Lithium Ion Battery Anode Aging Mechanisms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Formation of Passivated Surface Layer

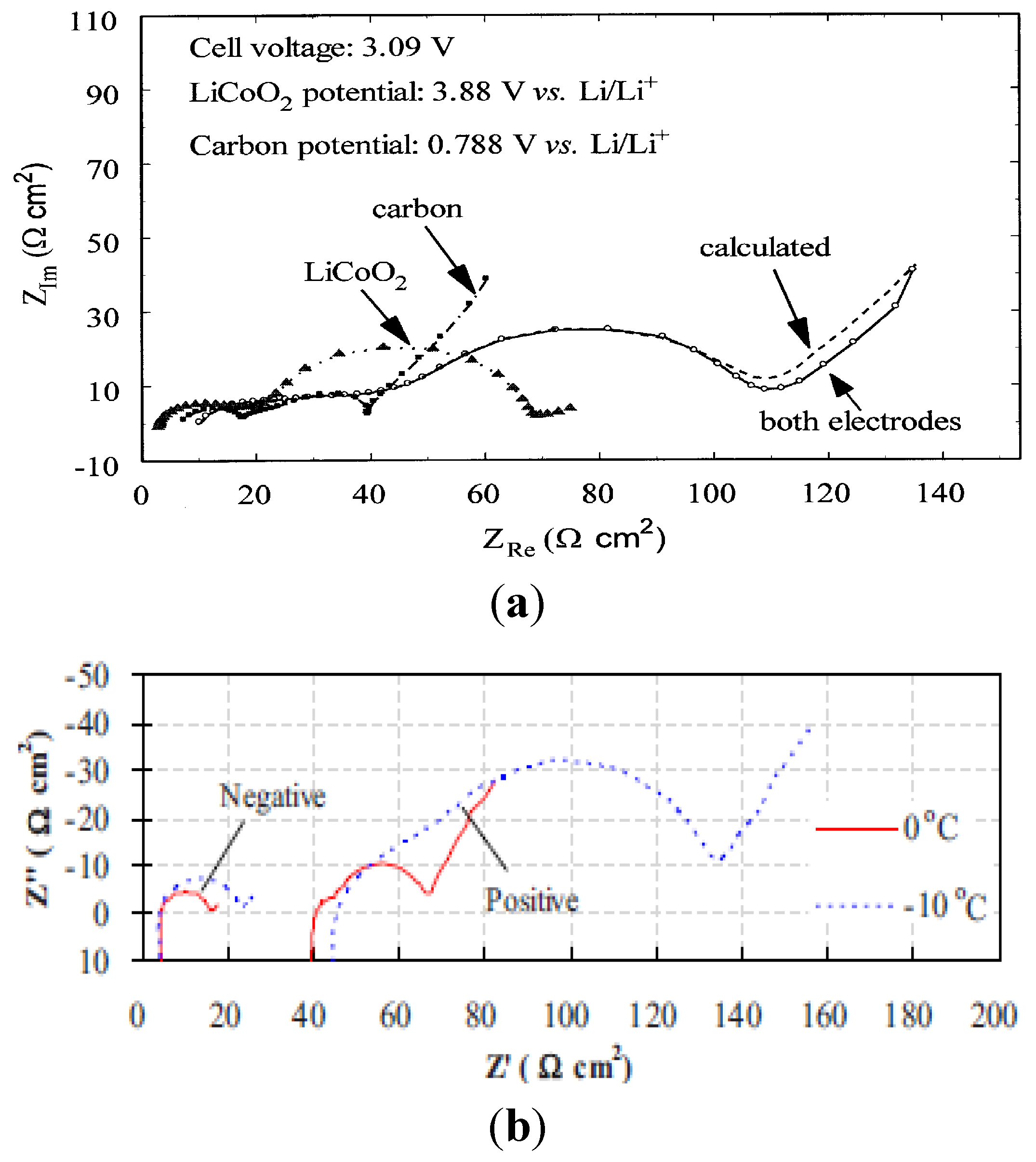
3. Anode Impedance

4. Degradation Due to the Loss of Recyclable Lithium Ions
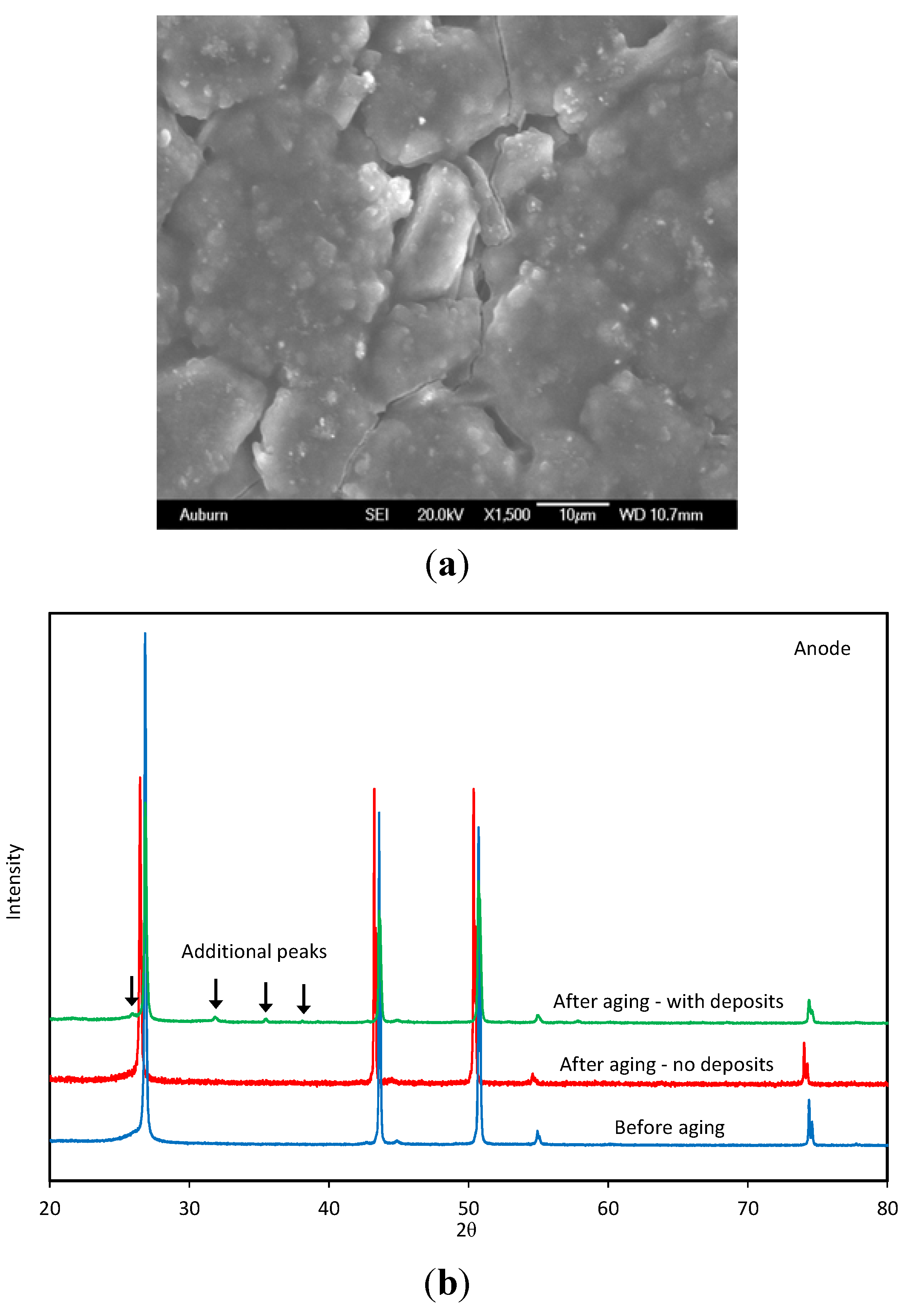
5. Anode Degradation Due to Structural Changes
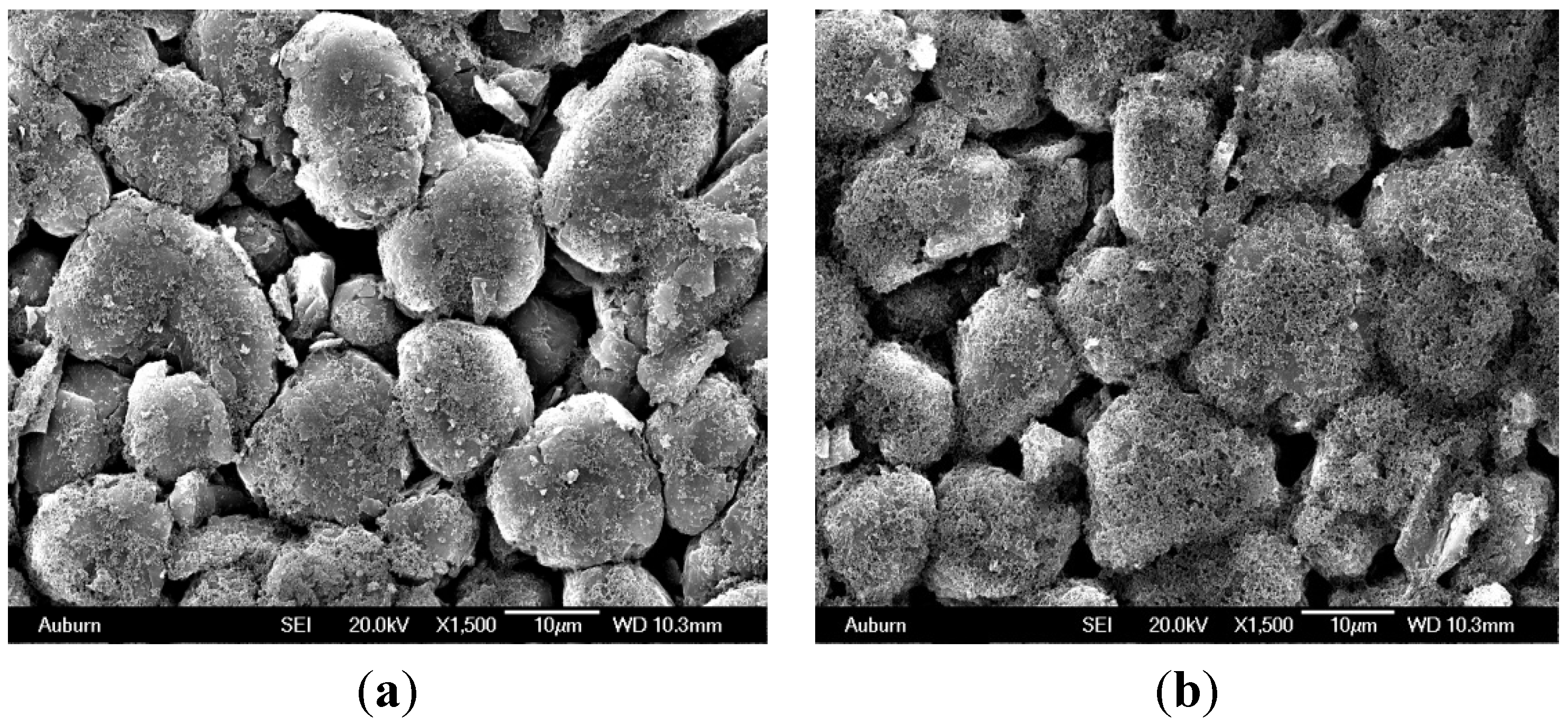
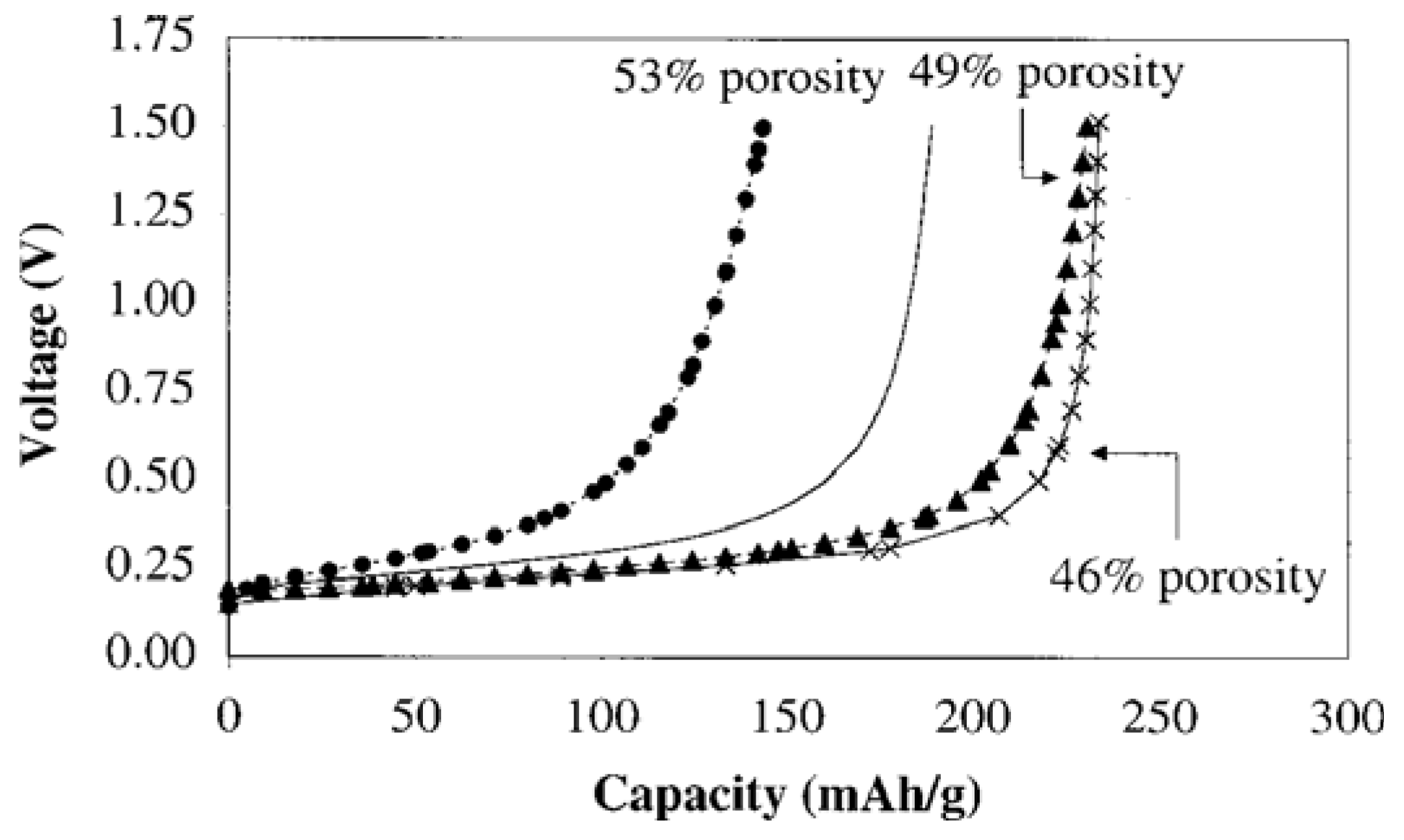
6. Influence of Particle Size, Active Surface Area and Porosity
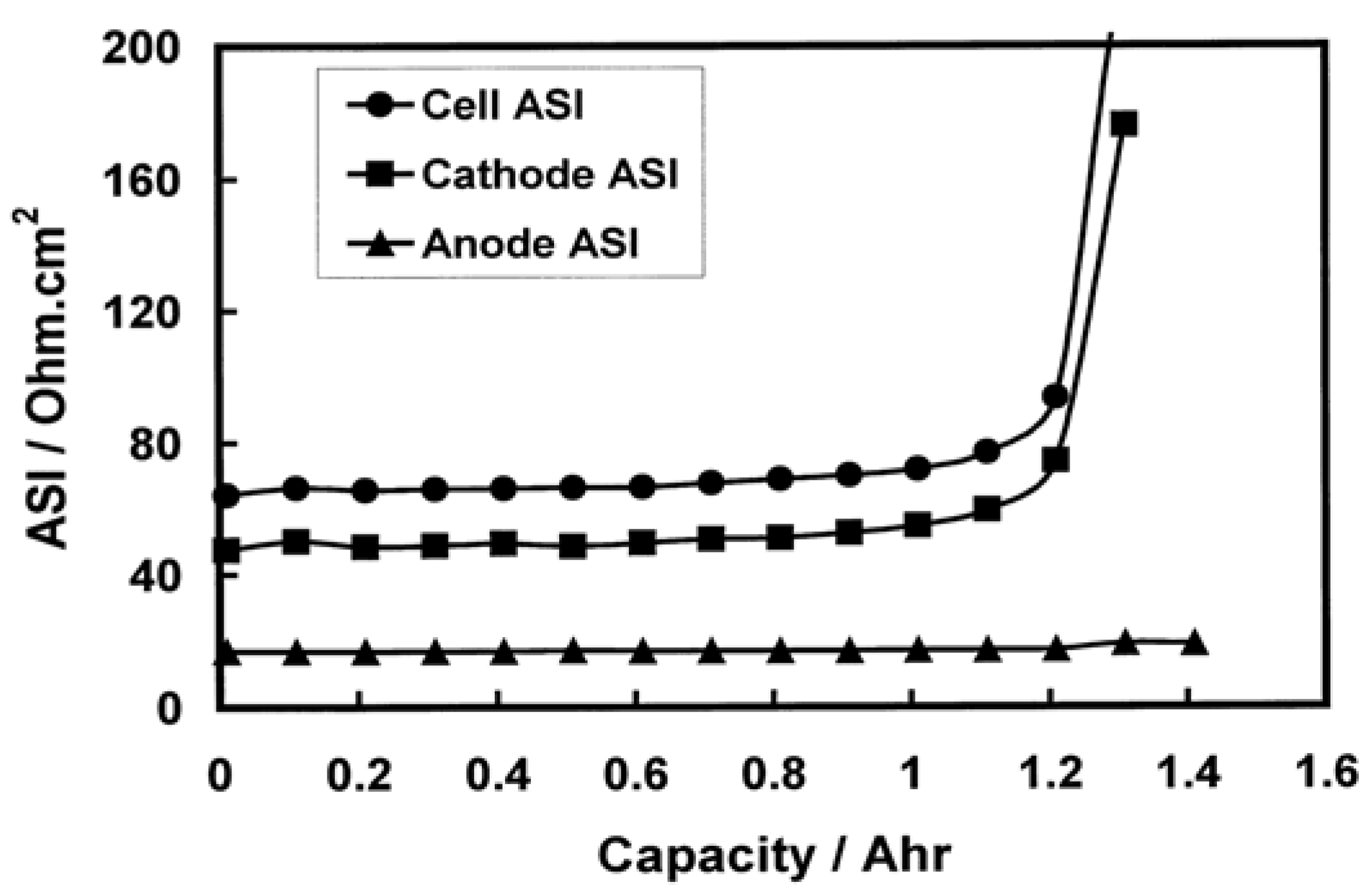
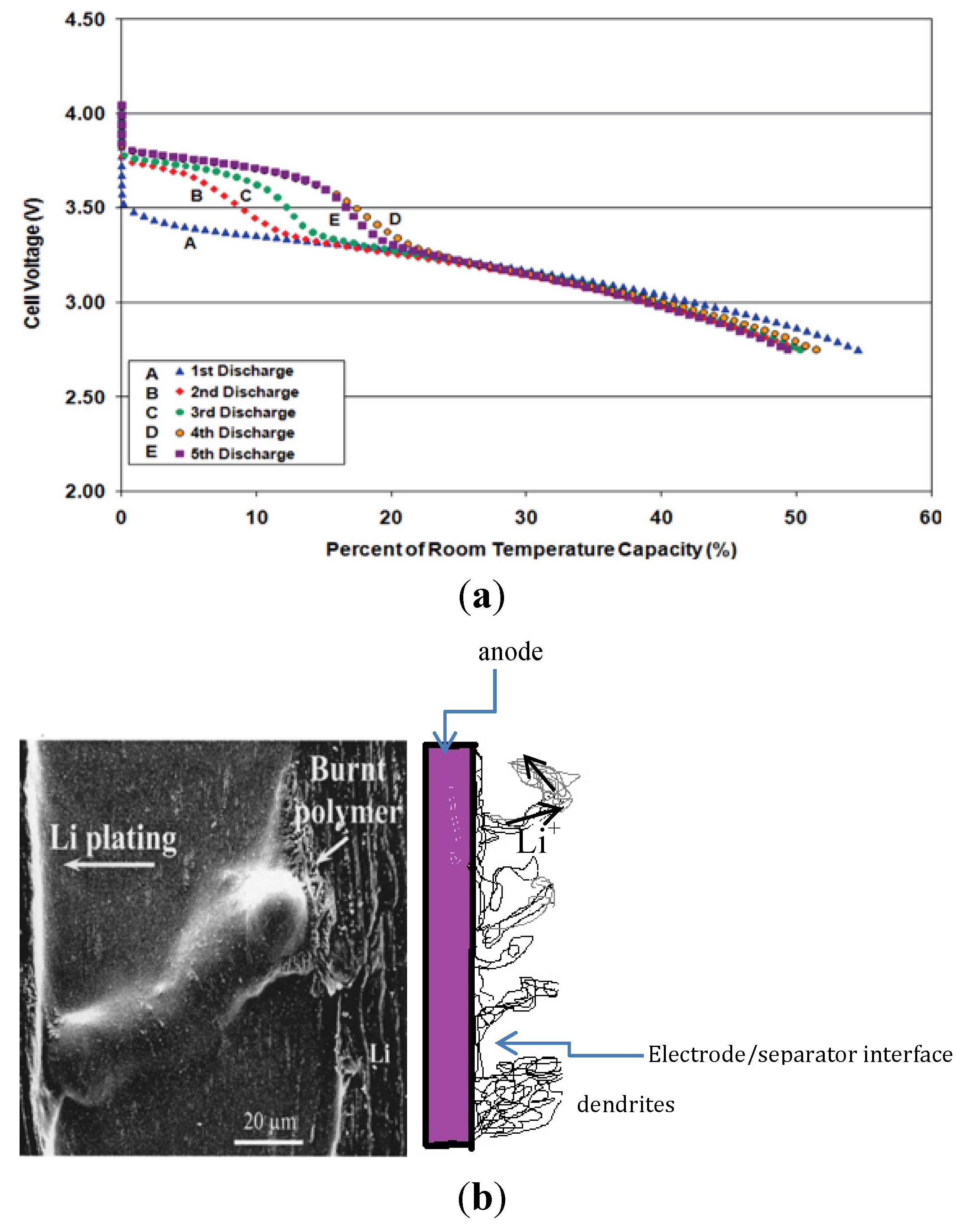
7. Metallic Lithium Plating on the Anode
8. Conclusions
References
- Whittingham, M.S. Material challenges facing electrical energy storage. MRS Bull. 2008, 33, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, A.; Patil, V.; Shin, W.D.; Choi, J.W.; Paik, D.S.; Yoon, J. Issues and challenges facing rechargeable thin film lithium batteries. Mater. Res. Bull. 2008, 43, 1913–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, A.K.; Kumar, T.P. Materials for the next generation lithium ion batteries. Curr. Sci. 2008, 94, 314–331. [Google Scholar]
- Endo, M.; Kim, C.; Nishimura, K.; Fujino, T.; Miyashita, K. Recent development of carbon materials for Li Ion batteries. Carbon 2000, 38, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, S.; Newman, J. Measuring the salt activity coefficient in Lithium-battery electrolytes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2008, 155, A458–A463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Cheng, H.; Yang, Y. A comparison of solid electrolyte interphase on the artificial graphite anode of the aged and cycled commercial lithium ion cells. Eelectrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 3539–3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belharouak, I.; Koening, G., Jr.; Tan, T.; Yumoto, H.; Ota, N. Performance degradation and gassing of Li4Ti5O12/LiMn2O4 lithium-ion cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2012, 159, 1165–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, M.D.; Wang, C.; Gnanara, J.S.; Aurbach, D. Electrochemical behavior of graphite anode at elevated temperature in organic carbonate solution. J. Power Sources 2003, 119, 538–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadass, P.; Haran, B; White, R; Popov, B N. Capacity fade of Sony 18650 cells cycled at elevated temperatures Part I. Cycling performance. J. Power Sources 2002, 112, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haran, B.; White, R.; Popov, B.N. Capacity fade of Sony 18650 cells cycled at elevated temperatures Part II. Capacity fade analysis. J. Power Sources 2002, 112, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Tang, X. Cycling degradation of automotive LiFePO4 lithium-ion battery. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 1513–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Takahashi, M.; Wang, B. A study on capacity fading of lithium-ion battery with a manganese positive electrode during cycling. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 51, 3228–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.J.; Hannah, M.; Dahn, J.R. Long-term low rate cycling of LiCoO2 graphite Li-ion cells at 55 °C. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2012, 159, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, D.P.; Reynolds, E.M.; Samman, E.; Jansen, A.N.; Dees, D.W. Aging characteristics of high-power lithium ion cells with LiNi0.8Co0.15Al0.05O2 and Li4/3Ti5/3O4 electrodes. Electrochim. Acta 2005, 51, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochida, M.; Domi, Y.; Doi, T.; Tsubouchi, S.; Nakagawa, H.; Yamanaka, T.; Abe, T.; Ogumi, Z. Influence of manganese dissolution on the degradation of surface films on edge plane graphite negative -electrodes in lithium -ion batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2012, 159, A961–A966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumaresan, K.; Guo, O.; Ramada, P.; White, R.E. Cycle life performance of lithium-ion pouch cells. J. Power Sources 2006, 158, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, D.P.; Liua, J.; Chen, C.H.; Hyung, Y.E.; Stolla, M.; Elsena, N.; MacLaren, S.; Twesten, R.; Haasch, R.; Sammann, E.; et al. Diagnosis of power fade mechanisms in high-power lithium-ion cells. J. Power Sources 2003, 119, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodenes, L.; Dedryvere, R.; Martinez, H.; Fischer, F.; Tessier, C.; Peres, J.P. Lithium-ion batteries working at 85 °C: Aging phenomena and electrode/electrolyte interfaces studied by XPS. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2012, 159, 1739–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Pyun, S. The effect of electrolyte temperature on the passivity of the solid electrolyte interphase formed on a graphite. Carbon 2002, 40, 2333–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, G.; Haran, B.; Popov, B.N. Capacity fade of lithium ion batteries cycled at high discharge rates. J. Power Sources 2003, 117, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markovsky, B.; Rodkin, A.; Cohen, Y.S.; Palchik, O.; Levi, E.; Aurbach, D.; Kim, H.-J.; Schmidt, M. The study of capacity fading processes of Li-ion batteries: Major factors that play a role. J. Power Sources 2003, 119–121, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braithwaite, J.W.; Gonzales, A.; Nagasubramanian, G.; Lucero, S.J.; Peebles, D.E.; Ohlhausen, J.A.; Cieslak, W.R. Corrosion of lithium-ion battery current collectors. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1999, 146, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Park, Y.T. Characteristics of surface films formed at a mesocarbon microbead electrode in a Li-ion battery. J. Power Sources 2000, 91, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Murphy, E.; Winnick, J.; Kohl, A.P. The effect of pulse charge on cycling characteristics of commercial lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2001, 102, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broussely, M.; Herreyre, S.; Biensan, P.; Kasztejna, P.; Nechev, K.; Staniewicz, R.J. Aging Mechanisms in Li ion cells and calendar life predictions. J. Power Sources 2001, 97, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Murphy, E.; Winnick, J.; Kohl, P.A. Studies on the cycle life of commercial lithium ion batteries during the charge-discharge cycling. J. Power Sources 2001, 102, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurbach, D.; Markovsky, B.; Talyossef, Y.; Salitra, G.; Kim, H.; Choi, S. Studies of cycling behaviour, ageing, and interfacial reactions of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 and carbon electrode for lithium-ion 5-V cells. J. Power Sources 2006, 162, 780–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keun, C.; Yin, R.; Shin, S.; Lee, Y.; Choi, W.; Kim, Y. Electrochemical properties and gas evolution behavior of overlithiated Li2NiO2 as cathode active mass for rechargeable Li ion batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2012, 159, 887–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, D.P.; Knuth, J.L.; Dees, D.W.; Bloom, I. Performance degradation of high power lithium ion cells- electrochemistry of harvested electrodes. J. Power Sources 2007, 170, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broussely, M.; Biensan, P.H.; Bonhomme, F.; Balnchard, P.H.; Herreyre, S.; Nechev, K.; Staniewicz, R.J. Main aging mechanisms in lithium ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2005, 146, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, H.; Watanabe, Y.; Moriguchi, I.; Kudo, T. Rate capability of lithium intercalation into nano-porous graphitized carbon. Solid State Ionics 2008, 179, 1706–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellner, J.P.; Loeber, G.J.; Sandhu, S.S. Testing of lithium-ion 18650 cells and characterizing/predicting cell performance. J. Power Sources 1999, 81, 867–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smart, M.C.; Ratnakumar, B.V.; Surapudi, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Greenbaum, S.G.; Hightower, A.; Ahn, C.C.; Fultz, B. Irreversible capacities of graphite in low temperature electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1999, 46, 3963–3969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, P.L.; Au, G.; Plichta, E.J.; Zheng, P.J. Study of capacity fade of lithium-ion polymer rechargeable batteries with continuous cycling. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2010, 157, A1–A7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfgang, M.; Lu, C.; Novak, P. Morphology of the solid electrolyte interphase of the graphite I dependency of the formation current. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2011, 1478–1482. [Google Scholar]
- Nakura, K.; Ohsugi, Y.; Imazaki, M.; Ariyoshi, K.; Ohzuku, T. Extended cycle life of lithium-ion batteries consisting of lithium insertion electrodes: cycle efficiency versus Ah efficiency. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2011, 158, 1243–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, J.; Striebel, K. Characterization of high-power lithium-ion cells during constant cycling: Part I cycling performance and electrochemical diagnostics. J. Power Sources 2003, 122, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, J.; Kostecki, R.; Richardson, T.; Song, X.; Striebel, K.A. Electrochemical analysis for cycle performance and capacity fading of a lithium-ion battery cycled at elevated temperature. J. Power Sources 2002, 112, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Haran, B.S.; Durirajan, A.; White, R.E.; Podrazhansky, Y.M.; Popov, B.N. Studies on capacity fade of lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2000, 91, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kida, Y.; Kinoshita, A.; Yanagida, K.; Funahashi, A.; Nohma, T.; Yonezu, I. Study on capacity fade factors of lithium secondary batteries using LiNi0.7 Co0.3O2 and graphite-coke hybrid carbon. Electrochim. Acta 2002, 47, 4157–4162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utsunomiya, T.; Hatozaki, O.; Yoshimoto, N.; Egashira, M.; Morita, M. Influence of particle size on the self-discharge behavior of graphite electrodes in lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 8675–8682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.C.; Guo, Z.Z.; Wen, H.P.; Yang, M.Y. Study the fading mechanism of LiMn2O4 battery with spherical and flake type graphite as anode material. J. Power Sources 2005, 146, 736–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikha, G.; Ramadass, P.; Haran, B.S.; White, R.E.; Popov, B.N. Comparison of the capacity fade of Sony US 18650 cells charged with different protocols. J. Power Sources 2003, 122, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Appleby, A.J.; Little, F.E. Low-temperature characterization of lithium-ion carbon anodes via microperturbation measurement. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2002, 149, 754–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.Y. Cycle-life characterization of automotive lithium-ion batteries with LiNiO2. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2009, 156, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Notten, P.H.L. Studies on degradation of Li-ion batteries by the use of micro reference electrodes. J. Power Sources 2008, 177, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasen, N.A.; Dees, D.W.; Abraham, D.P.; Amine, K.; Henriksen, G.L. Low temperature study of lithium-ion cells using LiySn micro-reference electrode. J. Power Sources 2007, 174, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujikawa, T.; Yabuta, K.; Matsushita, T.; Arakawa, M.; Hayashi, K. A study on the cause of deterioration in float-charged lithium-ion batteries using LiMn2O4 as a cathode active material. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2011, 158, 322–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarre, G.; Balanchard, P.; Broussely, M. Aging of lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2004, 127, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.; Ogawa, K.; Kumeuchi, Y.; Enomoto, S.; Uno, M.; Saito, H.; Yoshisugu, S.; Abraham, D.; Lindberg, G. Cycle life evaluation of 3 Ah LixMn2O4-based lithium-ion secondary cells for low-earth-orbit satellites. J. Power Sources 2008, 185, 1444–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostecki, R.; Lei, J.; McLarnon, F.; Shim, J.; Striebel, K. Diagnostic evaluation of detrimental phenomena in high-power lithium-ion batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2006, 153, A669–A672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safari, M.; Delacourt, C. Aging of a commercial graphite LiFePO4 cell. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2011, 158, 1123–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, N.N.; Smith, A.J.; Burns, J.C.; Gaurav, J.; Eberman, K.W.; Scott, E.; Gardner, J.P.; Dahn, J.R. The use of elevated temperature storage experiments to learn about parasitic reaction in wound LiCoO2/graphite cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2011, 158, 1194–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, N.N.; Marks, T.H.; Dahn, H.M.; Smith, A.J.; Burn, J.C.; Coyle, D.J.; Dahn, J.J.; Dahn, J.R. The rate of active lithium loss from a soft carbon negative electrode as a function of temperature, time and electrode potential. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2012, 159, 1672–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, P.; Lanz, M.; Allia, D.; Rykart, B.; Paniz, J.; Haas, O. The complex electrochemistry of graphite electrodes in lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2001, 97, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Jang, Y.; Huang, B.; Sadoway, R.D.; Chiang, Y.M. TEM Study of Electrochemical Cycling-Induced Damage and Disorder in LiCoO2 Cathodes for Rechargeable Lithium Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1999, 146, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schranzhofer, H.; Bugajski, J.; Santner, H.J.; Korepp, C.; Moller, K.C.; Besenhard, J.O.; Winter, M.; Sitte, W. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy study of the SEI formation on graphite and metal electrode. J. Power Sources 2006, 153, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markervich, E.; Salitra, G.; Levi, M.D.; Aurbach, D. Capacity fading of lithiated graphite electrodes studied by a combination of electroanalytical methods, Raman spectroscopy and SEM. J. Power Sources 2005, 146, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossein, M.; Guoping, D.; Anaba, A.; Howard, J. Thermal Stability Studies of Li-Ion Cells and Components. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1999, 146, A3224–A3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Li, H.; Wu, L.; Lu, T. Irreversible capacity loss of graphite electrode in lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 1997, 68, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, J.; Striebel, A.K. The dependence of natural graphite anode performance on electrode density. J. Power Sources 2004, 130, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Cao, Z.; Haishen, S.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, X.; Lu, H.; Jia, M.; Li, J. Influence of Fe(II) species in electrolyte on performance of graphite anode for lithium-ion batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2012, 159, 1961–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, K.; Kirkham, M.; Meisner, R.; Parish, M.C.; Dudney, N. Novel cell design for combined in situ acoustic emission and x-ray diffraction study during electrochemical cycling of batteries. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2011, 82, 75–107. [Google Scholar]
- Nagpure, S.C.; Bhushan, B.; Babu, S.; Rizzoni, G. Scanning spreading resistance characterization of aged Li-ion batteries using atomic force microscopy. Scripta Mater. 2009, 60, 933–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohzuku, T.; Ueda, A.; Yamamoto, N.; Yasunobu, I. Factor affecting the capacity retention of lithium-ion cells. J. Power Sources 1995, 54, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.K.; Inaba, M.; Takeshi, A.; Ogumi, Z. Surface film formation on graphite negative electrode in lithium-ion batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2001, 148, A989–A993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvakkumar, S.R.; Nerkar, J.Y. Rate capability of graphite materials as negative electrodes in lithium ion capacitors. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 3330–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, B.; Flandrois, S.; Guerin, K.; Ferrier-Bouvier, A.; Teulat, I.; Biensan, P. On the choice of graphite for lithium ion batteries. J. Power Sources 1999, 81, 312–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridgway, P.; Zheng, H.; Bello, A.F.; Song, X.; Xun, S.; Chong, J.; Vincent, B. Comparison of cycling performance of lithium ion cell anode graphites. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2012, 159, 520–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, A.M.; Edstrom, K.; Thomas, J.O. Characterization of the ambient and elevated temperature performance of graphite electrode. J. Power Sources 1999, 81–82, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.D.; Feikert, J.H.; Pekala, R.W. Rate effect on lithium-ion graphite electrode performance. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1996, 26, 1161–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Lee, S. Effect of particle size on the thermal stability of lithiated graphite. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 3339–3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nga, S.H.; Vix-Guterl, C.; Bernardo, P.H.; Tran, N.; Ufheil, J.; Buqa, H.; Dentzer, J.; Gadiou, R.; Spahr, M.E.; Goers, D.; et al. Correlations between surface properties of graphite and the first cycle specific charge loss in lithium-ion batteries. Carbon 2009, 47, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joho, F.; Rykart, B.; Wilhem, H.; Novak, P.; Spahr, M.E.; Monnier, A. Relation between surface properties, pore structure and first cycle charge loss of graphite as negative electrode in lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2001, 97, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurbach, D.; Teller, H.; Koltypin, M.; Levi, E. On the behaviour of different types of graphite anodes. J. Power Sources 2003, 119–121, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Lu, W.; Prakash, J. Charaterization of commercial size cylindrical Li-ion cell with a reference electrode. J. Power Sources 2000, 88, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubino, S.R.; Gan, H.; Takeuchi, S.E. A study of capacity fades in cylindrical and prismatic lithium-ion batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2001, 148, 1029–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, J.; Striebel, A.K. Effect of electrode density on cycle performance and irreversible capacity loss for natural graphite anode in lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2003, 119, 934–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leising, A.R.; Palazzo, M.J.; Takeuchi, S.E.; Takeuchi, J.K. Abuse Testing of Lithium-Ion Batteries Characterization of the Overcharge Reaction of LiCoO2/Graphite Cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2001, 148, 838–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanz, M.; Novak, P. DEMS study of gas evolution at thick graphite electrodes for lithium-ion batteries: The effect of the γ-butyrolactone. J. Power Sources 2001, 102, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnakumar, B.V.; Smart, M.C. Lithium plating behavior in lithium-ion cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. Trans. 2010, 25, 241–252. [Google Scholar]
- Dolle, M.; Sannier, L.; Beaudion, B.; Trentin, M. Live scanning electron microscope observation of dendrite growth in lithium polymer cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2002, 5, 286–289. [Google Scholar]
- Smart, M.C.; Ratnakumar, B.V. Effects of electrolyte composition on lithium plating in lithium-ion cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2011, 158, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honbo, H.; Takei, K.; Ishii, Y.; Nishida, T. Electrochemical properties and Li deposition morphologies of surface modified graphite after grinding. J. Power Sources 2009, 189, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosso, M.; Gobron, T.; Brissot, C.; Chazalviel, J.N.; Lascaud, S. Onset of dendritic growth in lithium/polymer cells. J. Power Sources 2001, 97, 804–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ornini, F.; Pasquier, D.A.; Beaudion, B.; Tarason, J.M.; Trentin, M. In situ scanning electron microscope observation of interfaces within plastic lithium batteries. J. Power Sources 1998, 76, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leising, R.A.; Palazzo, M.J.; Takeuchi, E.S.; Takeuchi, K.J. A study of the overcharge reaction of lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2001, 97, 681–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Yoon, W. Observation of dendritic growth on Li powder anode using the optical cell. Electrochim. Acta 2004, 50, 541–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, S.; Kim, B.; Yoon, W. Electrochemical behavior of Li-powder anode in high Li capacity used. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2012, 159, 1551–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, R.; Key, B.; Chen, H.; Best, A.S.; Hollenkamp, A.F.; Grey, C.P. In situ NMR observation of the formation of metallic microstructure in lithium batteries. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 504–510. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, W.; Carmen, M.; Liu, N.; Vaughely, T.J.; Jansen, A.; Dees, D.W. Overcharge effect on morphology and structure of carbon electrodes for lithium-ion batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2012, 159, 566–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Tan, S. Studies on charging lithium-ion cells at low temperatures. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2006, 153, 1081–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joho, F.; Rykart, B.; Imhof, R.; Novak, P.; Spahr, M.E.; Monnier, A. Key factors for the cycling stability of graphite intercalation electrodes for lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 1999, 81, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Bang, H.J.; Oh, S.; Sun, Y.; Lee, S. Effect of carbon coating on thermal stability of natural graphite spheres used as anode materials in lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2009, 190, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevsllier, F.; Gautier, S.; Salvetat, J.P.; Clinard, C.; Frackowiak, E.; Rouzaud, J.N.; Beguin, F. Effects of post-treatment on performance of hard carbons in lithium cells. J. Power Sources 2001, 97, 143–145. [Google Scholar]
- Natarajan, C.; Fujimoto, H.; Tokumitsu, K.; Mabuchi, A.; Kasuh, T. Reduction of irreversible capacity of a graphite anode by the CVD process. Carbon 2001, 39, 1409–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Striebel, K.A.; Sierra, A.; Shim, J.; Wang, C.W.; Saatry, A.M. The effect of compression on natural graphite anode performance and matrix conductivity. J. Power Sources 2004, 234, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, J.; Striebel, K.A. Electrochemical characterization of thermally oxidized natural graphite anodes in lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2007, 164, 862–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.S.; Lim, H.S. Factors that affect cycle life and possible degradation mechanisms of a Li-ion cell based on LiCoO2. J. Power Sources 2002, 111, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobili, F.; Mancini, M.; Dsoke, S.; Tossici, R.; Marassi, R. Low-temperature behavior of graphite–tin composite anodes for Li-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 7090–7097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubino, R.S.; Takeuchi, S.E. The study of irreversible capacity in lithium-ion anodes prepared with thermally oxidized graphite. J. Power Sources 1999, 81, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Agubra, V.; Fergus, J. Lithium Ion Battery Anode Aging Mechanisms. Materials 2013, 6, 1310-1325. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma6041310
Agubra V, Fergus J. Lithium Ion Battery Anode Aging Mechanisms. Materials. 2013; 6(4):1310-1325. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma6041310
Chicago/Turabian StyleAgubra, Victor, and Jeffrey Fergus. 2013. "Lithium Ion Battery Anode Aging Mechanisms" Materials 6, no. 4: 1310-1325. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma6041310
APA StyleAgubra, V., & Fergus, J. (2013). Lithium Ion Battery Anode Aging Mechanisms. Materials, 6(4), 1310-1325. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma6041310