Abstract
Current state-of-the-art medical deformable image registration (DIR) methods optimize a weighted sum of key objectives of interest. Having a pre-determined weight combination that leads to high-quality results for any instance of a specific DIR problem (i.e., a class solution) would facilitate clinical application of DIR. However, such a combination can vary widely for each instance and is currently often manually determined. A multi-objective optimization approach for DIR removes the need for manual tuning, providing a set of high-quality trade-off solutions. Here, we investigate machine learning for a multi-objective class solution, i.e., not a single weight combination, but a set thereof, that, when used on any instance of a specific DIR problem, approximates such a set of trade-off solutions. To this end, we employed a multi-objective evolutionary algorithm to learn sets of weight combinations for three breast DIR problems of increasing difficulty: 10 prone-prone cases, 4 prone-supine cases with limited deformations and 6 prone-supine cases with larger deformations and image artefacts. Clinically-acceptable results were obtained for the first two problems. Therefore, for DIR problems with limited deformations, a multi-objective class solution can be machine learned and used to compute straightforwardly multiple high-quality DIR outcomes, potentially leading to more efficient use of DIR in clinical practice.
1. Introduction
Deformable image registration (DIR) [1], i.e., the process of searching for the optimal non-linear transformation to align two images, plays an increasingly important role in radiotherapy [2], with applications ranging from radiotherapy planning [3], dose accumulation [4], contour propagation [5], to radiotherapy response monitoring [6].
One of the challenges of DIR in clinical practice concerns the parameter choices that need to be made for each registration instance, since the success of most registration methods depends on setting a variety of parameters well (e.g., the weights in the cost function, the number of registration levels, the control point grid spacing). The weights of the cost function are especially important, as they determine the trade-off between all the objectives of interest, including the effect of regularization of the DIR problem, which is necessary, as DIR is inherently ill-posed [7].
Optimizing these parameters for each individual DIR instance is challenging in clinical practice. Having a class solution for DIR, i.e., a configuration of parameters for which DIR performs well on all instances of a DIR problem, would facilitate wide-scale clinical application. Although several approaches have been proposed [8,9,10], still, often, parameters are manually tuned for each case of the DIR problem separately via trial-and-error adaptations, followed by visual inspection of the registration outcome.
Finding a class solution may, however, be impossible for challenging DIR cases, as it was shown that preferred parameter settings can vary greatly even for different instances of the same type of registration problem [9,10,11]. Different parameter configurations lead to different DIR outcomes, due to different trade-offs between the objectives of interest in DIR, such as similarity between the images and the amount of deformation.
The fact that different trade-offs may be preferable for different instances of a DIR problem indicates that DIR, although currently typically solved as a single-objective optimization problem, where all objectives of interest are combined in one cost function, is inherently a multi-objective optimization problem. In multi-objective optimization, the objectives of interest are not combined into one cost function, but optimized simultaneously, resulting in a set of DIR outcomes that represent high-quality trade-offs between the objectives of interest. If the multi-objective problem is solved to optimality, then this set of DIR outcomes is called the Pareto front. In cases where the Pareto front is not known (such as in the case of DIR), it can be said that a non-dominated front is obtained, i.e., a front where no solution is better in both objectives than any other solution in this front. Recently, it was shown that using a patient-specific multi-objective optimization approach can be useful for challenging DIR cases, for which manual tuning becomes far more complex [10]. This multi-objective, patient-specific approach can also be considered an online tuning approach: online in the sense that here, the tuning algorithm is run to search for the best parameter settings for the DIR algorithm for a specific patient. This approach removes the challenge of manual parameter tuning and provides the expert with a non-dominated front of DIR outcomes. Such a solution can be navigated to find a preferred DIR outcome insightfully. However, it can be computationally expensive, as it involves running a search algorithm on top of a DIR algorithm every time a DIR case needs to be solved. Furthermore, the more parameters to be tuned, the more time consuming this process becomes [12,13].
In this work, we consider an alternative approach for efficient parameter tuning: an evolutionary multi-objective machine learning approach that computes, in an offline training phase, a multi-objective class solution, i.e., a set of parameter configurations, that, when used on any instance of a DIR problem, yields DIR outcomes that approximate the non-dominated front. To this end, we re-design the parameter optimization problem, and we evaluate the performance of the evolutionary machine learning approach by performing a comparison with the method presented in [10]. Since computing the multi-objective class solution needs to be performed only once, it is then sufficient for a new DIR instance to run multiple DIRs straightforwardly using the class solutions to obtain a navigable set of DIR outcomes for that instance. These runs can be executed in parallel, resulting in a large reduction in computation time, compared to a patient-specific multi-objective tuning approach.
We developed and tested our evolutionary multi-objective machine learning approach on two breast magnetic resonance (MR) DIR problems of different levels of complexity. The first one is prone-prone breast MR DIR of patients undergoing pre-operative partial breast radiotherapy. Registering images of the patients before and after therapy can be used to monitor therapy response. The second DIR problem is prone-supine breast MR DIR (in this work, data from healthy volunteers are used), which presents a significantly higher challenge due to the very large deformation occurring between the two positions (i.e., lying face down versus lying face up). Prone-supine DIR can be used to map pre-surgical diagnostic imaging to the radiotherapy planning geometry, e.g., for radiotherapy after breast-conserving surgery.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Datasets
2.1.1. Prone-Prone
We used retrospectively 10 pairs of T1-weighted MR images without contrast enhancement, acquired pre- and post-radiotherapy, of breast cancer patients (age ≥60 years, tumour size ≤30 mm on pre-radiotherapy MR images) in prone orientation (Figure 1). These patients underwent pre-operative partial breast radiotherapy [14] between December 2012 and June 2015, prior to breast-conserving surgery. The images had a voxel size of mm. The trial for which these data were acquired was approved by the institutional review boards of the participating institutes, and written informed consent was obtained from participants.
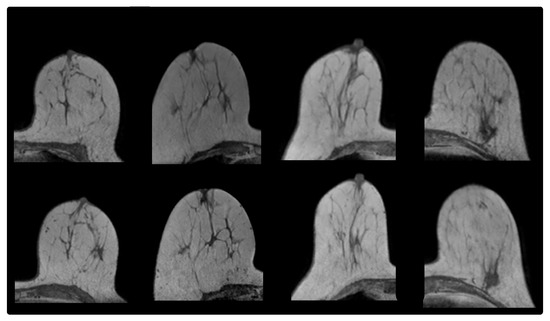
Figure 1.
From (left) to (right): prone-prone Cases 3, 6, 8, 9. (Upper) row: MR image acquired before radiotherapy. (Lower) row: MR image acquired after radiotherapy.
2.1.2. Prone-Supine
This dataset consisted of 10 pairs of healthy volunteer MR images without contrast enhancement, acquired in prone and supine orientation during the same scan session. The images had a voxel size of mm. Nine MR-visible fiducial markers (MM3005, IZI Medical Products Corporation, Baltimore, MD, USA) were attached to the breast, evenly spaced on its surface. We subdivided our prone-supine cases as follows. Given that via patient-specific parameter optimization, potentially clinically-useful registration results (on the basis of achieved mean target registration error (TRE)) were found for four cases [10], we grouped these cases together. We call this prone-supine Group A (Figure 2). We grouped the remaining six registration cases in prone-supine Group B. After rigid registration on bony anatomy, for Group A, the mean Euclidean distance between external marker locations in the rigidly-transformed source and target image was 24.7 mm (SD 8.1 mm), whereas for Group B, the mean Euclidean distance was 42.2 mm (SD 12.5 mm), i.e., there were larger deformations in Group B. Further, large intensity inhomogeneities were present in multiple images of Group B (Figure 3).
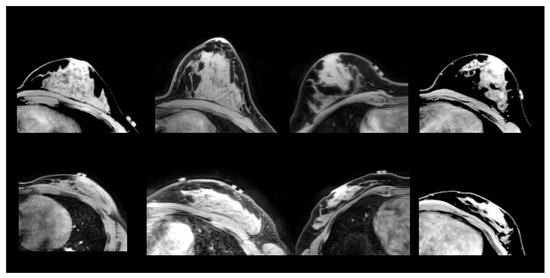
Figure 2.
From (left) to (right): Cases A1, A2, A3 and A4 (from prone-supine Group A). (Upper) row: source image acquired in prone orientation. (Lower) row: target image acquired in supine orientation.
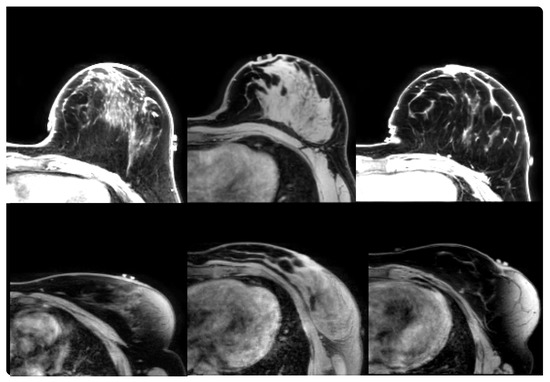
Figure 3.
From (left) to (right): Cases B6, B9 and B10 (from prone-supine Group B). (Upper) row: source image acquired in prone orientation. (Lower) row: target image acquired in supine orientation.
2.2. Patient-Specific Multi-Objective DIR
DIR is typically formulated as the minimization of a single cost function that consists of several terms describing objectives of interest, such as the degree of dissimilarity between the two images and the amount of deformation. The typical formulation is to find, for a given weight vector , the transformation that minimizes:
Here, , are the m objectives considered in the DIR method. The weight vector determines the trade-off between the objectives and needs to be set before the start of optimization. Each different weight vector corresponds to a different cost function and therefore to a different (local) minimum. The objectives can be highly non-convex, as is often the case, e.g., with the objective describing the (dis)similarity between the images to be registered [15].
Now, let be the transformation resulting from performing DIR with a typical DIR method on instance i. The more complex the registration problem (e.g., content mismatch, large deformations), the more likely does not correspond to the global optimum of , given the local nature of the gradient descent optimizers typically used in DIR.
We can use this definition to formulate the patient-specific multi-objective weight-tuning problem:
Solving this multi-objective parameter-tuning problem to optimality results in a set of solutions that can be considered equally good, i.e., no solution can be improved in one objective without deteriorating one or more other objectives. This set of solutions in parameter space is called the Pareto set, and the set of corresponding objective values in objective space is called the Pareto front [16]. When solving this problem in practice, however, the solutions obtained may or may not lie on the Pareto front; therefore, these solutions form a trade-off, or non-dominated, front.
2.3. Evolutionary Multi-Objective Class Solution Learning for DIR
To avoid solving this problem each time we want to use DIR in clinical practice, as it can be very time consuming, we are interested in finding weight vectors that are expected to give good results on any instance of a DIR problem. Good expected performance from the DIR method means that the expected value of each objective needs to be minimized. Given a finite training set of n image pairs, an approximation thereof can be obtained, by using the mean, or for optimization purposes, equivalently, the sum, of observed objective values on the training set, i.e.,
This is now a class-specific multi-objective optimization problem aimed at optimizing the performance of a model on a set of example image pairs representing multiple instances of a certain DIR problem class, essentially making it a machine learning problem. To solve this, we use an evolutionary algorithm (EA) that minimizes the sum of DIR objective values after a single-objective DIR method has converged to a (local) minimum on the training set. A flowchart that describes the procedure is given in Figure 4.
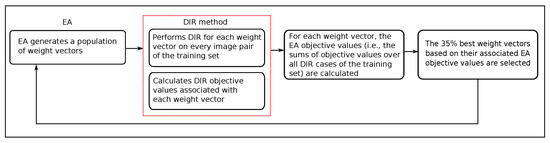
Figure 4.
A flowchart of the proposed multi-objective evolutionary class solution learning approach. It contains a double optimization loop: in the inner loop (red dashed line), each DIR problem instance for a given weight vector is solved; in the outer loop (black solid line), the weight optimization problem is solved by the EA.
2.3.1. DIR Method
The underlying single-objective DIR method we used in this study is elastix [17], a well-known open-source image registration toolbox, which uses a B-spline transformation model [18].
For the prone-prone registration problem, we used two objectives: dissimilarity as described by the negative normalized correlation coefficient [19] and deformation magnitude as described by the bending energy penalty [20], both to be minimized. This corresponds to a vector of two weights.
For the prone-supine registration problem, we used, in addition to dissimilarity and deformation magnitude, a third objective: the so-called guidance error [21], to be minimized, resulting in a vector of three weights for optimization. Guidance information was provided via the presence of the external fiducial markers on the breast surface. We explicitly annotated their location, i.e., the centre of the marker, on the source, as well as on the target image. The guidance error was then defined as the sum of Euclidean distances between pairs of transformed marker source locations and marker target locations.
2.3.2. Evolutionary Algorithm
To learn multi-objective class solutions, we employed a multi-objective EA. EAs are among the state-of-the-art in multi-objective optimization [16,22,23]. We used a specific type of EA, called an estimation-of-distribution algorithm (EDA) [24]. EDAs build and sample a probability distribution (in the specific algorithm, we employed an l-dimensional Gaussian mixture distribution, where l is the number of parameters, i.e., the number of weights) to generate new solutions.
The EA-specific parameter settings were set according to the literature [25], where the performance of the EA was tested on benchmark problems with the same number of objectives as our problems here. Although for these benchmark problems, the EA was found to obtain high-quality results already after 100 generations, in this work, we allowed the EA to run for 200 generations, as we observed that a notably better non-dominated front (with a larger number of points) could be obtained. This is most probably due to the higher complexity of the problem at hand, i.e., the presence of more local optima than most benchmark problems, due to the multiple combinations of image pairs to be registered.
We used three objectives for the EA for both the prone-prone, as well as the prone-supine problem. The first two objectives were formulated as the sum of the dissimilarity and deformation magnitude objective values over all the images in the training set.
The third EA objective makes use of guidance information of anatomical landmarks, similar to the guidance error objective used within the DIR method elastix. However, since for the prone-prone DIR problem, no external landmarks were available, the location of internal landmarks was used. The sum of the distances between transformed internal landmark source locations and their corresponding target locations was minimized; this objective is calculated within the EA optimization flow and not within elastix. For the prone-supine DIR problem, both internal as well as external landmark locations (in the form of the fiducial markers) were utilized, again within the EA and not within elastix, which calculated the objectives separately and then passed the value of the dissimilarity and deformation magnitude to the EA. Note that the internal landmark locations can be used for the evaluation of the registration quality, as they were not used by the DIR method itself, which only used external landmark locations in the prone-supine problem, but only by the EA that finds the class solution. This is because the objective values for the EA are calculated after the DIR method has terminated, as illustrated in Figure 4. We decided to use both the internal and external landmarks as guidance information to the EA, since the class-solution-learning problem is a challenging optimization problem and we wanted to maximize performance.
2.4. Evaluation
To evaluate the quality of registration outcomes, an experienced breast radiologist annotated eight to twelve internal anatomical landmarks in the source image and their corresponding locations in the target image. These pairs of annotations were distributed as uniformly as possible throughout the breast volume in order to obtain a representative overall estimation of the registration accuracy.
We calculated the mean TRE as the mean Euclidean distance between the internal landmark locations in the target image and their locations in the transformed source image.
To assess the quality of the learned class solutions, we compared them to the solutions obtained by our previously-introduced patient-specific multi-objective optimization approach [10], where for each individual patient, the optimal weight configurations that yield a non-dominated front of DIR outcomes were found. These results were considered the best possible outcomes for these individual DIR cases. For this, we used the inverted generational distance (IGD) [26,27], a well-known performance indicator that describes how close one non-dominated front (called the reference front) is approximated by another. Given a set of class solutions and a reference front (here, the non-dominated front obtained by patient-specific optimization) , the is defined as follows:
where d is the Euclidean distance in objective space. IGD is a common descriptor in the multi-objective EA literature, with a value around 0.001 to be considered a very good approximation of a non-dominated front that is ranging between zero and one in every objective and has 5000 points on its front [24]. Here, after normalizing every objective to [0, 1] and adjusting for the size of our non-dominated fronts, which was on average of 500 points, we considered a value of to be a very good approximation.
From a clinical standpoint, however, it is important to observe whether a solution in the reference front is covered by the existence of a class solution with similar TRE. For this reason, in Equation (2), we replaced the Euclidean distance in objective space with the distance (in mm) between points in TRE space, by calculating additionally (we denote with the mean TRE associated with solution a):
Moreover, in recent work, it was observed that, when provided a potentially navigable patient-specific front [10] and the right user interface, decision makers can actually easily identify preferred solutions that have the near best TRE [28]. Following from this, we are interested in the TRE difference between the potentially best solution found by the patient-specific approach (i.e., the solution with the lowest mean TRE) and the best solution among the class solutions:
Finally, we measured computation time for each DIR outcome on a six-core PC (Intel Xeon E5-1650). In patient-specific optimization, 100 generations were used to compute results, where the DIR method elastix was called 100 times in each generation (see [10]). In the case of prone-prone DIR, performing DIR on one core took approximately 20 s, whereas for prone-supine DIR, this was 60 s. For patient-specific optimization, this resulted in a total computation time of approximately 12 h for prone-prone and 27 h for prone-supine cases, making use of the parallelization feature of elastix [29].
2.5. Experimental Setup
To estimate the performance of our evolutionary machine learning approach for multi-objective class solutions, we performed leave-one-out cross-validation [30], i.e., assuming we have a dataset of n cases for a DIR task, we learned multi-objective class solutions on cases, and we used the learned class solutions, i.e., the sets of parameter configurations, to perform DIR on the left-out case. Note that the resulting DIR outcomes on the left-out case do not necessarily form a non-dominated front in objective space, as opposed to the DIR outcomes obtained by patient-specific optimization. We repeated this procedure n times, i.e., ten times for the prone-prone registration group, four times for prone-supine Group A and six times for Group B.
3. Results
3.1. Prone-Prone
The multi-objective class solution learning approach showed good performance, obtaining very good approximations of the patient-specific non-dominated fronts in eight out of ten cases, in objective space and in TRE space (see Table 1). For Case 1, despite the larger , the was very low, indicating that the class solutions were in their entirety very similar in quality to the patient-specific solutions, while for Case 8, the was larger. This happened because all the weight combinations in the multi-objective class solution led to outcomes that were located only in one part of the non-dominated front (see Figure 5). However, the part of the non-dominated front that was not covered by these class solutions mostly contained solutions that were uninteresting, as they were the ones with less deformation and larger TRE values. Consequently, was extremely small for all ten cases (Table 1), indicating that the class solution approach was capable of obtaining a solution(s) of high quality, in spite of the poor result for Case 8 from an evolutionary multi-objective machine learning standpoint.

Table 1.
Inverted generational distance (IGD) values in objective and target registration error (TRE) space and for the prone-prone deformable image registration (DIR) group.
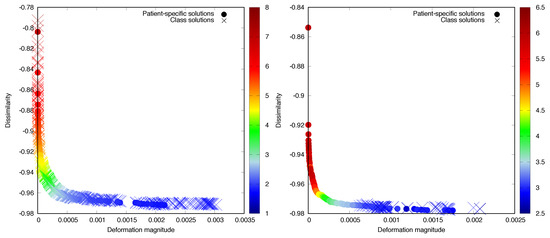
Figure 5.
Non-dominated front of patient-specific solutions and class solutions for Test Cases 6 (left) and 8 (right), colour coded with the mean TRE in mm. The colour scales are different for each case, to illustrate the different TRE distributions better.
Computation time associated with applying a multi-objective class solution on a six-core PC ranged from 12.5 min to 42 min (depending on the size of the class solution).
3.2. Prone-Supine
For Group A, the multi-objective class-solution approach found good approximations of the patient-specific non-dominated fronts (Table 2 and Figure 6a,b), with the exception of Case A1, where the mean TRE associated with the best DIR outcome found by using the class solutions was 1.2 mm larger than the mean TRE associated with the best patient-specific DIR outcome. A1 was the only case in Group A that exhibited image inhomogeneities, making finding a good match very challenging, despite the limited deformation. For Group B, the and were larger, and the quality of the class solutions that were obtained was clearly inferior to the patient-specific ones for three out of six cases, as described by (see Cases B6, B7 and B8 in Table 3). This is illustrated further for Case B6 in Figure 6c), which was one of the most difficult cases in this set in terms of large breast volume, coupled with the presence of image intensity inhomogeneities. These registration cases were, however, already unsuccessful also with patient-specific optimization, resulting in relatively large mean TREs. The fact that, additionally, a well-covering multi-objective class solution cannot be found, in objective or TRE space, signifies the complexity of such cases resulting from the large diversity among the individual cases in addition to the large deformations present.

Table 2.
IGD values for prone-supine Group A.
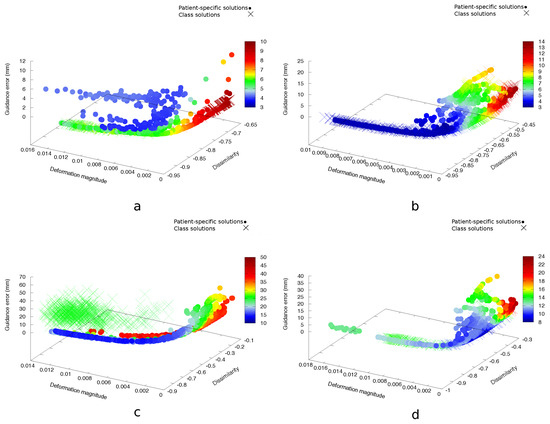
Figure 6.
Non-dominated fronts of patient-specific solutions and their class solutions for prone-supine Test Cases A1 (a), A2 (b), B6 (c) and B9 (d), colour coded with the mean TRE in mm. The colour scales are different for each case, to illustrate the different TRE distributions better.

Table 3.
IGD values for prone-supine Group B.
Computation time associated with applying a multi-objective class solution on a six-core PC ranged from 24 min to one hour and 28 min (depending on the size of the class solution).
4. Discussion
We presented an evolutionary multi-objective class-solution learning approach for DIR, which we applied to breast MR DIR problems of increasing difficulty. We used our approach to learn weights typically used in DIR software, but the approach was general and could straightforwardly be used to consider other parameters, as well. The multi-objective class-solution approach presented in this work kept the benefits of a multi-objective perspective [10] and was more efficient than multi-objective patient-specific parameter optimization, by allowing parallel computation of DIRs without any further tuning or optimization, thereby much more so facilitating the use of multi-objective DIR in clinical practice.
Although the concept of a class solution implies the existence of a unique solution that solves all instances of a particular problem well, we considered a set of class solutions, i.e., a multi-objective class solution, to be more appropriate for the problem of DIR. The idea that a single trade-off can work for all DIR cases of a certain type comes from a single-objective optimization perspective, but even among registration problems of the same type, parameter settings that give the desired results can differ [10]. A multi-objective optimization approach instead has the ability to capture high-quality trade-offs among which the preferred outcome is likely present. Moreover, selecting this outcome is insightful and easy [28]. It was also observed that what the users thought was a high-quality solution coincided with a mean TRE (very) close to the minimum mean TRE obtained, indicating that the results obtained by our method can be considered reliable.
The evaluation of the quality of the DIR outcomes, in the absence of a ground truth, relied on the annotated landmarks, which has known limitations (it may not be representative of the quality of the deformation throughout the entire volume). A realistic phantom-based study could potentially circumvent this, but such an elaborate study is out of the scope of this work. We further saw that when the solutions were visually inspected by observers, what the users thought was a high-quality solution coincided with a mean TRE (very) close to the minimum mean TRE obtained [28], indicating that the mean TRE was representative of the overall quality of the solutions.
Since EAs are state-of-the-art for multi-objective black-box optimization and given the limited amount of data present for the DIR problems studied in this work, the choice of an EA as a machine learning technique, as opposed to more widely-used machine learning approaches such as, e.g., convolutional neural networks, seems reasonable. Using the EA to tackle this problem, even in the presence of very limited data, was possible since the problem concerned a limited number of parameters (i.e., a low-dimensional manifold) to be learned and the learning of point sets. The EA employed in this work was specifically chosen as it was designed for continuous, multi-objective problems, and it has been shown to perform well for those problems [25]. Given that the bulk of the computation was in the DIRs during meta-optimization and given the performance of this EA on different benchmark problems compared to other EAs, we do not expect that choosing a different EA as a meta-optimizer would yield significant differences in terms of computation time.
The results of this approach, which may be considered an evolutionary multi-objective machine learning approach [31], indicate that deriving a multi-objective class solution for DIR is feasible, even with a limited amount of data, for DIR problem classes that are solvable and for which the variation within the class is not too large, as in the case of prone-prone breast MR image registration. It may be feasible even for quite challenging DIR problems, as in the case of the prone-supine DIR problems, provided that the underlying DIR method, on which our approach was ultimately dependent, can actually solve the DIR problem, and the variation in (quality of) the images and their content was limited.
Further, for our approach to work properly, it was necessary to perform a classification of prone-supine DIR instances, into two groups, one with larger and one with smaller deformations. It may be challenging to always classify correctly the prone-supine DIR instance at hand. One solution could be to pre-process the data. For instance, classification could be performed by quantifying breast volume (e.g., with breast cup size) and/or based on age. DIR cases with small breast volumes (and therefore with limited deformation present) and of young patients, which tend to have breasts with more fibroglandular tissue (therefore with more information present in the images), are most likely easier to solve.
Further research could involve using the approach presented in this work to tune multiple parameters, with very few parameters subsequently tuned patient-specifically, to perhaps obtain even higher quality solutions for challenging DIR problems. In the case of tuning multiple parameters, the computational benefit of using a class solution approach instead of a patient-specific approach increases. Moreover, a so-called adaptive steering mechanism in the EA could be incorporated in order to obtain more solutions in the region of the non-dominated front that is of interest [32]. Lastly, we note that the number of DIRs to be performed and the total online computation time can potentially be reduced by selecting a diverse, but front-spanning subset of the multi-objective class solution of a limited, pre-defined size.
5. Conclusions
In this work, we presented an evolutionary multi-objective machine learning approach that computed a set of so-called class solutions, for problems of increasing difficulty: prone-prone breast DIR, prone-supine breast DIR with limited deformations and prone-supine breast DIR with large deformations. We showed that, for DIR problems with limited deformations (prone-prone, as well as prone-supine), it is feasible for a multi-objective class solution to straightforwardly obtain a set of high-quality outcomes for every DIR instance of those problems without additional parameter tuning. This allows selection of the preferred outcome by an expert, potentially leading to more efficient use of DIR in clinical practice.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.P., P.A.N.B., J.-J.S., M.v.H. and T.A.; methodology, K.P., P.A.N.B. and T.A.; formal analysis, K.P.; resources, J.-J.S., P.A.N.B. and T.A.; writing, original draft preparation, K.P.; writing, review and editing, P.A.N.B., J.-J.S., M.v.H. and T.A.; supervision, funding acquisition, T.A.
Funding
This work was funded by the Dutch Cancer Society (KWF; Grant No. KWF 2012-5716).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the volunteers that participated in the study, A.N. Scholten for the PAPBIstudy, N.N.Y. Janssen for the prone-supine image acquisition and C.E. Loo for providing the landmark annotations. The authors acknowledge the financial support provided by the Maurits en Anna de Kock Stichting for a high-performance computing system and the Nijbakker-Morra Stichting for financing a high-performance computing system.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sotiras, A.; Davatzikos, C.; Paragios, N. Deformable medical image registration: A survey. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2013, 32, 1153–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brock, K.K.; Mutic, S.; McNutt, T.R.; Li, H.; Kessler, M.L. Use of image registration and fusion algorithms and techniques in radiotherapy: Report of the AAPM Radiation Therapy Committee Task Group No. 132. Med. Phys. 2017, 44, e43–e76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, E.S.; Muren, L.P.; Sørensen, T.S.; Noe, K.Ø.; Thor, M.; Petersen, J.B.; Høyer, M.; Bentzen, L.; Tanderup, K. Bladder dose accumulation based on a biomechanical deformable image registration algorithm in volumetric modulated arc therapy for prostate cancer. Phys. Med. Biol. 2012, 57, 7089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraus, K.M.; Jäkel, O.; Niebuhr, N.I.; Pfaffenberger, A. Generation of synthetic CT data using patient specific daily MR image data and image registration. Phys. Med. Biol. 2017, 62, 1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thor, M.; Petersen, J.B.; Bentzen, L.; Høyer, M.; Muren, L.P. Deformable image registration for contour propagation from CT to cone-beam CT scans in radiotherapy of prostate cancer. Acta Oncol. 2011, 50, 918–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brock, K.K.; Dawson, L.A.; Sharpe, M.B.; Moseley, D.J.; Jaffray, D.A. Feasibility of a novel deformable image registration technique to facilitate classification, targeting, and monitoring of tumor and normal tissue. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2006, 64, 1245–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, B.; Modersitzki, J. Ill-posed medicine—An introduction to image registration. Inverse Probl. 2008, 24, 034008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, B.T.T.; Sabuncu, M.R.; Vercauteren, T.; Holt, D.J.; Amunts, K.; Zilles, K.; Golland, P.; Fischl, B. Learning task-optimal registration cost functions for localizing cytoarchitecture and function in the cerebral cortex. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2010, 29, 1424–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Groot, M.; Vernooij, M.W.; Klein, S.; Ikram, M.A.; Vos, F.M.; Smith, S.M.; Niessen, W.J.; Andersson, J.L. Improving alignment in Tract-based spatial statistics: Evaluation and optimization of image registration. NeuroImage 2013, 76, 400–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirpinia, K.; Bosman, P.A.N.; Loo, C.E.; Winter-Warnars, G.; Janssen, N.N.Y.; Scholten, A.N.; Sonke, J.J.; van Herk, M.; Alderliesten, T. The feasibility of manual parameter tuning for deformable breast MR image registration from a multi-objective optimization perspective. Phys. Med. Biol. 2017, 62, 5723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, T.H.; Min, Y.; Neylon, J.; Thomas, D.; Kupelian, P.; Santhanam, A.P. Fast simulated annealing and adaptive Monte Carlo sampling based parameter optimization for dense optical-flow deformable image registration of 4DCT lung anatomy. In Proceedings of SPIE Medical Imaging; Webster, R.J., Yaniv, Z.R., Eds.; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2016; p. 97860N. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francesca, G.; Pellegrini, P.; Stützle, T.; Birattari, M. Off-line and on-line tuning: a study on operator selection for a memetic algorithm applied to the QAP. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Evolutionary Computation in Combinatorial Optimization, Torino, Italy, 27–29 April 2011; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2011; pp. 203–214. [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrini, P.; Stützle, T.; Birattari, M. Off-line vs. On-line Tuning: A Study on MAX–MIN Ant System for the TSP. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Swarm Intelligence, Beijing, China, 12–15 June 2010; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2010; pp. 239–250. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Leij, F.; Bosma, S.C.J.; van de Vijver, M.J.; Wesseling, J.; Vreeswijk, S.; Rivera, S.; Bourgier, C.; Garbay, J.R.; Foukakis, T.; Lekberg, T.; et al. First results of the preoperative accelerated partial breast irradiation (PAPBI) trial. Radiother. Oncol. 2015, 114, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pluim, J. Mutual Information Based Registration of Medical Images. Ph.D. Thesis, Utrecht University of Applied Sciences, Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Deb, K. Multi-Objective Optimization Using Evolutionary Algorithms; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2001; p. 497. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, S.; Staring, M.; Murphy, K.; Viergever, M.A.; Pluim, J.P.W. elastix: A toolbox for intensity-based medical image registration. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2010, 29, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rueckert, D.; Sonoda, L.I.; Hayes, C.; Hill, D.L.; Leach, M.O.; Hawkes, D.J. Nonrigid registration using free-form deformations: Application to breast MR images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 1999, 18, 712–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roche, A.; Malandain, G.; Pennec, X.; Ayache, N. The correlation ratio as a new similarity measure for multimodal image registration. In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI’98, Cambridge, MA, USA, 11–13 October 1998; Wells, W.M., Colchester, A., Delp, S., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; pp. 1115–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahba, G. Spline Models for Observational Data; Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics (SIAM): Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1990; Volume 59. [Google Scholar]
- Baiker, M.; Staring, M.; Löwik, C.W.; Reiber, J.H.; Lelieveldt, B.P. Automated registration of whole-body follow-up MicroCT data of mice. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Toronto, ON, Canada, 18–22 September 2011; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2011; pp. 516–523. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, A.; Qu, B.Y.; Li, H.; Zhao, S.Z.; Suganthan, P.N.; Zhang, Q. Multiobjective evolutionary algorithms: A survey of the state of the art. Swarm Evolut. Comput. 2011, 1, 32–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coello Coello, C.A.; Lamont, G.B.; Van Veldhuizen, D.A. Evolutionary Algorithms for Solving Multi-Objective Problems; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2007; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, S.; Bauer, P.; Bosman, P.A.N. A novel population-based multi-objective CMA-ES and the impact of different constraint handling techniques. In Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Genetic and Evolutionary Computation—GECCO’14, Granada, Spain, 9–11 December 2014; ACM Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 991–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosman, P.A.N.; Alderliesten, T. Incremental Gaussian model-building in multi-objective EDAs with an application to deformable image registration. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Genetic and Evolutionary Computation—GECCO 2012, Sydney, Australia, 4–7 December 2012; ACM Press: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibuchi, H.; Masuda, H.; Tanigaki, Y.; Nojima, Y. Modified distance calculation in generational distance and inverted generational distance. In Evolutionary Multi-Criterion Optimization; Gaspar-Cunha, A., Henggeler Antunes, C., Coello, C.C., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 110–125. [Google Scholar]
- Bosman, P.A.N.; Thierens, D. The balance between proximity and diversity in multiobjective evolutionary algorithms. IEEE Trans. Evolut. Comput. 2003, 7, 174–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirpinia, K.; Bosman, P.A.N.; Sonke, J.J.; van Herk, M.; Alderliesten, T. Simplex-based navigation tool for a posteriori selection of the preferred deformable image registration outcome from a set of trade-off solutions obtained with multiobjective optimization for the case of breast MRI. J. Med. Imaging 2018, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamonin, D.; Bron, E.; Lelieveldt, B.; Smits, M.; Klein, S.; Staring, M. Fast parallel image registration on CPU and GPU for diagnostic classification of alzheimer’s disease. Front. Neuroinform. 2014, 7, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, D.M. The relationship between variable selection and data augmentation and a method for prediction. Technometrics 1974, 16, 125–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y. Multi-Objective Machine Learning; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2006; Volume 16. [Google Scholar]
- Alderliesten, T.; Bosman, P.A.N.; Bel, A. Getting the most out of additional guidance information in deformable image registration by leveraging multi-objective optimization. In Proceedings of SPIE Medical Imaging; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2015; Volume 9413, pp. 9413–9417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).