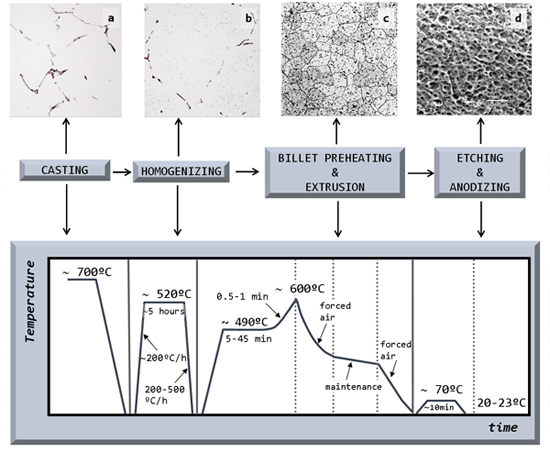
Effect of Processing Steps on the Mechanical Properties and Surface Appearance of 6063 Aluminium Extruded Products
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
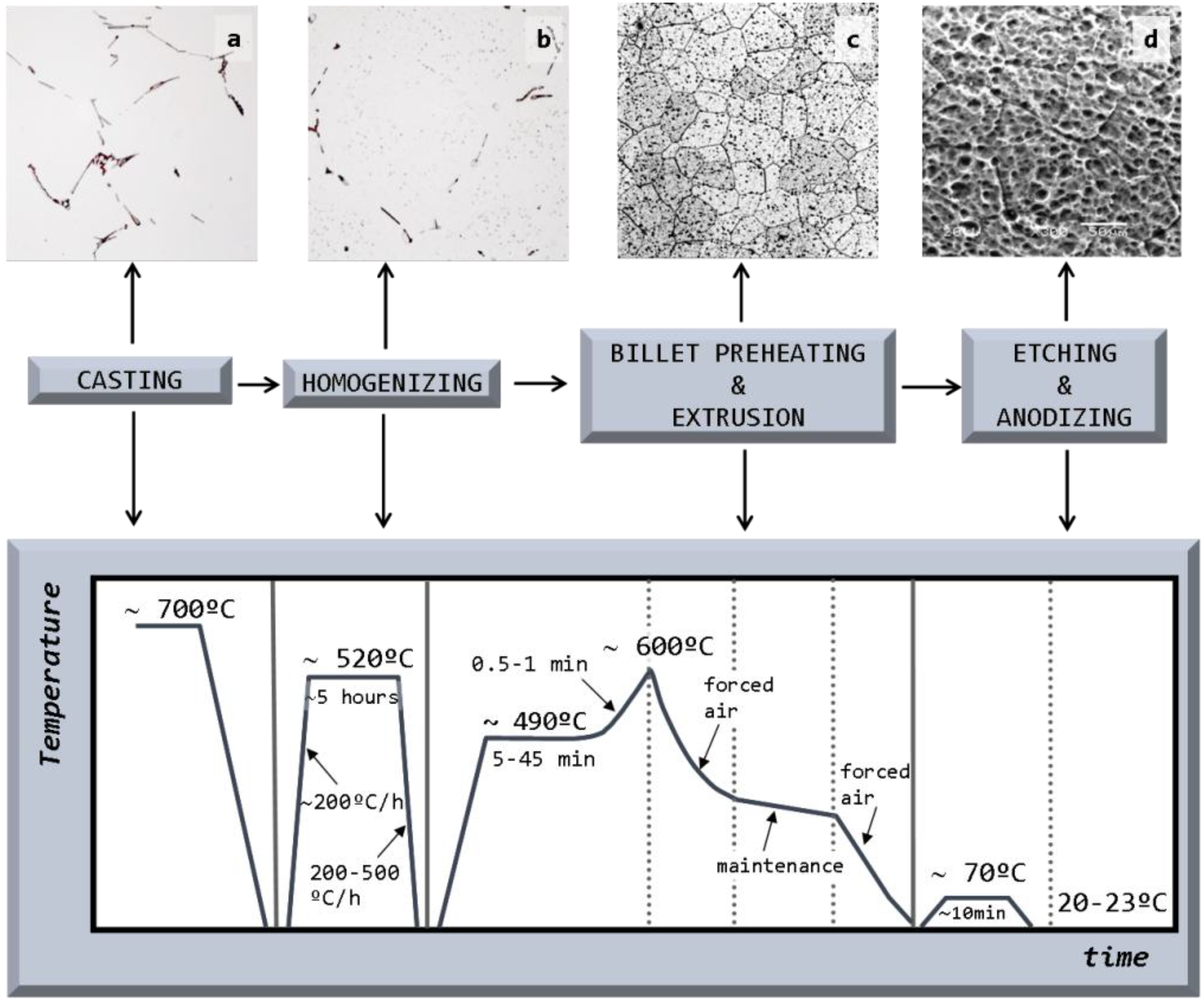
2.1. Billet Quality
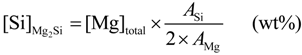
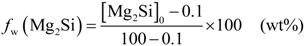
2.1.1. Billet Casting

| Alloy | Chemical composition (wt%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6063 | Si | Fe | Cu | Mn | Mg | Zn | Ti | Al |
| 0.45 | 0.19 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.45 | 0.03 | 0.02 | Balanced | |
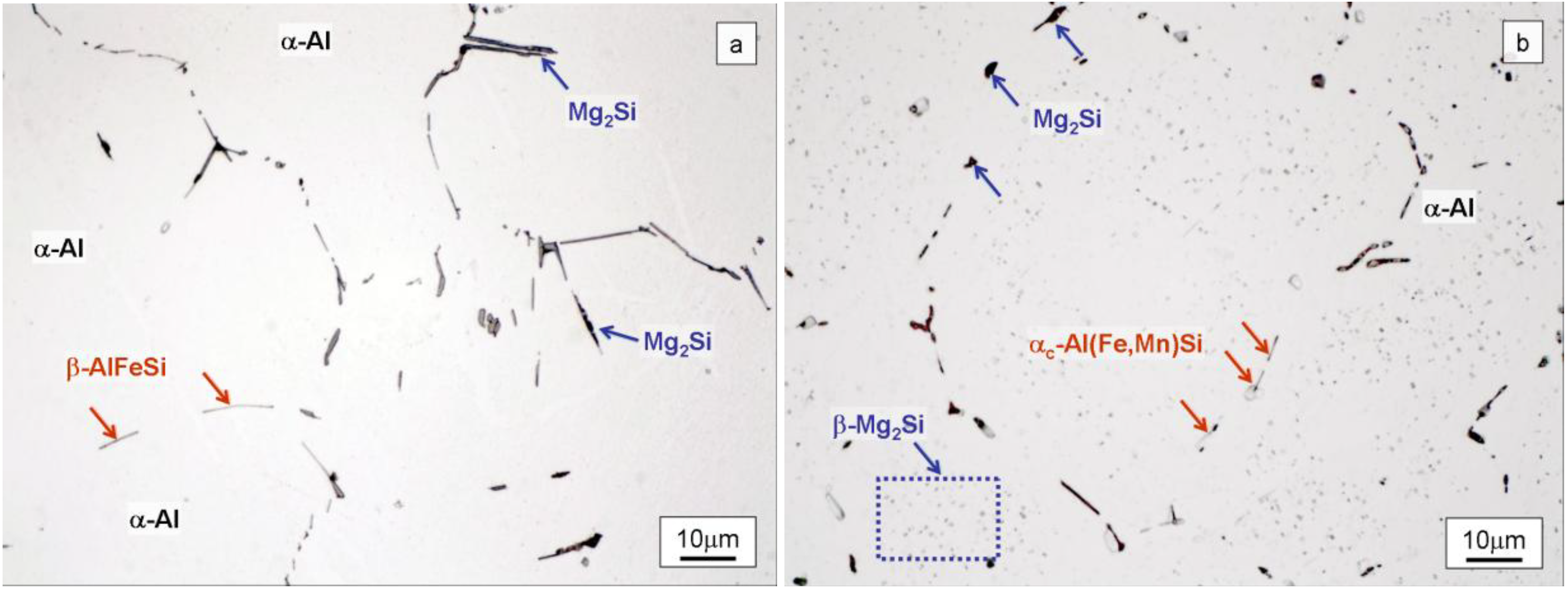
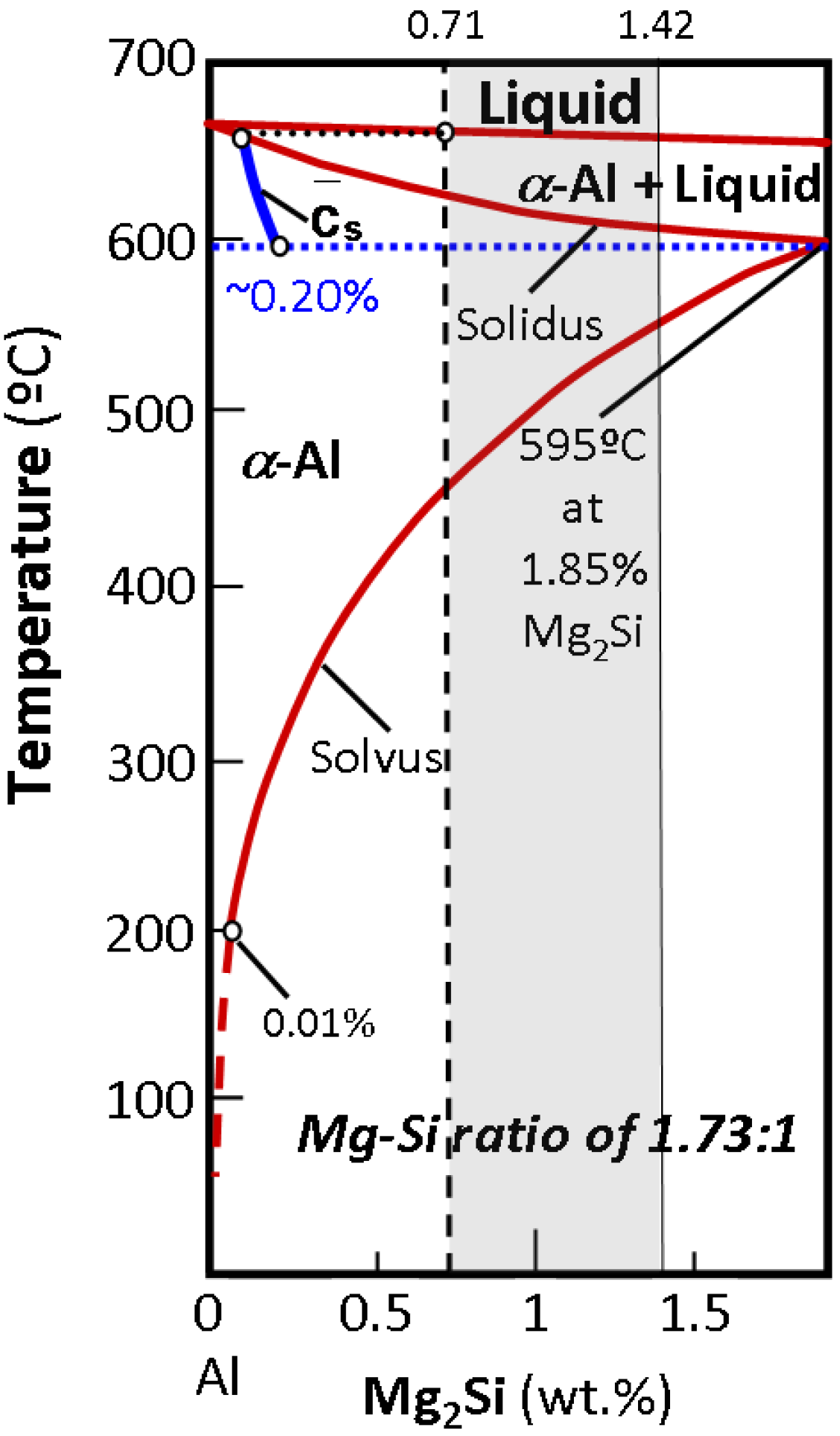
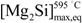 , i.e., 1.85 wt% (Figure 2). The aforementioned solidification strategy entails a new maximum Mg2Si solubility limit,
, i.e., 1.85 wt% (Figure 2). The aforementioned solidification strategy entails a new maximum Mg2Si solubility limit, 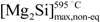 , for α-Al under non-equilibrium conditions. This value has to be derived from the average composition of the solid at the eutectic temperature and because of the presence of liquid phase at this temperature:
, for α-Al under non-equilibrium conditions. This value has to be derived from the average composition of the solid at the eutectic temperature and because of the presence of liquid phase at this temperature: 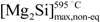 < 1.85 wt% [21]. The solubility limit in the specific DC non-equilibrium condition,
< 1.85 wt% [21]. The solubility limit in the specific DC non-equilibrium condition, 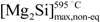 , is calculated as follows:
, is calculated as follows:
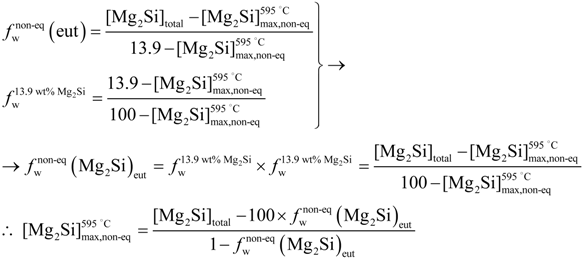
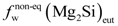 is the eutectic Mg2Si weight fraction.
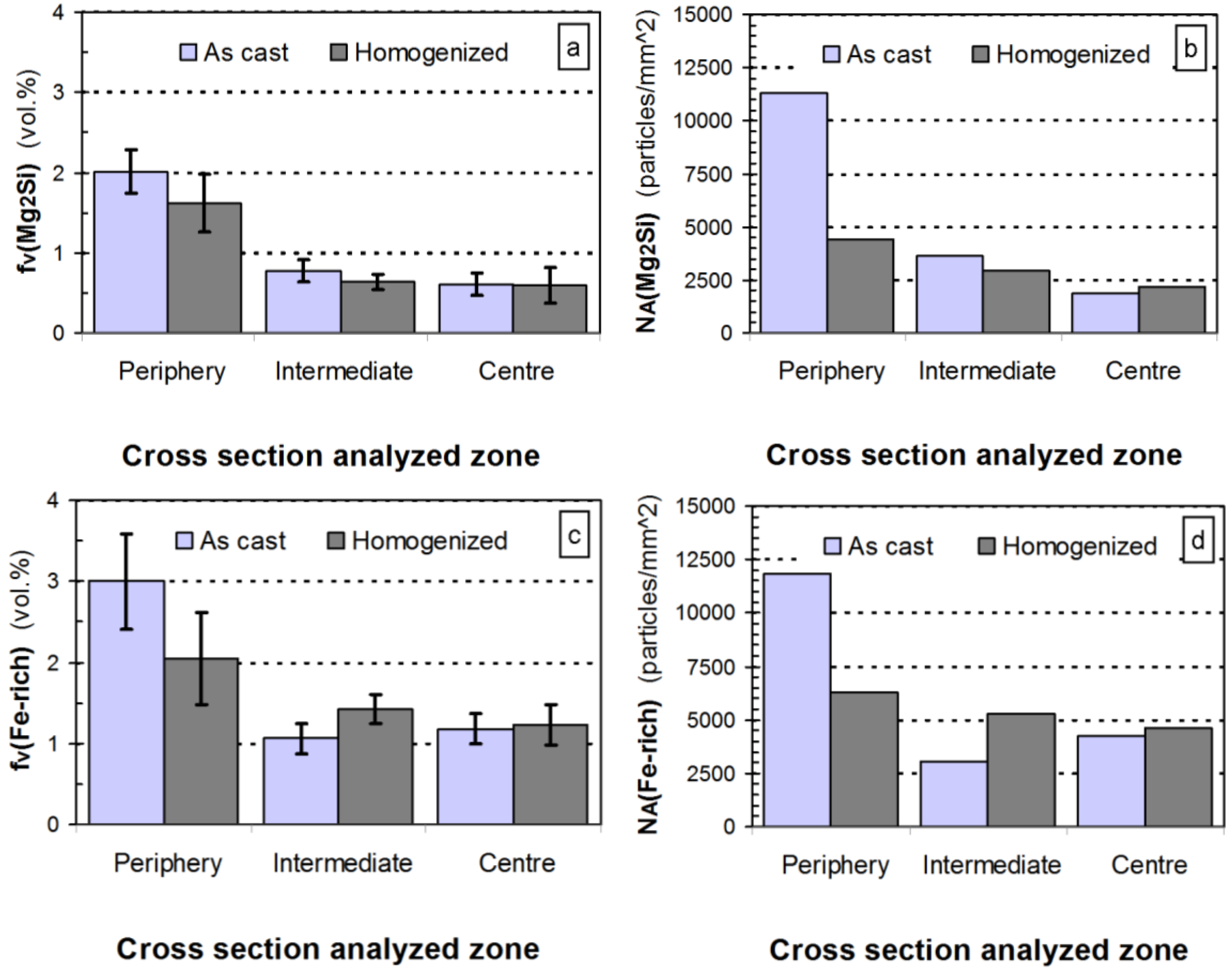
is the eutectic Mg2Si weight fraction.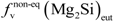 , (Figure 4a). Assuming the specific weights for Mg2Si and for the 6063 alloy to be 1.99 [22] and 2.69 g × cm−3, respectively [14], it is possible to calculate the eutectic Mg2Si weight fraction,
, (Figure 4a). Assuming the specific weights for Mg2Si and for the 6063 alloy to be 1.99 [22] and 2.69 g × cm−3, respectively [14], it is possible to calculate the eutectic Mg2Si weight fraction, 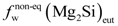 . As for the calculations, we took into consideration the quantitative metallographic determinations of the most representative areas in the billet, i.e., the intermediate zone and the central zone. The mean value of the eutectic Mg2Si volume fraction,
. As for the calculations, we took into consideration the quantitative metallographic determinations of the most representative areas in the billet, i.e., the intermediate zone and the central zone. The mean value of the eutectic Mg2Si volume fraction, 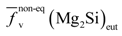 , is 0.69 vol% (Figure 4a), its corresponding calculated weight percent being calculated according to:
, is 0.69 vol% (Figure 4a), its corresponding calculated weight percent being calculated according to:
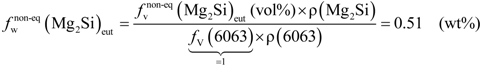
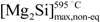 can hence be operated from the final expression in Equation (6):
can hence be operated from the final expression in Equation (6):
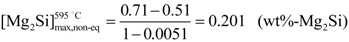
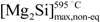 , will be set at ~0.20 wt%-Mg2Si (Figure 2). The weight fraction of fine precipitates that originated in the solid state, fw(β-Mg2Si), will thus be:
, will be set at ~0.20 wt%-Mg2Si (Figure 2). The weight fraction of fine precipitates that originated in the solid state, fw(β-Mg2Si), will thus be:

2.2. Homogenization Heat Treatment
2.2.1. Microstructural Aspects
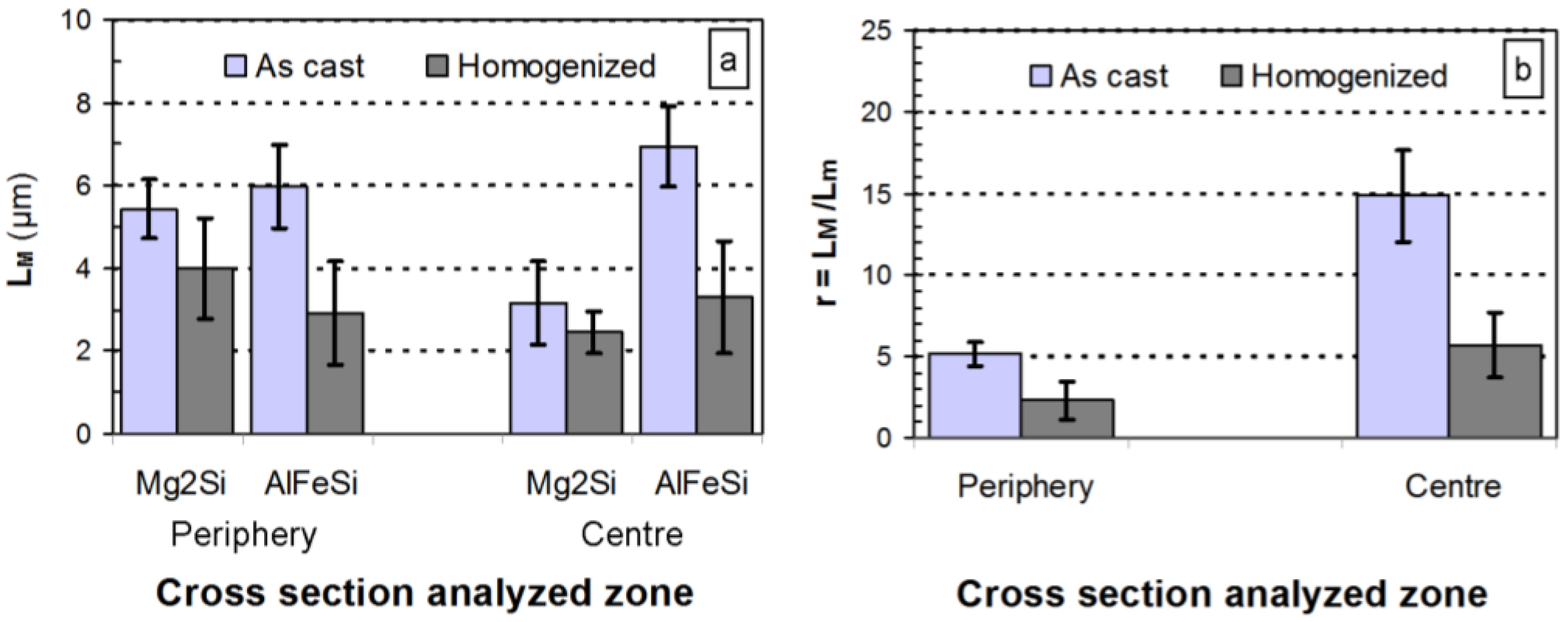
2.2.2. Mechanical Characterization
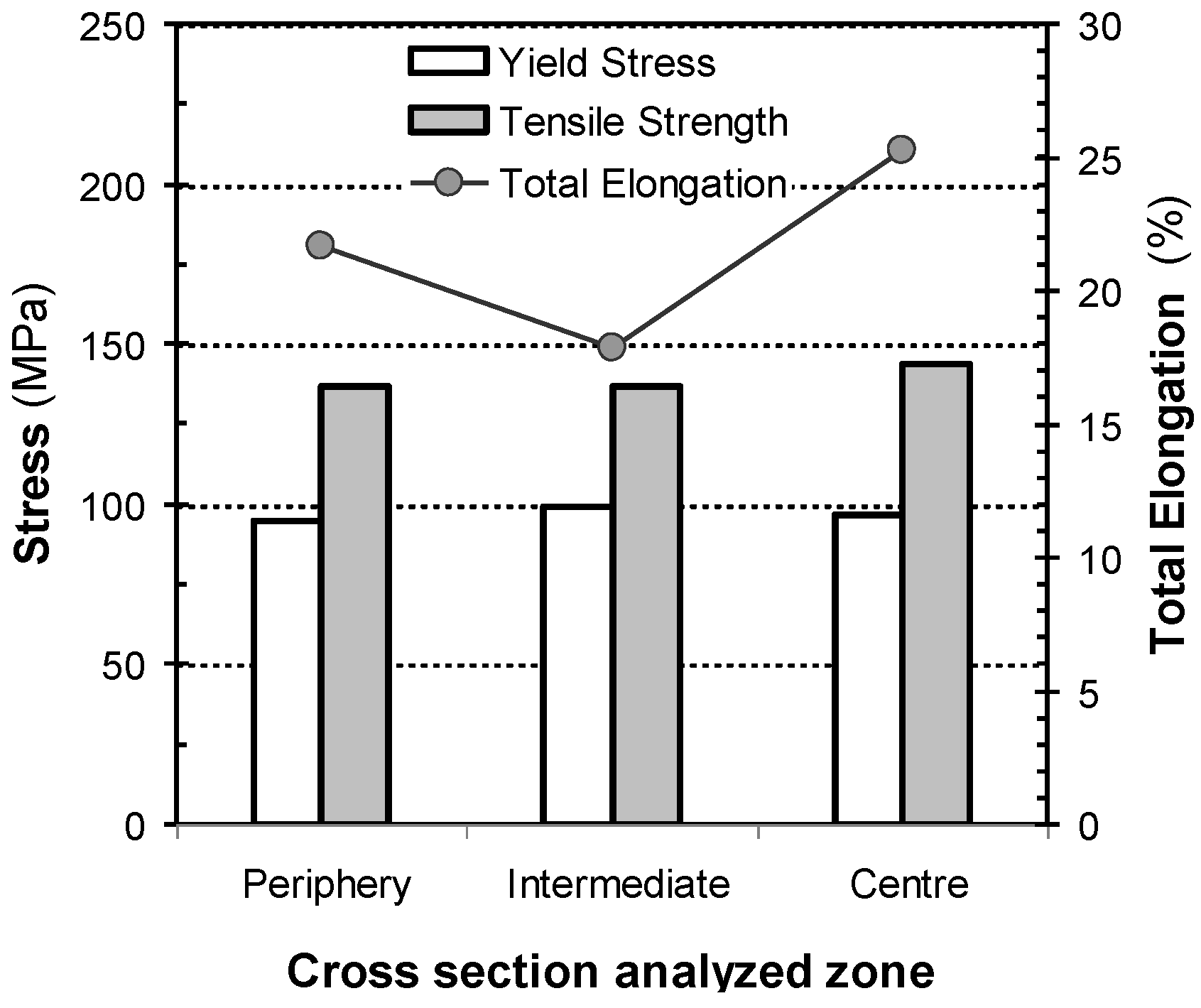
2.3. Billet Preheating and Extrusion
2.3.1. Microstructural Aspects
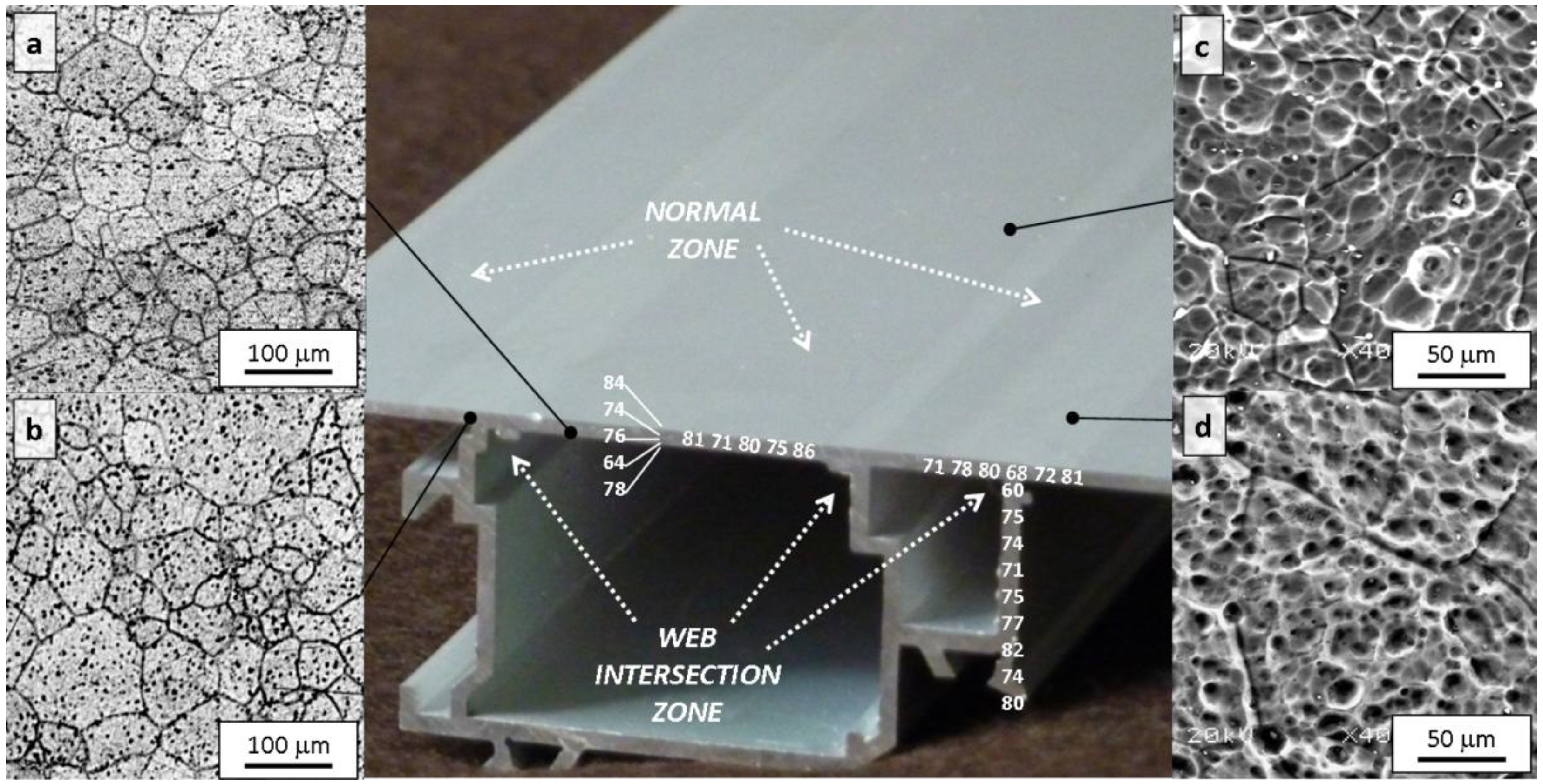
| Zone | α-Al Grain size | Mg2Si particles | HV (200g) | σTS (MPa) | σy (MPa) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L (µm) | CL-95% (µm) | ge (ASTM) | CL-95% (ASTM) | NA (part./mm2) | dp (µm) | HV (Kg/mm2) | CL-95% (Kg/mm2) | |||
| N | 52.37 | 2.32 | 5.2 | 0.13 | 5546 | 2.29 | 76.95 | ±4.70 | 181.52 | 135.12 |
| WI | 52.31 | 2.77 | 5.2 | 0.15 | 4972 | 2.65 | 74.80 | ±3.27 | 175.92 | 130.73 |
2.3.2. Mechanical Characterization
2.4. Etching and Anodizing
3. Experimental Method and Materials
3.1. Mechanical Characterization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nadella, R.; Eskin, D.G.; Du, Q.; Katgerman, L. Macrosegregation in Direct-Chill Casting of Aluminium Alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2008, 53, 421–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliravci, C.A.; Pekgüleryüz, M.Ö. Calculation of Phase Diagrams for the Metastable Al-Fe Phases Forming in Direct-Chill (DC)-Cast Aluminum Alloy Ingots. Calphad 1998, 22, 147–l55. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, A.; Sheppard, T. Extrusion Limit Diagrams: Effect of Homogenizing Conditions and Extension to Productivity Analysis. Mater. Sci. Tech. Lond. 1997, 13, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavgali, M.; Aksakal, B. Effects of Various Homogenization Treatments on the Hot Workability of Ingot Aluminum Alloy AA2014. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1998, 254, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, G.; O’Reilly, K.; Cantor, B.; Worth, J.; Hamerton, R. Growth Related Metastable Phase Selection in a 6xxx Series Wrought Al Alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2001, 304–306, 612–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto, K.S.; Claves, S.R.; Van Geertruyden, W.H.; Misiolek, W.Z.; Goncalves, M. Treatment Effects of Homogenization on Microstructure and Hot Ductility of Aluminum Alloy 6063. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2005, 21, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Marahleh, G. Effect of Heat Treatment on Distribution Parameters and Volume Fraction of Mg2Si in Structural Al Alloy 6063. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 2006, 3, 1819–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaber, A.; Mossad, A.; Matsuda, A.K.; Kawabata, T.; Yamazaki, T.; Ikeno, S. Study of the Developed Precipitates in Al-0.63Mg-0.37Si-0.5Cu (wt%) Alloy by Using DSC and TEM Techniques. J. Alloy. Compd. 2007, 432, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassance, D.; Fabregue, D.; Delannay, F.; Pardoen, T. Micromechanics Temperature Fracture in 6xxx Al Alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2007, 52, 62–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Zhang, X.; Couper, M.J.; Dahle, A.K. Effect of Initial Microstructure of Anodized Aluminum Extrusions. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2009, 40, 3264–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauge, T.; Karhausen, K.F. Extrusion Parameters Influencing the Anodizing Quality. Aluminum. Extrusion. 1998, 3, 32–37. [Google Scholar]
- Sheppard, T. Extrusion of Aluminum Alloys; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Zhang, X.; Couper, M.J.; Dahle, A.K. The Formation of Streak Defects on Anodized Aluminum Extrusions. JOM 2010, 62, 46–51. [Google Scholar]
- Aluminum and Aluminum Alloys; ASM Specialty Handbook; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 2002.
- Meng, C. Effect of Preheating Condition on Strength of AA6060 Aluminium Alloy for Extrusion. Master’s Thesis, School of Engineering, Auckland University of Technology, Auckland, New Zealand, March 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, G.A.; Stilloer, K.; Dunlop, G.L.; Couper, M.J. The Precipitation Sequence in Al-Mg-Si Alloys. Acta. Mater. 1998, 46, 3893–3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.; Oreily, K.A.Q.; Cantor, B.; Hamerton, R. Non-equilibrium Reactions in 6xxx Series Al Alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2001, 304–306, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanihata, H.; Sugawara, T.; Matsuda, K.; Ikeno, S. Effect of Casting and Homogenizing Treatment Conditions on the Formation of Al-Fe-Si Intermetallic Compounds in 6063 Al-Mg-Si Alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 1999, 34, 1205–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassance, D. Modelling of Study of Damage Mechanism in AlMgSi Alloys. Ph.D. Thesis, Presses Universitaires de Louvain, Louvain, Belgium, March 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Callister, W.D., Jr. Materials Science and Engineering: An Introduction; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Reed-Hill, R.E.; Abbaschian, R. Physical Metallurgy Principles; PWS Publishing Company: Boston, MA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Cafri, M.; Malka, A.; Dilman, H.; Dariel, M.P.; Frage, N. Reaction-Bonded Boron Carbide/Magnesium–Silicon Composites. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2013, 11, 273–279. [Google Scholar]
- Gruzleski, J.E. Microstructure Development during Metalcasting; AFS: Des Plaines, IL, USA, 2000; pp. 117–130. [Google Scholar]
- Finn, T.L.; Chu, M.G.; Bennon, W.D. The Influence of Mushy Region. Microstructure on Macrosegregation in Direct Chill Cast Aluminum-Copper Round Ingots; ASME: New York, NY, USA, 1992; pp. 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Langsrud, Y. Silicon in Commercial Aluminium Alloys—What Becomes of it During DC Casting? Key Eng. Mater. 1990, 44–45, 95–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zajac, S.; Hutchinson, B.; Johansson, A.; Gullman, L. Microstructure Control and Extrudability of Al-Mg-Si Alloys Microalloed with Manganese. Mater. Sci. Tech. Lond. 1994, 10, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onurlu, S.; Tekin, A. Effect of Heat Treatment on the Insoluble Intermetallic Phases Pesent in an AA6063 Alloy. J. Mater. Sci. 1994, 29, 1652–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flitta, I.; Sheppard, T. Simulation of Bridge Die Extrusion Using the Finite Element Method. Mater. Sci. Tech. Lond. 2002, 18, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valberg, H. Metal Flow in the Direct Axisymmetric Extrusion Aluminium. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 1992, 31, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayser, T.; Klusemann, B.; Lambers, H.G.; Maier, H.J.; Svendsen, B. Characterization of Grain Microstructure Development in the Aluminum Alloy EN AW-6060 During Extrusion. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 6568–6573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermolen, F.; Vuik, K.; Vander Zwaag, S. A Mathematical Model for the Dissolution Kinetics of Mg2Si Phases in Al-Mg-Si Alloys During Homogenization Under Industrial Conditions. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1998, 254, 13–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Zhang, X.; Couper, M.J.; Dahle, A.K. Effect of Process Variables on Mg-Si Particles and Extrudability of 6xxx Series Aluminum Extrusions. JOM 2011, 63, 66–71. [Google Scholar]
- Askeland, D.R. The Science and Engineering of Materials; Chapman & Hall: Oxford, UK, 1996; pp. 223–225. [Google Scholar]
- Ashby, M.F.; Jones, D.R.H. Engineering Materials 2: An Introduction to Microstructures, Processing and Design; Pergamon Press: Exeter, UK, 1988; pp. 95–103. [Google Scholar]
- Petty, E.R. Relationship between Hardness and Tensile Properties over a Wide Range of Temperature for Aluminum Alloys. Metallurgia 1962, 65, 25–26. [Google Scholar]
- Marchive, D. High Extrudability Alloys in the 6000 Series. Light Metal. Age 1983, 41, 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Zhang, X.; Couper, M.J.; Dahle, A.K. Effect of Primary Intermetallic Particles on Surface Microstructure and Appearance of Aluminium Extrusions. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2009, 113, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokit, Y.; Gavgali, M.; Salender, R.; Kaymaz, I. The Effect of the Microestructural Difference between Surface and Center of the Workability of AA6063 Homogenized Ingot. J. Adv. Mater. 2004, 36, 53–59. [Google Scholar]
- Mulazimoglu, M.H.; Zaluska, A.; Gruzleski, J.E.; Paray, F. Electron Al-Fe-Si Intermetallics in 6201 Aluminum Alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 1996, 27, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vander Voort, G.F. Practical Guide to Image Analysis; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Warmuzek, M. Metallography and Microstructures; Vander Voort, G.F., Ed.; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Vander Voort, G.F. Metallography: Principles and Practice; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Muirhead, J.; Cawley, J.; Strang, A. Quantitative Aspects of Grain Size Measurement. Mater. Sci. Tech. Lond. 2000, 16, 1160–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higginson, R.L.; Sellars, C.M. Worked Examples in Quantitative Metallography; Institute of Metals, Maney Publishing: London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Standard Test Methods for Determining Volume Fraction by Systematic Manual Point Count; ASTM E562–11; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2011.
- Vander Voort, G.F. Quantitative Microscopy and Image Analysis; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 1994; pp. 21–34. [Google Scholar]
- Kuijpers, N.C.W.; Kool, W.H.; Koenis, P.T.G.; Nilsen, K.E.; Toody, I.; van der Zwaag, S. Assessment of Different Techniques for Quantification of α-Al(FeMn)Si and β-AlFeSi Intermetallics in AA 6XXX Alloys. Mater. Charact. 2003, 49, 409–420. [Google Scholar]
- Standard Test Methods for Tension Testing Wrought and Cast Aluminum and Magnesium-Alloy Products; ASTM B557–10; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2010.
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Asensio-Lozano, J.; Suárez-Peña, B.; Vander Voort, G.F. Effect of Processing Steps on the Mechanical Properties and Surface Appearance of 6063 Aluminium Extruded Products. Materials 2014, 7, 4224-4242. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma7064224
Asensio-Lozano J, Suárez-Peña B, Vander Voort GF. Effect of Processing Steps on the Mechanical Properties and Surface Appearance of 6063 Aluminium Extruded Products. Materials. 2014; 7(6):4224-4242. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma7064224
Chicago/Turabian StyleAsensio-Lozano, Juan, Beatriz Suárez-Peña, and George F. Vander Voort. 2014. "Effect of Processing Steps on the Mechanical Properties and Surface Appearance of 6063 Aluminium Extruded Products" Materials 7, no. 6: 4224-4242. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma7064224
APA StyleAsensio-Lozano, J., Suárez-Peña, B., & Vander Voort, G. F. (2014). Effect of Processing Steps on the Mechanical Properties and Surface Appearance of 6063 Aluminium Extruded Products. Materials, 7(6), 4224-4242. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma7064224