Statistical and Machine Learning Models for Air Quality: A Systematic Review of Methods and Challenges
Abstract
1. Introduction
- RQ1: What are the main anthropogenic and natural factors affecting air quality?
- RQ2: How do machine learning models compare with statistical approaches in terms of accuracy, generalizability, and interpretability in air quality prediction?
- RQ3: What are the main challenges in implementing predictive air quality models?
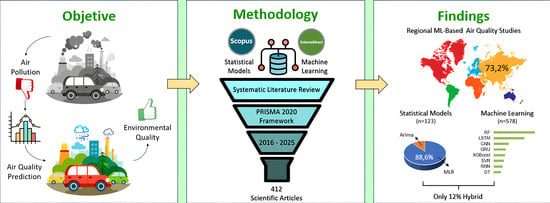
2. Methodology
2.1. Identification Stage
2.2. Filtering Stage
2.3. Eligibility Stage: Analysis and Synthesis
2.4. Quality Assessment Stage
- Registration statement
3. Results
- (i)
- Sheets—Perspectives (2022–2025, n = 307, 74.51%)
- (ii)
- Trunk—Structural (2019–2021, n = 87, 21.12%)
- (iii)
- Root—Classics (≤2018, n = 18, 4.37%)
3.1. Typology of Applied Predictive Models
3.2. Variables Used in Modeling
3.3. Performance Evaluation Indicators
3.4. Comparison Between Statistical and Machine Learning Models
3.5. Factors, Performance, and Challenges in the Implementation of Predictive Air Quality Models
- RQ1: What are the main anthropogenic and natural factors affecting air quality?
- RQ2: How do machine learning models compare with statistical approaches?
- RQ3: What are the main challenges in the implementation of predictive air quality models?
4. Discussion
4.1. Models Used and Overall Performance
4.2. Specific Applications of ML Models
4.3. Guidelines for Model Selection
4.4. Integration of Diverse Data and Emerging Opportunities
- Smart Cities and Data Openness: Studies by [178,197] demonstrate that open-access urban sensing platforms and automated AI-based systems (e.g., AI-Air) significantly improve model responsiveness and real-time forecasting accuracy. These platforms enable continuous updates, increase model efficiency, and reduce systematic biases when compared to traditional deterministic models.
- Sustainable Development Synergies: Studies by [198,199] illustrate how machine learning frameworks can better capture complex, nonlinear relationships among environmental, social, and economic dimensions of sustainability. This integration contributes to more context-sensitive and operationally relevant decision-making tools.
- Citizen Science and Community Engagement: Studies by [199,200] show how participatory data collection using low-cost mobile sensors empowers communities and enhances spatial granularity. These approaches allow detection of localized pollution episodes, particularly in under-monitored regions, and foster co-creation of air sensing schemes through inclusive citizen engagement.
- Algorithmic Innovations and Explainability: ref. [178] present an automated ML system that improves forecasting accuracy for both inland and coastal urban areas. This work highlights the role of AI-enhanced methods in identifying key meteorological drivers of pollution and correcting overestimation or underestimation errors. Furthermore, the use of explainability tools such as SHAP and LIME ensures transparency in predictive outputs.
4.5. Regulatory Considerations and Industry Standards
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| List of Machine Learning Acronyms | |
| RF | Random Forest: ensemble of decision trees for classification or regression |
| K-NN | K-Nearest Neighbors: classification based on proximity to k closest neighbors |
| LASSO | Linear regression with L1 penalty for feature selection |
| DT | Decision Tree: sequential decision-making structure |
| SVR | Support Vector Regression: regression using support vector machines |
| XGBoost | Extreme Gradient Boosting: optimized and efficient boosting algorithm |
| DNN | Deep Neural Network: multilayered neural architecture |
| Stacked-BDLSTM | Bidirectional LSTM stacked for time series modeling |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory: RNN specialized in long temporal sequences |
| RNN | Recurrent Neural Network: neural network with memory of prior states |
| GRU | Gated Recurrent Unit: efficient LSTM variant |
| DTMC | Discrete Time Markov Chain: stochastic prediction using transition probabilities |
| EML | Extreme Machine Learning: single-layer fast neural network |
| NNs | Classical Neural Networks |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine: margin-based classifier |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network: spatial pattern extraction in time series |
| Bayesian LSTM | LSTM with Bayesian inference optimization |
| CNN-LSTM | Combined CNN and LSTM model |
| DL-CTEM | Deep Learning Complex Trait Estimation Model for industrial gas prediction |
| ConvLSTM | Convolutional LSTM: LSTM with spatial convolution layers |
| GCN | Graph Convolutional Network: graph-based deep learning for spatial dependencies |
| List of Target Variables and Air Pollutants | |
| PM2.5 | Fine particulate matter (≤2.5 µm), highly penetrative and harmful |
| PM10 | Coarse particulate matter (≤10 µm), affects upper respiratory tract |
| AQI | Air Quality Index: composite air quality score |
| Ozone/O3 | Tropospheric ozone, a secondary pollutant causing respiratory irritation |
| NO2 | Nitrogen dioxide, from traffic and industrial combustion |
| CO2 | Carbon dioxide, greenhouse gas |
| H2S | Hydrogen sulfide, toxic industrial gas |
| NH3 | Ammonia, emitted from fertilizers and waste |
| SO2 | Sulfur dioxide, from fossil fuel combustion |
| CO | Carbon monoxide, from incomplete combustion |
| NOx | Nitrogen oxides, precursors to ozone and smog |
| CFCs | Chlorofluorocarbons, ozone-depleting substances |
| Propylene | Volatile organic compound from industrial sources |
| CH4 | Methane, powerful greenhouse gas |
| HC | Hydrocarbons, ozone and smog precursors |
| Deaths | Deaths attributable to poor air quality |
| API | Air Pollution Index: alternative pollution index used in some regions |
References
- Pak, A.; Rad, A.K.; Nematollahi, M.J.; Mahmoudi, M. Application of the Lasso regularisation technique in mitigating overfitting in air quality prediction models. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dongre, P.K.; Patel, V.; Bhoi, U.; Maltare, N.N. An outlier detection framework for Air Quality Index prediction using linear and ensemble models. Decis. Anal. J. 2025, 14, 100546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindiran, G.; Karthick, K.; Rajamanickam, S.; Datta, D.; Das, B.; Shyamala, G.; Hayder, G.; Maria, A. Ensemble stacking of machine learning models for air quality prediction for Hyderabad City in India. iScience 2025, 28, 111894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omer, M.; Ali, S.J.; Raza, S.M.; Le, D.-T.; Choo, H. Integrating Temporal Analysis with Hybrid Machine Learning and Deep Learning Models for Enhanced Air Quality Prediction. In Proceedings of the 2025 19th International Conference on Ubiquitous Information Management and Communication (IMCOM), Bangkok, Thailand, 3–5 January 2025; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2025; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Chaturvedi, P. Air Quality Prediction System Using Machine Learning Models. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2024, 235, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadriddin, Z.; Mekuria, R.R.; Gaso, M.S. Machine Learning Models for Advanced Air Quality Prediction. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Systems and Technologies 2024, Ruse, Bulgaria, 14–15 June 2024; pp. 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, H.K.; Patel, P.K.; Singh, S. Evaluation of Predictive Models for Air Quality Index Prediction in an Indian Urban Area. J. Indian Assoc. Environ. Manag. (JIAEM) 2024, 42, 31–40. [Google Scholar]
- Dawar, I.; Singal, M.; Singh, V.; Lamba, S.; Jain, S. Air Quality Prediction Using Machine Learning Models: A Predictive Study in the Himalayan City of Rishikesh. SN Comput. Sci. 2024, 5, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pande, C.B.; Radhadevi, L.; Satyanarayana, M.B. Evaluation of machine learning and deep learning models for daily air quality index prediction in Delhi city, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthwal, A.; Goel, A.K. Advancing air quality prediction models in urban India: A deep learning approach integrating DCNN and LSTM architectures for AQI time-series classification. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2024, 10, 2935–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-H.; Chen, P.-H.; Yang, C.-S.; Chuang, L.-Y. Analysis and Forecasting of Air Pollution on Nitrogen Dioxide and Sulfur Dioxide using Deep Learning. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 165236–165252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochadiani, T.H. Prediction of Air Quality Index Using Ensemble Models. J. Appl. Inform. Comput. 2024, 8, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B. Comparative Investigation of Machine Learning and Deep Learning Approaches for Air Quality Prediction. ITM Web Conf. 2024, 73, 02002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutar, A.; Rane, K.P.; Bansal, R.P.; Srivastava, V.; Prasad, P.V.; Lakshmi, T.R. A Legal Optimized Hybrid Deep Learning Models for Enhanced Real-Time Air Quality Prediction and Environmental Monitoring Using LSTM and CNN Architectures. Libr. Prog.-Libr. Sci. Inf. Technol. Comput. 2024, 44, 22091. [Google Scholar]
- Vonitsanos, G.; Panagiotakopoulos, T.; Kameas, A. Comparative Analysis of Time Series and Machine Learning Models for Air Quality Prediction Utilizing IoT Data. In IFIP International Conference on Artificial Intelligence Applications and Innovations; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 221–235. [Google Scholar]
- Aldape-Pérez, M.; Argüelles-Cruz, A.J.; Rodríguez-Molina, A.; Villarreal-Cervantes, M.G. Air Quality Prediction in Smart Cities Using Wireless Sensor Network and Associative Models. In International Congress of Telematics and Computing; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 216–240. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.; Han, H.; Wang, W.; Kang, Y.; Lee, H.; Kim, H.S. Application of deep learning models and network method for comprehensive air-quality index prediction. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X. Construction of Air Pollutant Monitoring and Air Quality Prediction Models based on Optimized Random Forests. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Integrated Intelligence and Communication Systems (ICIICS), Kalaburagi, India, 24–25 November 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Karimi, F.; Amanollahi, J.; Reisi, M.; Darand, M. Prediction of air quality using vertical atmospheric condition and developing hybrid models. Adv. Space Res. 2023, 72, 1172–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehshiri, S.S.H.; Firoozabadi, B. A multi-objective framework to select numerical options in air quality prediction models: A case study on dust storm modeling. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 863, 160681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Chau, L.; Miao, Y.; Lee, P.U.S. Prediction of Indoor Bioaerosol Concentrations from Indoor Air Quality Sensor Data by Artificial Intelligence Models. Patent Application No. 17/992,232, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Fathi, S.; Makar, P.; Gong, W.; Gordon, M.; Zhang, J.; Hayden, K. A New Plume Rise Algorithm—Incorporating the Thermodynamic Effects of Water for Plume Rise Prediction in Air Quality Models. In Proceedings of the 25th EGU General Assembly, Vienna, Austria, 23–28 April 2023; p. EGU-7984. [Google Scholar]
- Gradišar, D.; Shao, H.; Grašič, B. Evaluation of Delta Tool for comparison of different Air Quality Prediction models. Sci. Eng. Educ. 2018, 3, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, S. Assessment of prediction accuracy in autonomous air quality models. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 1322–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatram, A.; Tripathi, A.; France, F. Comparison and Performance Evaluation of CFD based Numerical Model and Gaussian based Models for Urban Air Quality Prediction. In Proceedings of the Conference of the Air and Waster Management Association, San Diego, CA, USA, 22–26 June 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Croitoru, C.; Nastase, I. A state of the art regarding urban air quality prediction models. E3S Web Conf. 2018, 32, 01010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Martín, J.; Kraakman, N.J.R.; Pérez, C.; Lebrero, R.; Muñoz, R. A state–of–the-art review on indoor air pollution and strategies for indoor air pollution control. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 128376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Harbawi, M. Air quality modelling, simulation, and computational methods: A review. Environ. Rev. 2013, 21, 149–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangwar, A.; Singh, S.; Mishra, R.; Prakash, S. The state-of-the-art in air pollution monitoring and forecasting systems using IoT, big data, and machine learning. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2023, 130, 1699–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwitondi, K.; Mak, H.W.L. Robust Machine Learning Algorithmic Rules for Detecting Air Pollution in the Lower Parts of the Atmosphere. Data Sci. J. 2025, 24, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Zhan, Y.; Yang, F. A review of machine learning for modeling air quality: Overlooked but important issues. Atmos. Res. 2024, 300, 107261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbagna, L.; Saheer, L.B.; Oghaz, M.M.D. AI-driven approaches for air pollution modelling: A comprehensive systematic review. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 373, 125937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Z.; Li, H.; Chen, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y. Advancements in machine learning for spatiotemporal urban on-road traffic-air quality study: A review. Atmos. Environ. 2025, 346, 121054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbehadji, I.E.; Obagbuwa, I.C. Systematic Review of Machine Learning and Deep Learning Techniques for Spatiotemporal Air Quality Prediction. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essamlali, I.; Nhaila, H.; El Khaili, M. Supervised machine learning approaches for predicting key pollutants and for the sustainable enhancement of urban air quality: A systematic review. Sustainability 2024, 16, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houdou, A.; El Badisy, I.; Khomsi, K.; Abdala, S.A.; Abdulla, F.; Najmi, H.; Obtel, M.; Belyamani, L.; Ibrahimi, A.; Khalis, M. Interpretable machine learning approaches for forecasting and predicting air pollution: A systematic review. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2024, 24, 230151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, J.; Dutta, M.; Marques, G. Machine Learning for Indoor Air Quality Assessment: A Systematic Review and Analysis. Environ. Model. Assess. 2024, 30, 417–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaini, N.; Ean, L.W.; Ahmed, A.N.; Malek, M.A. A systematic literature review of deep learning neural network for time series air quality forecasting. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 4958–4990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybarczyk, Y.; Zalakeviciute, R. Machine learning approaches for outdoor air quality modelling: A systematic review. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Moher, D. Updating guidance for reporting systematic reviews: Development of the PRISMA 2020 statement. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2021, 134, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddaway, N.R.; Page, M.J.; Pritchard, C.C.; McGuinness, L.A. PRISMA2020: An R package and Shiny app for producing PRISMA 2020-compliant flow diagrams, with interactivity for optimised digital transparency and Open Synthesis. Campbell Syst. Rev. 2022, 18, e1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rethlefsen, M.L.; Page, M.J. PRISMA 2020 and PRISMA-S: Common questions on tracking records and the flow diagram. J. Med. Libr. Assoc. 2022, 110, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tugwell, P.; Tovey, D. PRISMA 2020. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2021, 134, A5–A6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastidas-Orrego, L.M.; Jaramillo, N.; Castillo-Grisales, J.A.; Ceballos, Y.F. A systematic review of the evaluation of agricultural policies: Using prisma. Heliyon 2023, 9, e20292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taneja, S.; Jaggi, P.; Jewandah, S.; Ozen, E. Role of social inclusion in sustainable urban developments: An analyse by PRISMA technique. Int. J. Des. Nat. Ecodynamics 2022, 17, 937–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricco, A.C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W.; O’Brien, K.K.; Colquhoun, H.; Levac, D.; Moher, D.; Peters, M.D.J.; Horsley, T.; Weeks, L.; et al. PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and explanation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondel, V.D.; Guillaume, J.L.; Lambiotte, R.; Lefebvre, E. Fast unfolding of communities in large networks. J. Stat. Mech. Theory Exp. 2008, 2008, 10008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambiotte, R.; Delvenne, J.C.; Barahona, M. Laplacian dynamics and multiscale modular structure in networks. arXiv 2009, arXiv:0812.1770. Available online: http://arxiv.org/pdf/0812.1770v3.pdf (accessed on 1 November 2025).
- Ordenshiya, K.; Revathi, G. A comparative study of traditional machine learning and hybrid fuzzy inference system machine learning models for air quality index forecasting. Int. J. Data Sci. Anal. 2025, 20, 4321–4342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emeç, M.; Yurtsever, M. A novel ensemble machine learning method for accurate air quality prediction. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 22, 459–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, A.; Quaff, A.R. Advanced machine learning techniques for precise hourly air quality index (AQI) prediction in Azamgarh, India. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2025, 19, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousan, S.; Wu, R.; Popoviciu, C.; Fresquez, S.; Park, Y.M. Advancing Low-cost Air Quality Monitor Calibration with Machine Learning Methods. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 374, 126191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, T.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, X.; Wu, Q.; Meng, C.; Deng, Q. Air pollution and prostate cancer: Unraveling the connection through network toxicology and machine learning. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 292, 117966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colléaux, Y.; Willaume, C.; Mohandes, B.; Nebel, J.-C.; Rahman, F. Air pollution monitoring using cost-effective devices enhanced by machine learning. Sensors 2025, 25, 1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pande, C.B.; Radwan, N.; Heddam, S.; Ahmed, K.O.; Alshehri, F.; Pal, S.C.; Pramanik, M. Forecasting of monthly air quality index and understanding the air pollution in the urban city, India based on machine learning models and cross-validation. J. Atmos. Chem. 2025, 82, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Wang, K.; Yang, W.; Wang, P.; Ao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, J. Mechanism Model Combined with Deep Learning Models for Accurate Prediction of Indoor Air Pollution in Residential and Commercial Spaces. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 103, 112008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Chen, D.; Wang, P.; Wang, W.; Shen, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, M. Predicting On-Road Air Pollution Coupling Street View Images and Machine Learning: A Quantitative Analysis of the Optimal Strategy. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 59, 3582–3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deveer, L.; Minet, L. Real-time air quality prediction using traffic videos and machine learning. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2025, 142, 104688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cengil, E. The Power of Machine Learning Methods and PSO in Air Quality Prediction. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binbusayyis, A.; Khan, M.A.; Ahmed A, M.M.; Emmanuel, W.R.S. A deep learning approach for prediction of air quality index in smart city. Discov. Sustain. 2024, 5, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Geng, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, D.; Yoo, C.; Liu, H. A novel deep learning framework with variational auto-encoder for indoor air quality prediction. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2024, 18, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baruah, A.; Bousiotis, D.; Damayanti, S.; Bigi, A.; Ghermandi, G.; Ghaffarpasand, O.; Harrison, R.M.; Pope, F.D. A novel spatiotemporal prediction approach to fill air pollution data gaps using mobile sensors, machine learning and citizen science techniques. npj Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2024, 7, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.; Shakil, S.U.P.; Nayan, N.M.; Kashem, M.A.; Uddin, J. Air Pollution Monitoring Using IoT and Machine Learning in the Perspective of Bangladesh. Ann. Emerg. Technol. Comput. (AETiC) 2024, 8, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Nayeem, M.E.H.; Ahmed, M.S.; Tanha, K.A.; Sakib, M.S.A.; Uddin, K.M.M.; Babu, H.M.H. AirNet: Predictive machine learning model for air quality forecasting using web interface. Environ. Syst. Res. 2024, 13, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deo, A.; Khan, S.S.; Doohan, N.V.; Jain, A.; Nighoskar, M.; Dandawate, A. Analysis for Predicting Respiratory Diseases from Air Quality Attributes Using Recurrent Neural Networks and Other Deep Learning Techniques. Ing. Syst. d’Information 2024, 29, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahrari, P.; Khaledi, S.; Keikhosravi, G.; Alavi, S.J. Application of machine learning and deep learning techniques in modeling the associations between air pollution and meteorological parameters in urban areas of Tehran metropolis. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Sharma, R. Enhancing Air Pollution Monitoring and Prediction using African Vulture Optimization Algorithm with Machine Learning Model on Internet of Things Environment. J. Intell. Syst. Internet Things 2024, 13, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, P.S.G.; Puthussery, J.V.; Mao, Y.; Salana, S.; Nguyen, T.H.; Newell, T.; Verma, V. Influence of human activities and occupancy on the emission of indoor particles from respiratory and nonrespiratory sources. ACS ES&T Air 2024, 1, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.M.T.; Cai, J.; Molla, A.H.; Kurniawan, T.A.; Kong, S.S.-K. Evaluation of Machine Learning Models in Air Pollution Prediction for a Case Study of Macau as an Effort to Comply with UN Sustainable Development Goals. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, M.W.; Saritha; Kallapu, B.; Hejamadi, R.M.; Jijo, J.; Ramesh, R.K.; Aslam, M.; Jilani, S.F. Exploring the Influence of Tropical Cyclones on Regional Air Quality Using Multimodal Deep Learning Techniques. Sensors 2024, 24, 6983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Son, J.Y.; Junger, W.; Bell, M.L. Exposure to particulate matter and ozone, locations of regulatory monitors, and sociodemographic disparities in the city of Rio de Janeiro: Based on local air pollution estimates generated from machine learning models. Atmos. Environ. 2024, 322, 120374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasudevan, P.; Ekambaram, C. HYAQP: A Hybrid Meta-Heuristic Optimization Model for Air Quality Prediction Using Unsupervised Machine Learning Paradigms. Int. Arab J. Inf. Technol. 2024, 21, 953–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folifack Signing, V.R.; Taamté, J.M.; Noube, M.K.; Yerima, A.H.; Azzopardi, J.; Tchuente Siaka, Y.F.; Saïdou. IoT-based monitoring system and air quality prediction using machine learning for a healthy environment in Cameroon. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaberi, A.H.M.; Hamzah, A.; Dzulkifly, S.; Li, W.S.; Gaus, Y.F.A. Machine Learning Approaches for Predicting Occupancy Patterns and its Influence on Indoor Air Quality in Office Environments. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2024, 15, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zareba, M.; Cogiel, S.; Danek, T.; Weglinska, E. Machine Learning Techniques for Spatio-Temporal Air Pollution Prediction to Drive Sustainable Urban Development in the Era of Energy and Data Transformation. Energies 2024, 17, 2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathnayake, L.R.S.D.; Sakura, G.B.; Weerasekara, N.A.; Sandaruwan, P.D. Machine Learning-based Calibration Approach for Low-cost Air Pollution Sensors MQ-7 and MQ-131. Nat. Environ. Pollut. Technol. 2024, 23, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anggraini, T.S.; Irie, H.; Sakti, A.D.; Wikantika, K. Machine learning-based global air quality index development using remote sensing and ground-based stations. Environ. Adv. 2024, 15, 100456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aram, S.A.; Nketiah, E.A.; Saalidong, B.M.; Wang, H.; Afitiri, A.-R.; Akoto, A.B.; Lartey, P.O. Machine learning-based prediction of air quality index and air quality grade: A comparative analysis. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 21, 1345–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suthar, G.; Kaul, N.; Khandelwal, S.; Singh, S. Predicting land surface temperature and examining its relationship with air pollution and urban parameters in Bengaluru: A machine learning approach. Urban Clim. 2024, 53, 101830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Photsathian, T.; Suttikul, T.; Tangsrirat, W. Prediction of air pollution from power generation using machine learning. EUREKA Phys. Eng. 2024, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhope, T.S.; Shaikh, A.; Simunic, D.; Patil, P.P.; Wagh, K.S.; Wagh, S.K. Real Time Air Quality Surveillance & Forecasting System (Rtaqsfs) in Pune City Using Machine Learning-Based Predictive Model. Proc. Eng. 2024, 6, 505–512. [Google Scholar]
- Topalović, D.B.; Tasić, V.M.; Petrović, J.S.S.; Vlahović, J.L.; Radenković, M.B.; Smičiklas, I.D. Unveiling the potential of a novel portable air quality platform for assessment of fine and coarse particulate matter: In-field testing, calibration, and machine learning insights. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerges, F.; Llaguno-Munitxa, M.; Zondlo, M.A.; Boufadel, M.C.; Bou-Zeid, E. Weather and the City: Machine learning for predicting and attributing fine scale air quality to meteorological and urban determinants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 6313–6325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morapedi, T.D.; Obagbuwa, I.C. Air pollution particulate matter (PM2.5) prediction in South African cities using machine learning techniques. Front. Artif. Intell. 2023, 6, 1230087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samad, A.; Garuda, S.; Vogt, U.; Yang, B. Air pollution prediction using machine learning techniques—An approach to replace existing monitoring stations with virtual monitoring stations. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 310, 119987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, X.; Fahad, S.; Han, M.S.; Naeem, M.R.; Room, S. Air quality index prediction via multi-task machine learning technique: Spatial analysis for human capital and intensive air quality monitoring stations. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2023, 16, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindra, K.; Bahadur, S.S.; Katoch, V.; Bhardwaj, S.; Kaur-Sidhu, M.; Gupta, M.; Mor, S. Application of machine learning approaches to predict the impact of ambient air pollution on outpatient visits for acute respiratory infections. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Xu, X.; Ma, X.; Wang, Z.; You, Q.; Shan, W.; Yang, Y.; Bo, X.; Yin, C. Application of machine learning to predict hospital visits for respiratory diseases using meteorological and air pollution factors in Linyi, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 88431–88443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhang, Q.; Peng, Y.; Guan, X.; Li, L.; Mu, J.; Wang, X.; Yin, X.; Wang, Q. Contributions of various driving factors to air pollution events: Interpretability analysis from Machine learning perspective. Environ. Int. 2023, 173, 107861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumtaz, R.; Amin, A.; Khan, M.A.; Asif, M.D.A.; Anwar, Z.; Bashir, M.J. Impact of Green Energy Transportation Systems on Urban Air Quality: A predictive analysis using spatiotemporal deep learning techniques. Energies 2023, 16, 6087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alolayan, M.A.; Almutairi, A.; Aladwani, S.M.; Alkhamees, S. Investigating major sources of air pollution and improving spatiotemporal forecast accuracy using supervised machine learning and a proxy. J. Eng. Res. 2023, 11, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez, M.; Merayo, M.G.; Núñez, M. Machine learning algorithms to forecast air quality: A survey. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2023, 56, 10031–10066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mogaraju, J.K. Machine learning strengthened prediction of tracheal, bronchus, and lung cancer deaths due to air pollution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 100539–100551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamei, M.; Ali, M.; Jun, C.; Bateni, S.M.; Karbasi, M.; Farooque, A.A.; Yaseen, Z.M. Multi-step ahead hourly forecasting of air quality indices in Australia: Application of an optimal time-varying decomposition-based ensemble deep learning algorithm. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2023, 14, 101752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanalakshmi, M.; Radha, V. Novel Regression and Least Square Support Vector Machine Learning Technique for Air Pollution Forecasting. Int. J. Eng. Trends Technol. 2023, 71, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Li, J.; Sulaiman, R.; Alotaibi, B.S.; Elattar, S.; Abuhussain, M. Air Quality Prediction and Multi-Task Offloading based on Deep Learning Methods in Edge Computing. J. Grid Comput. 2023, 21, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devasekhar, V.; Natarajan, P. Prediction of air quality and pollution using statistical methods and machine learning techniques. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2023, 14, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abirami, S.; Chitra, P. Probabilistic air quality forecasting using deep learning spatial–temporal neural network. GeoInformatica 2023, 27, 199–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.; Baek, K.; So, H. Rapid monitoring of indoor air quality for efficient HVAC systems using fully convolutional network deep learning model. Build. Environ. 2023, 234, 110191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Tian, H.; Luo, L.; Liu, S.; Bai, X.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, K.; Lin, S.; Zhao, S.; Guo, Z.; et al. Understanding and revealing the intrinsic impacts of the COVID-19 lockdown on air quality and public health in North China using machine learning. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Cai, W.; Tao, Y.; Sun, Q.C.; Wong, P.P.Y.; Huang, X.; Liu, Y. Unpacking the inter- and intra-urban differences of the association between health and exposure to heat and air quality in Australia using global and local machine learning models. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 871, 162005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Graham, D.J.; Stettler, M.E.J. Using explainable machine learning to interpret the effects of policies on air pollution: COVID-19 lockdown in london. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 18271–18281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorek-Hamer, M.; Von Pohle, M.; Sahasrabhojanee, A.; Asanjan, A.A.; Deardorff, E.; Suel, E.; Lingenfelter, V.; Das, K.; Oza, N.C.; Ezzati, M.; et al. A deep learning approach for meter-scale air quality estimation in urban environments using very high-spatial-resolution satellite imagery. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.; Sharma, S.; Chowdhury, K.R.; Sharma, P. A novel seasonal index–based machine learning approach for air pollution forecasting. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agibayeva, A.; Khalikhan, R.; Guney, M.; Karaca, F.; Torezhan, A.; Avcu, E. An Air Quality Modeling and Disability-Adjusted Life Years (DALY) Risk Assessment Case Study: Comparing Statistical and Machine Learning Approaches for PM2.5 Forecasting. Sustainability 2022, 14, 16641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alazmi, A.; Rakha, H. Assessing and validating the ability of machine learning to handle unrefined particle air pollution mobile monitoring data randomly, spatially, and spatiotemporally. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partheeban, P.; Balamurali, R.; Elamparithi, P.N.; Rohith, K.; Gupta, R.; Somasundaram, K. Deep Learning Models to Predict COVID-19 Cases in India Using Air Pollution and Meteorological Data. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2022, 21, 1171–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Najjar, D.; Al-Najjar, H.; Al-Rousan, N.; Assous, H.F. Developing machine learning techniques to investigate the impact of air quality indices on tadawul exchange index. Complexity 2022, 2022, 4079524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baqer, N.S.; Albahri, A.S.; Mohammed, H.A.; Zaidan, A.A.; Amjed, R.A.; Al-Bakry, A.M.; Albahri, O.S.; Alsattar, H.A.; Alnoor, A.; Alamoodi, A.H.; et al. Indoor air quality pollutants predicting approach using unified labelling process-based multi-criteria decision making and machine learning techniques. Telecommun. Syst. 2022, 81, 591–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthivel, S.; Chidambaranathan, M. Machine learning approaches used for air quality forecast: A review. Rev. d’Intelligence Artif. 2022, 36, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murali, M.; Satish, M.; Rajalakshmi, V.R. Prediction and analysis of air pollution using machine learning. SN Comput. Sci. 2022, 3, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukor, A.S.A.; Cheik, G.C.; Kamarudin, L.M.; Mao, X.; Nishizaki, H.; Zakaria, A.; Syed Zakaria, S.M.M. Predictive analysis of in-vehicle air quality monitoring system using deep learning technique. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kow, P.-Y.; Hsia, I.-W.; Chang, L.-C.; Chang, F.-J. Real-time image-based air quality estimation by deep learning neural networks. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 307, 114560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, S.; Luo, Z.; Dixon, T.; Manla, G.; Francis, D.; Chen, H.; Liu, Y. The impact of smart traffic interventions on roadside air quality employing machine learning approaches. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2022, 110, 103408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, L.-T.; Mui, K.-W.; Tsang, T.-W. Updating indoor air quality (IAQ) assessment screening levels with machine learning models. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.M.T.; Siu, S.W.I.; Monjardino, J.; Mendes, L.; Ferreira, F. Using machine learning methods to forecast air quality: A case study in macao. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janarthanan, R.; Partheeban, P.; Somasundaram, K.; Elamparithi, P.N. A deep learning approach for prediction of air quality index in a metropolitan city. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 67, 102720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balogun, A.-L.; Tella, A.; Baloo, L.; Adebisi, N. A review of the inter-correlation of climate change, air pollution and urban sustainability using novel machine learning algorithms and spatial information science. Urban Clim. 2021, 40, 100989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Bherwani, H.; Gautam, S.; Anjum, S.; Musugu, K.; Kumar, N.; Anshul, A.; Kumar, R. Air pollution aggravating COVID-19 lethality? Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 6408–6417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimpour, A.; Amanollahi, J.; Tzanis, C.G. Air quality data series estimation based on machine learning approaches for urban environments. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2021, 14, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljanabi, M.; Shkoukani, M.; Hijjawi, M. Comparison of multiple machine learning algorithms for urban air quality forecasting. PEN 2021, 9, 1013–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashad, K.; Gu, J.; Yang, B.; Rong, M.; Chen, E.; Ma, X.; Zhang, K.M. Designing roadside green infrastructure to mitigate traffic-related air pollution using machine learning. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 773, 144760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.-Y.; Chang, Y.-S.; Abimannan, S. Ensemble multifeatured deep learning models for air quality forecasting. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 101045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliardi, R.V.; Andenna, C. Machine learning meteorological normalization models for trend analysis of air quality time series. Int. J. Environ. Impacts 2021, 4, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, W.; Wang, W.; Jiao, L.; Zhao, S.; Liu, A. Modeling air quality prediction using a deep learning approach: Method optimization and evaluation. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 65, 102567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonawani, S.; Patil, K.; Chumchu, P. NO2 pollutant concentration forecasting for air quality monitoring by using an optimised deep learning bidirectional GRU model. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2021, 24, 64–73. [Google Scholar]
- Goh, C.C.; Kamarudin, L.M.; Zakaria, A.; Nishizaki, H.; Ramli, N.; Mao, X.; Zakaria, S.M.M.S.; Kanagaraj, E.; Sukor, A.S.A.; Elham, F. Real-time in-vehicle air quality monitoring system using machine learning prediction algorithm. Sensors 2021, 21, 4956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovrić, M.; Pavlović, K.; Vuković, M.; Grange, S.K.; Haberl, M.; Kern, R. Understanding the true effects of the COVID-19 lockdown on air pollution by means of machine learning. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 274, 115900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabregat, A.; Vázquez, L.; Vernet, A. Using Machine Learning to estimate the impact of ports and cruise ship traffic on urban air quality: The case of Barcelona. Environ. Model. Softw. 2021, 139, 104995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelli, M.; Clemente, F.M.; Popovič, A.; Silva, S.; Vanneschi, L. A Machine learning approach to predict air quality in california. Complexity 2020, 2020, 8049504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Xie, M.; Wu, Z.; Liu, B.; Gao, Y.; Chen, G.; Li, Z. Adjusting PM2.5 prediction of the numerical air quality forecast model based on machine learning methods in Chengyu region. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2020, 40, 4419–4431. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, X.; Mi, Z.; Georgopoulos, P.G. Comparison of Machine Learning and Land Use Regression for fine scale spatiotemporal estimation of ambient air pollution: Modeling ozone concentrations across the contiguous United States. Environ. Int. 2020, 142, 105827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gryech, I.; Ghogho, M.; Elhammouti, H.; Sbihi, N.; Kobbane, A. Machine learning for air quality prediction using meteorological and traffic related features. J. Ambient. Intell. Smart Environ. 2020, 12, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steininger, M.; Kobs, K.; Zehe, A.; Lautenschlager, F.; Becker, M.; Hotho, A. Maplur: Exploring a new paradigm for estimating air pollution using deep learning on map images. ACM Trans. Spat. Algorithms Syst. (TSAS) 2020, 6, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Lautenschlager, F.; Becker, M.; Kobs, K.; Steininger, M.; Davidson, P.; Krause, A.; Hotho, A. OpenLUR: Off-the-shelf air pollution modeling with open features and machine learning. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 233, 117535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Xu, J.; Tu, R.; Saleh, M.; Hatzopoulou, M. Potential of machine learning for prediction of traffic related air pollution. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2020, 88, 102599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, A.; Singh, S. Review on air pollution of Delhi zone using machine learning algorithm. J. Air Pollut. Health 2020, 5, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, M.D.; Massey, F.; Chastko, K.; Cupini, C. Spatial modelling of particulate matter air pollution sensor measurements collected by community scientists while cycling, land use regression with spatial cross-validation, and applications of machine learning for data correction. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 230, 117479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljuaid, H.; Alwabel, N. Air pollution prediction using machine learning algorithms. Int. J. Eng. Adv. Technol. 2019, 8, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, Q.; Yu, D.; Gu, Y. Air quality index and air pollutant concentration prediction based on machine learning algorithms. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, K.M.; Beulah, J.R. Air quality prediction based on supervised machine learning methods. IJITEE 2019, 8, 206–212. [Google Scholar]
- Ameer, S.; Shah, M.A.; Khan, A.; Song, H.; Maple, C.; Islam, S.U.; Asghar, M.N. Comparative analysis of machine learning techniques for predicting air quality in smart cities. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 128325–128338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Yang, W.; Ma, Z.; Geng, W.; Bai, Z. Comparative statistical models for estimating potential roles of relative humidity and temperature on the concentrations of secondary inorganic aerosol: Statistical insights on air pollution episodes at Beijing during January 2013. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 212, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Cheng, J.C.P.; Lin, C.; Tan, Y.; Zhang, J. Improving air quality prediction accuracy at larger temporal resolutions using deep learning and transfer learning techniques. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 214, 116885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masih, A. Machine learning algorithms in air quality modeling. GJESM 2019, 5, 515–534. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, W.; Ramalho, O.; Malingre, L.; Sivanantham, S.; Little, J.C.; Mandin, C. Machine learning and statistical models for predicting indoor air quality. Indoor Air 2019, 29, 704–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.C.; Kim, H.; Vilcassim, M.R.; Thurston, G.D.; Gordon, T.; Chen, L.-C.; Lee, K.; Heimbinder, M.; Kim, S.-Y. Mapping urban air quality using mobile sampling with low-cost sensors and machine learning in Seoul, South Korea. Environ. Int. 2019, 131, 105022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Cai, C.; Yang, T.; Zhou, X. A machine learning approach for air quality prediction: Model regularization and optimization. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2018, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlos, G.; Valeria, F.; Guillermo, V. Use of non-industrial environmental sensors and machine learning techniques in telemetry for indoor air pollution. ARPN J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2018, 13, 2702–2712. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, H.; Lima, A.R.; Teakles, A.; Jin, J.; Cannon, A.J.; Hsieh, W.W. Evaluating hourly air quality forecasting in Canada with nonlinear updatable machine learning methods. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2017, 10, 195–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Rahman, A.; Bhrugubanda, H.; Sivaraman, V. HazeEst: Machine learning based metropolitan air pollution estimation from fixed and mobile sensors. IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 17, 3517–3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Riley, E.A.; Austin, E.; Sasakura, M.; Schaal, L.; Gould, T.R.; Hartin, K.; Simpson, C.D.; Sampson, P.D.; Yost, M.G.; et al. Use of mobile and passive badge air monitoring data for NOX and ozone air pollution spatial exposure prediction models. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2017, 27, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stingone, J.A.; Pandey, O.P.; Claudio, L.; Pandey, G. Using machine learning to identify air pollution exposure profiles associated with early cognitive skills among US children. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 230, 730–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Peng, L.; Hu, Y.; Shao, J.; Chi, T. Deep learning architecture for air quality predictions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 22408–22417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, B.C.M.; Tang, S.-K.; Cardoso, A. Multi-level lag scheme significantly improves training efficiency in deep learning: A case study in air quality alert service over sub-tropical area. J. Big Data 2025, 12, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-H.; Chen, P.-H.; Wu, C.-H.; Yang, C.-S.; Chuang, L.-Y. Deep learning-based air pollution analysis on carbon monoxide in Taiwan. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 80, 102477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Gupta, Y. Comparative analysis of Air Quality Index prediction using deep learning algorithms. Spat. Inf. Res. 2024, 32, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Tian, Y.; Wu, C.H. Air Quality Prediction and Ranking Assessment Based on Bootstrap-XGBoost Algorithm and Ordinal Classification Models. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Chen, C.; Yuan, J. A systematic survey of air quality prediction based on deep learning. Alex. Eng. J. 2024, 93, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unnikrishnan, A.; Rajeswari, S. Optimal Prediction of Air Quality Index in Metropolitan Cities Using Fuzzy Time Series with Deep Learning Approach. Ecol. Eng. Environ. Technol. 2024, 25, 341–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, A.T.; Pham, D.H.; Oo, B.L.; Ahn, Y.; Lim, B.T.H. Predicting air quality index using attention hybrid deep learning and quantum-inspired particle swarm optimization. J. Big Data 2024, 11, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furizal; Ma’ARif, A.; Suwarno, I.; Masitha, A.; Aulia, L.; Sharkawy, A.-N. Real-Time Mechanism Based on Deep Learning Approaches for Analyzing the Impact of Future Timestep Forecasts on Actual Air Quality Index of PM10. Results Eng. 2024, 24, 103434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltare, N.N.; Vahora, S. Air Quality Index prediction using machine learning for Ahmedabad city. Digit. Chem. Eng. 2023, 7, 100093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zukaib, U.; Maray, M.; Mustafa, S.; Haq, N.U.; Khan, A.U.R.; Rehman, F. Impact of COVID-19 lockdown on air quality analyzed through machine learning techniques. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2023, 9, e1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middya, A.I.; Roy, S. Pollutant specific optimal deep learning and statistical model building for air quality forecasting. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 301, 118972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gocheva-Ilieva, S.G.; Ivanov, A.V.; Livieris, I.E. High performance machine learning models of large scale air pollution data in urban area. Cybern. Inf. Technol. 2020, 20, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, J.W.; Wong, S.W.; Selvachandran, G.; Long, H.V.; Son, L.H. Prediction of Air Pollution Index in Kuala Lumpur using fuzzy time series and statistical models. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2020, 13, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García Nieto, P.J.; Sánchez Lasheras, F.; García-Gonzalo, E.; de Cos Juez, F.J. Estimation of PM10 concentration from air quality data in the vicinity of a major steelworks site in the metropolitan area of Avilés (Northern Spain) using machine learning techniques. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2018, 32, 3287–3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.-P. AIoT-based indoor air quality prediction for building using enhanced metaheuristic algorithm and hybrid deep learning. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 105, 112448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, E.; Banerjee, C.; Poonia, A.S. HDLP: Air quality modeling with hybrid deep learning approaches and particle swam optimization. Innov. Syst. Softw. Eng. 2024, 20, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quynh, T.P.T.; Viet, T.N.; Thi, H.D.; Manh, K.H. Enhancing air quality prediction accuracy using hybrid deep learning. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Dev. 2023, 14, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakht, A.; Sharma, S.; Park, D.; Lee, H. Deep learning-based indoor air quality forecasting framework for indoor subway station platforms. Toxics 2022, 10, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, A.K.; Sampson, J.; Ahmad, S.; Avudaiappan, T.; Narayanasamy, K.; Pustokhina, I.V.; Pustokhin, D.A. Hybrid Deep Learning Enabled Air Pollution Monitoring in ITS Environment. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2022, 72, 1157–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, L.; Maheswaravenkatesh, P.; Shanthi, G.; Surya, G. Internet of things enabled automated air pollution monitoring using oppositional swallow swarm optimisation with deep learning model. J. Environ. Prot. Ecol. 2022, 23, 462–473. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Q.; Ni, J.-Q.; Li, E.; Bao, J.; Zheng, P. Sequential air pollution emission estimation using a hybrid deep learning model and health-related ventilation control in a pig building. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 371, 133714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Lu, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Fung, J.C. AirQFormer: Improving regional air quality forecast with a hybrid deep learning model. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2025, 119, 106113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshaboury, N.; Abdelkader, E.M.; Al-Sakkaf, A. Convolutional neural network-based deep learning model for air quality prediction in October city of Egypt. Constr. Innov. 2025, 25, 620–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Ke, H.; Gong, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, C.; Mo, J.; You, Y. Enhanced forecasting and assessment of urban air quality by an automated machine learning system: The AI-Air. Earth Space Sci. 2025, 12, e2024EA003942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.A.; Faheem, M.; Mehmood, T.; Yin, Y.; Liu, J. Assessment of meteorological and air quality drivers of elevated ambient ozone in Beijing via machine learning approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 104086–104099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaman, M.; Southworth, J.; Amanambu, A.C.; Tefera, B.B.; Alruzuq, A.R.; Safaei, M.; Hasan, M.; Smith, A.C. Combining deep learning and machine learning techniques to track air pollution in relation to vegetation cover utilizing remotely sensed data. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 376, 124323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gond, A.K.; Jamal, A.; Verma, T. Developing a machine learning model using satellite data to predict the Air Quality Index (AQI) over Korba Coalfield, Chhattisgarh (India). Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2025, 16, 102398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Ma, J. Graph-based machine learning for high-resolution assessment of pedestrian-weighted exposure to air pollution. Resour. Environ. Sustain. 2025, 20, 100219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abalo-García, A.; Hernández-García, S.; Ramírez, I.; Schiavi, E. MPD: A Meteorological and Pollution Dataset. A comprehensive study of Machine and Deep Learning methods for air pollution forecasting. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 41282–41299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafi, J.; Ijaz, R.; Kumar, Y.; Ijaz, M.F. Prediction of air quality levels to support sustainable development goal—11 using multiple deep learning classifiers. Smart Sustain. Built Environ. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, L.; Tang, J.; Li, G.; Ma, J.; Gao, H.; Huang, T.; Mao, X. A novel approach combining indoor mobile measurements and interpretable machine learning to unveil highly-resolved indoor air pollution. Build. Environ. 2025, 270, 112552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, V.O.; Rocha, P.A.C.; Thé, J.V.G.; Gharabaghi, B. Optimizing the Architecture of a Quantum–Classical Hybrid Machine Learning Model for Forecasting Ozone Concentrations: Air Quality Management Tool for Houston, Texas. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakya, D.; Deshpande, V.; Goyal, M.K.; Agarwal, M. PM2.5 air pollution prediction through deep learning using meteorological, vehicular, and emission data: A case study of New Delhi, India. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 427, 139278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, W.-T.; Lu, C.-H.S.; Alessandrini, S.; Kumar, R.; Lin, C.-A. The impacts of transported wildfire smoke aerosols on surface air quality in New York State: A multi-year study using machine learning. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 259, 118513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkayal, S.; Almisbahi, H.; Baowidan, S.; Alkayal, E. Air Pollution Trends and Predictive Modeling for Three Cities with Different Characteristics Using Sentinel-5 Satellite Data and Deep Learning. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, R.; Stratoulias, D.; Kim, H.C.; Yoon, J.-H. Estimation of surface PM2.5 concentrations from atmospheric gas species retrieved from TROPOMI using deep learning: Impacts of fire on air pollution over Thailand. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2023, 14, 101875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaev, E.; Ajikeev, B.; Shamyrkanov, U.; Kalnur, K.-U.; Maisalbek, K.; Sidle, R.C. Impact of climate change and air pollution forecasting using machine learning techniques in Bishkek. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2022, 22, 210336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magazzino, C.; Mele, M.; Sarkodie, S.A. The nexus between COVID-19 deaths, air pollution and economic growth in New York state: Evidence from Deep Machine Learning. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 286, 112241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahadur, F.T.; Shah, S.R.; Nidamanuri, R.R. Applications of remote sensing vis-à-vis machine learning in air quality monitoring and modelling: A review. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Hu, S.; Liu, X.; Dong, Z. A data-driven air quality assessment method based on unsupervised machine learning and median statistical analysis: The case of China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 328, 129531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerezuela-Escudero, E.; Montes-Sanchez, J.M.; Dominguez-Morales, J.P.; Duran-Lopez, L.; Jimenez-Moreno, G. A systematic comparison of different machine learning models for the spatial estimation of air pollution. Appl. Intell. 2023, 53, 29604–29619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadtler, S.; Betancourt, C.; Roscher, R. Explainable machine learning reveals capabilities, redundancy, and limitations of a geospatial air quality benchmark dataset. Mach. Learn. Knowl. Extr. 2022, 4, 150–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, H.W.L.; Lam, Y.F. Comparative assessments and insights of data openness of 50 smart cities in air quality aspects. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 69, 102868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Gómez, N.I.; Díaz-Arévalo, J.L.; López-Jiménez, P.A. Air quality and urban sustainable development: The application of machine learning tools. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 18, 1029–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, S.; Mondardini, R.; Helbing, D. Democratizing air: A co-created citizen science approach to indoor air quality monitoring. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 116, 105890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, S.; Kumar, P.; Pinto, J.A.; Riccetti, A.; Schaaf, K.; Camprodon, G.; Smári, V.; Passani, A.; Forino, G. A citizen science approach for enhancing public understanding of air pollution. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 52, 101800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Author–Year | Studies | Method | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Du et al., 2025 [33] | 103 | SRL + Prisma | Low interpretability and lack of real-time models |
| Agbehadji, 2024 [34] | 80 | SRL + Prisma | Search biases and nonlinear data complexity |
| Essamlali, 2024 [35] | SRL + Prisma | High demand for data and the need for precision | |
| Houdou, 2024 [36] | 56 | SRL | Few studies and precision–explainability trade-off |
| Saini, 2024 [37] | 18 | SRL | Few studies and lack of integration with data |
| Zaini, 2022 [38] | SRL | Hybrid modelling need | |
| Rybarczyk, 2018 [39] | 46 | SRL | Low prediction of emerging pollutants |
| This Paper | 412 | SRL + Prisma | Low geographical coverage and comparative modelling need |
| Challenges | Author–Year | Opportunities | Author–Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heterogeneity in data quality and resolution | Bahadur, 2023 [193]; Lin et al., 2021 [123] | Integration of satellite data and IoT sensors | Bahadur, 2023 [193]; Lin et al., 2021 [123] |
| Low availability of monitoring stations in underrepresented regions | Shafi et al., 2025 [184]; Unnikrishnan 2024 [160] | Development of robust spatiotemporal models | Wu, 2024 [61]; Devasekhar, 2023 [97] |
| Lack of standardization in variable selection and preprocessing | Sousan et al., 2025 [52]; Devasekhar, 2023 [97] | Application of transfer learning | Lei, 2024 [69]; Shaberi, 2024 [74] |
| High computational complexity of advanced models | Wu, 2024 [61]; Lei, 2024 [69] | Use of dimensionality reduction techniques (PCA, autoencoders) | Sousan et al., 2025 [52] |
| Limited interpretability in deep learning models | Agibayeva, 2022 [105]; Wang et al., 2021 [194] | Emergence of adaptive hybrid models | Shafi et al., 2025 [184]; Unnikrishnan, 2024 [160] |
| Lack of replicable comparative frameworks between models | Pande et al., 2025 [55]; Cerezuela-Escudero, 2023 [195] | Advances in interpretation techniques such as SHAP and LIME | Cerezuela-Escudero, 2023 [195]; Agibayeva, 2022 [105] |
| Imbalance in the use of assessment indicators | Shaberi, 2024 [74]; Sukor, 2022 [112] | Increasing availability of open source platforms | Ma, 2019 [144] |
| Dependence on meteorological variables not always available | Bahadur, 2023 [193]; Lin et al., 2021 [123] | Potential of multi-city modeling for generalization | Devasekhar, 2023 [97] |
| Geographical fragmentation of scientific knowledge | Sousan et al., 2025 [52]; Shafi et al., 2025 [184] | Improvements in accuracy through deep architectures | Wu, 2024 [61]; Shin et al., 2023 [99] |
| Poor integration between accuracy and explainability | Janarthanan, 2021 [117]; Ma, 2019 [144] | Growing interest in replicable and explainable frameworks | Janarthanan, 2021 [117] |
| Low adoption of Explainable AI techniques | Cerezuela-Escudero, 2023 [195]; Stadtler et al., 2022 [196] | Application of artificial intelligence in developing regions | Bahadur, 2023 [193] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peinado, L.B.; Guarda, T.; Herrera-Vidal, G.; Minnaard, C.; Coronado-Hernández, J.R. Statistical and Machine Learning Models for Air Quality: A Systematic Review of Methods and Challenges. Algorithms 2025, 18, 783. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18120783
Peinado LB, Guarda T, Herrera-Vidal G, Minnaard C, Coronado-Hernández JR. Statistical and Machine Learning Models for Air Quality: A Systematic Review of Methods and Challenges. Algorithms. 2025; 18(12):783. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18120783
Chicago/Turabian StylePeinado, Luzneyda Ballesteros, Teresa Guarda, Germán Herrera-Vidal, Claudia Minnaard, and Jairo R. Coronado-Hernández. 2025. "Statistical and Machine Learning Models for Air Quality: A Systematic Review of Methods and Challenges" Algorithms 18, no. 12: 783. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18120783
APA StylePeinado, L. B., Guarda, T., Herrera-Vidal, G., Minnaard, C., & Coronado-Hernández, J. R. (2025). Statistical and Machine Learning Models for Air Quality: A Systematic Review of Methods and Challenges. Algorithms, 18(12), 783. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18120783