Bioactivity of Sodium Free Fluoride Containing Glasses and Glass-Ceramics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Apatite Formation
2.1.1. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) Results
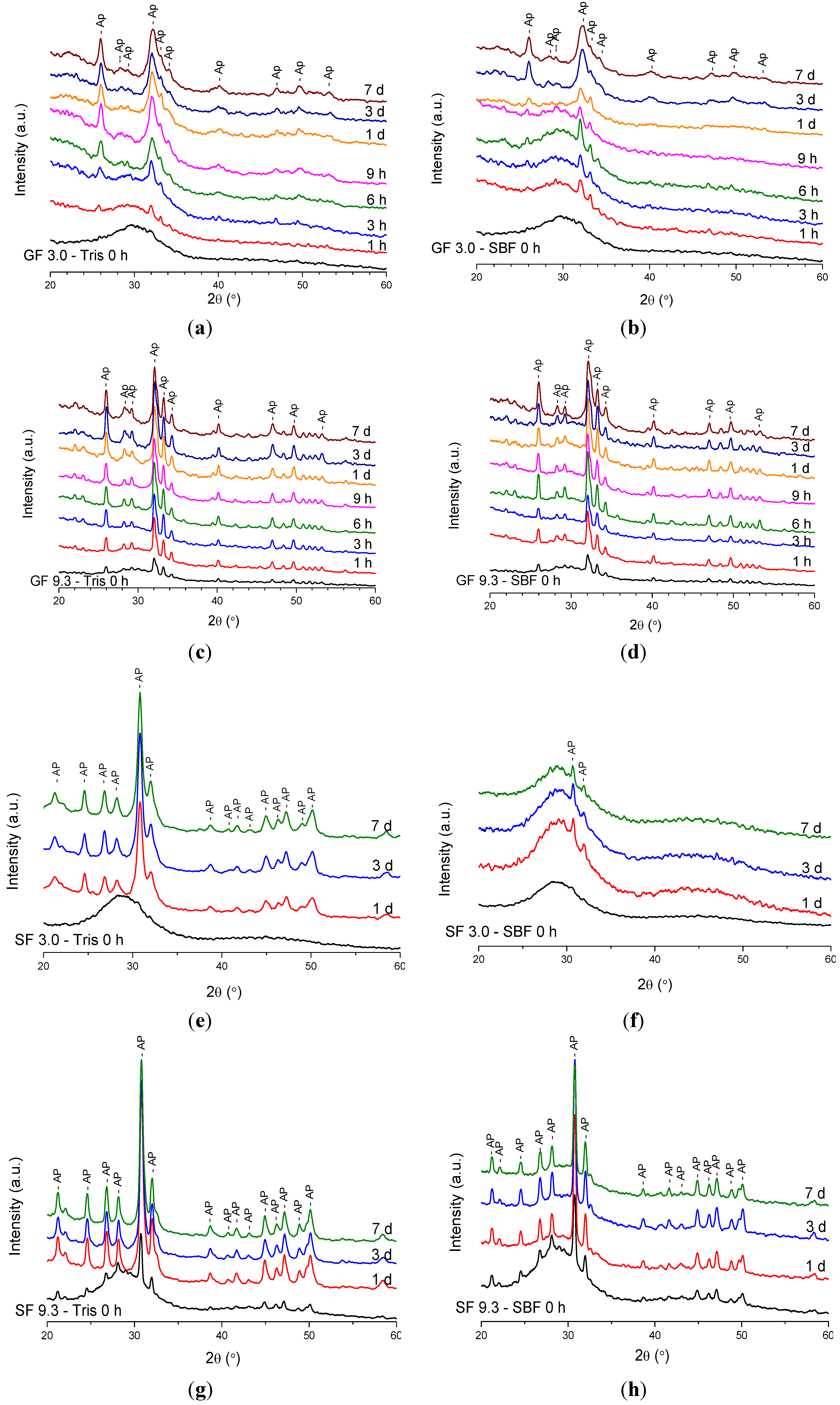
2.1.2. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy Results
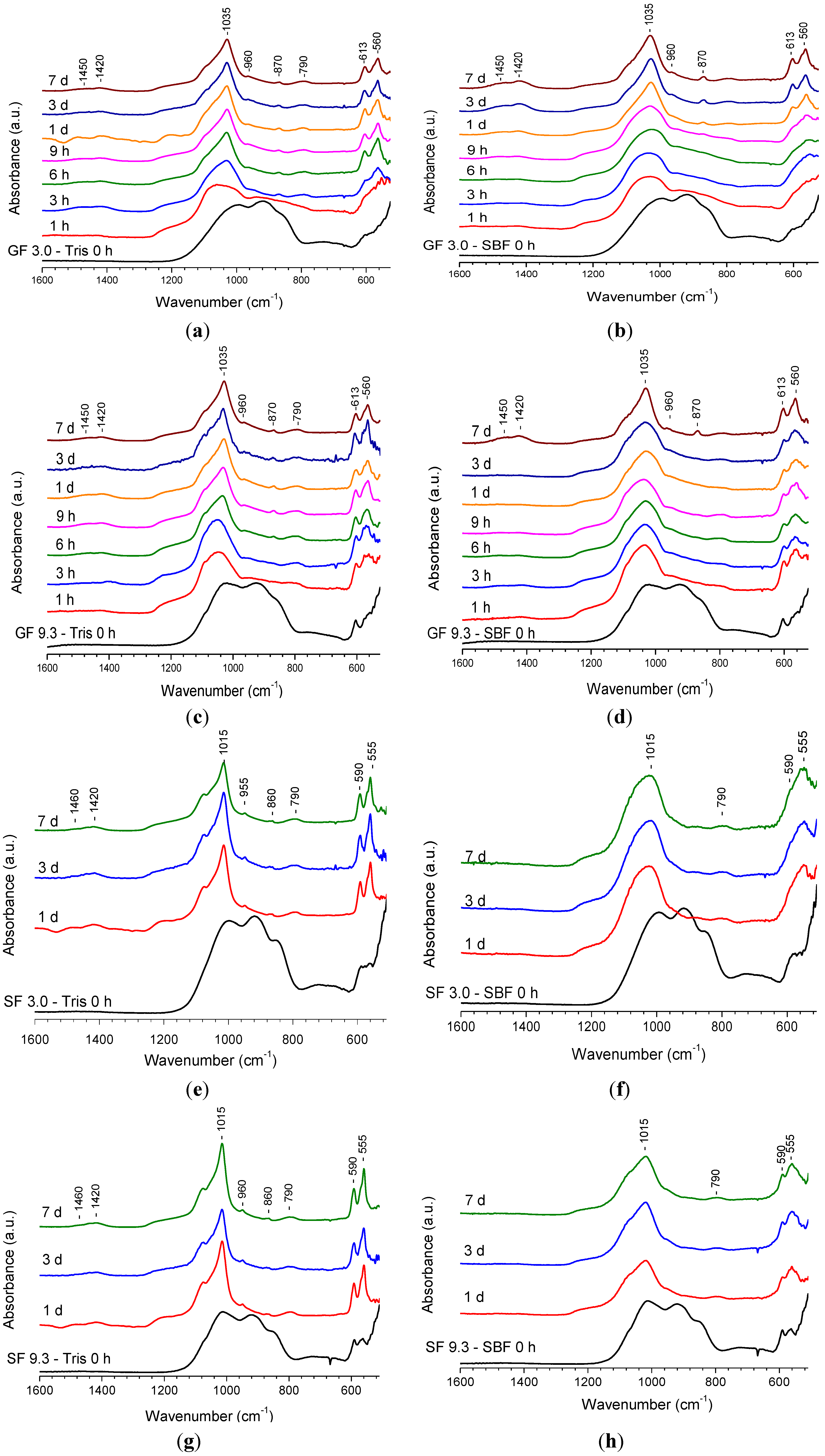
2.1.3. Magic Angle Spinning-Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (MAS-NMR) Spectroscopy Results
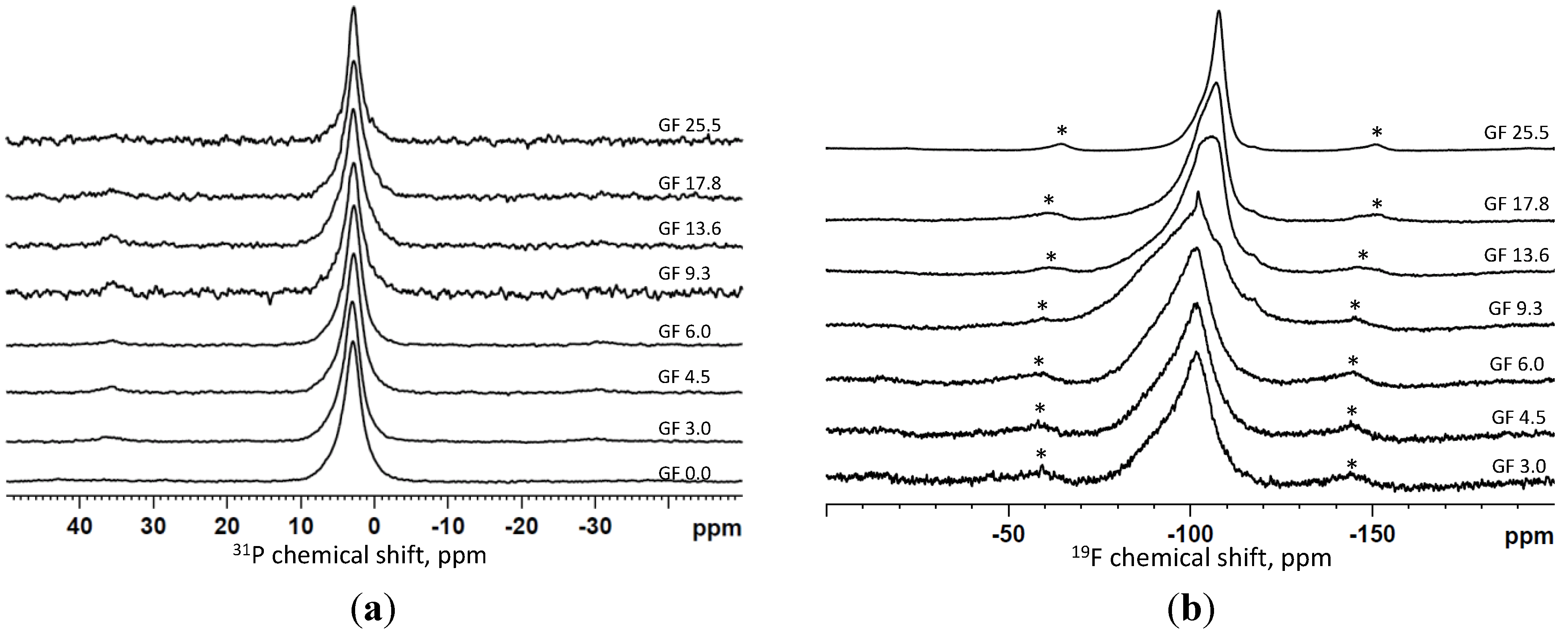
2.2. Dissolution Study
2.2.1. pH Measurements Results
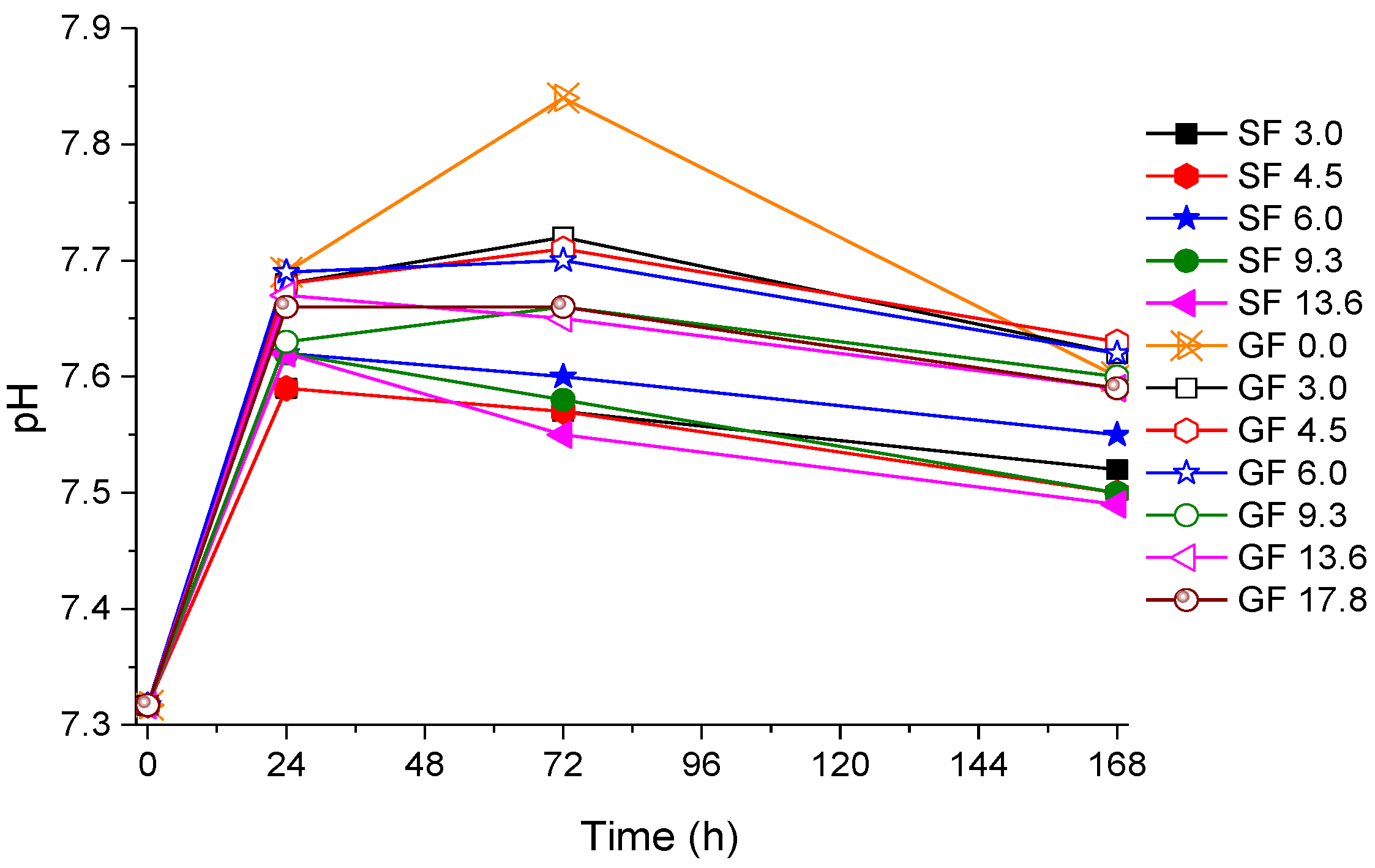
2.2.2. Ion Release Results
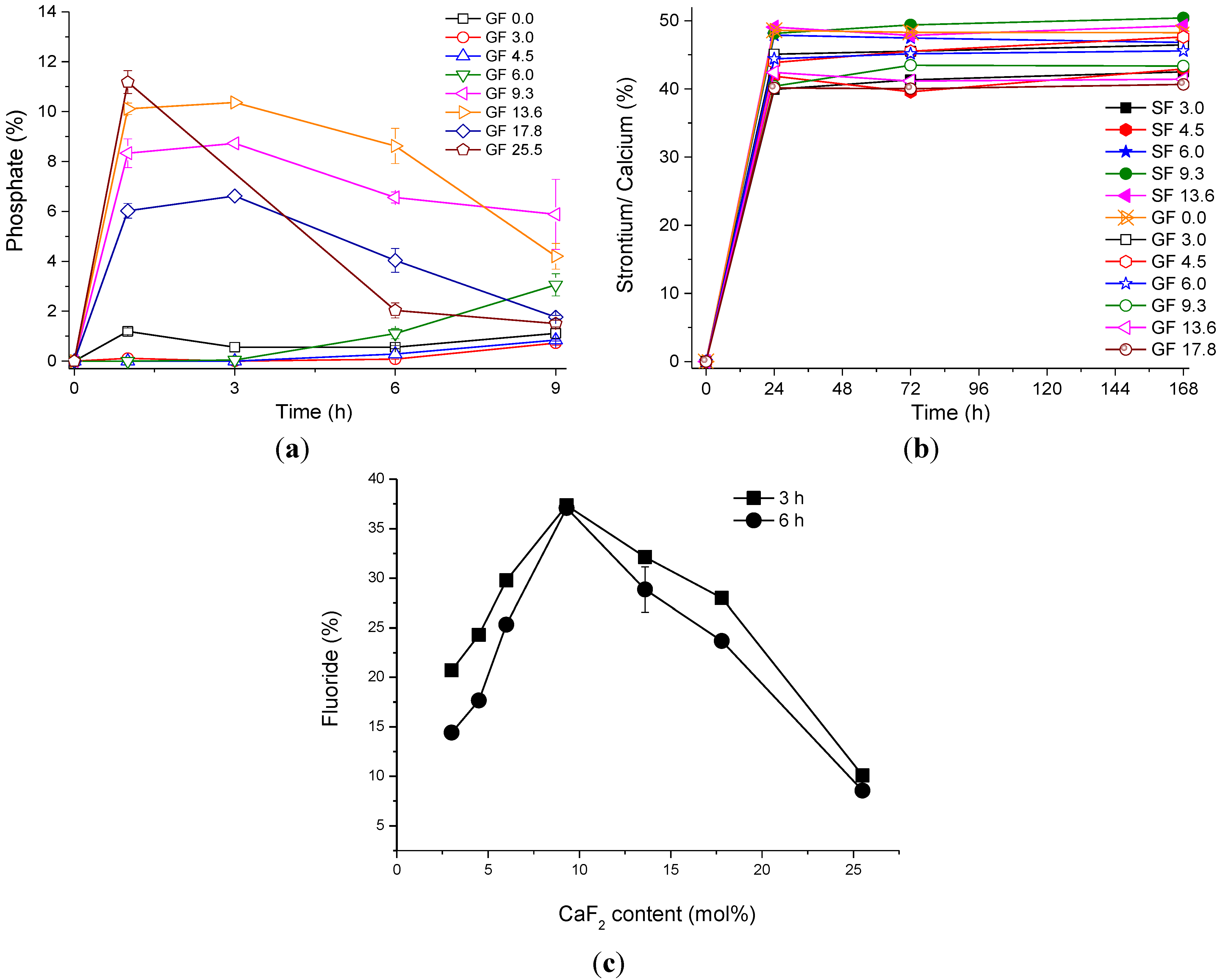
2.3. Final Discussion
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Glass Preparation
| Glass code | SiO2 | CaO/SrO | P2O5 | CaF2/SrF2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GF/SF 0.0 | 38.1 | 55.5 | 6.3 | 0.0 |
| GF/SF 3.0 | 37.0 | 53.9 | 6.1 | 3.0 |
| GF/SF 4.5 | 36.4 | 53.0 | 6.0 | 4.5 |
| GF/SF 6.0 | 35.9 | 52.2 | 5.9 | 6.0 |
| GF/SF 9.3 | 34.6 | 50.4 | 5.7 | 9.3 |
| GF/SF 13.6 | 32.9 | 48.0 | 5.5 | 13.6 |
| GF/SF 17.8 | 31.4 | 45.7 | 5.2 | 17.8 |
| GF/SF 25.5 | 28.4 | 41.4 | 4.7 | 25.5 |
3.2. Bioactivity Testing and Ion Release Measurements
3.3. Characterisation of Apatite Formation after Immersion
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bohner, M.; Lemaitre, J. Can bioactivity be tested in vitro with sbf solution? Biomaterials 2009, 30, 2175–2179. [Google Scholar]
- Kokubo, T.; Takadama, H. How useful is sbf in predicting in vivo bone bioactivity? Biomaterials 2006, 27, 2907–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, K.E.; Hill, R.G.; Pembroke, J.T.; Brown, C.J.; Hatton, P.V. Influence of sodium oxide content on bioactive glass properties. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 1999, 10, 697–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hench, L.L. Glass and glass-ceramic technologies to transform the world. Int. J. Appl. Glass Sci. 2011, 2, 162–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hench, L.; Wilson, J. An Introduction to Bioceramics; World Scientific Publishing: Singapore, Singapore, 1993; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Shirtliff, V.J.; Hench, L.L. Bioactive materials for tissue engineering, regeneration and repair. J. Mater. Sci. 2003, 38, 4697–4707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasuga, T.; Maeda, H.; Kato, K.; Nogami, M.; Hata, K.; Ueda, M. Preparation of poly (lactic acid) composites containing calcium carbonate (vaterite). Biomaterials 2003, 24, 3247–3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainz, M.A.; Pena, P.; Serena, S.; Caballero, A. Influence of design on bioactivity of novel CaSiO3-CaMg(SiO3)(2) bioceramics: In vitro simulated body fluid test and thermodynamic simulation. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 2797–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Aza, P.N.; Guitian, F.; de Aza, S. Bioactivity of wollastonite ceramics—In vitro evaluation. Scripta Metall. Mater. 1994, 31, 1001–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mneimne, M.; Hill, R.G.; Bushby, A.J.; Brauer, D.S. High phosphate content significantly increases apatite formation of fluoride-containing bioactive glasses. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 1827–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauer, D.S.; Karpukhina, N.; O’Donnell, M.D.; Law, R.V.; Hill, R.G. Fluoride-containing bioactive glasses: Effect of glass design and structure on degradation, ph and apatite formation in simulated body fluid. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 3275–3282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, A.; Kapoor, S.; Rajagopal, R.R.; Pascual, M.J.; Kim, H.W.; Ferreira, J.M. Alkali-free bioactive glasses for bone tissue engineering: A preliminary investigation. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, S.; Goel, A.; Pascual, M.J.; Ferreira, J.M.F. Thermo-mechanical behaviour of alkali free bioactive glass-ceramics co-doped with strontium and zinc. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2013, 375, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kansal, I.; Goel, A.; Tulyaganov, D.U.; Rajagopal, R.R.; Ferreira, J.M.F. Structural and thermal characterization of CaO-MgO-SiO2-P2O5-CaF2 glasses. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2012, 32, 2739–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedone, A.; Charpentier, T.; Menziani, M.C. Multinuclear nmr of CaSiO3 glass: Simulation from first-principles. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 6054–6066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayon, F.; Duée, C.; Poumeyrol, T.; Allix, M.; Massiot, D. Evidence of nanometric-sized phosphate clusters in bioactive glasses as revealed by solid-state 31p nmr. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 2283–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Chen, C.Z.; Wang, D.G.; Meng, X.G.; Shi, J.Z. In vitro degradability and bioactivity of mesoporous CaO-MgO-P2O5-SiO2 glasses synthesized by sol-gel method. J. Sol Gel Sci. Technol. 2010, 54, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Chen, C.Z.; Wang, D.G.; Jiao, Y.; Shi, J.Z. Effect of magnesia on the degradability and bioactivity of sol-gel derived SiO2-CaO-MgO-P2O5 system glasses. Coll. Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 81, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Pariente, J.; Balas, F.; Vallet-Regi, M. Surface and chemical study of SiO2 center dot P2O5 center dot cao center dot(mgo) bioactive glasses. Chem. Mater. 2000, 12, 750–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saboori, A.; Rabiee, M.; Mutarzadeh, F.; Sheikhi, M.; Tahriri, M.; Karimi, M. Synthesis, characterization and in vitro bioactivity of sol-gel-derived SiO2-CaO-P2O5-MgO bioglass. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Biomim. Supramol. Syst. 2009, 29, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.B.; Turdean-Ionescu, C.A.; Martin, R.A.; Newport, R.J.; Hanna, J.V.; Smith, M.E.; Jones, J.R. Effect of calcium source on structure and properties of sol-gel derived bioactive glasses. Langmuir 2012, 28, 17465–17476. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.; Ionescu, C.; Baker, S.; Smith, M.E.; Jones, J.R. Characterisation of the inhomogeneity of sol-gel-derived SiO2-CaO bioactive glass and a strategy for its improvement. J. Sol Gel Sci. Technol. 2010, 53, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-M.; Himeno, T.; Kokubo, T.; Nakamura, T. Process and kinetics of bonelike apatite formation on sintered hydroxyapatite in a simulated body fluid. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 4366–4373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clupper, D.C.; Hench, L.L.; Mecholsky, J.J. Strength and toughness of tape cast bioactive glass 45S5 following heat treatment. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2004, 24, 2929–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peitl, O.; Zanotto, E.D.; Hench, L.L. Highly bioactive P2O5-Na2O-CaO-SiO2 glass-ceramics. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2001, 292, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, J.; Teixeira, L.N.; Ravagnani, C.; Peitl, O.; Zanotto, E.D.; Beloti, M.M.; Panzeri, H.; Rosa, A.L.; de Oliveira, P.T. In vitro osteogenesis on a highly bioactive glass-ceramic (biosilicate (r)). J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2007, 82A, 545–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arstila, H.; Hupa, L.; Karlsson, K.H.; Hupa, M. Influence of heat treatment on crystallization of bioactive glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2008, 354, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedone, A.; Charpentier, T.; Menziani, M.C. The structure of fluoride-containing bioactive glasses: New insights from first-principles calculations and solid state nmr spectroscopy. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 12599–12608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusvardi, G.; Malavasi, G.; Tarsitano, F.; Menabue, L.; Menziani, M.C.; Pedone, A. Quantitative structure-property relationships of potentially bioactive fluoro phospho-silicate glasses. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 10331–10338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusvardi, G.; Malavasi, G.; Menabue, L.; Aina, V.; Morterra, C. Fluoride-containing bioactive glasses: Surface reactivity in simulated body fluids solutions. Acta Biomater. 2009, 5, 3548–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiprianov, A.A.; Karpukhina, N.G. Oxyhalide silicate glasses. Glass Phys. Chem. 2006, 32, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauer, D.S.; Karpukhina, N.; Law, R.V.; Hill, R.G. Structure of fluoride-containing bioactive glasses. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 5629–5636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauer, D.S.; Anjum, M.N.; Mneimne, M.; Wilson, R.M.; Doweidar, H.; Hill, R.G. Fluoride-containing bioactive glass-ceramics. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2012, 358, 1438–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edén, M. The split network analysis for exploring composition–structure correlations in multi-component glasses: I. Rationalizing bioactivity-composition trends of bioglasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2011, 357, 1595–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, R.G.; Brauer, D.S. Predicting the bioactivity of glasses using the network connectivity or split network models. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2011, 357, 3884–3887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedone, A.; Charpentier, T.; Malavasi, G.; Menziani, M.C. New insights into the atomic structure of 45S5 bioglass by means of solid-state nmr spectroscopy and accurate first-principles simulations. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 5644–5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FitzGerald, V.; Pickup, D.M.; Greenspan, D.; Sarkar, G.; Fitzgerald, J.J.; Wetherall, K.M.; Moss, R.M.; Jones, J.R.; Newport, R.J. A neutron and X-ray diffraction study of bioglass with reverse monte carlo modelling. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2007, 17, 3746–3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, M.; Nabeshima, N.; Fukuyama, H.; Nagata, K. Effect of fluorine on silicate network for CaO-CaF2-SiO2 and CaO-CaF2-SiO2-feox glasses. ISIJ Int. 2002, 42, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, X.; Brauer, D.S.; Wilson, R.M.; Hill, R.G.; Karpukhina, N. Novel alkali free bioactive fluorapatite glass ceramics. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2014, 402, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corno, M.; Pedone, A.; Dovesi, R.; Ugliengo, P. B3LYP simulation of the full vibrational spectrum of 45S5 bioactive silicate glass compared to v-silica. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 5610–5621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corno, M.; Pedone, A. Vibrational features of phospho-silicate glasses: Periodic B3LYP simulations. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2009, 476, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.Y.; Clark, A.E.; Hench, L.L. Early stages of calcium-phosphate layer formation in bioglasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1989, 113, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredholm, Y.C.; Karpukhina, N.; Brauer, D.S.; Jones, J.R.; Law, R.V.; Hill, R.G. Influence of strontium for calcium substitution in bioactive glasses on degradation, ion release and apatite formation. J. R. Soc. Interface 2012, 9, 880–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massiot, D.; Fayon, F.; Capron, M.; King, I.; Le Calvé, S.; Alonso, B.; Durand, J.-O.; Bujoli, B.; Gan, Z.; Hoatson, G.; et al. Modelling one- and two-dimensional solid-state nmr spectra. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2002, 40, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, M.D.; Watts, S.J.; Hill, R.G.; Law, R.V. The effect of phosphate content on the bioactivity of soda-lime-phosphosilicate glasses. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2009, 20, 1611–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauer, D.S.; Mneimne, M.; Hill, R.G. Fluoride-containing bioactive glasses: Fluoride loss during melting and ion release in tris buffer solution. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2011, 357, 3328–3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diba, M.; Tapia, F.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Strobel, L.A. Magnesium-containing bioactive glasses for biomedical applications. Int. J. Appl. Glass Sci. 2012, 3, 221–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Noaman, A.; Rawlinson, S.C.F.; Hill, R.G. The role of mgo on thermal properties, structure and bioactivity of bioactive glass coating for dental implants. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2012, 358, 3019–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Chen, X.; Brauer, D.S.; Wilson, R.M.; Hill, R.G.; Karpukhina, N. Bioactivity of Sodium Free Fluoride Containing Glasses and Glass-Ceramics. Materials 2014, 7, 5470-5487. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma7085470
Chen X, Chen X, Brauer DS, Wilson RM, Hill RG, Karpukhina N. Bioactivity of Sodium Free Fluoride Containing Glasses and Glass-Ceramics. Materials. 2014; 7(8):5470-5487. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma7085470
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xiaojing, Xiaohui Chen, Delia S. Brauer, Rory M. Wilson, Robert G. Hill, and Natalia Karpukhina. 2014. "Bioactivity of Sodium Free Fluoride Containing Glasses and Glass-Ceramics" Materials 7, no. 8: 5470-5487. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma7085470
APA StyleChen, X., Chen, X., Brauer, D. S., Wilson, R. M., Hill, R. G., & Karpukhina, N. (2014). Bioactivity of Sodium Free Fluoride Containing Glasses and Glass-Ceramics. Materials, 7(8), 5470-5487. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma7085470




