A Crowd Cooperative Spectrum Sensing Algorithm Using a Non-Ideal Channel
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- Under non-ideal channel, we propose a system model which combines crowd sensing incentive mechanism with cooperative spectrum sensing, and define SU’s utility expectation function which considers the SUs’ sensing time and transmission power at the same time.
- (2)
- We construct an optimization problem about the SU’s utility expectation, and prove that the optimization problem is a convex optimization problem. We obtained the optimal solution by using KKT conditions.
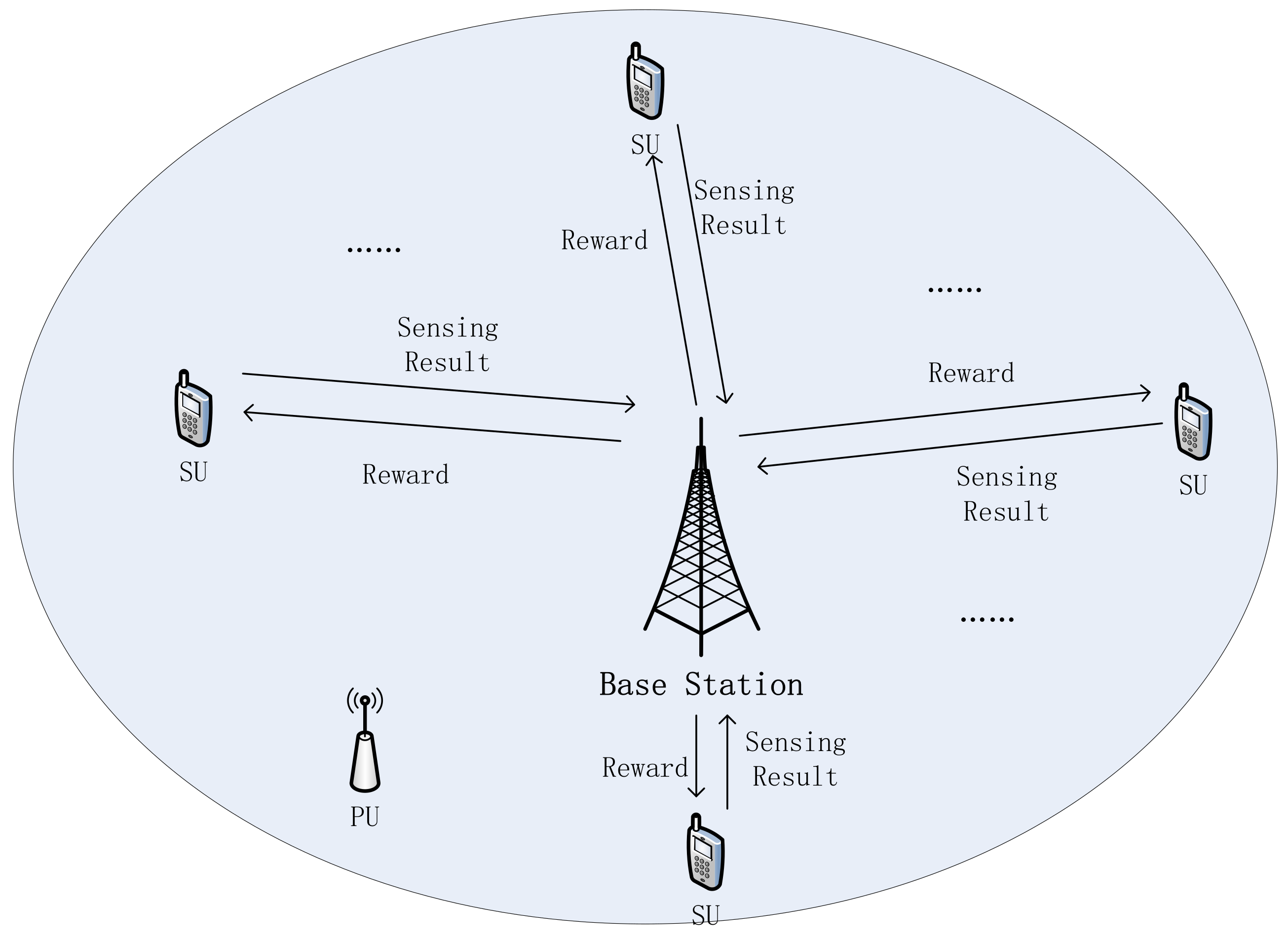
2. System Model
3. Utility Optimal Algorithm
| Algorithm 1 Crowd Cooperative Spectrum Sensing Algorithm under Non-Ideal Channel. |
| 1: for all SUs do |
| 2: Solve the Equations (17) and get the optimal sensing time and emission power ; |
| 3: Calculate the according to (10); |
| 4: if |
| 5: SU take part in the spectrum sensing and send the result to the base station; |
| 6: The base station receives the sensing result from SU ; |
| 7: end if |
| 8: end for |
| 9: The base station fuses the results from SUs and gets the fusion result ; |
| 10: for all SUs participating in the sensing do |
| 12: if = |
| 13: SU gets correct reward ; |
| 14: else |
| 15: SU gets incorrect reward ; |
| 16: end if |
| 17: end for |
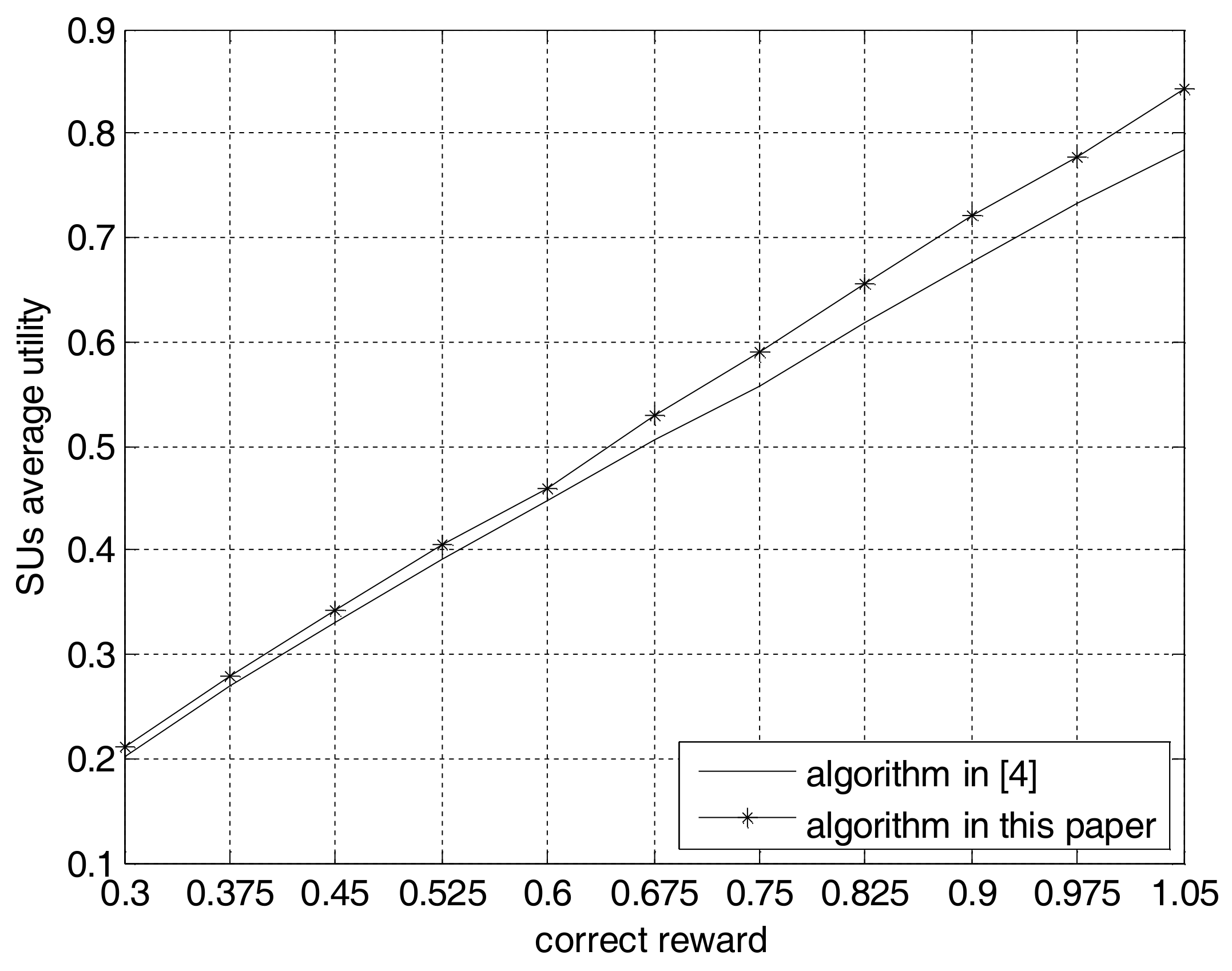
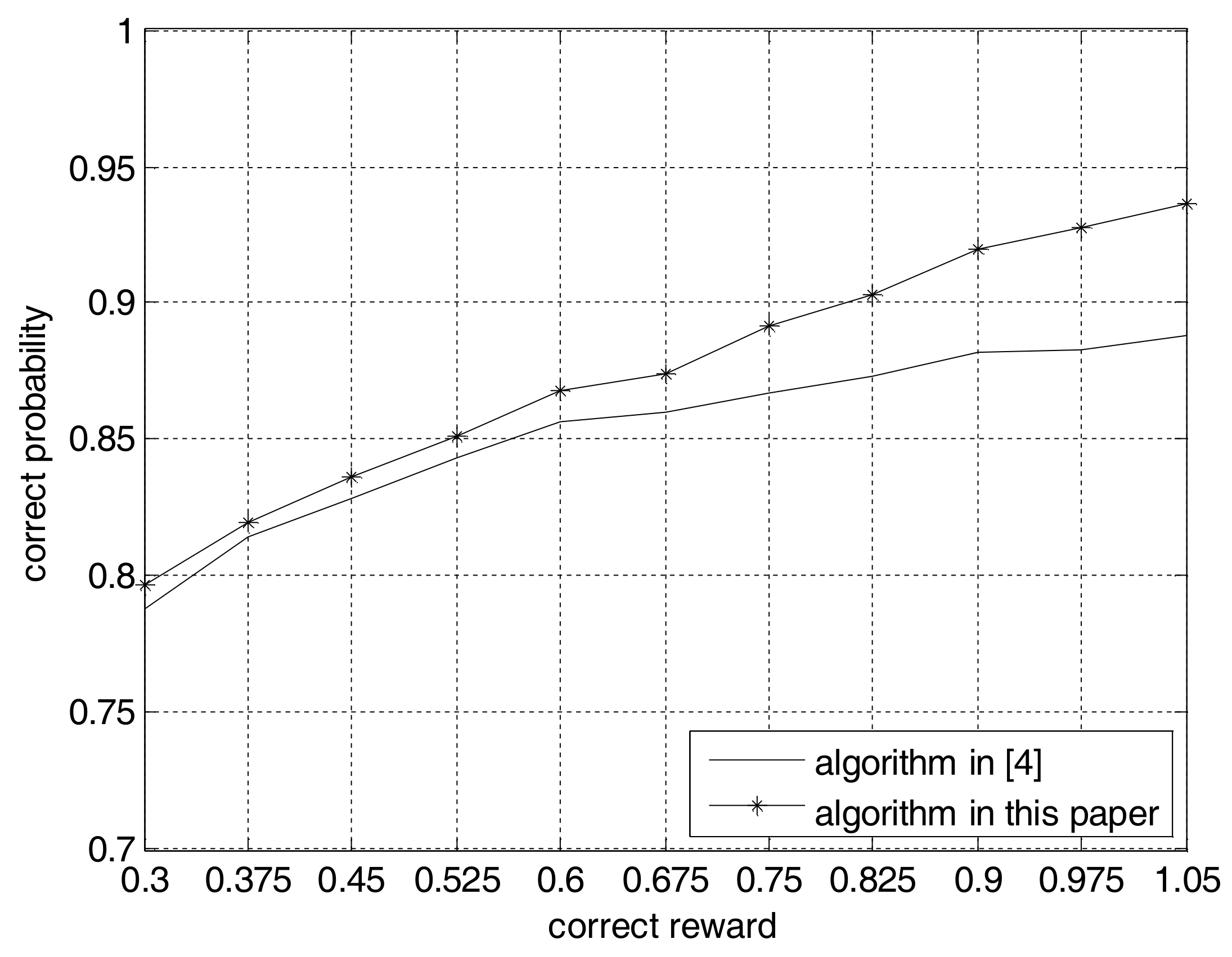
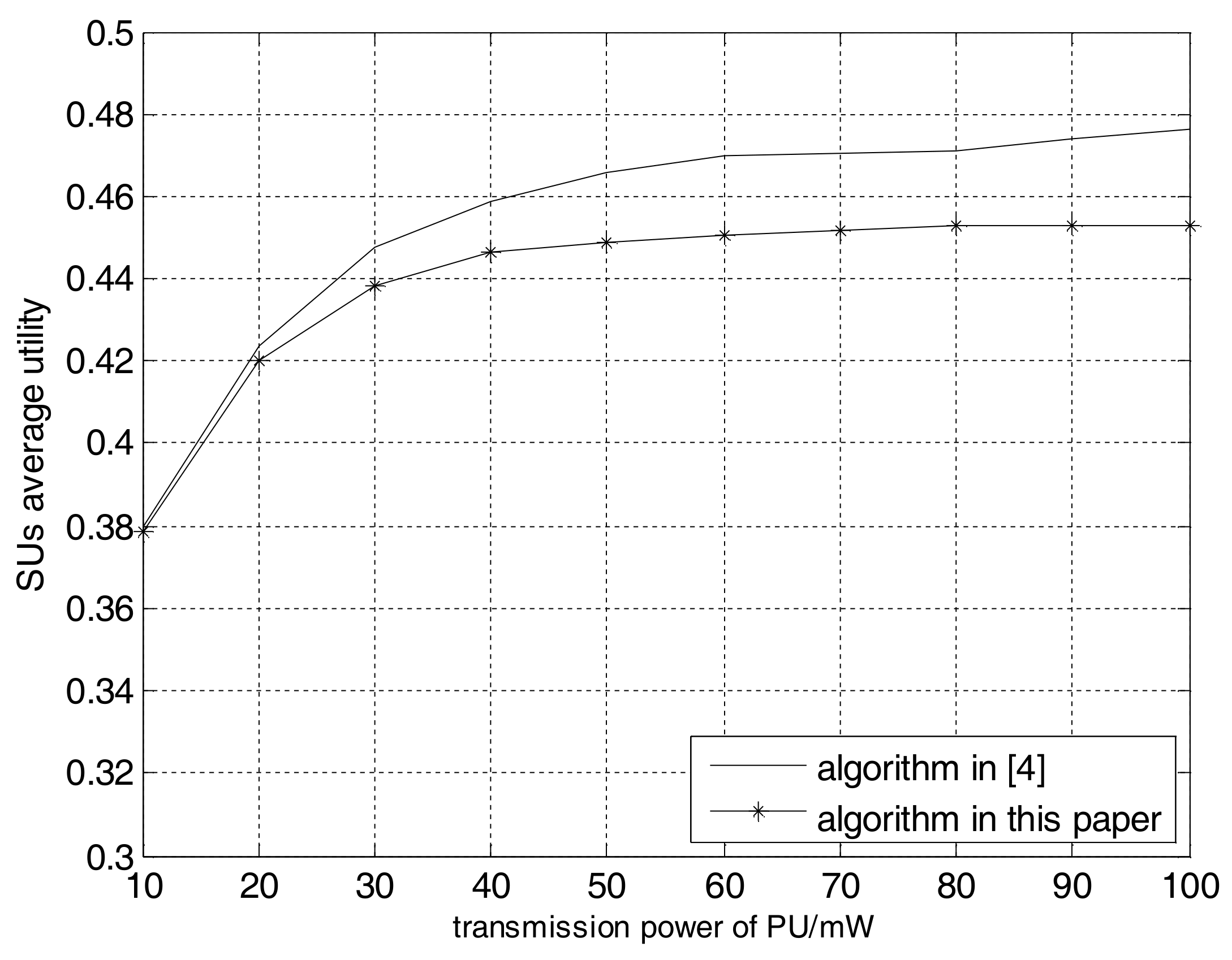
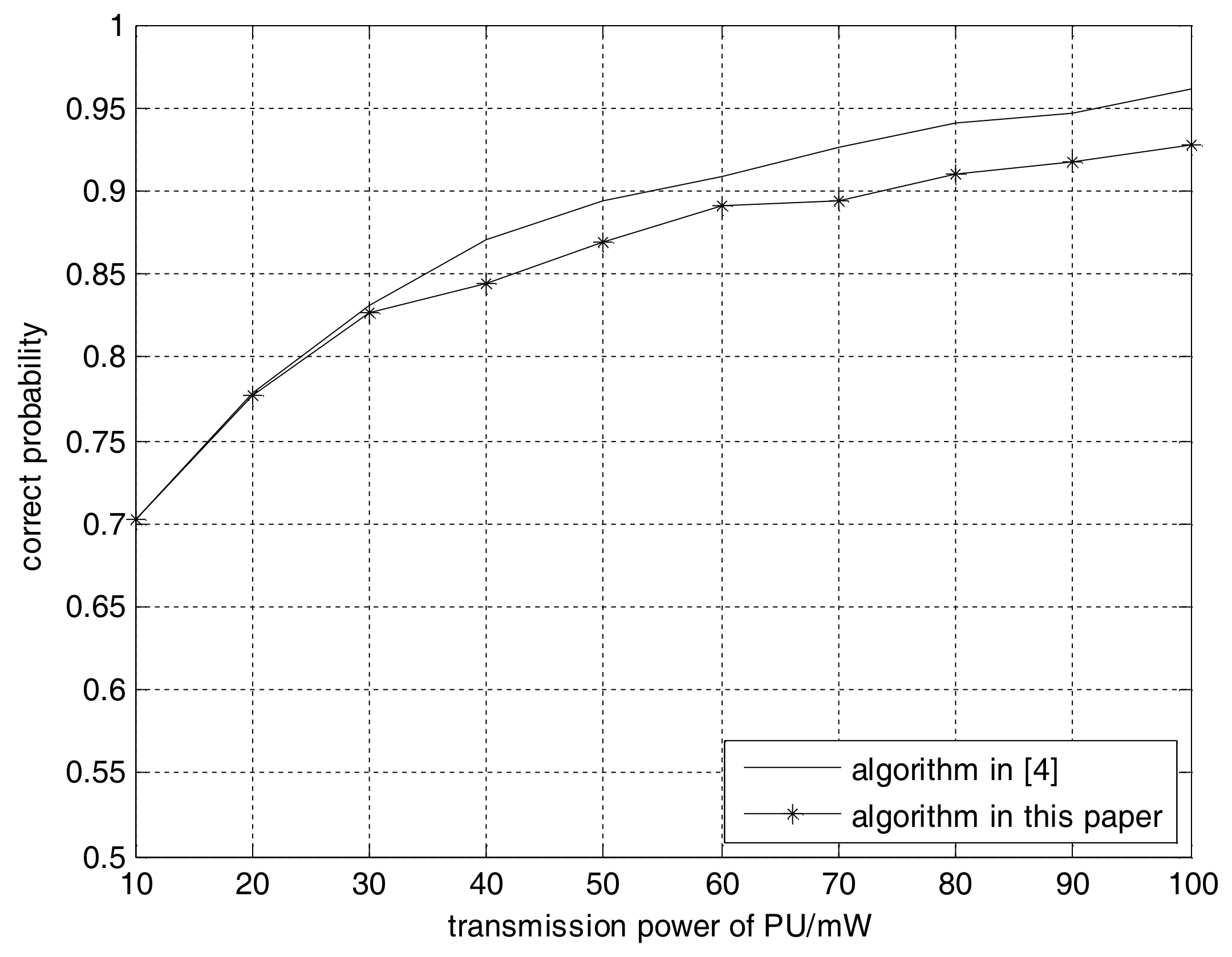
4. Computer Simulations
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Mishra, S.M.; Sahai, A.; Brodersen, R.W. Cooperative Sensing among Cognitive Radios. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Communications, Istanbul, Turkey, 11–15 June 2006; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 1658–1663. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Qi, Z. Cooperative Spectrum Sensing Algorithm Based on Data Fusion. J. NJUPT 2009, 29, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nallagonda, S.; Kumar, Y.R.; Shilpa, P. Analysis of Hard-Decision and Soft-Data Fusion Schemes for Cooperative Spectrum Sensing in Rayleigh Fading Channel. In Proceedings of the Advance Computing Conference, Istanbul, Turkey, 11–15 June 2006; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 220–225. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Cuthbert, L. Optimization of collaborating secondary users in a cooperative sensing under noise uncertainty. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Personal Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications, London, UK, 8–11 September 2013; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 2502–2506. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wu, Q.; Feng, S.; Anpalagan, A. Near Optimal Distributed Cooperative Spectrum Sensing and Access: A Benefit-and-Compensation Approach. In Proceedings of the IEEE Vehicular Technology Conference, Toronto, ON, Canada, 24–27 September 2017; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Zhang, B.; Yu, J.L.; Zhu, H. An indirect reciprocity based incentive framework for cooperative spectrum sensing. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Communications, Paris, France, 21–25 May 2017; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, R.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Shu, W.; Mao, T.; Jalaian, B. ERDT: Energy-Efficient Reliable Decision Transmission for Intelligent Cooperative Spectrum Sensing in Industrial IoT. IEEE Access 2015, 3, 2366–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetto, F.; Giunta, G. A Theoretical Analysis of Asymptotical Performance of Cooperative Spectrum Sensing in the Presence of Malicious Users. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2017, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetto, F.; Tedeschi, A.; Giunta, G.; Coronas, P. Performance improvements of reputation-based cooperative spectrum sensing. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Personal, Indoor, and Mobile Radio Communications, Valencia, Spain, 4–8 September 2016; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, G.; Song, F.; Wu, Q.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Feng, S.; Yao, Y.-D. Robust Spectrum Sensing with Crowd Sensors. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2014, 9, 3129–3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Ding, G.; Du, Z.; Sun, Y.; Jo, M.; Vasilakos, A.V. A Cloud-Based Architecture for the Internet of Spectrum Devices over Future Wireless Networks. IEEE Access 2017, 4, 2854–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, G.; Wang, J.; Wu, Q.; Yao, Y.D.; Song, F.; Tsiftsis, T.A. Cellular-base-station-assisted device-to-device communications in tv white space. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2015, 34, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ser, J.D.; Alonso, A.; Gil-Lopez, S.; Garay, M. On the design of an heuristically optimized multiband spectrum sensing approach for cognitive radio systems. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE 17th International Workshop on Computer Aided Modeling and Design of Communication Links and Networks (CAMAD), Barcelona, Spain, 17–19 September 2012; pp. 168–169. [Google Scholar]
- Ser, J.D.; Matinmikko, M.; Gil-López, S.; Mustonen, M. Centralized and distributed spectrum channel assignment in cognitive wireless networks: A Harmony Search approach. Appl. Soft Comput. 2012, 12, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tragos, E.Z.; Zeadally, S.; Fragkiadakis, A.G.; Siris, V.A. Spectrum Assignment in Cognitive Radio Networks: A Comprehensive Survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2013, 15, 1108–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobron, I.; Martins, W.A.; de Campos, M.L.R.; Elez, M. Incumbent and LSA Licensee Classification through Distributed Cognitive Networks. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2016, 1, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaimes, L.G.; Vergara-Laurens, I.J.; Raij, A. A Survey of Incentive Techniques for Mobile Crowd Sensing. IEEE Internet Things J. 2015, 2, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Hoh, B. Dynamic pricing incentive for participatory sensing. Pervasive Mob. Comput. 2010, 6, 693–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Xiao, M.; Hu, C.; Gao, G.; Wang, B. A QoS-sensitive task assignment algorithm for mobile crowdsensing. Pervasive Mob. Comput. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Rao, Z.; Xu, L.; Yang, D.; Li, T. Mobile Crowd Sensing via Online Communities: Incentive Mechanisms for Multiple Cooperative Tasks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Mobile Ad Hoc and Sensor Systems, Orlando, FL, USA, 22–25 October 2017; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 171–179. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B. The Study of the Cooperative Spectrum Sensing Algorithm in Cognitive Radio based on Data Fusion; NJUPT: Nan Jing, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, C.; Cao, L. Principles of Communications, 7th ed.; National Defense Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2012; pp. 204–205. ISBN 978-7-118-08768-0. [Google Scholar]
- Stephen, B.; Lieven, V. Convex Optimization; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 2013; pp. 61–65. ISBN 978-7-302-29756-7. [Google Scholar]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lv, X.; Zhu, Q. A Crowd Cooperative Spectrum Sensing Algorithm Using a Non-Ideal Channel. Algorithms 2018, 11, 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/a11040051
Lv X, Zhu Q. A Crowd Cooperative Spectrum Sensing Algorithm Using a Non-Ideal Channel. Algorithms. 2018; 11(4):51. https://doi.org/10.3390/a11040051
Chicago/Turabian StyleLv, Xinxin, and Qi Zhu. 2018. "A Crowd Cooperative Spectrum Sensing Algorithm Using a Non-Ideal Channel" Algorithms 11, no. 4: 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/a11040051
APA StyleLv, X., & Zhu, Q. (2018). A Crowd Cooperative Spectrum Sensing Algorithm Using a Non-Ideal Channel. Algorithms, 11(4), 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/a11040051



