Progress in Nano-Engineered Anodic Aluminum Oxide Membrane Development
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Aluminum (III) Oxide, [Al2O3], Alumina
2.1. Introduction
2.2. Types of Oxide Films on Aluminum
3. Anodic Aluminum Membrane (AAO)
3.1. Introduction
3.2. AAO Electrochemistry
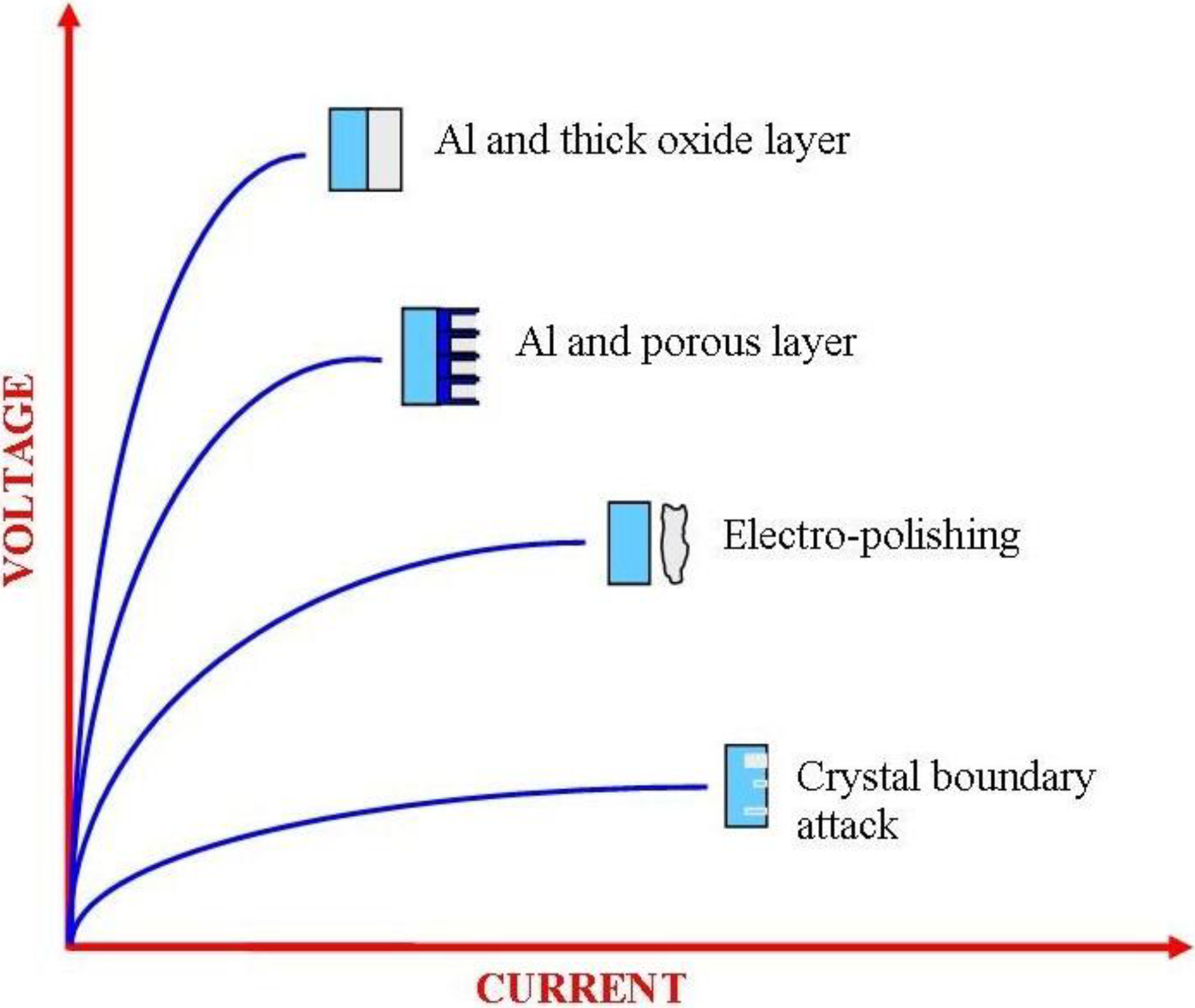
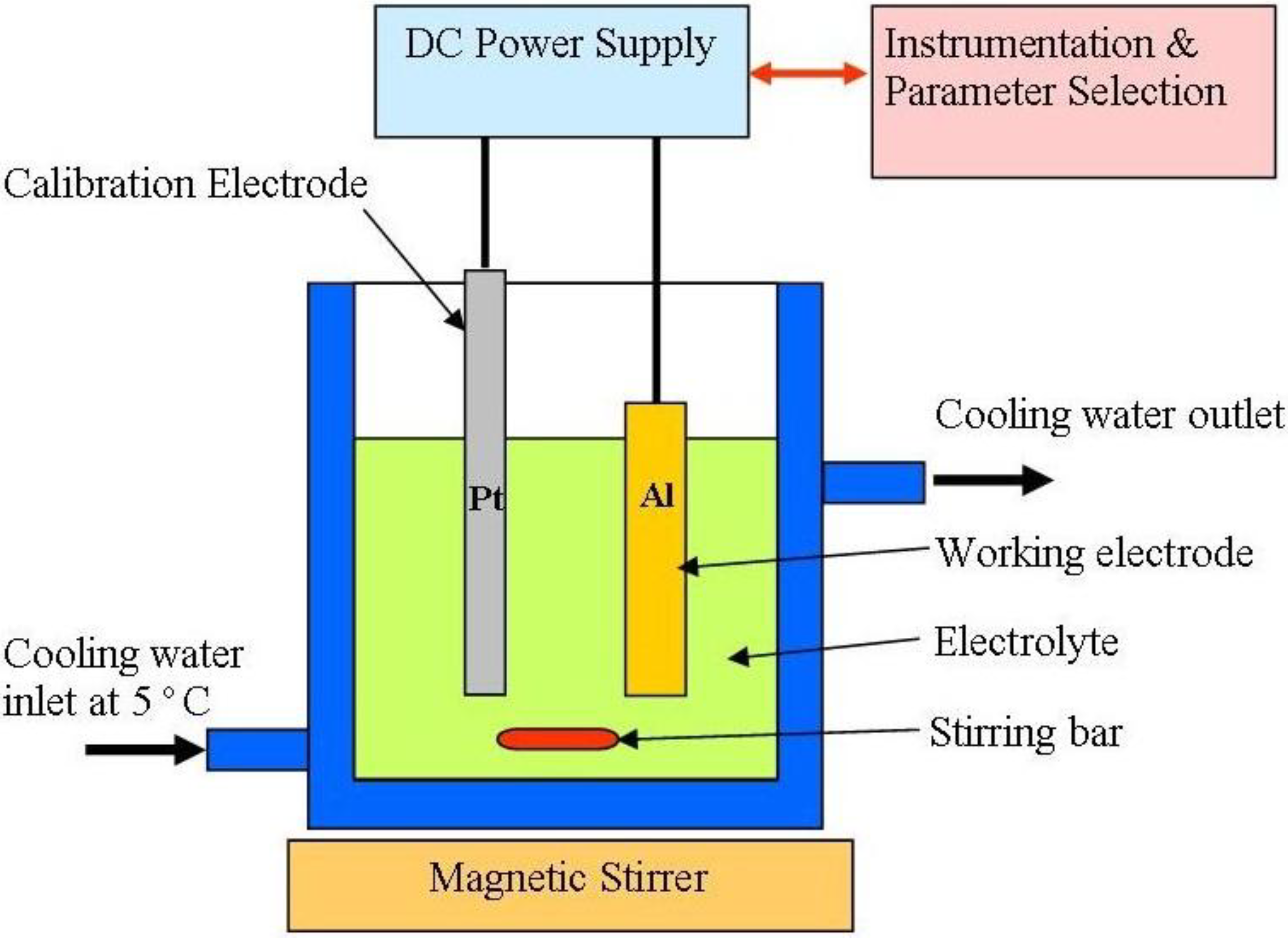
3.2.1. Materials

3.2.2. Electrolytes
3.2.2.1. Acids
| Main Acid used in Electrolyte | Molecular Formula | Concentration (M) | Pore Size Range (nm) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acetic | CH3CO2H | 1 | Not specified | [28] |
| Citric | HO2CCH2(OH)(CO2H)CH2CO2H | 0.1 to 2 | 90 to 250 | [30,31,32] |
| Chromic | H2CrO4 | 0.3, 0.44 | 17 to 100 | [33,34,35] |
| Glycolic | CH2(OH)CO2H | 1.3 | 35 | [30] |
| Malic | HO2CH2CH(OH)CO2H | 0.15 to 0.3 | Not specified | [30,32] |
| Malonic | CH2(CO2H)2 | 0.1 to 5 | Not specified | [32,36,37] |
| Oxalic | C2H2O4 | 0.2 to 0.5 | 20 to 80 | [40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48] |
| Phosphoric | H3PO4 | 0.04 to 1.1 | 30 to 235 | [9,34,49,50] |
| Sulfuric | H2SO4 | 0.18 to 2.5 | 12 to 100 | [41,48,51,52] |
| Tartaric | HO2CCH(OH)CH(OH)CO2H | 0.1 to 3 | Not specified | [30,32,37] |
| Acid | Concentration. (M) | Voltage (volts) | Pore Size (nm) | Time (hours) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oxalic | 0.25 | 60 | 75 | 8,8 | [40] |
| 0.3 | 40 | Not specified | variable | [41] | |
| 0.3 | 40 | 80 | 8, variable | [42] | |
| 0.3 | 40 | 50 | 10,5 min | [43] | |
| 0.3 | 60 | 80 | 3,8 | [44] | |
| 0.3 | 40 | 40–50 | 40 min, 2 | [44] | |
| 0.3 | 40, 50 | 20,35 | variable | [45] | |
| 0.3 | 30 | 40 | 8,10 | [46] | |
| 0.4 | 40 | 50 | 8,10 | [46] | |
| 0.5 | 50 | 80 | 8,10 | [47] | |
| 0.3 | 40 | 22 | 12,4,8,12& 16 | [48] | |
| Phosphoric | Not specified | 195 | 200 | variable | [9] |
| 0.4 | 5 to 40 | 20 to 75 | 1 step/variable | [34] | |
| 0.4 | 80 | 80 | 1 step | [49] | |
| 0.42 | 87 to 117 | 64 to 79 | 1 step/variable | [50] | |
| Sulfuric | 0.5 | 18 | 70 | 4, variable | [41] |
| 2.4 | 15 to 25 | 13 to 27 | 2 step/variable | [51] | |
| Not specified | 12, 25, 40 | 25,50, 100 | Not specified | [52] | |
| 0.3 | 25 | 20 | 12, 4,8,12&16 | [48] |
3.2.2.2. Non Acids and Neutral Solutions
| Non Acid | Equation | Concentration (M) | pH | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammonium Adipate | NH4OCO(CH2)4COONH4 | 150g/L | 6.4 | [29] |
| Sodium Borate | Na2B4O7 | 2.2 | 7 | [20] |
| Sodium chromate | Na2CrO4 | 0.1 | 10 | [38] |
| Sodium hydrogen phosphate | Na2HPO4 | 0.1 | 9.4 | [38] |
| Sodium hydroxide | NaOH | 0.01, 0.03 & 0.1 | Not specified | [39] |
| Sodium sulfate | Na2SO4 | 0.1 | 5.8 | [38] |
3.2.3. Voltage Conditions
3.2.4. Formation Mechanisms for Producing Barrier Layers and Nanoporous Alumina
3.2.4.1. Introduction
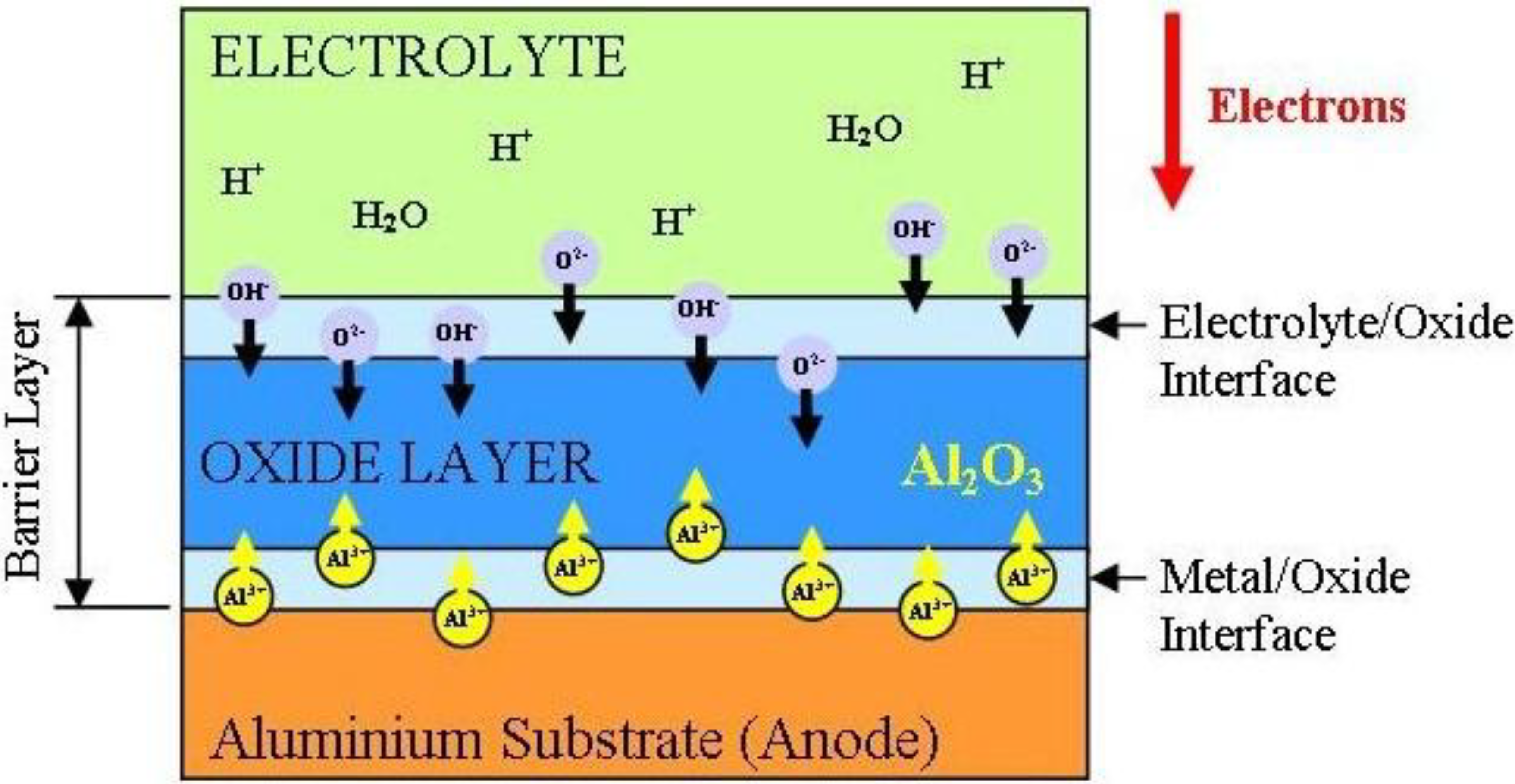
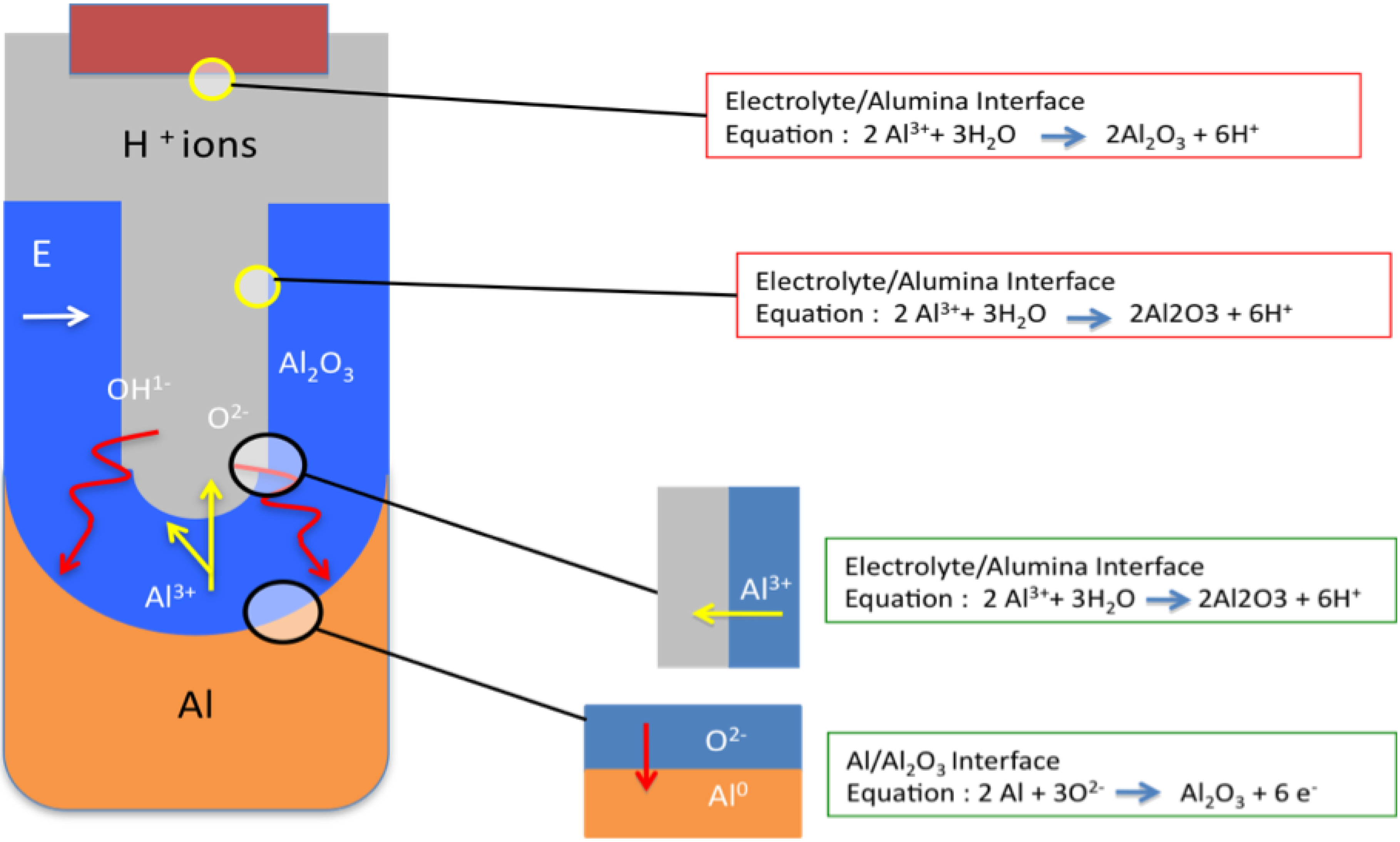
3.2.4.2. Barrier Layer Formation
3.2.4.3. Nano-Porous Alumina Formation

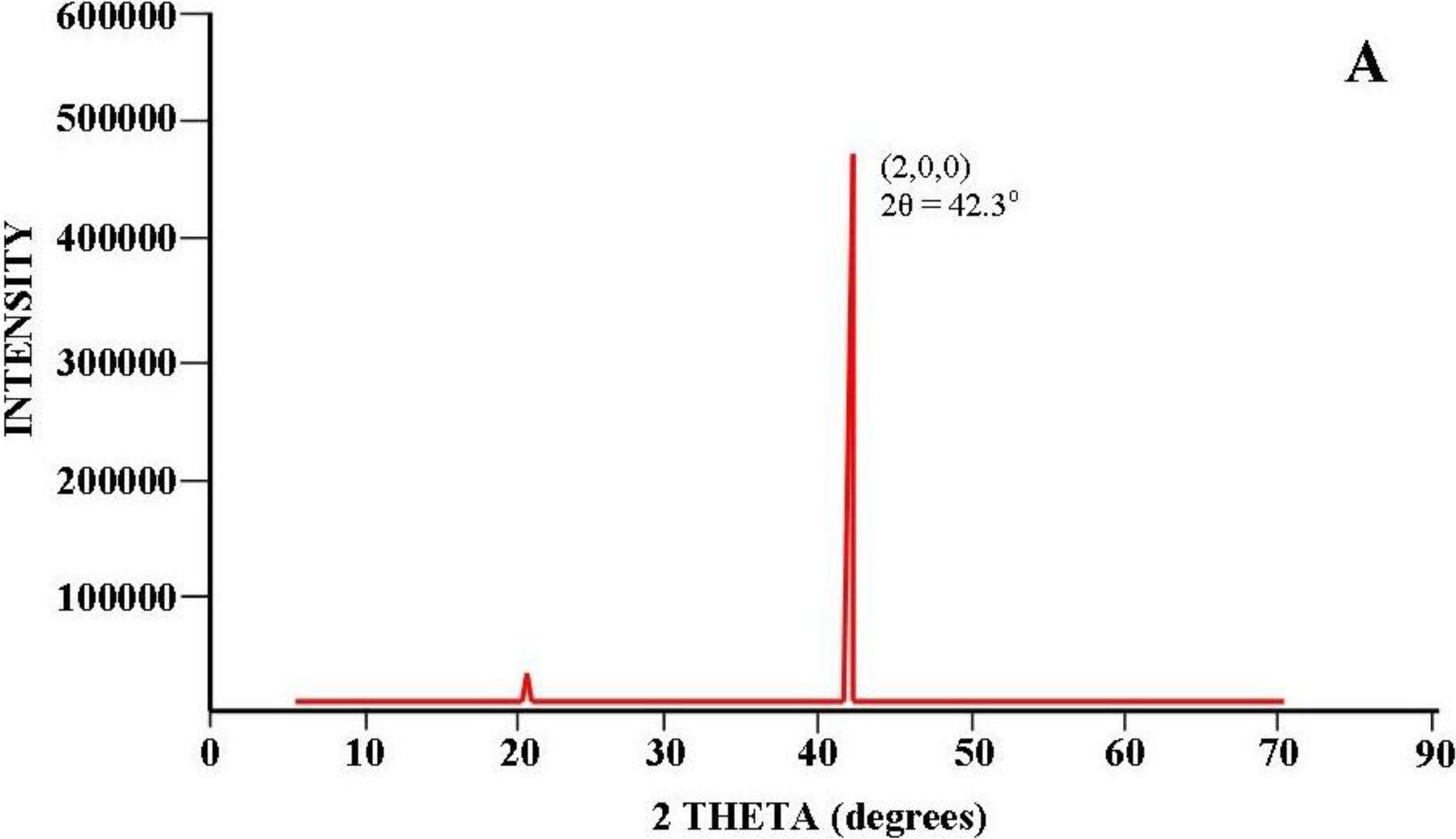
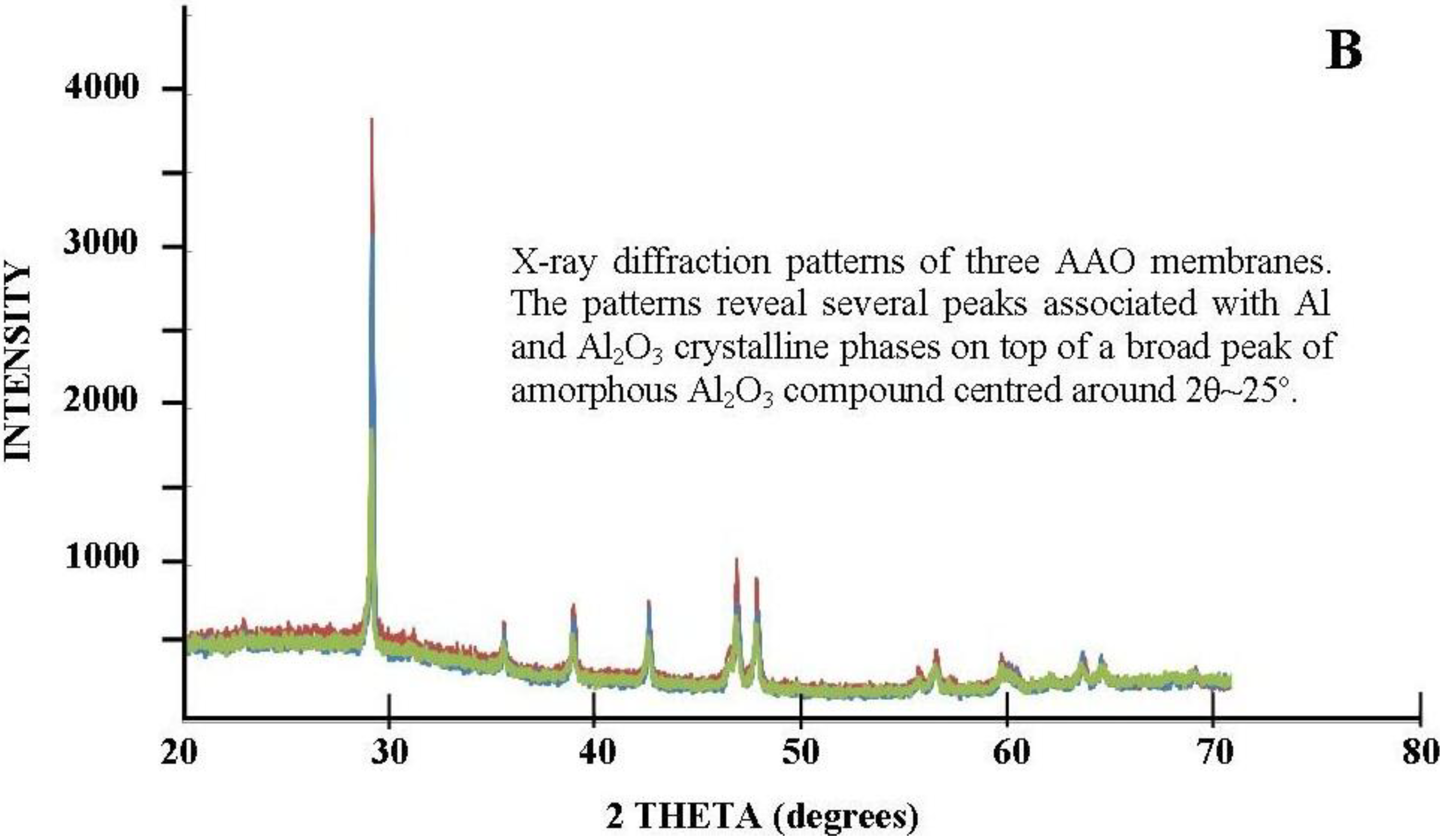


3.2.4.4. Two-Step Anodization of Aluminum

| Electrolyte | Concentration (M) | Potential (V) | 1st Anodization (Hours) | 2nd Anodization (Hours) |
| Sulfuric Acid | 0.3 | 24 | 5 | 3 |
| Oxalic Acid | 0.3 | 30 | 8 | 5 |
| Oxalic Acid | 0.3 | 60 | 5 | 3 |
| Phosphoric Acid | 2.5 | 60 | 8 | 5 |
3.2.4.5. A Typical AAO Membrane Fabrication Technique
4. Applications of AAO Layers and Membranes
4.1. Introduction
4.2. Engineering Applications of AAO Layers
4.2.1. Pore Sealing, Dyeing and Surface Textures
4.2.2. Electronic and Photoluminescence Properties of AAO Membranes
4.3. Nanotechnology Applications
4.3.1. Introduction
4.3.2. Nanomaterials and Devices
4.3.2.1. Nano-Dots and Nano-Magnets
4.3.2.2. Nanowires/Nanorods/Nanotubes
| Structure | Material | Substrate | Process | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nanodots | Mn | Si | Molecular beam epitaxy-scanning tunneling microscopy | [113] |
| Ultrahigh vacuum System | ||||
| Ag | Si | Molecular beam epitaxy | [129] | |
| InAs | Si | Electrochemical anodization | [130] | |
| SiO2, Ta2O5 | Si, AAO | Electro-deposition | [131] | |
| Nanowires | Au | Si | Electro-deposition | [132] |
| Co, Fe | Au | Electro-deposition | [133] | |
| Ni, Bi | Al | Electro-deposition | [134] | |
| Au, Ag | AAO | Photochemical Synthesis | [135] | |
| Sol-Gel solution | ||||
| LiMn2O4 | AAO | Electro-deposition | [136] | |
| Fe/Co | AAO | Cyclic volt-ammetry | [137] | |
| Ag | Ag | Several Tested | [138] | |
| Au / Bi | Si, Pt,Cu, Ag,Pd | Electro-deposition | [139] | |
| Ferromagnetic | Au | Electro-deposition | [140] | |
| M-CdSe-M | AAO/Ti/Si | Electrochemical replication | [141] | |
| Ni | AAO/Ti/Si | Electro-deposition | [124] | |
| CdS | AAO/Au/Si | Electro-deposition | [142] | |
| Au | NW/AAO | Electro-deposition | [143] | |
| MnO2 | AAO/Ti/Si | Electro-deposition | [144] | |
| M NWs | AAO, DMSO | Electro-deposition | [145] | |
| Bi2Te3 | AAO | Electrochemical deposition | [146] | |
| Ag | Si | Ultrahigh Vacuum System | [129] | |
| Nanorods | Al | AAO | Electro-deposition | [147] |
| Ni | AAO / Al | Electro-deposition | [148] | |
| Pt | AAO | Magnetron Sputtering | [149] | |
| Pyroelectric triglycine sulfate | AAO | Aqueous Solution | [150] | |
| Au | ||||
| Ni, Co, Au, Pb, Bi | Au | Cyclic volt-ammetry | [151] | |
| Polymeric (PMMA) | Au | Electro-deposition | [152] | |
| Nanotubes | M-Al-O | AAO | Thermal decomposition | [153] |
| ZnO,MgO, BaO | Calcination | |||
| C {C2H2} | AAO/Si | Plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) | [154] | |
| C | AAO/Cr/Au | Chemical vapor deposition | [155] | |
| C | AAO/Fe/Ti/Al | PECVD | [156] | |
| C | AAO/Si | Thermal evaporation | [128] |
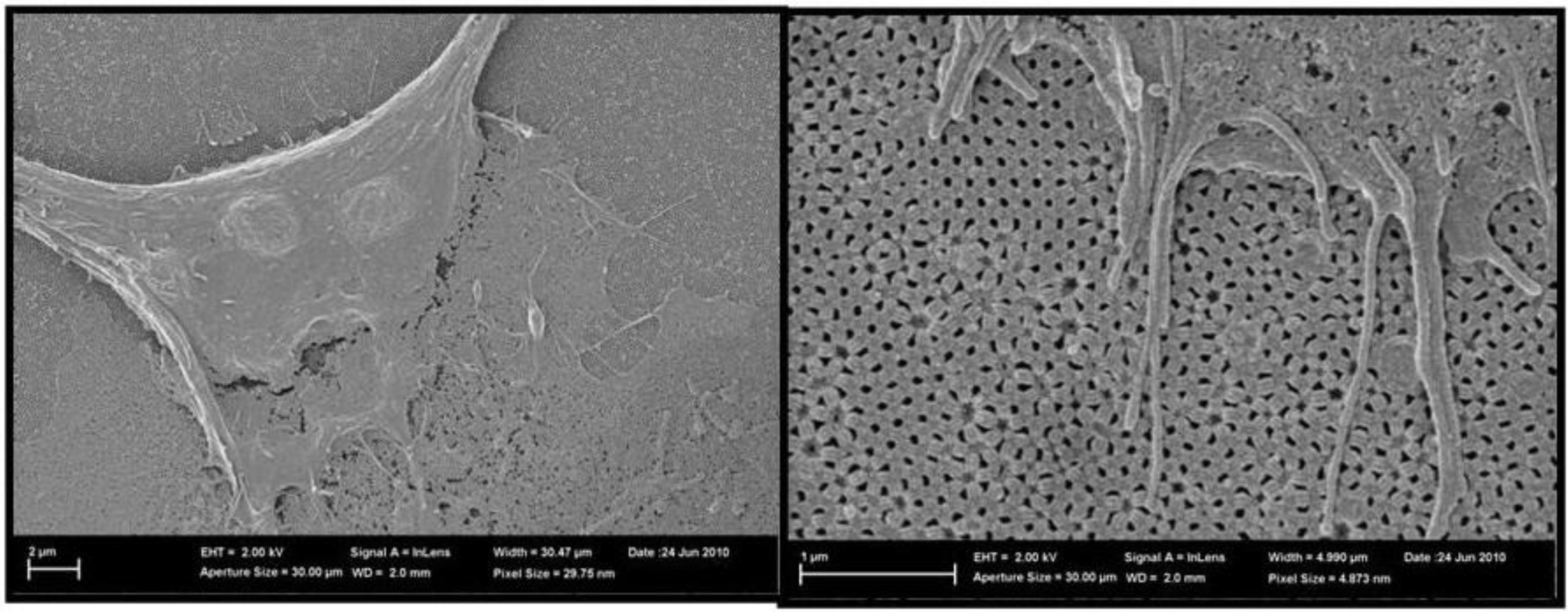
4.3.3. Biological Applications

5. Concluding Remarks
Acknowledgements
Disclosure
References
- Smallman, R.E.; Bishop, R.J. Modern Physical Metallurgy and Materials Engineering, 6th ed.; Butterworth Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 1999; Chapter 9. [Google Scholar]
- Anodisation of aluminium: New applications for a common technology; Nano Wizard Application Report; Cambridge, UK, September 2003.
- HM Wire International Inc. Bengough-Stuart Process. Available online: http://www.litz-wire.com (accessed on 29 June 2010).
- Masuda, H.; Yada, K.; Osaka, A. Self-ordering of cell configuration of anodic porous alumina with large-size pores in phosphoric acid solution. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1998, 37, L1340–L1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishna, S.; Ramalingam, M.; Sampath Kumar, T.S.; Soboyejo, W.O. Recent trends in biomaterials. In Biomaterials a Nano Approach, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; pp. 22–27. [Google Scholar]
- Greco, R.S.; Prinz, F.B.; Smith, R.L. Nanoscale Technology in Biological Systems, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Lines, M.G. Nanomaterials for practical functional uses. J. Alloys Componds 2008, 449, 242–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sclippa, E.; Piekarski, K. Carbon fibre reinforced polyethylene for possible orthopaedic uses. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1973, 7, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shingubara, S. Fabrication of nanomaterials using porous alumina templates. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2003, 5, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chik, H.; Xu, J.M. Nanometric superlattices: Non-lithographic fabrication, materials and prospects. Mat. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 43, 103–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Geological Survey. Available online: http://minerals.usgs.gov/minerals/pubs/commodity/aluminium (accessed on 15 February 2011).
- Dignam, M.J. Oxide films on aluminium. J. Electrochemical. Soc. 1962, 109, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, G.E. TALAT Lecture 5101: Surface characteristics of aluminium and aluminium alloys. European Al Ass. 30 April 2010. Available online: http://core.materials.ac.uk/search/detail.php?id=2243 (accessed on 7 January 2011).
- Verwey, E.J.W. Electrolytic conduction of a solid insulator at high fields for the formation of the anodic oxide film on aluminium. Physica 1935, 2, 1059–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diggle, J.W.; Downie, T.C.; Goulding, C.W. Anodic oxide films on aluminium. Chem. Rev. 1969, 69, 365–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gultepe, E.; Nagesha, D.; Sridhar, S.; Amiji, M. Nanoporous inorganic membranes or coatings for sustained drug delivery in implantable devices. Adv. Drug Deliv Rev. 2010, 62, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, G.E. Porous anodic alumina: Fabrication, characterisation and application. Thin Solid Films 1997, 297, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, F.; Hunter, M.S.; Robinson, D.L. Structural features of oxide coatings on aluminium. J. Electrochemical. Soc. 1953, 100, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, S.R. Electrochemistry at Semiconductor and Oxidized Metal Electrodes; Plenum: New York, NY, USA, 1980; Chapter 8; pp. 306–318. [Google Scholar]
- Uchi, H.; Kanno, T.; Alwitt, R.S. Structural features of crystalline anodic alumina films. J. Electron. Soc. Vol. 2001, 148, B17–B23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brace, A.W.; Sheasby, P.G. The Technology of Anodising Aluminium; Technicopy Limited: London, UK, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Surface characteristics of aluminium and aluminium alloys. Available online: http://www.eaa.net/eaa/education/TALAT (accessed on 20 August 2010).
- Zaraska, L.; Sulka, G.D.; Szeremeta, J.; Jaskula, M. Porous anodic alumina formed by anodisation of aluminium alloy (AA1050) and high purity aluminium. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 4377–4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenny, A.; Lewis, W. The Anodic Oxidation of Aluminium and Its Alloy; Charles Griffin and Company Limited: London, UK, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Hoar, T.P.; Mott, N.F. A mechanism for the formation of porous anodic oxide films on aluminium. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1959, 9, 97–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoar, T.P.; Yahaloom, J. The initiation of pores in anodic oxide films formed on aluminium in acid solutions. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1963, 110, 614–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houghton, P.S. Heat Treatment of Metals; Machinery Pub.: London, UK, 1960; Volume 2, p. 89. [Google Scholar]
- Larsson, C.; Thomsaon, P.; Aronsson, B.-O.; Rodahl, M.; Lausmaa, J.; Kasemo, B.; Erison, L.E. Boneresponse to surface-modified titanium implants: studies on the early tissue response to machined and electropolished implants with different oxide thickness. Biomaterials 1996, 17, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, H.J.; Park, G.S.; Kim, J.G.; Jeong, Y.; Chi, C.S. Surface roughness factor of anodic oxide layer for electrolytic capacitors. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2003, 82, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, S.Z.; Wada, K.; Inoue, S.; Isogai, M.; Katsuta, Y.; Yasumori, A. Large-scale fabrication of ordered nanoporous Alumina films with arbitrary pore intervals by critical-potential anodization. J. Electrochemical. Soc. 2006, 153, B384–B391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozalev, A.; Mozaleva, I.; Sakairi, M.; Takahashi, H. Anodic film growth on Al layers and Ta-Al metal bilayers in citric acid electrolytes. Electrochim. Acta 2005, 50, 5065–5075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajima, S.; Baba, N.; Shimizu, K.; Mizuki, I. Photoluminescence of anodic oxide films on aluminium. Electrocomp. Sci. Tech. 1976, 3, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Thompson, G.E.; Potts, G. Effects of chromic acid anodizing of aluminium on adhesion and durability of bonded joints. Trans. Inst. Met. Finish 2000, 78, 210–214. [Google Scholar]
- Ono, S.; Masuko, N. Evaluation of pore diameter of anodic porous films formed on aluminium. J. Surf. Coat Tech. 2003, 169-170, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadasivan, V.; Richter, C.P.; Menon, L.; Williams, P.F. Electrochemical self-assembly of porous alumina template. AICHE J. 2005, 51, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, S.; Saito, M.; Asoh, H. Self ordering of anodic porous alumina formed in organic acid electrolytes. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 2004, 7, B21–B24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, S.; Saito, M.; Asoh, H. Nanopatterning of silicon with the use of self-oraganised porous alumina and colloidal crystals as mask. Electrochim. Acta 2005, 51, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, G.C.; Skeldon, P.; Thompson, G.E.; Shimizu, K. A model for the incorporation of electrolyte species into anodic alumina. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1996, 43, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.M.; Pyun, S.I. The formation and dissolution of anodic oxide films on pure aluminium in alkaline solution. Electrochim. Acta 1999, 44, 2445–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Flamme, K.E.; Popat, K.C.; Leoni, L.; Markiewicz, E.; La Tempa, T.J.; Roman, B.B.; Grimes, C.A.; Desai, T.A. Biocompatibility of nanoporous alumina membranes for immunoisolation. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 2638–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Azevedo, W.M.; de Carvalho, D.D.; Khoury, H.J.; de Vasconcelos, E.A.; Da Silva, E.F., Jr. Spectroscopic characteristics of doped nanoporous aluminium oxide. Mater. Sci. Eng. B. 2004, 112, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Jung, B.; Lee, H.; Kim, H.; Lee, K.; Park, H. Capacitive humidity sensor design based on aluminium oxide. Sensor. Actuator. B 2009, 141, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, H.; Satoh, M. Fabrication of gold nanodot array using anodic porous alumina as an evaporation mask. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1996, 35, L126–L129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, M.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, T.; Liu, W. A facile approach to formation of through-hole porous anodic aluminium oxide film. Mater. Lett. 2005, 59, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Han, G. Fabrication and characterization of anodic aluminium oxide template. Microelectron Eng. 2003, 66, 166–170. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, N.-Q.; Jiang, X.-X.; Shi, C.-S.; Li, J.-J.; Zhao, Z.-G.; Du, X.-W. Effects of anodizing conditions on anodic alumina structure. J. Mater. Sci. 2006, 42, 3878–3882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Jiang, X.; Shi, C.; Li, J.; Zhao, Z.; Du, X. Effects of anodizing conditions on anodic alumina structure. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 3878–3882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, J.S.; Lee, J.S. Highly ordered two-dimensional carbon nanotube arrays. Appl. Phys Lett. 1999, 75, 2047–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagminience, A.; Valincius, G.; Riaukaite, A.; Jagminas, A. The influence of the alumina barrier layer thickness on the subsequent AC growth of copper nano-wires. J. Cryst. Growth Des. 2005, 274, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, G.C.; O’Sullivan, J.P.; Vaszko, B. The direct observation of barrier layers in porous anodic oxide films. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1968, 115, 618–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulka, G.D.; Parkola, K. Anodising potemtial influence on well-ordered nanostructures formed by anodisations of aluminium in sulphuric acid. Thin Solid Films 2006, 515, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.; Quijano, J. Development of nanostructured biomedical micro-drug testing device based on in situ cellular activity monitoring. Bioelectronics 2006, 7, 1219–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwitt, R.S. Anodizing; Electrochemistry Encyclopaedia Boundary Technologies Inc: Northbrook, IL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Zhang, L.; Metzger, R.M. On the growth of highly ordered pores in anodized aluminium oxide. Chem. Mater 1998, 10, 2470–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jessensky, O.; Muller, F.; Gosele, U. Self-organized formation of hexagonal pore arrays in anodic alumina. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1998, 72, 1173–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jessensky, O.; Muller, F.; Gosele, U. Self-organised formation of hexagonal pore structures in anodic alumina. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1998, 145, 3735–3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhang, L.; Metzger, R.M. On the growth of highly ordered pores in anodized aluminium oxide. Chem. Mater. 1998, 10, 2470–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.P.; Muller, F.; Birner, A.; Nielsch, K.; Gosele, U. Polycrytalline nanopore arrays with hexagonal ordering on aluminium. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 1999, 17, 1428–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.P.; Muller, F.; Birner, A.; Nielsch, K.; Gosele, U. Hexagonal pore arrays with a 50–420 interpore distance formed by self-organisation in anodic alumina. J. Appl. Phys. 1998, 84, 6023–6026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cho, H.S.; Li, F.; Metzger, R.M.; Doyle, W.D. Cellular growth of highly ordered porous anodic films on aluminium. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 1998, 17, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, K.; Tu, J.P.; Zhang, X.B. Preparation of porous alumina film on aluminium substrate by anodisation in oxalic acid. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2002, 13, 689–692. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.S.; Pyun, S.I.; Moon, S.M.; Kim, J.D. The effects of applied potential and pH on the electrochemical dissolution of the barrier layer in porous anodic oxide film on pure aluminium. Corros. Sci. 1996, 38, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, J.P.; Wood, G.C. Nucleation and growth of porous anodic films on aluminium. P Roy. Lond. A Mat. 1970, A317, 511–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoar, T.P.; Mott, N.F. A mechanism for the formation of porous anodic oxide films on aluminium. J. Phys. Chem. Solid. 1959, 9, 97–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, G.E.; Furneaux, R.C.; Wood, G.C.; Richardson, J.A.; Goode, J.S. Nucleation and growth of porous anodic films on aluminium. Nature 1978, 272, 433–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrublevsky, I.; Jagminas, A.; Schreckenbach, J.; Goedel, W.A. Electronic properties of electrolyte/anodic alumina junction during porous anodizing. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2007, 253, 4680–4687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, G.E.; Xu, Y.; Skeldon, P.; Shimizu, K.; Han, S.H.; Wood, G.C. Anodic oxidation of aluminium. Philos. Mag. Part B 1987, 55, 651–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Vergara, S.J.; Iglesias-Rubianes, L.; Blanco-Pinzon, C.E.; Skeldon, P.; Thompson, G.E.; Campestrini, P. Mechanical instability and pore generation in anodic alumina. P. Roy Soc. Lond. A Mat. 2006, 462, 2345–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patermarakis, G. The origin of nucleation and development of porous nanostructure of anodic alumina films. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2009, 635, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habazaki, H.; Shimizu, K.; Skeldon, P.; Thompson, G.E.; Wood, G.C.; Zhou, X. Nanoscale enrichments of substrate elements in the growth of thin oxide films. Corros. Sci. 1997, 39, 731–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patermarakis, G. Development of a theory for the determination of the composition of the anodising solution inside the pores during the growth of porous anodic Al2O3 films on aluminium by a transport phenomenon analysis. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1998, 447, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palbroda, E. Aluminium porous growth—II on the rate determining step. Electrochim. Acta 1995, 40, 1051–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawaqfeh, A.T.; Baltus, R.E. Fabrication and characterization of single layer and muti-layer anodic alumina membrane. J. Membrane Sci. 1999, 157, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Cos, F.; Arurault, L.; Fontorbes, S.; Vilar, V.; Datas, L.; Winerton, P. Chemical composition and structural changes of porous templates obtained by anodising aluminium in phosphoric acid electrolyte. Surf. Interface Anal. 2010, 42, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T. Mechanism of electrophoretic deposition of organic coatings on anodised aluminium. Trans. Inst. Met. Finish 1982, 60, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Nanostructured Materials in Electrochemistry, 1st ed.; Eftekhai, A. (Ed.) Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2008; pp. 24–25.
- Brown, I.W.M.; Bowden, M.E.; Kemmitt, T.; Mackenzie, K.J.D. Structural and thermal characterisation of nanostructured alumina templates. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2006, 6, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Li, S.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J. Size-controlled synthesis of highly ordered nanoporous AAO membranes. Nanoscience 2006, 11, 157–160. [Google Scholar]
- Yakovleva, N.M.; Yakovlev, A.N.; Chupakhina, E.A. Structural analysis of alumina films produced by two-step electrochemical oxidation. Thin Solid Films 2000, 366, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkhutik, V.P.; Belov, V.T.; Chernyckh, M.A. Study of aluminium anodization in sulphuric and chromic acid solutions-II. Oxide morphology and structure. Electrochimica. Acta 1990, 35, 961–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jessensky, O.; Muller, F.; Gosele, U. Self-organised formation of hexagonal pore structures in anodic alumina. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1998, 145, 3735–3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Y.C.; Saniger, J.M. Characterisation of anodic porous alumina by AFM. Mater. Lett. 2001, 48, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asoh, H.; Ono, S.; Hirose, T.; Nakao, M.; Masuda, H. Growth of anodic porous alumina with square cells. Electrochimica. Acta 2003, 48, 3171–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.H.; Lee, P.S.; Hwang, W.; Lee, K.H.; Park, H.C. Measurement of pore sizes for anodic aluminium oxide (AAO). Curr. Appl. Phys. 2006, 6S1, e125–e129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Thompson, G.E.; Wood, G.C. Mechanism of anodic film growth on aluminium. Trans. Inst. Met. Finish 1986, 63, 98–103. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, T.T.; Piner, R.D.; Ruoff, R.S. An improved method to strip aluminum from porous anodic alumina films. Langmuir 2003, 19, 1443–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.P.; Mueller, F.; Birner, A.; Nielsch, K.; Goesele, U. Fabrication and Microstructuring of hexagonally ordered two-dimensional Nanopore Arrays in Anodic Alumina. Adv. Mater. 1999a, 11, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.P.; Mueller, F.; Birner, A.; Nielsch, K.; Goesele, U. Polycrystalline nanopore arrays with hexagonal ordering on aluminum. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 1999b, 17, 1428–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belwalker, A.; Grasing, E.; Van Geertruyden, W.; Huang, Z.; Misiolek, W.Z. Effect of processing parameters on pore structure and thickness of anodic aluminium oxide (AAO) tubular membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 319, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chui, R.L.; Chang, P.H.; Tung, C.H. The effect of anodizing temperature on anodic oxide formed on pure Al thin films. Thin Solid Films 1995, 260, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melendres, C.A.; Van Gils, S.; Terryn, H. Toward a quantitive description of the anodic oxide films on aluminium. Electrochem. Commun. 2001, 3, 737–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, A.; Hu, C.C.; Yang, Y.F.; Lin, C.C. Pore diameter control of anodic aluminium oxide with ordered array of nanopores. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 2258–2264. [Google Scholar]
- Ebihara, K.; Takahashi, H.; Nagayama, J. Structure and density of anodic oxide films formed on aluminium in oxalic acid solutions. J. Met. Finish. Soc. Jpn. 1983, 34, 548–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsch, K.; Choi, J.; Schwirn, K.; Wehrspohn, R.B.; Gosele, U. Self ordering regimes of porous alumina: the 10% porosity rule. Nano Lett. 2002, 2, 677–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, M.; Nasirpouri, F.; Iraji zad, A.; Saedi, A. On the growth sequence of highly ordered nano-porous anodic aluminium oxide. Mater. Des. 2006, 27, 983–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Butler, W.H.; Zanari, G. Tailoring morphology in free-standing anodic aluminium oxide: Control of barrier layer opening down to the sub-10 nm diameter. Nanoscale 2010, 2, 778–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, S.; Uchibori, K.; Asoh, H. Control of nano/microstructure and pit initiation sites on aluminium surface by use of self-assembled spheres. Surf. Interface. Anal. 2010, 42, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popat, K.C.; Mor, G.; Grimes, C.; Desai, T.A. Poly (ethylene glycol) grafted nanoporous alumina membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 243, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.R. Membrane based synthesis of nanomaterials. Chem. Mater. 1996, 8, 1739–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, A.Y.Y.; Gao, H.; Lam, Y.C.; Rodriguez, I. Controlled fabrication of multi-tiered three dimensional nanostructures in porous alumina. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2008, 18, 2057–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asoh, H.; Nishio, K.; Nakao, M.; Tammamura, T.; Masuda, H. Conditions for ideally ordered anodic porous alumina pretextured Al. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2001, 148, B152–B156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shingubara, S.; Murakami, Y.; Morimoto, K.; Takahagi, T. Formation of aluminium nanodot array by combination of nanoindentation and anodic oxidation of aluminium. Surf. Sci. 2003, 532-535, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, A.P.; Burnell, G.; Hu, M.; MacManus-Driscoll, J.L. Controlled, perfect ordering in ultrathin anodic aluminium oxide templates on silicon. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91, 143. [Google Scholar]
- Zavadil, K.R.; Ohlhausen, J.A.; Kotula, P.G. Nanoscale void nucleation and growth in the passive oxide on aluminium as a prepitting process. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2006, 153, B296–B303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulka, G. Electrochemical Nanostructuring of Aluminium based on Anodizing and a Consecutive Electroplating of Magnetic Material into Plates; Katholieke Universiteit: Leuven, Belgium, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, T.T.; Piner, R.D.; Ruoff, R.S. An improved method to strip aluminium from porous anodic alumina films. Langmuir 2003, 19, 1443–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.H.; Chen, W.; Hui, R.J.; Hu, Y.L.; Xia, X.H. Mechanism of one-step voltage pulse detachment of porous anodic alumina membranes. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 51, 4589–4595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Yin, Q.; Zhou, Y. Superhydrophilicity of anodic aluminium oxide films: From honeycomb to birds nest. Thin Solid Films 2009, 517, 6012–6015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feliu, S.; Bartolome, M.J.; Gonzalez, J.A.; Feliu, S. XPS characterisation of porous and sealed anodic films on aluminium alloys. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2007, 154, C241–C248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; Jianmin, C.; Jiazheng, Z.; Hongxin, D. The pore-enlargement and self-lubrication treatment of anodic oxide film of aluminium. Wear 1996, 196, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirage, K.B.; Hulteen, J.C.; Martin, C.R. Nanotubule-based molecular filtration membrane. Science 1997, 278, 655–658. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, J.; Chik, H.; Yin, A.; Xu, J.M. Two-dimensional lateral superlattices of nanostructures: Nonlithographic formation by anodic membrane template. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 91, 2544–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zou, Z.Q. Self-organized growth of Mn nanocluster arrays on Si (111)-n (7 × 7) surfaces. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 103–115. [Google Scholar]
- Drak, M.; Dobrzański, L.A. Corrosion of Nd-Fe-B permanent magnets. J. Achievements Mater. Manuf. Eng. 2007, 20, 239–242. [Google Scholar]
- Knaack, S.A.; Eddington, J.; Leonard, Q.; Cerrina, F.; Onellion, M. Dense arrays of nanopore as X-rays lithiography masks. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 84, 3388–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.J.; Zhu, F.; Mu, C.; Liang, Y.; Xu, L.; Chen, Q.; Chen, R.; Xu, D. Electrochemical synthesis and applications of oriented and hierarchically quasi-1D semiconducting nanostructures. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2010, 254, 1135–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudiksen, M.S.; Lauhon, L.J.; Wang, J.; Smith, D.C.; Lieber, C.M. Growth of nanowire superlattice structures for nanoscale photonics and electronics. Nature 2002, 415, 617–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Duan, X.; Cui, Y.; Lauhon, L.J.; Kim, K.H.; Lieber, C. Directed assembly of one-dimensional nanostructures into functional networks. Science 2001, 294, 1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.R.; Oh, H.; So, H.M.; Kim, J.J.; Kim, J.; Lee, C.J.; Lyu, S.C. Schottky diodes based on a single GaN nanowire. Nanotechnology 2002, 13, 701–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Duan, X.; Wei, Q.; Lieber, C.M. Logic gates and computation from assembled nanowire building blocks. Science 2001, 291, 630–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, X.; Huang, Y.; Lieber, C.M. Gallium nitride nanowire nanodevice. Nano. Lett. 2002, 2, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Huang, Y.; Cui, Y.; Wang, J.; Lieber, C.M. Indium phosphide nanowires as building blocks for nanoscale electronic and optoelectronic devices. Nature 2001, 409, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hicks, L.A.; Dresselhaus, M.S. effect of quantum-well structures on the thermoelectric figure merit. Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 1993, 47, 12727–12732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.-L.; Li, H.; Zhao, G.-Y.; Li, H.-L. Electrodeposition and magnetic properties of Ni nanowire arrays on anodic aluminum oxide/Ti/Si substrate. Appl. Sur. Sci. 2006, 253, 139–1403. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, J.; Noguēs, J.; Mikhaylova, M.; Roig, A.; Muńoz, J.S.; Muhammed, M. Differences in the magnetic properties of Co, Fe, and Ni 250–300 nm wide nanowires electrodeposited in anodized alumina templates. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 1829–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, N.; Deng, P.; Chen, J.; Chai, L.; Gao, H.; Chen, Y. Electrophoric deposition of metal oxide films aimed for gas sensors application: The role of anodic aluminium oxide (AAO)/Al composite structure. Sens. Actuators, B. 2010, 144, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xu, L.; Li, W.; Gou, X. α-Fe2O3 Nanotubes in gas sensor and lithium-ion battery applications. Adv. Mater. 2005, 17, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, O.-J.; Hwang, S.-K.; Jeong, S.-H.; Lee, P.S.; Lee, K.-H. Synthesis of carbon nanotubes with identical dimensions using an anodic aluminum oxide template on a silicon wafer. Synth. Met. 2005, 148, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhachuk, R.A.; Teys, S.A.; Dolbak, A.E.; Olshanetsky, B.Z. Formation of ordered arrays of Ag nanowires and nanodots on Si surface. Surf. Sci. 2004, 565, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, L.; Bensing, F.; Waag, A. InAs quantum dots embedded in silicon. Thin Solid Films 2000, 367, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, Y.K.; Seo, D.; Yoo, K.; Park, S.; Jeong, S.H.; Chung, C.W. Non-lithographic SiO2 nanodot arrays via template synthesis approach. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2004, 43, 5657–5659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.J.; Zou, C.W.; Yang, B.; Lu, H.B.; Tian, C.X.; Yang, H.J.; Li, M.; Liu, C.S.; Fu, D.J.; Liu, J.R. Electro-deposition of tubular-rod structure gold nano wires using nanoporous anodic oxide as template. Electrochem. Commun. 2009, 11, 2019–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikaylova, M.; Toprak, M.; Kim, D.K.; Zhang, Y.; Muhammed, M. Nanowire formation by electro deposition in modified nanoporous polycrystalline anodic alumina templates. Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 2002, 704, W6.34.1–W6.34.6. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, A.J.; Li, J.; Jian, W.; Bennett, A.J.; Xu, J.M. Fabrication of highly ordered metallic nano-wire arrays by electrodeposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2001, 79, 1039–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.B.; Zhu, J.J.; Chen, H.Y. Photochemical synthesis of Au and Ag nanowires on a porous aluminium oxide template. J. Cryst. Growth 2003, 258, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.L.; Jia, J.F.; Liang, X.J.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.Z.; Xue, Q.K.; Li, Z.K.; Tse, J.S.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Zhang, S.B. Spontaneous Assembly of perfectly ordered identical size nanocluster arrays. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 88, 066101:1–066101:4. [Google Scholar]
- Zhixun, L.; Yan, F.; Xiaofang, Z.; Jiannian, Y. Synthesis of highly ordered iron/cobalt nanowire arrays in AAO templates and their structural properties. Mat. Chem. Phys. 2008, 107, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.Y.; Xu, F.Q.; Li, Z.M.; Zhang, W.H. Cyclic voltammetry for the fabrication of high dense silver nanowire arrays with the assistance of AAO template. Mat. Chem. Phys. 2005, 90, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabin, O.; Herz, P.R.; Lin, Y.M.; Akinwande, A.I.; Cronin, S.B.; Dresselhaus, M.S. Formation of thick porous anodic alumina films and nanowire arrays on silicon wafers and glass. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2003, 13, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.L.; Li, H.; Zhao, G.Y.; Li, H.L. Electro-deposition of ferromagnetic nanowire arrays on AAO/Ti/Si substrate for ultrahigh-density magnetic storage devices. Mater. Lett. 2006, 60, 2335–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peńa, D.J.; Mbindyo, J.K.N.; Carado, A.J.; Mallouk, T.E.; Keating, C.D.; Razavi, D.; Mayer, T.S. Template growth of photoconductive Metal-CdSe-Metal nanowires. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2002, 106, 7458–7462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, H.; Mei, Y.; Chen, J.; Wu, X.; Bao, X. Anodic alumina template on Au/Si substrate and preparation of CdS nanowires. Solid. State Commun. 2002, 123, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Lee, W.; Huang, Z.; Scholz, R.; Gosele, U. Fabrication and characterization of a flow-through nanoporous gold nanowire/AAO composite membrane. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 335604–335609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.-L.; Bao, S.-J.; Kong, L.-B.; Li, H.; Li, H.-L. Highly ordered MnO2 nanowire array thin films on Ti/Si substrate as an electrode for electrochemical capacitor. J. Solid. State. Chem. 2006, 179, 1351–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, A.J.; Li, J.; Jian, W.; Bennett, A.J.; Xu, J.M. Fabrication of highly ordered metallic nanowire arrays by electrodeposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2001, 79, 1039–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sander, M.S.; Prieto, A.L.; Gronsky, R.; Sands, T.; Stacy, A.M. Fabrication of high-density, high aspect ratio large-area Bismuth Telluride nanowire arrays by electrodeposition into porus anodic alumina templates. Adv. Mater. 2002, 14, 665–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perre, E.; Nyholm, L.; Gustafsson, T.; Taberna, P.L.; Simon, P.; Edstrom, K. Direct electrodeposition of aluminium nano-rods. Electrochem. Commun. 2008, 10, 1467–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.F.; Zhou, Y.C.; Pan, Y.; Wang, X.G. Growth of the nickel nanorod arrays fabricated using electrochemical deposition on anodised Al templates. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 3419–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.T.; Kuo, P.C.; Yao, Y.D. Formation of Pt nanorods on nanoporous anodic aluminium oxides by controlled nucleation sites. Thin Solid Films 2009, 517, 3243–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitzani, M.; Berger, S. Pyroelectric nano-rods grown inside alumina nano-pores. Phys. E. 2007, 37, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.C.; Juo, T.J.; Chen, Y.J.; Chiou, C.H.; Wang, H.W.; Liu, Y.L. Enhanced cyclic voltammetry using 1-D gold nanorods synthesized via AAO template electrochemical deposition. Desalination 2008, 233, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.H.; Han, C.Y.; Willing, G.A.; Xiao, Z. Nanowire and nanotube syntheses through self-assembled nanoporous AAO templates. Mater. Res. Soc. Sym. Proc. 2003, 775, 107–112. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Huang, H.; Yang, S. Synthesis of ceramic nanotubes using aao templates. J. Eur. Cerm. Soc. 2009, 29, 1387–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Choi, J.H.; Park, J.B.; Kim, S.K.; Yoo, J.B.; Park, C.Y. Growth characteristics of carbon nanotubes via aluminium nanopore template on Si substrate using PECVD. Thin Solid Films 2003, 435, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelucci, R.; Boscolo, I.; Ciorba, A.; Cuffiani, M.; Malferrari, L.; Montanari, A.; Odorici, F.; Orlanducci, S.; Rizzoli, R.; Rossi, M.; Sessa, V.; Terranova, M.L.; Veronese, G.P. Honeycomb arrays of carbon nanotubes in alumina templates for field emission based devices and electron sources. Phys. E. 2010, 42, 1469–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, A.D.; Janes, D.B.; Claussen, J.; Fisher, T.; Sands, T.D. Independently addressed fields of porous anodic alumina embedded in SiO2 on Si. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 013122:1–013122:3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutin, P.; Hamadouche, M.; Daussange, J.; Bolander, M.E.; Sedel, L. Alumina-on-Alumina Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Minimum 18.5-Year Follow-up Study. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2002, 84, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Karlson, M. Nano-Porous Aluminia, a Potential Bone Implant Coating; Comprehensive Summaries of Uppsala Dissertations; The Faculty Of Science And Technology, Acta Universitatis Upsaliensis: Kiruna, Sweden, 2004; Volume 997, pp. 1–75. [Google Scholar]
- Hoess, A.; Teuscher, N.; Thormann, A.; Aurich, H.; Heilmann. Cultivation of hepatoma cell line HepG2 on nanoporous aluminium oxide membranes. Acta Biomater. 2007, 3, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlsson, M.; Pålsgård, E.; Wilshaw, P.R.; Di Silvio, L. Initial in vitro interaction of osteoblasts with nano-porous alumina. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 3039–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Li, D.; Zue, N.; Xu, X.; Li, J. Oriented nano-structured hydroxiapatite from the template. Chem. Phy. Lett. 2003, 376, 493–497. [Google Scholar]
- Popat, K.C.; Leary Swan, E.E.; Mukhatyar, V.; Chatvanichkul, K.I.; Mor, G.K.; Grimes, C.A.; Desai, T.A. Influence of nanoporous alumina membranes on long-term osteoblast response. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 4516–4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.-J.; He, L.-P.; Chen, Z.-Z. Fabrication and characterization of hydroxyapatite/Al2O3 biocomposite coating on titanium. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. 2006, 16, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walpole, A.R.; Briggs, E.P.; Karlsson, M.; Palsagard, E.; Wilshaw, P.R. Nano-porous alumina coatings for improved bone implant interfaces. Mater. Wiss. U. Werkstofftech 2003, 34, 1064–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saji, V.S.; Choe, H.C.; Brantley, W.A. An electrochemical study on self-ordered nanoporous and nanotubular oxide on Ti-35Nb-5Ta-7Zr alloy for biomedical applications. Acta Biomater. 2009, 5, 2303–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkinson, L.G.; Giles, L.N.; Katharine, F.A.; Fear, M.W.; Wood, F.M.; Poinern, G.E. The Potential of Nanoporous Anodic Aluminium Oxide Membranes to Influence Skin Wound Repair. Tissue Eng. 2009, 15, 3753–3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poinern, G.E.J.; Fawcett, D.; Ng, Y.J.; Ali, N.; Brundavanam, R.K.; Jiang, Z.T. Nanoengineering a biocompatible inorganic scaffold for skin wound healing. J. BioMed. Nanotech. 2010, 6, 497–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gultepe, E.; Nagesha, D.; Sridhar, S.; Amiji, M. Nanoporous inorganic membranes or coatings for sustained drug delivery in implantable devices. Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, G.B.; Filho, J.L.L.; Chaves, M.E.C.C.; Azevedo, W.M.; Carvalho, L.B. Enzyme immobilization on anodic aluminium oxide/polyethyleneimine or polyaniline composites. React. Funct. Polym. 2008, 68, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.S.; Kim, H.J.; Ahn, J.K.; Kim, D.H. Microfluidic chip with porous anodic alumina integrated with PDMS/glass substrate for immune-diagnosis. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2009, 9, e60–e65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Poinern, G.E.J.; Ali, N.; Fawcett, D. Progress in Nano-Engineered Anodic Aluminum Oxide Membrane Development. Materials 2011, 4, 487-526. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma4030487
Poinern GEJ, Ali N, Fawcett D. Progress in Nano-Engineered Anodic Aluminum Oxide Membrane Development. Materials. 2011; 4(3):487-526. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma4030487
Chicago/Turabian StylePoinern, Gerrard Eddy Jai, Nurshahidah Ali, and Derek Fawcett. 2011. "Progress in Nano-Engineered Anodic Aluminum Oxide Membrane Development" Materials 4, no. 3: 487-526. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma4030487
APA StylePoinern, G. E. J., Ali, N., & Fawcett, D. (2011). Progress in Nano-Engineered Anodic Aluminum Oxide Membrane Development. Materials, 4(3), 487-526. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma4030487




