The Change from Past to Future for Adsorbent Materials in Treatment of Dyeing Wastewaters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
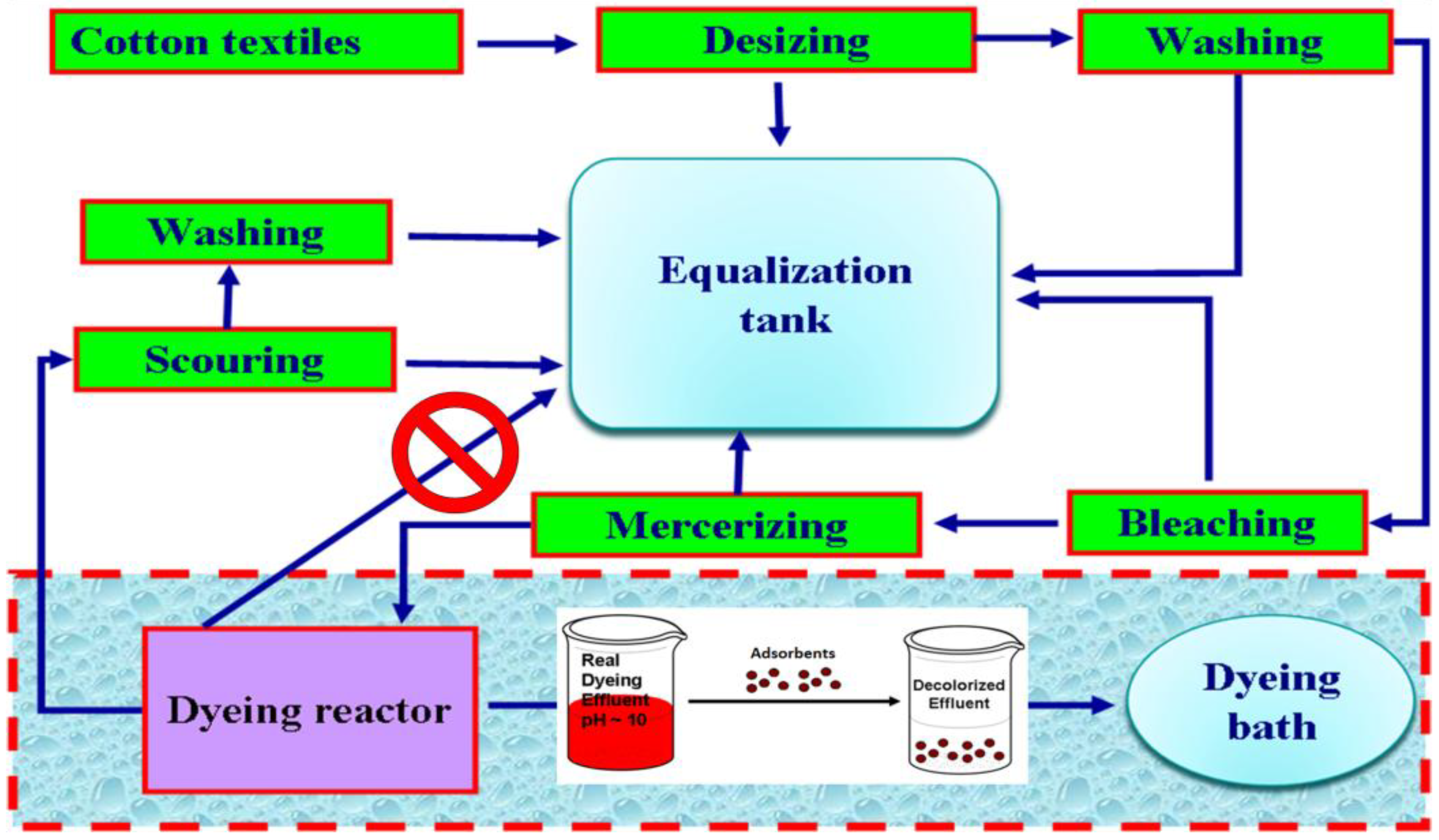
2. Adsorbents for Dyeing Wastewaters
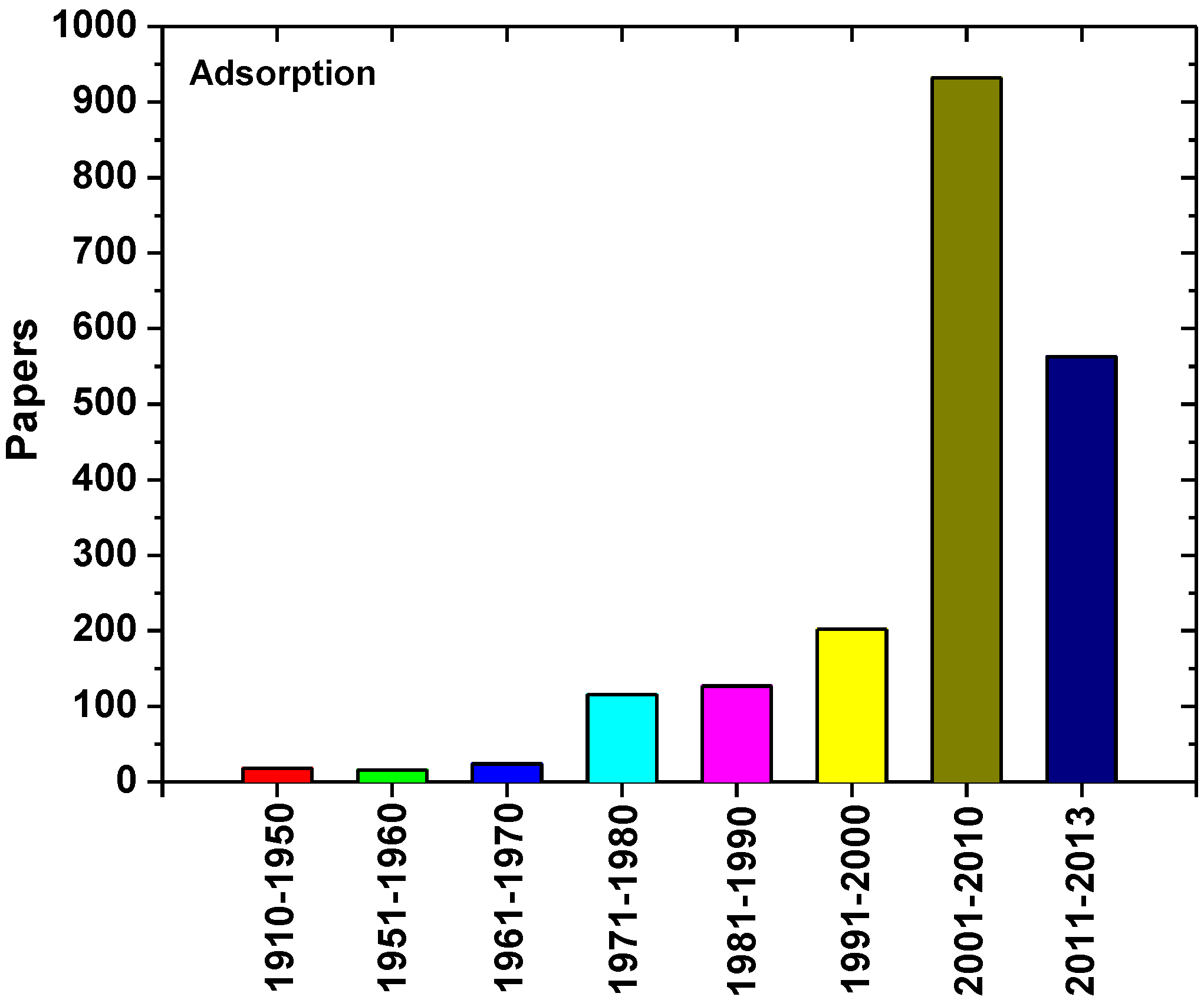
3. Change from Past to Future
3.1. First Attempts (1910–1950)
3.2. Initial Knowledge (1951–1970)
3.3. Economic Development (1971–2000)
3.4. 21st Century
3.4.1. Activated Carbon
3.4.2. Chitosan-Based Adsorbents
3.4.3. Low-Cost Agricultural Wastes as Adsorbents
| Adsorbent | Dye | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Sugar beet pulp | Gemazol turquoise blue-G | [116] |
| Powdered peanut hull | Sunset yellow, Amaranth, Fast green | [117] |
| Rice husk ash | Indigo Carmine | [118] |
| Chemically modified peanut hull | Methylene Blue, Brilliant cresyl blue, Neutral red, Sunset yellow, Fast green | [119] |
| Peanut hull | Methylene Blue, Brilliant cresyl blue, Neutral red | [120] |
| Coir pith activated carbon | Reactive Orange 12, Reactive Red 2, Reactive Blue 4 | [121] |
| Coir pith activated carbon | Congo Red | [3] |
| Coir pith carbon | Methylene Blue | [122] |
| ZnCl2 activated coir pith carbon | Acid brilliant blue, Acid violet, Methylene Blue, Rhodamine B | [123] |
| Coir pith | Acid violet | [71] |
| Rice husks activated carbon | Malachite green | [124] |
| Rice husk-based porous carbon | Malachite green | [125] |
| Rice husk | Congo Red | [126] |
| Tea waste | Methylene Blue | [127] |
| Coniferous pinus bark powder | Crystal violet | [128] |
| Orange peel activated carbon | Direct Blue-106 | [129] |
| Neem sawdust | Malachite green | [130] |
| Guava seed carbon | Acid blue 80 | [131] |
| Peanut hull | Reactive Black 5 | [132] |
| Loofa activated carbon | Reactive orange | [133] |
| Apricot stone activated carbon | Astrazon yellow 7 GL | [134] |
| Almond shells | Direct red 80 | [135] |
| Lemon peel | Malachite green | [136] |
| Bagasse fly ash | Methyl violet | [137] |
| Polygonum orientale Linn activated carbon | Malachite green | [138] |
3.4.4. Fungi, Bacteria, Algae
3.4.5. Nanomaterials
3.5. Future Plans
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharma, P.; Kaur, H.; Sharma, M.; Sahore, V. A review on applicability of naturally available adsorbents for the removal of hazardous dyes from aqueous waste. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 183, 151–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attia, A.A.; Girgis, B.S.; Fathy, N.A. Removal of methylene blue by carbons derived from peach stones by H3PO4 activation: Batch and column studies. Dye. Pigment. 2008, 76, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namasivayam, C.; Kavitha, D. Removal of Congo Red from water by adsorption onto activated carbon prepared from coir pith, an agricultural solid waste. Dye. Pigment. 2002, 54, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, M.; Singh, S.; Bansal, R.C. Equilibrium and dynamic adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solutions by surface modified activated carbons. Carbon Sci. 2004, 5, 170–179. [Google Scholar]
- Khattri, S.D.; Singh, M.K. Colour removal from aqueous solutions by adsorption. Indian J. Chem. Technol. 1998, 5, 230–234. [Google Scholar]
- Karadag, D.; Akgul, E.; Tok, S.; Erturk, F.; Kaya, M.A.; Turan, M. Basic and reactive dye removal using natural and modified zeolites. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2007, 52, 2436–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karcher, S.; Kornmüller, A.; Jekel, M. Anion exchange resins for removal of reactive dyes from textile wastewaters. Water Res. 2002, 36, 4717–4724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purkait, M.K.; DasGupta, S.; De, S. Adsorption of eosin dye on activated carbon and its surfactant based desorption. J. Environ. Manag. 2005, 76, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, C.I.; Lloyd, J.R.; Guthrie, J.T. The removal of colour from textile wastewater using whole bacterial cells: A review. Dye. Pigment. 2003, 58, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMullan, G.; Meehan, C.; Conneely, A.; Kirby, N.; Robinson, T.; Nigam, P.; Banat, I.M.; Marchant, R.; Smyth, W.F. Microbial decolourisation and degradation of textile dyes. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2001, 56, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, T.; McMullan, G.; Marchant, R.; Nigam, P. Remediation of dyes in textile effluent: A critical review on current treatment technologies with a proposed alternative. Bioresour. Technol. 2001, 77, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, C.; Hawkes, F.R.; Hawkes, D.L.; Lourenço, N.D.; Pinheiro, H.M.; Delée, W. Colour in textile effluents—Sources, measurement, discharge consents and simulation: A review. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 1999, 74, 1009–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandevivere, P.C.; Bianchi, R.; Verstraete, W. Treatment and reuse of wastewater from the textile wet-processing industry: Review of emerging technologies. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 1998, 72, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.N.V.R.; Sridhari, T.R.; Bhavani, K.D.; Dutta, P.K. Trends in color removal from textile mill effluents. Colourage 1998, 45, 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Q.; Yang, L. The adsorption of basic dyes from aqueous solution on modified peat-resin particle. Water Res. 2003, 37, 1535–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, G.; Tripathy, M. A critical review of the treatments for decolourization of textile effluent. Colourage 1993, 40, 35–38. [Google Scholar]
- Zollinger, H. Color Chemistry: Synthesis, Properties and Applications of Organic Dyes and Pigments; VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Chiou, M.S.; Ho, P.Y.; Li, H.Y. Adsorption of anionic dyes in acid solutions using chemically cross-linked chitosan beads. Dye. Pigment. 2004, 60, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackburn, R.S. Natural polysaccharides and their interactions with dye molecules: Applications in effluent treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 4905–4909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiou, M.S.; Li, H.Y. Adsorption behavior of reactive dye in aqueous solution on chemical cross-linked chitosan beads. Chemosphere 2003, 50, 1095–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allègre, C.; Moulin, P.; Maisseu, M.; Charbit, F. Treatment and reuse of reactive dyeing effluents. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 269, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, T.; Chandran, B.; Nigam, P. Studies on desorption of individual textile dyes and a synthetic dye effluent from dye-adsorbed agricultural residues using solvents. Bioresour. Technol. 2002, 84, 299–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, T.; Chandran, B.; Nigam, P. Removal of dyes from a synthetic textile dye effluent by biosorption on apple pomace and wheat straw. Water Res. 2002, 36, 2824–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crini, G. Non-conventional low-cost adsorbents for dye removal: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 1061–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorentin, L.D.; Trigueros, D.E.G.; Módenes, A.N.; Espinoza-Quiñones, F.R.; Pereira, N.C.; Barros, S.T.D.; Santos, O.A.A. Biosorption of reactive blue 5G dye onto drying orange bagasse in batch system: Kinetic and equilibrium modeling. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 163, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, C.P.; Tuteja, R.; Kaushik, N.; Sharma, J.K. Minimization of organic chemical load in direct dyes effluent using low cost adsorbents. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 155, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konaganti, V.K.; Kota, R.; Patil, S.; Madras, G. Adsorption of anionic dyes on chitosan grafted poly(alkyl methacrylate)s. Eng. J. 2010, 158, 393–401. [Google Scholar]
- Kyzas, G.Z. A decolorization technique with spent “Greek coffee” grounds as zero-cost adsorbents for industrial textile wastewaters. Materials 2012, 5, 2069–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyzas, G.Z.; Lazaridis, N.K.; Mitropoulos, A.C. Removal of dyes from aqueous solutions with untreated coffee residues as potential low-cost adsorbents: Equilibrium, reuse and thermodynamic approach. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 189–190, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyzas, G.Z.; Kostoglou, M.; Vassiliou, A.A.; Lazaridis, N.K. Treatment of real effluents from dyeing reactor: Experimental and modeling approach by adsorption onto chitosan. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 168, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, A.C.; Siebold, A. On the application of adsorption to the detection and separation of certain dyes. Analyst 1912, 37, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, P.P.; France, W.G. Adsorption at crystal-solution interfaces. VIII. Influence of dyes and other organic compounds on the crystal habit of barium and lead nitrates. J. Phys. Chem. 1936, 40, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinland Sr, L.A.; France, W.G. Adsorption at crystal solution interfaces. VI. Macroscopic sodium nitrate crystals grown in the presence of dyes and other foreign materials. J. Phys. Chem. 1932, 36, 2832–2839. [Google Scholar]
- Kolthoff, I.M.; von Fischer, W.; Rosenblum, C. The adsorption of wool violet (4BN) by lead sulfate and the influence of the adsorbed dye on the speed of kinetic exchange. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1934, 56, 832–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibby, C.W.; Argument, C. Adsorption at the interface between two fluids. Part III. The adsorption of five dyes at a mercury-water interface. J. Chem. Soc. 1940, 596–600. [Google Scholar]
- Ewing, W.W.; Liu, F.W.J. Adsorption of dyes from aqueous solutions on pigments. J. Colloid Sci. 1953, 8, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whetstone, J. The adsorption of dyes by crystals. Discuss. Faraday Soc. 1954, 16, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldeman, R.G.; Emmett, P.H. Specific adsorption of alkyl orange dyes on silica gel. J. Phys. Chem. 1955, 59, 1039–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, R.; Dey, A.K. Adsorption of dyestuffs by hydrous thorium oxide: Heat of adsorption of the dyes by various samples of the hydroxide. Kolloid Z. Z. Polym. 1962, 183, 153–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, C.S. Mechanism of methylene blue dye adsorption on siliceous minerals. Kolloid Z. Z. Polym. 1964, 199, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padday, J.F. Adsorption of cyanine dyes at silver-halide surfaces. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1964, 60, 1325–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padday, J.F.; Wickham, R.S. Adsorption of cyanine dyes at silver halide surfaces: Part 2—Spectral properties and coverage. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1966, 62, 1283–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, G.A.; Joyce, I.H.; Worrall, W.E. Effect of surface characteristics of ceramic raw materials on dye adsorption. Brit. Cer. Soc-Trans. 1969, 68, 215–221. [Google Scholar]
- Iyer, S.R.S.; Chanekar, A.S.; Srinivasan, G. Adsorption of dyes on water-swollen and non-swelling solid substreates. ACS Symp. Ser. 1974, 79–95. [Google Scholar]
- Rock, S.L.; Stevens, B.W. Polymeric adsorption ion exchange process for decolorizing dye waste streams. Text. Chem. Color. 1975, 7, 57–59. [Google Scholar]
- Sethuraman, V.V.; Raymahashay, B.C. Color removal by clays. Kinetic study of adsorption of cationic and anionic dyes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1975, 9, 1139–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, M.; Ernst, W.R.; Lightsey, G.R.; Rasmussen, E.T.; Bagherzadeh, P. Adsorption of textile dyes by activated carbon produced from agricultural, municipal and industrial wastes. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1978, 19, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKay, G. Adsorption of acidic and basic dyes onto activated carbon in fluidised beds. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 1983, 61, 29–36. [Google Scholar]
- McKay, G.; Allen, S.J.; McConvey, I.F. The adsorption of dyes from solution—Equilibrium and column studies. Water Air Soil Poll. 1984, 21, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConvey, I.F.; McKay, G. Mass transfer model for the adsorption of basic dyes on woodmeal in agitated batch adsorbers. Chem. Eng. Process. 1985, 19, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKay, G.; McConvey, I.F. Adsorption of acid dye onto woodmeal by solid diffusional mass transfer. Chem. Eng. Process. 1985, 19, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKay, G.; Otterburn, M.S.; Aga, J.A. Pore diffusion and external mass transport during dye adsorption on to Fuller’s earth and silica. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 1987, 37, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, Z.; Tanaka, T.; Motomura, H. Diffusion/adsorption model of cellulose dyeing. II. Ordinary cellulose-direct dye system. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1985, 30, 3697–3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babel, S.; Kurniawan, T.A. Low-cost adsorbents for heavy metals uptake from contaminated water: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2003, 97, 219–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramakrishna, K.R.; Viraraghavan, T. Dye removal using low cost adsorbents. Water Sci. Technol. 1997, 36, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhu, Z.H. Effects of acidic treatment of activated carbons on dye adsorption. Dye. Pigment. 2007, 75, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, K.; Namba, A.; Mukai, S.R.; Tamon, H.; Ariyadejwanich, P.; Tanthapanichakoon, W. Adsorption of phenol and reactive dye from aqueous solution on activated carbons derived from solid wastes. Water Res. 2004, 38, 1791–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Snoeyink, V.L.; Campos, C.; Mariñas, B.J. Displacement effect of NOM on atrazine adsorption by PACs with different pore size distributions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 1510–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choy, K.K.H.; Porter, J.F.; McKay, G. Langmuir isotherm models applied to the multicomponent sorption of acid dyes from effluent onto activated carbon. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2000, 45, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karanfil, T.; Dastgheib, S.A.; Mauldin, D. Exploring molecular sieve capabilities of activated carbon fibers to reduce the impact of NOM preloading on trichloroethylene adsorption. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 1321–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannan, N.; Sundaram, M.M. Kinetics and mechanism of removal of methylene blue by adsorption on various carbons—A comparative study. Dye. Pigment. 2001, 51, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirankova, H.; Cakl, J.; Markvartova, O.; Dolecek, P. Combined membrane process at wastewater treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2007, 58, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKay, G.; Sze, M.F.F. The removal of organic pollutants from industrial effluents via tapered bed adsorption columns. Int. J. Environ. Technol. Manag. 2008, 9, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Degs, Y.S.; El-Barghouthi, M.I.; El-Sheikh, A.H.; Walker, G.M. Effect of solution pH, ionic strength, and temperature on adsorption behavior of reactive dyes on activated carbon. Dye. Pigment. 2008, 77, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, M.M.; Magdy, Y.H. Removal of different basic dyes from aqueous solutions by adsorption on palm-fruit bunch particles. Chem. Eng. J. 1997, 66, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.F.R.; Soares, S.F.; Órfão, J.J.M.; Figueiredo, J.L. Adsorption of dyes on activated carbons: Influence of surface chemical groups. Carbon 2003, 41, 811–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbas, A. Agricultural based activated carbons for the removal of dyes from aqueous solutions: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 167, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, N.; Tiwari, D.P.; Singh, S.K. Decolourisation of synthetic dyes by agricultural waste—A review. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2012, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Annadurai, G.; Juang, R.S.; Lee, D.J. Use of cellulose-based wastes for adsorption of dyes from aqueous solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2002, 92, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banat, F.; Al-Asheh, S.; Al-Makhadmeh, L. Evaluation of the use of raw and activated date pits as potential adsorbents for dye containing waters. Process Biochem. 2003, 39, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namasivayam, C.; Dinesh Kumar, M.; Selvi, K.; Ashruffunissa Begum, R.; Vanathi, T.; Yamuna, R.T. ‘Waste’ coir pith—A potential biomass for the treatment of dyeing wastewaters. Biomass Bioenergy 2001, 21, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattri, S.D.; Singh, M.K. Colour removal from synthetic dye wastewater using a bioadsorbent. Water Air Soil Poll. 2000, 120, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, V.K.; Gupta, R.; Yadav, A.B.; Kumar, R. Dye removal from aqueous solution by adsorption on treated sawdust. Bioresour. Technol. 2003, 89, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagreev, A.; Rahman, H.; Bandosz, T.J. Thermal regeneration of a spent activated carbon previously used as hydrogen sulfide adsorbent. Carbon 2001, 39, 1319–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabio, E.; González, E.; González, J.F.; González-Garcı́a, C.M.; Ramiro, A.; Gañan, J. Thermal regeneration of activated carbon saturated with p-nitrophenol. Carbon 2004, 42, 2285–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Miguel, G.; Lambert, S.D.; Graham, N.J.D. The regeneration of field-spent granular-activated carbons. Water Res. 2001, 35, 2740–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez, P.M.; Beltrán, F.J.; Gómez-Serrano, V.; Jaramillo, J.; Rodrı́guez, E.M. Comparison between thermal and ozone regenerations of spent activated carbon exhausted with phenol. Water Res. 2004, 38, 2155–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, R.J.; Ng, W.J. The repeated exhaustion and chemical regeneration of activated carbon. Water Res. 1987, 21, 961–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aizpuru, A.; Malhautier, L.; Roux, J.C.; Fanlo, J.L. Biofiltration of a mixture of volatile organic compounds on granular activated carbon. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2003, 83, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narbaitz, R.M.; Karimi-Jashni, A. Electrochemical regeneration of granular activated carbons loaded with phenol and natural organic matter. Environ. Technol. 2008, 30, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.-L.; Okada, M. Regeneration of granular activated carbon using ultrasound. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2005, 12, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shende, R.V.; Mahajani, V.V. Wet oxidative regeneration of activated carbon loaded with reactive dye. Waste Manag. 2002, 22, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.C.; Tseng, R.L.; Juang, R.S. Kinetic modeling of liquid-phase adsorption of reactive dyes and metal ions on chitosan. Water Res. 2001, 35, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.C.; Tseng, R.L.; Juang, R.S. Enhanced abilities of highly swollen chitosan beads for color removal and tyrosinase immobilization. J. Hazard. Mater. 2001, 81, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.C.; Tseng, R.L.; Juang, R.S. Comparative adsorption of metal and dye on flake-and bead-types of chitosans prepared from fishery wastes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2000, 73, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annadurai, G. Design of optimum response surface experiments for adsorption of direct dye on chitosan. Bioprocess. Eng. 2000, 23, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annadurai, G. Adsorption of basic dye on strongly chelating polymer: Batch kinetics studies. Iran. Polym. J. 2002, 11, 237–244. [Google Scholar]
- Annadurai, G.; Lee, D.J.; Juang, R.S. Box-Behnken studies on dye removal from water using chitosan and activated carbon adsorbents. J. Chin. Inst. Chem. Eng. 2000, 31, 609–615. [Google Scholar]
- Crini, G.; Martel, B.; Torri, G. Adsorption of C.I. Basic Blue 9 on chitosan-based materials. Int. J. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 34, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzun, I. Kinetics of the adsorption of reactive dyes by chitosan. Dye. Pigment. 2006, 70, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzun, I.; Güzel, F. Kinetics and thermodynamics of the adsorption of some dyestuffs and p-nitrophenol by chitosan and MCM-chitosan from aqueous solution. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 274, 398–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzun, I.; Güzel, F. External mass transfer studies during the adsorptions of some dyestuffs and p-nitrophenol onto chitosan from aqueous solution. Turk. J. Chem. 2004, 28, 731–740. [Google Scholar]
- Uzun, I.; Güzel, F. Rate studies on the adsorption of some dyestuffs and p-nitrophenol by chitosan and monocarboxymethylated(mcm)-chitosan from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2005, 118, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crini, G. Recent developments in polysaccharide-based materials used as adsorbents in wastewater treatment. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2005, 30, 38–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.Y.; Cho, S.Y. Adsorption equilibria of reactive dye onto highly polyaminated porous chitosan beads. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2005, 22, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, I.S.; Ribeiro, E.S.; Airoldi, C. The use of chemically modified chitosan with succinic anhydride in the methylene blue adsorption. Quím. Nova 2006, 29, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, Y.C.; Szeto, Y.S.; Cheung, W.H.; McKay, G. Equilibrium studies for acid dye adsorption onto chitosan. Langmuir 2003, 19, 7888–7894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, Y.C.; Szeto, Y.S.; Cheung, W.H.; McKay, G. Adsorption of acid dyes on chitosan—Equilibrium isotherm analyses. Process Biochem. 2004, 39, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, Y.C.; Szeto, Y.S.; Cheung, W.H.; McKay, G. Pseudo-first-order kinetic studies of the sorption of acid dyes onto chitosan. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 92, 1633–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, G.; Tobin, J.M.; Guibal, E. Sorption of Acid Green 25 on chitosan: Influence of experimental parameters on uptake kinetics and sorption isotherms. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 90, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, G.; Tobin, J.M.; Guibal, E. Influence of chitosan preprotonation on Reactive Black 5 sorption isotherms and kinetics. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2004, 43, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guibal, E.; McCarrick, P.; Tobin, J.M. Comparison of the sorption of anionic dyes on activated carbon and chitosan derivatives from dilute solutions. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2003, 38, 3049–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guibal, E.; Touraud, E.; Roussy, J. Chitosan interactions with metal ions and dyes: Dissolved-state vs. solid-state application. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2005, 21, 913–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G.; Gimbert, F.; Robert, C.; Martel, B.; Adam, O.; Morin-Crini, N.; de Giorgi, F.; Badot, P.M. The removal of Basic Blue 3 from aqueous solutions by chitosan-based adsorbent: Batch studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 153, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabaharan, M.; Mano, J.F. Chitosan derivatives bearing cyclodextrin cavitiesas novel adsorbent matrices. Carbohydr. Polym. 2006, 63, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, R.; Prabaharan, M.; Reis, R.L.; Mano, J.F. Graft copolymerized chitosan—Present status and applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2005, 62, 142–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, A.-C.; Shyu, S.-S.; Lin, Y.-C.; Mi, F.-L. Enzymatic grafting of carboxyl groups on to chitosan––To confer on chitosan the property of a cationic dye adsorbent. Bioresour. Technol. 2004, 91, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, Y.; Tanigawa, S.; Saito, Y.; Nakamura, T. Synthesis of chemically modified chitosans with a higher fatty acid glycidyl and their adsorption abilities for anionic and cationic dyes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 96, 2423–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaffar, M.A.; El-Rafie, S.M.; El-Tahlawy, K.F. Preparation and utilization of ionic exchange resin via graft copolymerization of β-CD itaconate with chitosan. Carbohyd. Polym. 2004, 56, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martel, B.; Devassine, M.; Crini, G.; Weltrowski, M.; Bourdonneau, M.; Morcellet, M. Preparation and sorption properties of a β-cyclodextrin-linked chitosan derivative. J. Polym. Sci. A Polym. Chem. 2001, 39, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cestari, A.R.; Vieira, E.F.S.; dos Santos, A.G.P.; Mota, J.A.; de Almeida, V.P. Adsorption of anionic dyes on chitosan beads. 1. The influence of the chemical structures of dyes and temperature on the adsorption kinetics. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 280, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiou, M.S.; Ho, P.Y.; Li, H.Y. Adsorption behavior of dye AAVN and RB4 in acid solutions on chemically cross-linked Chitosan beads. J. Chin. Inst. Chem. Eng. 2003, 34, 625–634. [Google Scholar]
- </i>Chiou, M.S.; Kuo, W.S.; Li, H.Y. Removal of reactive dye from wastewater by adsorption using ECH cross-linked chitosan beads as medium. J. Environ. Sci. Health A Toxic/Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 2003, 38, 2621–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafatullah, M.; Sulaiman, O.; Hashim, R.; Ahmad, A. Adsorption of methylene blue on low-cost adsorbents: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 177, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franca, A.S.; Oliveira, L.S.; Ferreira, M.E. Kinetics and equilibrium studies of methylene blue adsorption by spent coffee grounds. Desalination 2009, 249, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksu, Z.; Isoglu, I.A. Use of agricultural waste sugar beet pulp for the removal of Gemazol turquoise blue-G reactive dye from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 137, 418–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, R.; Ding, Y.; Li, M.; Yang, C.; Liu, H.; Sun, Y. Utilization of powdered peanut hull as biosorbent for removal of anionic dyes from aqueous solution. Dye. Pigment. 2005, 64, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi, U.R.; Srivastava, V.C.; Mall, I.D.; Lataye, D.H. Rice husk ash as an effective adsorbent: Evaluation of adsorptive characteristics for Indigo Carmine dye. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 710–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, R.; Sun, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, H.; Yang, C. Effect of chemical modification on dye adsorption capacity of peanut hull. Dye. Pigment. 2005, 67, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, R.; Li, M.; Yang, C.; Sun, Y.; Chen, J. Removal of cationic dyes from aqueous solution by adsorption on peanut hull. J. Hazard. Mater. 2005, 121, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santhy, K.; Selvapathy, P. Removal of reactive dyes from wastewater by adsorption on coir pith activated carbon. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 1329–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavitha, D.; Namasivayam, C. Experimental and kinetic studies on methylene blue adsorption by coir pith carbon. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namasivayam, C.; Sangeetha, D. Recycling of agricultural solid waste, coir pith: Removal of anions, heavy metals, organics and dyes from water by adsorption onto ZnCl2 activated coir pith carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 135, 449–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, I.A.; Saad, B.; Shaidan, S.; Sya Rizal, E.S. Adsorption characteristics of malachite green on activated carbon derived from rice husks produced by chemical-thermal process. Bioresour. Technol. 2005, 96, 1578–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Zhang, H.; Tao, N.; Liu, Y.; Qi, J.; Wang, Z.; Xu, H. Adsorption of malachite green and iodine on rice husk-based porous carbon. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2003, 82, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.; Ding, D.; Xu, Y.; Zou, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zou, L. Use of rice husk for the adsorption of congo red from aqueous solution in column mode. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 2938–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uddin, M.T.; Islam, M.A.; Mahmud, S.; Rukanuzzaman, M. Adsorptive removal of methylene blue by tea waste. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 164, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, R. Studies on adsorption of crystal violet dye from aqueous solution onto coniferous pinus bark powder (CPBP). J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 171, 767–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaled, A.; Nemr, A.E.; El-Sikaily, A.; Abdelwahab, O. Removal of Direct N Blue-106 from artificial textile dye effluent using activated carbon from orange peel: Adsorption isotherm and kinetic studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 165, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khattri, S.D.; Singh, M.K. Removal of malachite green from dye wastewater using neem sawdust by adsorption. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 167, 1089–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elizalde-González, M.P.; Hernández-Montoya, V. Guava seed as an adsorbent and as a precursor of carbon for the adsorption of acid dyes. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 2111–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanyildizi, M.T. Modeling of adsorption isotherms and kinetics of reactive dye from aqueous solution by peanut hull. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 168, 1234–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelwahab, O. Evaluation of the use of loofa activated carbons as potential adsorbents for aqueous solutions containing dye. Desalination 2008, 222, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbas, E.; Kobya, M.; Sulak, M.T. Adsorption kinetics of a basic dye from aqueous solutions onto apricot stone activated carbon. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 5368–5373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doulati Ardejani, F.; Badii, K.; Limaee, N.Y.; Shafaei, S.Z.; Mirhabibi, A.R. Adsorption of Direct Red 80 dye from aqueous solution onto almond shells: Effect of pH, initial concentration and shell type. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 151, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, K.V. Optimum sorption isotherm by linear and non-linear methods for malachite green onto lemon peel. Dye. Pigment. 2007, 74, 595–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mall, I.D.; Srivastava, V.C.; Agarwal, N.K. Removal of Orange-G and Methyl Violet dyes by adsorption onto bagasse fly ash—Kinetic study and equilibrium isotherm analyses. Dye. Pigment. 2006, 69, 210–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, R.; Li, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, C. Adsorption of basic dyes on activated carbon prepared from Polygonum orientale Linn: Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Desalination 2010, 254, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, A.; Viraraghavan, T. Decolorization of dye wastewaters by biosorbents: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2010, 91, 1915–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Viraraghavan, T. Fungal decolorization of dye wastewaters: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2001, 79, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Viraraghavan, T. Removal of CI Acid Blue 29 from an aqueous solution by Aspergillus niger. Aatcc Rev. 2001, 1, 36–40. [Google Scholar]
- Bilgic, H.; Gokcay, C.F.; Hasirci, N. Color removal by white-rot fungi. Glob. Environ. Biotechnol. 1997, 66, 211–222. [Google Scholar]
- Cammarota, M.C.; Sant’Anna, G.L., Jr. Decolorization of kraft bleach plant E1 stage effluent in a fungal bioreactor. Environ. Technol. 1992, 13, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lankinen, V.P.; Inkeroinen, M.M.; Pellinen, J.; Hatakka, A.I. The onset of lignin-modifying enzymes, decrease of AOX and color removal by white-rot fungi grown on bleach plant effluents. Water Sci. Technol. 1991, 24, 189–198. [Google Scholar]
- Tatarko, M.; Bumpus, J.A. Biodegradation of Congo Red by Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Water Res. 1998, 32, 1713–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraco, V.; Pezzella, C.; Miele, A.; Giardina, P.; Sannia, G. Bio-remediation of colored industrial wastewaters by the white-rot fungi Phanerochaete chrysosporium and Pleurotus ostreatus and their enzymes. Biodegradation 2009, 20, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomaa, O.M.; Linz, J.E.; Reddy, C.A. Decolorization of Victoria blue by the white rot fungus, Phanerochaete chrysosporium. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 24, 2349–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Singh, L.; Dilbaghi, N. Biodegradation of Orange II dye by Phanerochaete chrysosporium in simulated wastewater. J. Sci. Ind. Res. 2009, 68, 157–161. [Google Scholar]
- Young, L.; Yu, J. Ligninase-catalysed decolorization of synthetic dyes. Water Res. 1997, 31, 1187–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Viraraghavan, T. Removal of a dye from an aqueous solution by the fungus Aspergillus niger. Water Qual. Res. J. Can. 2000, 35, 95–111. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.; Viraraghavan, T. Removal of Congo Red from an aqueous solution by fungus Aspergillus niger. Adv. Environ. Res. 2002, 7, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.L.; Banks, C.J. Removal of humic acid fractions by Rhizopus arrhizus: Uptake and kinetic studies. Environ. Technol. 1991, 12, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, K.A.; Healy, M.G.; Allen, S.J. Biosorption of synthetic dye and metal ions from aqueous effluents using fungal biomass. Glob. Environ. Biotechnol. 1997, 27–50. [Google Scholar]
- Raghukumar, C.; Chandramohan, D.; Michel, F.C., Jr.; Reddy, C.A. Degradation of lignin and decolorization of paper mill bleach plant effluent (BPE) by marine fungi. Biotechnol. Lett. 1996, 18, 105–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, P.; Malik, A. Fungal dye decolourization: Recent advances and future potential. Environ. Int. 2009, 35, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, H. Mycoremediation: Fungal Bioremediation; John Wiley & Sons Inc: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.; Viraraghavan, T. Dye biosorption sites in Aspergillus niger. Bioresour. Technol. 2002, 82, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forgacs, E.; Cserháti, T.; Oros, G. Removal of synthetic dyes from wastewaters: A review. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 953–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Won, S.W.; Choi, S.B.; Yun, Y.-S. Interaction between protonated waste biomass of Corynebacterium glutamicum and anionic dye Reactive Red 4. Colloid Surface A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2005, 262, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beveridge, T.J. Ultrastructure, chemistry, and function of the bacterial wall. Int. Rev. Cytol. 1981, 72, 229–317. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dijkstra, A.J.; Keck, W. Peptidoglycan as a barrier to transenvelope transport. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 5555–5562. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Beveridge, T.J. Structures of gram-negative cell walls and their derived membrane vesicles. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 4725–4733. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hu, T.L. Removal of reactive dyes from aqueous solution by different bacterial genera. Water Sci. Technol. 1996, 34, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Wal, A.; Norde, W.; Zehnder, A.J.B.; Lyklema, J. Determination of the total charge in the cell walls of Gram-positive bacteria. Colloids Surface B Biointerfaces 1997, 9, 81–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaraghavan, K.; Yun, Y.-S. Utilization of fermentation waste (Corynebacterium glutamicum) for biosorption of Reactive Black 5 from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 141, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Şatiroǧlu, N.; Yalçinkaya, Y.; Denizli, A.; Arica, M.Y.; Bektaş, S.; Genç, Ö. Application of NaOH treated Polyporus versicolor for removal of divalent ions of Group IIB elements from synthetic wastewater. Process Biochem. 2002, 38, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özer, A.; Akkaya, G.; Turabik, M. The removal of Acid Red 274 from wastewater: Combined biosorption and biocoagulation with Spirogyra rhizopus. Dye. Pigment. 2006, 71, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, A.; Zhang, Y.H.; Dubey, P.; Margrave, J.L.; Shukla, S.S. The role of sawdust in the removal of unwanted materials from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2002, 95, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkata Mohan, S.; Chandrasekhar Rao, N.; Krishna Prasad, K.; Karthikeyan, J. Treatment of simulated Reactive Yellow 22 (Azo) dye effluents using Spirogyra species. Waste Manag. 2002, 22, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Koliadima, A.; Her, Y.S.; Matijević, E. Adsorption of dyes on nanosize modified silica particles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1997, 195, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.S.; Ahmad, A.; Bangash, F.U.K.; Shah, S.S.; Khan, P. Removal of basic dye from aqueous solutions using nano scale zero valent iron (NZVI) as adsorbent. J. Chem. Soc. Pak. 2013, 35, 744–748. [Google Scholar]
- Zarezadeh-Mehrizi, M.; Badiei, A.; Mehrabadi, A.R. Ionic liquid functionalized nanoporous silica for removal of anionic dye. J. Mol. Liq. 2013, 180, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, N.M. Nickel ferrite nanoparticle: Synthesis, modification by surfactant and dye removal ability. Water Air Soil Poll. 2013, 224. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, T.; Xie, S.; Lu, X.; Xiang, L.; Yu, M.; Li, W.; Liang, C.; Mo, C.; Zeng, F.; Luan, T.; Tong, Y. Porous Pr(OH)3 nanostructures as high-efficiency adsorbents for dye removal. Langmuir 2012, 28, 11078–11085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Zhang, L. Adsorption of dyes from aqueous solutions or suspensions with clay nano-adsorbents. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2007, 58, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, W.H.; Szeto, Y.S.; McKay, G. Enhancing the adsorption capacities of acid dyes by chitosan nano particles. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 1143–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Luo, C.; Sun, M.; Qiu, H.; Li, X. Synthesis of magnetic β-cyclodextrin-chitosan/graphene oxide as nanoadsorbent and its application in dye adsorption and removal. Colloids Surface B Biointerfaces 2013, 103, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, M.H.; Wu, K.Y.; Chen, D.H. Fast removal of basic dyes by a novel magnetic nano-adsorbent. Chem. Lett. 2003, 32, 488–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afkhami, A.; Moosavi, R. Adsorptive removal of Congo Red, a carcinogenic textile dye, from aqueous solutions by maghemite nanoparticles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 174, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.H.; Zhang, X.R.; Zeng, G.M.; Gong, J.L.; Niu, Q.Y.; Liang, J. Simultaneous removal of Cd(II) and ionic dyes from aqueous solution using magnetic graphene oxide nanocomposite as an adsorbent. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 226, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrakian, T.; Afkhami, A.; Ahmadi, M. Adsorption and kinetic studies of seven different organic dyes onto magnetite nanoparticles loaded tea waste and removal of them from wastewater samples. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2012, 99, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, F.; Ye, H.; Li, M.M.; Zhao, B.X. Efficient removal of cationic dyes from aqueous solution by polymer-modified magnetic nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 198–199, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Feng, C.; Gao, Y.; Ma, X.; Wu, Q.; Wang, Z. Preparation of a graphene-based magnetic nanocomposite for the removal of an organic dye from aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 173, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.L.; Wang, B.; Zeng, G.M.; Yang, C.P.; Niu, C.G.; Niu, Q.Y.; Zhou, W.J.; Liang, Y. Removal of cationic dyes from aqueous solution using magnetic multi-wall carbon nanotube nanocomposite as adsorbent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 164, 1517–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, A.K.; Arockiadoss, T.; Ramaprabhu, S. Study of removal of azo dye by functionalized multi walled carbon nanotubes. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 162, 1026–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayarajan, M.; Arunachalam, R.; Annadurai, G. Agricultural wastes of Jackfruit peel nano-porous adsorbent for removal of Rhodamine dye. Asian J. Appl. Sci. 2011, 4, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsezos, M. Biosorption of metals. The experience accumulated and the outlook for technology development. Hydrometallurgy 2001, 59, 241–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wase, J.; Forster, C. Biosorbents for Metal Ions; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Chen, C. Biosorbents for heavy metals removal and their future. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 195–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, W.; Nightingale, P. Organizing for innovation: Towards successful translational research. Trends Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 558–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2013 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Kyzas, G.Z.; Fu, J.; Matis, K.A. The Change from Past to Future for Adsorbent Materials in Treatment of Dyeing Wastewaters. Materials 2013, 6, 5131-5158. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma6115131
Kyzas GZ, Fu J, Matis KA. The Change from Past to Future for Adsorbent Materials in Treatment of Dyeing Wastewaters. Materials. 2013; 6(11):5131-5158. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma6115131
Chicago/Turabian StyleKyzas, George Z., Jie Fu, and Kostas A. Matis. 2013. "The Change from Past to Future for Adsorbent Materials in Treatment of Dyeing Wastewaters" Materials 6, no. 11: 5131-5158. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma6115131
APA StyleKyzas, G. Z., Fu, J., & Matis, K. A. (2013). The Change from Past to Future for Adsorbent Materials in Treatment of Dyeing Wastewaters. Materials, 6(11), 5131-5158. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma6115131







