Prospect of Tellurium in High-Temperature Carburizing Gear Steels: An Industrial Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
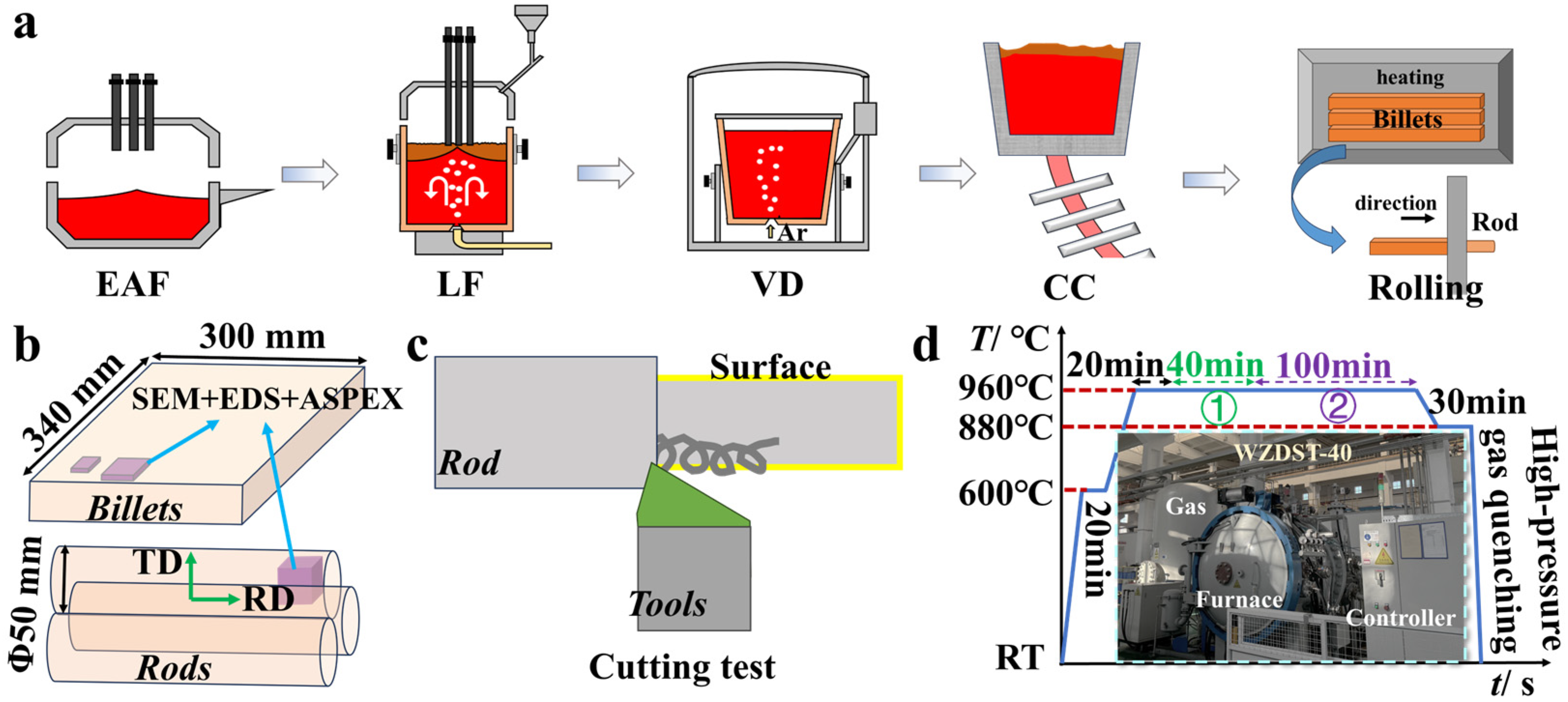
2.1. Industrial Production
2.2. Inclusion Characterization and Rod Cutting Test
2.3. High-Temperature Vacuum Carburizing Experiment
3. Results and Discussion
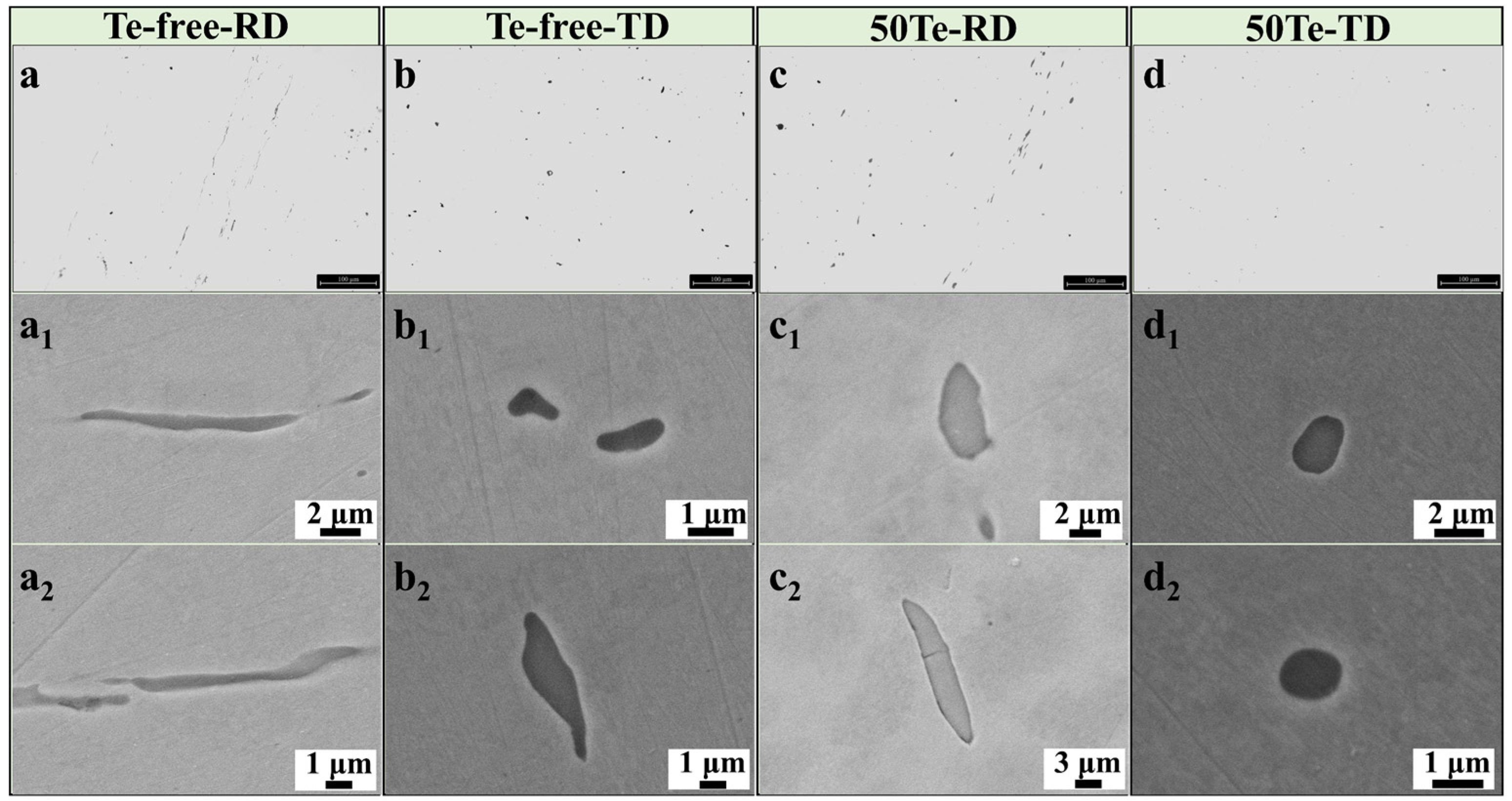
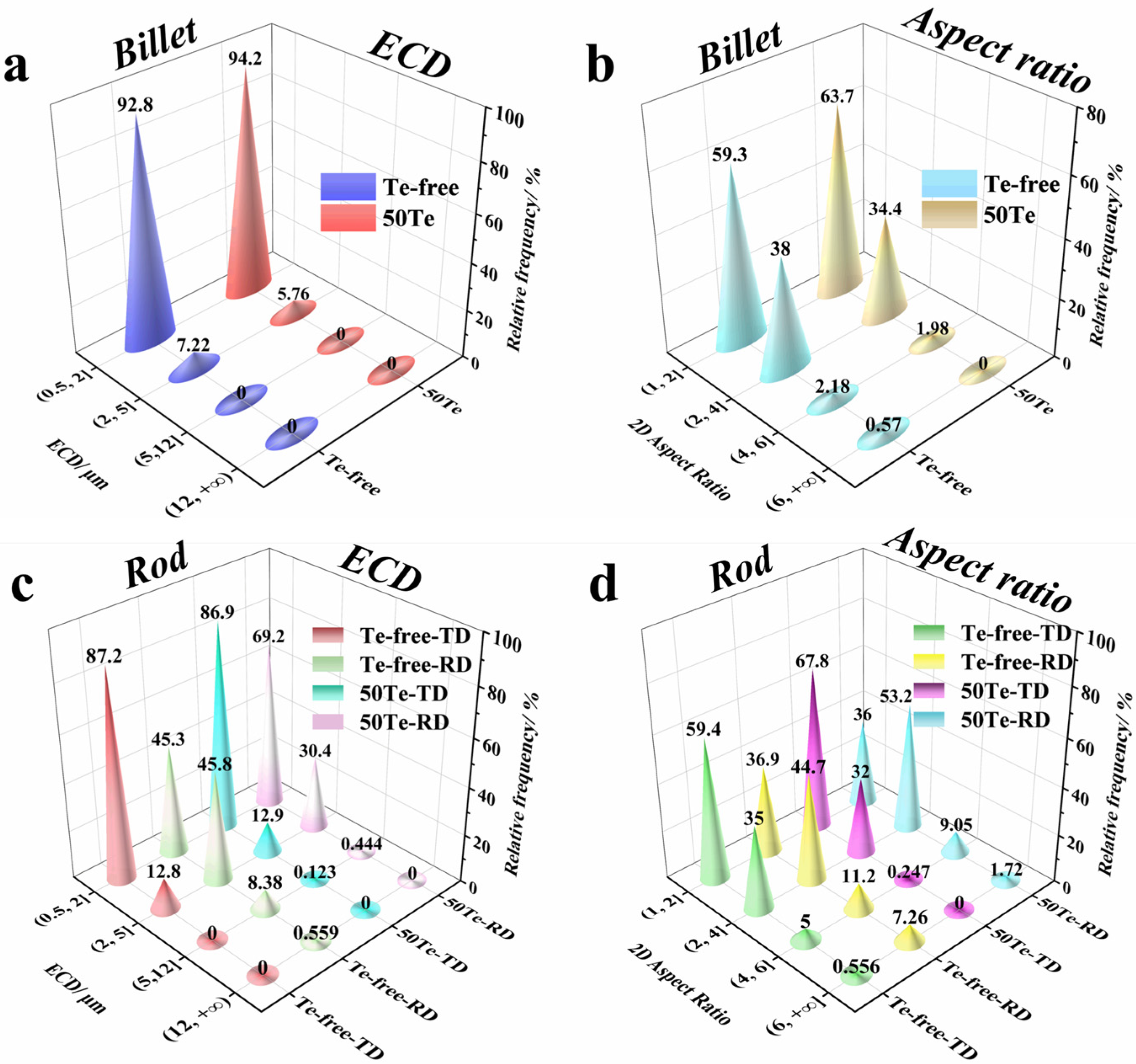
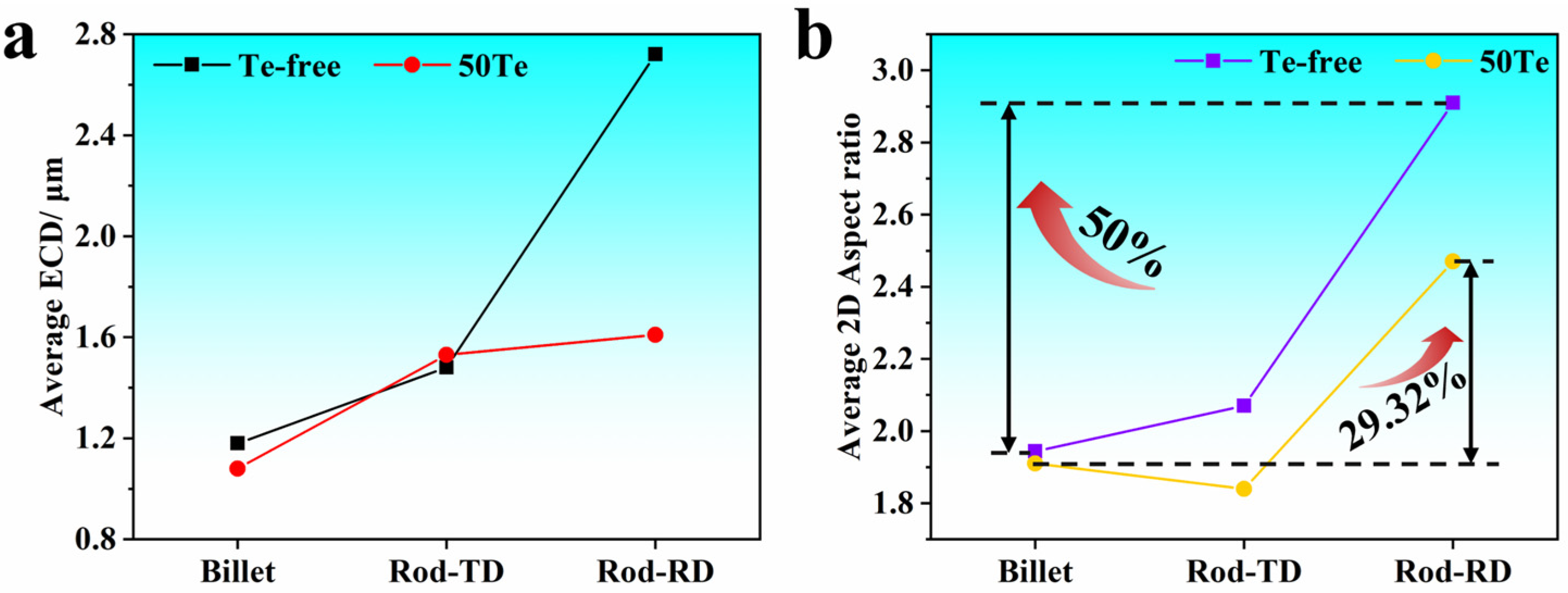
3.1. Effect of Te on MnS Inclusions Precipitation and Rolling Deformation in Industrial Cast Billets and Rods
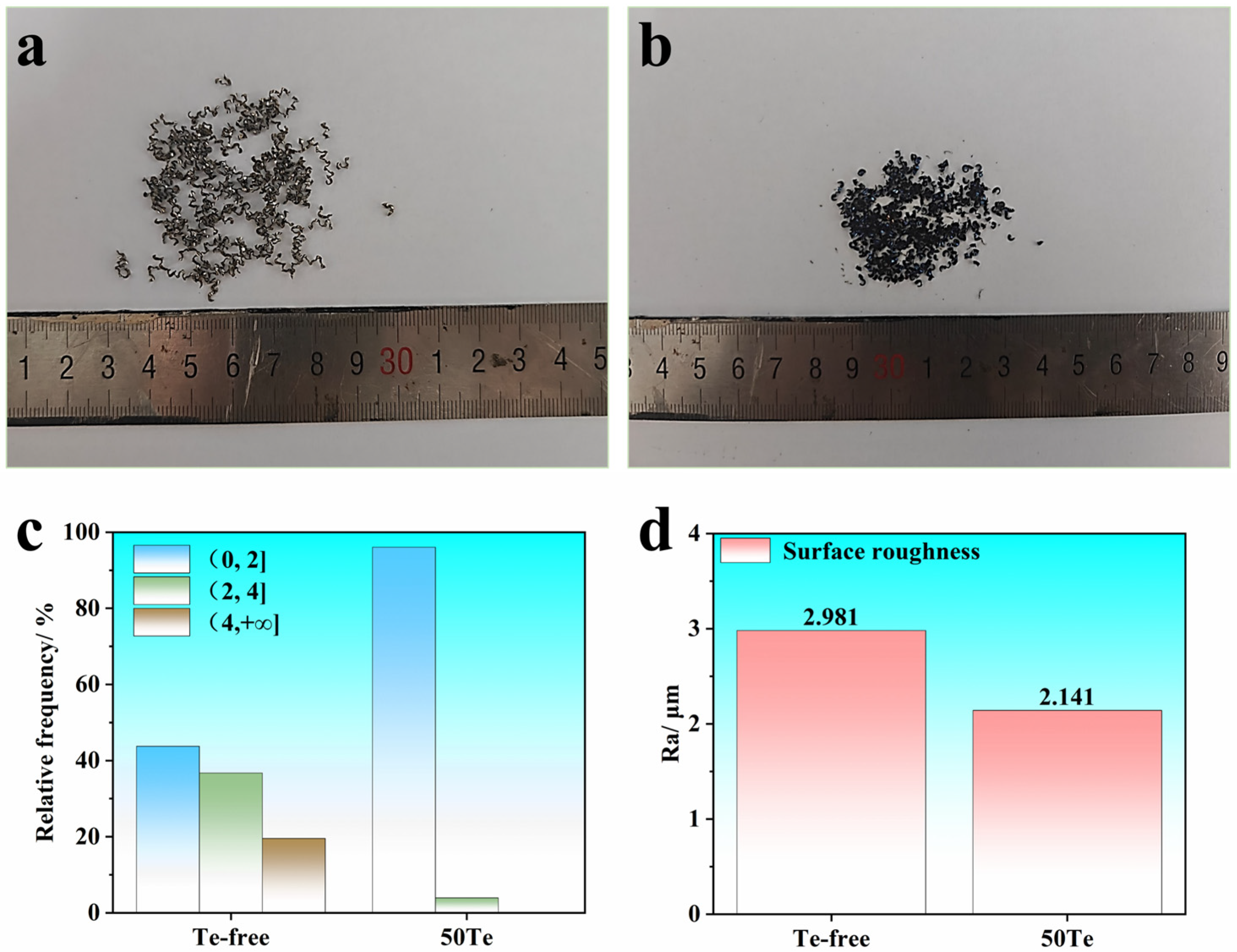
3.2. Effect of Te on the Cutting Performance of Industrial Rods
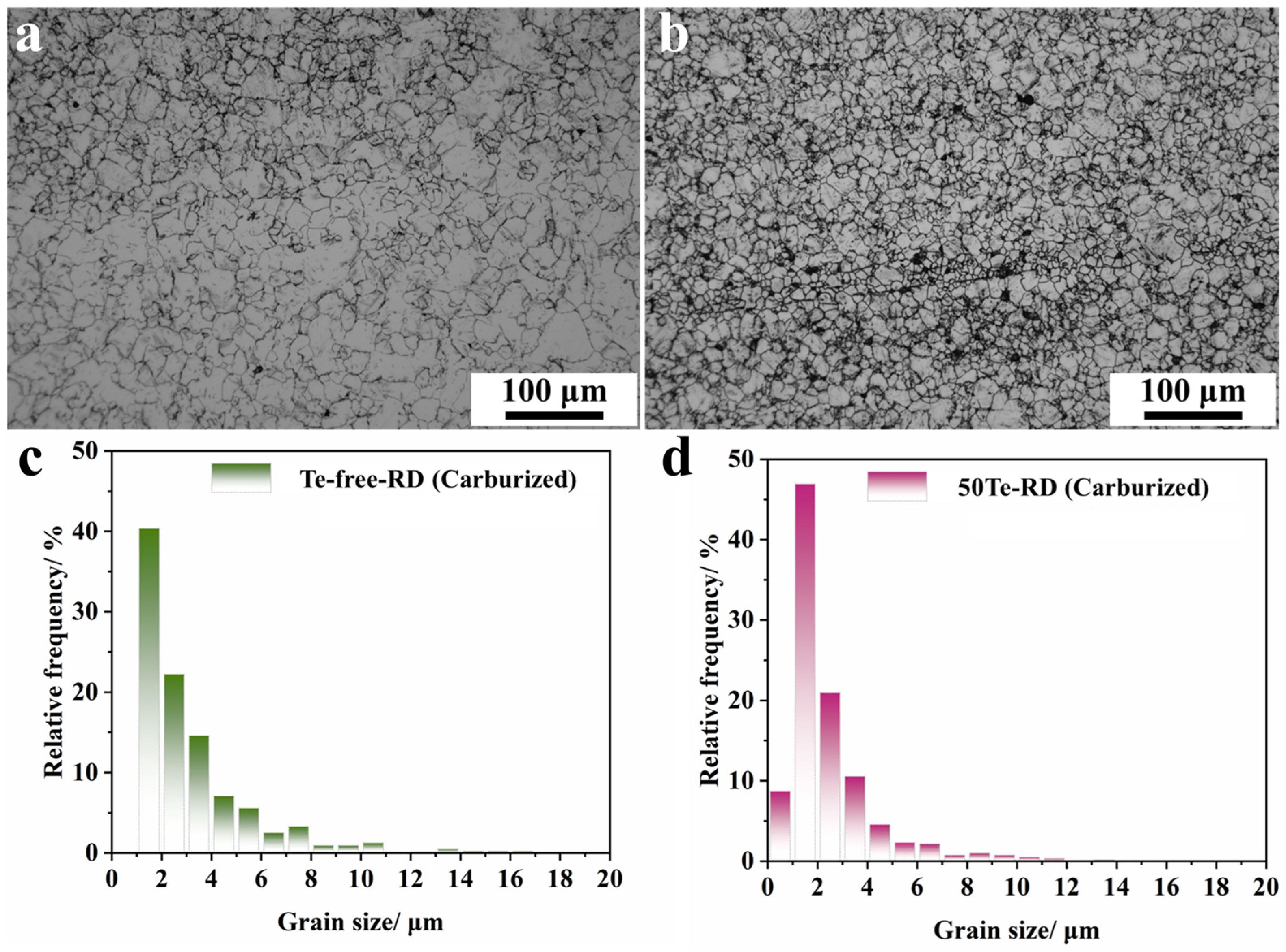
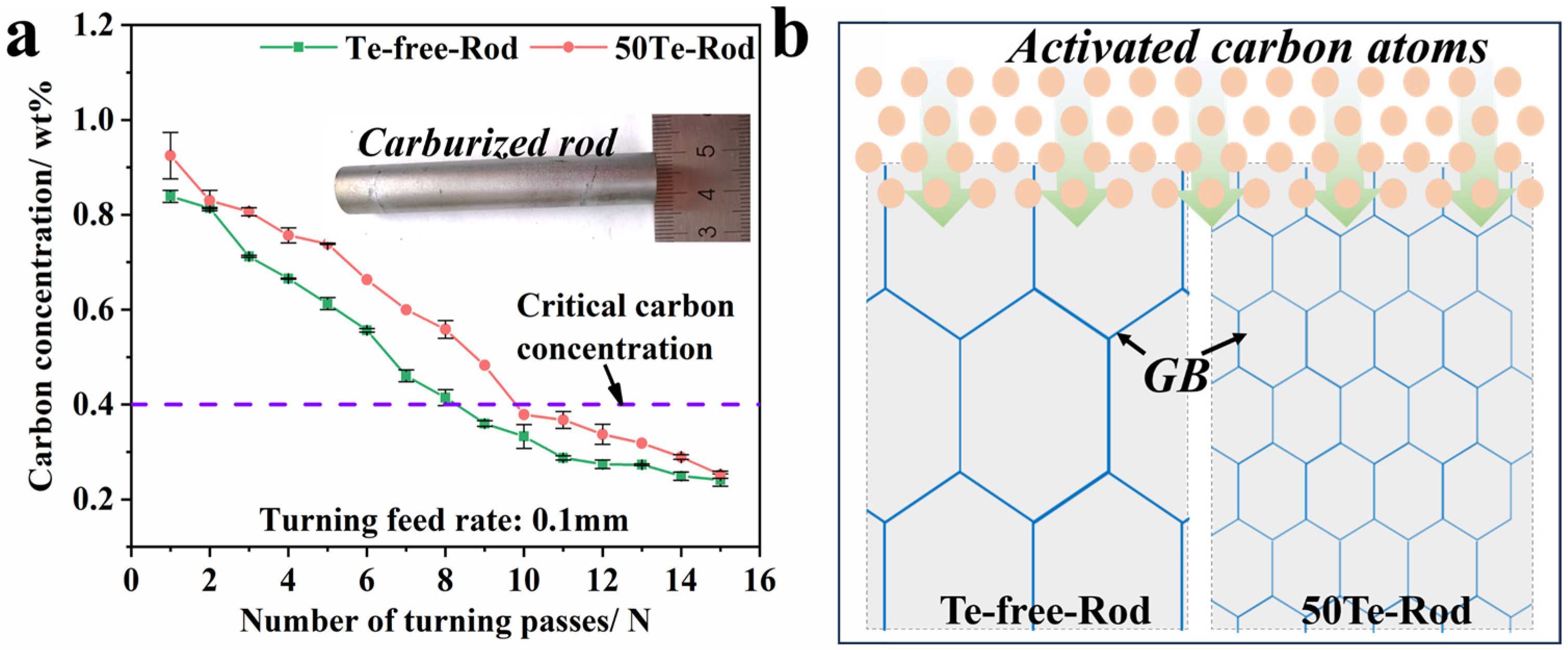
3.3. Effect of Te on High-Temperature Vacuum Carburizing Properties of Industrial Rods
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Feeding Te-containing cored wire into the molten steel using a wire feeder is an effective way to add Te in industrial production. Choosing to feed the wire after the ladle refining process can achieve a good alloy recovery rate without affecting the on-site production.
- (2)
- Te showed similar results in industrial production to those observed in laboratory-scale studies. Te can promote the precipitation of MnS inclusions in the billet with a smaller size and a lower aspect ratio. After hot rolling, the rolling deformation rate of MnS inclusions in the Te-containing gear steel rod was 29.32%, lower than that in the Te-free gear steel rod. The stress buffering provided by the MnTe phase during rolling and the increased hardness of the MnS-MnTe inclusions are the key factors of the reduced rolling deformation.
- (3)
- The addition of Te can effectively optimize chip breaking behavior during the machining of the Te-containing industrial rod. The globular MnS inclusions act as stress concentration sources at the interface, which is the main reason for the large production of short spiral chips during the machining of Te-containing steel. In addition, the surface roughness of the Te-containing industrial rod after machining is lower, which is beneficial for improving the machining accuracy of gear components.
- (4)
- The vacuum carburizing test at 960 °C verified the role of Te in stabilizing high-temperature grain growth in gear steel. The grain structure of the Te-containing gear steel rod after high-temperature carburizing is more refined and uniformly distributed compared to that of the Te-free gear steel rod. In terms of carburizing layer depth, the fine-grained structure of the Te-containing gear steel rod provides more grain boundary channels for high-temperature carbon diffusion, ultimately resulting in a more excellent carbon concentration gradient.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, X.; Tian, Y. Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of High-Temperature Carburized 18Cr2Ni4WA Steel. Materials 2024, 17, 4820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tinoco, H.A.; Fintova, S.; Heikkila, I.; Herrero, D.; Vuoristo, T.; Dlouhy, I.; Hutar, P. Experimental and numerical study of micromechanical damage induced by MnS-based inclusions. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 856, 144009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akasawa, T.; Sakurai, H.; Nakamura, M.; Tanaka, T.; Takano, K. Effects of free-cutting additives on the machinability of austenitic stainless steels. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2003, 143, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.-j.; Wang, X.-h.; Ji, C.-x.; Li, H.-b.; Cui, Y.; Zhu, G.-s. Morphology, size and distribution of MnS inclusions in non-quenched and tempered steel during heat treatment. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2015, 22, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Fang, W.; Chen, R.-M.; Jiang, B.; Wang, H.-B.; Liu, Y.-Z.; Liang, H.-L. Mechanical anisotropy and local ductility in transverse tensile deformation in hot rolled steels: The role of MnS inclusions. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 744, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temmel, C.; Ingesten, N.-G.; Karlsson, B. Fatigue anisotropy in cross-rolled, hardened medium carbon steel resulting from MnS inclusions. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2006, 37, 2995–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Shen, Z.; Yu, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhu, M. Effect of Ce addition on inclusions and grain structure in gear steel 20CrNiMo. Steel Res. Int. 2021, 92, 2000394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, Z.; Li, B.; Chen, W.; Zhang, J.; Mao, J. Inclusions modification by rare earth in steel and the resulting properties: A review. J. Rare Earths 2024, 42, 431–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Yang, J.; Fu, X. Effect of Ce Content on Modification Behavior of Inclusions and Corrosion Resistance of 316L Stainless Steel. Materials 2024, 18, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Tian, J.; Hu, S.; Lv, M.; Li, X.; Qu, T.; Wang, D.; Zhan, T. Effect of Ca/Mg on distribution and morphology of MnS inclusions in 45MnVS non-quenched and tempered steel. Metals 2023, 13, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X. Effect of magnesium on inclusions in a high sulfur steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2022, 53, 848–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, L.; Long, M.; Chen, H.; Chen, D.; Duan, H.; Huang, Y.; Liu, T. Effect of MnS precipitation on solute equilibrium partition coefficients in high sulfur steel during solidification. J. Mater. Res. 2018, 33, 3490–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Ren, Y.; Luo, Y.; Ji, S.; Zhang, L. Deformation of MnS–MnTe Inclusions in a Sulfur-Containing Free-Cutting Steel with Tellurium Treatment. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2022, 54, 370–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, T.; Abeyama, S.; Kimura, A.; Nakamura, S. A study on resulfurized free-machining steel containing a small amount of tellurium. Denki Seiko (Electr. Furn. Steel) 1982, 53, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Li, Y.; Hu, T.; Xu, X.; Liu, N.; Fu, J. The Forms and Evolution of Free-Cutting Phase in Bi–Te–S Free-Cutting Steel. Steel Res. Int. 2023, 95, 2300608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, F.; Qi, Z.; Liu, W.; Liu, Q.; Yang, S.; Li, J. Theoretical precipitation modeling and multidimensional characterization of sulfide inclusions in tellurium-containing steels. Mater. Charact. 2024, 218, 114546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, C.; Liu, R.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Hao, X.; Wu, H.; Sun, Y. Effect of Rare Earth Cerium Content on Manganese Sulfide in U75V Heavy Rail Steel. Metals 2022, 12, 1012–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Song, B.; Yang, Z.; Mao, J. Effect of rare earth Ce on modifying inclusions in Al-killed X80 pipeline steel. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2022, 75, 2837–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Song, G.; He, J.; Zhang, D.; Fu, J.; Shen, P. Influence Factors of SEN Clogging of Rare-Earth Steel Continuous Casting and Solve Ideas of Japanese Steel Enterprises. Steel Res. Int. 2023, 94, 2300078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, W.; Wang, M.; Zhang, J.; Yang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Li, J. Tellurium-Induced Reduction in Heat Susceptibility of Gear Steel During High-Temperature Carburizing. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2024, 55, 4829–4840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Guo, H.; Liu, W.; Yang, S.; Zhang, S.; Li, J. Control of MnS Inclusions in High- and Low-Sulfur Steel by Tellurium Treatment. Materials 2019, 12, 1034–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, P.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, D.; Yang, S.; Fu, J. The Effect of Tellurium on the Formation of MnTe-MnS Composite Inclusions in Non-Quenched and Tempered Steel. Metals 2018, 8, 639–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-h.; Wang, M.-q.; Chen, J.-c.; Dong, H. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Gear Steels After High Temperature Carburization. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2013, 20, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Zhang, N.; Wan, S.; Zhao, H.; Jiang, B.; Liu, Y.; Wu, C. The Carburizing Behavior of High-Temperature Short-Time Carburizing Gear Steel: Effect of Nb Microalloying. Steel Res. Int. 2022, 93, 2200427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.-q.; He, X.-f.; Zhang, Q.-z.; Wang, W.-j.; Wang, M.-q. Comparison of microstructure and heat treatment distortion of gear steels with and without Nb addition. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2021, 28, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, E.; Yuan, Q.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Mo, J.; Liang, W.; Xu, G. On the grain coarsening behavior of 20CrMnTi gear steel during pseudo carburizing: A comparison of Nb-Ti-Mo versus Ti-Mo microalloyed steel. Mater. Charact. 2023, 203, 113138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Tian, Y.; Wang, H.; Shen, Y.; Wang, Z. Suppression of austenite grain coarsening by using Nb–Ti microalloying in high temperature carburizing of a gear steel. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2019, 21, 1900132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Feng, Y.; Jiang, B.; Wu, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, H.; Liu, Y. Corrosion and abrasion behavior of high-temperature carburized 20MnCr5 gear steel with Nb and B microalloying. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 25, 5845–5854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.w.; Gao, X.y.; Zhang, L.f. Effect of Sulfur Content on Precipitation Behavior of Dendrite Sulfide Inclusion in Continuous Casted 20CrMnTi Gear Steel. Steel Res. Int. 2024, 95, 2400587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.; Park, D.; Shim, S.; Na, H.; Bae, G.; Seo, S.-J.; Lee, J. Prediction of Behavior of Alumina Inclusion in Front of Solid–Liquid Interface in SPFH590 Steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2020, 51, 690–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Bai, Y.; Liu, W.; Yang, S.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, J. Effect of tellurium treatment on wear resistance and inclusions deformation of 20MnCrS5 gear steel. Iron Steel 2025, 60, 128–140. [Google Scholar]
- Yaguchi, H.; Onodera, N. The effect of tellurium on the machinability of AISI 12L14+ Te steel. Trans. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. 1988, 28, 1051–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, P.; Yang, Q.-k.; Zhang, D.; Wu, Y.-x.; Fu, J.-x. Application of tellurium in free-cutting steels. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2018, 25, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, M.; Jiangang, W.; Dongying, J.; Huijun, Z.; Mengyuan, Y. Improvement and analysis of fatigue strength for mild steel 20MnCrS5 during carburizing and quenching. Mater. Sci. 2020, 26, 192–198. [Google Scholar]


| Steel/Composition | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Al | O | N | Te |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Te-free | 0.201 | 0.134 | 1.2 | 0.019 | 0.02 | 1.19 | 0.029 | <0.001 | <0.015 | - |
| 50Te | 0.197 | 0.112 | 1.0 | 0.015 | 0.02 | 1.13 | 0.024 | <0.001 | <0.015 | 0.0051 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Bai, Y.; Liu, W.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, G.; Yang, S.; Li, J. Prospect of Tellurium in High-Temperature Carburizing Gear Steels: An Industrial Study. Materials 2025, 18, 2162. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18092162
Wang J, Bai Y, Liu W, Xu H, Zhang Q, Wang G, Yang S, Li J. Prospect of Tellurium in High-Temperature Carburizing Gear Steels: An Industrial Study. Materials. 2025; 18(9):2162. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18092162
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jin, Yun Bai, Wei Liu, Huiyu Xu, Qingsong Zhang, Guangwei Wang, Shufeng Yang, and Jingshe Li. 2025. "Prospect of Tellurium in High-Temperature Carburizing Gear Steels: An Industrial Study" Materials 18, no. 9: 2162. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18092162
APA StyleWang, J., Bai, Y., Liu, W., Xu, H., Zhang, Q., Wang, G., Yang, S., & Li, J. (2025). Prospect of Tellurium in High-Temperature Carburizing Gear Steels: An Industrial Study. Materials, 18(9), 2162. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18092162






