An Improved Greedy Heuristic for the Minimum Positive Influence Dominating Set Problem in Social Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Problem Background and Motivation
1.2. Problem Description and Existing Work
1.3. Motivation and Contribution
1.4. Structure of the Paper
2. The Minimum Positive Influence Dominating Set Problem
3. Greedy Heuristics
| Algorithm 1 MPIDS_Greedy() |
| Input: a simple, connected undirected graph |
| Output: a positive influence dominating set S |
| 1: |
| 2: while (S is not a valid PIDS solution) do |
| 3: argmax{greedy_function} |
| 4: |
| 5: end while |
| 6: return S |
| Algorithm 2 Pan’s greedy algorithm [17] |
| Input: a simple, connected undirected graph |
| Output: a positive influence dominating set S |
| 1: Rename the vertices from V such that are the vertices in ascending order of the degree |
| 2: |
| 3: |
| 4: for to n do |
| 5: if : is an uncovered vertex then |
| 6: |
| 7: for to do |
| 8: argmax |
| 9: |
| 10: |
| 11: end for |
| 12: end if |
| 13: end for |
| 14: return S |
4. The Proposed Algorithm
4.1. The Greedy Procedure
| Algorithm 3 IGA-PIDS: Improved greedy algorithm for the MPIDS problem |
| Input: a simple, connected undirected graph |
| Output: a positive influence dominating set S |
| 1: GraphPruning(G) |
| 2: set of all so-far uncovered vertices |
| 3: Rename the vertices from C such that are the vertices in ascending order of the degree |
| 4: |
| 5: while S is not a valid PIDS solution do |
| 6: Let be an un-covered vertex with the smallest sub-index in C |
| 7: |
| 8: for to do |
| 9: |
| 10: |
| 11: |
| 12: |
| 13: end for |
| 14: |
| 15: end while |
| 16: Reduce(S) |
| 17: return S |
| Algorithm 4 Function GraphPruning(G) |
| Input: a simple, connected undirected graph |
| Output: a partial solution S |
| 1: |
| 2: for each pendant vertex do |
| 3: Let u be the unique neighbor of v |
| 4: if then |
| 5: |
| 6: end if |
| 7: if and then |
| 8: Let be the second neighbor of u |
| 9: if then |
| 10: |
| 11: end if |
| 12: end if |
| 13: end for |
| 14: return S |
4.2. Removing Redundant Vertices
| Algorithm 5 Function Reduce(S) |
| Input: a valid solution S that may contain redundant vertices |
| Output: a valid solution S without redundant vertices |
| 1: for each vertex do |
| 2: if for all then |
| 3: |
| 4: for all do |
| 5: |
| 6: end for |
| 7 end if |
| 8: end for |
| 9: return S |
4.3. Complexity
5. Experimental Evaluation
5.1. Computational Setting
5.2. Problem Instances
- Small social networks: this class of instances contains four well-known real and synthetic networks namely American College Football (Football) [25], Zachary’s Karate Club (Karate) [26], the Dolphins Network (Dolphins) [27] and the Jazz Network (Jazz) [28]. Characteristics such as the number of vertices and the number of edges of these networks are provided in Table 2. The values of the optimal solutions for each instance (except for the last one) were taken from [20] in which the authors also made use of CPLEX.
- SNAP social networks: this class of instances contains 22 real complex networks with sizes ranging from vertices to . It was download from the Stanford Large Network Dataset Collection [30]. All these instances were originally directed graphs and they are transformed to undirected graphs by neglecting arc orientations and considering parallel edges as one edge. Table 4 gives a brief description of the SNAP networks used in our experiments after preprocessing.
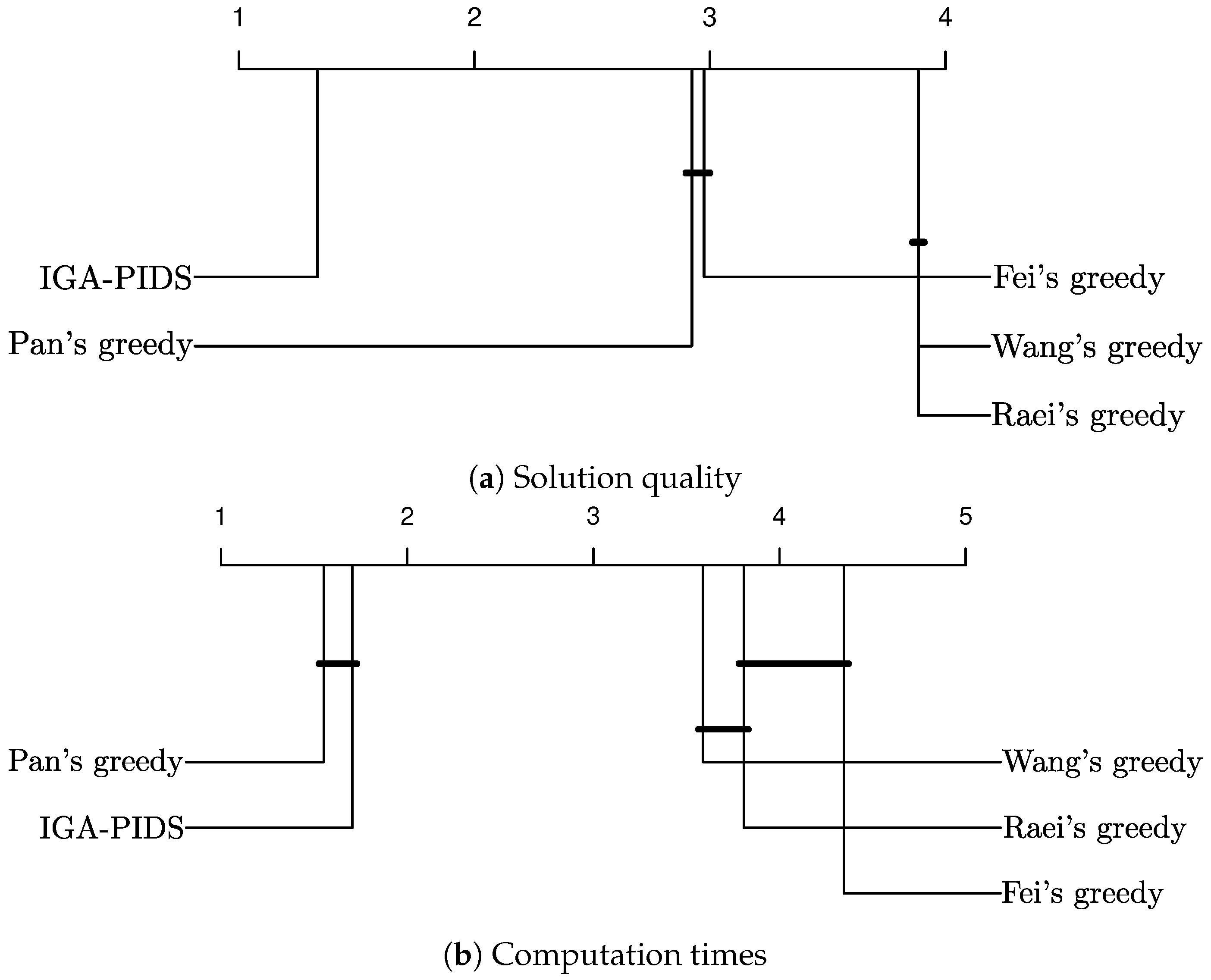
5.3. Results and Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cai, S.; Hou, W.; Wang, Y.; Luo, C.; Lin, Q. Two-goal Local Search and Inference Rules for Minimum Dominating Set. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Ninth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, IJCAI-20, Yokohama, Japan, 11–17 July 2020; pp. 1467–1473. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Potru, R.; Shahrokhi, F. A Performance Study of Some Approximation Algorithms for Computing a Small Dominating Set in a Graph. Algorithms 2020, 13, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Hu, S.; Liu, H.; Li, R.; Ouyang, D.; Yin, M. Multi-Start Local Search Algorithm for the Minimum Connected Dominating Set Problems. Mathematics 2019, 7, 1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Li, C.; Gao, X.; Yin, M.; Wang, Y. A novel hybrid algorithm for minimum total dominating set problem. Mathematics 2019, 7, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Lv, S.; Lai, Y.; Wang, J. Improved Memetic Algorithm for Solving the Minimum Weight Vertex Independent Dominating Set. Mathematics 2020, 8, 1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Camacho, E.; Xu, K. Positive influence dominating set in online social networks. In International Conference on Combinatorial Optimization and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 313–321. [Google Scholar]
- Tankovska, H. Global Social Networks Ranked by Number of Users 2021. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/272014/global-social-networks-ranked-by-number-of-users/ (accessed on 22 February 2021).
- Fournier, A.K.; Hall, E.; Ricke, P.; Storey, B. Alcohol and the social network: Online social networking sites and college students’ perceived drinking norms. Psychol. Pop. Media Cult. 2013, 2, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, C.; Wong, R.C.W. Minimizing seed set for viral marketing. In Proceedings of the 2011 11th IEEE International Conference on Data Mining, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 11–14 December 2011; pp. 427–436. [Google Scholar]
- Günneç, D.; Raghavan, S.; Zhang, R. Least-cost influence maximization on social networks. Informs J. Comput. 2020, 32, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G. Domination Problems in Social Networks. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Southern Queensland, Queensland, Australia, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Rad, A.A.; Benyoucef, M. Towards detecting influential users in social networks. In E-Technologies: Transformation in a Connected World; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 227–240. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Du, H.; Camacho, E.; Xu, K.; Lee, W.; Shi, Y.; Shan, S. On positive influence dominating sets in social networks. Theor. Comput. Sci. 2011, 412, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungnickel, D. Graphs, Networks and Algorithms; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Raei, H.; Yazdani, N.; Asadpour, M. A new algorithm for positive influence dominating set in social networks. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Advances in Social Networks Analysis and Mining, Istanbul, Turkey, 26–29 August 2012; pp. 253–257. [Google Scholar]
- Fei, M.; Weidong, C. An improved algorithm for finding minimum positive influence dominating sets in social networks. J. South China Norm. Univ. 2016, 48, 59–63. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, J.; Bu, T.M. A Fast Greedy Algorithm for Finding Minimum Positive Influence Dominating Sets in Social Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE INFOCOM 2019-IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops (INFOCOM WKSHPS), Paris, France, 29 April–2 May 2019; pp. 360–364. [Google Scholar]
- Blum, C.; Roli, A. Metaheuristics in combinatorial optimization: Overview and conceptual comparison. ACM Comput. Surv. 2003, 35, 268–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, K.; Salleh, M.N.M.; Cheng, S.; Shi, Y. Metaheuristic research: A comprehensive survey. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2019, 52, 2191–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Guan, J.; Feng, H. An ILP based memetic algorithm for finding minimum positive influence dominating sets in social networks. Phys. Stat. Mech. Appl. 2018, 500, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feo, T.A.; Resende, M.G. Greedy randomized adaptive search procedures. J. Glob. Optim. 1995, 6, 109–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Luo, J.; Xu, H.; Xu, M. A Hybrid Swarm Intelligence-Based Algorithm for Finding Minimum Positive Influence Dominating Sets. In The International Conference on Natural Computation, Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 506–511. [Google Scholar]
- Bouamama, S.; Blum, C. A hybrid algorithmic model for the minimum weight dominating set problem. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 2016, 64, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggs, N.; Lloyd, E.K.; Wilson, R.J. Graph Theory, 1736–1936; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Girvan, M.; Newman, M.E. Community structure in social and biological networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 7821–7826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachary, W.W. An information flow model for conflict and fission in small groups. J. Anthropol. Res. 1977, 33, 452–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusseau, D.; Schneider, K.; Boisseau, O.J.; Haase, P.; Slooten, E.; Dawson, S.M. The bottlenose dolphin community of Doubtful Sound features a large proportion of long-lasting associations. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2003, 54, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleiser, P.M.; Danon, L. Community structure in jazz. Adv. Complex Syst. 2003, 6, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, R.A.; Ahmed, N.K. The Network Data Repository with Interactive Graph Analytics and Visualization. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Ninth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Austin, TX, USA, 25–30 January 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Leskovec, J.; Krevl, A. SNAP Datasets: Stanford Large Network Dataset Collection. 2014. Available online: https://snap.stanford.edu/data/ (accessed on 26 February 2021).
- Calvo, B.; Santafé, G. scmamp: Statistical Comparison of Multiple Algorithms in Multiple Problems. R. J. 2016, 8, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, S.; Herrera, F. An Extension on “Statistical Comparisons of Classifiers over Multiple Data Sets” for all Pairwise Comparisons. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2008, 9, 2677–2694. [Google Scholar]

| Algorithm Name | Algorithm Type | Greedy Function | Complexity | Year | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wang’s algorithm | Greedy | cover-degree | 2011 | [13] | |
| Raei’s algorithm | Greedy | need-degree | 2012 | [15] | |
| Fei’s algorithm | Greedy | both | - | 2016 | [16] |
| Pan’s algorithm | Greedy | cover-degree | 2019 | [17] | |
| ILPMA | A hybrid metaheuristic (GA + TS) | cover-degree | - | 2018 | [20] |
| HSIA | A hybrid metaheuristic (GA + PSO) | cover-degree | - | 2019 | [22] |
| Network | n | m | Opt [20] | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Karate | 34 | 78 | 15 | Social network of friendships in a Karate club |
| Dolphins | 62 | 159 | 30 | Dolphin social network |
| Football | 115 | 613 | 63 | Network of American college football teams |
| Jazz | 198 | 2742 | - | Collaboration network between Jazz Musicians |
| Network | n | m | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| CA-GrQc | 5241 | 14,484 | Collaboration network of Arxiv General Relativity |
| CA-HepTh | 9875 | 25,973 | Collaboration network of Arxiv High Energy Physics Theory |
| CA-HepPh | 12,006 | 118,489 | Collaboration network of Arxiv High Energy Physics |
| CA-AstroPh | 18,771 | 198,050 | Collaboration network of Arxiv Astro Physics |
| CA-CondMat | 23,133 | 93,439 | Collaboration network of Arxiv Condensed Matter |
| Email-Enron | 36,692 | 183,831 | Email communication network from Enron |
| ncsrrlwg2 | 6396 | 15,872 | Collaboration network between by scientists |
| actors-data | 10,042 | 145,682 | Collaboration network between by actors |
| ego-facebook | 4039 | 88,234 | Social circles from Facebook |
| socfb-nips-ego | 2888 | 2981 | Social friendship network extracted from Facebook |
| socfb-Mich67 | 3748 | 81,903 | Social friendship network extracted from Facebook |
| socfb-Brandeis99 | 3898 | 137,567 | Social friendship network extracted from Facebook |
| soc-gplus | 23,628 | 39,194 | Social network extracted from Google+ |
| Network | n | m | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| amazon0302 | 262,111 | 899,792 | Amazon product co-purchasing network from 2 March 2003 |
| amazon0312 | 400,727 | 2,349,869 | Amazon product co-purchasing network from 12 March 2003 |
| amazon0505 | 410,236 | 2,439,437 | Amazon product co-purchasing network from 5 May 2003 |
| amazon0601 | 403,394 | 2,443,408 | Amazon product co-purchasing network from 1 June 2003 |
| cit-HepPh | 34,546 | 420,877 | Arxiv High Energy Physics paper citation network |
| cit-HepTh | 2777 | 352,285 | Arxiv High Energy Physics paper citation |
| email-EuAll | 265,214 | 364,481 | Email network from a EU research institution |
| p2p-Gnutella04 | 10,876 | 39,994 | Gnutella peer to peer network from 4 August 2002 |
| p2p-Gnutella24 | 26,518 | 65,369 | Gnutella peer to peer network from 24 August 2002 |
| p2p-Gnutella25 | 22,687 | 54,705 | Gnutella peer to peer network from 25 August 2002 |
| p2p-Gnutella30 | 36,682 | 88,328 | Gnutella peer to peer network from 30 August 2002 |
| p2p-Gnutella31 | 62,586 | 147,892 | Gnutella peer to peer network from 31 August 2002 |
| soc-Slashdot0811 | 7736 | 469,180 | Slashdot social network from November 2008 |
| soc-Slashdot0922 | 82,168 | 504,230 | Slashdot social network from February 2009 |
| soc-Epinions1 | 75,879 | 405,740 | Who-trusts-whom network of Epinions.com |
| wiki-Vote | 7115 | 100,762 | Wikipedia who-votes-on-whom network |
| web-NotreDame | 325,729 | 1,090,108 | Web graph of Notre Dame |
| web-Stanford | 281,903 | 1,992,636 | Web graph of Stanford.edu |
| wiki-Talk | 2,394,385 | 4,659,565 | Wikipedia talk (communication) network |
| web-BerkStan | 685,230 | 6,649,470 | Web graph of Berkeley and Stanford |
| web-Google | 875,713 | 4,322,051 | Web graph from Google |
| cit-Patents | 3,774,768 | 16,518,947 | Citation network among US Patents |
| Network | Wang’s Greedy | Raei’s Greedy | Fei’s Greedy | Pan’s Greedy | IGA-PIDS | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Val | Time (s) | Val | Time (s) | Val | Time (s) | Val | Time (s) | Val | Time (s) | |
| CA-GrQc | 2626 | 0.28 | 2623 | 0.30 | 2622 | 0.36 | 2612 | 0.0 | 2607 | 0.0 |
| CA-HepTh | 4598 | 0.95 | 4602 | 0.94 | 4582 | 1.17 | 4565 | 0.0 | 4544 | 0.0 |
| CA-HepPh | 4887 | 2.91 | 4886 | 2.91 | 4876 | 3.27 | 4857 | 0.015 | 4817 | 0.015 |
| CA-AstroPh | 7081 | 7.92 | 7085 | 7.91 | 7062 | 8.59 | 7030 | 0.031 | 6953 | 0.031 |
| CA-CondMat | 9869 | 7.58 | 9853 | 7.64 | 9837 | 8.11 | 9816 | 0.0 | 9748 | 0.015 |
| Email-Enron | 12,015 | 13.52 | 12,184 | 15.75 | 11,958 | 15.23 | 11,952 | 0.047 | 11,843 | 0.031 |
| ncstrlwg2 | 3034 | 0.39 | 3025 | 0.39 | 3023 | 0.44 | 3026 | 0.0 | 3010 | 0.015 |
| actors-data | 3199 | 2.33 | 3205 | 2.41 | 3187 | 2.44 | 3215 | 0.015 | 3174 | 0.016 |
| ego-facebook | 1976 | 0.75 | 1975 | 0.84 | 1975 | 0.84 | 1978 | 0.062 | 1975 | 0.078 |
| socfb-nips-ego | 1398 | 0.02 | 1398 | 0.05 | 1398 | 0.05 | 1398 | 0.0 | 1398 | 0.016 |
| socfb-Mich67 | 1481 | 0.56 | 1478 | 0.63 | 1473 | 0.55 | 1458 | 0.016 | 1427 | 0.015 |
| socfb-Brandeis99 | 1535 | 0.97 | 1539 | 1.64 | 1529 | 0.98 | 1522 | 0.031 | 1502 | 0.032 |
| soc-gplus | 8341 | 1.97 | 8247 | 2.22 | 8267 | 2.56 | 8351 | 0.031 | 8289 | 0.031 |
| Karate | 31 | 0.0 | 31 | 0.0 | 30 | 0.0 | 32 | 0.0 | 31 | 0.0 |
| Dolphins | 15 | 0.0 | 15 | 0.0 | 15 | 0.0 | 15 | 0.0 | 15 | 0.0 |
| Football | 68 | 0.015 | 68 | 0.0 | 69 | 0.0 | 69 | 0.0 | 68 | 0.0 |
| Jazz | 81 | 0.015 | 82 | 0.0 | 81 | 0.0 | 83 | 0.0 | 81 | 0.0 |
| Avg | 3660.88 | 2.363 | 3664.47 | 2.565 | 3646.12 | 2.623 | 3645.82 | 0.015 | 3616.59 | 0.017 |
| Network | Before | After | CPLEX | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Val | Time (s) | Val | Time (s) | Val | Gap (%) | |
| CA-GrQc | 2610 | 0.0 | 2607 | 0.0 | 2587 * | 0.77 |
| CA-HepTh | 4559 | 0.0 | 4544 | 0.0 | 4471 * | 1.63 |
| CA-HepPh | 4855 | 0.0 | 4817 | 0.015 | 4718 | 2.1 |
| CA-AstroPh | 7034 | 0.031 | 6953 | 0.031 | 6740 | 3.16 |
| CA-CondMat | 9804 | 0.015 | 9748 | 0.015 | 9584 | 1.71 |
| Email-Enron | 11,914 | 0.047 | 11,843 | 0.031 | 11,682 * | 1.38 |
| ncstrlwg2 | 3014 | 0.0 | 3010 | 0.015 | 2994 * | 0.53 |
| actors-data | 3214 | 0.015 | 3174 | 0.016 | 3092 | 2.65 |
| ego-facebook | 1977 | 0.062 | 1975 | 0.078 | 1973 * | 0.1 |
| socfb-nips-ego | 1398 | 0.015 | 1398 | 0.016 | 1398 * | 0 |
| socfb-Mich67 | 1452 | 0.0 | 1427 | 0.015 | 1329 | 7.37 |
| socfb-Brandeis99 | 1517 | 0.016 | 1502 | 0.032 | 1400 | 7.29 |
| soc-gplus | 8294 | 0.031 | 8289 | 0.031 | 8244 * | 0.55 |
| Karate | 31 | 0.0 | 31 | 0.0 | 30 * | 3.33 |
| Dolphins | 15 | 0.0 | 15 | 0.0 | 15 * | 0 |
| Football | 70 | 0.0 | 68 | 0.0 | 63 * | 7.93 |
| Jazz | 82 | 0.0 | 81 | 0.0 | 79 * | 2.53 |
| Avg | 3637.65 | 0.014 | 3616.59 | 0.017 | 3552.88 | 2.53 |
| Network | Wang’s Greedy | Raei’s Greedy | Fei’s Greedy | Pan’s Greedy | IGA-PIDS | CPLEX | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Val | Time (s) | Val | Time (s) | Val | Time (s) | Val | Time (s) | Val | Time (s) | Val | Gap (%) | |
| Amazon0302 | 136,448 | 1680.11 | 136,177 | 1565.20 | 135,502 | 1619.34 | 136,723 | 0.19 | 134,569 | 0.23 | 262,111 | −48.66 |
| Amazon0312 | 186,772 | 5862.28 | 188,194 | 5676.23 | 186,009 | 5777.75 | 183,108 | 0.56 | 180,853 | 0.67 | 400,727 | −54.87 |
| Amazon0505 | 189,392 | 6152.06 | - | - | - | - | 185,307 | 0.56 | 183,114 | 0.64 | 410,236 | −55.63 |
| Amazon0601 | 184,892 | 6833.42 | 186,126 | 6077.13 | - | - | 182,291 | 0.63 | 179,964 | 0.66 | 403,394 | −55.39 |
| Cit-HepPh | 13,340 | 47.08 | 13,394 | 39.11 | 13,316 | 37.40 | 13,340 | 0.078 | 13,111 | 0.08 | 12,350 | 6.16 |
| Cit-HepTh | 11,549 | 24.81 | 11,671 | 25.31 | 11,531 | 25.77 | 11,544 | 0.078 | 11,399 | 0.08 | 10,740 | 6.14 |
| Email-EuAll | 106,178 | 521.58 | 105,691 | 676.42 | 105,815 | 1038.92 | 106,220 | 0.89 | 105,906 | 1.25 | 105,659 * | 0.23 |
| p2p-Gnutella04 | 4310 | 1.41 | 4297 | 1.42 | 4294 | 1.68 | 4243 | 0.0 | 4170 | 0.0 | 3995 | 4.38 |
| p2p-Gnutella24 | 8812 | 6.61 | 8794 | 6.63 | 8776 | 6.84 | 8750 | 0.015 | 8665 | 0.015 | 8457 | 2.46 |
| p2p-Gnutella25 | 7682 | 4.69 | 7653 | 4.70 | 7659 | 4.86 | 7635 | 0.016 | 7555 | 0.0 | 7370 | 2.51 |
| p2p-Gnutella30 | 12,321 | 16.41 | 12,314 | 16.27 | 12,285 | 17.19 | 12,254 | 0.016 | 12,125 | 0.015 | 11,859 | 2.24 |
| p2p-Gnutella31 | 20,614 | 61.08 | 20,604 | 60.42 | 20,541 | 63.56 | 20,448 | 0.032 | 20,268 | 0.016 | 19,876 * | 1.97 |
| Slashdot0811 | 19,115 | 98.34 | 19,567 | 101.80 | 19,126 | 137.48 | 18,571 | 0.047 | 18,515 | 0.032 | 18,419 * | 0.52 |
| Slashdot0902 | 21,417 | 107.20 | 21,856 | 78.92 | 21,403 | 85.19 | 20,857 | 0.063 | 20,782 | 0.031 | 20,629 * | 0.74 |
| soc-Epinions1 | 21,227 | 52.86 | 21,494 | 88.59 | 21,241 | 82.89 | 21,015 | 0.046 | 20,986 | 0.031 | 20,960 * | 0.12 |
| Wiki-Vote | 1570 | 0.75 | 1593 | 0.77 | 1564 | 0.83 | 1506 | 0.016 | 1499 | 0.015 | 1461 * | 2.60 |
| web-NotreDame | 144,654 | 1172.89 | 144,696 | 1223.31 | 144,391 | 1366.73 | 145,564 | 0.55 | 144,385 | 0.84 | 143,742 | 0.45 |
| web-Stanford | 139,970 | 2944.28 | 140,577 | 3635.30 | 139,812 | 3405.31 | 140,630 | 114.64 | 139,346 | 139.45 | 137,175 | 1.58 |
| Wiki-Talk | - | - | - | - | - | - | 499,392 | 46.125 | 490,133 | 42.13 | 480,063 * | 2.10 |
| web-BerkStan | - | - | - | - | - | - | 339,452 | 209.27 | 337,388 | 259.81 | 335,493 | 0.56 |
| web-Google | - | - | - | - | - | - | 396,836 | 3.49 | 394,806 | 3.67 | 389,079 | 1.47 |
| cit-Patents | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1,599,417 | 6.0 | 1,576,091 | 5.73 | 3,774,768 | −57.63 |
| Avg | - | - | - | - | - | - | 184,322.86 | 17.42 | 182,074.09 | 20.70 | 317,207.41 | −42.60 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bouamama, S.; Blum, C. An Improved Greedy Heuristic for the Minimum Positive Influence Dominating Set Problem in Social Networks. Algorithms 2021, 14, 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/a14030079
Bouamama S, Blum C. An Improved Greedy Heuristic for the Minimum Positive Influence Dominating Set Problem in Social Networks. Algorithms. 2021; 14(3):79. https://doi.org/10.3390/a14030079
Chicago/Turabian StyleBouamama, Salim, and Christian Blum. 2021. "An Improved Greedy Heuristic for the Minimum Positive Influence Dominating Set Problem in Social Networks" Algorithms 14, no. 3: 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/a14030079
APA StyleBouamama, S., & Blum, C. (2021). An Improved Greedy Heuristic for the Minimum Positive Influence Dominating Set Problem in Social Networks. Algorithms, 14(3), 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/a14030079