Seismic Response Mitigation of Reinforced-Concrete High-Speed Railway Bridges with Hierarchical Curved Steel Dampers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mechanical Characterization of the CSD
2.1. Introduction
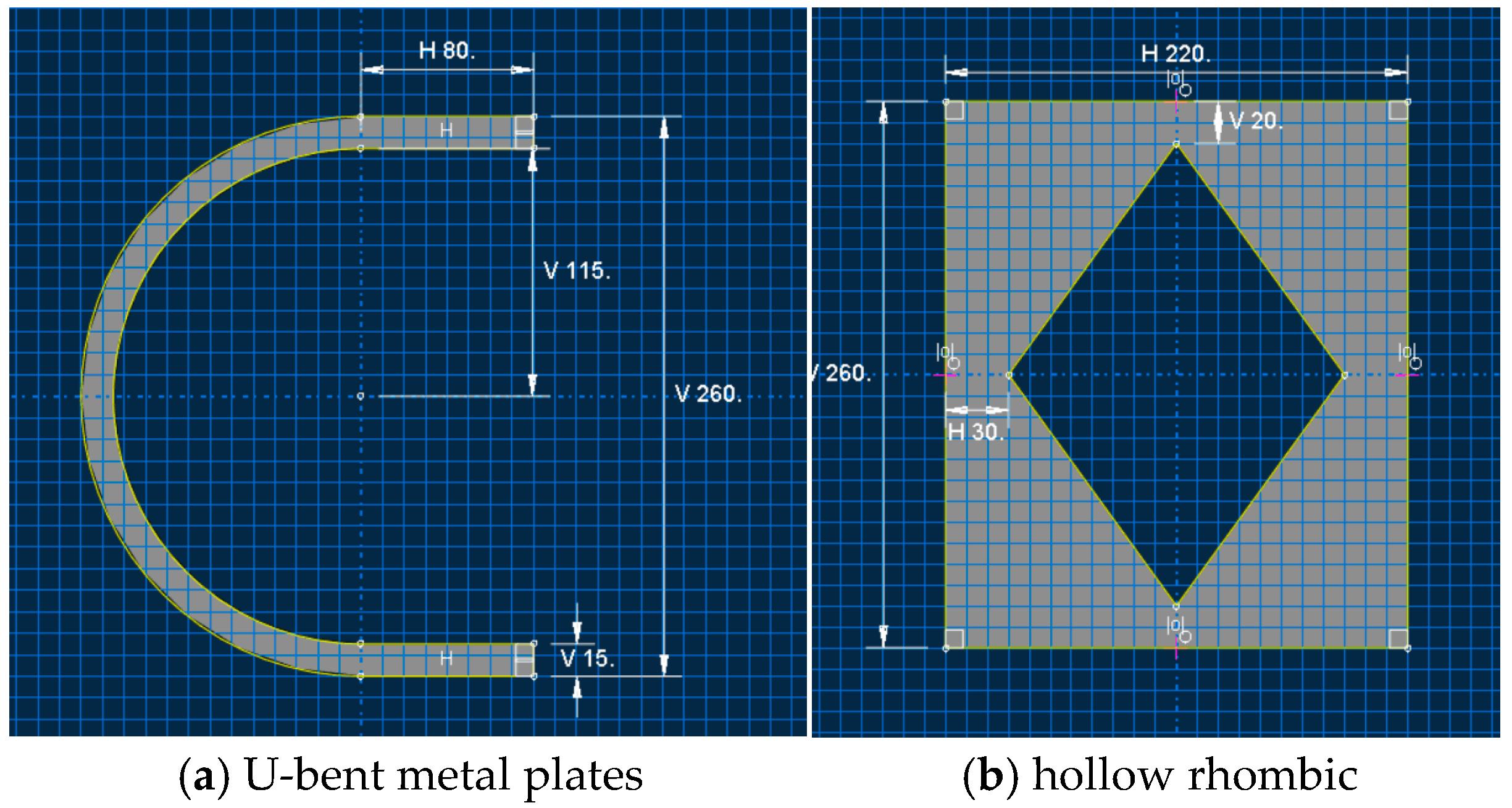
2.2. Design of the CSD
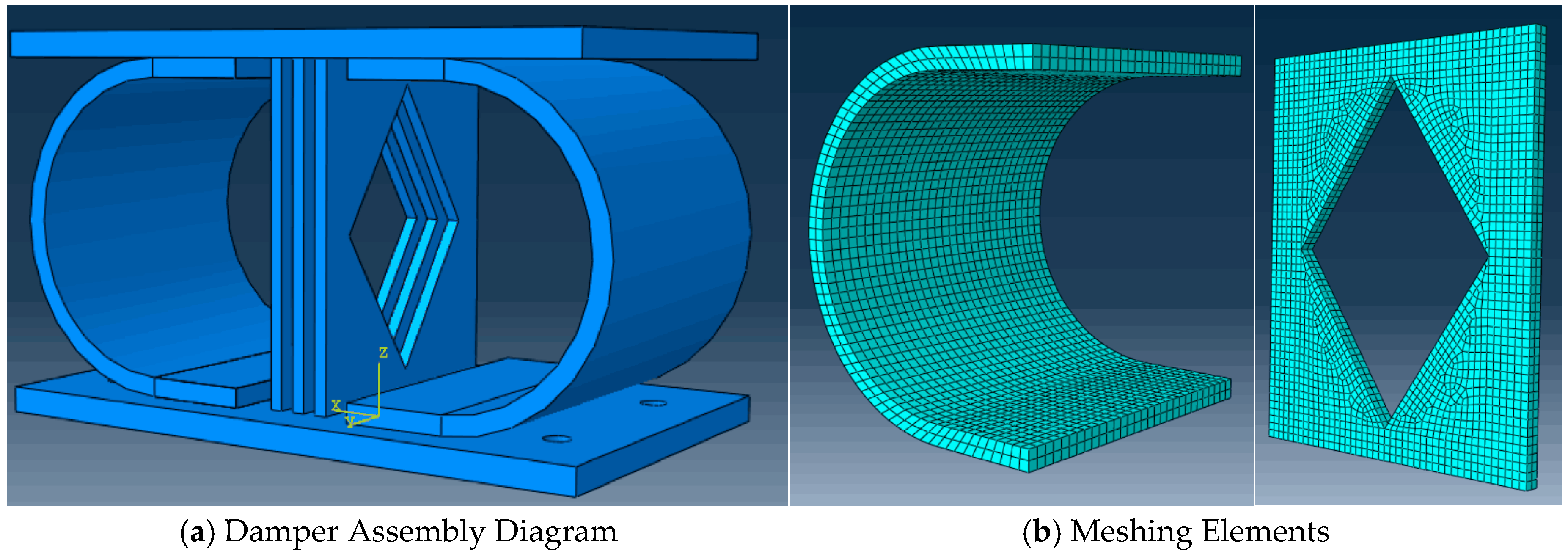
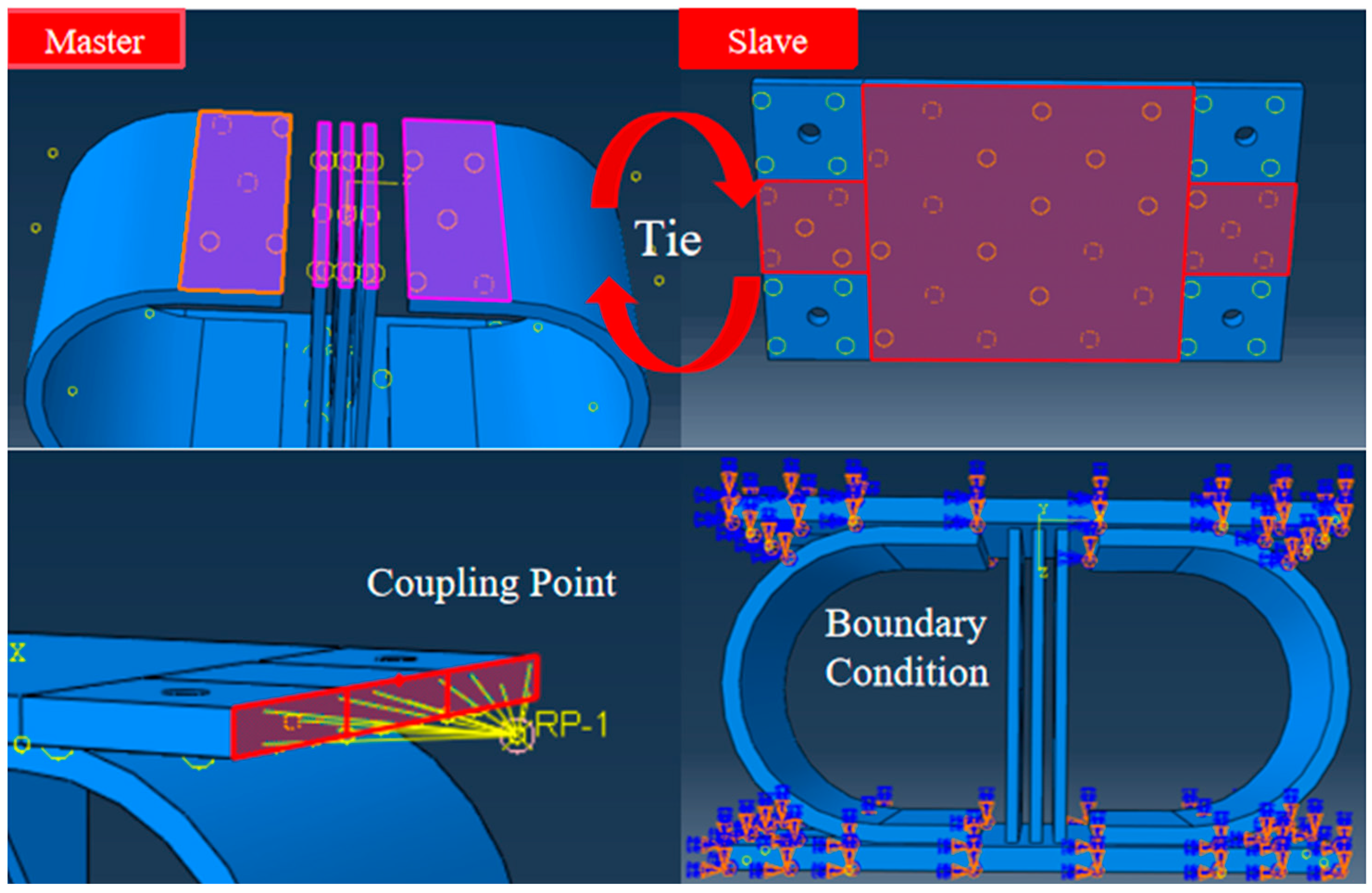
2.3. Finite Element Modeling Framework
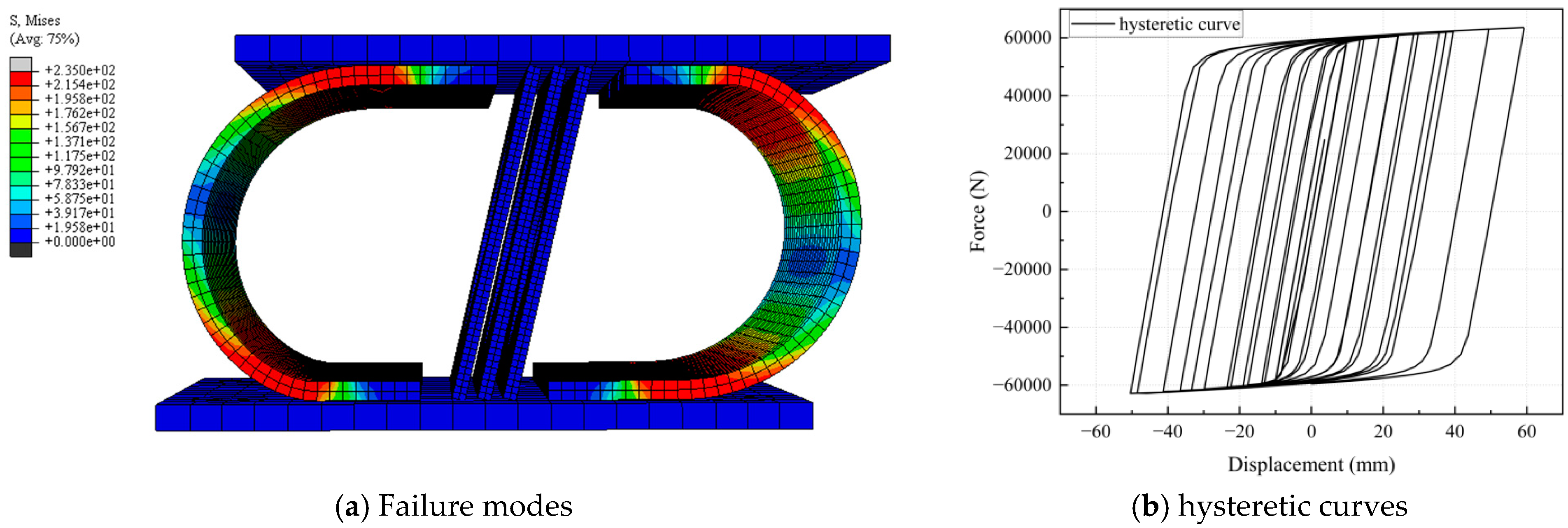
2.4. Analysis of Deformation Modes and Hysteretic Performance Evaluation
3. Seismic Analysis of the HSR Track–Bridge System Integrated with CSD
3.1. Introduction
3.2. Finite Element Modeling of the HSRVTBD System
3.3. Ground Motion Selection and Spectral Matching
4. Seismic Mitigation Efficacy of CSD Dampers in HSR Bridge–Track Systems
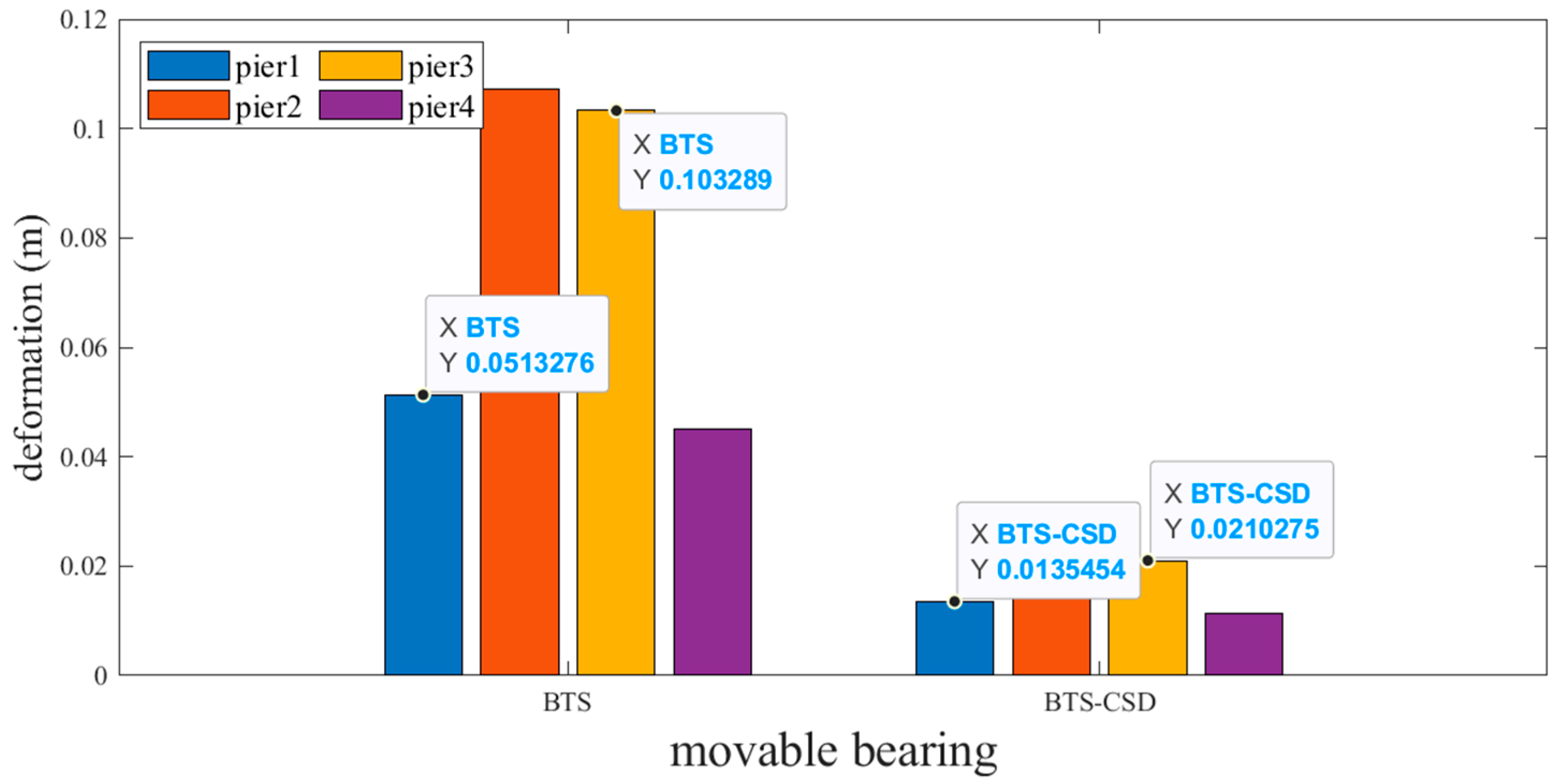
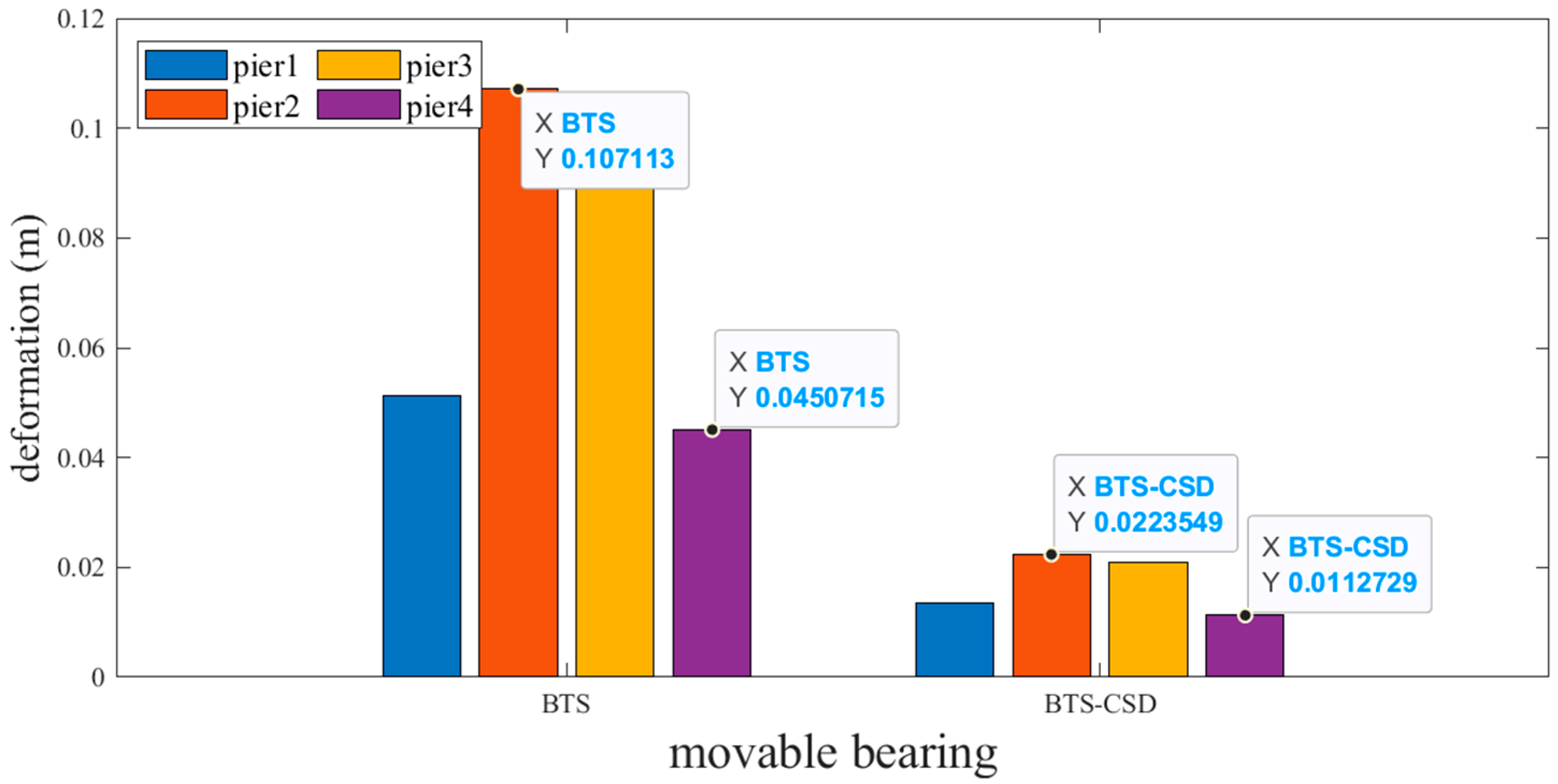
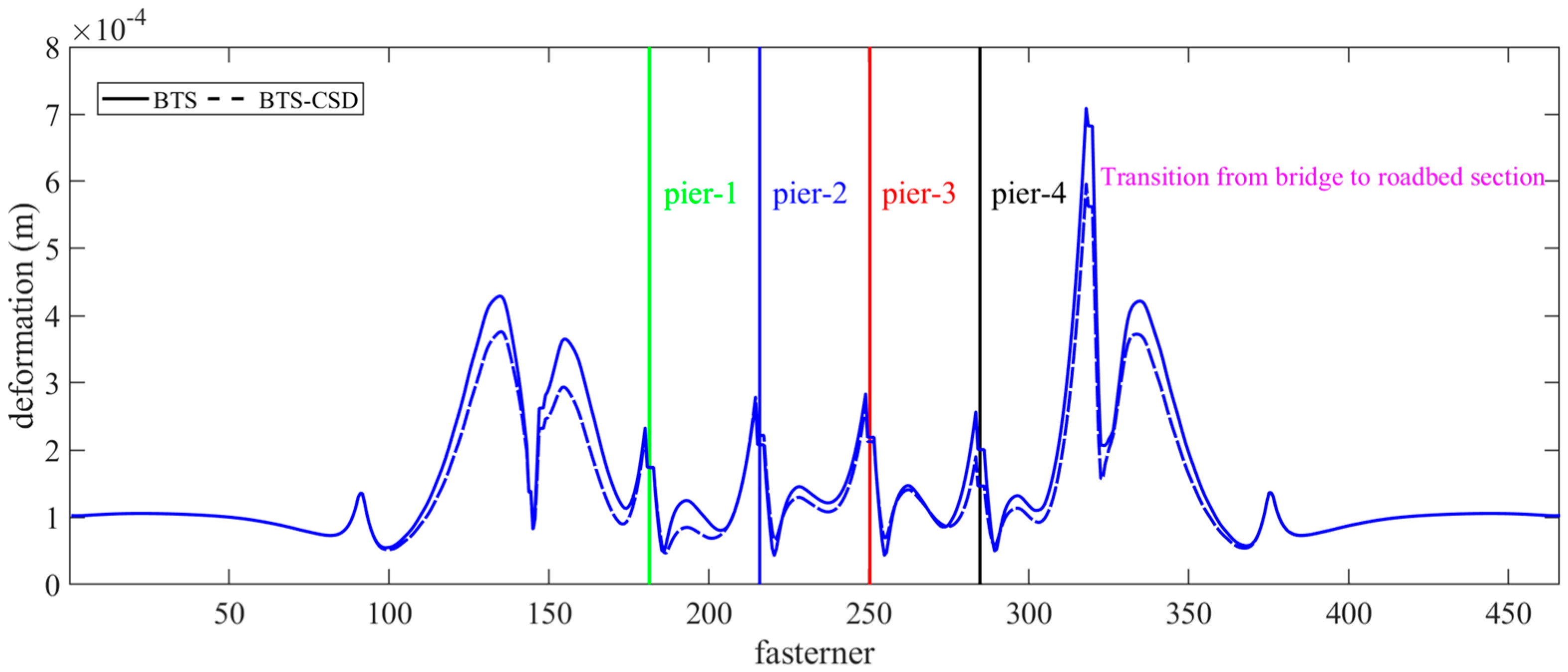
4.1. Component-Level Deformation Analysis via MATLAB Visualization
4.2. Synthesis of Seismic Retrofitting Outcomes
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, L.; Zhong, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Lai, Z. A Novel Seismic-Resistant Design for Track Structures in the Bridge-Embankment Transition Zone of Multi-Span High-Speed Railways Simply Supported Bridges. Eng. Struct. 2025, 324, 119349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Jiang, L.; Wen, T.; Jiang, L. An Improved Interlayer Area Damage Model for Seismic Damage Assessment of a High-Speed Railway Long-Span Arch Bridge-Track System. SOIL Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2024, 184, 108811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Gao, C.; Yang, S.; Guo, W.; Jiang, L. Seismic Fragility Analysis of Reinforced Concrete Simply Supported Girder Bridges Resting on Double-Column Piers for High Speed Railway. Buildings 2024, 14, 3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Xiong, L.; Jiang, L. Multi-Parameter Seismic Fragility Analysis of High-Speed Railway Track-Bridges: Embracing Structural and Earthquake Uncertainties. Int. J. Struct. Stab. Dyn. 2024, 2630001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Wu, L.; Zhong, T.; Jiang, L.; Liu, S. Impact of Vertical Girder Deformations on the High-Speed Train Operation Performance. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2024, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, G.; Wei, T.; Mahunon, A.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, Y. Experimental Study of the Temperature Distribution in CRTS-II Ballastless Tracks on a High-Speed Railway Bridge. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Duan, H.; Wen, T.; Jiang, L. Effects of Near-Fault Pulse-like Ground Motions and Pulse Parameters on a High-Speed Railway Long-Span Arch Bridge-Track System. J. Bridge Eng. 2025, 30, 04024112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Yu, K.; Jiang, L.; Wen, T.; Hu, Y.; Pang, L. Effects of Shear Panel Dampers on Seismic Response Mitigation of High-Speed Railway Simply Supported Bridge-Track System under Far-Field and near-Field Ground Motions. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2023, 23, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Liu, J.; Wen, T.; Jiang, L.; Yan, Y.; He, C. Damage Dispersion Study of High-Speed Railway Track-Bridge System with the UCSD Considering Train Effects. Structures 2024, 68, 107213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Z.; Jiang, L.; Chen, Y.; Wei, B. An Improved Model for the Nonlinear Simulation of the High-Speed Vehicle-Track-Bridge Coupling System under Seismic Shaking. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2024, 53, 3775–3797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Xiao, J.; Liu, S.; Jiang, L.; Yu, J.; Zu, L.; Wu, L.; Ren, Z. Analysis of Key Influencing Factors of Track Dynamic Irregularity Induced by Earthquakes in the High-Speed Railway Track-Bridge System. Int. J. Struct. Stab. Dyn. 2024, 24, 2450246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Xiong, L.; Jiang, L.; Zhong, B. Innovative Approaches in High-Speed Railway Bridge Model Simplification for Enhanced Computational Efficiency. J. Cent. South Univ. 2024, 31, 4203–4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Wang, P.; Yan, B.; Jiang, L.; He, X. Parameter Optimization of Damper-Friction Isolation Systems Using Concave Friction Distribution. J. Vibroengineering 2016, 18, 1668–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wen, T.; Jiang, L.; Jiang, L.; Zhou, W.; Du, Y. Interlayer Area Damage Modeling and Damage-Based Seismic Fragility Analysis of High-Speed Railway Bridge and Track System. Eng. Struct. 2022, 272, 114989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Xiong, L.; Jiang, L. New Parameter Updating Method for Bidirectional Simplified Seismic Models of High-Speed Railway Bridges. Structures 2025, 71, 107959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Duan, H.; Jiang, L.; Zhou, W.; Du, Y.; Jiang, L. Refined Probabilistic Seismic Demand Modeling of High-Speed Railway Bridge under near-Fault Hanging-Wall Effects and Velocity Pulse Effects by a Novel Ground Motion Selection Approach. Int. J. Struct. Stab. Dyn. 2024, 2650074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Li, W.; Jiang, L.; Wang, Z.; Wen, T. Railway Alignment Optimization and Seismic Responses of High-Speed Railway Bridge Considering the Spatial Effects of Mountainous-Plateau. Int. J. Struct. Stab. Dyn. 2024, 2550170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Xiao, B.; Tan, H.; Yang, Z.; Jiang, L.; Yu, Y. Energy Response Analysis and Seismic Isolation Strategy Optimization of High-Speed Railway Bridge-Track System under Earthquake Action. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2024, 186, 108917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; He, C.; Lai, Z.; Jiang, L.; Li, D. Elastoplastic Bridge Deck Response Spectra of High-Speed Railway Simply-Supported Girder Bridge with CRTSII Track System. J. Cent. South Univ. 2024, 31, 4174–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wei, B.; Zhang, P.; Guo, P.; Shao, Z.; Xu, S.; Jiang, L.; Hu, H.; Zeng, Y.; Xiang, P. Safety Analysis of High-Speed Trains on Bridges under Earthquakes Using a LSTM-RNN-Based Surrogate Model. Comput. Struct. 2024, 294, 107274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Jiang, L.; Jiang, L.; Zhou, W.; Du, Y. Seismic Response of High-Speed Railway Simple-Supported Girder Track-Bridge System Considering Spatial Effect at near-Fault Region. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2022, 158, 107283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Jiang, L.; Jiang, L.; Jin, Z.; Du, Y.; Pang, L. Repair Cost Assessment of Longitudinal Continuous Ballastless Track Structure on High-Speed Railway Bridge with Spatially Distributed Interlayer Area Damage. Structures 2023, 57, 105157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Jiang, L.; Jiang, L.; Zhou, W.; Du, Y. Optimal Intensity Measure Selection in Incremental Dynamic Analysis: Methodology Improvements and Application to a High-Speed Railway Bridge. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2024, 22, 2059–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jiang, L.; Xiang, P.; Jiang, L.; Lai, Z. Safety and Comfort Assessment of a Train Passing over an Earthquake-Damaged Bridge Based on a Probability Model. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2023, 19, 525–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xiang, P.; Wei, B.; Zuo, C.; Jiang, L.; He, W. Interface Friction Effects on Scaling a Vertical Spring-Viscous Damper Isolation System in a Shaking Table Test. Structures 2021, 33, 1878–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Wei, B.; Wang, W.; Xiao, B.; Li, S.; Jiang, L. Influence of Pier Height and Ground Motion Parameters on Seismic Response and Energy Dissipation of Isolated Railway Bridges. Structures 2024, 68, 107236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Wang, P.; He, X.; Jiang, L. Seismic Response of Spring-Damper-Rolling Systems with Concave Friction Distribution. Earthq. Struct. 2016, 11, 25–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Zeng, C.; Gou, H.; Hu, Y.; Xu, H.; Guo, L. Rotational Friction Damper’s Performance for Controlling Seismic Response of High Speed Railway Bridge-Track System. CMES-Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2019, 120, 491–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isacchi, G.; Ripamonti, F.; Corsi, M. Innovative Passive Yaw Damper to Increase the Stability and Curve-Taking Performance of High-Speed Railway Vehicles. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2023, 61, 2273–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahya, V.; Araz, O. A Simple Design Method for Multiple Tuned Mass Dampers in Reduction of Excessive Vibrations of High-Speed Railway Bridges. J. Fac. Eng. Archit. Gazi Univ. 2020, 35, 607–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luu, M.; Martinez-Rodrigo, M.D.; Zabel, V.; Koenke, C. Semi-Active Magnetorheological Dampers for Reducing Response of High-Speed Railway Bridges. Control Eng. Pract. 2014, 32, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moliner, E.; Museros, P.; Martinez-Rodrigo, M.D. Retrofit of Existing Railway Bridges of Short to Medium Spans for High-Speed Traffic Using Viscoelastic Dampers. Eng. Struct. 2012, 40, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tell, S.; Leander, J.; Andersson, A.; Ulker-Kaustell, M. Probability-Based Evaluation of the Effect of Fluid Viscous Dampers on a High-Speed Railway Bridge. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2021, 17, 1730–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.; Liu, Z.; Sun, S.; Ren, Z.; Deng, L.; Yang, B.; Christie, M.D.; Li, W. Development and Evaluation of a Versatile Semi-Active Suspension System for High-Speed Railway Vehicles. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2020, 135, 106338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Rodrigo, M.D.; Lavado, J.; Museros, P. Dynamic Performance of Existing High-Speed Railway Bridges under Resonant Conditions Retrofitted with Fluid Viscous Dampers. Eng. Struct. 2010, 32, 808–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luu, M.; Martinez-Rodrigo, M.D.; Zabel, V.; Koenke, C. H∞ Optimization of Fluid Viscous Dampers for Reducing Vibrations of High-Speed Railway Bridges. J. Sound Vib. 2014, 333, 2421–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Chen, X.; Hu, H.; Zhou, X.; Cheng, M.; Sun, L.; Li, X. Energy Dissipation and Seismic Response Reduction System for High-Speed Railway Bridges Based on Multiple Performance Requirements. Eng. Struct. 2024, 307, 117919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, B.; Di Gialleonardo, E.; Kovacic, I.; Bruni, S. Application of Semi-Active Yaw Dampers for the Improvement of the Stability of High-Speed Rail Vehicles: Mathematical Models and Numerical Simulation. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2022, 60, 2608–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alehashem, S.M.S.; Ni, Y.Q.; Liu, X.Z. A Full-Scale Experimental Investigation on Ride Comfort and Rolling Motion of High-Speed Train Equipped With MR Dampers. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 118113–118123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, H.; Zeng, J.; Gan, F.; Mu, J.; Qi, Y. A Study of Wheel Wear on a High-Speed Railway Motor Car. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part F J. Rail Rapid Transit 2023, 237, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Li, Q.; Ren, Z.; Yang, G. A New Hydraulic Damper Dynamics Model and the Availability on High Speed Vehicle Dynamics Investigation. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2023, 61, 356–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.K. Interaction Between Simply-Supported Beam Bridges and CRTS II Slab Ballastless Track in High-Speed Railways. Master’s Thesis, Central South University, Changsha, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.; Song, D.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, W. Analysis of the Service Life of Railway Hydraulic Dampers Considering Temperature and Loading. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part F J. Rail Rapid Transit 2021, 235, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Liu, S. Design and Parameters Influence Analysis of Dynamic Vibration Absorber for Fastener Clips in High-Speed Railway. J. Vib. Control 2024, 30, 472–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

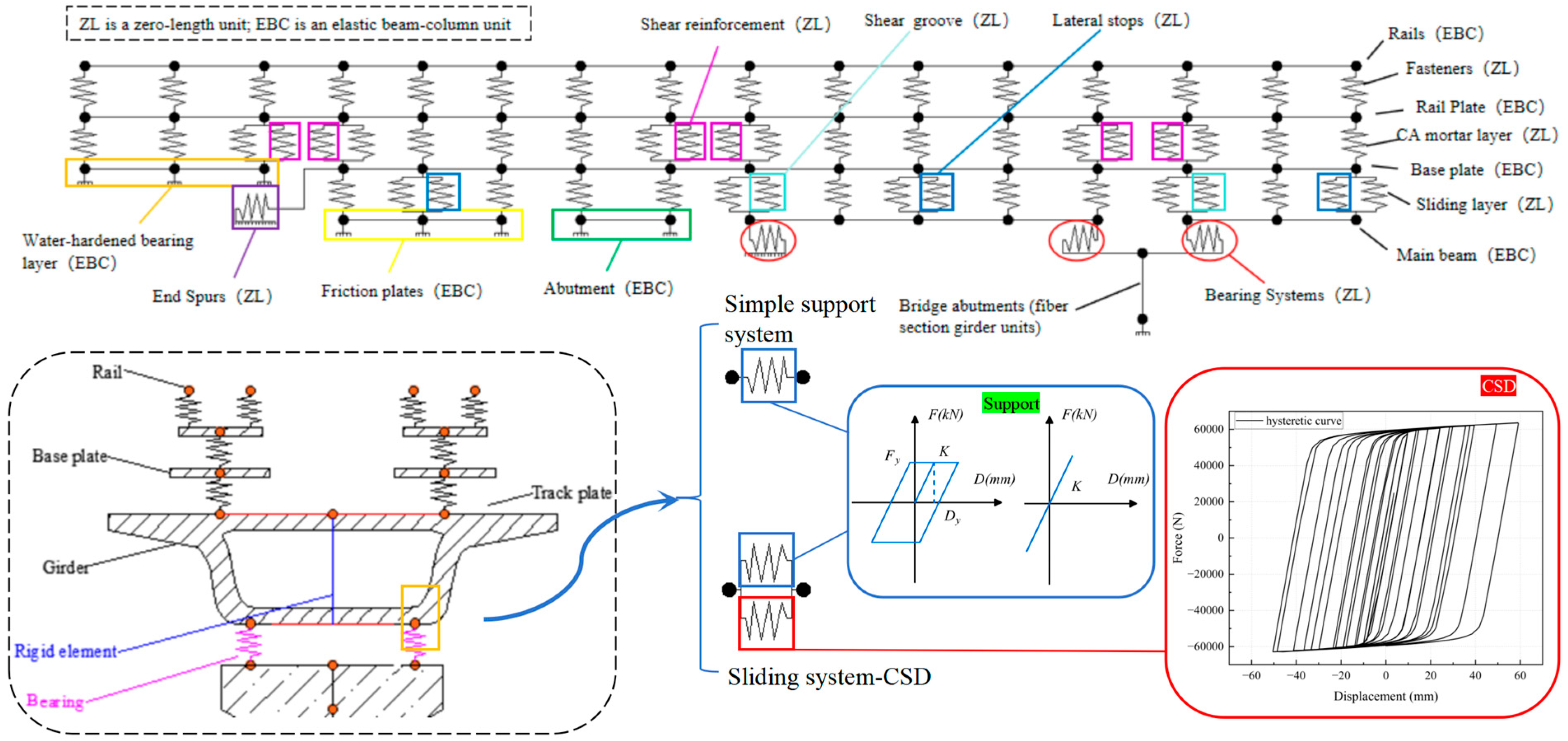
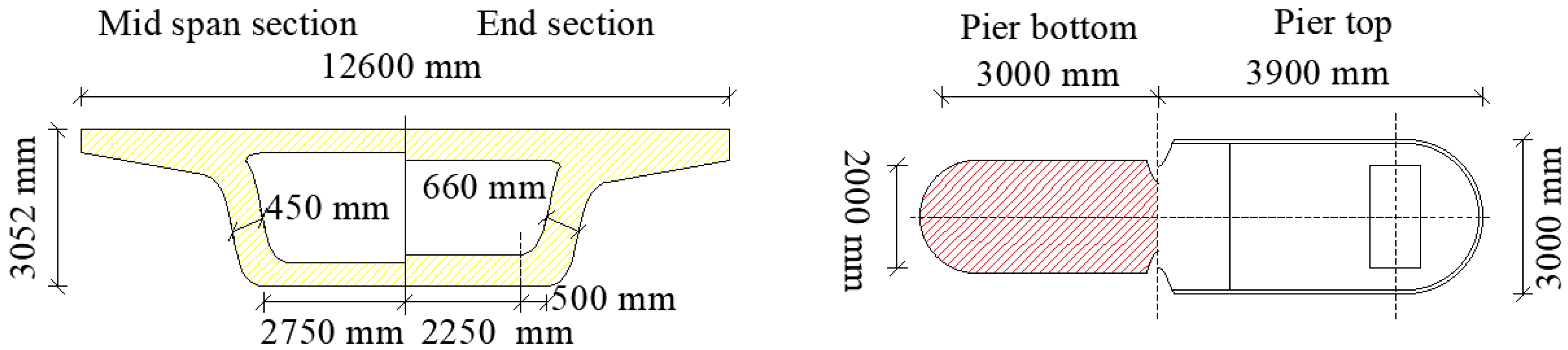


| Component | Material | E (MPa) | S (m2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Main girder (mid-span) | C50 | 3.55 × 104 | 8.722 |
| Main girder (end) | C50 | 3.55 × 104 | 14.22 |
| Steel rail | Q235 | 2.06 × 105 | 0.007745 |
| Rail plate | C55 | 3.65 × 104 | 0.51 |
| Base plate | C30 | 3.25 × 104 | 0.5605 |
| Friction plate | C30 | 3.25 × 104 | 3.6 |
| Water-hardened bearing layer | water-hard material | 1.80 × 104 | 0.92 |
| Component | Horizontal Direction | Vertical Direction | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fl (kN) | Dl (mm) | Ft (kN) | Dt (mm) | Kv (kN/mm) | |
| Fastener | 15 | 2 | 15 | 2 | 2.4 × 103 |
| CA mortar layer | 45 | 0.5 | 45 | 0.5 | 2.0 × 103 |
| Sliding layer on bridge | 6 | 0.5 | 6 | 0.5 | / |
| Friction plate sliding layer | 14 | 0.5 | 14 | 0.5 | / |
| Shear groove | 1200 | 0.12 | 1200 | 0.12 | 2.3 × 104 |
| Shear reinforcement | 173 | 0.075 | 173 | 0.075 | 0 |
| Lateral block | 0 | 0 | 453 | 2 | 0 |
| Fixed end of support | 1000 | 2 | 1000 | 2 | 1.0 × 104 |
| Sliding end of support | 100 | 2 | 100 | 2 | 1.0 × 104 |
| Force–displacement curve | 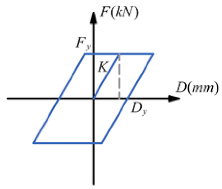 |  | |||
| Record | Seismic Intensity | Epicenter Distance (km) | Nearest Distance (km) | Preferred Vs30 (m/s) | FN Pulse | Pulse Period (s) | Conversion Factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 7.0 | 13.0 | 6.1 | 213 | 0 | −99.00 | 3.63 |
| 2 | 6.5 | 2.6 | 0.7 | 275 | 1 | 2.30 | 4.28 |
| 3 | 6.5 | 43.2 | 10.4 | 209 | 1 | 4.03 | 5.23 |
| 4 | 6.5 | 18.9 | 7.3 | 275 | 0 | −99.00 | 3.54 |
| 5 | 6.5 | 19.4 | 0.1 | 186 | 1 | 3.35 | 2.41 |
| 6 | 6.5 | 26.3 | 6.2 | 203 | 1 | 4.49 | 4.10 |
| 7 | 6.5 | 29.4 | 12.5 | 196 | 1 | 7.36 | 3.96 |
| 8 | 6.5 | 32.0 | 17.9 | 197 | 0 | −99.00 | 7.18 |
| 9 | 6.5 | 28.7 | 12.9 | 163 | 1 | 5.24 | 4.41 |
| 10 | 6.5 | 27.1 | 7.1 | 209 | 1 | 4.61 | 2.48 |
| 11 | 6.5 | 27.8 | 4.0 | 206 | 1 | 4.05 | 2.33 |
| 12 | 6.5 | 27.5 | 1.4 | 203 | 1 | 3.84 | 2.08 |
| 13 | 6.5 | 28.1 | 3.9 | 206 | 1 | 5.39 | 2.87 |
| 14 | 6.5 | 27.2 | 5.1 | 202 | 1 | 5.86 | 2.43 |
| 15 | 6.5 | 19.8 | 7.7 | 203 | 1 | 4.80 | 3.93 |
| 16 | 6.5 | 48.6 | 12.7 | 349 | 0 | −99.00 | 8.00 |
| 17 | 6.3 | 36.7 | 19.0 | 275 | 0 | −99.00 | 5.82 |
| 18 | 5.9 | 20.5 | 16.7 | 349 | 1 | 3.58 | 3.66 |
| 19 | 6.2 | 20.3 | 17.2 | 271 | 0 | −99.00 | 6.20 |
| 20 | 6.2 | 24.8 | 17.6 | 207 | 0 | −99.00 | 8.00 |
| 21 | 6.5 | 35.8 | 18.2 | 192 | 0 | −99.00 | 3.13 |
| 22 | 6.5 | 19.5 | 13.0 | 194 | 0 | −99.00 | 3.88 |
| 23 | 6.9 | 32.4 | 14.3 | 222 | 0 | −99.00 | 3.84 |
| 24 | 6.9 | 27.2 | 8.5 | 371 | 1 | 4.47 | 2.97 |
| 25 | 6.7 | 9.0 | 4.4 | 275 | 1 | 2.65 | 1.78 |
| 26 | 6.7 | 11.1 | 8.7 | 298 | 0 | −99.00 | 3.59 |
| 27 | 6.7 | 4.9 | 14.7 | 267 | 0 | −99.00 | 2.45 |
| 28 | 6.7 | 13.0 | 5.4 | 373 | 1 | 3.53 | 1.60 |
| 29 | 6.7 | 13.1 | 12.5 | 446 | 0 | −99.00 | 4.13 |
| 30 | 6.7 | 20.3 | 5.9 | 269 | 0 | −99.00 | 1.70 |
| 31 | 6.7 | 19.3 | 7.3 | 508 | 0 | −99.00 | 2.90 |
| 32 | 6.7 | 10.9 | 6.5 | 282 | 1 | 1.23 | 1.42 |
| 33 | 6.7 | 12.4 | 10.1 | 309 | 0 | −99.00 | 3.17 |
| 34 | 6.7 | 13.6 | 5.2 | 371 | 1 | 3.49 | 1.45 |
| 35 | 6.9 | 46.0 | 19.2 | 256 | 0 | −99.00 | 3.67 |
| 36 | 7.1 | 41.3 | 12.0 | 326 | 0 | −99.00 | 1.93 |
| 37 | 7.1 | 1.6 | 6.6 | 276 | 0 | −99.00 | 1.85 |
| 38 | 6.2 | 25.5 | 19.7 | 428 | 1 | 3.19 | 6.82 |
| 39 | 6.2 | 10.1 | 6.2 | 553 | 0 | −99.00 | 2.85 |
| 40 | 6.2 | 14.5 | 12.5 | 553 | 0 | −99.00 | 8.00 |
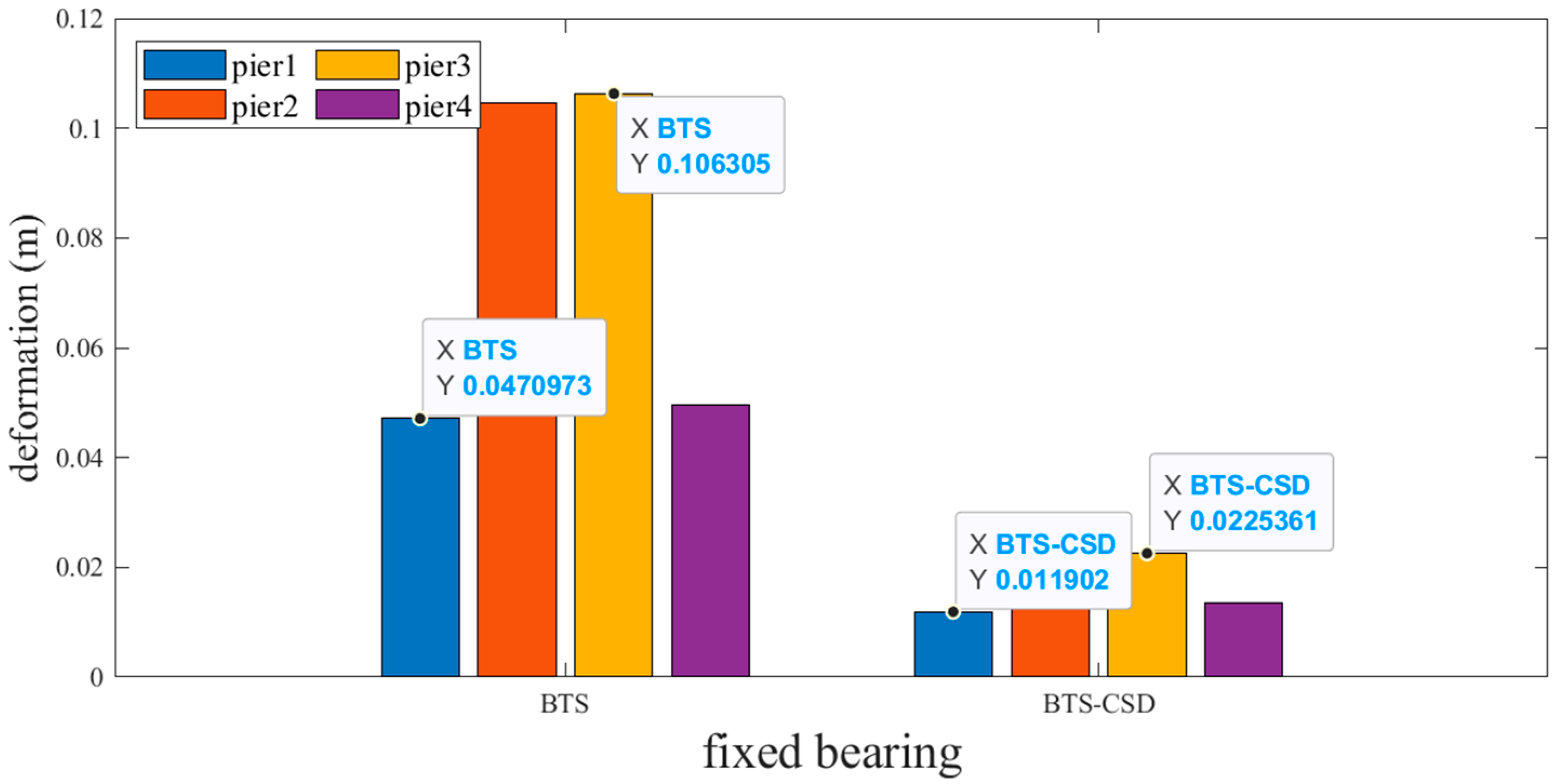
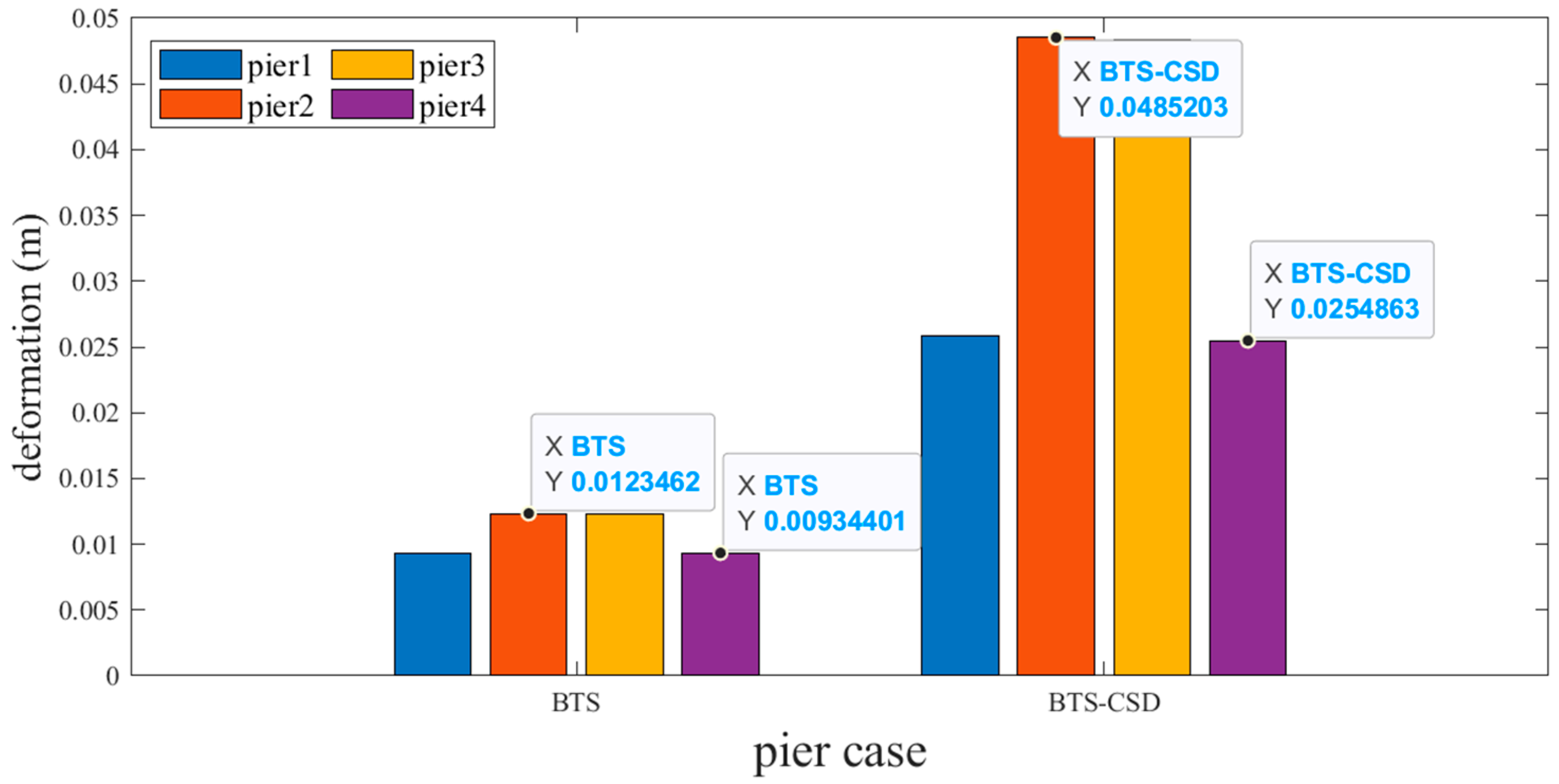
| Sliding Support | BTS | BTS-CSD | Difference | Percentage Reduction |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pier 1 | 0.0513 | 0.0135 | 0.0378 | 73.7% |
| Pier 2 | 0.1071 | 0.0223 | 0.0848 | 79.2% |
| Pier 3 | 0.1033 | 0.0211 | 0.0822 | 79.6% |
| Pier 4 | 0.0451 | 0.0113 | 0.0338 | 74.9% |
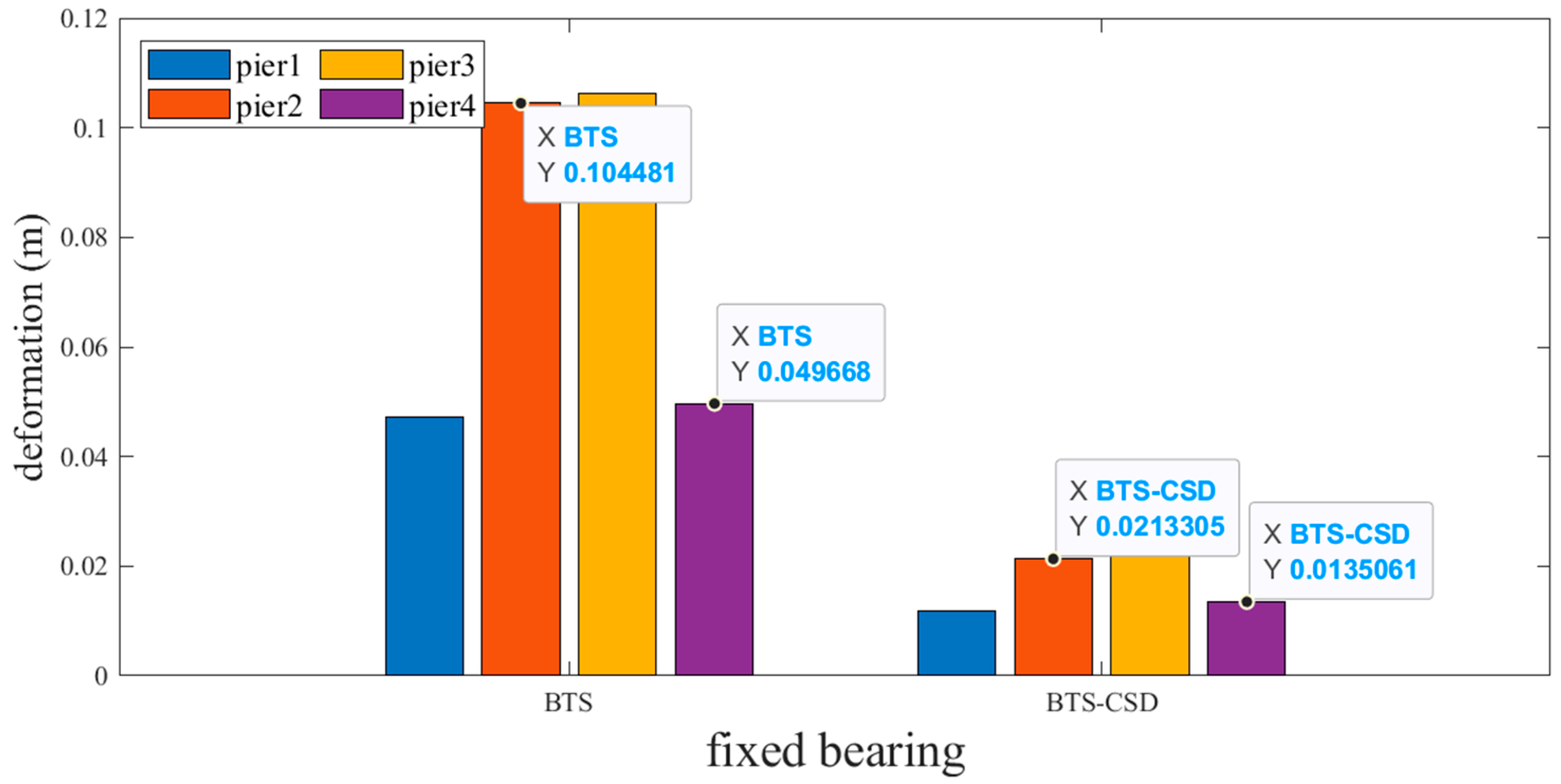
| Fixed Support | BTS | BTS-CSD | Difference | Percentage Reduction |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pier 1 | 0.0471 | 0.0119 | 0.0352 | 74.7% |
| Pier 2 | 0.1045 | 0.0213 | 0.0832 | 79.6% |
| Pier 3 | 0.1063 | 0.0225 | 0.0838 | 78.8% |
| Pier 4 | 0.0497 | 0.0135 | 0.0362 | 72.8% |
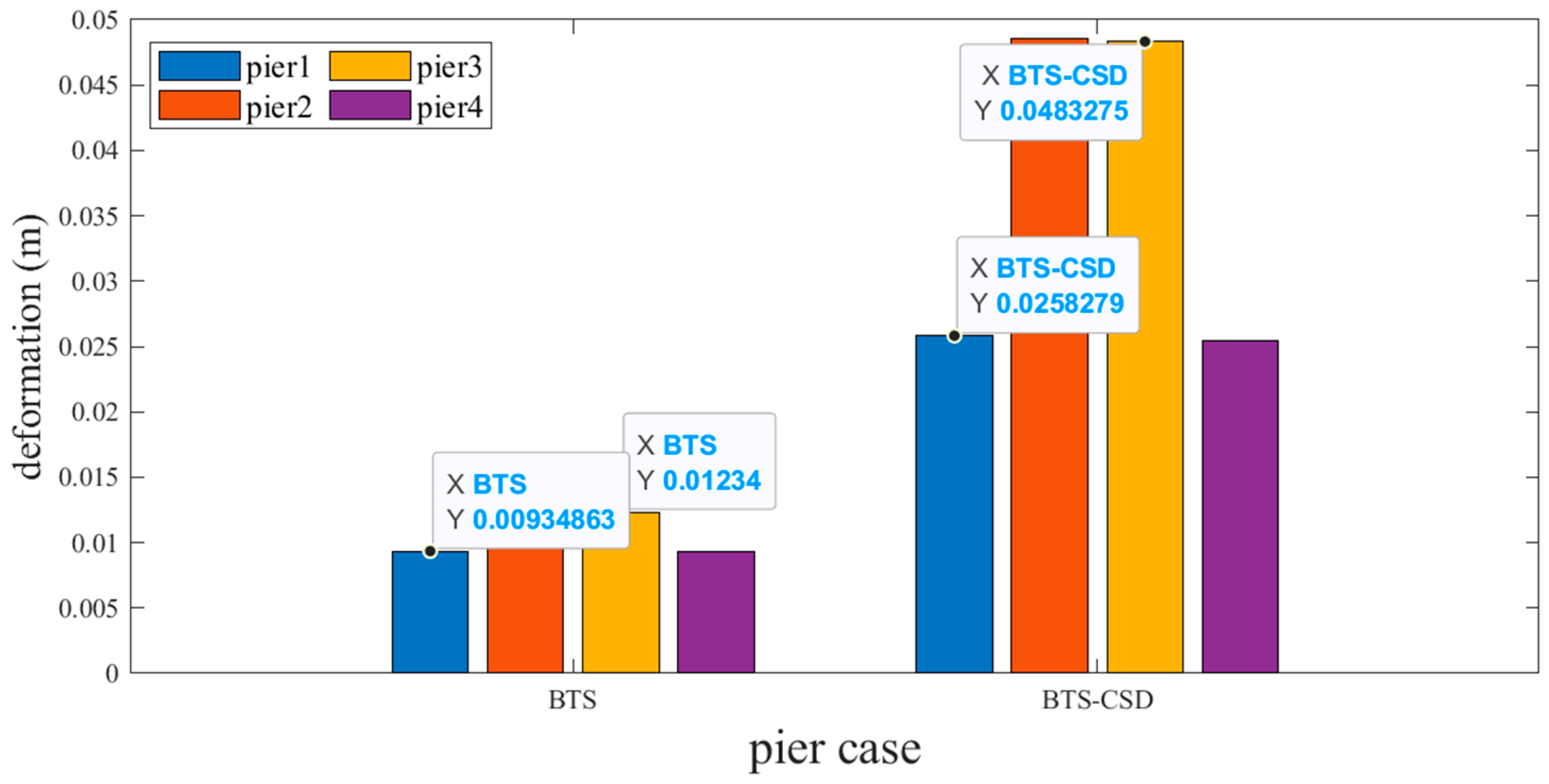
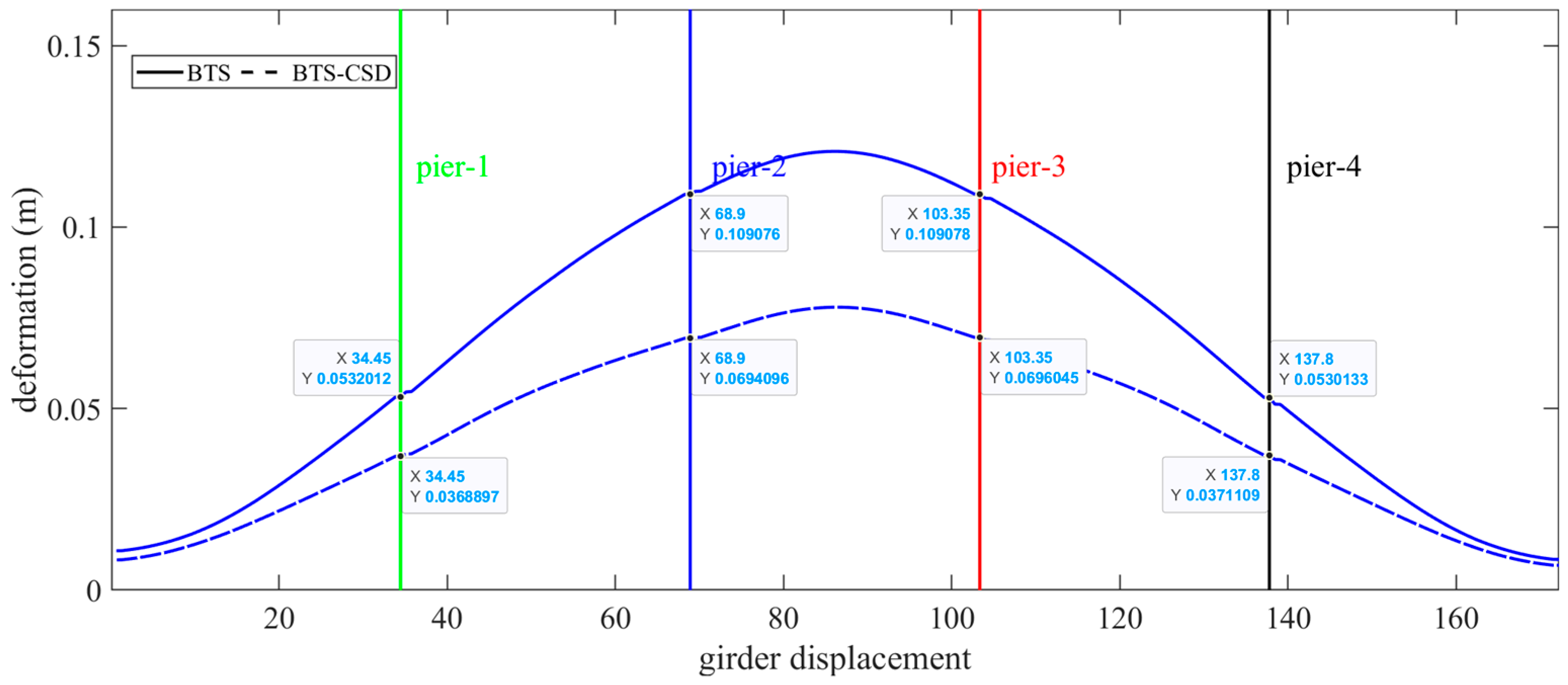
| Main Beam Deformation | BTS | BTS-CSD | Difference | Percentage Reduction |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pier 1 | 0.0532 | 0.0369 | 0.0163 | 30.6% |
| Pier 2 | 0.1091 | 0.0694 | 0.0397 | 36.4% |
| Pier 3 | 0.1091 | 0.0696 | 0.0395 | 36.2% |
| Pier 4 | 0.0531 | 0.0371 | 0.016 | 30.1% |
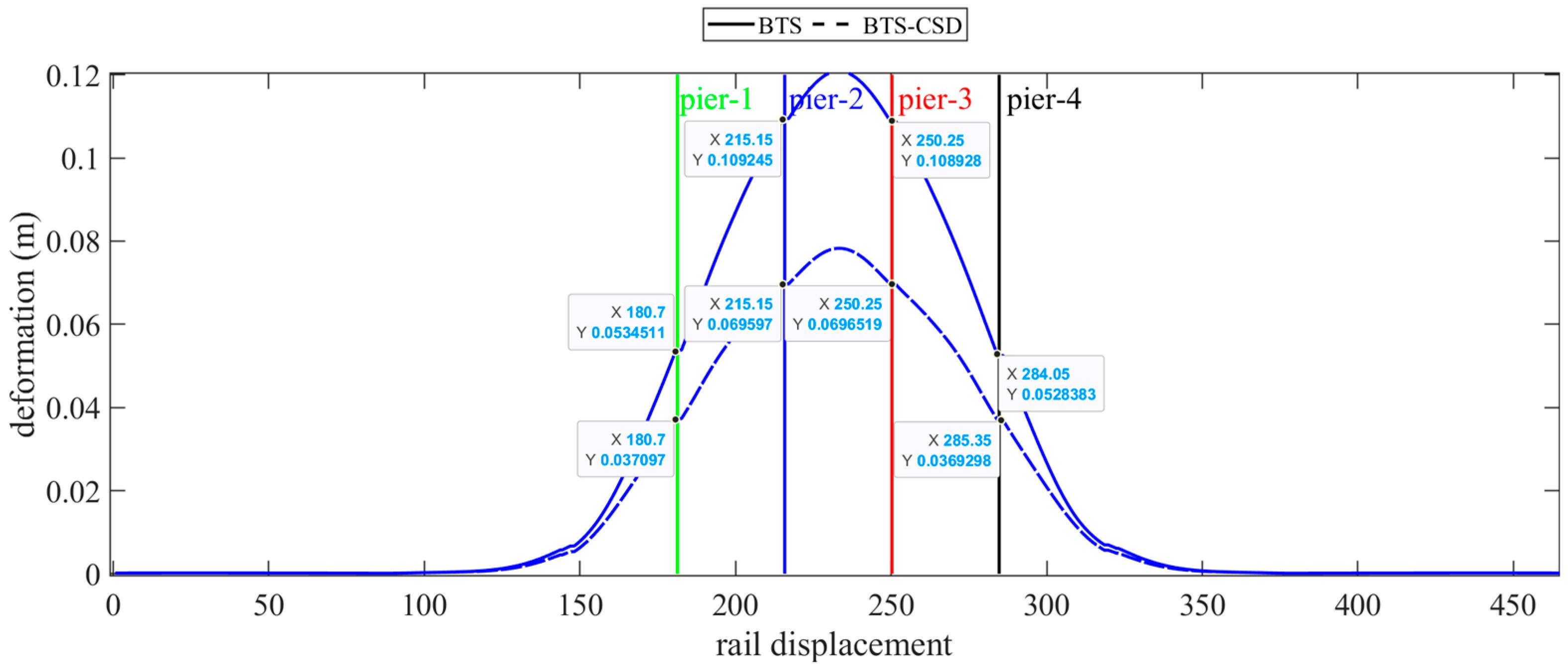
| Bridge Track Deformation | BTS | BTS-CSD | Difference | Percentage Reduction |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pier 1 | 0.0534 | 0.0371 | 0.0163 | 30.5% |
| Pier 2 | 0.1092 | 0.0696 | 0.0396 | 36.3% |
| Pier 3 | 0.1089 | 0.0697 | 0.0392 | 36.0% |
| Pier 4 | 0.0528 | 0.0371 | 0.0157 | 29.7% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, M.; Jiang, L.; He, J. Seismic Response Mitigation of Reinforced-Concrete High-Speed Railway Bridges with Hierarchical Curved Steel Dampers. Materials 2025, 18, 2120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18092120
Liang M, Jiang L, He J. Seismic Response Mitigation of Reinforced-Concrete High-Speed Railway Bridges with Hierarchical Curved Steel Dampers. Materials. 2025; 18(9):2120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18092120
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Mingshi, Liqiang Jiang, and Jianguang He. 2025. "Seismic Response Mitigation of Reinforced-Concrete High-Speed Railway Bridges with Hierarchical Curved Steel Dampers" Materials 18, no. 9: 2120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18092120
APA StyleLiang, M., Jiang, L., & He, J. (2025). Seismic Response Mitigation of Reinforced-Concrete High-Speed Railway Bridges with Hierarchical Curved Steel Dampers. Materials, 18(9), 2120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18092120







