Spark Plasma Sintering of Commercial Zirconium Carbide Powders: Densification Behavior and Mechanical Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Mathematical Model of Power-Law Creep of Powder Materials
3. Experimental Procedures
3.1. Starting Powders
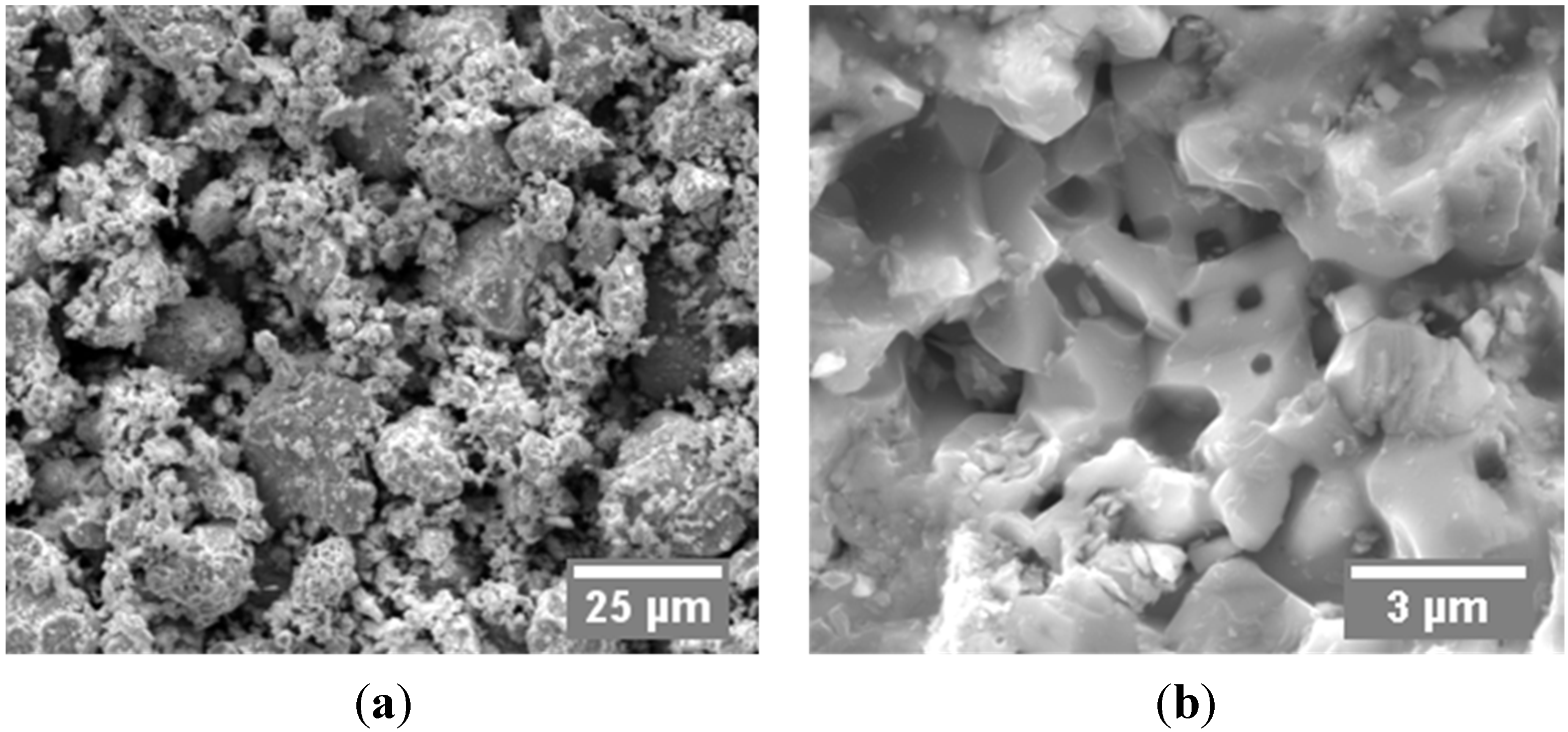
| Powder Supplier | Absolute Density (g/cm3) | Average Particle Size (µm) | Average Grain Size (µm) | Zr (at. %) | C (at. %) | O (at. %) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma Aldrich | 6.498 | 10 | <1 µm | 44.74 | 52.91 | 2.35 |
3.2. Spark Plasma Sintering Process
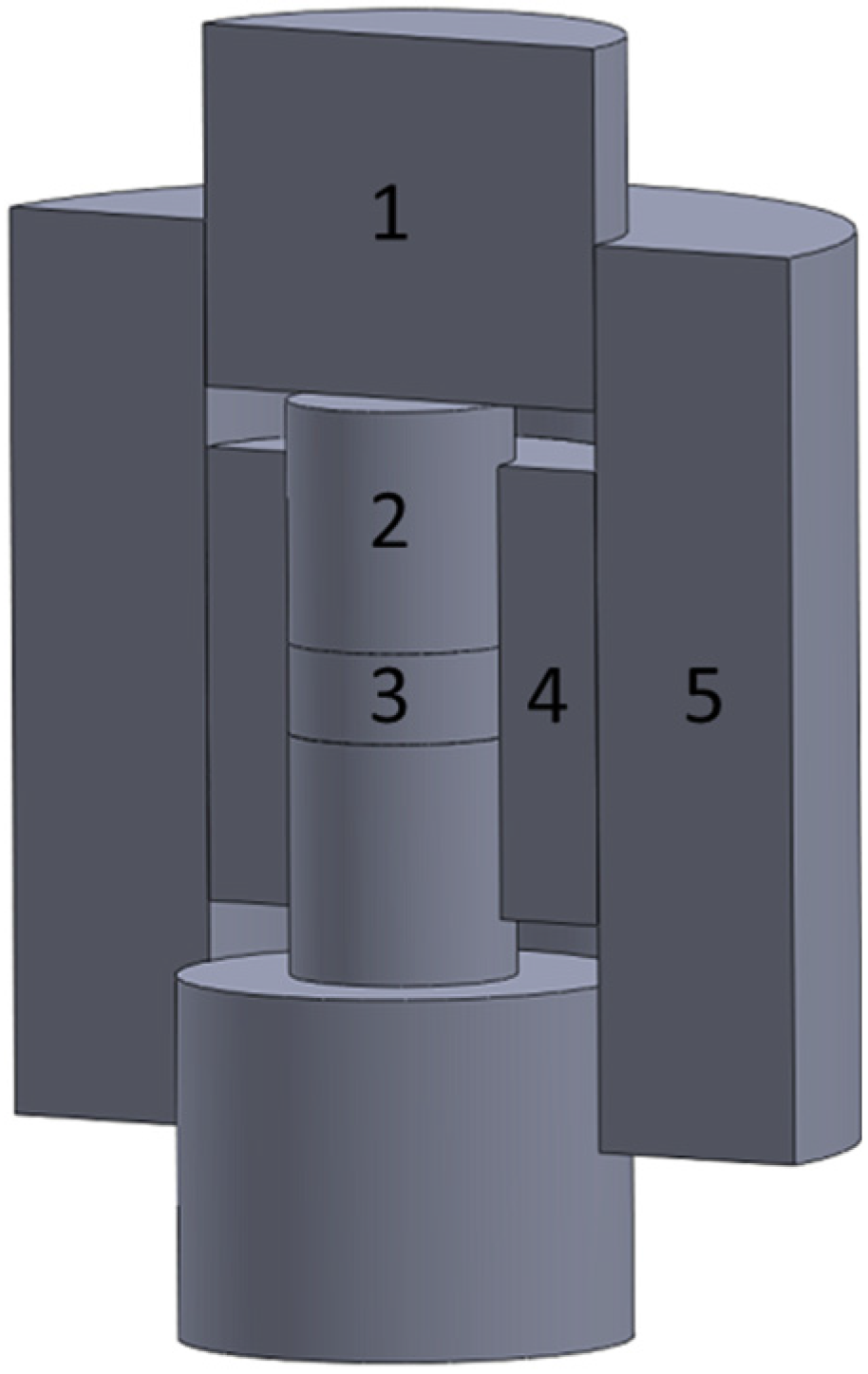
3.3. Characterization of Processed Specimens
4. Results and Discussion
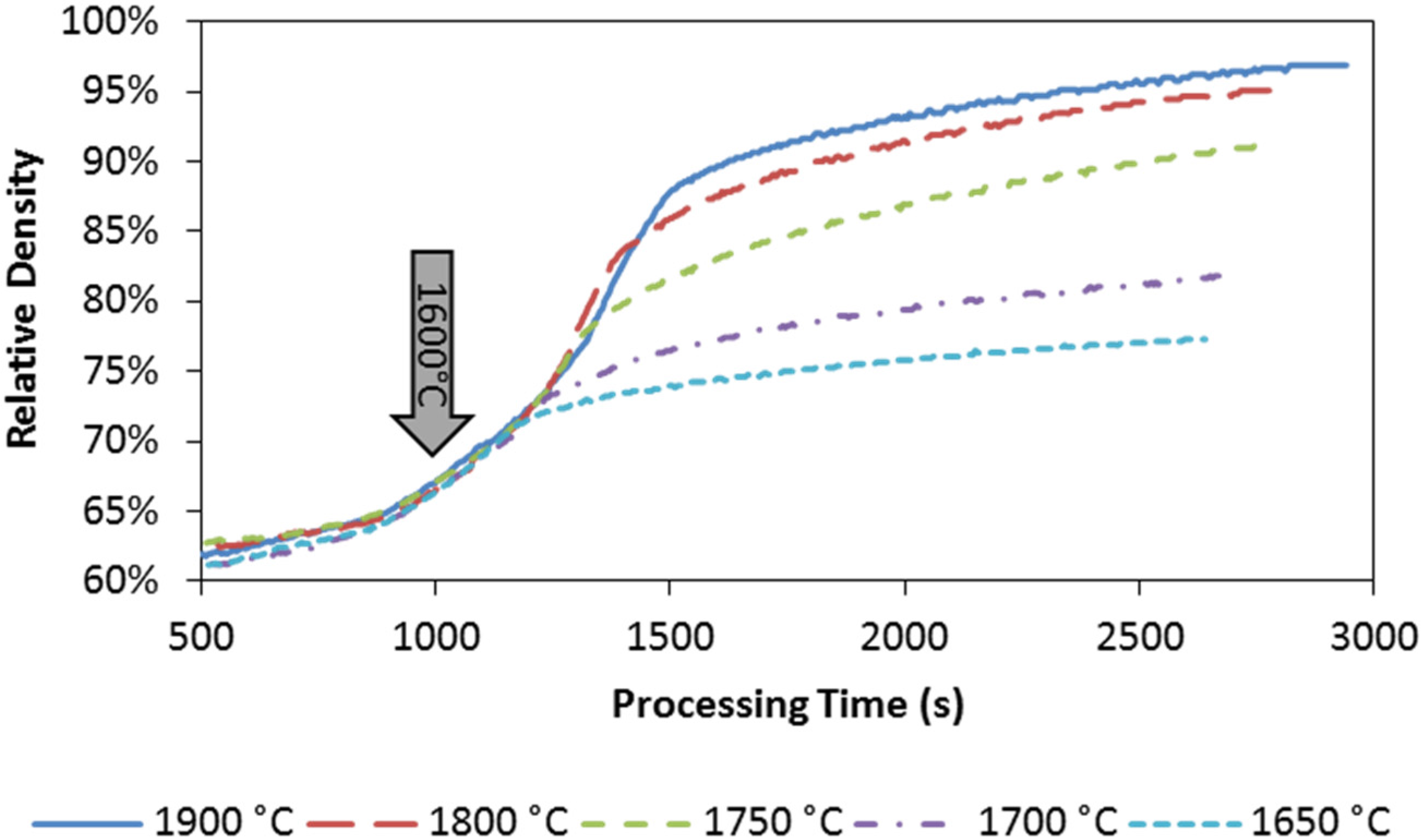
4.1. Densification Behavior and Microstructures
| Specimen # | Tooling Setup | Peak Temperature (°C) | Pressure (MPa) | Holding (min) | Initial Density | Final Density | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Archimedes | Geometry | ||||||
| 1 | Single-die | 2100 | 60 | 25 | 61.08% | 97.28% | 97.35% |
| 2 | Single-die | 1900 | 60 | 25 | 61.16% | 96.29% | 96.37% |
| 3 | Single-die | 1800 | 60 | 25 | 61.55% | 95.16% | 95.29% |
| 4 | Single-die | 1750 | 60 | 25 | 61.65% | 91.21% | 91.18% |
| 5 | Single-die | 1700 | 60 | 25 | 60.86% | 81.52% | 81.98% |
| 6 | Single-die | 1650 | 60 | 25 | 60.08% | 77.70% | 77.31% |
| 7 | Double-die | 1800 | 200 | 10 | 61.23% | 97.87% | 97.84% |
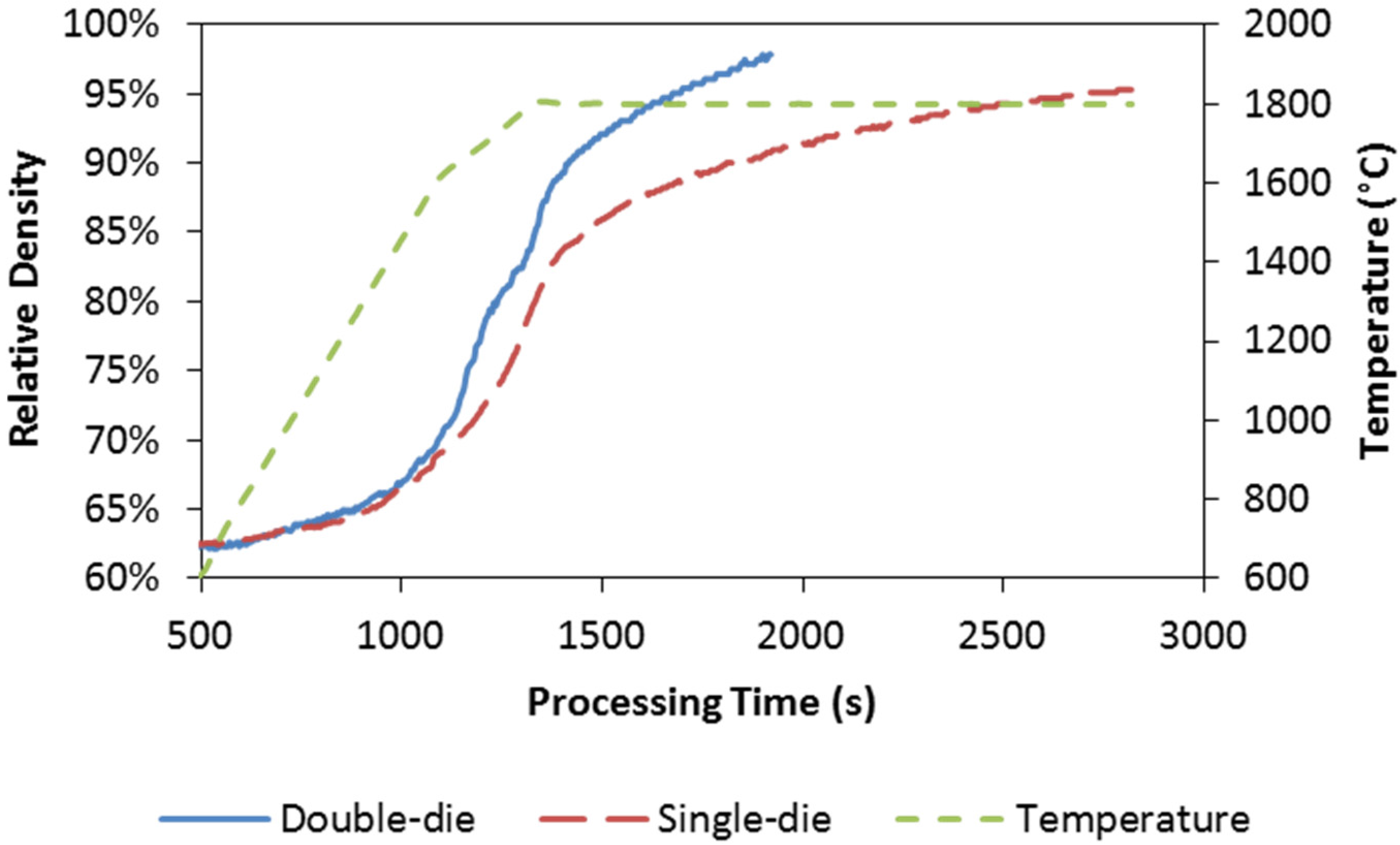
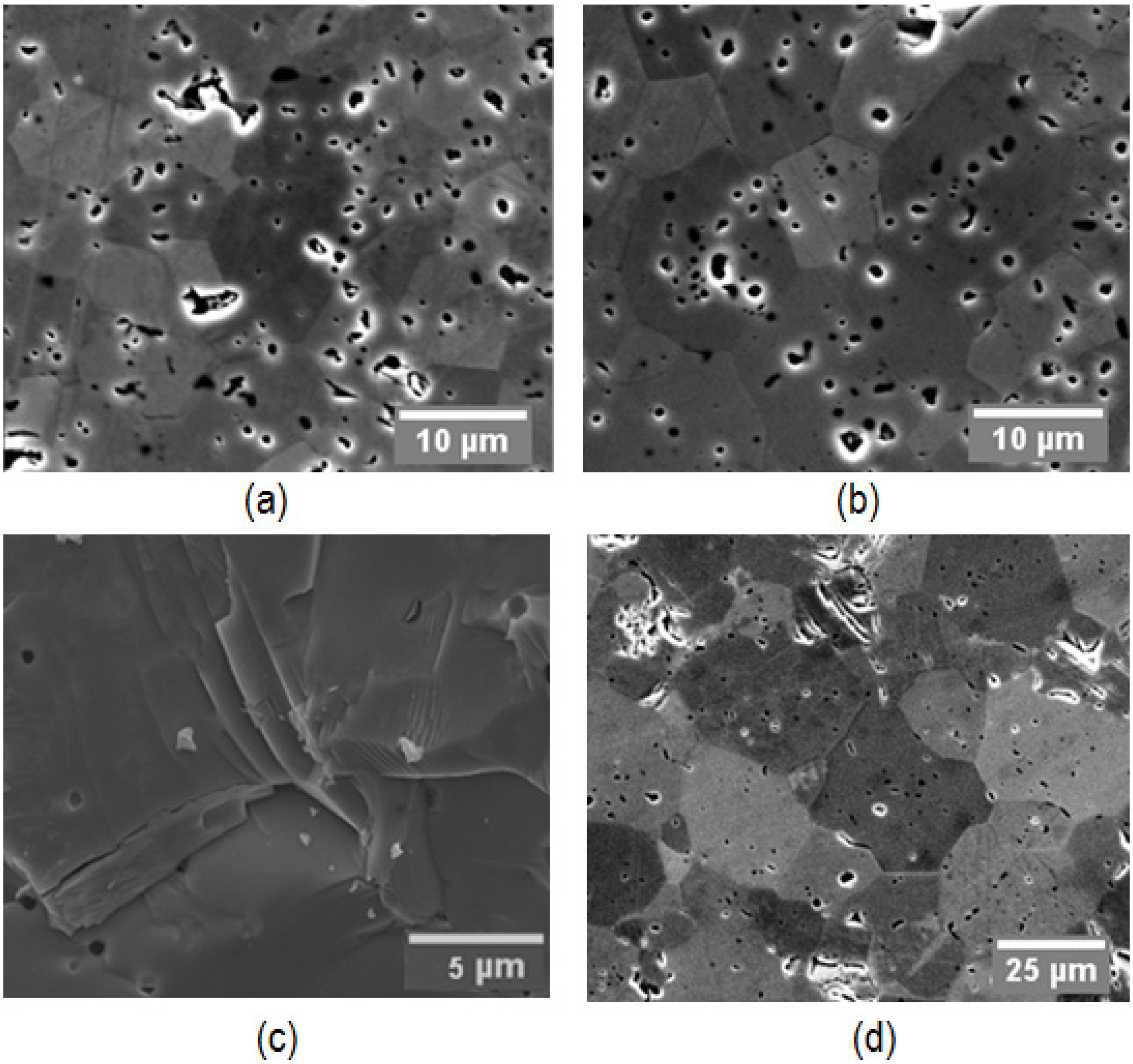
4.2. Densification Mechanism
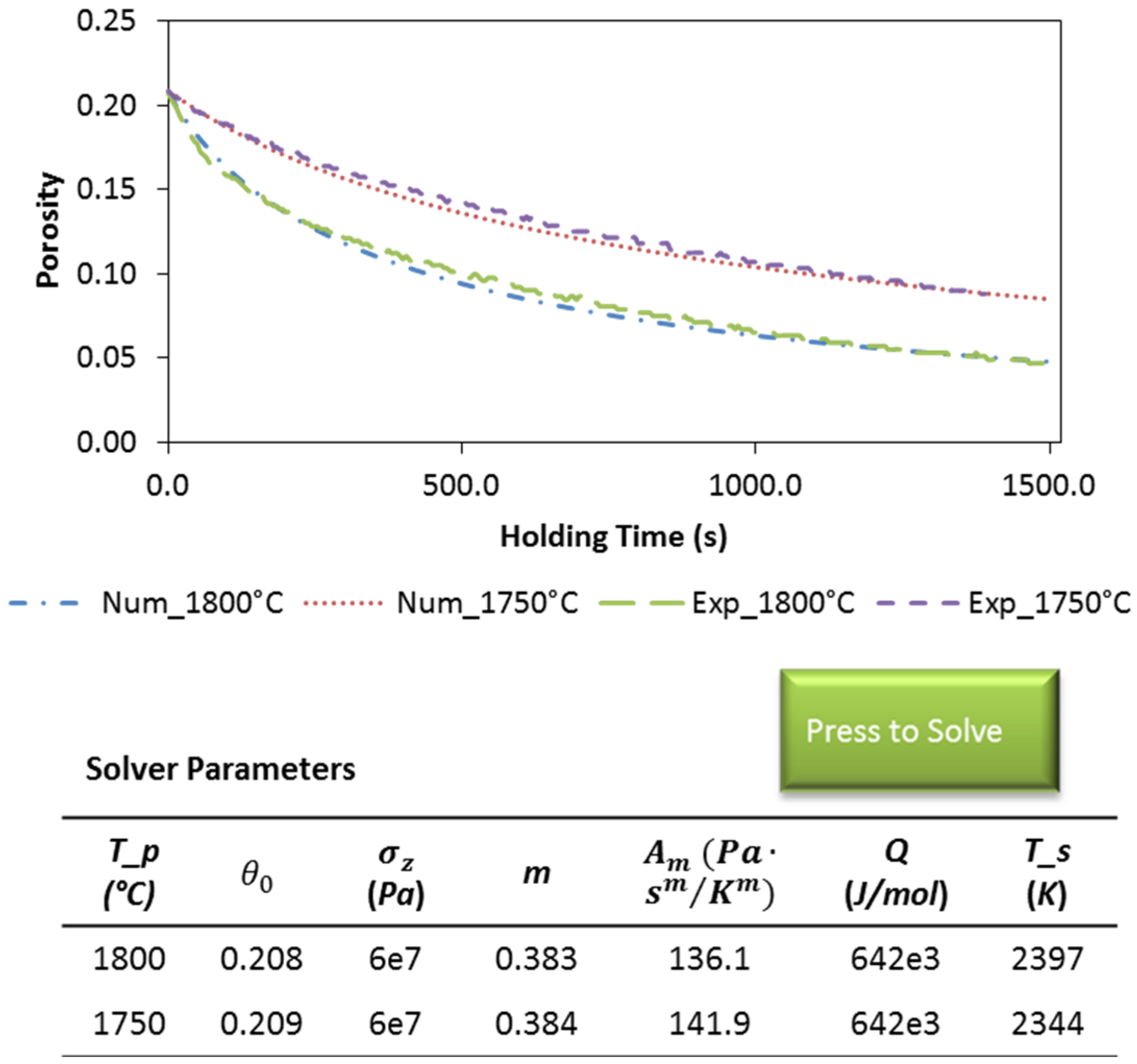
| Specimen # | Tooling Setup | Temperature (°C) | Pressure (MPa) | m | n | Q (kJ/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Single-die | 2100 | 40 | 0.379 | 2.63 | 644 |
| 2 | Single-die | 1900 | 60 | 0.381 | 2.62 | 640 |
| 3 | Single-die | 1800 | 60 | 0.383 | 2.61 | 642 |
| 4 | Single-die | 1750 | 60 | 0.384 | 2.60 | 642 |
| 7 | Double-die | 1800 | 200 | 0.412 | 2.43 | 643 |
4.3. Transverse Rupture Strength of the Specimens Processed by SPS
| Specimen # | Tooling Setup | Temperature (°C) | Relative Density | Ave. Grain Size (µm) | TRS (MPa) | HV (GPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Single-die | 2100 | 97.28% | 30.92 | 378.8 | 23.66 |
| 2 | Single-die | 1900 | 96.29% | 14.60 | 319.8 | 22.87 |
| 3 | Single-die | 1800 | 95.16% | 11.42 | 270.1 | 21.29 |
| 4 | Single-die | 1750 | 91.21% | 7.34 | 214.6 | 18.01 |
| 5 | Single-die | 1700 | 81.52% | 5.12 | 154.8 | 11.56 |
| 6 | Single-die | 1650 | 77.70% | 2.58 | 150.3 | 7.90 |
| 7 | Double-die | 1800 | 97.87% | 37.08 | N.A. | 24.68 |

4.4. Microhardness of the Specimens Processed by SPS

5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gendre, M.; Maître, A.; Trolliard, G. A study of the densification mechanisms during spark plasma sintering of zirconium (oxy-)carbide powders. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 2598–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.J.; Lee, Y.W.; Cha, S.I.; Hong, S.H. Sintering behaviour and microstructures of carbides and nitrides for the inert matrix fuel by spark plasma sintering. J. Nucl. Mater. 2006, 352, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, Y.; Vasudevamurthy, G.; Nozawa, T.; Snead, L.L. Properties of zirconium carbide for nuclear fuel applications. J. Nucl. Mater. 2013, 441, 718–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gendre, M.; Maître, A.; Trolliard, G. Synthesis of zirconium oxycarbide (ZrCxOy) powders: Influence of stoichiometry on densification kinetics during spark plasma sintering and on mechanical properties. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2011, 31, 2377–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulychev, V.P.; Andrievskii, R.A.; Nezhevenko, L.B. The sintering of zirconium carbide. Sov. Powder Metall. Met. Ceram. 1977, 16, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spivak, I.I.; Klimenko, V.V. Densification kinetics in the hot pressing and recrystallization of carbides. Sov. Powder Metall. Met. Ceram. 1973, 12, 883–887. [Google Scholar]
- Barnier, P.; Brodhag, C.; Thevenot, F. Hot-pressing kinetics of zirconium carbide. J. Mater. Sci. 1986, 21, 2547–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-G.; Guo, W.-M.; Kan, Y.-M.; Zhang, G.-J.; Wang, P.-L. Densification behavior and properties of hot-pressed ZrC ceramics with Zr and graphite additives. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2011, 31, 1103–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minhaga, E.; Scott, W.D. Sintering and mechanical-properties of ZrC-ZrO2 composites. J. Mater. Sci. 1988, 23, 2865–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachiappan, C.; Rangaraj, L.; Divakar, C.; Jayaram, V. Synthesis and densification of monolithic zirconium carbide by reactive hot pressing. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2010, 93, 1341–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, Z.A.; Anselmi-Tamburini, U.; Ohyanagi, M. The effect of electric field and pressure on the synthesis and consolidation of materials: A review of the spark plasma sintering method. J. Mater. Sci. 2006, 41, 763–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orru, R.; Licheri, R.; Locci, A.M.; Cincotti, A.; Cao, G.C. Consolidation/synthesis of materials by electric current activated/assisted sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 2009, 63, 127–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olevsky, E.; Aleksandrova, E.; Ilyina, A.; Dudina, D.; Novoselov, A.; Pelve, K.; Grigoryev, E. Outside mainstream electronic databases: Review of studies conducted in the USSR and post-soviet countries on electric current-assisted consolidation of powder materials. Materials 2013, 6, 4375–4440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurlova, M.S.; Demenyuk, V.D.; Lebedeva, L.Y.; Dudina, D.V.; Grigoryev, E.G.; Olevsky, E.A. Electric pulse consolidation: an alternative to spark plasma sintering. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 952–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciti, D.; Guicciardi, S.; Nygren, M. Spark plasma sintering and mechanical behaviour of ZrC-based composites. Scr. Mater. 2008, 59, 638–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez-González, B.; Ortiz, A.L.; Guiberteau, F.; Nygren, M.; Shaw, L. Improvement of the Spark-Plasma-Sintering Kinetics of ZrC by High-Energy Ball-Milling. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2012, 95, 453–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Fu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Lee, S.W.; Niihara, K. Synthesis of nanosized zirconium carbide powders by a combinational method of sol-gel and pulse current heating. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2014, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaim, R. Densification mechanisms in spark plasma sintering of nanocrystalline ceramics. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 443, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olevsky, E.; Kandukuri, S.; Froyen, L. Analysis of mechanisms of spark-plasma sintering. Key Eng. Mater. 2008, 368–372, 1580–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olevsky, E.; Froyen, L. Constitutive modeling of spark-plasma sintering of conductive materials. Scr. Mater. 2006, 55, 1175–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groza, J.R.; Zavaliangos, A. Sintering activation by external electrical field. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2000, 287, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olevsky, E.A.; Kandukuri, S.; Froyen, L. Consolidation enhancement in spark-plasma sintering: Impact of high heating rates. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olevsky, E.A.; Froyen, L. Impact of thermal diffusion on densification during SPS. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2009, 92, S122–S132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuntini, D.; Wei, X.; Maximenko, A.L.; Wei, L.; Ilyina, A.M.; Olevsky, E.A. Initial stage of free pressureless spark-plasma sintering of vanadium carbide: Determination of surface diffusion parameters. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2013, 41, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard-Granger, G.; Guizard, C. Spark plasma sintering of a commercially available granulated zirconia powder: I. Sintering path and hypotheses about the mechanism(s) controlling densification. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 3493–3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Olevsky, E.A.; McKittrick, J.; Maximenko, A.L.; German, R.M. Densification mechanisms of spark plasma sintering: Multi-step pressure dilatometry. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 7036–7046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helle, A.S.; Easterling, K.E.; Ashby, M.F. Hot-isostatic pressing diagrams—New developments. Acta Metall. 1985, 33, 2163–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, D.S.; Ashby, M.F. Pressure sintering by power law creep. Acta Metall. 1975, 23, 1277–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabarro, F.R.N. Do we have an acceptable model of power-law creep? Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 387–389, 659–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olevsky, E.A. Theory of sintering: From discrete to continuum. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 1998, 23, 41–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olevsky, E.A.; Garcia-Cardona, C.; Bradbury, W.L.; Haines, C.D.; Martin, D.G.; Kapoor, D.; Kang, S.J. Fundamental aspects of spark plasma sintering: II. Finite element analysis of scalability. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2012, 95, 2414–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olevsky, E.; Rein, R. Kinetics of sintering for powder systems with bimodal pore-size distribution. High Temp. High Press. 1995, 27/28, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Jia, D.; Duan, X.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, Y. Pressureless sintering of ZrC-based ceramics by enhancing powder sinterability. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2011, 29, 516–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olevsky, E.A.; Bradbury, W.L.; Haines, C.D.; Martin, D.G.; Kapoor, D.; Kang, S.J. Fundamental aspects of spark plasma sintering: I. Experimental analysis of scalability. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2012, 95, 2406–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselmi-Tamburini, U.; Garay, J.E.; Munir, Z.A. Fast low-temperature consolidation of bulk nanometric ceramic materials. Scr. Mater. 2006, 54, 823–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaleghi, E.; Lin, Y.S.; Meyers, M.A.; Olevsky, E.A. Spark plasma sintering of tantalum carbide. Scr. Mater. 2010, 63, 577–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Olevsky, E.A.; Khasanov, O.L.; Back, C.A.; Izhvanov, O.; Opperman, J.; Khalifa, H.E. Spark plasma sintering of agglomerated vanadium carbide powder. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 3748–3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antou, G.; Mathieu, G.; Trolliard, G.; Maître, A. Spark plasma sintering of zirconium carbide and oxycarbide: Finite element modeling of current density, temperature, and stress distributions. J. Mater. Res. 2011, 24, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuntini, D.; Olevsky, E.A.; Garcia-Cardona, C.; Maximenko, A.L.; Yurlova, M.S.; Haines, C.D.; Martin, D.G.; Kapoor, D. Localized overheating phenomena and optimization of spark-plasma sintering tooling design. Materials 2013, 6, 2612–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Giuntini, D.; Maximenko, A.L.; Haines, C.D.; Olevsky, E.A. Experimental investigation of electric contact resistance in spark plasma sintering tooling setup. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herring, C. Diffusional viscosity of a polycrystalline solid. J. Appl. Phys. 1950, 21, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabarro, F.R.N. Steady-state diffusional creep. Philos. Mag. 1967, 16, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gifkins, R.C. Grain-boundary sliding and its accommodation during creep and superplasticity. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1976, 7, 1225–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weertman, J. Steady-state creep of crystals. J. Appl. Phys. 1957, 28, 1185–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weertman, J. Theory of steady-state creep based on dislocation climb. J. Appl. Phys. 1955, 26, 1213–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weertman, J. Steady-state creep through dislocation climb. J. Appl. Phys. 1957, 28, 362–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, J.P.; Graeve, O.A. Mechanisms of pore formation in high-temperature carbides: Case study of TaC prepared by spark plasma sintering. Acta Mater. 2015, 84, 472–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, M.A.; Chawla, K.K. Mechanical Behavior of Materials; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Balshin, M.Y. Relation of mechanical properties of powder metals and their porosity and the ultimate properties of porous-metal ceramic materials. Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR 1949, 67, 831–834. [Google Scholar]
- Libardi, S.; Zadra, M.; Casari, F.; Molinari, A. Mechanical properties of nanostructured and ultrafine-grained iron alloys produced by spark plasma sintering of ball milled powders. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 478, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Stevens, R. Porosity-dependence of elastic moduli and hardness of 3Y-TZP ceramics. Ceram. Int. 1999, 25, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milman, Y.V.; Chugunova, S.I.; Goncharova, I.V.; Chudoba, T.; Lojkowski, W.; Gooch, W. Temperature dependence of hardness in silicon-carbide ceramics with different porosity. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 1999, 17, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, X.; Back, C.; Izhvanov, O.; Khasanov, O.L.; Haines, C.D.; Olevsky, E.A. Spark Plasma Sintering of Commercial Zirconium Carbide Powders: Densification Behavior and Mechanical Properties. Materials 2015, 8, 6043-6061. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma8095289
Wei X, Back C, Izhvanov O, Khasanov OL, Haines CD, Olevsky EA. Spark Plasma Sintering of Commercial Zirconium Carbide Powders: Densification Behavior and Mechanical Properties. Materials. 2015; 8(9):6043-6061. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma8095289
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Xialu, Christina Back, Oleg Izhvanov, Oleg L. Khasanov, Christopher D. Haines, and Eugene A. Olevsky. 2015. "Spark Plasma Sintering of Commercial Zirconium Carbide Powders: Densification Behavior and Mechanical Properties" Materials 8, no. 9: 6043-6061. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma8095289
APA StyleWei, X., Back, C., Izhvanov, O., Khasanov, O. L., Haines, C. D., & Olevsky, E. A. (2015). Spark Plasma Sintering of Commercial Zirconium Carbide Powders: Densification Behavior and Mechanical Properties. Materials, 8(9), 6043-6061. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma8095289









