The Novel EfficientNet Architecture-Based System and Algorithm to Predict Complex Human Emotions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Materials and Methods
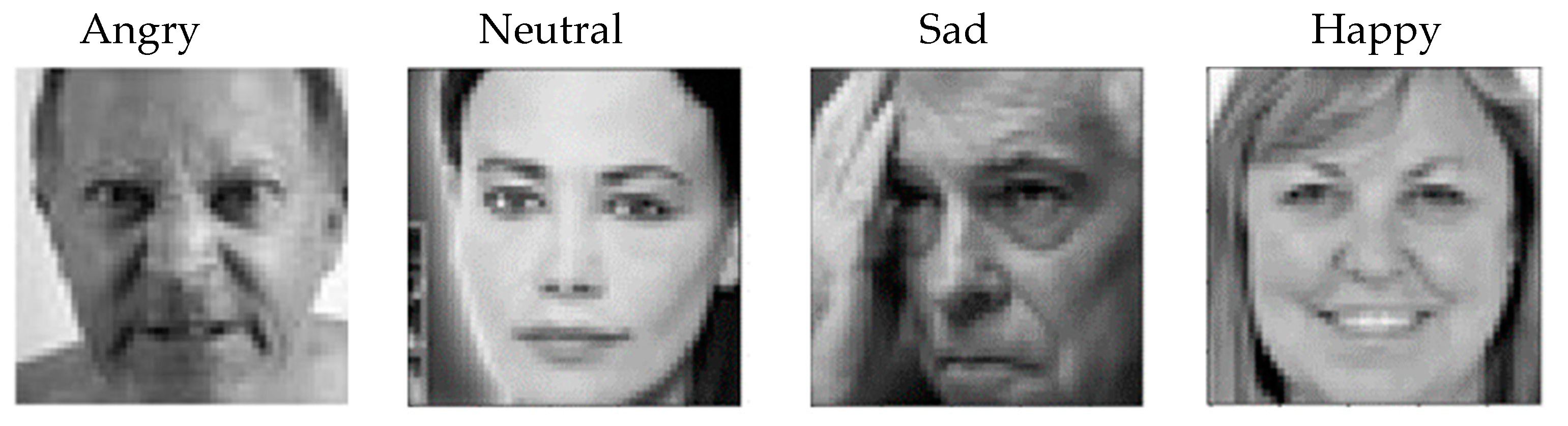
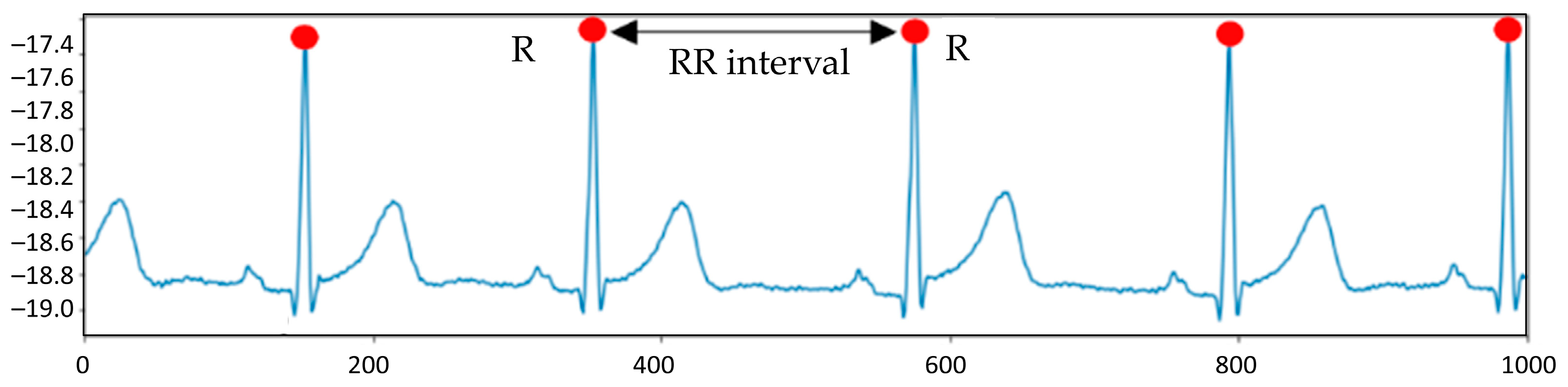
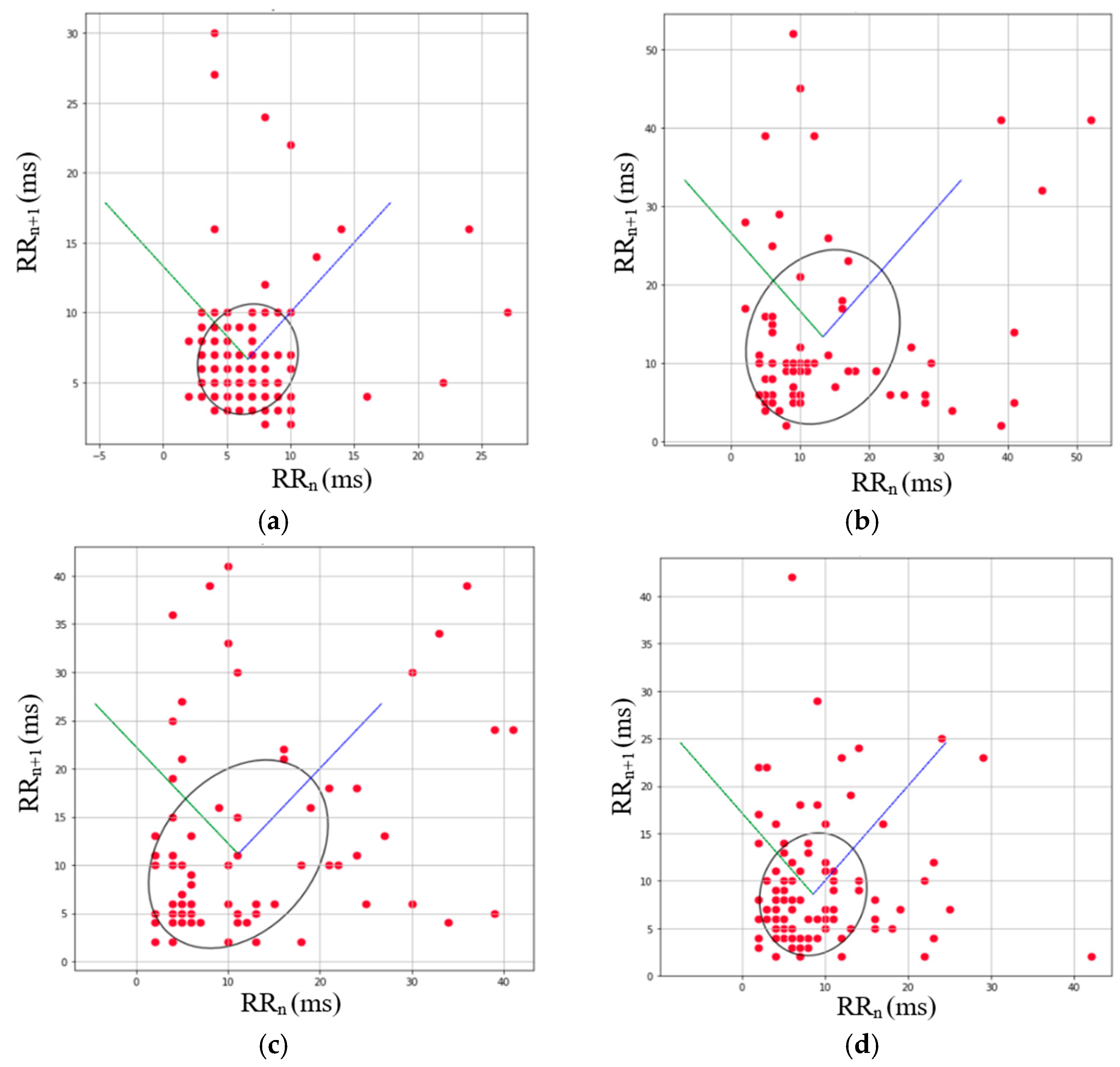
3.1. Data Acquisition
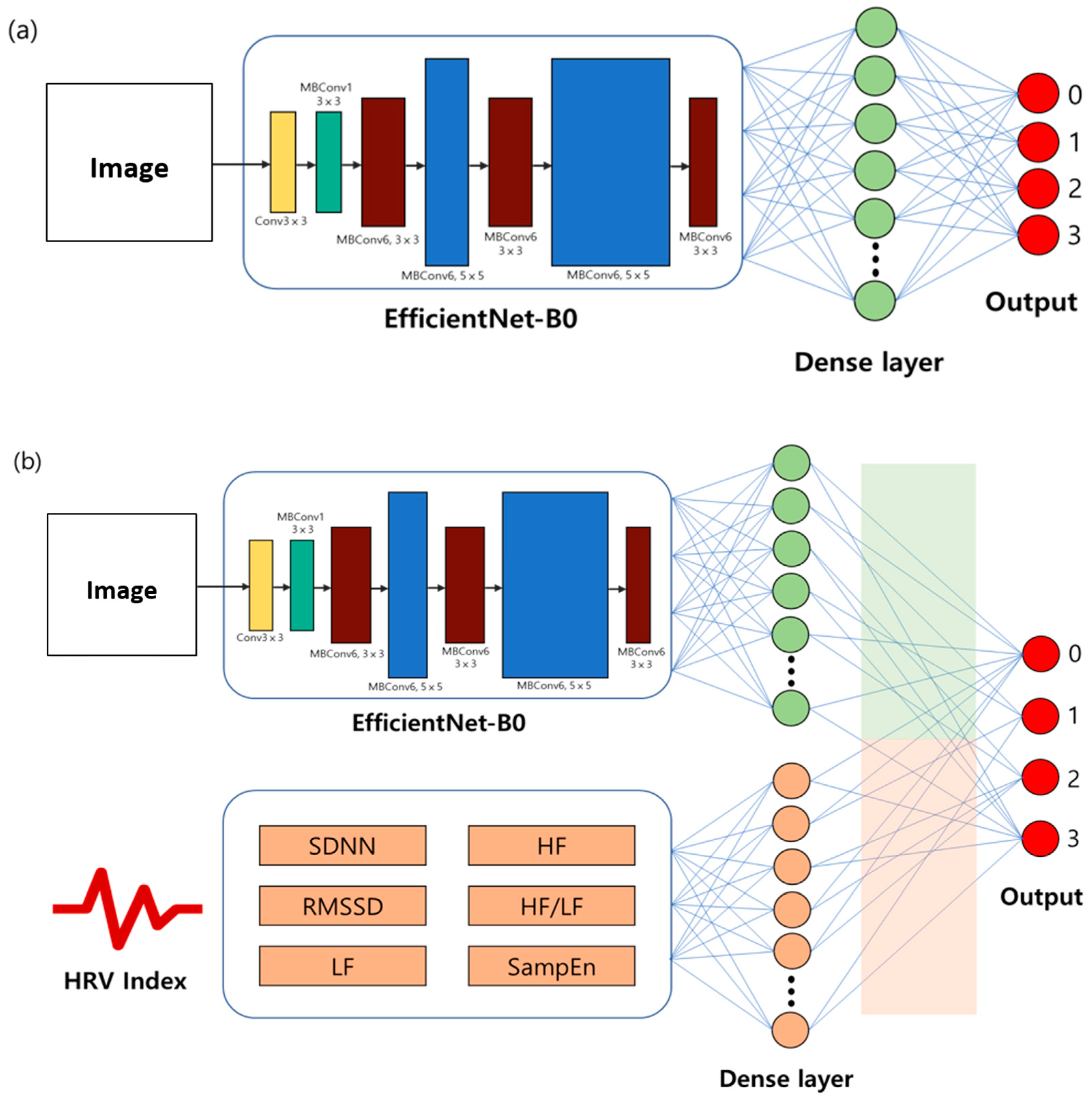
3.2. Designing the Model
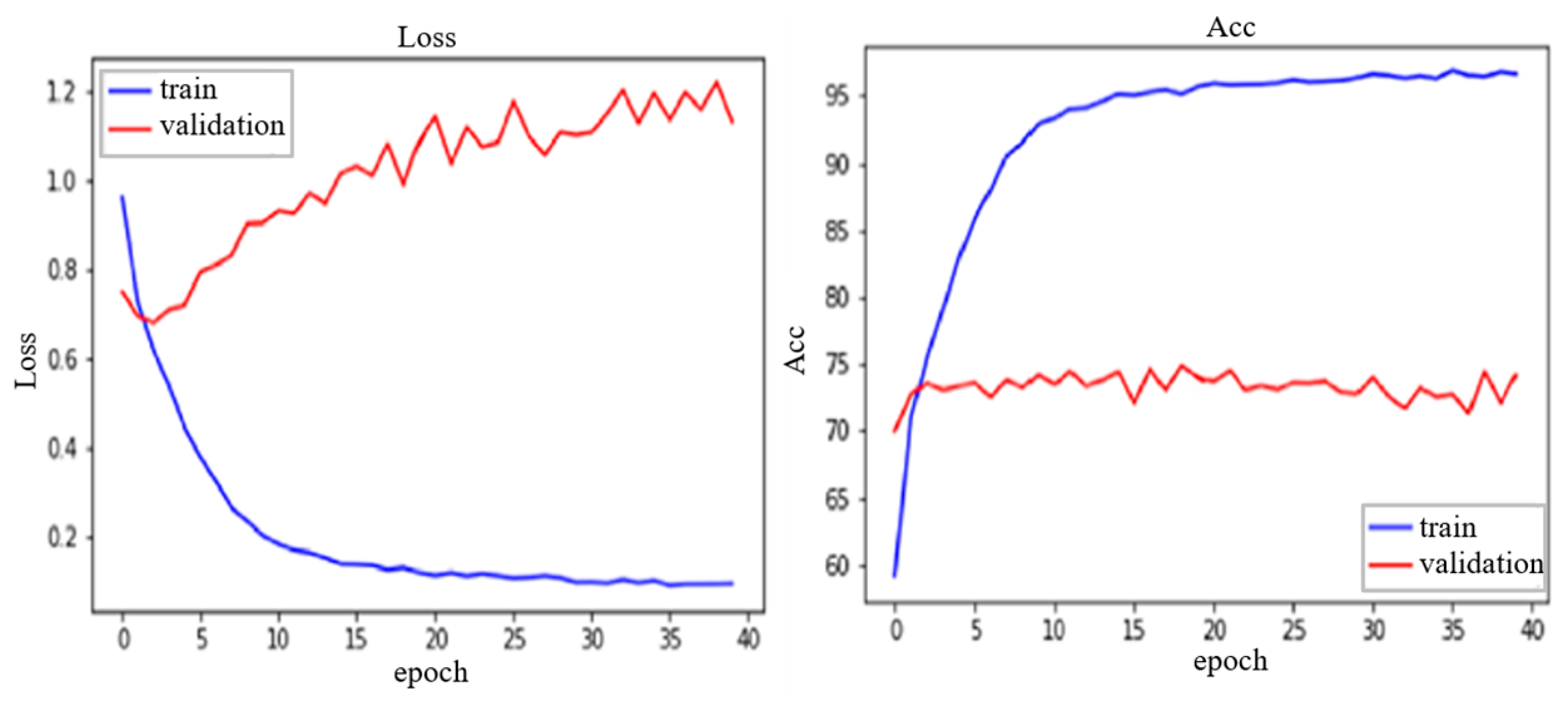
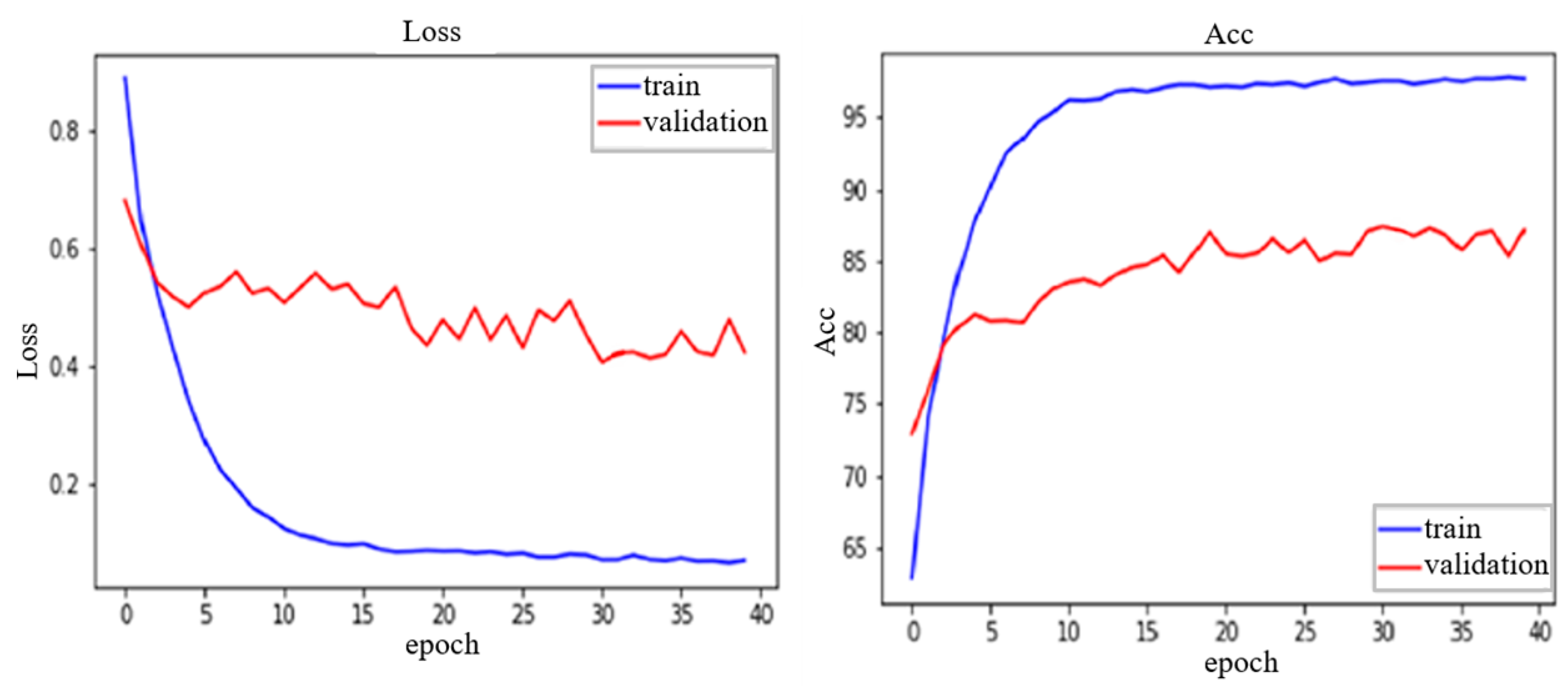
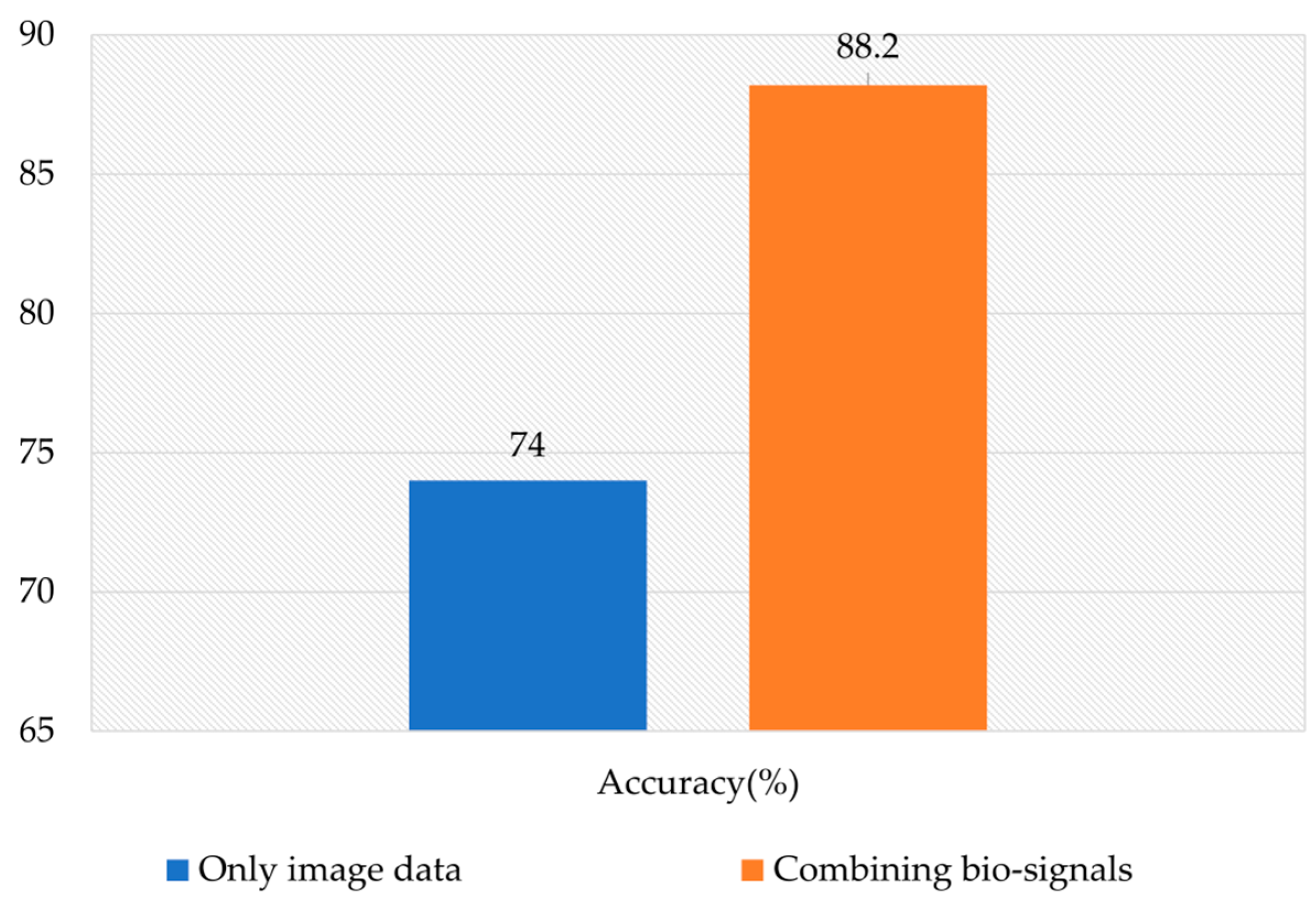
4. Result and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cha, W.-Y.; Shin, D.-K.; Shin, D.-I. Analysis and Comparison of The Emotion Recognition by Multiple Bio-Signal. In Proceedings of the Korean Information Science Society Conference, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 10–13 December 2017; pp. 104–105. [Google Scholar]
- Kortelainen, J.; Tiinanen, S.; Huang, X.; Li, X.; Laukka, S.; Pietikäinen, M.; Seppänen, T. Multimodal emotion recognition by combining physiological signals and facial expressions: A preliminary study. In Proceedings of the 2012 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, San Diego, CA, USA, 28 August–1 September 2012; pp. 5238–5241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannou, S.V.; Raouzaiou, A.T.; Tzouvaras, V.A.; Mailis, T.P.; Karpouzis, K.C.; Kollias, S.D. Emotion recognition through facial expression analysis based on a neurofuzzy network. Neural Netw. 2005, 18, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-D.; Yang, Z.-J.; Lu, H.-M.; Zhou, X.-X.; Phillips, P.; Liu, Q.-M.; Wang, S.-H. Facial Emotion Recognition Based on Biorthogonal Wavelet Entropy, Fuzzy Support Vector Machine, and Stratified Cross Validation. IEEE Access 2016, 4, 8375–8385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, L.F.; Russell, J.A. Independence and bipolarity in the structure of current affect. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 1998, 74, 967–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacconi, D.; Mayora, O.; Lukowicz, P.; Arnrich, B.; Setz, C.; Troster, G.; Haring, C. Activity and emotion recognition to support early diagnosis of psychiatric diseases. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Pervasive Computing Technologies for Healthcare, Tampere, Finland, 30 January–1 February 2008; pp. 100–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujol, F.A.; Mora, H.; Martínez, A. Emotion Recognition to Improve e-Healthcare Systems in Smart Cities. In Research & Innovation Forum 2019: Technology, Innovation, Education, and their Social Impact 1; Visvizi, A., Lytras, M., Eds.; Springer Proceedings in Complexity; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wioleta, S. Using physiological signals for emotion recognition. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Human System Interactions (HSI), Gdansk, Poland, 6–8 June 2013; pp. 556–561. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, J.; Maeng, J.; Kim, D.-H. Inner Emotion Recognition Using Multi Bio-Signals. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics—Asia (ICCE-Asia), Jeju, Republic of Korea, 24–26 June 2018; pp. 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri-Benssassi, E.; Ye, J. Generalisation and robustness investigation for facial and speech emotion recognition using bio-inspired spiking neural networks. Soft Comput. 2021, 25, 1717–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana, D.S.; Guastella, A.J.; Outhred, T.; Hickie, I.B.; Kemp, A.H. Heart rate variability is associated with emotion recognition: Direct evidence for a relationship between the autonomic nervous system and social cognition. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2012, 86, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roveda, J.M.; Fink, W.; Chen, K.; Wu, W.-T. Psychological health monitoring for pilots and astronauts by tracking sleep-stress-emotion changes. In Proceedings of the IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 5–12 March 2016; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randazzo, V.; Ferretti, J.; Pasero, E. Anytime ECG Monitoring through the Use of a Low-Cost, User-Friendly, Wearable Device. Sensors 2021, 21, 6036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jing, C.; Liu, G.; Hao, M. The Research on Emotion Recognition from ECG Signal. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information Technology and Computer Science, Kiev, Ukraine, 25–26 July 2009; pp. 497–500. [Google Scholar]
- Ravindran, A.S.; Nakagome, S.; Wickramasuriya, D.S.; Contreras-Vidal, J.L.; Faghih, R.T. Emotion Recognition by Point Process Characterization of Heartbeat Dynamics. In Proceedings of the IEEE Healthcare Innovations and Point of Care Technologies, Bethesda, MD, USA, 20–22 November 2019; pp. 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Khomidov, M.; Lee, D.; Kim, C.-H.; Lee, J.-H. The Real-Time Image Sequences-Based Stress Assessment Vision System for Mental Health. Electronics 2024, 13, 2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.J.; Erhan, D.; Carrier, P.L.; Courville, A.; Mirza, M.; Hamner, B.; Cukierski, W.; Tang, Y.; Thaler, D.; Lee, D.-H.; et al. Challenges in representation learning: A report on three machine learning contests. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Information Processing, Daegu, Republic of Korea, 3–7 November 2013; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Zhang, M.; Pan, Z. Facial Expression Recognition with CNN Ensemble. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Cyberworlds (CW), Chongqing, China, 28–30 September 2016; pp. 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fard, A.P.; Mahoor, M.H. Ad-Corre: Adaptive Correlation-Based Loss for Facial Expression Recognition in the Wild. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 26756–26768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chollet, F. Xception: Deep Learning with Depthwise Separable Convolutions. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1800–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vulpe-Grigoraşi, A.; Grigore, O. Convolutional Neural Network Hyperparameters optimization for Facial Emotion Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2021 12th International Symposium on Advanced Topics in Electrical Engineering (ATEE), Bucharest, Romania, 25–27 March 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignesh, S.; Savithadevi, M.; Sridevi, M.; Sridhar, R. A novel facial emotion recognition model using segmentation VGG-19 architecture. Int. J. Inf. Technol. 2023, 15, 1777–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, L.; Vu, T.H.; Tran, T.A. Facial Expression Recognition Using Residual Masking Network. In Proceedings of the 2020 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Milan, Italy, 10–15 January 2021; pp. 4513–4519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.-W.; Huang, Y.-S.; Lin, C.-H.; Chien, J.-C.; Haraikawa, K.; Shieh, J.-S. Heart Rate Variability Signal Features for Emotion Recognition by Using Principal Component Analysis and Support Vectors Machine. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 16th International Conference on Bioinformatics and Bioengineering (BIBE), Taichung, Taiwan, 31 October–2 November 2016; pp. 274–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vapnik, V. Statistical Learning Theory; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Ferdinando, H.; Seppänen, T.; Alasaarela, E. Emotion Recognition Using Neighborhood Components Analysis and ECG/HRV-Based Features. In Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods: 6th International Conference, ICPRAM 2017, Porto, Portugal, 24–26 February 2017; De Marsico, M., di Baja, G., Fred, A., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 10857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberger, J.; Roweis, S.; Hinton, G.; Salakhutdinov, R. Neighbourhood Components Analysis. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2004, 17, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M.; Lee, Y.K.; Lim, M.-T.; Kang, T.-K. Emotion Recognition Using Convolutional Neural Network with Selected Statistical Photoplethysmogram Features. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngai, W.K.; Xie, H.; Zou, D.; Chou, K.-L. Emotion recognition based on convolutional neural networks and heterogeneous bio-signal data sources. Inf. Fusion 2022, 77, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassouneh, A.; Mutawa, A.M.; Murugappan, M. Development of a Real-Time Emotion Recognition System Using Facial Expressions and EEG based on machine learning and deep neural network methods. Inform. Med. Unlocked 2020, 20, 100372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godin, C.; Prost-Boucle, F.; Campagne, A.; Charbonnier, S.; Bonnet, S.; Vidal, A. Selection of the Most Relevant Physiological Features for Classifying Emotion. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Physiological Computing Systems, Loire Valley, France, 11–13 February 2015; pp. 17–25. [Google Scholar]
- Dzedzickis, A.; Kaklauskas, A.; Bucinskas, V. Human Emotion Recognition: Review of Sensors and Methods. Sensors 2020, 20, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singson, L.N.B.; Sanchez, M.T.U.R.; Villaverde, J.F. Emotion Recognition Using Short-Term Analysis of Heart Rate Variability and ResNet Architecture. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Computer and Automation Engineering (ICCAE), Melbourne, Australia, 20–22 March 2021; pp. 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, G.; Long, S.; Yuan, H. Non-Contact Emotion Recognition Combining Heart Rate and Facial Expression for Interactive Gaming Environments. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 11896–11906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q.V. EfficientNet: Rethinking Model Scaling for Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; pp. 6105–6114. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, K.K.; Sudeep, K.S. Preprocessing for image classification by convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Recent Trends in Electronics, Information & Communication Technology (RTEICT), Bangalore, India, 20–21 May 2016; pp. 1778–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Jolfaei, A.; Alazab, M. A Face Emotion Recognition Method Using Convolutional Neural Network and Image Edge Computing. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 159081–159089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Yang, L.; Shi, H.; Xia, Y.; Li, F.; Liu, C. Evaluation of consistency of HRV indices change among different emotions. In Proceedings of the Chinese Automation Congress (CAC), Jinan, China, 20–22 October 2017; pp. 4783–4786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitaloka, D.A.; Wulandari, A.; Basaruddin, T.; Liliana, D.Y. Enhancing CNN with Preprocessing Stage in Automatic Emotion Recognition. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2017, 116, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Song, D.; Zhang, P.; Yu, G.; Hou, Y.; Hu, B. Emotion recognition from multi-channel EEG data through Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), Shenzhen, China, 15–18 December 2016; pp. 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaireddin, Y.; Chen, Z. Facial Emotion Recognition: State of the Art Performance on FER2013. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2105.03588. [Google Scholar]


| Emotions | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Index | Neutral | Sad | Happy | Angry | |
| SDNN | Mean ± SD | 50 ± 18 | 47 ± 16 | 55 ± 19 | 51 ± 18 |
| RMSSD | Mean ± SD | 41 ± 19 | 40 ± 18 | 43 ± 18 | 44 ± 21 |
| LF | Mean ± SD | 0.54 ± 0.17 | 0.54 ± 0.16 | 0.66 ± 0.15 | 0.53 ± 0.18 |
| HF | Mean ± SD | 0.46 ± 0.17 | 0.46 ± 0.16 | 0.34 ± 0.15 | 0.47 ± 0.18 |
| LF/HF | Mean ± SD | 1.6 ± 1.2 | 1.5 ± 1.0 | 2.9 ± 3.6 | 1.5 ± 1.1 |
| SampEn | Mean ± SD | 1.78 ± 0.25 | 1.90 ± 0.262 | 1.90 ± 0.28 | 1.97 ± 0.24 |
| Model Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Input Size | 224 × 224 |
| Learning Rate | 0.0001 |
| Epoch | 40 |
| Batch Size | 16 |
| Authors | Method | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| Liu et al. [18] | CNN Ensemble | 65.3% |
| Vulpe-Grigoraşi et al. [22] | CNN-Hyperparameter optimization | 72.16% |
| Fard et al. [19] | Ad-Corre Loss | 72.3% |
| Khaireddin et al. [42] | VGG with hyper-parameters fine-tuning | 73.28% |
| Pham et al. [24] | ResMaskingNet (ResNet with spatial attention) | 74.14% |
| Vignesh et al. [23] | U-Net segmentation layers in between (VGG) | 75.97% |
| Pham et al. [24] | ensemble of 6 convolutional neural networks | 76.82% |
| Ours without HRV | EfficientNet | 74% |
| Ours with HRV | EfficientNet | 88.2% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khomidov, M.; Lee, J.-H. The Novel EfficientNet Architecture-Based System and Algorithm to Predict Complex Human Emotions. Algorithms 2024, 17, 285. https://doi.org/10.3390/a17070285
Khomidov M, Lee J-H. The Novel EfficientNet Architecture-Based System and Algorithm to Predict Complex Human Emotions. Algorithms. 2024; 17(7):285. https://doi.org/10.3390/a17070285
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhomidov, Mavlonbek, and Jong-Ha Lee. 2024. "The Novel EfficientNet Architecture-Based System and Algorithm to Predict Complex Human Emotions" Algorithms 17, no. 7: 285. https://doi.org/10.3390/a17070285
APA StyleKhomidov, M., & Lee, J.-H. (2024). The Novel EfficientNet Architecture-Based System and Algorithm to Predict Complex Human Emotions. Algorithms, 17(7), 285. https://doi.org/10.3390/a17070285







