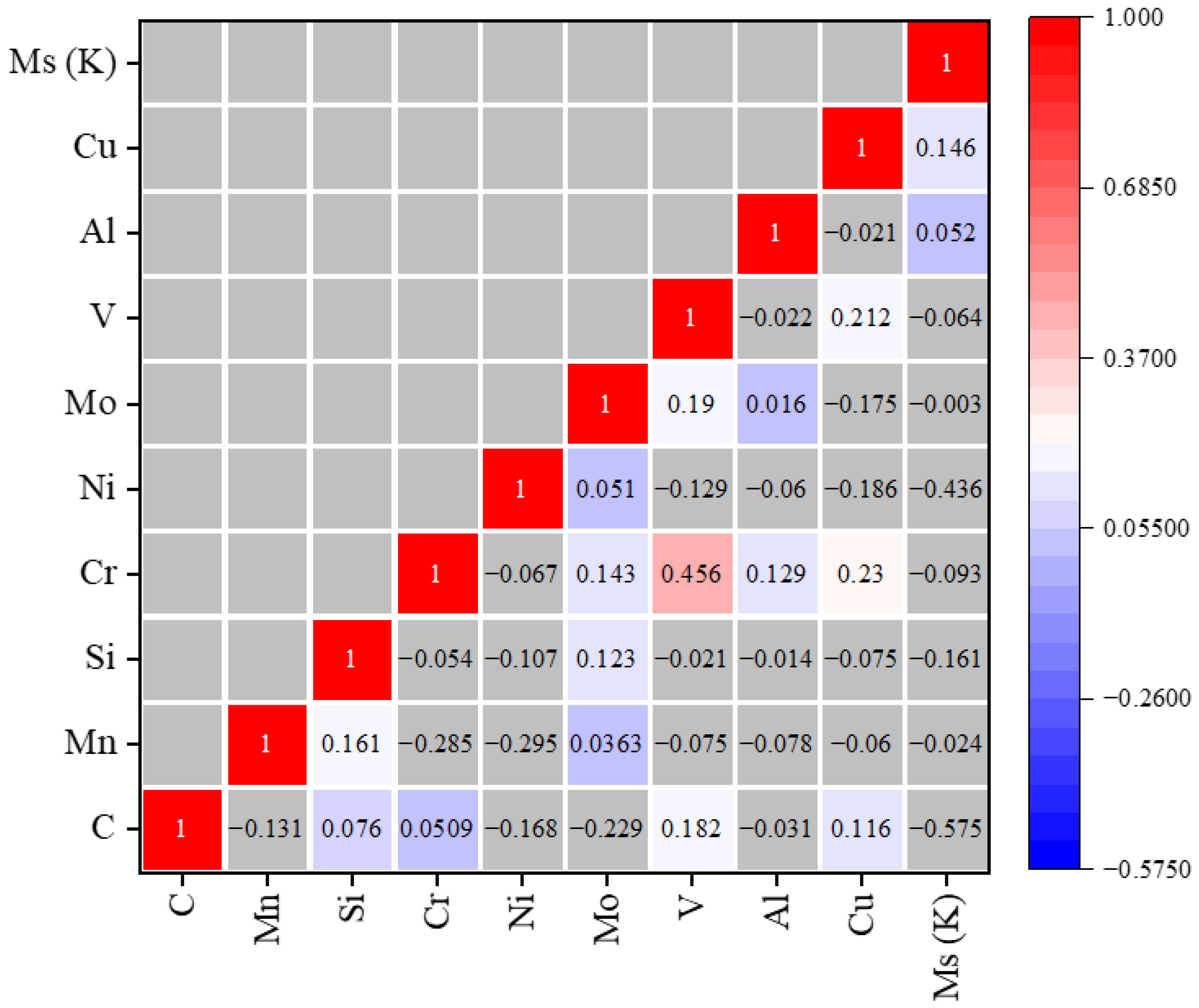
2. Methodology and Experimental Database
- Collection of data.
- 2.
- Grouping of data.
- 3.
- Training of ANN.
- 4.
- Correlation Analysis.
- 5.
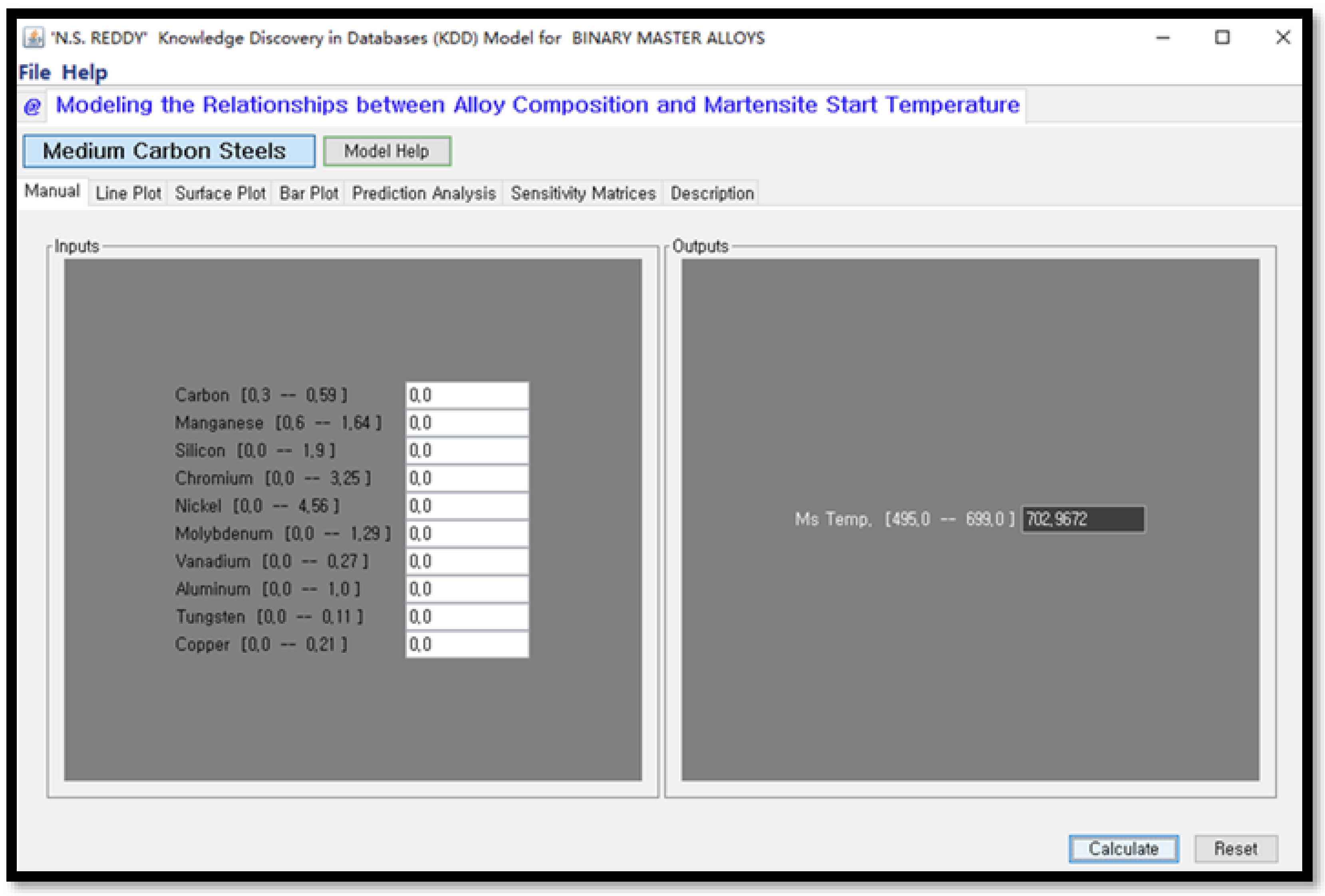
- Simulation and prediction using the trained ANN model.
3. Results and Discussion
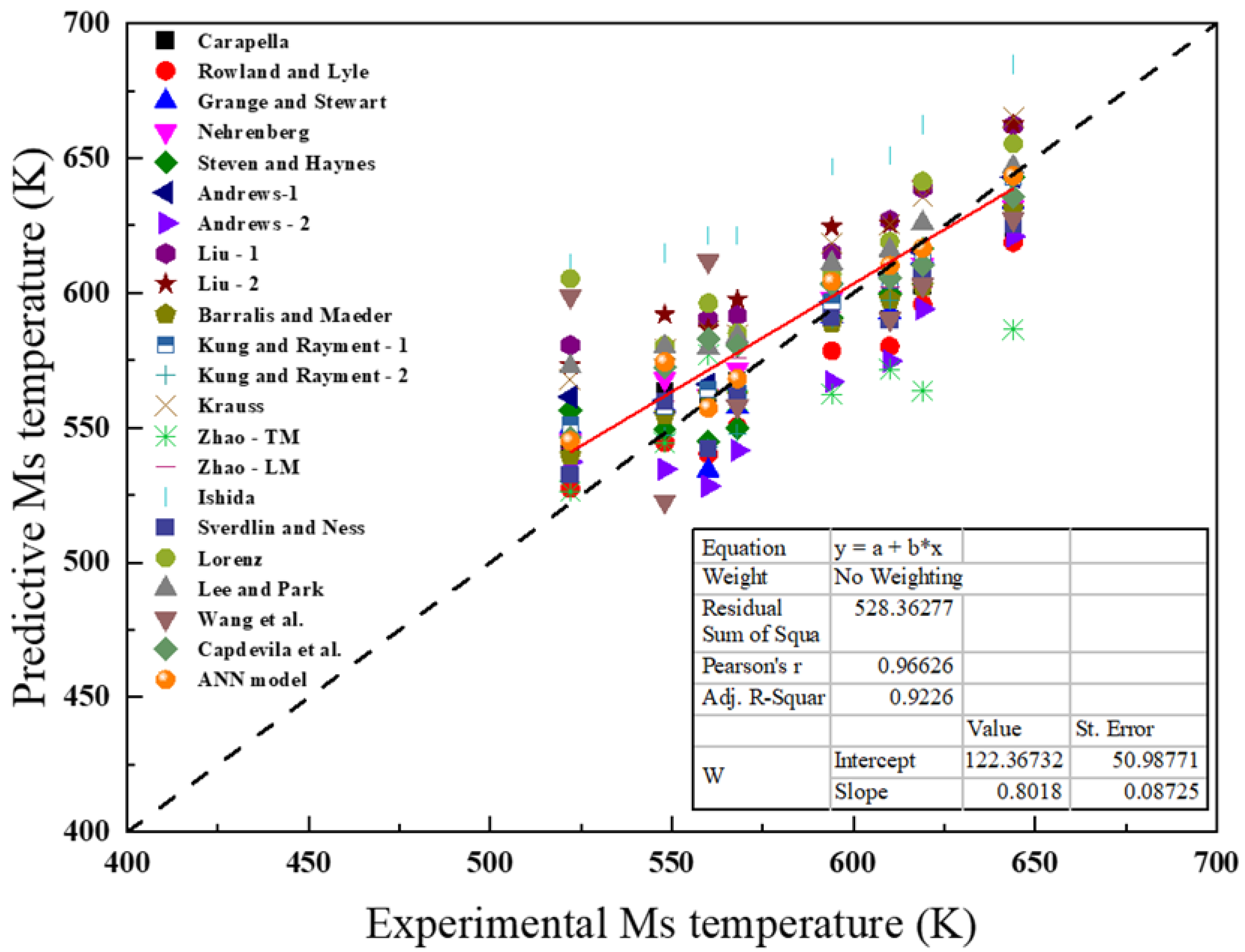
3.1. Comparisons Among the Predicted Ms Temperature Results
3.2. Quantitative Effect of Individual Alloying Element
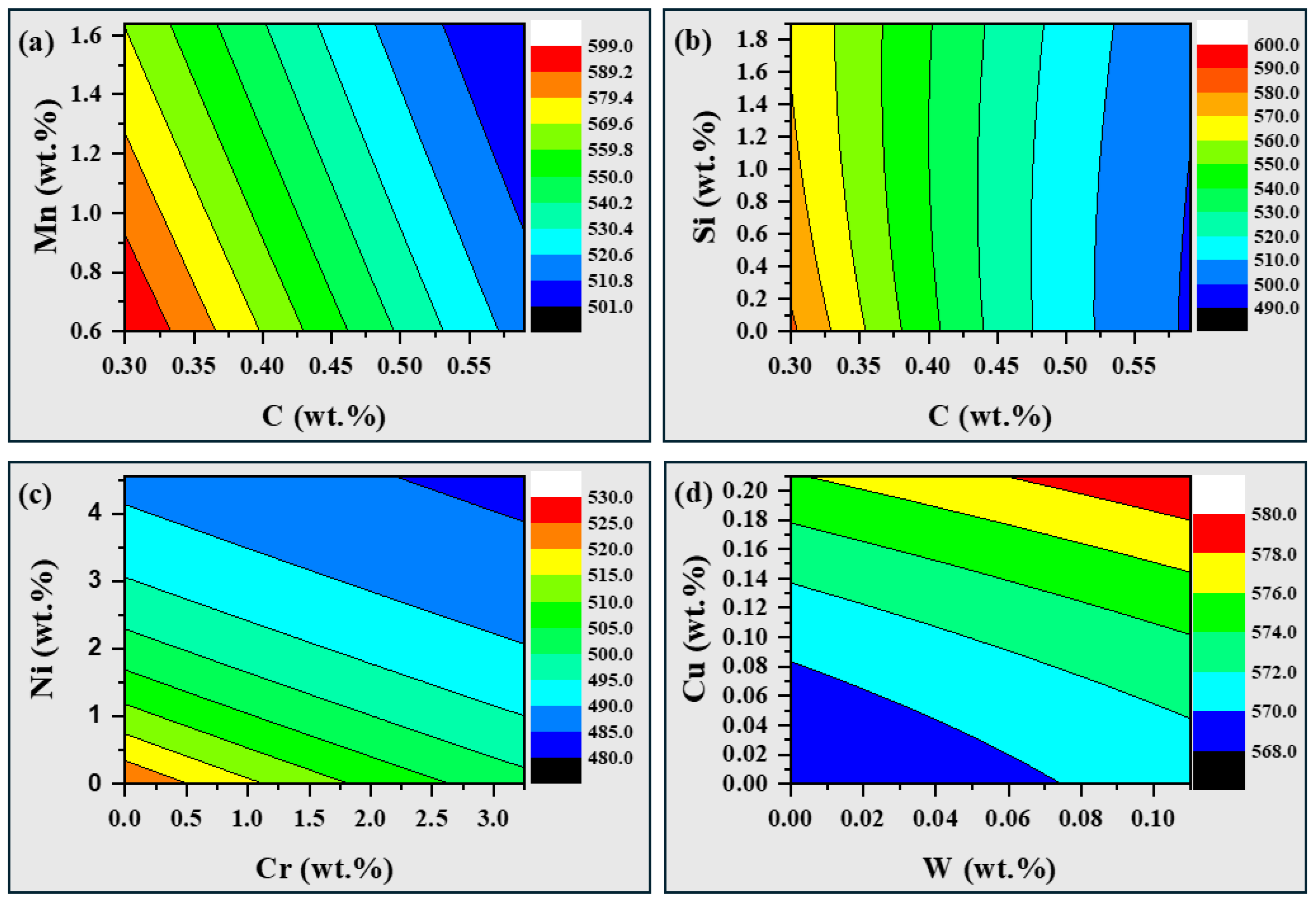
3.3. Varying Effect of Dual Alloying Elements
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Ms | Martensite start |
| ANN | Artificial neural network |
| MAE | Mean absolute error |
| AAE | Average absolute error |
| MSE | Mean squared error |
| MPE | Mean percentage error |
| GUI | Graphical user interface |
| KDD | Knowledge discovery in databases |
References
- Wiewiórowska, S.; Muskalski, Z. The Application of Low and Medium Carbon Steel with Multiphase TRIP Structure in Drawing Industry. Procedia Manuf. 2015, 2, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, O.N. 13—Forging Grade Steels for Automotives. In Automotive Steels; Rana, R., Singh, S.B., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2017; pp. 413–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, K.-i.; Hojo, T.; Srivastava, A.K. Low and Medium Carbon Advanced High-Strength Forging Steels for Automotive Applications. Metals 2019, 9, 1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Feng, H.; Wang, S.; Gao, J.; Zhao, H.; Wu, H.; Xu, S.; Feng, Q.; Li, H.; Liu, X.; et al. Phase Transformation Behaviors of Medium Carbon Steels Produced by Twin Roll Casting and Compact Strip Production Processes. Materials 2023, 16, 1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishtiaq, M.; Inam, A.; Tiwari, S.; Seol, J.B. Microstructural, mechanical, and electrochemical analysis of carbon doped AISI carbon steels. Appl. Microsc. 2022, 52, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Bohemen, S.M.C.; Sietsma, J. Kinetics of martensite formation in plain carbon steels: Critical assessment of possible influence of austenite grain boundaries and autocatalysis. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2014, 30, 1024–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payson, P. Martensite reactions in alloy steels. Trans. Am. Soc. Met. 1944, 33, 261–280. [Google Scholar]
- Nehrenberg, A. Contribution to discussion on grange and stewart. Trans. Am. Inst. Min. Met. Eng 1946, 167, 494–498. [Google Scholar]
- Grange, R. The temperature range of martensite formation. Trans. Am. Inst. Min. Metall. Eng. 1946, 167, 467–501. [Google Scholar]
- Steven, W. The temperature of martensite and bainite in low-alloy steels. J. Iron Steel Inst. 1956, 183, 349–359. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, K. Empirical formulae for the calculation of some transformation temperatures. J. Iron Steel Inst. 1965, 203, 721–727. [Google Scholar]
- Van Bohemen, S. Bainite and martensite start temperature calculated with exponential carbon dependence. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2012, 28, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capdevila, C.; Caballero, F.G.; De Andrés, C.G. Determination of Ms temperature in steels: A Bayesian neural network model. ISIJ Int. 2002, 42, 894–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, L.; Hollomon, J. Hardenability and quench cracking. AIME TRANS 1946, 13, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Kung, C.; Rayment, J. An Examination of the Validity of Existing Empirical Formulae for the Calculation of Ms Temperature. 1981. Available online: https://escholarship.org/content/qt9mh7k297/qt9mh7k297.pdf (accessed on 13 February 2025).
- Li, C.; Liu, P.; Wang, M. Computation of Ms temperature in carbon equivalence method. J. Liaoning Tech. Univ. Nat. Sci. 1998, 17, 293–295. [Google Scholar]
- Pickering, F. Physical metallurgical development of stainless steels. In Proceedings of the Stainless Steels 84, Goteborg, Sweden, 3–4 September 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Rowland, E.; Lyle, S. The application of Ms points to case depth measurement. Trans. ASM 1946, 37, 27–47. [Google Scholar]
- Sverdlin, A.; Ness, A. The effects of alloying elements on the heat treatment of steel. In Steel Heat Treatment Handbook; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1997; pp. 45–92. [Google Scholar]
- Trzaska, J. Calculation of critical temperatures by empirical formulae. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2016, 61, 981–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramlich, A.; van der Linde, C.; Ackermann, M.; Bleck, W. Effect of molybdenum, aluminium and boron on the phase transformation in 4 wt.–% manganese steels. Results Mater. 2020, 8, 100147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, K. Calculation of the effect of alloying elements on the Ms temperature in steels. J. Alloys Compd. 1995, 220, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhao, Z.; Northwood, D.O.; Liu, Y. A new empirical formula for the calculation of MS temperatures in pure iron and super-low carbon alloy steels. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2001, 113, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, A.; Ozer, T. Determination of martensite transformation temperatures associated with Fe-Mn-Si-Ni-Cr-Ce-Ti-N shape memory alloys. Can. Metall. Q. 2005, 44, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-J.; Park, K.-S. Prediction of Martensite Start Temperature in Alloy Steels with Different Grain Sizes. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2013, 44, 3423–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wolk, P.J.V.d.; Zwaag, S.V.d. Determination of Martensite Start Temperature in Engineering Steels Part I. Empirical Relations Describing the Effect of Steel Chemistry. Mater. Trans. JIM 2000, 41, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.-S.; Jang, J.H.; Bhadeshia, H.; Suh, D.-W. Critical assessment: Martensite-start temperature for the γ→ε transformation. Calphad-Comput. Coupling Phase Diagr. Thermochem. 2012, 36, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peet, M. Prediction of martensite start temperature. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2015, 31, 1370–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carapella, L. Computing A” or ms (transformation temperature on quenching) from analysis. Met. Prog. 1944, 46, 108. [Google Scholar]
- Ishibe, T.; Maeda, Y.; Terada, T.; Naruse, N.; Mera, Y.; Kobayashi, E.; Nakamura, Y. Resistive switching memory performance in oxide hetero-nanocrystals with well-controlled interfaces. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2020, 21, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garmroudi, F.; Riss, A.; Parzer, M.; Reumann, N.; Müller, H.; Bauer, E.; Khmelevskyi, S.; Podloucky, R.; Mori, T.; Tobita, K.; et al. Boosting the thermoelectric performance of Fe2Val—Type Heusler compounds by band engineering. Phys. Rev. B 2021, 103, 085202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishtiaq, M.; Tiwari, S.; Panigrahi, B.B.; Seol, J.B.; Reddy, N.S. Neural Network-Based Modeling of the Interplay between Composition, Service Temperature, and Thermal Conductivity in Steels for Engineering Applications. Int. J. Thermophys. 2024, 45, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paturi, U.M.R.; Cheruku, S.; Reddy, N.S. The Role of Artificial Neural Networks in Prediction of Mechanical and Tribological Properties of Composites—A Comprehensive Review. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2022, 29, 3109–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Gahtani, K.S.; Alsugair, A.M.; Alsanabani, N.M.; Alabduljabbar, A.A.; Almohsen, A.S. ANN prediction model of final construction cost at an early stage. J. Asian Archit. Build. Eng. 2024, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daoud, M.; Mayo, M. A survey of neural network-based cancer prediction models from microarray data. Artif. Intell. Med. 2019, 97, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkáč, M.; Verner, R. Artificial neural networks in business: Two decades of research. Appl. Soft Comput. 2016, 38, 788–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-S.; Narayana, P.L.; Maurya, A.K.; Kim, H.-I.; Hur, B.-Y.; Reddy, N.S. Modeling the quantitative effect of alloying elements on the Ms temperature of high carbon steel by artificial neural networks. Mater. Lett. 2021, 291, 129573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.-C. Continuous cooling transformations in steels. Mater. Sci. Technol. 1992, 8, 997–1003. [Google Scholar]
- Barralis, J.; Maeder, G. Métallurgie-Tome I: Métallurgie Physique; Collection Scientifique ENSAM; Communication Actives: Paris, France, 1982; p. 270. [Google Scholar]
- Krauss, G. Steels: Heat Treatment and Processing Principles; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz, U. Anwendung von Werkstoffmodellen auf die Phasenumwandlung und die Austenitkonditionierung von Stählen. Ph.D. Thesis, Institut für Eisenhüttenkunde der RWTH Aachen, Aachen, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Capdevila, C.; Caballero, F.G.; García De Andrés, C. Analysis of effect of alloying elements on martensite start temperature of steels. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2003, 19, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
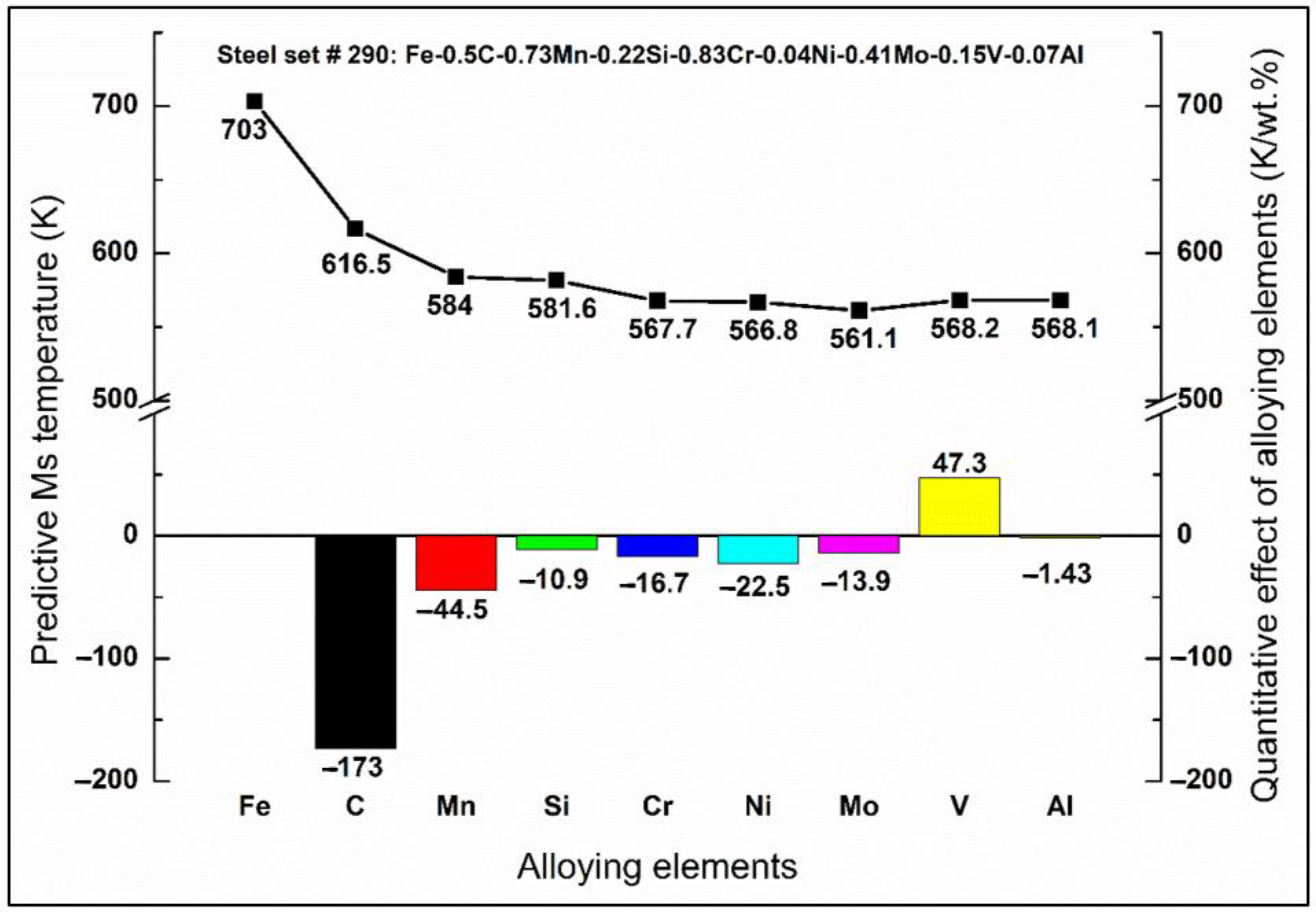
| Data No. | C | Mn | Si | Cr | Ni | Mo | V | Al | W | Cu | Experimental Ms (K) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 206 | 0.41 | 1.42 | 1.42 | 0.78 | 1.37 | 0.03 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 522 |
| 221 | 0.51 | 0.72 | 0.27 | 0.94 | 0.15 | 0.05 | 0.2 | 0 | 0.11 | 0.15 | 548 |
| 236 | 0.45 | 0.8 | 0.25 | 1.15 | 0.55 | 1 | 0.05 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 560 |
| 244 | 0.3 | 0.8 | 0 | 0.55 | 0.54 | 0.21 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 644 |
| 246 | 0.43 | 0.74 | 0 | 0.92 | 0 | 0 | 0.16 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 594 |
| 266 | 0.35 | 0.65 | 0.13 | 0.55 | 1.27 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 619 |
| 290 | 0.5 | 0.73 | 0.22 | 0.83 | 0.04 | 0.41 | 0.15 | 0.07 | 0 | 0 | 568 |
| 308 | 0.39 | 0.82 | 0.31 | 0.96 | 0.13 | 0.2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.08 | 610 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.-S.; Maurya, A.K.; Ishtiaq, M.; Kang, S.-G.; Reddy, N.G.S. Knowledge Discovery in Predicting Martensite Start Temperature of Medium-Carbon Steels by Artificial Neural Networks. Algorithms 2025, 18, 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18020116
Wang X-S, Maurya AK, Ishtiaq M, Kang S-G, Reddy NGS. Knowledge Discovery in Predicting Martensite Start Temperature of Medium-Carbon Steels by Artificial Neural Networks. Algorithms. 2025; 18(2):116. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18020116
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiao-Song, Anoop Kumar Maurya, Muhammad Ishtiaq, Sung-Gyu Kang, and Nagireddy Gari Subba Reddy. 2025. "Knowledge Discovery in Predicting Martensite Start Temperature of Medium-Carbon Steels by Artificial Neural Networks" Algorithms 18, no. 2: 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18020116
APA StyleWang, X.-S., Maurya, A. K., Ishtiaq, M., Kang, S.-G., & Reddy, N. G. S. (2025). Knowledge Discovery in Predicting Martensite Start Temperature of Medium-Carbon Steels by Artificial Neural Networks. Algorithms, 18(2), 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18020116








