The Micropillar Structure on Silk Fibroin Film Influence Intercellular Connection Mediated by Nanotubular Structures
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
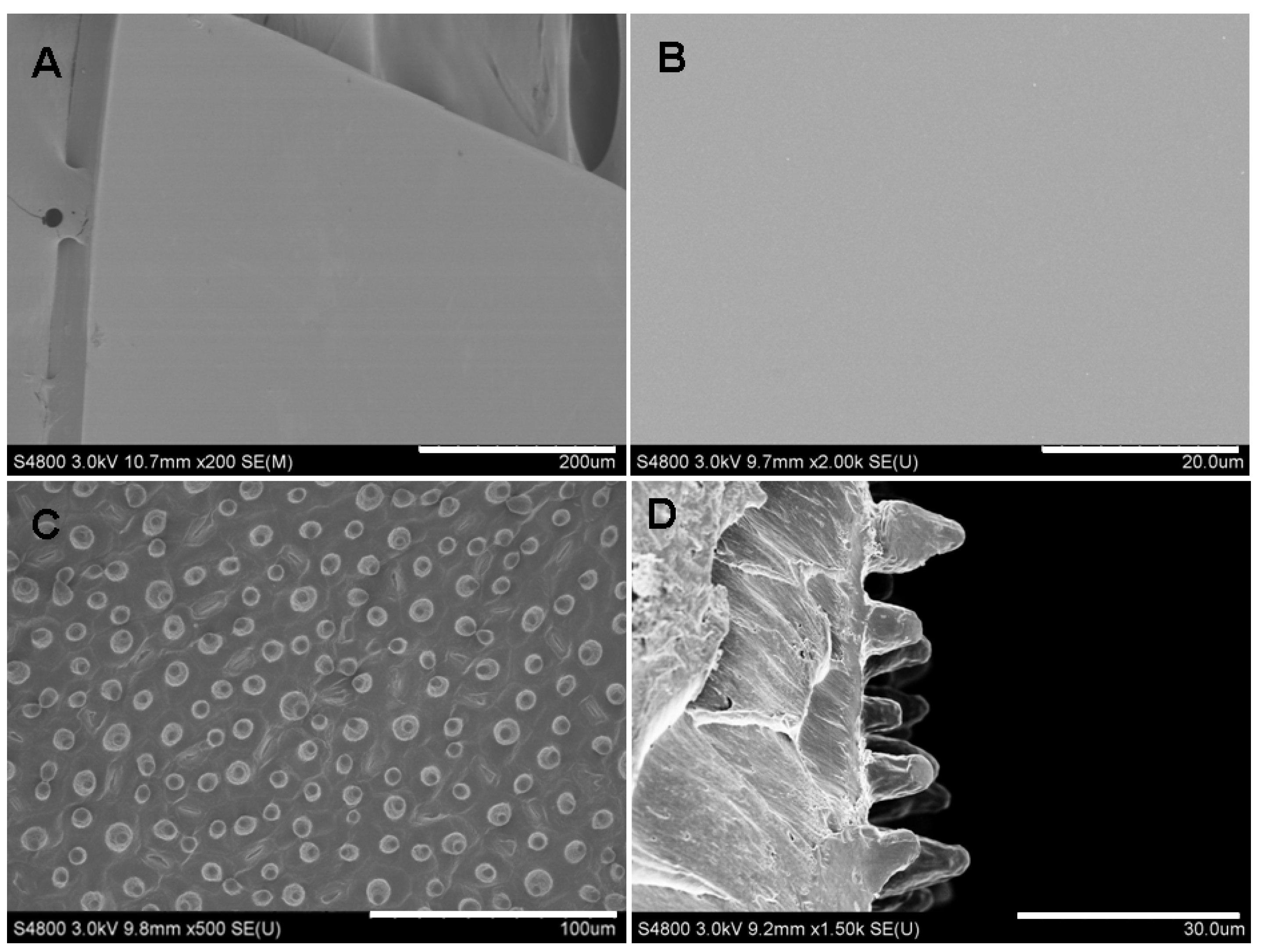
2.1. Surface Characterization of Silk Fibroin Films
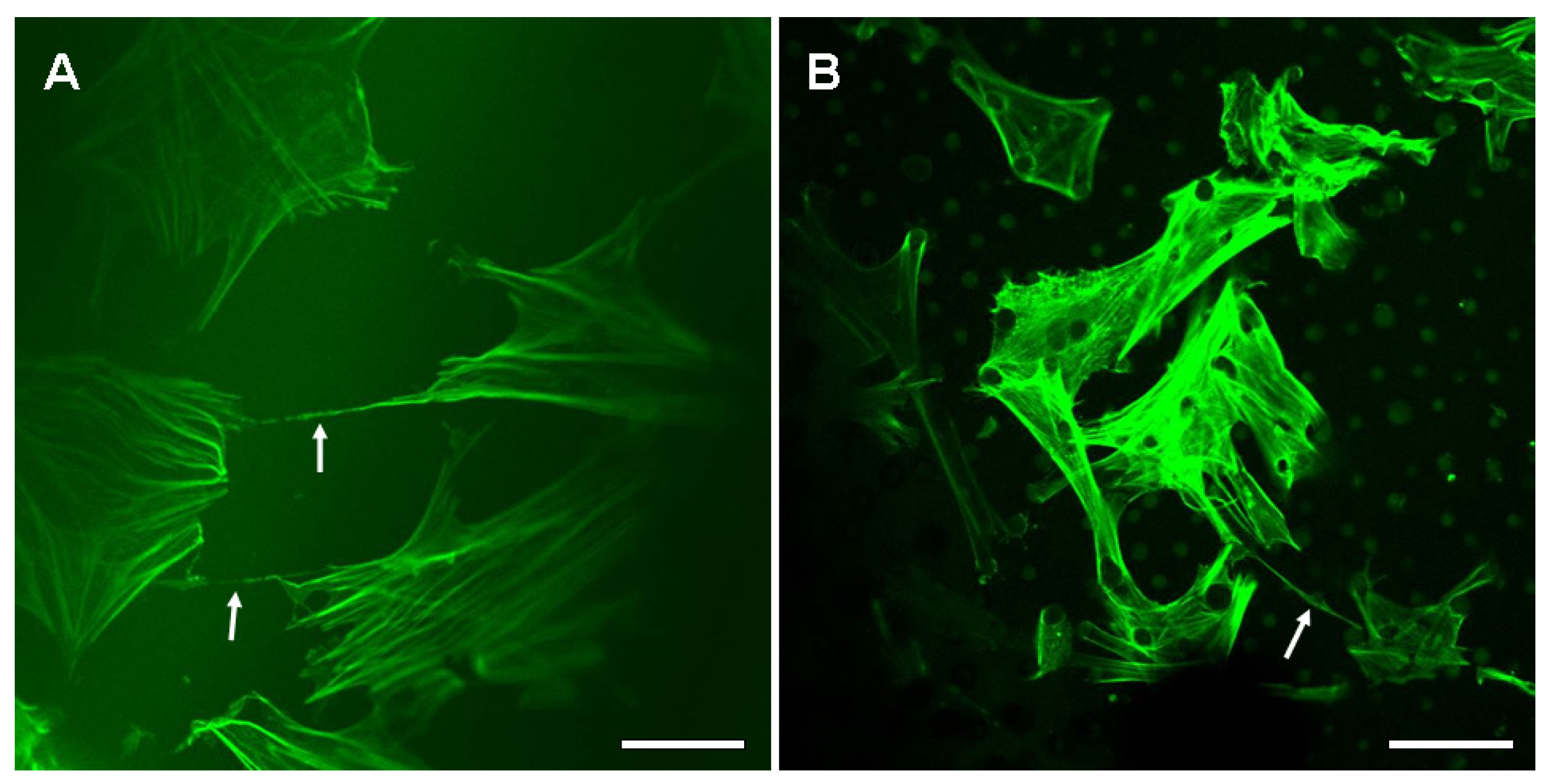
2.2. The Nanotubular Connection of BMSCs on the Silk Fibroin Films
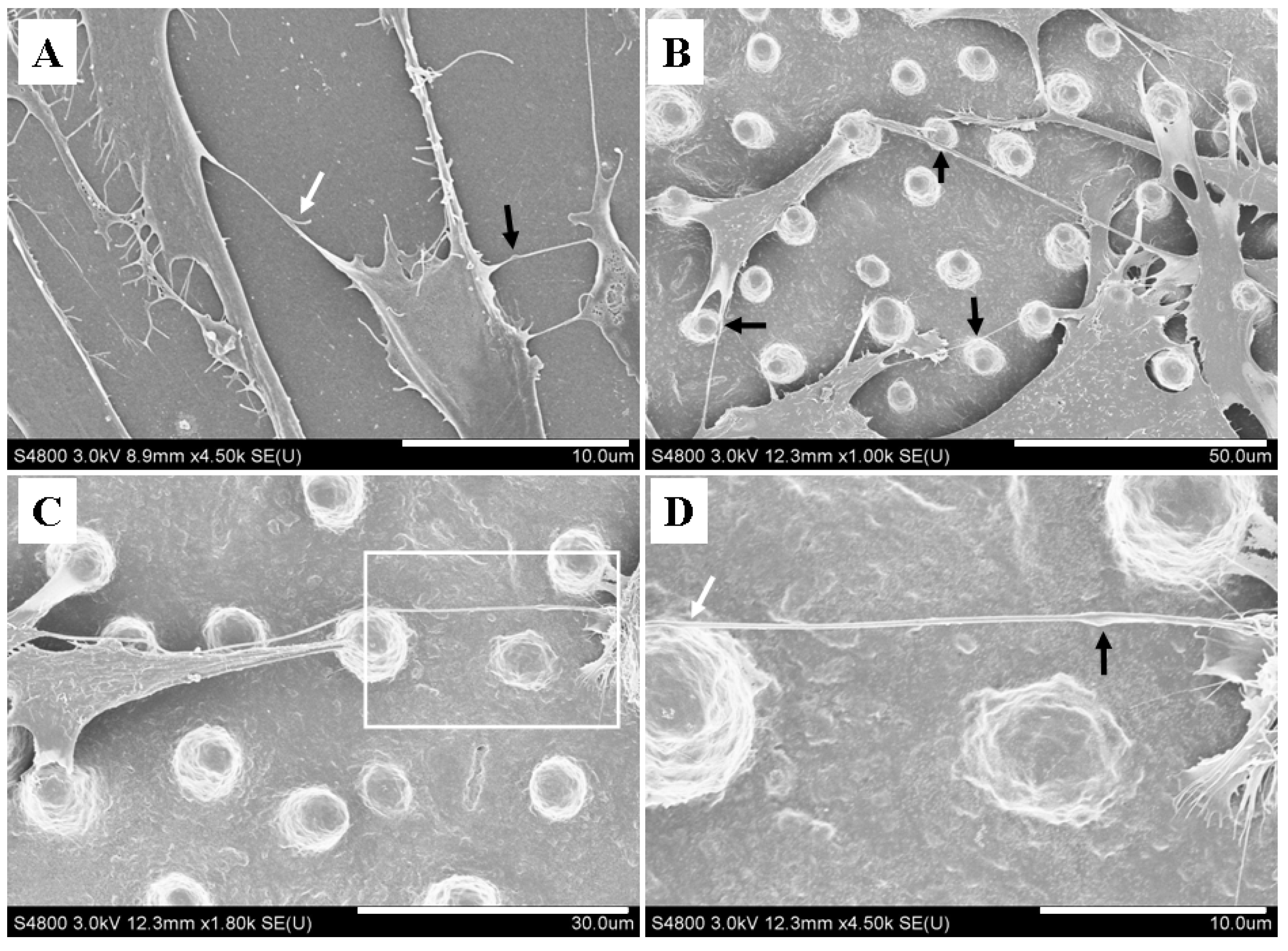
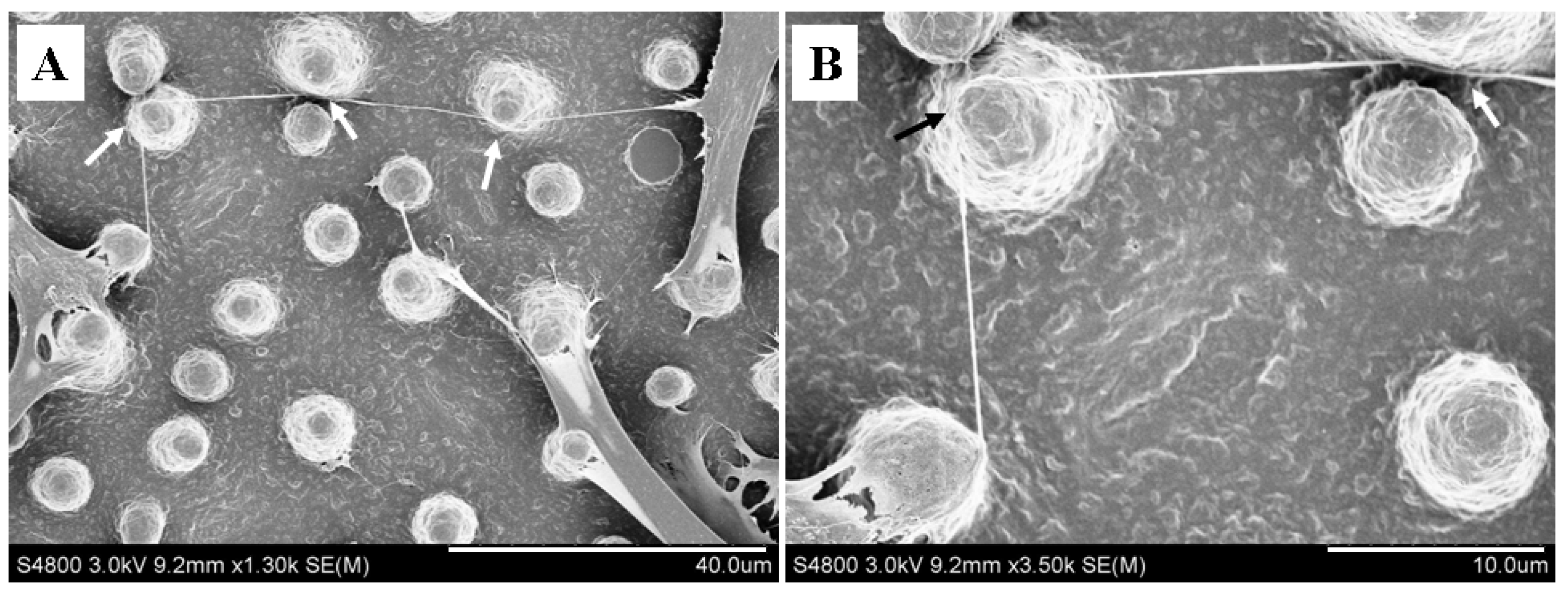
2.3. Micropillars Provided Supporting Points for Nanotubular Connection
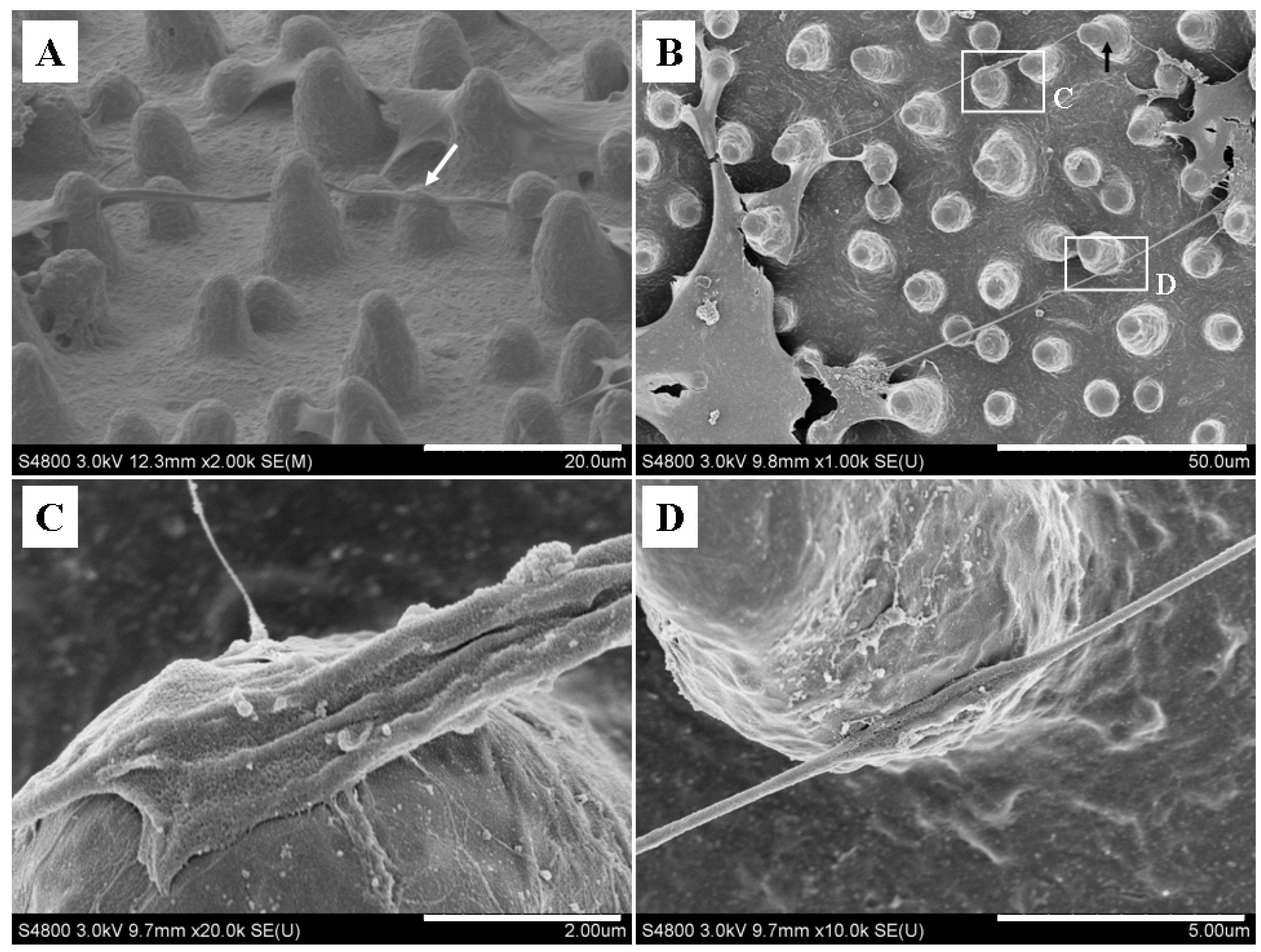
2.4. Micropillars Influenced the Extension Direction of Nanotubular Structure
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Preparation of Silk Fibroin Solution
3.2. Mold Preparation
3.3. Preparation of Silk Fibroin Films
3.4. Cell Culture
3.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy
3.6. Immunofluorescence Labeling
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maeda, S.; Tsukihara, T. Structure of the gap junction channel and its implications for its biological functions. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2011, 68, 1115–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, R.D.; Stevens-Graham, B. New insights into neuron-glia communication. Science 2002, 298, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rustom, A.; Saffrich, R.; Markovic, I.; Walther, P.; Gerdes, H.H. Nanotubular highways for intercellular organelle transport. Science 2004, 303, 1007–1010. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.M.; Shi, X.L.; Zhang, X.J.; Dang, S.; Ma, X.W.; Liu, F.; Xu, M.; Lv, Z.; Han, D.; Fang, X.; et al. Long-distance intercellular connectivity between cardiomyocytes and cardiofibroblasts mediated by membrane nanotubes. Cardiovasc. Res. 2011, 92, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyanagi, M.; Brandes, R.P.; Haendeler, J.; Zeiher, A.M.; Dimmeler, S. Cell-to-cell connection of endothelial progenitor cells with cardiac myocytes by nanotubes: A novel mechanism for cell fate changes? Circ. Res. 2005, 96, 1039–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrati, S.; Shamsudeen, S.; Summers, H.; Rees, P.; Abbey, J.V.A.; Schmulen, J.; Liu, X.; Wong, S.T.C.; Bean, A.J.; Ferrari, M.; et al. Inter-endothelial transport of microvectors using cellular shuttles and tunneling nanotubes. Small 2012, 8, 3151–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Önfelt, B.; Nedvetzki, S.; Yanagi, K.; Davis, D.M. Cutting edge: Membrane nanotubes connect immune cells. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 1511–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowinski, S.; Jolly, C.; Berninghausen, O.; Purbhoo, M.A.; Chauveau, A.; Köhler, K.; Oddos, S.; Eissmann, P.; Brodsky, F.M.; Hopkins, C.; et al. Membrane nanotubes physically connect T cells over long distances presenting a novel route for HIV-1 transmission. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauveau, A.; Aucher, A.; Eissmann, P.; Vivier, E.; Davis, D.M. Membrane nanotubes facilitate long-distance interactions between natural killer cells and target cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 5545–5550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cui, J.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Y. Tunneling-nanotube development in astrocytes depends on p53 activation. Cell Death Differ. 2011, 18, 732–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.H.; Tan, K.S.; Zhang, X.L.; Sun, A.Y.; Sun, G.Y.; Lee, J.C.M. Hydrogen peroxide alters membrane and cytoskeleton properties and increases intercellular connections in astrocytes. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 3695–3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerdes, H.H.; Bukoreshtliev, N.V.; Barroso, J.F.V. Tunneling nanotubes: A new route for the exchange of components between animal cells. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 2194–2201. [Google Scholar]
- Önfelt, B.; Nedvetzki, S.; Benninger, R.K.P.; Purbhoo, M.A.; Sowinski, S.; Hume, A.N.; Seabra, M.C.; Neil, M.A.A.; French, P.M.W.; Davis, D.M. Structurally distinct membrane nanotubes between human macrophages support long-distance vesicular traffic or surfing of bacteria. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 8476–8483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gousset, K.; Schiff, E.; Langevin, C.; Marijanovic, Z.; Caputo, A.; Browman, D.T.; Chenouard, N.; Chaumont, F.; Martino, A.; Enninga, J.; et al. Prions hijack tunneling nanotubes for intercellular spread. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascoal, P.; Kosanic, D.; Gjoni, M.; Vogel, H. Membrane nanotubes drawn by optical tweezers transmit electrical signals between mammalian cells over long distances. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 2235–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Veruki, M.L.; Bukoreshtliev, N.V.; Hartveit, E.; Gerdes, H.H. Animal cells connected by nanotubes can be electrically coupled through interposed gap-junction channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 17194–17199. [Google Scholar]
- Hase, K.; Kimura, S.; Takatsu, H.; Ohmae, M.; Kawano, S.; Kitamura, H.; Ito, M.; Watarai, H.; Hazelett, C.C.; Yeaman, C.; et al. M-Sec promotes membrane nanotube formation by interacting with Ral and the exocyst complex. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 1427–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, S.; Hase, K.; Ohno, H. Tunneling nanotubes: Emerging view of their molecular components and formation mechanisms. Exp. Cell Res. 2012, 318, 1699–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokar, M.; Iglič, A.; Veranič, P. Protruding membrane nanotubes: Attachment of tubular protrusions to adjacent cells by several anchoring junctions. Protoplasma 2010, 246, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.M.; Luo, W.X.; Zhang, Y.L.; Liu, F.; Liu, D.; Xu, L.; Qin, L.; Xiong, C.; Lu, Z.; Fang, X.; et al. Intercellular transportation of quantum dots mediated by membrane nanotubes. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 3015–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosi, G.; Vilella, A.; Chhabra, R.; Schmeisser, M.J.; Boeckers, T.M.; Ruozi, B.; Vandelli, M.A.; Forni, F.; Zoli, M.; Grabrucker, A.M. Insight on the fate of CNS-targeted nanoparticles. Part II: Intercellular neuronal cell-to-cell transport. J. Controlled Release 2014, 177, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, M.P.; Riese, S.R.; Schlicker, O.; Bukoreshtliev, N.V.; Gerdes, H.H.; Spatz, J.P.; Rustom, A. Microstructured platforms to study nanotube-mediated long-distance cell-to-cell connections. Biointerphases 2011, 6, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, R.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, G.; Lu, S.; Li, M. Response of filopodia and lamellipodia to surface topography on micropatterned silk fibroin films. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettinger, C.J.; Langer, R.; Borenstein, J.T. Engineering substrate topography at the micro- and nanoscale to control cell function. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 5406–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikkhah, M.; Edalat, F.; Manoucheri, S.; Khademhosseini, A. Engineering microscale topographies to control the cell substrate interface. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 5230–5246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matschegewski, C.; Staehlke, S.; Loeffler, R.; Lange, R.; Chai, F.; Kern, D.P.; Beck, U.; Nebe, B.J. Cell architecture-cell function dependencies on titanium arrays with regular geometry. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 5729–5740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.; Choi, S.-E.; Jang, H.S.; Cho, W.K.; Nam, Y.; Choi, I.S.; Lee, J.S. In vitro developmental acceleration of hippocampal neurons on nanostructures of self-assembled silica beads in filopodium-size ranges. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 2855–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austefjord, M.W.; Gerdes, H.H.; Wang, X. Tunneling nanotubes: Diversity in morphology and structure. Commun. Integr. Biol. 2014, 7, e27934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vepari, C.; Kaplan, D.L. Silk as a biomaterial. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2007, 32, 991–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, B.; Rajkhowa, R.; Kundu, S.C.; Wang, X. Silk fibroin biomaterials for tissue regenerations. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 65, 457–470. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Yan, S.; Li, M. Silk fibroin based porous materials. Materials 2009, 2, 2276–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, B.D.; Pan, Z.; Liu, A.; Kaplan, D.L.; Rosenblatt, M.I. Human corneal limbal epithelial cell response to varying silk film geometric topography in vitro. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 3732–3743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, K.; Bhushan, B.; Jung, Y.C.; Barthlott, W. Fabrication of artificial Lotus leaves and significance of hierarchical structure for superhydrophobicity and low adhesion. Soft Matter 2009, 5, 1386–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, E.; Fujisawa, S.; Morozov, A.; Barlas, A.; Romin, Y.; Dogan, Y.; Gholami, S.; Moreira, A.L.; Manova-Todorova, K.; Moore, M.A.S. Tunneling nanotubes provide a unique conduit for intercellular transfer of cellular contents in human malignant pleural mesothelioma. PLoS One 2012, 7, e33093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerdes, H.H.; Carvalho, R.N. Intercellular transfer mediated by tunneling nanotubes. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2008, 20, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherer, N.M.; Mothes, W. Cytonemes and tunneling nanotubules in cell-cell communication and viral pathogenesis. Trends Cell Biol. 2008, 17, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzo, L.; Gousset, K.; Zurzolo, C. Multifaceted roles of tunneling nanotubes in intercellular communication. Front Physiol. 2012, 3, 72. [Google Scholar]
- Wittig, D.; Wang, X.; Walter, C.; Gerdes, H.H.; Funk, R.H.W.; Roehlecke, C. Multi-level communication of human retinal pigment epithelial cells via tunneling nanotubes. PLoS One 2012, 7, e33195. [Google Scholar]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
You, R.; Li, X.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Lu, S.; Li, M. The Micropillar Structure on Silk Fibroin Film Influence Intercellular Connection Mediated by Nanotubular Structures. Materials 2014, 7, 4628-4639. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma7064628
You R, Li X, Xu Y, Liu Y, Lu S, Li M. The Micropillar Structure on Silk Fibroin Film Influence Intercellular Connection Mediated by Nanotubular Structures. Materials. 2014; 7(6):4628-4639. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma7064628
Chicago/Turabian StyleYou, Renchuan, Xiufang Li, Yamei Xu, Yu Liu, Shenzhou Lu, and Mingzhong Li. 2014. "The Micropillar Structure on Silk Fibroin Film Influence Intercellular Connection Mediated by Nanotubular Structures" Materials 7, no. 6: 4628-4639. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma7064628
APA StyleYou, R., Li, X., Xu, Y., Liu, Y., Lu, S., & Li, M. (2014). The Micropillar Structure on Silk Fibroin Film Influence Intercellular Connection Mediated by Nanotubular Structures. Materials, 7(6), 4628-4639. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma7064628





