Polypropylene/Short Glass Fibers Composites: Effects of Coupling Agents on Mechanical Properties, Thermal Behaviors, and Morphology
Abstract
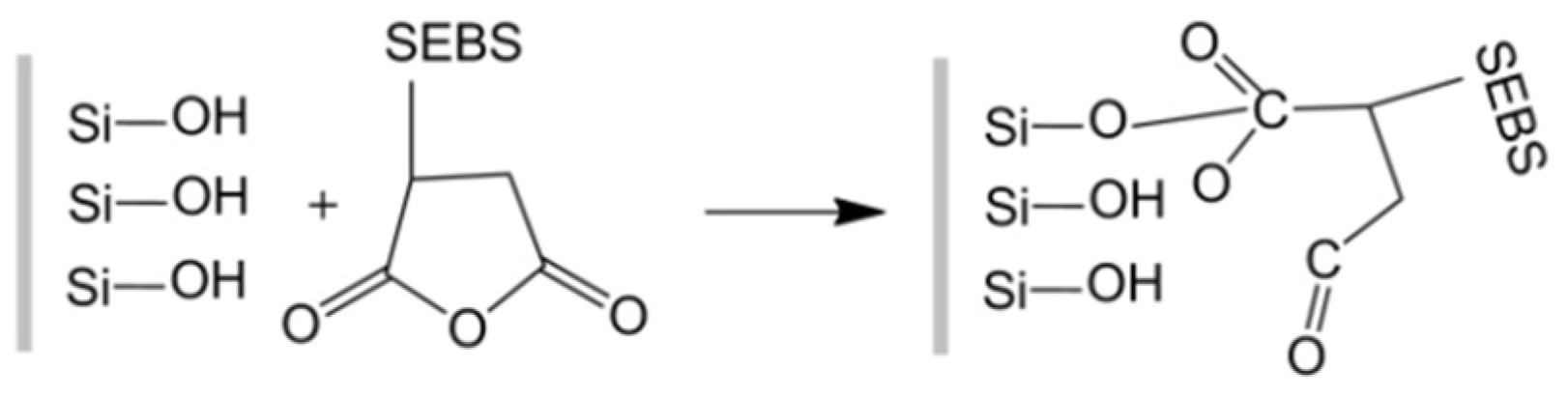
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
| Material | Density (g/cm3) | Melt Index (g/10 min) | Diameter (µm) | Length (mm) | Graft Weight (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PP | 0.900 | 10 (230 °C / 2.16 Kg measured) | - | - | - |
| SGF | - | - | 13 | 3.2 | - |
| PP-g-MA | 0.903 | 120 (190 °C / 2.16 Kg calculated) | - | - | 0.5 |
| SEBS-g-MA | 0.910 | 22 (230 °C / 5 Kg measured) | - | - | 1.5 |
2.2. Methods
2.3. Measurements
2.3.1. Tensile Tests
2.3.2. Flexural Tests
2.3.3. Izod Impact Tests
2.3.4. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.3.5. Polarized Light Microscopy (PLM)
2.3.6. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effects of Two Coupling Agents (PP-g-MA or SEBS-g-MA) on Mechanical Properties of PP/SGF Composites
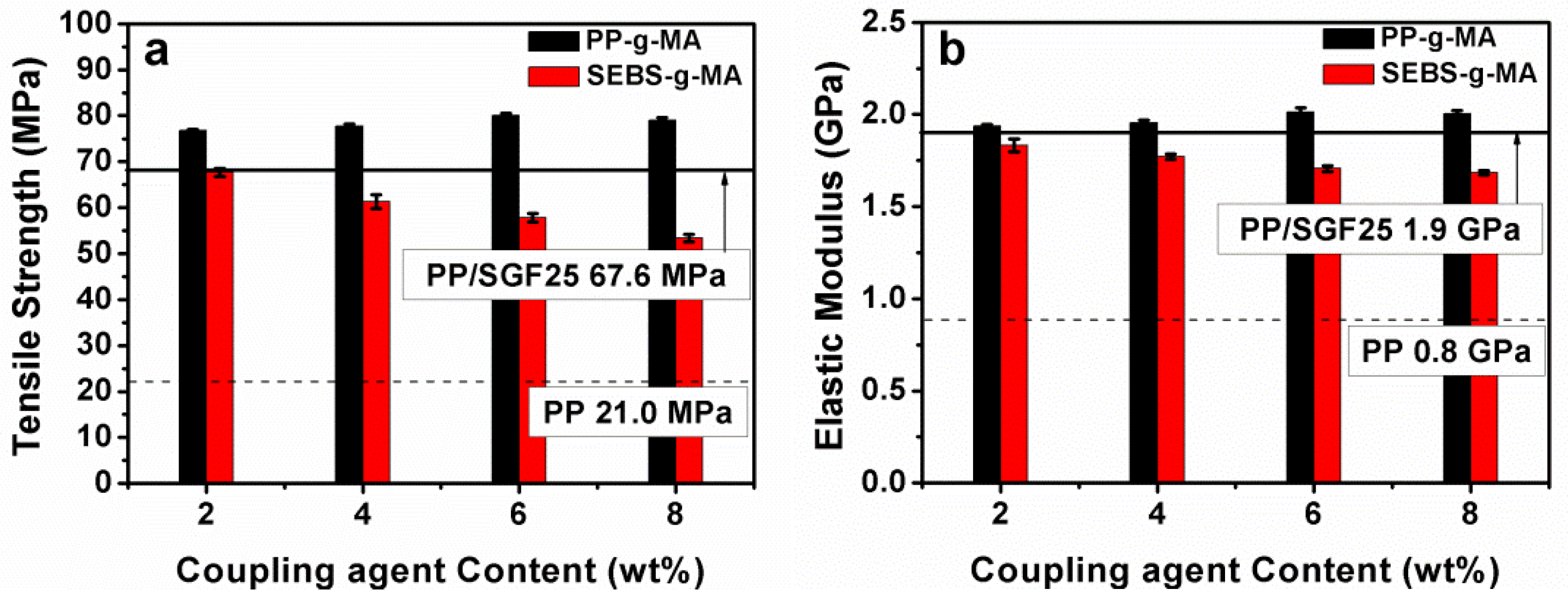
| Composite | σT (MPa) | ET (GPa) | σF (MPa) | EF (GPa) | IS (J/m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PP | 21.0 ± 0.8 | 0.8 ± 0.032 | 47.9 ± 1.3 | 1.3 ± 0.051 | 44.8 ± 0.0 |
| PP/SGF25 | 67.6 ± 0.9 | 1.9 ± 0.026 | 99.3 ± 2.7 | 3.5 ± 0.045 | 73.7 ± 3.3 |
| PP-g-MA (2 wt %) | 76.8 ± 0.2 | 1.9 ± 0.008 | 120.0 ± 4.2 | 3.2 ± 0.268 | 101.9 ± 7.5 |
| PP-g-MA (4 wt %) | 77.7 ± 0.4 | 1.9 ± 0.013 | 123.3 ± 1.0 | 3.4 ± 0.031 | 103.5 ± 10.1 |
| PP-g-MA (6 wt %) | 80.0 ± 0.6 | 2.0 ± 0.022 | 127.2 ± 0.9 | 3.5 ± 0.032 | 103.5 ± 3.6 |
| PP-g-MA (8 wt %) | 79.0 ± 0.5 | 2.0 ± 0.016 | 123.4 ± 2.8 | 3.6 ± 0.035 | 97.5 ± 5.6 |
| SEBS-g-MA (2 wt %) | 61.3 ± 1.5 | 1.8 ± 0.035 | 97.8 ± 2.9 | 3.2 ± 0.320 | 77.7 ± 0.0 |
| SEBS-g-MA (4 wt %) | 57.8 ± 0.9 | 1.8 ± 0.014 | 90.6 ± 1.0 | 3.2 ± 0.031 | 82.0 ± 3.5 |
| SEBS-g-MA (6 wt %) | 53.4 ± 0.8 | 1.7 ± 0.016 | 84.8 ± 1.0 | 3.0 ± 0.052 | 86.2 ± 2.7 |
| SEBS-g-MA (8 wt %) | 50.6 ± 0.9 | 1.7 ± 0.012 | 81.4 ± 1.2 | 2.9 ± 0.076 | 90.3 ± 2.7 |
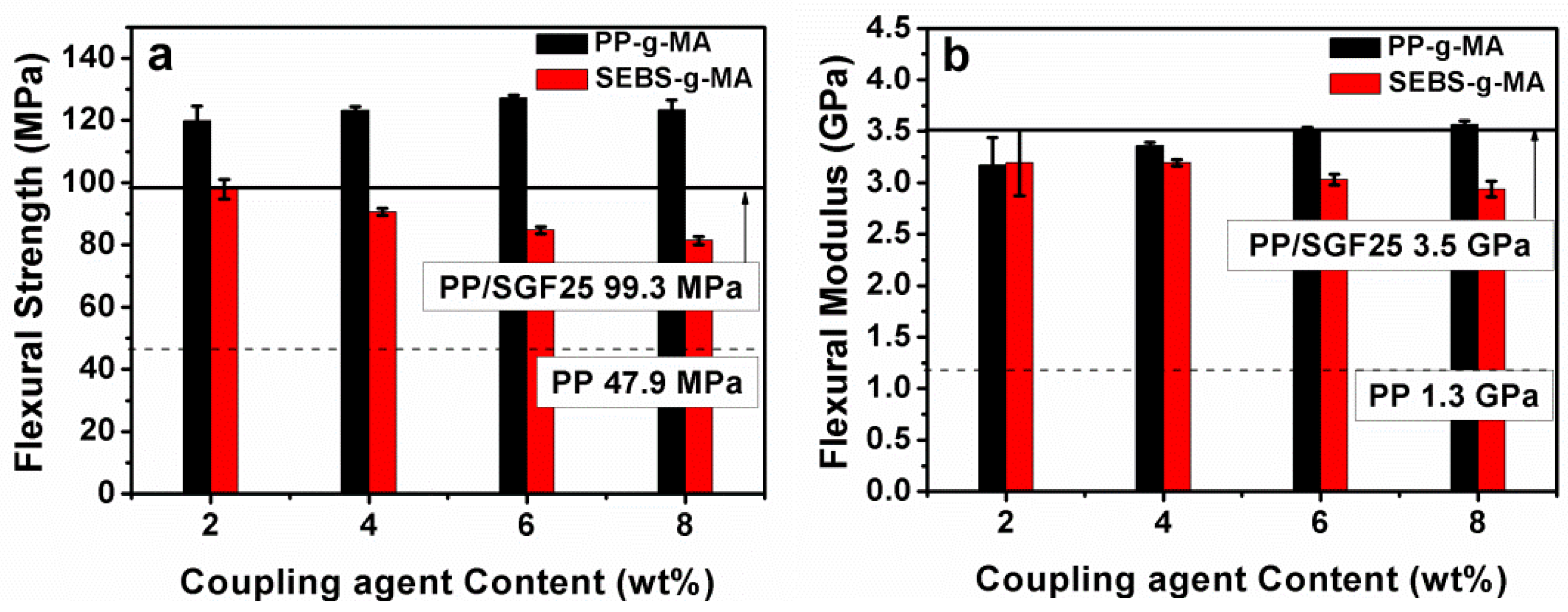
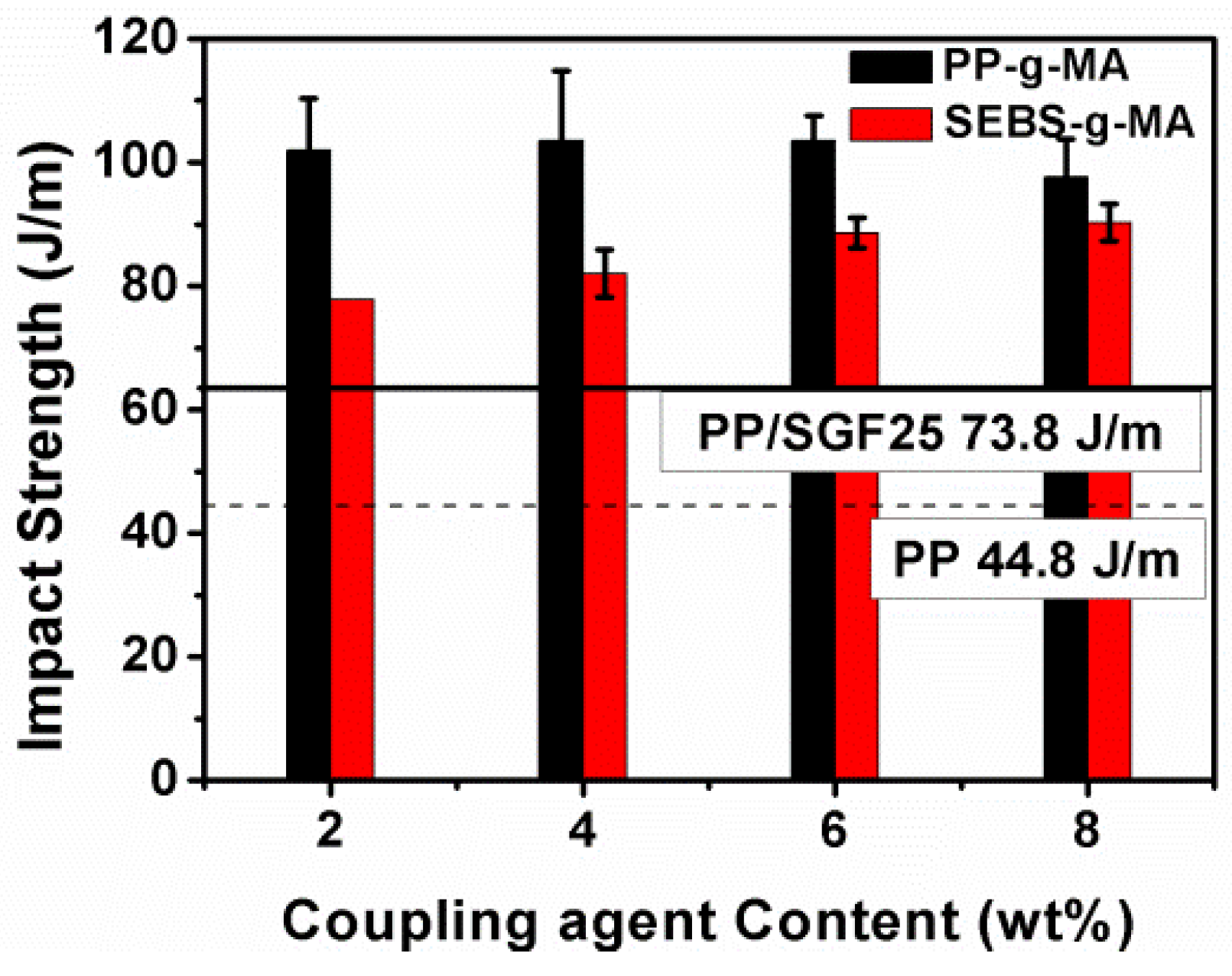
| Coupling Agent (wt %) | PP-g-MA | SEBS-g-MA | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| σT (%) | ET (%) | σF (%) | EF (%) | IS (%) | σT (%) | ET (%) | σF (%) | EF (%) | IS (%) | |
| PP/SGF25 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 wt % | 14 | −3 | 21 | −9 | 38 | −8 | −8 | −2 | −8 | 5 |
| 4 wt % | 15 | −2 | 24 | −4 | 41 | −14 | −11 | −9 | −8 | 12 |
| 6 wt % | 18 | 1 | 28 | 1 | 41 | −21 | −14 | −15 | −13 | 17 |
| 8 wt % | 18 | 0 | 24 | 2 | 33 | −25 | −15 | −18 | −16 | 23 |
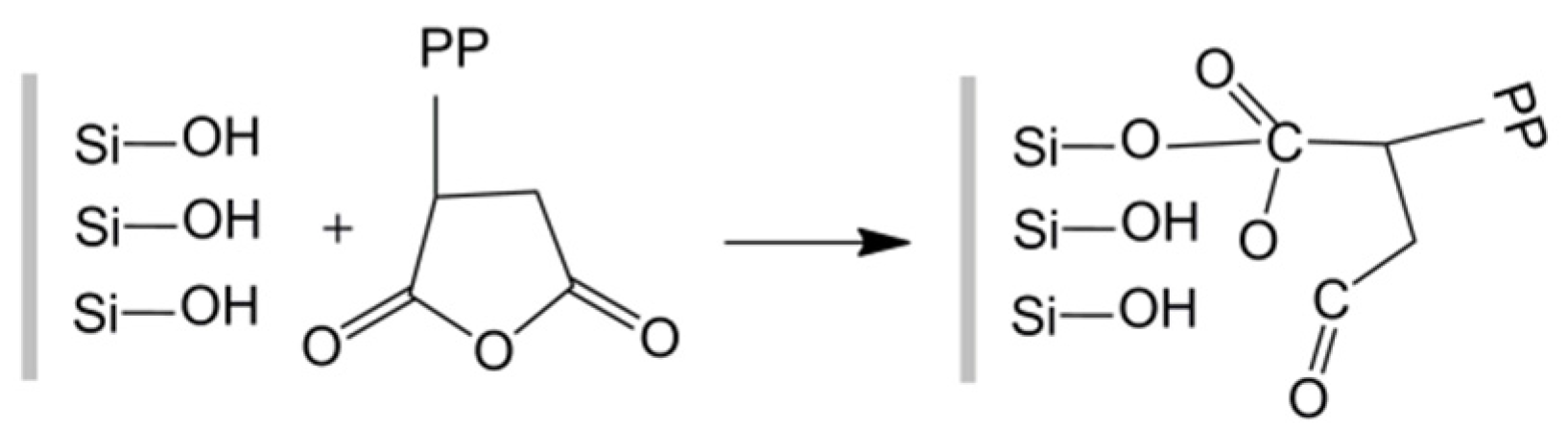
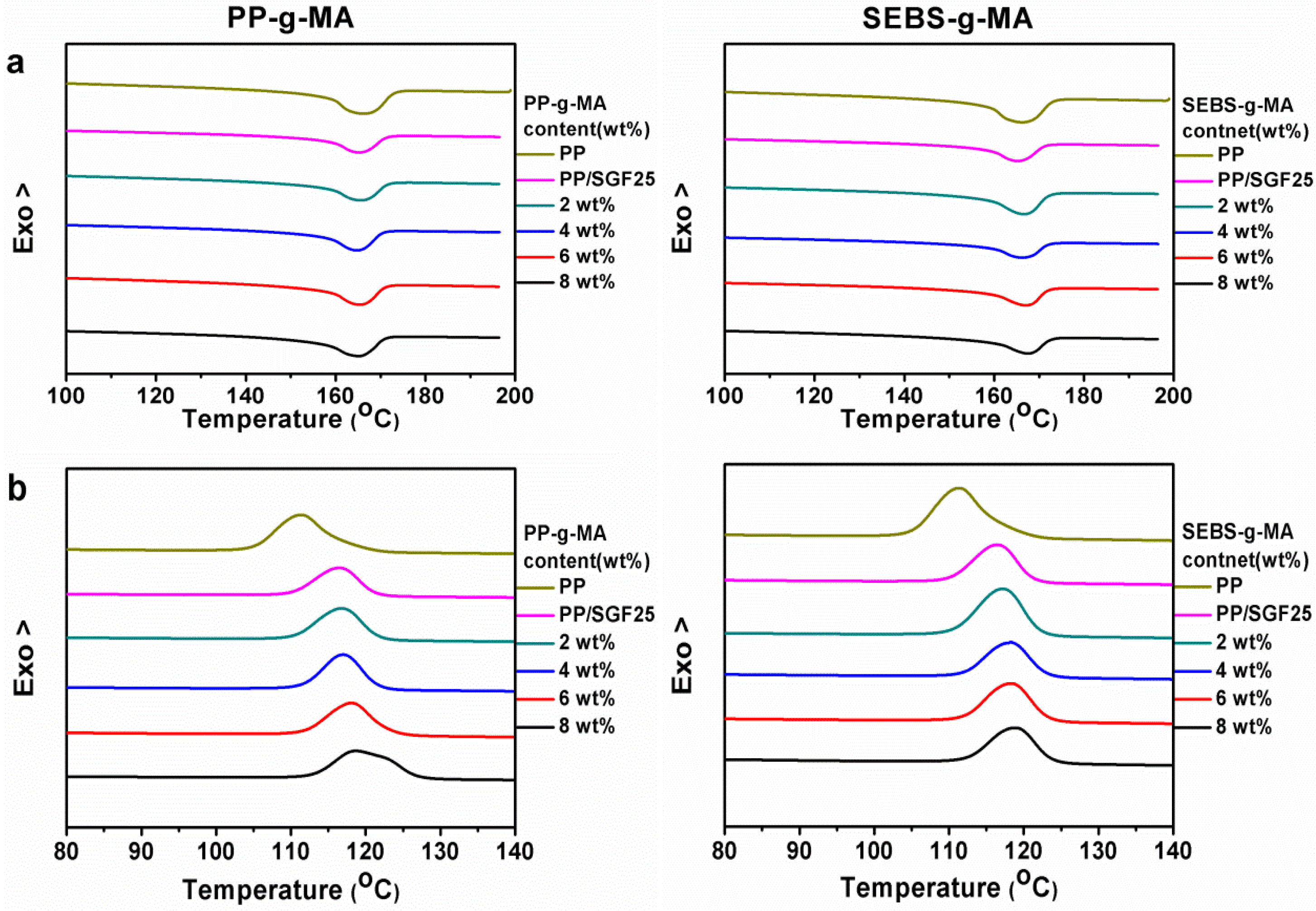
3.2. Effects of Two Coupling Agents (PP-g-MA or SEBS-g-MA) on Thermal Behaviors of PP/SGF Composites
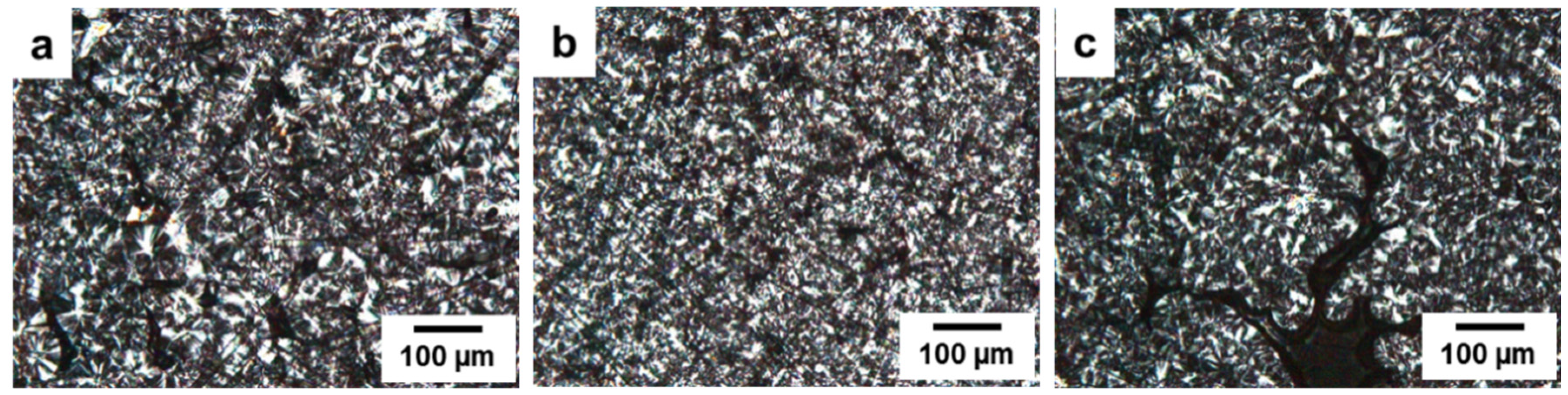
3.3. Effects of Two Coupling Agents (PP-g-MA or SEBS-g-MA) on Spherulite Morphology of PP/SGF Composites
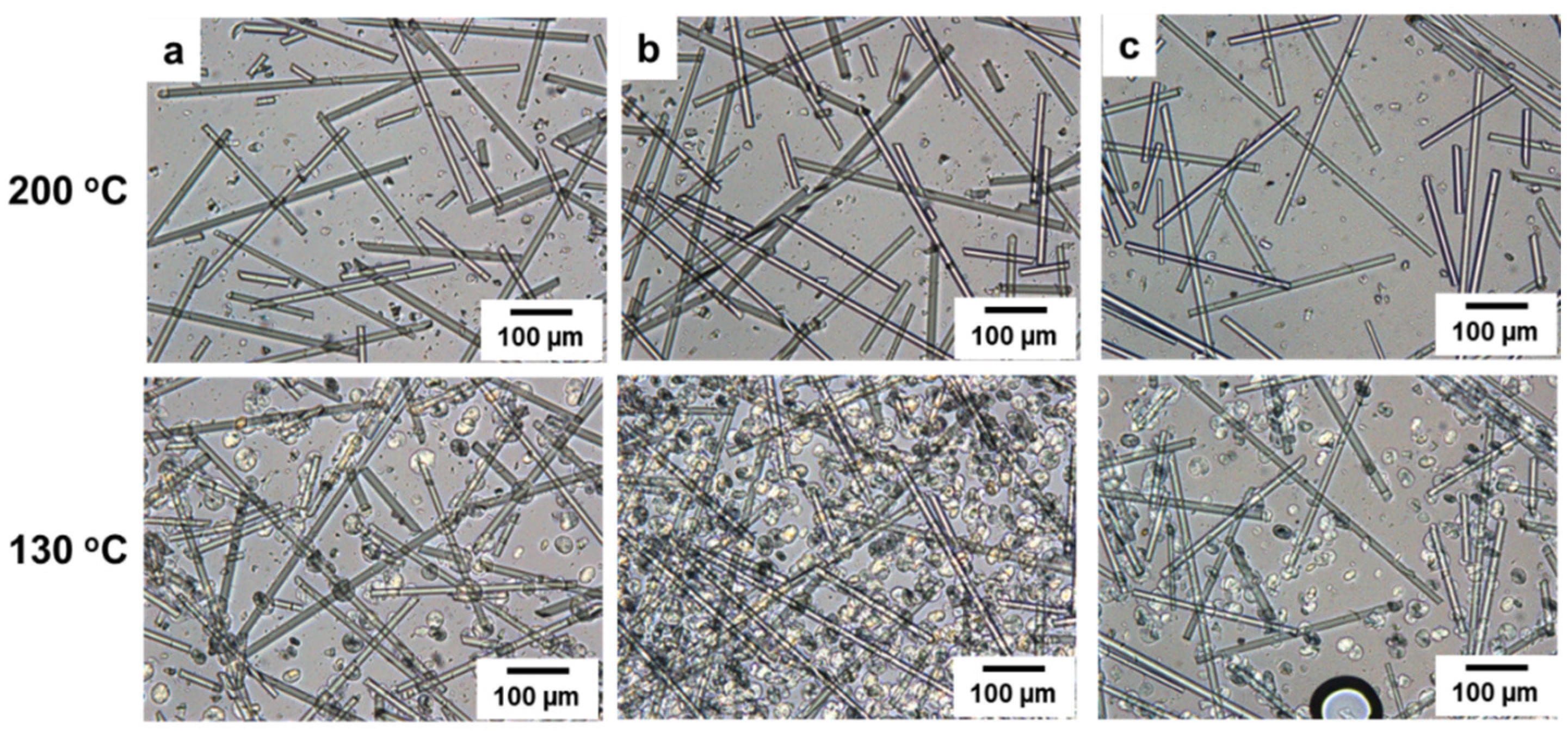
| Coupling Agent (wt %) | PP-g-MA | SEBS-g-MA | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔHm (J/g) | Tm (°C) | Tc (°C) | Xc (%) | ΔHm (J/g) | Tm (°C) | Tc (°C) | Xc (%) | |
| PP | 93.1 | 166.0 | 111.4 | 44.5 | 93.1 | 166.0 | 111.4 | 44.5 |
| PP/SGF25 | 61.5 | 165.2 | 116.4 | 39.2 | 61.5 | 165.2 | 116.4 | 39.2 |
| 2 | 68.4 | 165.7 | 116.8 | 44.8 | 66.0 | 166.6 | 117.2 | 43.2 |
| 4 | 67.1 | 164.8 | 116.9 | 45.1 | 59.2 | 166.2 | 118.2 | 39.8 |
| 6 | 75.5 | 165.4 | 118.1 | 52.1 | 62.6 | 167.1 | 118.5 | 43.2 |
| 8 | 65.1 | 165.1 | 118.8 | 46.0 | 59.6 | 167.5 | 118.8 | 42.2 |
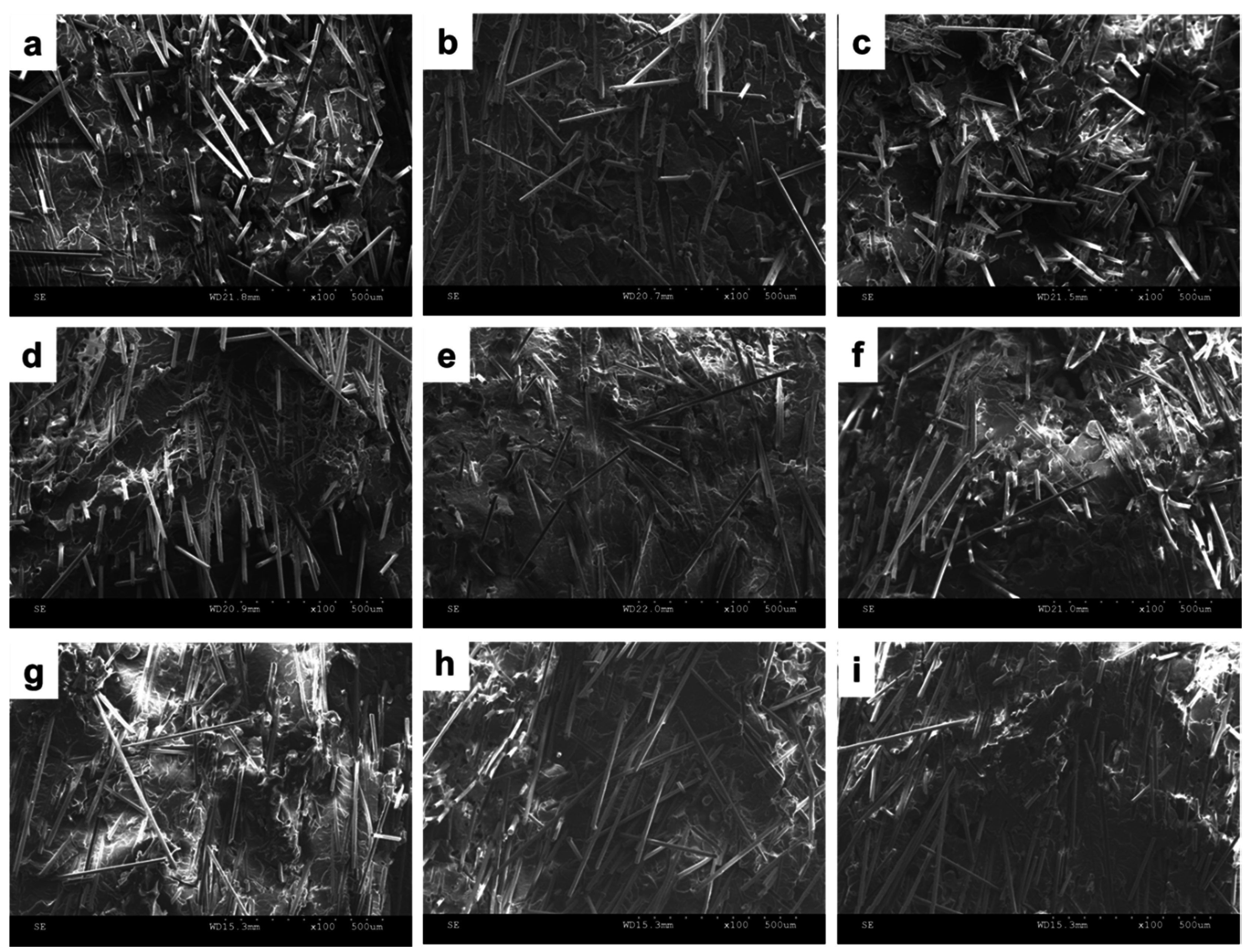
3.4. Effects of Two Coupling Agents (PP-g-MA or SEBS-g-MA) on Spherulite Morphology of PP/SGF Composites
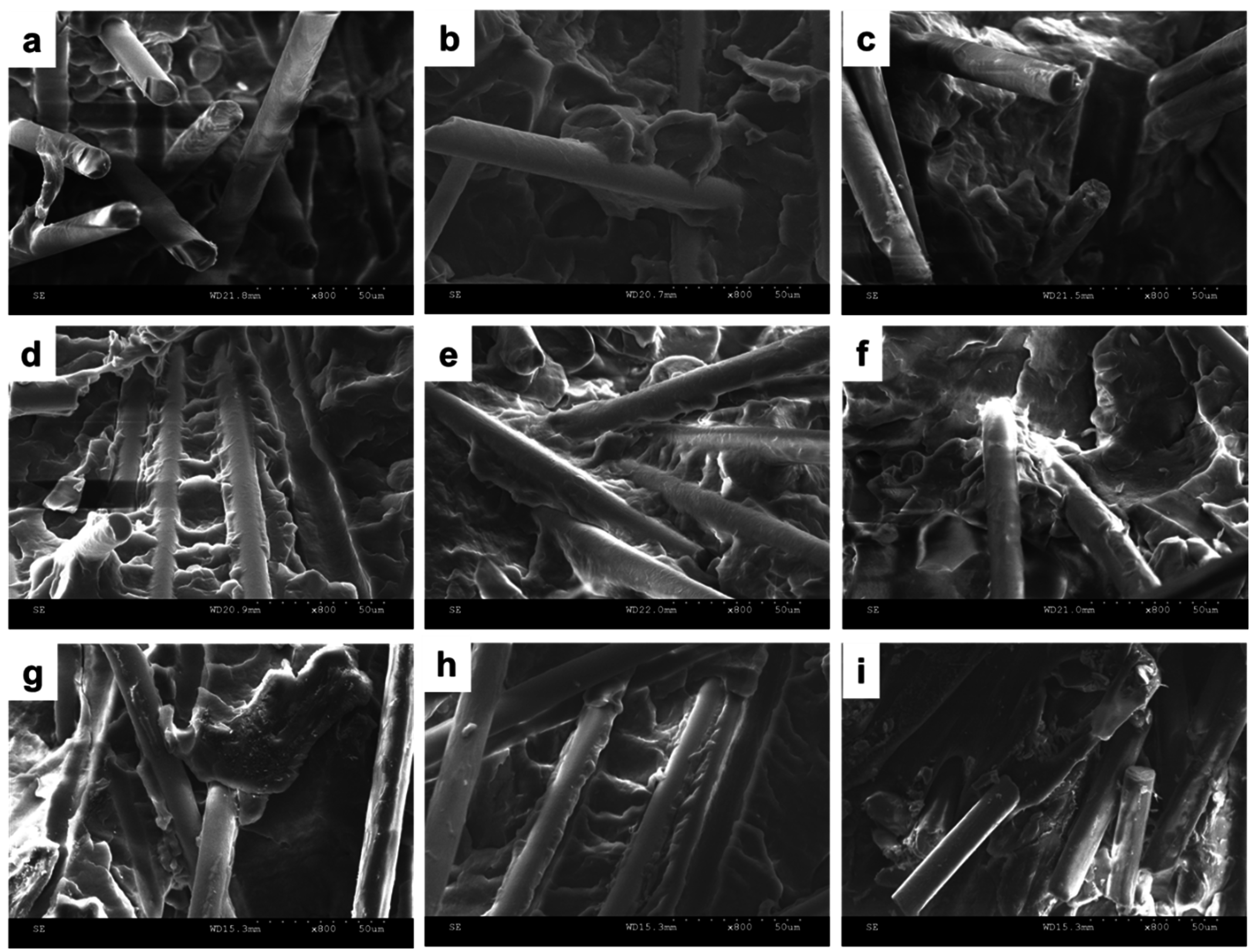
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tam, W.Y.; Cheung, T.Y.H.; Li, R.K.Y. Impact properties of glass fibre/impact modifier/polypropylene hybrid composites. J. Mater. Sci. 2000, 35, 1525–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shubhra, Q.T.; Alam, A.; Quaiyyum, M. Mechanical properties of polypropylene composites: A review. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2013, 26, 362–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Gong, J.; Wen, X.; Xue, J.; Chen, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Tian, N.; Tang, T. Effect of carbon black on improving thermal stability, flame retardancy and electrical conductivity of polypropylene/carbon fiber composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2015, 113, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Chen, Y. New micro-structure designs of a polypropylene (pp) composite with improved impact property. Mater. Lett. 2015, 152, 210–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Castell, O.; Badia, J.D.; Teruel-Juanes, R.; Rodriguez, I.; Meseguer, F.; Ribes-Greus, A. Novel silicon microparticles to improve sunlight stability of raw polypropylene. Eur. Polymer J. 2015, 70, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liborio, P.; Oliveira, V.A.; Marques, M.D.F.V. New chemical treatment of bentonite for the preparation of polypropylene nanocomposites by melt intercalation. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 111, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szkudlarek, E.; Piorkowska, E.; Boyer, S.A.E.; Haudin, J.M.; Gadzinowska, K. Nonisothermal shear-induced crystallization of polypropylene-based composite materials with montmorillonite. Eur. Polymer J. 2013, 49, 2109–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.-H.; Lin, C.-W.; Huang, C.-H.; Huang, C.-L.; Lou, C.-W. Manufacturing technique and mechanical properties of plastic nanocomposite. Compos. Part B 2013, 44, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, S.N.; Sharma, K.K. Studies on polypropylene composites filled with talc particles. J. Mater. Sci. 1992, 27, 4605–4613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Rong, M.; Zhang, M.; Friedrich, K. Effects of reactive compatibilization on the performance of nano-silica filled polypropylene composites. J. Mater. Sci. 2006, 41, 5767–5770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.-S.; Hsu, P.P. Effects of silica particle size on the structure and properties of polypropylene/silica composites foams. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2013, 19, 1377–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unterweger, C.; Brüggemann, O.; Fürst, C. Effects of different fibers on the properties of short-fiber-reinforced polypropylene composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2014, 103, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unterweger, C.; Duchoslav, J.; Stifter, D.; Fürst, C. Characterization of carbon fiber surfaces and their impact on the mechanical properties of short carbon fiber reinforced polypropylene composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2015, 108, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, P. Characterization of short glass fiber reinforced polypropylene foam composites with the effect of compatibilizers: A comparison. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2015, 34, 534–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Liello, V.; Martuscelli, E.; Ragosta, G.; Zihlif, A. Effect of fibre surface treatment on yielding and fracture behaviour of glass fibre-polypropylene composite. J. Mater. Sci. 1991, 26, 2100–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-W.; Lin, Z.-Y.; Lou, C.-W.; Kuo, T.-L.; Lin, J.-H. Wood plastic composites: Using carbon fiber to create electromagnetic shielding effectiveness. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2015, 28, 1047–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-W.; Lou, C.-W.; Huang, C.-H.; Huang, C.-L.; Lin, J.-H. Electromagnetically shielding composite made from carbon fibers, glass fibers, and impact-resistant polypropylene: Manufacturing technique and evaluation of physical properties. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2014, 27, 1451–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czigány, T. Special manufacturing and characteristics of basalt fiber reinforced hybrid polypropylene composites: Mechanical properties and acoustic emission study. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2006, 66, 3210–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelnar, I. The effect of pp and epr grafted with acrylic acid on the properties and phase structure of polypropylene/elastomer/short glass fibre composites. Die Angew. Makromol. Chem. 1991, 189, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Guo, J.; Zhang, K. Effects of compatilizers on mechanical and dynamic mechanical properties of polypropylene-long glass fiber composites. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2015, 28, 643–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, D. Compatibilizing effects of maleic anhydride-grafted-polypropylene (pp) on long carbon fiber-reinforced pp composites. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wen, X.; Liu, J.; Tang, T. Synergetic effect of epoxy resin and maleic anhydride grafted polypropylene on improving mechanical properties of polypropylene/short carbon fiber composites. Compos. Part A 2014, 67, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Li, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Kang, M. Effect of surface silanization of carbon fiber on mechanical properties of carbon fiber reinforced polyurethane composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2015, 110, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.-Q.; Zhang, S.; Xie, D. An efficient way to improve the mechanical properties of polypropylene/short glass fiber composites. J. Appl. Polymer Sci. 2005, 96, 1414–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjong, S.C.; Xu, S.-A.; Li, R.K.Y.; Mai, Y.W. Fracture characteristics of short glass fibre/maleated styrene-ethylene-butylene-styrene/polypropylene hybrid composite. Polymer Int. 2002, 51, 1248–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Maiti, S.N. Effects of crystallinity of pp and flexibility of sebs-g-ma copolymer on the mechanical properties of pp/sebs-g-ma blends. Polymer Plast. Technol. Eng. 2014, 53, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslami-Farsani, R.; Reza Khalili, S.M.; Hedayatnasab, Z.; Soleimani, N. Influence of thermal conditions on the tensile properties of basalt fiber reinforced polypropylene-clay nanocomposites. Mater. Des. 2014, 53, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabr, M.H.; Okumura, W.; Ueda, H.; Kuriyama, W.; Uzawa, K.; Kimpara, I. Mechanical and thermal properties of carbon fiber/polypropylene composite filled with nano-clay. Compos. Part B 2015, 69, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Liu, Y.; Qu, C.-B.; Xiao, H.-M.; Hua, Y.; Sui, G.-X.; Fu, S.-Y. Enhanced mechanical properties of short carbon fiber reinforced polyethersulfone composites by graphene oxide coating. Polymer 2015, 59, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.H.; Syed Mohammed, D.; Pickering, S.J.; Brooks, R. Effect of coupling agents on reinforcing potential of recycled carbon fibre for polypropylene composite. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2012, 72, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broughton, W.R.; Lodeiro, M.J.; Pilkington, G.D. Influence of coupling agents on material behaviour of glass flake reinforced polypropylene. Compos. Part A 2010, 41, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo, M.; Lopez-Manchado, M.A.; Avalos, F. Crystallization kinetics of polypropylene: II. Effect of the addition of short glass fibres. Polymer 1997, 38, 5587–5593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Cao, W.; Liu, C.; Shen, C. Crystallization behavior and nucleation analysis of isotactic polypropylene with a multiamide nucleating agent. Polymer Test. 2014, 36, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjong, S.C.; Xu, S.-A.; Li, R.K.-Y.; Mai, Y.-W. Mechanical behavior and fracture toughness evaluation of maleic anhydride compatibilized short glass fiber/sebs/polypropylene hybrid composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2002, 62, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjong, S.C.; Xu, S.-A.; Mai, Y.-W. Impact-specific essential work of fracture of maleic anhydride-compatibilized polypropylene/elastomer blends and their composites. J. Polymer Sci. Part B 2002, 40, 1881–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denac, M.; Musil, V.; Šmit, I. Polypropylene/talc/sebs (sebs-g-ma) composites. Part 2. Mechanical properties. Compos. Part A 2005, 36, 1282–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjong, S.C.; Xu, S.A.; Yu Li, R.K.; Mai, Y.W. Preparation and performance characteristics of short-glass-fiber/maleated styrene-ethylene-butylene-styrene/polypropylene hybrid composites. J. Appl. Polymer Sci. 2002, 86, 1303–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denac, M.; Šmit, I.; Musil, V. Polypropylene/talc/sebs (sebs-g-ma) composites. Part 1. Structure. Compos. Part A 2005, 36, 1094–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, J.-H.; Huang, C.-L.; Liu, C.-F.; Chen, C.-K.; Lin, Z.-I.; Lou, C.-W. Polypropylene/Short Glass Fibers Composites: Effects of Coupling Agents on Mechanical Properties, Thermal Behaviors, and Morphology. Materials 2015, 8, 8279-8291. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma8125451
Lin J-H, Huang C-L, Liu C-F, Chen C-K, Lin Z-I, Lou C-W. Polypropylene/Short Glass Fibers Composites: Effects of Coupling Agents on Mechanical Properties, Thermal Behaviors, and Morphology. Materials. 2015; 8(12):8279-8291. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma8125451
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Jia-Horng, Chien-Lin Huang, Chi-Fan Liu, Chih-Kuang Chen, Zheng-Ian Lin, and Ching-Wen Lou. 2015. "Polypropylene/Short Glass Fibers Composites: Effects of Coupling Agents on Mechanical Properties, Thermal Behaviors, and Morphology" Materials 8, no. 12: 8279-8291. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma8125451
APA StyleLin, J.-H., Huang, C.-L., Liu, C.-F., Chen, C.-K., Lin, Z.-I., & Lou, C.-W. (2015). Polypropylene/Short Glass Fibers Composites: Effects of Coupling Agents on Mechanical Properties, Thermal Behaviors, and Morphology. Materials, 8(12), 8279-8291. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma8125451








