Graphene-Based Materials for Stem Cell Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Graphene and Graphene Oxide
| Material | Model | Maximum Dose (μg/mL) | Safe Dose (μg/mL) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Graphene | Monkey renal cells | 300 | <50 | [59] |
| GO | Neuroblastoma | 100 | <80 | [60] |
| Human retinal pigment epithelium cells | 100 | <100 | [61] | |
| Red blood cells | 75 | <75 | [62] | |
| Human fibroblast | 100 | <50 | [63] | |
| Human alveolar basal epithelial cells | 200 | <200 | [64] | |
| Mouse embryonic fibroblast | 1000 | <1000 | [65] |
2.1. Enhancing Osteogenesis with Graphene/Graphene Oxide
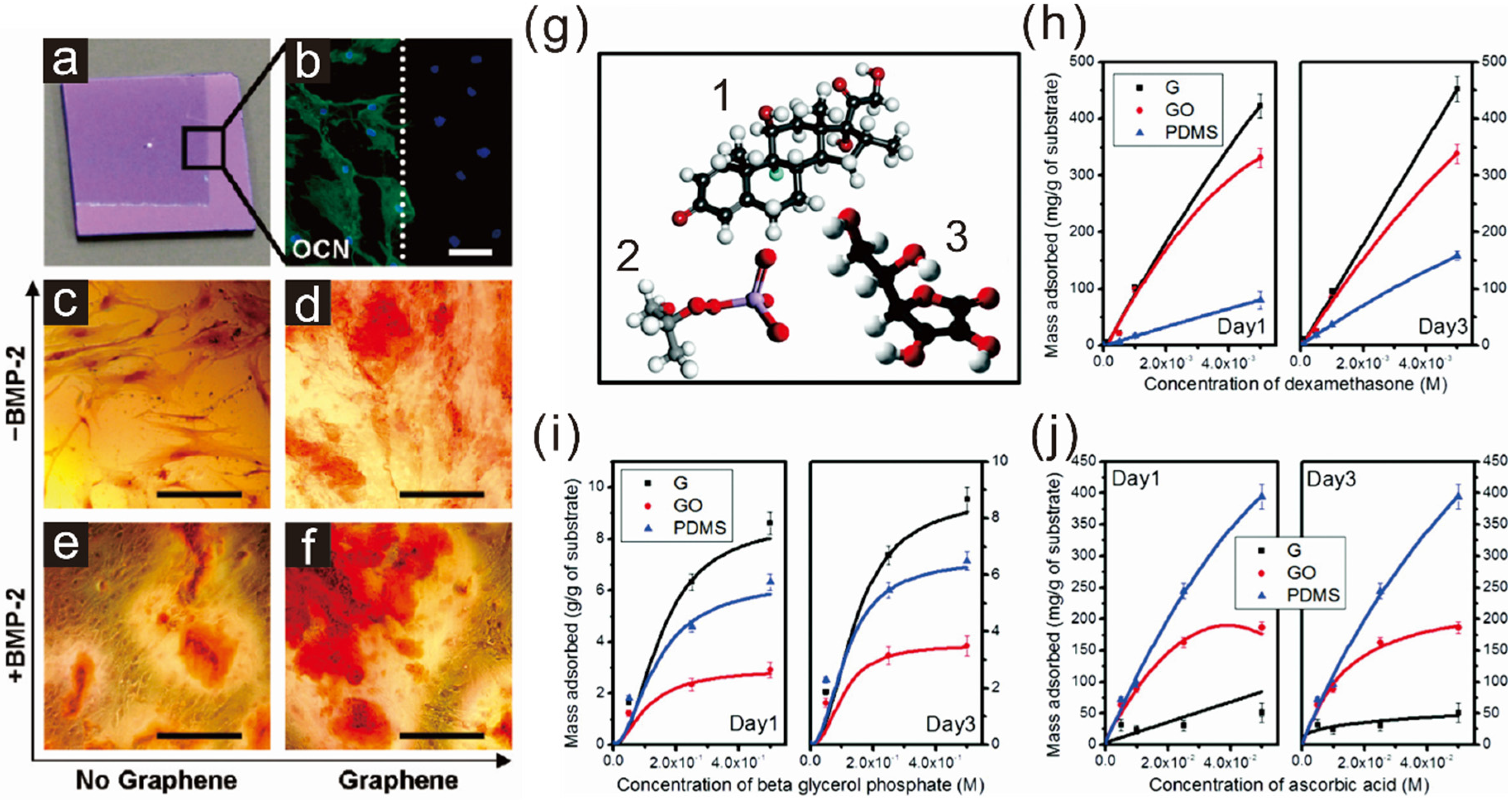
2.2. Enhancing Neurogenesis by Graphene/Graphene Oxide
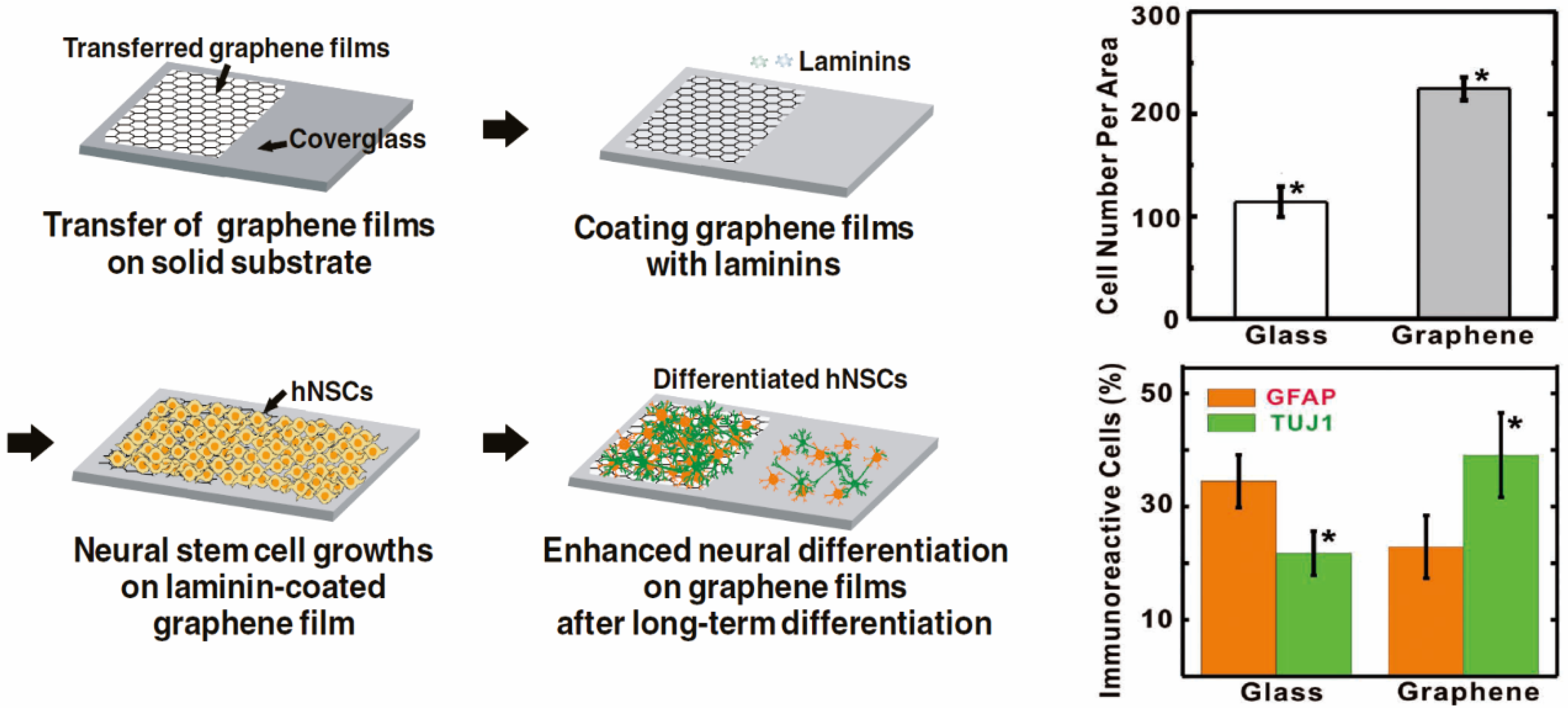
3. Graphene-Based Scaffold Materials
3.1. Graphene Polymer Scaffolds for Guiding Stem Cell Differentiation
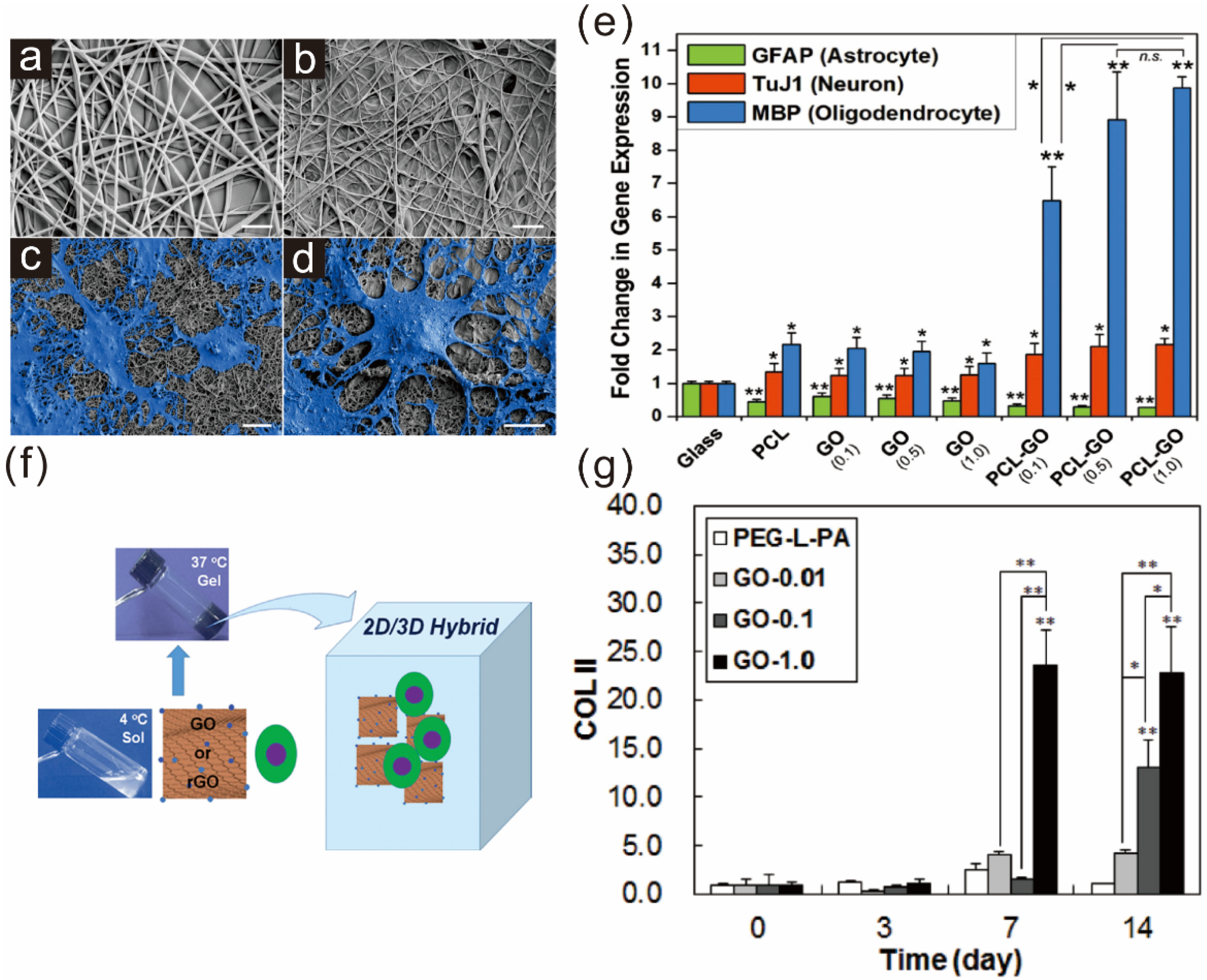
3.2. Graphene as a Biocompatible Material for Stable Stem Cell Growth and Implantation
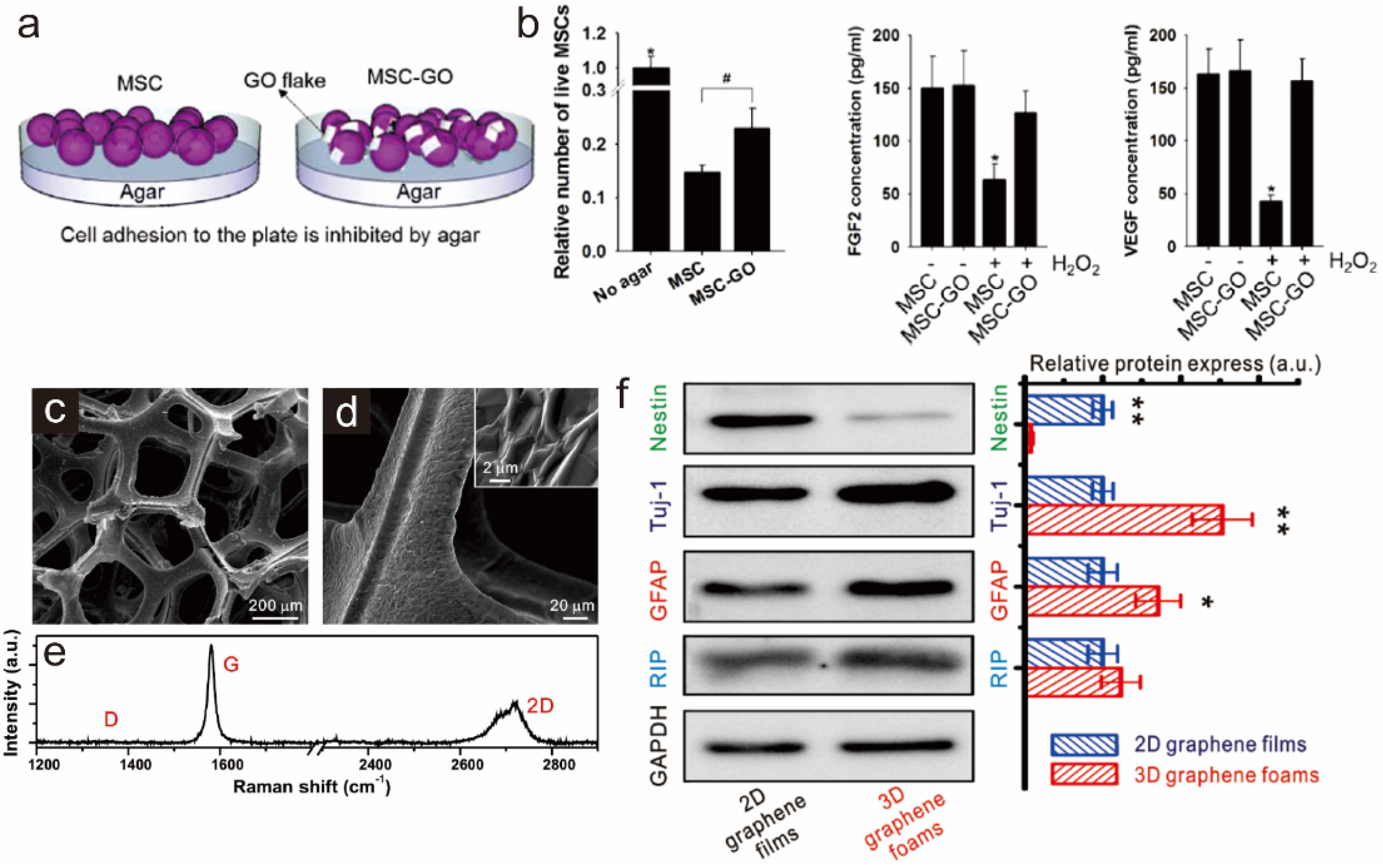
4. Graphene Patterns
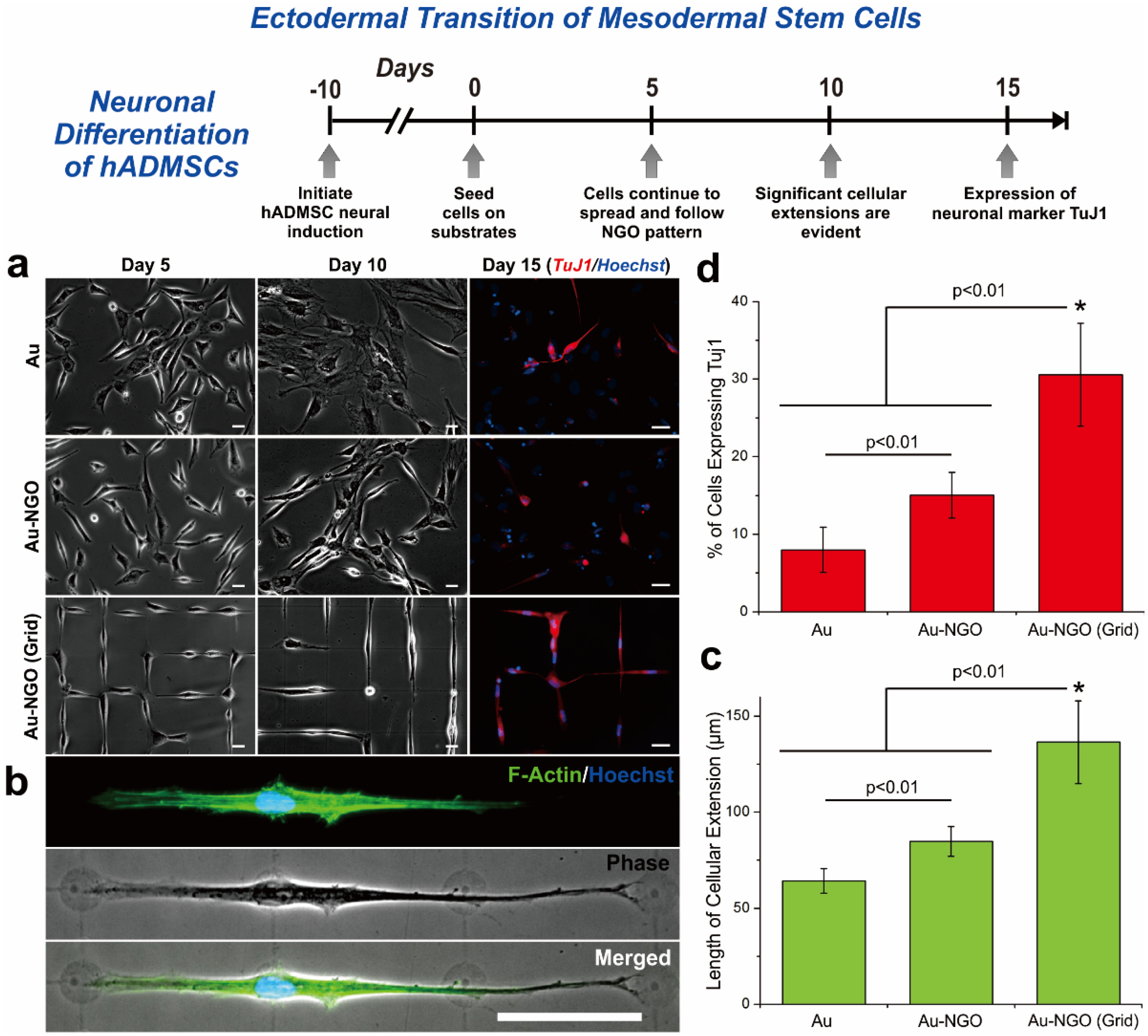
5. Graphene-Based Hybrid Nanoparticles
5.1. Graphene-Embedded Hybrid Nanoparticles for Guiding Stem Cell Growth
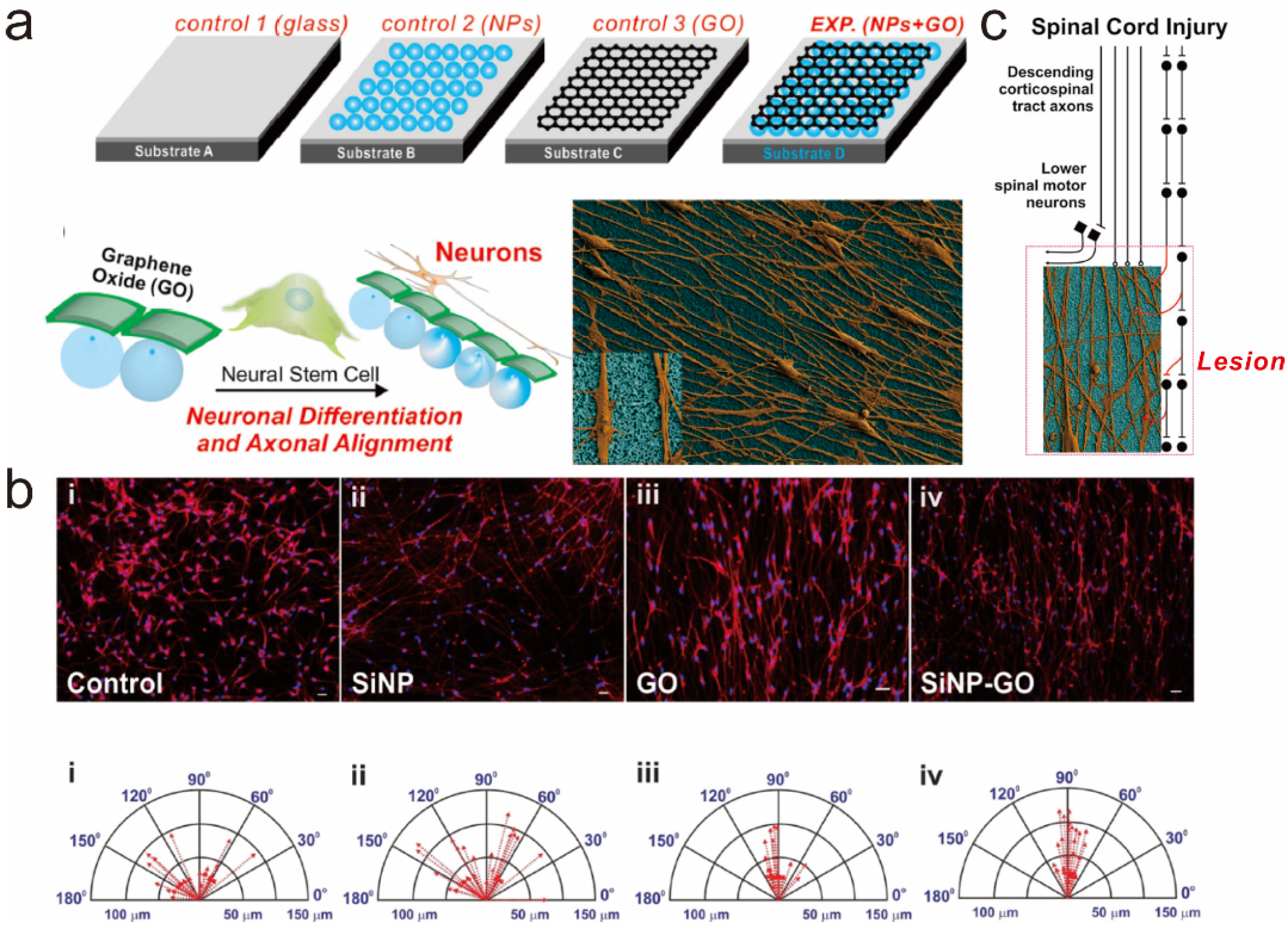
5.2. Graphene Hybrid Gold Nanoparticles for Monitoring Stem Cell Differentiation

6. Conclusions and Remarks
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Geim, A.K.; Novoselov, K.S. The rise of graphene. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.H.; Niu, L.Y.; Zheng, Z.J.; Yan, F. Photosensitive graphene transistors. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 5239–5273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stankovich, S.; Dikin, D.A.; Dommett, G.H.B.; Kohlhaas, K.M.; Zimney, E.J.; Stach, E.A.; Piner, R.D.; Nguyen, S.T.; Ruoff, R.S. Graphene-based composite materials. Nature 2006, 442, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balandin, A.A.; Ghosh, S.; Bao, W.Z.; Calizo, I.; Teweldebrhan, D.; Miao, F.; Lau, C.N. Superior thermal conductivity of single-layer graphene. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 902–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Navarro, C.; Weitz, R.T.; Bittner, A.M.; Scolari, M.; Mews, A.; Burghard, M.; Kern, K. Electronic transport properties of individual chemically reduced graphene oxide sheets. Nano Lett 2007, 7, 3499–3503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.; Wei, X.D.; Kysar, J.W.; Hone, J. Measurement of the elastic properties and intrinsic strength of monolayer graphene. Science 2008, 321, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parlak, O.; Turner, A.P.F.; Tiwari, A. On/off-switchable zipper-like bioelectronics on a graphene interface. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 482–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoller, M.D.; Park, S.J.; Zhu, Y.W.; An, J.H.; Ruoff, R.S. Graphene-based ultracapacitors. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 3498–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, C.; Kim, Y.K.; Shin, D.; Ryoo, S.R.; Hong, B.H.; Min, D.H. Biomedical applications of graphene and graphene oxide. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 2211–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.Q.; Li, Y.Y.; Yu, J.H.; Song, Y.Y.; Cai, X.J.; Liu, J.Q.; Zhang, J.M.; Ewing, R.C.; Shi, D.L. A versatile multicomponent assembly via-cyclodextrin hostguest chemistry on graphene for biomedical applications. Small 2013, 9, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Shi, Z.Q.; Ma, L.; Cheng, C.; Nie, C.X.; Zhou, M.; Zhao, C.S. Graphene oxide based heparin-mimicking and hemocompatible polymeric hydrogels for versatile biomedical applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 592–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Bae, J.W.; Thi, T.T.H.; Park, K.M.; Park, K.D. Injectable and mechanically robust 4-arm PPO-PEO/graphene oxide composite hydrogels for biomedical applications. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 8876–8879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Dang, Z.H.; Wang, Y.Y.; Huang, J.; Li, H. Hydroxyapatite/graphene-nanosheet composite coatings deposited by vacuum cold spraying for biomedical applications: Inherited nanostructures and enhanced properties. Carbon 2014, 67, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Singh, M.K.; Kulkarni, P.P.; Sonkar, V.K.; Gracio, J.J.A.; Dash, D. Amine-modified graphene. Thrombo-protective safer alternative to graphene oxide for biomedical applications. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 2731–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turcheniuk, K.; Boukherroub, R.; Szunerits, S. Gold-graphene nanocomposites for sensing and biomedical applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 4301–4324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Nayak, T.R.; Hong, H.; Cai, W.B. Graphene: A versatile nanoplatform for biomedical applications. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 3833–3842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, H.; Cao, T.; Gomes, J.V.; Neto, A.H.C.; Rosa, V. Two and three-dimensional graphene substrates to magnify osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells. Carbon 2015, 93, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Park, J.B.; Lee, T.J.; Ryu, S.; Bhang, S.H.; La, W.G.; Noh, M.K.; Hong, B.H.; Kim, B.S. Covalent conjugation of mechanically stiff graphene oxide flakes to three-dimensional collagen scaffolds for osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Carbon 2015, 83, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.H.; Bhang, S.H.; Kim, T.; Yu, T.; Hyeon, T.; Kim, B.S. Dual roles of graphene oxide in chondrogenic differentiation of adult stem cells: Cell-adhesion substrate and growth factor-delivery carrier. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 6455–6464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatavarty, R.; Ding, H.; Lu, G.J.; Taylor, R.J.; Bi, X.H. Synergistic acceleration in the osteogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells by graphene oxide-calcium phosphate nanocomposites. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 8484–8487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhavan, O.; Ghaderi, E.; Abouei, E.; Hatamie, S.; Ghasemi, E. Accelerated differentiation of neural stem cells into neurons on ginseng-reduced graphene oxide sheets. Carbon 2014, 66, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, S.; Kim, B.S. Culture of neural cells and stem cells on graphene. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2013, 10, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, Y.R.; Kim, Y.; Lim, K.T.; Seonwoo, H.; Park, S.; Cho, S.P.; Hong, B.H.; Choung, P.H.; Chung, T.D.; et al. Graphene-incorporated chitosan substrata for adhesion and differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Afrin, F.; Tripathi, R.P.; Gangenahalli, G. Transgene expression study of CXCR4 active mutants potential prospects in up-modulation of homing and engraftment efficiency of hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2014, 8, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shetty, P.; Thakur, A.M.; Viswanathan, C. Dopaminergic cells, derived from a high efficiency differentiation protocol from umbilical cord derived mesenchymal stem cells, alleviate symptoms in a parkinson's disease rodent model. Cell Biol. Int. 2013, 37, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parte, S.; Bhartiya, D.; Telang, J.; Daithankar, V.; Salvi, V.; Zaveri, K.; Hinduja, I. Detection, characterization, and spontaneous differentiation in vitro of very small embryonic-like putative stem cells in adult mammalian ovary. Stem Cells Dev. 2011, 20, 1451–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lequeux, C.; Oni, G.; Mojallal, A.; Damour, O.; Brown, S.A. Adipose derived stem cells: Efficiency, toxicity, stability of brdu labeling and effects on self-renewal and adipose differentiation. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2011, 351, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.A.; Emmert, M.R.; Marshall, A.G.; Ji, Y.J.; Conrad, C.A.; Priebe, W.; Colman, H.; Lang, F.F.; Madden, T.L. Induced phenotypic differentiation of glioblastoma stem cells revisited-detection of glycomic response based on metabolic labeling. Neuro Oncol. 2010, 12, 119–127. [Google Scholar]
- La Rocca, G.; Anzalone, R.; Corrao, S.; Magno, F.; Loria, T.; Lo Iacono, M.; Di Stefano, A.; Giannuzzi, P.; Marasa, L.; Cappello, F.; et al. Isolation and characterization of Oct-4+/HLA-G+ mesenchymal stem cells from human umbilical cord matrix: Differentiation potential and detection of new markers. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2009, 131, 267–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenner, S.; Whiting-Theobald, N.L.; Malech, H.L. Relationship between length of cell culture, cell division, transduction efficiency and engraftment in NOD/SCID mice of human mobilized CD34+ peripheral blood stem cells. Blood 2002, 100, 184A. [Google Scholar]
- Reubinoff, B.E.; Pera, M.F.; Fong, C.Y.; Trounson, A.; Bongso, A. Embryonic stem cell lines from human blastocysts: Somatic differentiation in vitro. Nat. Biotechnol. 2000, 18, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lowell, S.; Jones, P.; Le Roux, I.; Dunne, J.; Watt, F.M. Stimulation of human epidermal differentiation by delta-notch signalling at the boundaries of stem-cell clusters. Curr. Biol. 2000, 10, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Peng, R.; Ding, J.D. Cell-material interactions revealed via material techniques of surface patterning. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 5257–5286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Song, W.; Kawazoe, N.; Chen, G. The osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by controlled cell-cell interaction on micropatterned surfaces. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2013, 101, 3388–3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.; Kawazoe, N.; Chen, G.P. Dependence of spreading and differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells on micropatterned surface area. J. Nanomater. 2011, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, C.Y.; Yu, H.Y.; Pal, M.; Leong, W.S.; Tan, N.S.; Ng, K.W.; Leong, D.T.; Tan, L.P. Micropatterned matrix directs differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells towards myocardial lineage. Exp. Cell Res. 2010, 316, 1159–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solanki, A.; Shah, S.; Memoli, K.A.; Park, S.Y.; Hong, S.; Lee, K.B. Controlling differentiation of neural stem cells using extracellular matrix protein patterns. Small 2010, 6, 2509–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilian, K.A.; Bugarija, B.; Lahn, B.T.; Mrksich, M. Geometric cues for directing the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 4872–4877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; McBeath, R.; Chen, C.S. Stem cell shape regulates a chondrogenic versus myogenic fate through RAC1 and n-cadherin. Stem Cells 2010, 28, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McBeath, R.; Pirone, D.M.; Nelson, C.M.; Bhadriraju, K.; Chen, C.S. Cell shape, cytoskeletal tension, and rhoa regulate stem cell lineage commitment. Dev. Cell 2004, 6, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, T.R.; Andersen, H.; Makam, V.S.; Khaw, C.; Bae, S.; Xu, X.F.; Ee, P.L.R.; Ahn, J.H.; Hong, B.H.; Pastorin, G.; et al. Graphene for controlled and accelerated osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 4670–4678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.C.; Lim, C.H.Y.X.; Shi, H.; Tang, L.A.L.; Wang, Y.; Lim, C.T.; Loh, K.P. Origin of enhanced stem cell growth and differentiation on graphene and graphene oxide. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 7334–7341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talukdar, Y.; Rashkow, J.T.; Lalwani, G.; Kanakia, S.; Sitharaman, B. The effects of graphene nanostructures on mesenchymal stem cells. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 4863–4877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Park, S.; Kim, Y.J.; Jeon, C.S.; Lim, K.T.; Seonwoo, H.; Cho, S.-P.; Chung, T.D.; Choung, P.-H.; Choung, Y.-H.; et al. Monolayer graphene-directed growth and neuronal differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2015, 11, 2024–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.Y.; Park, J.; Sim, S.H.; Sung, M.G.; Kim, K.S.; Hong, B.H.; Hong, S. Enhanced differentiation of human neural stem cells into neurons on graphene. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, H263–H267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.; Yin, P.T.; Uehara, T.M.; Chueng, S.T.D.; Yang, L.T.; Lee, K.B. Guiding stem cell differentiation into oligodendrocytes using graphene-nanofiber hybrid scaffolds. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 3673–3680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, S.; Song, Q.; Huang, R.; Wang, L.; Liu, L.W.; Dai, J.W.; Tang, M.L.; Cheng, G.S. Three-dimensional graphene foam as a biocompatible and conductive scaffold for neural stem cells. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Kim, I.Y.; Patel, M.; Moon, H.J.; Hwang, S.J.; Jeong, B. 2D and 3D hybrid systems for enhancement of chondrogenic differentiation of tonsil-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 2573–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, B.; Han, J.; Oh, J.; Park, S.; Ryu, S.; Jung, S.; Shin, J.Y.; Lee, B.S.; Hong, B.H.; et al. Graphene oxide flakes as a cellular adhesive: Prevention of reactive oxygen species mediated death of implanted cells for cardiac repair. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 4987–4999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.H.; Lee, K.B.; Choi, J.W. 3D graphene oxide-encapsulated gold nanoparticles to detect neural stem cell differentiation. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 8660–8670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menaa, F. 2-D graphene and derivatives-based scaffolds in regenerative medicine: Innovative boosters mimicking 3-D cell microenvironment. J. Regen. Med. 2013, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menaa, F.; Abdelghani, A.; Menaa, B. Graphene nanomaterials as biocompatible and conductive scaffolds for stem cells: Impact for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. J Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, M.; Nancy, D.; Krishnan, A.G.; Anjusree, G.S.; Vadukumpully, S.; Nair, S.V. Graphene oxide nanoflakes incorporated gelatin-hydroxyapatite scaffolds enhance osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Nanotechnology 2015, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Park, S.; Ryu, S.; Bhang, S.H.; Kim, J.; Yoon, J.K.; Park, Y.H.; Cho, S.P.; Lee, S.; Hong, B.H.; et al. Graphene-regulated cardiomyogenic differentiation process of mesenchymal stem cells by enhancing the expression of extracellular matrix proteins and cell signaling molecules. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2014, 3, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhuri, B.; Bhadra, D.; Mondal, B.; Pramanik, K. Biocompatibility of electrospun graphene oxide poly(epsilon-caprolactone) fibrous scaffolds with human cord blood mesenchymal stem cells derived skeletal myoblast. Mater. Lett. 2014, 126, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Liu, Y.Y.; Liu, Y. Simultaneous synthesis of diverse graphene via electrochemical reduction of graphene oxide. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2015, 45, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, W.I.; Joseph, P.; Mughal, M.Z.; Papakonstantinou, P. Production of reduced graphene oxide via hydrothermal reduction in an aqueous sulphuric acid suspension and its electrochemical behaviour. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2015, 19, 361–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauppila, J.; Kunnas, P.; Damlin, P.; Viinikanoja, A.; Kvarnstrom, C. Electrochemical reduction of graphene oxide films in aqueous and organic solutions. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 89, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasidharan, A.; Panchakarla, L.S.; Chandran, P.; Menon, D.; Nair, S.; Rao, C.N.R.; Koyakutty, M. Differential nano-bio interactions and toxicity effects of pristine versus functionalized graphene. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 2461–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, M.; Zhang, Y.J.; Liang, L.; Wei, M.; Hu, W.B.; Li, X.M.; Huang, Q. Effect of graphene oxide on undifferentiated and retinoic acid-differentiated SH-SY5Y cells line. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 3861–3866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X.; Zeng, C.; Hou, J.; Lin, M.; Xu, J.; Sun, F.; Huang, X.; Dai, L.; et al. Can graphene oxide cause damage to eyesight? Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 1265–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasidharan, A.; Panchakarla, L.S.; Sadanandan, A.R.; Ashokan, A.; Chandran, P.; Girish, C.M.; Menon, D.; Nair, S.V.; Rao, C.N.R.; Koyakutty, M. Hemocompatibility and macrophage response of pristine and functionalized graphene. Small 2012, 8, 1251–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Ruan, J.; Song, H.; Zhang, J.L.; Wo, Y.; Guo, S.W.; Cui, D.X. Biocompatibility of graphene oxide. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.L.; Yang, S.T.; Liu, J.H.; Dong, E.; Wang, Y.W.; Cao, A.N.; Liu, Y.F.; Wang, H.F. In vitro toxicity evaluation of graphene oxide on A549 cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2011, 200, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpio, I.E.M.; Santos, C.M.; Wei, X.; Rodrigues, D.F. Toxicity of a polymer-graphene oxide composite against bacterial planktonic cells, biofilms, and mammalian cells. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 4746–4756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzhavan, O.; Ghaderi, E.; Shahsavar, M. Graphene nanogrids for selective and fast osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Carbon 2013, 59, 200–211. [Google Scholar]
- Orive, G.; Anitua, E.; Pedraz, J.L.; Emerich, D.F. Biomaterials for promoting brain protection, repair and regeneration. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 10, 682–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis-Behnke, R.G.; Liang, Y.X.; You, S.W.; Tay, D.K.C.; Zhang, S.G.; So, K.F.; Schneider, G.E. Nano neuro knitting: Peptide nanofiber scaffold for brain repair and axon regeneration with functional return of vision. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 5054–5059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, G.A.; Czeisler, C.; Niece, K.L.; Beniash, E.; Harrington, D.A.; Kessler, J.A.; Stupp, S.I. Selective differentiation of neural progenitor cells by high-epitope density nanofibers. Science 2004, 303, 1352–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhavan, O.; Ghaderi, E. Differentiation of human neural stem cells into neural networks on graphene nanogrids. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 6291–6301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.H.; Li, T.; Xu, M.H.; Gao, F.; Yang, J.; Yang, Z.; Le, W.D. Graphene oxide promotes the differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells to dopamine neurons. Nanomedicine 2014, 9, 2445–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezeshki-Modaress, M.; Mirzadeh, H.; Zandi, M. Gelatin-gag electrospun nanofibrous scaffold for skin tissue engineering: Fabrication and modeling of process parameters. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 48, 704–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J.J.; He, M.; Liu, H.; Niu, Y.Z.; Crawford, A.; Coates, P.D.; Chen, D.F.; Shi, R.; Zhang, L.Q. Drug loaded homogeneous electrospun PCL/gelatin hybrid nanofiber structures for anti-infective tissue regeneration membranes. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 9395–9405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulong, A.F.; Hassan, N.H.; Hwei, N.M.; Lokanathan, Y.; Naicker, A.S.; Abdullah, S.; Yusof, M.R.; Htwe, O.; Idrus, R.B.H.; Haflah, N.H.M. Collagen-coated polylactic-glycolic acid (PLGA) seeded with neural-differentiated human mesenchymal stem cells as a potential nerve conduit. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2014, 23, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iafisco, M.; Quirici, N.; Foltran, I.; Rimondini, L. Electrospun collagen mimicking the reconstituted extracellular matrix improves osteoblastic differentiation onto titanium surfaces. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2013, 13, 4720–4726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowder, S.W.; Prasai, D.; Rath, R.; Balikov, D.A.; Bae, H.; Bolotin, K.I.; Sung, H.J. Three-dimensional graphene foams promote osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 4171–4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano, M.C.; Patino, J.; Garcia-Rama, C.; Ferrer, M.L.; Fierro, J.L.G.; Tamayo, A.; Collazos-Castro, J.E.; del Monte, F.; Gutierrez, M.C. 3D free-standing porous scaffolds made of graphene oxide as substrates for neural cell growth. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 5698–5706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilak, F.; Cohen, D.M.; Estes, B.T.; Gimble, J.M.; Liedtke, W.; Chen, C.S. Control of stem cell fate by physical interactions with the extracellular matrix. Cell Stem Cell 2009, 5, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelham, R.J.; Wang, Y.L. Cell locomotion and focal adhesions are regulated by substrate flexibility. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 13661–13665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, C.; Sun, J.G.; Ding, J.D. Critical areas of cell adhesion on micropatterned surfaces. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 3931–3938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, R.; Yao, X.; Ding, J.D. Effect of cell anisotropy on differentiation of stem cells on micropatterned surfaces through the controlled single cell adhesion. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 8048–8057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.H.; Shah, S.; Yang, L.T.; Yin, P.T.; Hossain, M.K.; Conley, B.; Choi, J.W.; Lee, K.B. Controlling differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells using combinatorial graphene hybrid-pattern arrays. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 3780–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajaj, P.; Rivera, J.A.; Marchwiany, D.; Solovyeva, V.; Bashir, R. Graphene-based patterning and differentiation of C2C12 myoblasts. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2014, 3, 995–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, P.T.; Shah, S.; Chhowalla, M.; Lee, K.B. Design, synthesis, and characterization of graphene-nanoparticle hybrid materials for bioapplications. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 2483–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solanki, A.; Chueng, S.T.D.; Yin, P.T.; Kappera, R.; Chhowalla, M.; Lee, K.B. Axonal alignment and enhanced neuronal differentiation of neural stem cells on graphene-nanoparticle hybrid structures. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 5477–5482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, T.-H.; Lee, T.; El-Said, W.A.; Choi, J.-W. Graphene-Based Materials for Stem Cell Applications. Materials 2015, 8, 8674-8690. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma8125481
Kim T-H, Lee T, El-Said WA, Choi J-W. Graphene-Based Materials for Stem Cell Applications. Materials. 2015; 8(12):8674-8690. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma8125481
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Tae-Hyung, Taek Lee, Waleed A. El-Said, and Jeong-Woo Choi. 2015. "Graphene-Based Materials for Stem Cell Applications" Materials 8, no. 12: 8674-8690. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma8125481
APA StyleKim, T.-H., Lee, T., El-Said, W. A., & Choi, J.-W. (2015). Graphene-Based Materials for Stem Cell Applications. Materials, 8(12), 8674-8690. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma8125481







