Transfer Learning Approach for Human Activity Recognition Based on Continuous Wavelet Transform
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A novel deep-learning model pre-trained on CWT-generated scalograms was proposed, which is targeted specifically for sensor-based HAR classification problems. The suggested model outperformed the majority of state-of-the-art studies where the KU-HAR dataset was employed;
- It was experimentally established that the usage of the proposed pre-trained model, especially with layer freezing, results in a more stable gradient descent, faster training, and improved performance on small datasets;
- The impact of different CWT configurations on the performance of well-known neural network architectures was analyzed, which resulted in 60 combinations and over 300 models being trained and evaluated;
- The potential of the CNN/CWT-based approach for addressing wearable sensor-based HAR classification problems was demonstrated, and the directions for future works employing the scalogram-based pre-training technique were proposed.
2. Related Works
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Employed Datasets
3.1.1. KU-HAR Dataset
3.1.2. UCI-HAPT Dataset
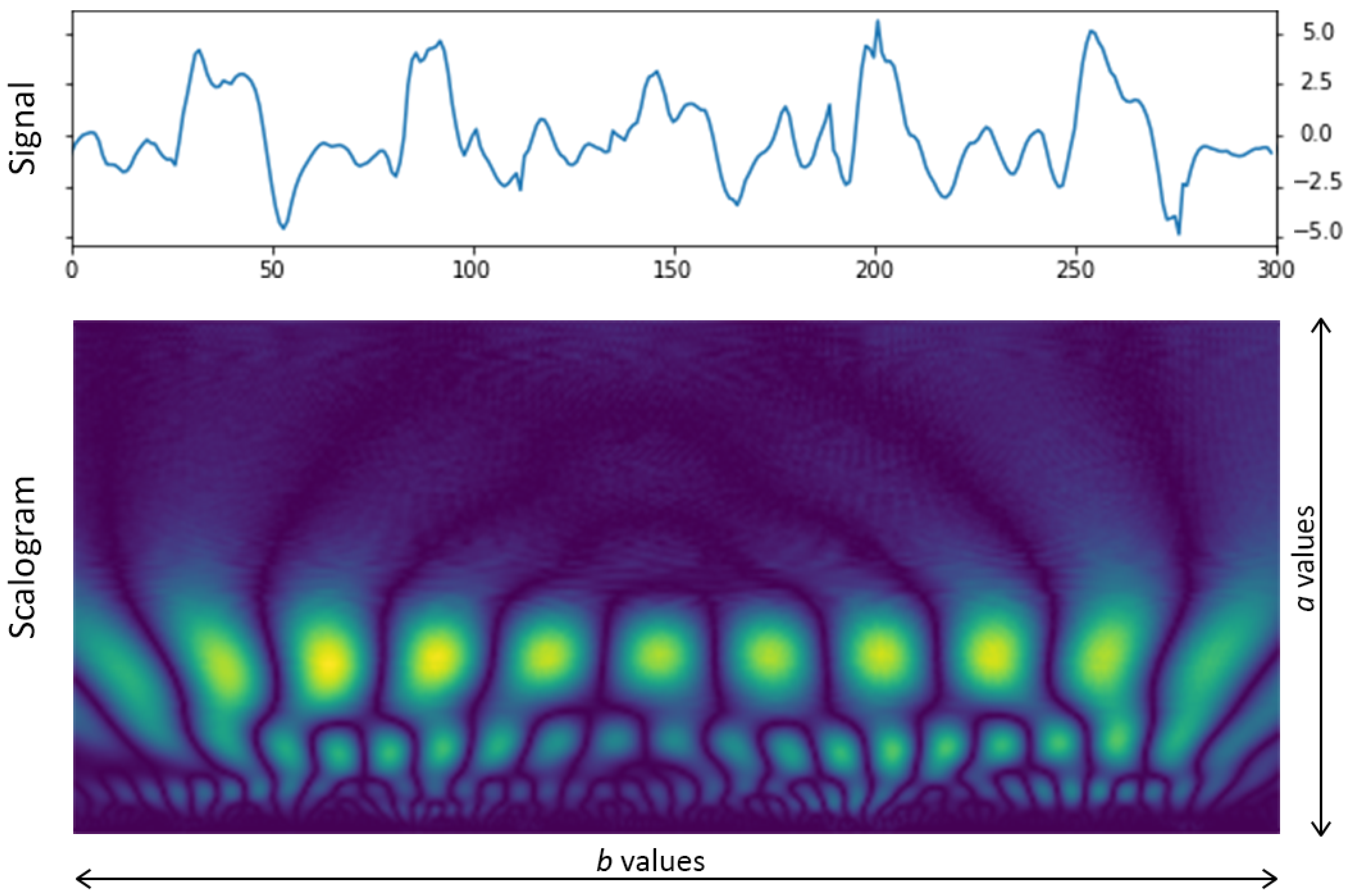
3.2. Scalogram Generation
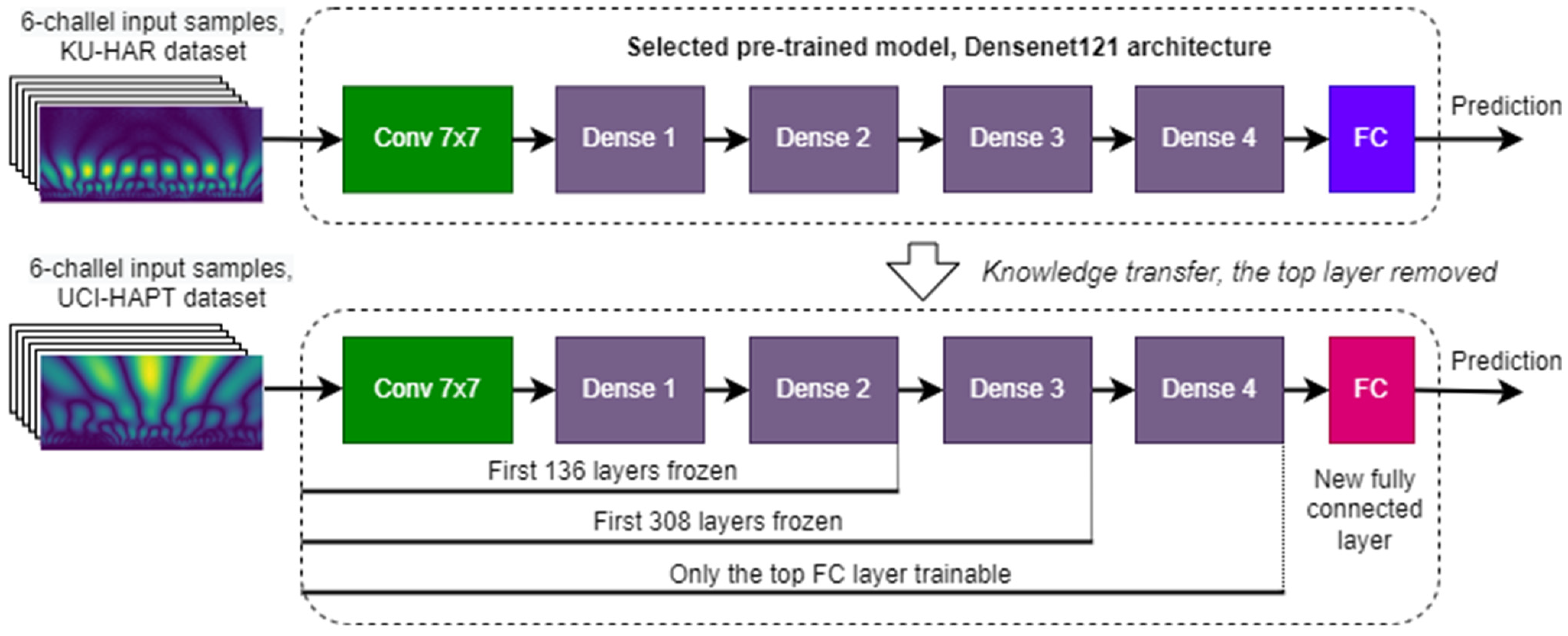
3.3. Knowledge Transfer and Model Testing
4. Results
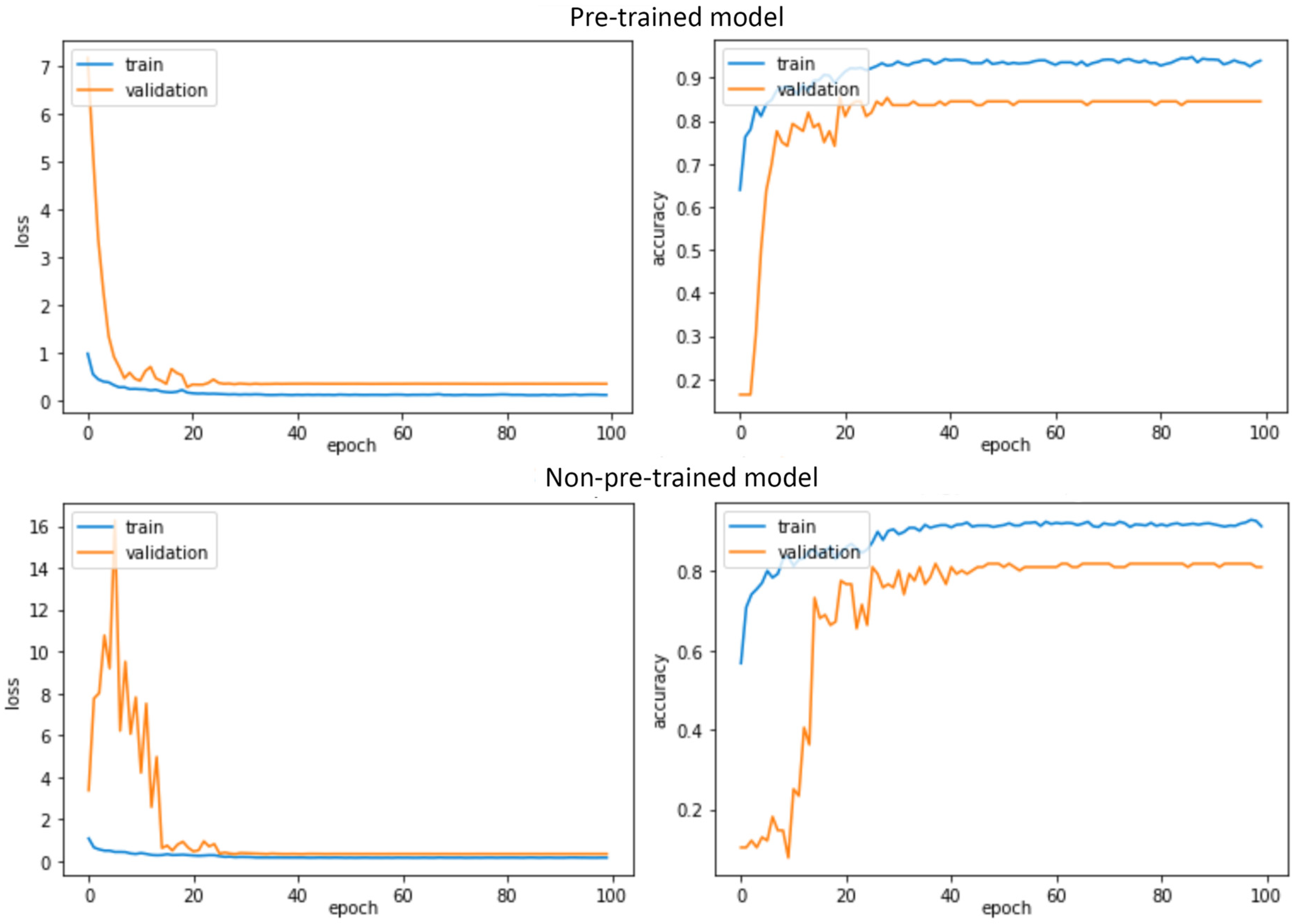
4.1. Model Selection Results
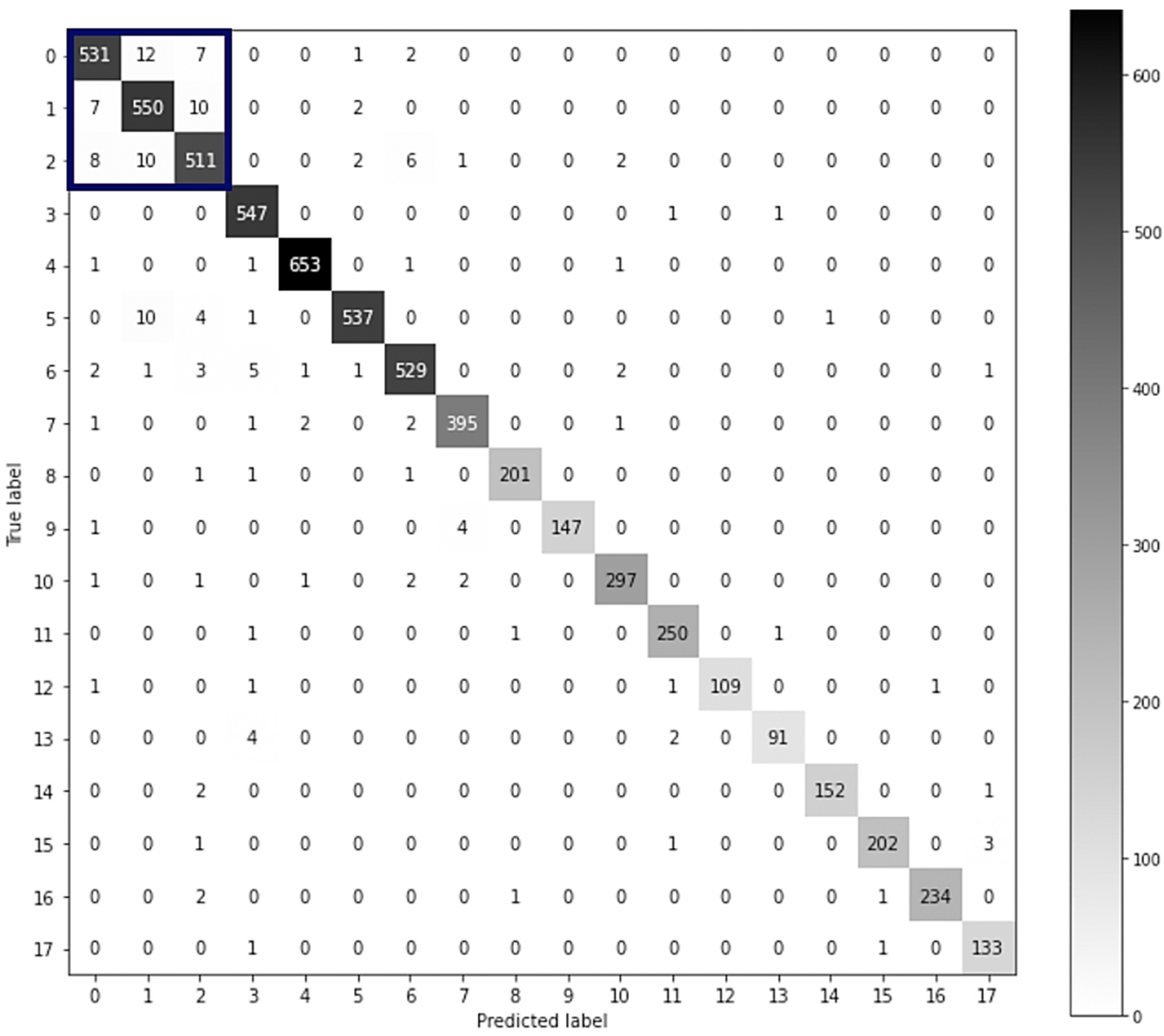
4.2. Model Testing Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Subasi, A.; Radhwan, M.; Kurdi, R.; Khateeb, K. IoT Based Mobile Healthcare System for Human Activity Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2018 15th Learning and Technology Conference (L&T), Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, 25–26 February 2018; pp. 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.-Y.; Harniss, M.; Patel, S.; Johnson, K. Implementing Technology-Based Embedded Assessment in the Home and Community Life of Individuals Aging with Disabilities: A Participatory Research and Development Study. Disabil. Rehabil. Assist. Technol. 2014, 9, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulsoom, F.; Narejo, S.; Mehmood, Z.; Chaudhry, H.N.; Butt, A.; Bashir, A.K. A Review of Machine Learning-Based Human Activity Recognition for Diverse Applications. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 18289–18324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Hoey, J.; Nugent, C.D.; Cook, D.J.; Yu, Z. Sensor-Based Activity Recognition. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part C 2012, 42, 790–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh Dang, L.; Min, K.; Wang, H.; Piran, M.J.; Lee, C.H.; Moon, H. Sensor-Based and Vision-Based Human Activity Recognition: A Comprehensive Survey. Pattern Recognit. 2020, 108, 107561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, D.; Ryoo, H.-Y.; Shin, B.-S. Sustainable Wearables: Wearable Technology for Enhancing the Quality of Human Life. Sustainability 2016, 8, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, A.; Javed, O.; Shah, M. Object Tracking: A Survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2006, 38, 13-es. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plötz, T.; Hammerla, N.Y.; Olivier, P. Feature Learning for Activity Recognition in Ubiquitous Computing. In Proceedings of the IJCAI 2011-22nd International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain, 16–22 July 2011; pp. 1729–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Shirahama, K.; Nisar, M.A.; Köping, L.; Grzegorzek, M. Comparison of Feature Learning Methods for Human Activity Recognition Using Wearable Sensors. Sensors 2018, 18, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoaib, M.; Bosch, S.; Incel, O.D.; Scholten, H.; Havinga, P.J.M. A Survey of Online Activity Recognition Using Mobile Phones. Sensors 2015, 15, 2059–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, M.H.; Nahid, A.-A.; Islam, M.R.; Parvez Mahmud, M.A. Human Activity Recognition Based on Wavelet-Based Features along with Feature Prioritization. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 6th International Conference on Computing, Communication and Automation (ICCCA), Arad, Romania, 17–19 December 2021; pp. 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Ortiz, J.-L.; Oneto, L.; Ghio, A.; Samá, A.; Anguita, D.; Parra, X. Human activity recognition on smartphones with awareness of basic activities and postural transitions. In Proceedings of the Artificial Neural Networks and Machine Learning–ICANN 2014, Hamburg, Germany, 15–19 September 2014; pp. 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.-L.; Lin, S.-L.; Chou, P.-H.; Lai, H.-C.; Chang, H.-C.; Yang, S.-C. Application of Nonparametric Weighted Feature Extraction for an Inertial-Signal-Based Human Activity Recognition System. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Applied System Innovation (ICASI), Sapporo, Japan, 13–17 May 2017; pp. 1718–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nematallah, H.; Rajan, S.; Cretu, A.-M. Logistic Model Tree for Human Activity Recognition Using Smartphone-Based Inertial Sensors. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE SENSORS, Montreal, QC, Canada, 27–30 October 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Dasgupta, S.; Ramirez, E.E.; Peterson, C.; Norman, G.J. Classification Accuracies of Physical Activities Using Smartphone Motion Sensors. J. Med. Internet Res. 2012, 14, e130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Wang, Z.; Kuen, J.; Ma, L.; Shahroudy, A.; Shuai, B.; Liu, T.; Wang, X.; Wang, G.; Cai, J.; et al. Recent Advances in Convolutional Neural Networks. Pattern Recognit. 2018, 77, 354–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya Rueda, F.; Grzeszick, R.; Fink, G.A.; Feldhorst, S.; ten Hompel, M. Convolutional Neural Networks for Human Activity Recognition Using Body-Worn Sensors. Informatics 2018, 5, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demrozi, F.; Pravadelli, G.; Bihorac, A.; Rashidi, P. Human Activity Recognition Using Inertial, Physiological and Environmental Sensors: A Comprehensive Survey. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 210816–210836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sikder, N.; Ahad, M.A.R.; Nahid, A.-A. Human Action Recognition Based on a Sequential Deep Learning Model. In Proceedings of the 2021 Joint 10th International Conference on Informatics, Electronics & Vision (ICIEV) and 2021 5th International Conference on Imaging, Vision & Pattern Recognition (icIVPR), Kitakyushu, Japan, 16–20 August 2021; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, T.; Sazzad Sayyed, A.Q.M.; Fattah, S.A.; Kung, S.-Y. A Novel Multi-Stage Training Approach for Human Activity Recognition from Multimodal Wearable Sensor Data Using Deep Neural Network. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 1715–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shorten, C.; Khoshgoftaar, T.M. A Survey on Image Data Augmentation for Deep Learning. J. Big Data 2019, 6, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, R.; Berangi, R.; Minaei, B. A Survey of Regularization Strategies for Deep Models. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2020, 53, 3947–3986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribani, R.; Marengoni, M. A Survey of Transfer Learning for Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 32nd SIBGRAPI Conference on Graphics, Patterns and Images Tutorials (SIBGRAPI-T), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 28–31 October 2019; pp. 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Girshick, R.; Dollar, P. Rethinking ImageNet Pre-Training. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 4917–4926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windrim, L.; Melkumyan, A.; Murphy, R.J.; Chlingaryan, A.; Ramakrishnan, R. Pretraining for Hyperspectral Convolutional Neural Network Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 2798–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Yishui, S.; Wei, C. Up and down Buses Activity Recognition Using Smartphone Accelerometer. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Information Technology, Networking, Electronic and Automation Control Conference, Chongqing, China, 20–22 May 2016; pp. 761–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandong, A.-M.; Munir, U. Smartphone Based Activity Recognition Using K-Nearest Neighbor Algorithm. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Engineering Technologies, Bangkok, Thailand, 22–23 November 2018; pp. 37–40. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Zhao, X.; Li, Z. A Comprehensive Study of Smartphone-Based Indoor Activity Recognition via Xgboost. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 80027–80042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusain, K.; Gupta, A.; Popli, B. Transition-Aware Human Activity Recognition Using EXtreme Gradient Boosted Decision Trees. In Proceedings of the Advanced Computing and Communication Technologies, Panipat, India, 17–18 February 2018; pp. 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Habre, R.; Deng, H.; Urman, R.; Morrison, J.; Gilliland, F.D.; Ambite, J.L.; Stripelis, D.; Chiang, Y.-Y.; Lin, Y.; et al. Applying Multivariate Segmentation Methods to Human Activity Recognition From Wearable Sensors’ Data. JMIR mHealth uHealth 2019, 7, e11201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayat, A.; Pomplun, M.; Tran, D.A. A Study on Human Activity Recognition Using Accelerometer Data from Smartphones. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2014, 34, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rustam, F.; Reshi, A.A.; Ashraf, I.; Mehmood, A.; Ullah, S.; Khan, D.M.; Choi, G.S. Sensor-Based Human Activity Recognition Using Deep Stacked Multilayered Perceptron Model. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 218898–218910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Suresh, S. Deep Learning Models for Recognizing the Simple Human Activities Using Smartphone Accelerometer Sensor. IETE J. Res. 2021, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Chai, D.; He, J.; Zhang, X.; Duan, S. InnoHAR: A Deep Neural Network for Complex Human Activity Recognition. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 9893–9902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronald, M.; Poulose, A.; Han, D.S. ISPLInception: An Inception-ResNet Deep Learning Architecture for Human Activity Recognition. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 68985–69001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, L. Human Activity Recognition Based on Residual Network and BiLSTM. Sensors 2022, 22, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luwe, Y.J.; Lee, C.P.; Lim, K.M. Wearable Sensor-Based Human Activity Recognition with Hybrid Deep Learning Model. Informatics 2022, 9, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.U.; Afzal, S.; Lee, J.W. Human Activity Recognition via Hybrid Deep Learning Based Model. Sensors 2022, 22, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, A.; Morgado-Dias, F.; Bhuyan, B.P.; Tomar, R. Human Activity Recognition for Elderly People Using Machine and Deep Learning Approaches. Information 2022, 13, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimani, E.; Nazerfard, E. Cross-Subject Transfer Learning in Human Activity Recognition Systems Using Generative Adversarial Networks. Neurocomputing 2021, 426, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Suresh, S. DeepTransHHAR: Inter-Subjects Heterogeneous Activity Recognition Approach in the Non-Identical Environment Using Wearable Sensors. Natl. Acad. Sci. Lett. 2022, 45, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Huang, M.; Yu, H. Cross-Position Activity Recognition with Stratified Transfer Learning. Pervasive Mob. Comput. 2019, 57, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, Y.; Tang, C.I.; Min, C.; Kawsar, F.; Mathur, A. ColloSSL: Collaborative Self-Supervised Learning for Human Activity Recognition. Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 2022, 6, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, A.; Ozcelebi, T.; Lukkien, J. Multi-Task Self-Supervised Learning for Human Activity Detection. Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 2019, 3, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russakovsky, O.; Deng, J.; Su, H.; Krause, J.; Satheesh, S.; Ma, S.; Huang, Z.; Karpathy, A.; Khosla, A.; Bernstein, M.; et al. ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2015, 115, 211–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ieracitano, C.; Mammone, N.; Hussain, A.; Morabito, F.C. A Novel Multi-Modal Machine Learning Based Approach for Automatic Classification of EEG Recordings in Dementia. Neural Netw. 2020, 123, 176–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadhav, P.; Mukhopadhyay, S. Automated Sleep Stage Scoring Using Time-Frequency Spectra Convolution Neural Network. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, F.S.; la Blunda, L.; Wagner, M.F.; Schäfer, J.; Medina-Bulo, I.; Gómez-Ullate, D. Fall Detection from Electrocardiogram (ECG) Signals and Classification by Deep Transfer Learning. Information 2021, 12, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalal, L.; Peer, A. Emotion Recognition from Physiological Signals Using Continuous Wavelet Transform and Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the HCI International 2022-Late Breaking Papers. Multimodality in Advanced Interaction Environments, Virtual Event, 26 June–1 July 2022; pp. 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, G.Q.; Al-Libawy, H. Time-Series Deep-Learning Classifier for Human Activity Recognition Based On Smartphone Built-in Sensors. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1973, 012127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izonin, I.; Tkachenko, R.; Holoven, R.; Shavarskyi, M.; Bukin, S.; Shevchuk, I. Multistage SVR-RBF-Based Model for Heart Rate Prediction of Individuals. In Proceedings of the International Conference of Artificial Intelligence, Medical Engineering, Wuhan, China, 19–21 August 2022; pp. 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Hossain, S.K.S.; Sarkar, R. Human Activity Recognition from Sensor Data Using Spatial Attention-Aided CNN with Genetic Algorithm. Available online: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-022-07911-0 (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Alzubaidi, L.; Zhang, J.; Humaidi, A.J.; Al-Dujaili, A.; Duan, Y.; Al-Shamma, O.; Santamaría, J.; Fadhel, M.A.; Al-Amidie, M.; Farhan, L. Review of Deep Learning: Concepts, CNN Architectures, Challenges, Applications, Future Directions. J. Big Data 2021, 8, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikder, N.; Nahid, A.-A. KU-HAR: An Open Dataset for Heterogeneous Human Activity Recognition. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2021, 146, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahid, A.-A.; Sikder, N.; Rafi, I. KU-HAR: An Open Dataset for Human Activity Recognition. Mendeley Data 2021. Available online: https://data.mendeley.com/datasets/45f952y38r/5 (accessed on 28 December 2022). [CrossRef]
- Jorge, L.; Ortiz, R.; Oneto, L.; SamÃ, A.; Parra, X.; Anguita, D. Smartphone-Based Recognition of Human Activities and Postural Transitions Data Set. Available online: http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/smartphone-based+recognition+of+human+activities+and+postural+transitions (accessed on 28 December 2022).
- Anguita, D.; Ghio, A.; Oneto, L.; Parra, X.; Reyes-Ortiz, J.L. A Public Domain Dataset for Human Activity Recognition Using Smartphones. In Proceedings of the 21th European Symposium on Artificial Neural Networks, Computational Intelligence and Machine Learning, Bruges, Belgium, 24–26 April 2013; pp. 437–442. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Weinberger, K.Q.; van der Maaten, L. Densely Connected Convolutional Networks. arXiv 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, J.; Mahmud, M.; Modasshir, M.; Shamim Kaiser, M. 3D DenseNet Ensemble in 4-Way Classification of Alzheimer’s Disease. In Proceedings of the Brain Informatics: 13th International Conference, BI 2020, Padua, Italy, 19 September 2020; pp. 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhu, H.; Chen, C.; Gao, M.; Xu, K.; Xu, J. Holistic Brain Tumor Screening and Classification Based on DenseNet and Recurrent Neural Network. In Proceedings of the Brainlesion: Glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries, Granada, Spain, 16 September 2018; pp. 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshni, D.; Thakral, K.; Agarwal, L.; Nijhawan, R.; Mittal, A. Pneumonia Detection Using CNN Based Feature Extraction. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Electrical, Computer and Communication Technologies (ICECCT), Coimbatore, India, 20–22 February 2019; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, H. Interstitial Lung Disease Classification Using Improved DenseNet. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2019, 78, 30615–30626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riasatian, A.; Babaie, M.; Maleki, D.; Kalra, S.; Valipour, M.; Hemati, S.; Zaveri, M.; Safarpoor, A.; Shafiei, S.; Afshari, M.; et al. Fine-Tuning and Training of Densenet for Histopathology Image Representation Using TCGA Diagnostic Slides. Med. Image Anal. 2021, 70, 102032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imran, H.A.; Latif, U. HHARNet: Taking Inspiration from Inception and Dense Networks for Human Activity Recognition Using Inertial Sensors. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 17th International Conference on Smart Communities: Improving Quality of Life Using ICT, IoT and AI (HONET), Charlotte, NC, USA, 14–16 December 2020; pp. 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irawan, A.; Putra, A.M.; Ramadhan, H. A DenseNet Model for Joint Activity Recognition and Indoor Localization. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Industry 4.0, Artificial Intelligence, and Communications Technology (IAICT), Bali, Indonesia, 28–30 July 2022; pp. 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, M.H.; Nahid, A.-A. Two Unorthodox Aspects in Handcrafted-Feature Extraction for Human Activity Recognition Datasets. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Electronics, Communications and Information Technology (ICECIT), Khulna, Bangladesh, 14–16 September 2021; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Mother Wavelet | Mex. Hat 32 | Mex. Hat 64 | Mex. Hat 128 | Mex. Hat 256 | Morlet 32 | Morlet 64 | Morlet 128 | Morlet 256 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scale Value | ||||||||
| ResNet50 | 96.21 | 95.79 | 96.06 | 96.27 | 94.06 | 95.47 | 96.15 | 96.71 |
| ResNet101 | 95.84 | 96.13 | 96.32 | 96.31 | 94.46 | 95.79 | 96.15 | 96.90 |
| ResNet152 | 95.78 | 96.11 | 96.45 | 96.63 | 92.77 | 95.18 | 96.24 | 96.63 |
| Xception | - | - | 97.33 | 97.29 | - | - | 96.93 | 97.16 |
| InceptionV3 | - | - | 95.81 | 95.49 | - | - | 96.34 | 96.40 |
| InceptionResNetV2 | - | - | 95.81 | 95.58 | - | - | 96.48 | 96.32 |
| DenseNet121 | 97.27 | 96.96 | 97.11 | 97.24 | 95.81 | 96.82 | 96.87 | 97.48 |
| DenseNet169 | 97.16 | 96.95 | 97.04 | 97.03 | 95.52 | 96.68 | 96.84 | 97.41 |
| DenseNet201 | 97.03 | 96.77 | 97.00 | 96.85 | 95.66 | 96.85 | 96.85 | 97.24 |
| Accuracy (%) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | AUC (%) | F1-Score (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 97.48 | 97.62 | 97.41 | 99.60 | 97.52 |
| Model | UCI-HAPT | UCI-HAPT Subset | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy (%) | F1-Score (%) | Accuracy (%) | F1-Score (%) | |
| Not pre-trained DenseNet121 | 92.23 | 92.19 | 86.29 | 86.38 |
| Pre-trained DenseNet121, only top layer trainable | 80.00 | 77.99 | 75.60 | 64.08 |
| Pre-trained DenseNet121, first 308 layers frozen | 92.44 | 92.52 | 86.90 | 87.11 |
| Pre-trained DenseNet121, first 136 layers frozen | 92.23 | 92.24 | 89.11 | 89.27 |
| Pre-trained DenseNet121, all layers trainable | 91.89 | 91.92 | 88.31 | 88.26 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pavliuk, O.; Mishchuk, M.; Strauss, C. Transfer Learning Approach for Human Activity Recognition Based on Continuous Wavelet Transform. Algorithms 2023, 16, 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/a16020077
Pavliuk O, Mishchuk M, Strauss C. Transfer Learning Approach for Human Activity Recognition Based on Continuous Wavelet Transform. Algorithms. 2023; 16(2):77. https://doi.org/10.3390/a16020077
Chicago/Turabian StylePavliuk, Olena, Myroslav Mishchuk, and Christine Strauss. 2023. "Transfer Learning Approach for Human Activity Recognition Based on Continuous Wavelet Transform" Algorithms 16, no. 2: 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/a16020077
APA StylePavliuk, O., Mishchuk, M., & Strauss, C. (2023). Transfer Learning Approach for Human Activity Recognition Based on Continuous Wavelet Transform. Algorithms, 16(2), 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/a16020077







