Investigation of Pozzolanic Reaction in Nanosilica-Cement Blended Pastes Based on Solid-State Kinetic Models and 29Si MAS NMR
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Solid-State Kinetic Models
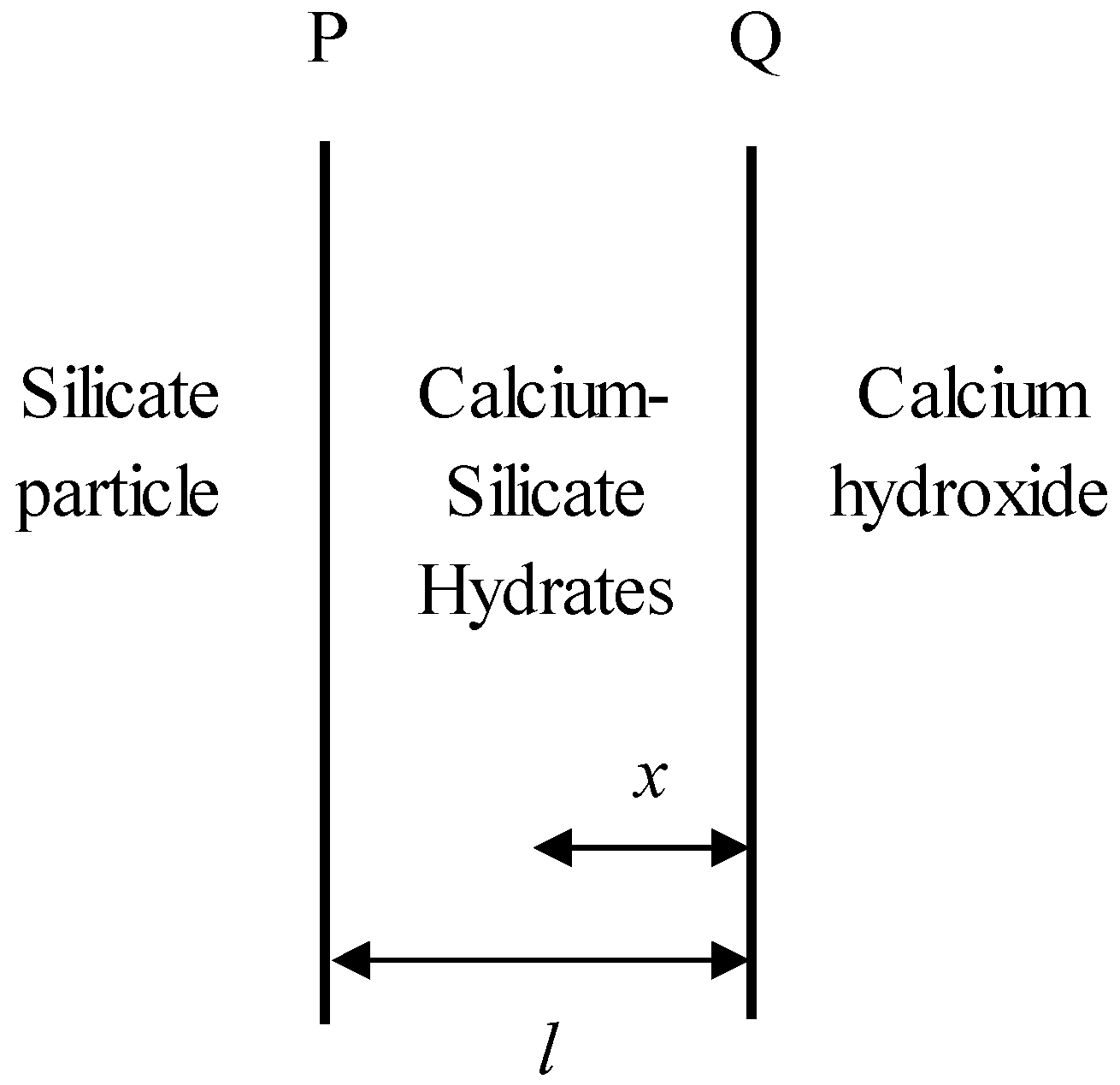
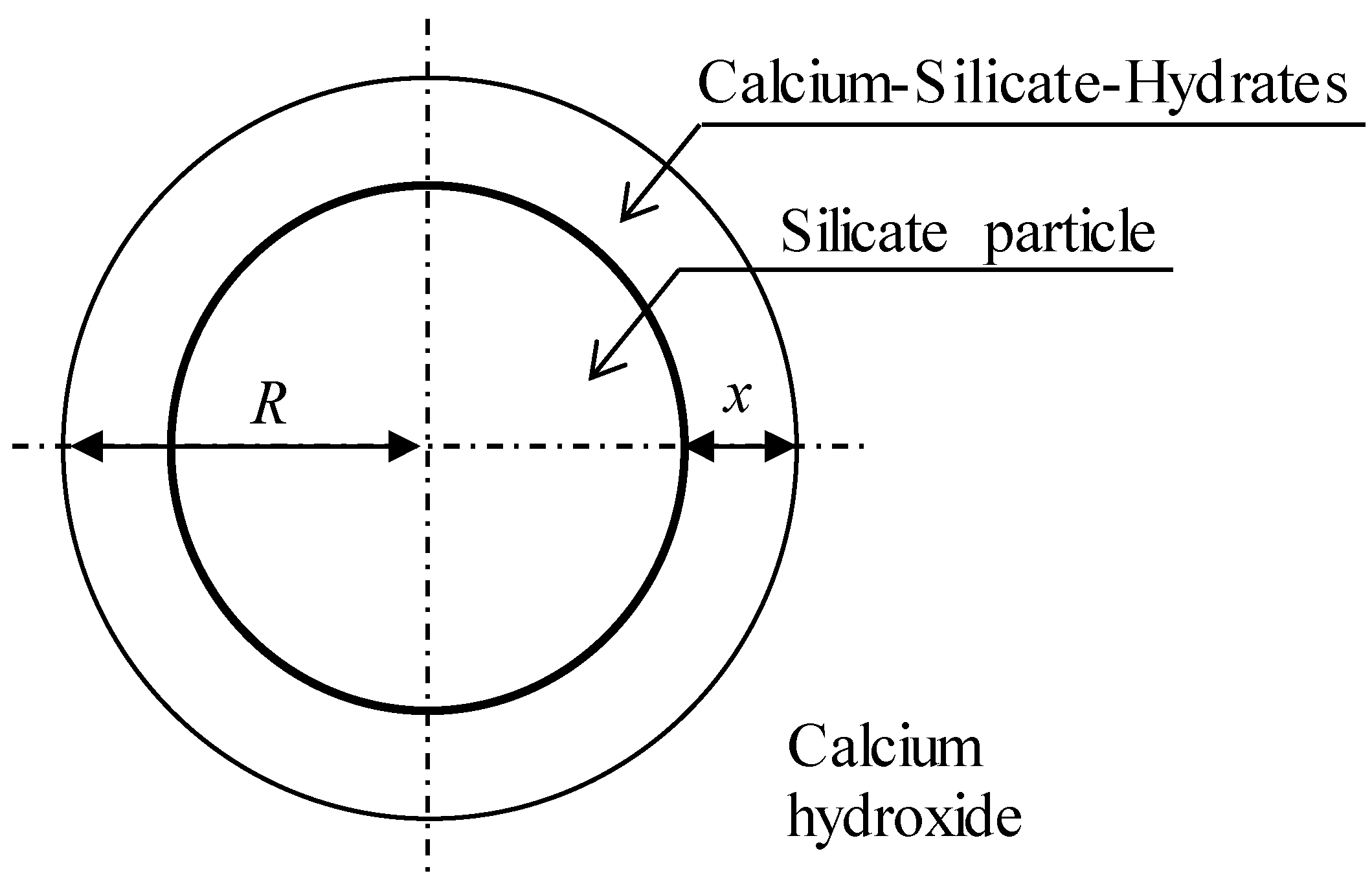
3. Experiments
3.1. Materials
| Composition | w/w (%) |
|---|---|
| C3S | 51.0 |
| C2S | 24.0 |
| C3A | 6.0 |
| C4AF | 11.0 |
3.2. 29Si MAS NMR
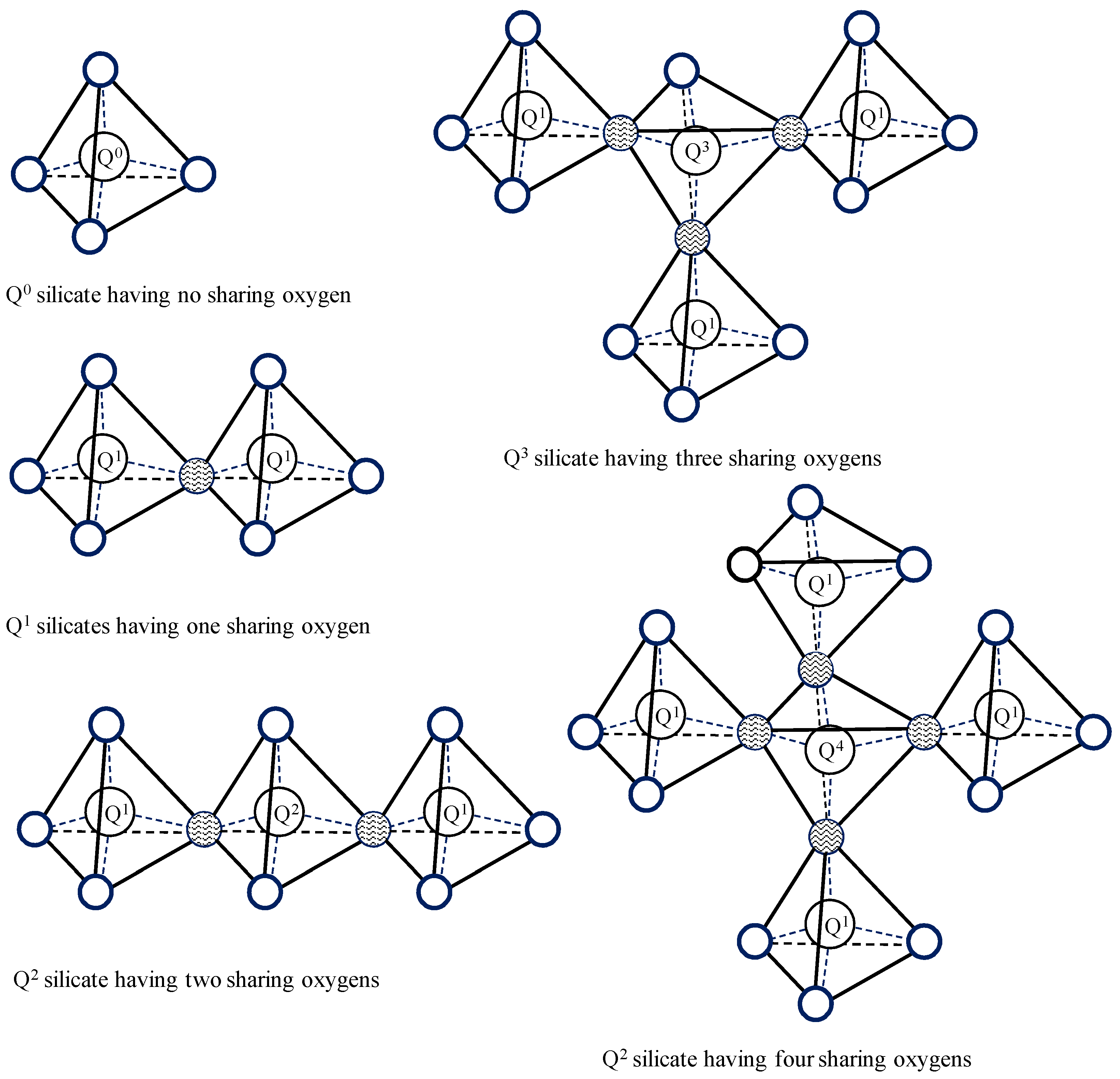

4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Full Reaction Time

4.2. The Conversion Fraction from 29Si MAS NMR Results
| Speciemns | Q0 (%) | Q1 (%) | Q2 (%) | Q3 (%) | Q4 (%) | Dc | l |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No nanosilica | 44.0 | 36.0 | 20.0 | – | – | 1.36 | 3.11 |
| 1% nanosilica | 29.6 | 39.4 | 29.5 | – | 1.5 | 1.43 | 3.50 |
| 3% nanosilica | 35.5 | 33.2 | 24.0 | – | 7.3 | 1.42 | 3.44 |


| Equation | 1% Nanosilica | 3% Nanosilica |
|---|---|---|
| Equation (7) | ||
| Equation (10) | ||
| Equation (9) | ||
4.3. The Effect of CH Concentration
| Reference Values | The Minimum CH Concentration from Equations (2) and (4) |
|---|---|
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, P.; Kirpatrick, R.J.; Poe, B.; McMillan, P.F.; Cong, X. Structure of calcium silicate hydrate (C–S–H): Near-, Mid- and Far- infrared spectroscopy. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1999, 82, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, I.G. Tobermorite/Jennite- and Tobermorite/Calcium Hydroxide-Based models for the structure of C–S–H: Applicability to hardened pastes of tricalcium silicate, β-dicalcium silicate, Portland cement, and blends of Portland cement with blast-durnace slag, Metakaolin, or silica fume. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 1733–1777. [Google Scholar]
- Korb, J.-P.; Monteilhet, L.; McDonald, P.J.; Mitchell, J. Microstructure and texture of hydrated cement-based materials: A proton field cycling relaxometry approach. Cem. Concr. Res. 2007, 37, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia Lodeiro, I.; Macphee, D.E.; Palomo, A.; Fernandez-Jimenez, A. Effect of alkalis on fresh C–S–H gels. FTIR analysis. Cem. Concr. Res. 2009, 39, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scrivener, K.; Kirkpatrick, R.J. Innovation in use and research on cementitious material. Cem. Concr. Res. 2008, 38, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, J. Recent advances in the field of cement hydration and microstructural analysis. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 666–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, H.M. A model for the microstructure of calicum silicate hydrate in cement paste. Cem. Concr. Res. 2000, 30, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, A.J.; Thomas, J.J. Analysis of C–S–H gel and cement paste by small-angle neutron scattering. Cem. Concr. Res. 2007, 37, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patural, L.; Porion, P.; van Damme, H.; Govin, A.; Grosseau, P.; Ruot, B.; Deves, O. A pulsed field gradient and NMR imaging investigations of the water retention mechanism by cellulose ethers in mortars. Cem. Concr. Res. 2010, 40, 1378–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larbi, J.A. Microstructure of the interfacial zone around aggregate particles in concrete. Heron 1993, 38, 1–69. [Google Scholar]
- Jennings, H.M.; Tennis, P.D. Model for the developing microstructure in Portland cement pastes. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1994, 77, 3161–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halim, S.C.; Brunner, T.J.; Grass, R.N.; Bohner, M.; Stark, W.J. Preparation of an ultra fast binding cement from calcium silicate-based mixed oxide nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, F.; Sobolev, K. Nanotechnology in concrete—A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 2060–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harsh, S.; Arora, A.K.; Thomas, V.; Ali, M.M. Studies on cement hydration in the presence of nanosilica. Cem. Int. 2014, 3, 74–78. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.-S.; Cho, H.-K.; Wang, X.-Y. Experimental investigation and theoretical modeling of nanosilica activity in concrete. J. Nanomater. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeWindt, L.; Deneele, D.; Maubec, N. Kinetics of lime/bentonite pozzolanic reactions at 20 and 50 °C: Batch tests and modeling. Cem. Concr. Res. 2014, 59, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Gao, H.; Scrivens, W.A.; Fei, D.; Thakur, V.; Sutton, M.A.; Reynolds, A.P.; Myrick, M.L. Structural and mechanical characterization of nanoclay-reinforced agarose nanocomposites. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 2020–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaipanich, A.; Nochaiya, T.; Wongkeo, W.; Torkittikul, P. Compressive strength and microstructure of carbon nanotubes-fly ash cement composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 1063–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, B.-W.; Kim, C.-H.; Tae, G.-H.; Park, J.-B. Characteristics of cement mortar with nano-SiO2 particles. Constr. Build. Mater. 2007, 21, 1351–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lothenbach, B.; Saout, G.L.; Gallucci, E.; Scrivener, K. Influence of limestone on the hydration of Portland cements. Cem. Concr. Res. 2008, 38, 848–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaitero, J.J.; Ibarra, Y.S.; Campillo, I. Silica nanoparticle addition to control the calcium-leaching in cement-based materials. Phys. State Solid 2006, 203, 1313–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaitero, J.J.; Campillo, I.; Guerrero, A. Reduction of the calcium leaching rate of cement paste by addition of silica nanoparticles. Cem. Concr. Res. 2008, 38, 1112–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.J.; Fan, T.; Reda Taha, M.M. Homogenization model examining the effect of nanosilica on concrete strength and stiffness. Trans. Res. Rec. 2010, 2141, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choolaei, M.; Rashidi, A.M.; Ardjmand, M.; Yadegari, A. The effect of nanosilica on the physical properties of oil well cement. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 538, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, A.; Saafi, M.; Romine, P. Temperature and moisture monitoring in concrete structures using embedded nanotechnology/microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) sensors. Constr. Build. Mater. 2008, 22, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, P. Structure and Performance of Cements; Applied Science Publishers: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Booth, F. A note on the theory of surface diffusion reactions. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1948, 44, 796–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khawam, A.; Flanagan, D.R. Solid-state kinetic models: Basic and mathematical fundamentals. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 17315–17328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.J.; Rahman, M.K.; Al-Majed, A.A.; Al-Zahrani, M.M.; Reda Taha, M.M. Nanosilica effects on composition and silicate polymerization in hardened cement paste cured under high temperature and pressure. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2013, 43, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crank, J. The Mathematics of Diffusion, 2nd ed.; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM-C305. Standard Practice for Mechanical Mixing of Hydraulic Cement Pastes and Mortars of Plastic Consistency; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Macomber, R.S. A Complete Introduction to Modern NMR Spectroscopy; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Lippmaa, E.; Mägi, M.; Samoson, A.; Engelhardt, G.; Grimmer, A.R. Structural studies of silicates by solid-state high-resolution 29Si NMR. Am. Chem. Soc. 1980, 102, 4889–4893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieker, W.; Grimmer, A.-R.; Winkler, A.; Mägi, M.; Tarmak, M.; Lippmaa, E. Solid-state high-resolution 29Si NMR spectroscopy of synthetic 14 Å, 11 Å and 9 Å tobermorites. Cem. Concr. Res. 1982, 12, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J.F. Investigations of calcium silicate hydrate structure using silicon-29 nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Am. Cerm. Soc. 1988, 71, C118–C120. [Google Scholar]
- Grutzeck, M.; Benesi, A.; Fanning, B. Silicon-29 magic-angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance study of calcium silicate hydrates. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1989, 72, 665–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saoût, G.L.; Le’colier, E.; Rivereau, A.; Zanni, H. Chemical structure of cement aged at normal and elevated temperatures and pressures, Part II: Low permeability class G oilwell cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 2006, 36, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, G.M.M.; Benstedm, J.; Glasser, F.P.; Lachowski, E.E.; Roberts, D.R.; Taylor, M.J. Study of calcium silicate hydrates by solid state high resolution 29Si nuclear magnetic resonance. Adv. Cem. Res. 1990, 3, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, X.; Kirkpatrick, R.J. 29Si MAS NMR study of the structure of calcium silicate hydrate. Adv. Cem. Based Mater. 1996, 3, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yajun, J.; Cahyadi, J.H. Simulation of silica fume blended cement hydration. Mater. Struct. 2004, 37, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monasterio, M.; Gaitero, J.J.; Erkizia, E.; Bustos, A.M.G.; Miccio, L.A.; Dolado, J.S.; Cerveny, S. Effect of addition of silica- and amine functionalized silica-nanoparticles on the microstructure of calcium silicate hydrate (C–S–H) gel. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 450, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ten, B.Y. Calculation of SiO2 diffusion coefficients based on kinetic curves of silica grain dissolution. Glass Ceram. 2004, 61, 13–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moon, J.; Taha, M.M.R.; Youm, K.-S.; Kim, J.J. Investigation of Pozzolanic Reaction in Nanosilica-Cement Blended Pastes Based on Solid-State Kinetic Models and 29Si MAS NMR. Materials 2016, 9, 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9020099
Moon J, Taha MMR, Youm K-S, Kim JJ. Investigation of Pozzolanic Reaction in Nanosilica-Cement Blended Pastes Based on Solid-State Kinetic Models and 29Si MAS NMR. Materials. 2016; 9(2):99. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9020099
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoon, Jiho, Mahmoud M. Reda Taha, Kwang-Soo Youm, and Jung J. Kim. 2016. "Investigation of Pozzolanic Reaction in Nanosilica-Cement Blended Pastes Based on Solid-State Kinetic Models and 29Si MAS NMR" Materials 9, no. 2: 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9020099
APA StyleMoon, J., Taha, M. M. R., Youm, K.-S., & Kim, J. J. (2016). Investigation of Pozzolanic Reaction in Nanosilica-Cement Blended Pastes Based on Solid-State Kinetic Models and 29Si MAS NMR. Materials, 9(2), 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9020099






