A Sparsity-Invariant Model via Unifying Depth Prediction and Completion
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We designed a depth completion model with high generalization capability, which effectively handles sparse depth maps with different sparse levels and irregular distribution, and ensures reliable depth prediction even when the input depth is limited or completely absent.
- We integrated effective designs from both depth completion and monocular depth estimation tasks, establishing a dual-branch structured model. A multi-scale local plane constraint module and a surface normal-based loss function are adopted to further exploit scene structure-related information.
- Our model achieves reliable depth results even when depth information is limited or completely absent, as demonstrated on the benchmark dataset NYU Depth V2 [37]. In real-world applications, this model can also effectively handle sparse depth maps with noise and irregular distribution.
2. Related Work
2.1. Monocular Depth Estimation
2.2. Image-Guided Depth Completion
2.3. Sparsity-Invariant Depth Completion
3. Preliminary: Pseudo-Plane Coefficients
4. The Proposed Method
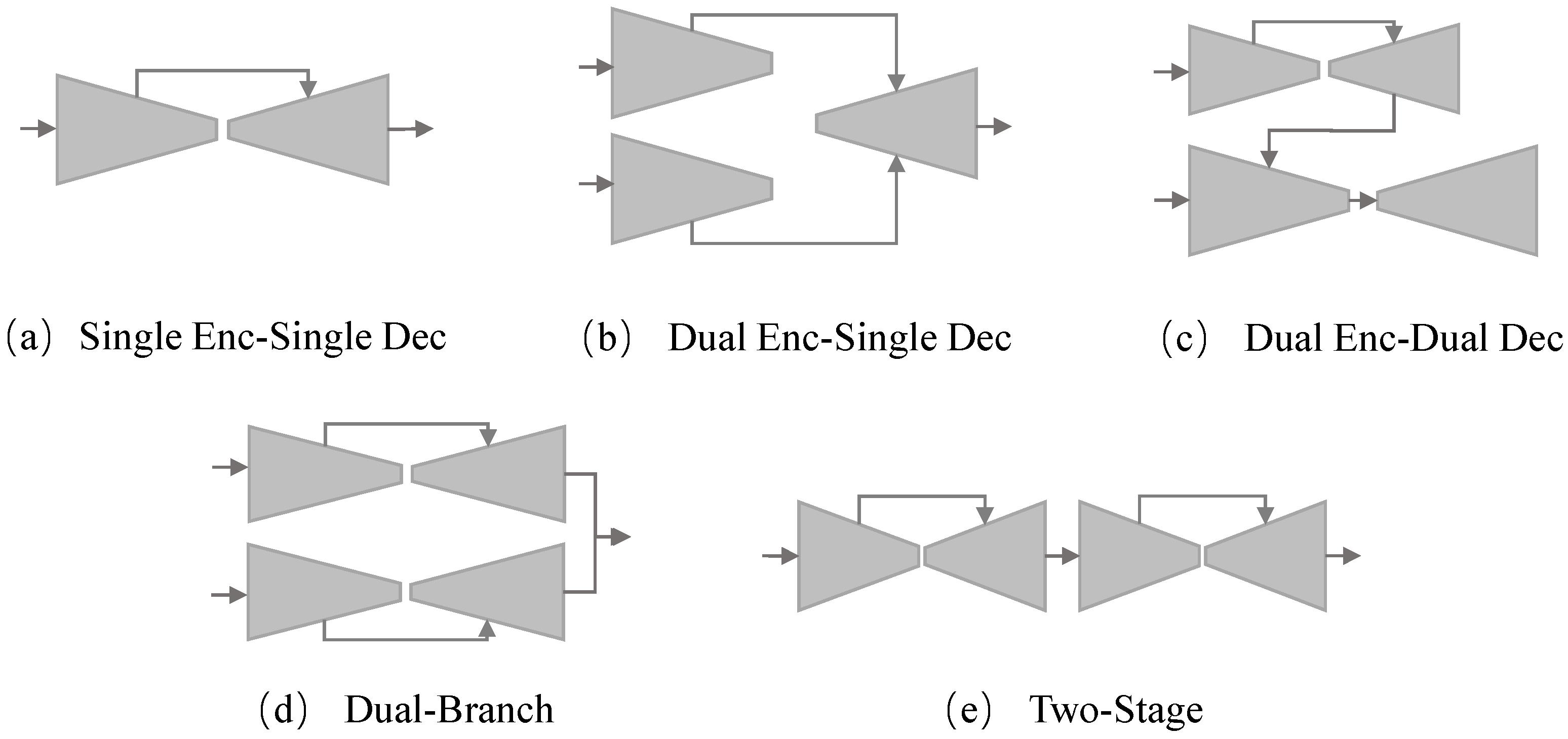
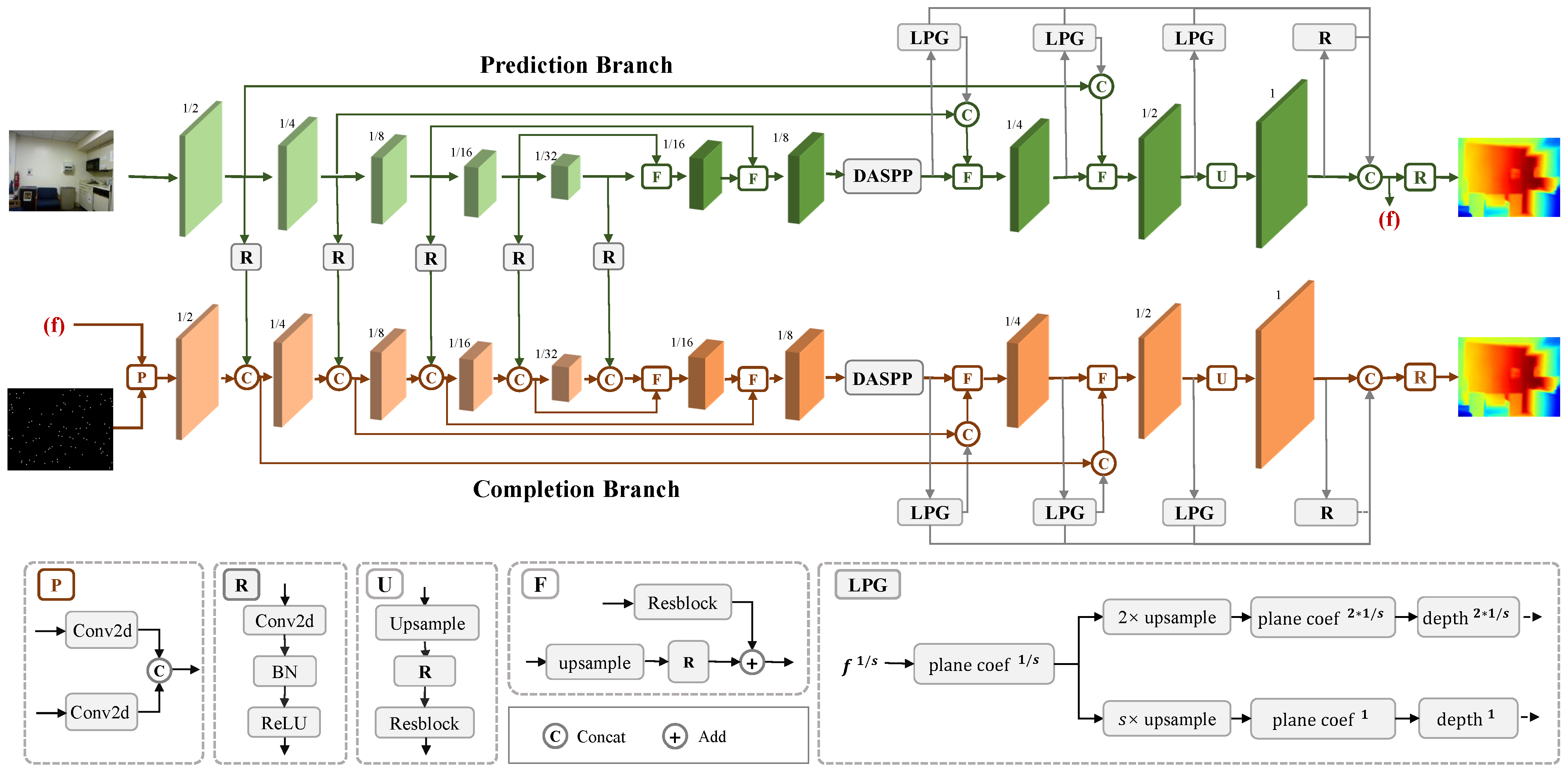
4.1. Dual-Branch Encoder–Decoder Architecture
4.2. Multi-Scale Local Planar Guidance Module
4.3. Training Loss
4.3.1. Scale-Invariant Loss
4.3.2. Mean Normal Loss
4.3.3. Gradient Loss
4.3.4. Overall Loss Function
5. Experiment
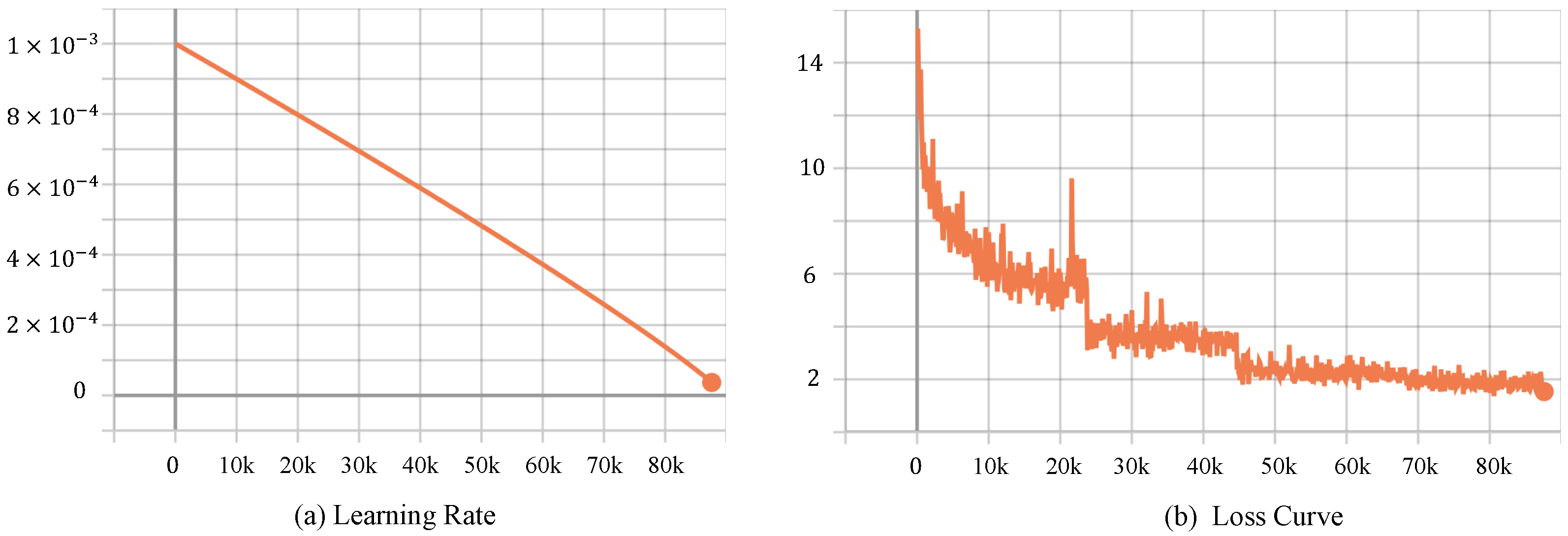
5.1. Experimental Setup
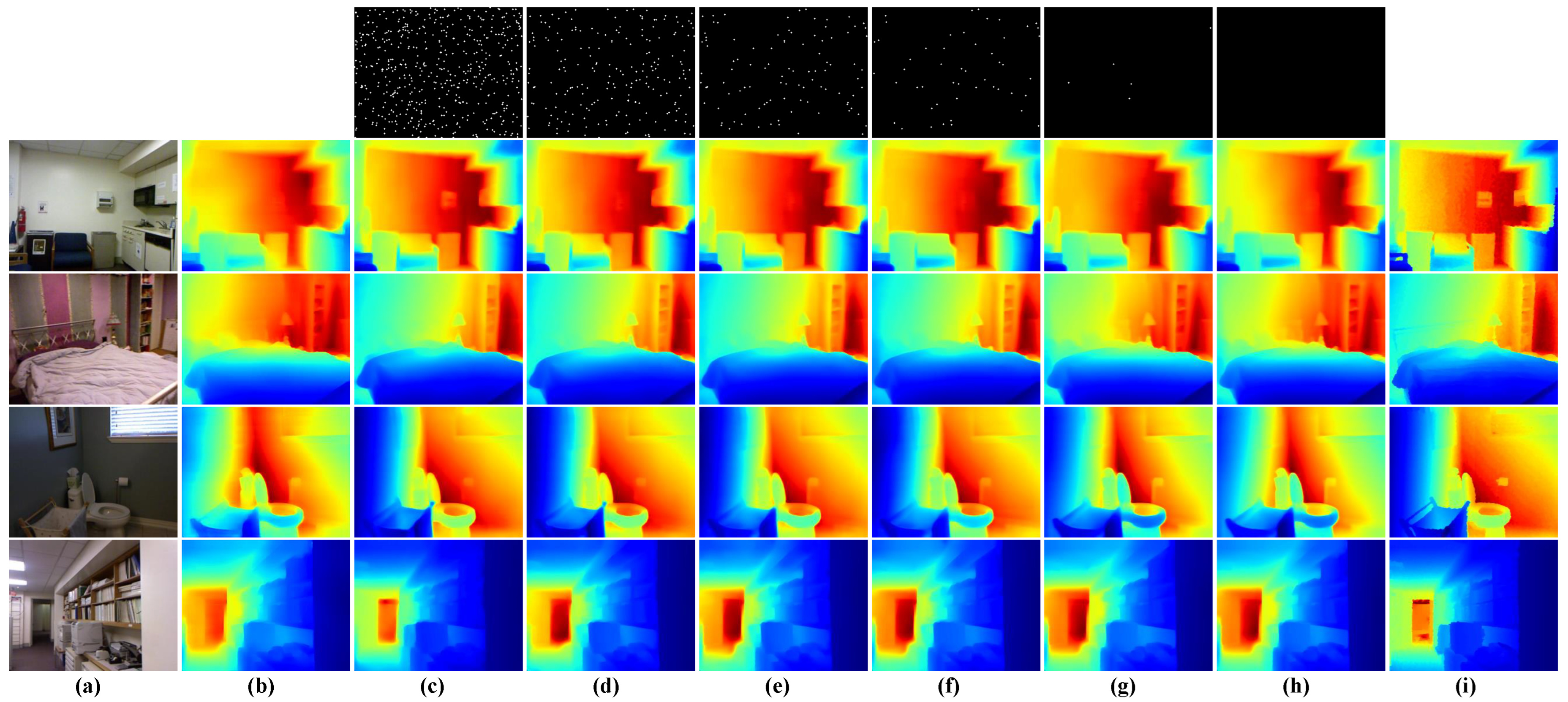
5.2. Visualization Results of the Model
5.3. Ablation Studies
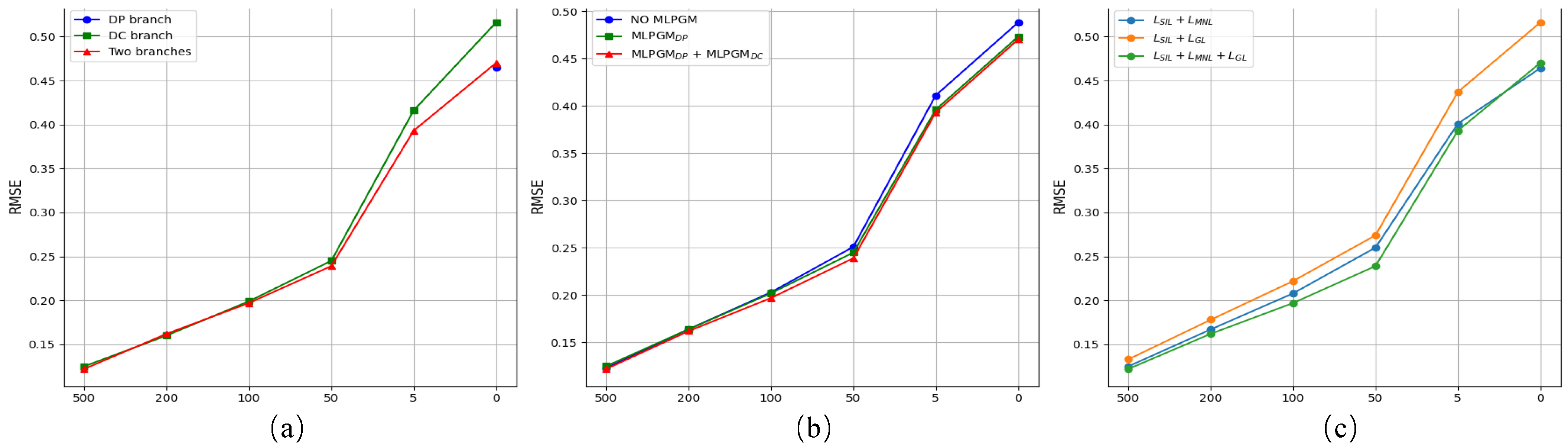
5.3.1. Effectiveness of the Dual-Branch Architecture
5.3.2. Effectiveness of the MLPGM
5.3.3. Effectiveness of the Training Loss
5.4. Comparison to State of the Art
5.5. Experimental Results in Real-World Application
5.5.1. Testset
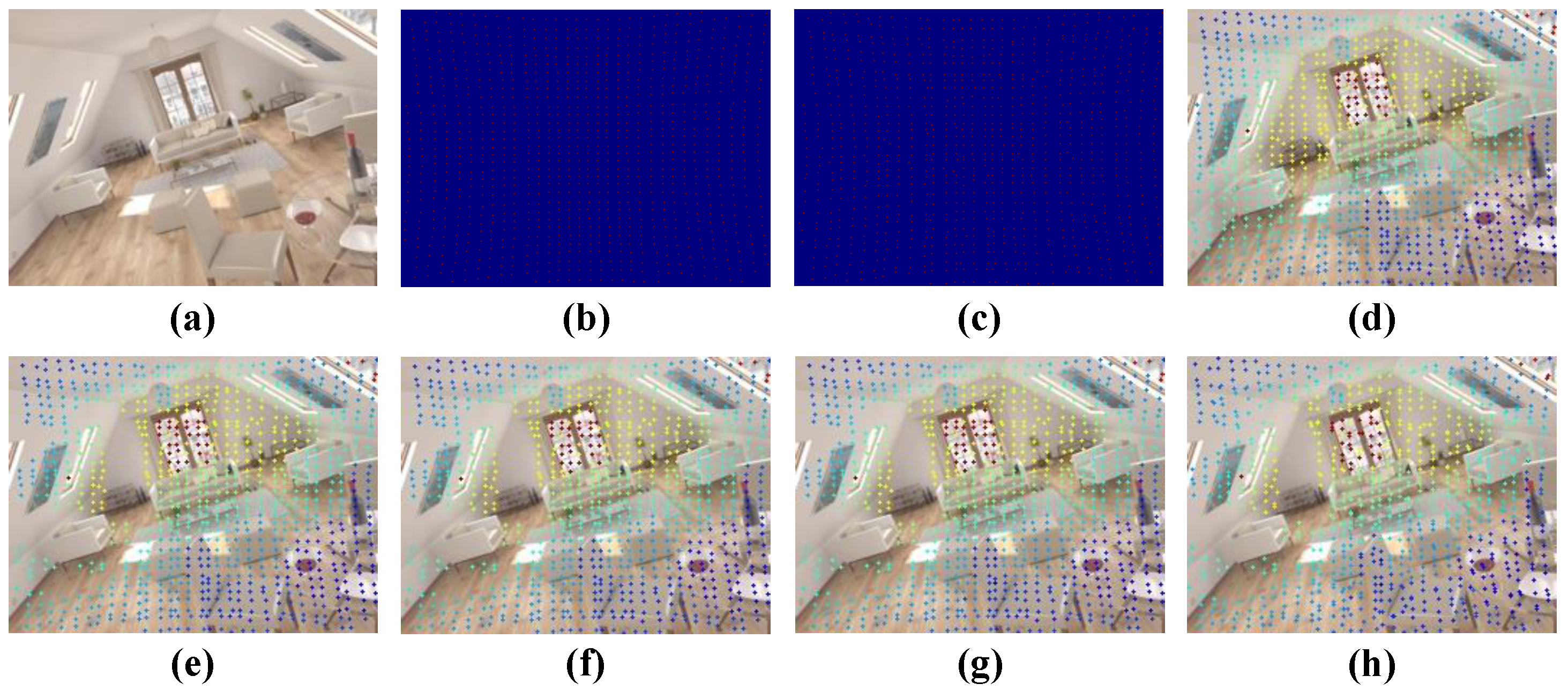
5.5.2. Construction of Trainset
- Step 1: The sparse depth map obtained from the iTOF sensor exhibits distinct distribution characteristics in rows and columns; thus, we first obtain a basic binary mask based on the fundamental row–column positions to represent the positions of valid depth points.
- Step 2: Considering that the sparse depth map generated by the iTOF sensor may not strictly adhere to the regular pattern of row–column positions due to inherent errors, we introduce random offsets to the positions in the basic binary mask to obtain a preliminary sparse mask.
- Step 3: We use the preliminary sparse mask to sample the dense depth map truth values, resulting in a preliminary sparse depth map.
- Step 4: Given that the sparse depth map obtained from the iTOF sensor may contain regions with missing depth values due to environmental factors, we generate random polygons in the sparse depth map to simulate these “black holes”.
- Step 5: Considering the randomness in the hardware measurement distance range, we randomly set the maximum value in the sparse depth map and filter out pixels exceeding this depth value.
- Step 6: Taking into account hardware noise and external interference, there may be deviations between the sparse depth map obtained from the iTOF sensor and the ground truth. We randomly add depth value offsets to the sparse depth points to simulate this noise.
- Step 7: Finally, considering the alignment issue between the color image and the sparse depth points, as well as potential noise near object edges, we randomly offset the positions of sparse depth points to simulate this scenario.
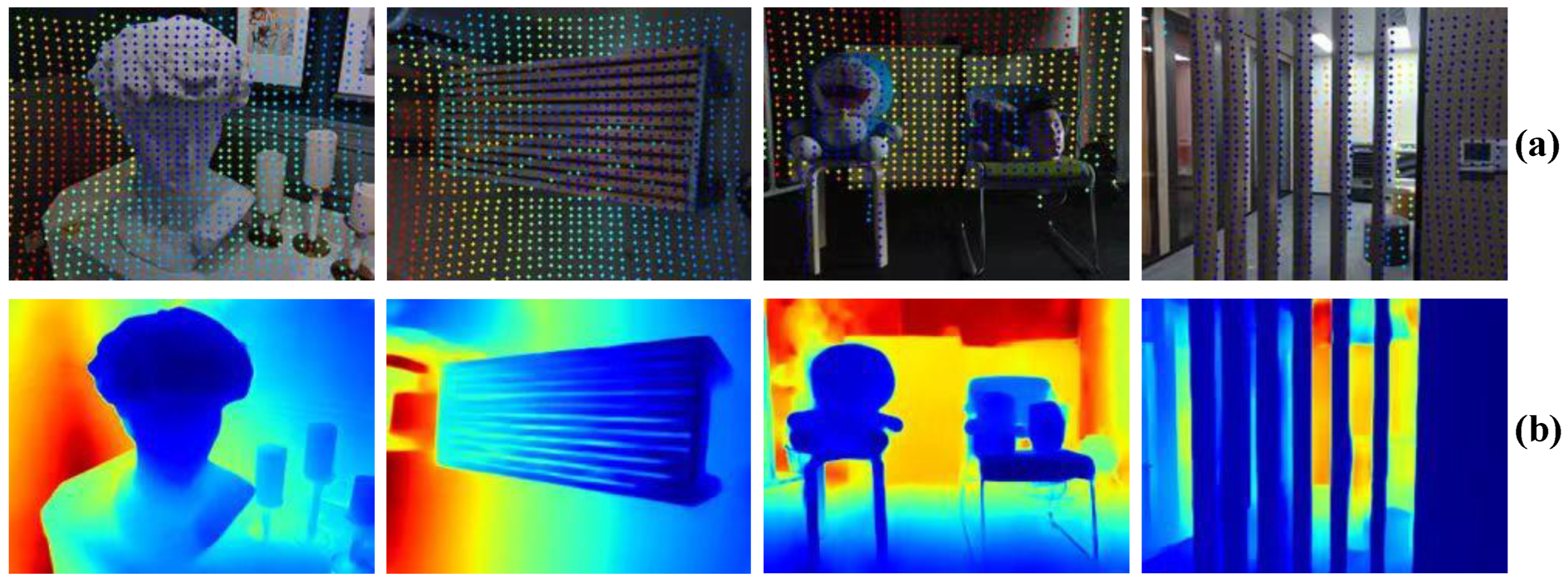
5.5.3. Visualization Results of the OPPO Prototype Equipped with Spot-iToF316
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DP | depth prediction |
| DC | depth completion |
| MLPGM | multi-scale local planar guidance module |
| BN | batch normalization |
| DASPP | dynamic atrous spatial pyramid pooling |
| LPG | local planar guidance |
| SIL | scale-invariant loss |
| MNL | mean normal loss |
| GL | gradient loss |
| RMSE | root mean square error |
References
- Yan, Z.; Wang, K.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Yang, J. RigNet: Repetitive image guided network for depth completion. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 214–230. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, F.; Karaman, S. Sparse-to-dense: Depth prediction from sparse depth samples and a single image. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Brisbane, Australia, 21–25 May 2018; pp. 4796–4803. [Google Scholar]
- Imran, S.; Liu, X.; Morris, D. Depth completion with twin surface extrapolation at occlusion boundaries. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 2583–2592. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, J.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, S.; Zeng, B.; Pollefeys, M. Deeplidar: Deep surface normal guided depth prediction for outdoor scene from sparse lidar data and single color image. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 3313–3322. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, X.; Wang, P.; Guan, C.; Yang, R. Cspn++: Learning context and resource aware convolutional spatial propagation networks for depth completion. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 10615–10622. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.; Joo, K.; Hu, Z.; Liu, C.K.; So Kweon, I. Non-local spatial propagation network for depth completion. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 120–136. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Yin, H.; Yao, J. Deformable spatial propagation networks for depth completion. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Virtual, 25–28 October 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 913–917. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.; Cheng, T.; Zhong, Q.; Zhou, W.; Yang, H. Dynamic spatial propagation network for depth completion. In Proceedings of the AAAI, Virtual, 21–23 March 2022; pp. 1638–1646. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Shao, X.; Wang, B.; Li, Y.; Wang, S. Graphcspn: Geometry-aware depth completion via dynamic gcns. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 90–107. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.; Tian, F.P.; An, B.; Li, J.; Tan, P. Bilateral Propagation Network for Depth Completion. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024; pp. 9763–9772. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, B.; Liang, M.; Urtasun, R. Learning joint 2d-3d representations for depth completion. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 10023–10032. [Google Scholar]
- Du, W.; Chen, H.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Y. Depth completion using geometry-aware embedding. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 23–27 May 2022; pp. 8680–8686. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Z.; Sarma, S.E.; Bronstein, M.M.; Solomon, J.M. Dynamic graph cnn for learning on point clouds. Acm Trans. Graph. 2019, 38, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Jampani, V.; Sun, D.; Maji, S.; Kalogerakis, E.; Yang, M.H.; Kautz, J. Splatnet: Sparse lattice networks for point cloud processing. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 2530–2539. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, X.; Poggi, M.; Zhu, Z.; Huang, G.; Mattoccia, S. Completionformer: Depth completion with convolutions and vision transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 18527–18536. [Google Scholar]
- Rho, K.; Ha, J.; Kim, Y. Guideformer: Transformers for image guided depth completion. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 6250–6259. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Zhang, G.; Liu, Q.; Gao, T.; Dai, Y. LRRU: Long-short Range Recurrent Updating Networks for Depth Completion. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 9422–9432. [Google Scholar]
- Uhrig, J.; Schneider, N.; Schneider, L.; Franke, U.; Brox, T.; Geiger, A. Sparsity invariant cnns. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), Qingdao, China, 10–12 October 2017; pp. 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, O.; Niklaus, S.; Chen, S.; Shen, C. Towards Domain-agnostic Depth Completion. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2207.14466. [Google Scholar]
- Ryu, K.; Lee, K.i.; Cho, J.; Yoon, K.J. Scanline resolution-invariant depth completion using a single image and sparse LiDAR point cloud. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 6961–6968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, J.; Gong, X. A normalized convolutional neural network for guided sparse depth upsampling. In Proceedings of the IJCAI, Stockholm, Sweden, 9–19 July 2018; pp. 2283–2290. [Google Scholar]
- Eldesokey, A.; Felsberg, M.; Khan, F.S. Confidence propagation through cnns for guided sparse depth regression. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2019, 42, 2423–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.H.; Wang, F.E.; Lin, J.T.; Tsai, Y.H.; Chiu, W.C.; Sun, M. Plug-and-play: Improve depth prediction via sparse data propagation. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 5880–5886. [Google Scholar]
- Long, Y.; Yu, H.; Liu, B. Depth completion towards different sensor configurations via relative depth map estimation and scale recovery. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2021, 80, 103272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Liao, R.; Liu, Z.; Urtasun, R.; Jia, J. Geonet: Geometric neural network for joint depth and surface normal estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 283–291. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, X.; Liu, Z.; Liao, R.; Torr, P.H.; Urtasun, R.; Jia, J. Geonet++: Iterative geometric neural network with edge-aware refinement for joint depth and surface normal estimation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 44, 969–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zhou, Z. Recovering 3d planes from a single image via convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 85–100. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zou, D.; Yu, W. StructDepth: Leveraging the structural regularities for self-supervised indoor depth estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 12663–12673. [Google Scholar]
- Long, X.; Lin, C.; Liu, L.; Li, W.; Theobalt, C.; Yang, R.; Wang, W. Adaptive surface normal constraint for depth estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 12849–12858. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.H.; Han, M.K.; Ko, D.W.; Suh, I.H. From big to small: Multi-scale local planar guidance for monocular depth estimation. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.10326. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, W.; Liu, Y.; Shen, C.; Yan, Y. Enforcing geometric constraints of virtual normal for depth prediction. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 5684–5693. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, W.; Liu, Y.; Shen, C. Virtual normal: Enforcing geometric constraints for accurate and robust depth prediction. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 44, 7282–7295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Ma, Z.; Ji, Z.; Ren, Z. Gedepth: Ground embedding for monocular depth estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2–3 October 2023; pp. 12719–12727. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, V.; Sakaridis, C.; Liniger, A.; Van Gool, L. P3Depth: Monocular Depth Estimation with a Piecewise Planarity Prior. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 1610–1621. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, M.; Wang, S.; Li, B.; Ning, S.; Fan, L.; Gong, X. Penet: Towards precise and efficient image guided depth completion. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Xi’an, China, 30 May–5 June 2021; pp. 13656–13662. [Google Scholar]
- Van Gansbeke, W.; Neven, D.; De Brabandere, B.; Van Gool, L. Sparse and noisy lidar completion with rgb guidance and uncertainty. In Proceedings of the 2019 16th International Conference on Machine Vision Applications (MVA), Tokyo, Japan, 27–31 May 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Silberman, N.; Hoiem, D.; Kohli, P.; Fergus, R. Indoor segmentation and support inference from rgbd images. ECCV (5) 2012, 7576, 746–760. [Google Scholar]
- Conti, A.; Poggi, M.; Mattoccia, S. Sparsity Agnostic Depth Completion. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 2–7 January 2023; pp. 5871–5880. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, C.S. Multi-loss rebalancing algorithm for monocular depth estimation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 785–801. [Google Scholar]
- Eigen, D.; Puhrsch, C.; Fergus, R. Depth map prediction from a single image using a multi-scale deep network. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2014, 27, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, H.; Gong, M.; Wang, C.; Batmanghelich, K.; Tao, D. Deep ordinal regression network for monocular depth estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 2002–2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bhat, S.F.; Alhashim, I.; Wonka, P. Adabins: Depth estimation using adaptive bins. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 4009–4018. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, A.; Arora, C. Attention attention everywhere: Monocular depth prediction with skip attention. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 2–7 January 2023; pp. 5861–5870. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, C.; Nguyen, T.; Taylor, C. Depth completion via deep basis fitting. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Snowmass Village, CO, USA, 1–5 March 2020; pp. 71–80. [Google Scholar]
- Senushkin, D.; Romanov, M.; Belikov, I.; Patakin, N.; Konushin, A. Decoder modulation for indoor depth completion. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Prague, Czech Republic, 27 September–1 October 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 2181–2188. [Google Scholar]
- Imran, S.; Long, Y.; Liu, X.; Morris, D. Depth coefficients for depth completion. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 12438–12447. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, F.; Cavalheiro, G.V.; Karaman, S. Self-supervised sparse-to-dense: Self-supervised depth completion from lidar and monocular camera. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 3288–3295. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Nguyen, T.; Miller, I.D.; Shivakumar, S.S.; Chen, S.; Taylor, C.J.; Kumar, V. Dfinenet: Ego-motion estimation and depth refinement from sparse, noisy depth input with rgb guidance. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1903.06397. [Google Scholar]
- Jaritz, M.; De Charette, R.; Wirbel, E.; Perrotton, X.; Nashashibi, F. Sparse and dense data with cnns: Depth completion and semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), Verona, Italy, 5–8 September 2018; pp. 52–60. [Google Scholar]
- Shivakumar, S.S.; Nguyen, T.; Miller, I.D.; Chen, S.W.; Kumar, V.; Taylor, C.J. Dfusenet: Deep fusion of rgb and sparse depth information for image guided dense depth completion. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference (ITSC), Auckland, New Zealand, 27–30 October 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 13–20. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, C.; Dong, C.; Mertz, C.; Dolan, J.M. Depth completion via inductive fusion of planar lidar and monocular camera. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 25–29 October 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 10843–10848. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Y.; Wu, C.Y.; You, S.; Neumann, U. Deep rgb-d canonical correlation analysis for sparse depth completion. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2019, 32, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Liu, W.; Tao, D.; Cheng, J. Canonical correlation analysis networks for two-view image recognition. Inf. Sci. 2017, 385, 338–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Shen, C.; Yang, Y.B. Image restoration using very deep convolutional encoder-decoder networks with symmetric skip connections. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2016, 29, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Siddiquee, M.M.R.; Tajbakhsh, N.; Liang, J. Unet++: Redesigning skip connections to exploit multiscale features in image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2019, 39, 1856–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wei, P.; Li, H.; Zheng, N. Multiscale adaptation fusion networks for depth completion. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Glasgow, UK, 19–24 July 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Li, A.; Yuan, Z.; Ling, Y.; Chi, W.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, C. A multi-scale guided cascade hourglass network for depth completion. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Snowmass Village, CO, USA, 1–5 March 2020; pp. 32–40. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.; Tian, F.P.; Feng, W.; Li, J.; Tan, P. Learning guided convolutional network for depth completion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 30, 1116–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuster, R.; Wasenmuller, O.; Unger, C.; Stricker, D. Ssgp: Sparse spatial guided propagation for robust and generic interpolation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2021; pp. 197–206. [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrievski, M.; Veelaert, P.; Philips, W. Learning morphological operators for depth completion. In Advanced Concepts for Intelligent Vision Systems: Proceedings of the 19th International Conference, ACIVS 2018, Poitiers, France, 24–27 September 2018; Proceedings 19; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 450–461. [Google Scholar]
- Hambarde, P.; Murala, S. S2DNet: Depth estimation from single image and sparse samples. IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging 2020, 6, 806–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Badrinarayanan, V.; Drozdov, G.; Rabinovich, A. Estimating depth from rgb and sparse sensing. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 167–182. [Google Scholar]
- Hegde, G.; Pharale, T.; Jahagirdar, S.; Nargund, V.; Tabib, R.A.; Mudenagudi, U.; Vandrotti, B.; Dhiman, A. Deepdnet: Deep dense network for depth completion task. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 2190–2199. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, Y.; Huang, L.; Wang, Y.; Kodagoda, S.; Yu, Y.; Liu, Y. Parse geometry from a line: Monocular depth estimation with partial laser observation. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Singapore, 29 May–3 June 2017; pp. 5059–5066. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, J.; Xiang, Z.; Ye, Y.; Wang, L. Denselidar: A real-time pseudo dense depth guided depth completion network. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 1808–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Dong, W.; Li, L.; Wu, J.; Li, X.; Shi, G. Robust depth completion with uncertainty-driven loss functions. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 20–27 February 2024; Volume 36, pp. 3626–3634. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wei, P.; Zheng, N. A multi-cue guidance network for depth completion. Neurocomputing 2021, 441, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Wang, P.; Yang, R. Depth estimation via affinity learned with convolutional spatial propagation network. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 103–119. [Google Scholar]
- Jeon, Y.; Kim, H.; Seo, S.W. ABCD: Attentive Bilateral Convolutional Network for Robust Depth Completion. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 7, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Xiong, H.; Xian, K.; Zhao, C.; Cao, Z.; Li, X. Sparse-to-dense depth completion revisited: Sampling strategy and graph construction. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 682–699. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Gong, M.; Fu, H.; Tao, D. Adaptive context-aware multi-modal network for depth completion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 5264–5276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Shi, J.; Zhang, G.; Bao, H.; Li, H. Depth completion from sparse lidar data with depth-normal constraints. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 2811–2820. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Yang, M.; Zheng, N. G2-MonoDepth: A General Framework of Generalized Depth Inference from Monocular RGB+ X Data. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 46, 3753–3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M. Towards precise and robust depth completion. Master’s Thesis, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.; Yu, K.; Zhang, C.; Li, Z.; Yang, K. Denseaspp for semantic segmentation in street scenes. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 3684–3692. [Google Scholar]
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Massa, F.; Lerer, A.; Bradbury, J.; Chanan, G.; Killeen, T.; Lin, Z.; Gimelshein, N.; Antiga, L.; et al. PyTorch: An Imperative Style, High-Performance Deep Learning Library. In Proceedings of the NeuroIPS, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Ishii, Y.; Yamashita, T. Cutdepth: Edge-aware data augmentation in depth estimation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.07684. [Google Scholar]
- Eldesokey, A.; Felsberg, M.; Holmquist, K.; Persson, M. Uncertainty-aware cnns for depth completion: Uncertainty from beginning to end. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 12014–12023. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, M.; Ramapuram, J.; Ranjan, A.; Kumar, A.; Bautista, M.A.; Paczan, N.; Webb, R.; Susskind, J.M. Hypersim: A photorealistic synthetic dataset for holistic indoor scene understanding. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 10912–10922. [Google Scholar]
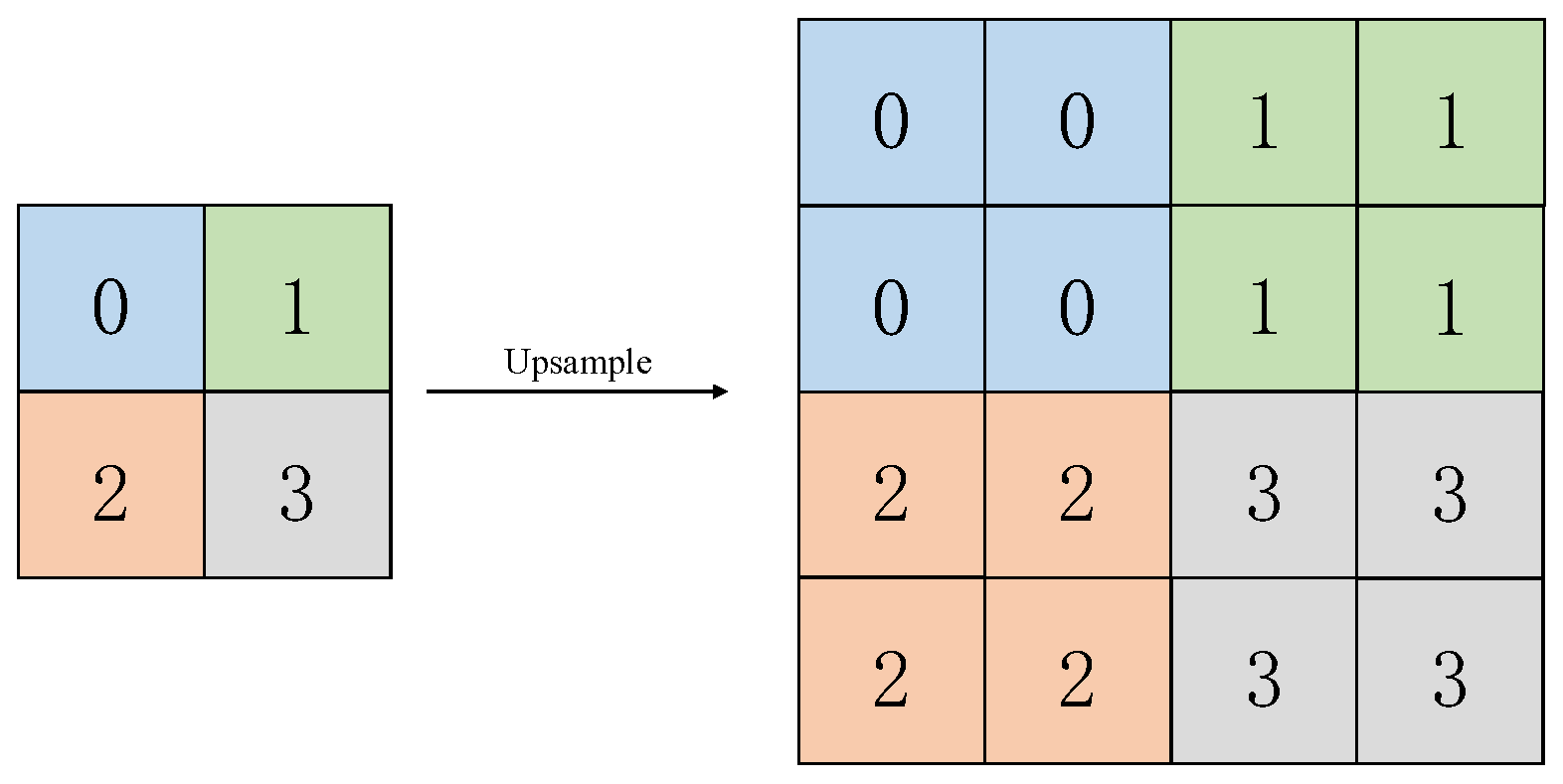
| Models | 500 | 200 | 100 | 50 | 5 | 0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DP branch | - | - | - | - | - | 0.465 |
| DC branch | 0.125 | 0.160 | 0.199 | 0.245 | 0.416 | 0.516 |
| Two branches | 0.122 | 0.162 | 0.197 | 0.239 | 0.393 | 0.470 |
| MLPGMDP | MLPGMDC | 500 | 200 | 100 | 50 | 5 | 0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.123 | 0.164 | 0.203 | 0.251 | 0.411 | 0.488 | ||
| ✓ | 0.125 | 0.164 | 0.202 | 0.245 | 0.396 | 0.473 | |
| ✓ | ✓ | 0.122 | 0.162 | 0.197 | 0.239 | 0.393 | 0.470 |
| Training Loss | 500 | 200 | 100 | 50 | 5 | 0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.125 | 0.167 | 0.208 | 0.260 | 0.401 | 0.464 | |
| 0.133 | 0.178 | 0.222 | 0.274 | 0.437 | 0.516 | |
| 0.122 | 0.162 | 0.197 | 0.239 | 0.393 | 0.470 |
| Methods | 500 | 200 | 100 | 50 | 5 | 0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pNCNN [80] | 0.170 | 0.237 | 0.338 | 0.568 | 2.412 | - |
| CSPN [68] | 0118 | 0.177 | 0.338 | 0.884 | 2.063 | - |
| NLSPN [6] | 0.101 | 0.142 | 0.246 | 0.423 | 1.033 | - |
| NConv-CNN [22] | 0.129 | 0.173 | - | - | - | - |
| G2-MonoDepth [73] | 0.118 | - | - | 0.248 | 1.321 | - |
| SpAgNet [38] | 0.114 | 0.155 | 0.209 | 0.272 | 0.469 | - |
| Ours | 0.122 | 0.162 | 0.197 | 0.239 | 0.393 | 0.470 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Jiang, F.; Gong, X. A Sparsity-Invariant Model via Unifying Depth Prediction and Completion. Algorithms 2024, 17, 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/a17070298
Wang S, Jiang F, Gong X. A Sparsity-Invariant Model via Unifying Depth Prediction and Completion. Algorithms. 2024; 17(7):298. https://doi.org/10.3390/a17070298
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shuling, Fengze Jiang, and Xiaojin Gong. 2024. "A Sparsity-Invariant Model via Unifying Depth Prediction and Completion" Algorithms 17, no. 7: 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/a17070298
APA StyleWang, S., Jiang, F., & Gong, X. (2024). A Sparsity-Invariant Model via Unifying Depth Prediction and Completion. Algorithms, 17(7), 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/a17070298






