Metal-Free Elemental Selenium Quantum Dots: A Novel and Robust Fluorescent Nanoprobe for Cell Imaging and the Sensitive Detection of Cr(VI)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Characterization
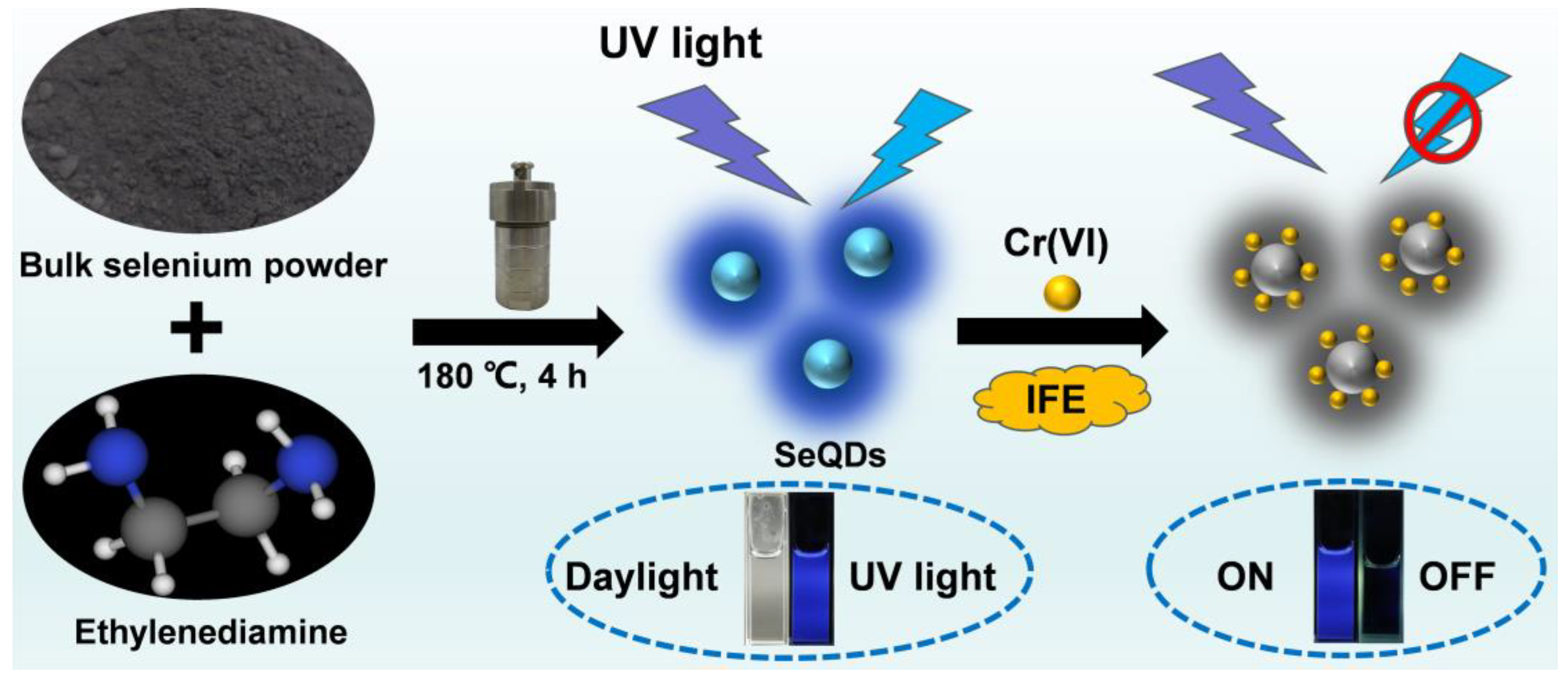
2.3. Preparation of Fluorescent SeQDs
2.4. Sensing of Cr(VI)
2.5. Cytotoxicity Evaluation
2.6. Cell Imaging and Monitoring of Cr(VI) in Cells
3. Results and Discussion
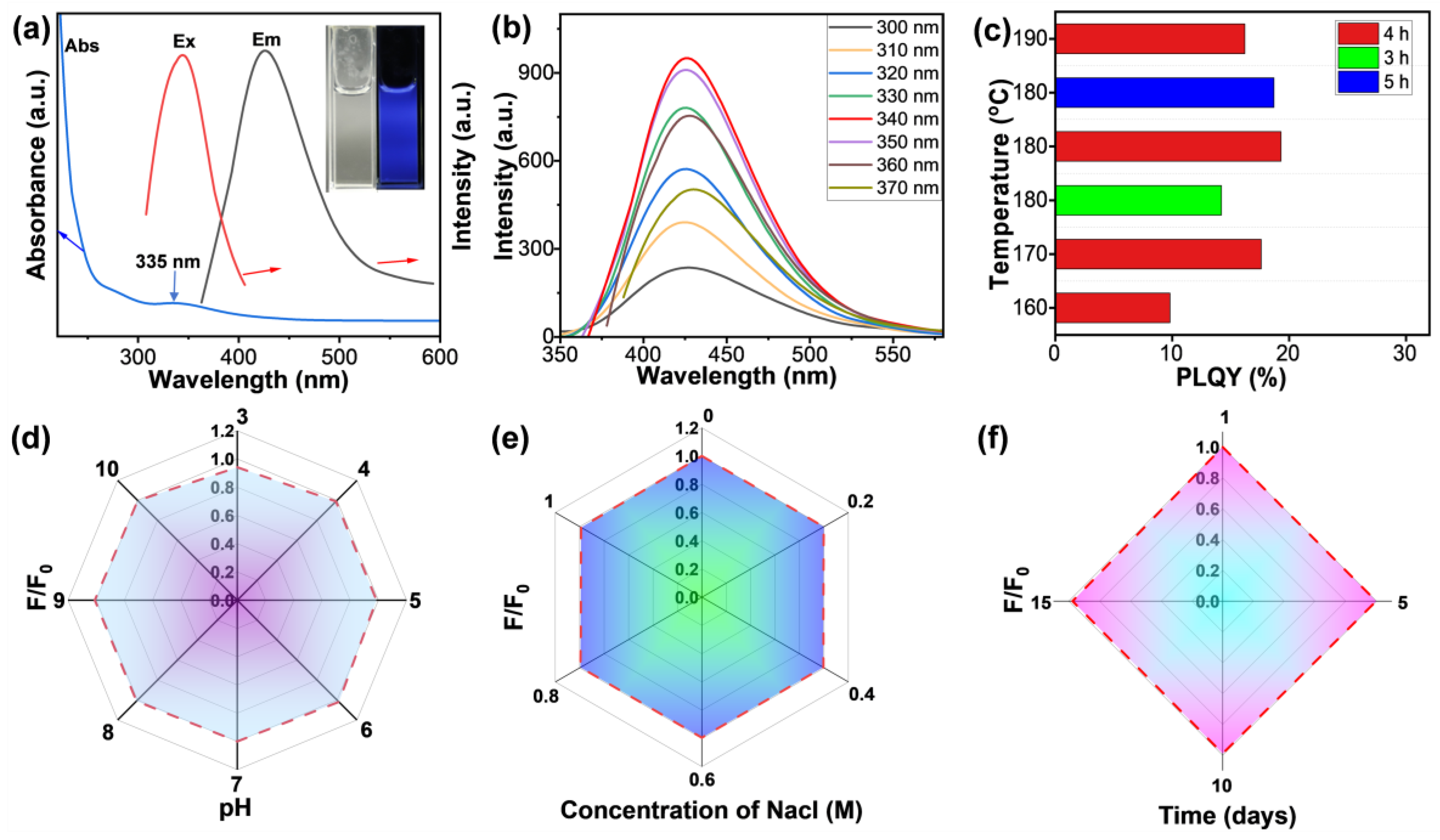
3.1. Preparation and Characterization of SeQDs
3.2. Optical Properties and Cytotoxicity Evaluation of SeQDs
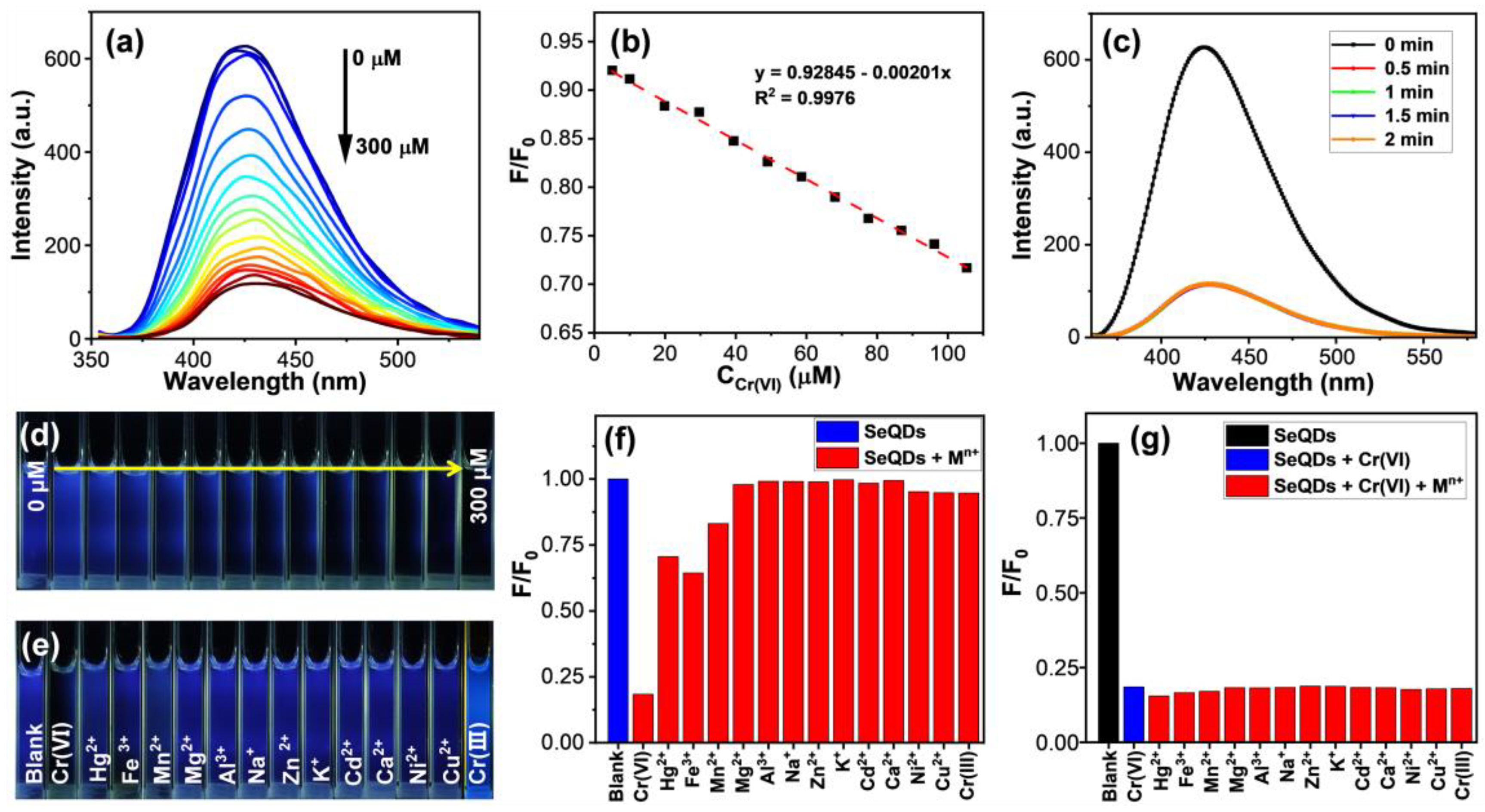
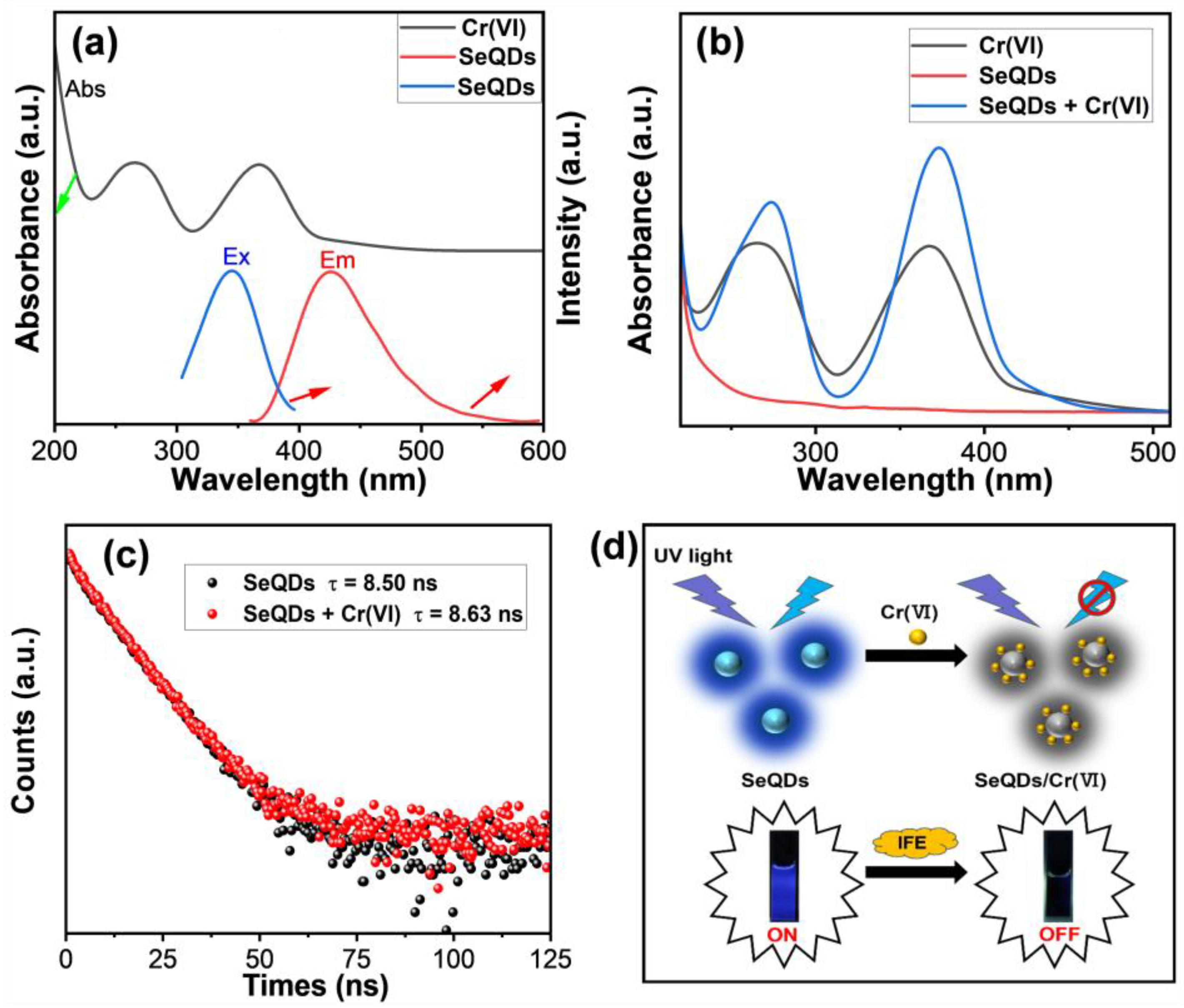
3.3. Detection of Cr(VI) by SeQDs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Srinivasan, P.R.; Indira, V.A. Acridinedione-based fluorescence ‘turn-off’ sensor for real-time detection of carcinogenic Cr(VI) ions. Inorg. Chem. Commum. 2024, 164, 112443. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, X.-Q.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.-R.; Liu, C.-C.; Li, C.-H.; Yang, P. Carbon dots with high brightness and stability towards efficient Cr(VI) and l-arginine sensors. Microchem. J. 2024, 207, 112092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, C.; Liu, Z.-S.; Liu, S.-C.; Li, B.-H.; Li, X.-H.; Hu, J.-B.; Wang, B.-S. Si,N co-doped carbon quantum dots in mesoporous molecular sieves: A fluorescence sensing platform for Cr(VI) detection. Microchem. J. 2024, 201, 110726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leese, E.; Morton, J.; Gardiner, P.H.; Carolan, V.A. Development of a method for the simultaneous detection of Cr(III) and Cr(VI) in exhaled breath condensate samples using μLC-ICP-MS. J. Anal. Atom. Spectrom. 2016, 31, 924–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, A.-M.; Chen, X.-W.; Chen, M.-L.; Wang, J.-H. Sequential injection reductive bio-sorption of Cr(VI) on the surface of egg-shell membrane and chromium speciation with detection by electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry. J. Anal. Atom. Spectrom. 2008, 23, 412–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, T.; Yue, Y.-L. Phosphor doped carbon dots with high photoluminescence and stability towards pH and Cr(VI) sensors. Microchem. J. 2024, 207, 112046. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Y.-X.; Tan, J.-S.; Huang, Z.-M.; Deng, Q.-M.; Liu, S.-J.; Wang, G.; Li, L.-G.; Zhou, L. Facile synthesis of carboxymethyl cellulose sulfur quantum dots for live cell imaging and sensitive detection of Cr(VI) and ascorbic acid. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 249, 116882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, B.B.; Algarra, M.; Alonso, B.; Casado, C.M.; Jiménez-Jiménez, J.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E.; Esteves da Silva, J.C.G. Fluorescent sensor for Cr(VI) based in functionalized silicon quantum dots with dendrimers. Talanta 2015, 144, 862–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Long, J.-W.; Dai, X.-J.; Wang, G.; Zhou, L. Simultaneous detection and adsorptive removal of Cr(VI) ions by fluorescent sulfur quantum dots embedded in chitosan hydrogels. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 1817–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.-F.; Huo, D.-Q.; Yang, M.; Hou, C.-J.; Li, J.-J.; Fa, H.-B.; Luo, H.-B.; Yang, P. Colorimetric detection of Cr(VI) based on the leaching of gold nanoparticles using a paper-based sensor. Talanta 2016, 161, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, C.-X.; Liu, Y.-F.; Zhang, W.; Li, P.; Zhang, D. CdTe-CdSe nanocrystals capped with dimethylaminoethanethiol as ultrasensitive fluorescent probes for chromium (VI). Microchim. Acta 2014, 181, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-Y.; Ding, Y.-J.; Meng, F.-S.; Liu, H.-M.; Wang, X.-Q. Two supramolecular architectures of Ni-based complexes for magnetic properties and the luminescent sensitive detection of Fe3+ and Cr6+. J. Solid State Chem. 2022, 309, 122949. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.-H.; Liu, Z.-H.; Gao, W.; Tang, B. Recent advancement in graphene quantum dots based fluorescent sensor: Design, construction and bio-medical applications. Coordin. Chem. Rev. 2023, 478, 214966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.V.; Rhim, J.W. Fluorescent carbon quantum dots for food contaminants detection applications. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 111999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.-X.; Wang, G.; Zhou, L. Luminescent sulfur quantum dots: Synthesis, properties and potential applications. Chem. Photo. Chem. 2022, 4, 5235–5244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.-X.; Dong, L.-X.; Ming, Y.-L.; Wang, M.; Lu, Z.-C.; Xu, Y.; Li, H.-R. A magnetofluorescent boron-doped carbon dots as a metal-free bimodal probe. Talanta 2019, 200, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorour, S.; Rhiannon, R.; Braden, G.; Chen, D.-C.; Thomas, B.; Oluwasesan, A.; Daéid, N.N.; Jia, G.-H.; Lewis, S.W. Luminescence detection of latent fingermarks on non-porous surfaces with heavy-metal-free quantum dots. Forensic Chem. 2020, 18, 100222. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.-D.; Chen, X.-K.; Guo, Y.; Gu, L.; Wu, Y.-L.; Bindra, A.K.; Teo, W.L.; Wu, F.-G.; Zhao, Y.-L. Thiolate-assisted route for constructing chalcogen quantum dots with photoinduced fluorescence enhancement. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 48449–48456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Tan, J.; Wang, G.; Zhou, L. Selenium nanoparticles for antioxidant activity and selenium enrichment in plants. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2024, 7, 12881–12890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-H.; Chen, Q.-L.; Zeng, H.; Yang, C.; Wang, G.; Zhou, L. A review of selenium (Se) nanoparticles: From synthesis to applications. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2023, 40, 2300098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skalickova, S.; Milosavljevic, V.; Cihalova, K.; Horky, P.; Richtera, L.; Adam, V. Selenium nanoparticles as a nutritional supplement. Nutrition 2017, 33, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.C.; Mishra, S.K.; Srivastava, R.K.; Gopal, R. Optical properties of selenium quantum dots produced with laser irradiation of water suspended Se nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 17374–17384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, F.-L.; Li, X.-M.; Tang, L.-B.; Lai, S.K.; Lu, C.-Y.; Lau, S.P. Selenium quantum dots: Preparation, structure, and properties. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2017, 110, 053104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Lie, Q.-S.; Liu, Y.-N.; Jia, Z.; Gong, Y.-C.; Yuan, X.-Y.; Liu, J. Multifunctional selenium quantum dots for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease by reducing Aβ-neurotoxicity and oxidative stress and alleviate neuroinflammation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 30261–30273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.-T.; Huang, W.-C.; Wang, R.; Li, H.-B.; Xia, X.-F.; Zhao, X.-M.; Hu, L.-P.; Chen, T.-T.; Tang, Y.-F.; Zhang, H. Photocarrier relaxation pathways in selenium quantum dots and their application in UV-Vis photodetection. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 11232–11241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-H.; Lu, G.-M.; Zhou, L. A mini review on selenium quantum dots: Synthesis and biomedical applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1332993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.-M.; Yang, H.; Gao, X.; Nie, C.; Gu, Y.; Shen, Y.-Z. Inner filter effect-based fluorescence assays toward environmental pesticides and antibiotics. Coordin. Chem. Rev. 2023, 493, 215305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragón, F.H.; Coaquira, J.A.H.; Villegas-Lelovsky, L.; da Silva, S.W.; Cesar, D.F.; Nagamine, L.C.C.M.; Cohen, R.; Menéndez-Proupin, E.; Morais, P.C. Evolution of the doping regimes in the Al-doped SnO2 nanoparticles prepared by a polymer precursor method. J. Phys-Condens. Mat. 2015, 27, 095301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, M.S.; Mesquita, M.S.; Garcia, L.M.; Dos Santos, P.R.; de Marangoni de Viveiros, C.C.; da Fonseca, R.D.; Xavier, M.A.; de Mendonça, G.W.; Rosa, S.S.; Silva, S.L.; et al. Radiofrequency driving antitumor effect of graphene oxide-based nanocomposites: A Hill model analysis. Nanomedicine 2023, 19, 397–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baral, A.; Engelken, R.D. Chromium-based regulations and greening in metal finishing industries in the USA. Environ. Sci. Policy 2002, 5, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.-Y.; Zou, X.; Wang, W.-J.; Wang, T.-F.; Zhang, S.-L.; Gong, Z.-J. Co-doped S, N-carbon dots and its fluorescent film sensors for rapid detection of Cr(VI) and ascorbic acid. Microchem. J. 2021, 167, 106284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.-D.; Sun, M.-L.; Wang, M.; Hou, H.-T.; Pang, S.-J.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, X.-D. Rapide synthesis of multifunctional copper nanoclusters for selective and sensitive detection of hexavalent chromium and anti-counterfeiting. Microchem. J. 2024, 208, 112403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.-Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Q.-Y.; Wu, Z.-L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Ren, H.-W.; Duan, E.-H. Nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots based on deep eutectic solvents precursors to detect Cr6+ in environmental water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, T.-T.; Luo, H.-M.; Li, H.-C.; Sun, J.-B.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, J.-Q.; Chen, Y.; Xu, D. Fe-doping green fluorescent carbon dots via co-electrolysis of chrysoidine G and potassium ferrocyanide for sensitive Cr(VI) detection. Spectrochim. Acta A 2024, 311, 124010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.-Q.; Li, R.-X.; Zhou, P.; Duan, C.-Y. Non-toxic carbon dots fluorescence sensor based on chitosan for sensitive and selective detection of Cr(VI) in water. Microchem. J. 2022, 180, 107627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- José, L.S.; Yuriychuk, N.; García, O.; López-González, M.; Quijada-Garrido, I. Exploring functional polymers in the synthesis of luminescent ZnO quantum dots for the detection of Cr6+, Fe2+, and Cu2+. Polymers 2024, 16, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.-T.; Zhang, Y.-W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.-H.; Tian, R.-F.; Zhao, L.-S. Visual fluorescence detection kit for Cr(VI) based on biological matrix-derived carbon dots and assisted for AA. Diamond Relat. Mater. 2024, 148, 111382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.-L.; Huang, C.-S.; Emery, B.P.; Sedgwick, A.C.; Bull, S.D.; He, X.-P.; Yoon, J.; Sessler, J.L.; James, T. Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET)-based small-molecule sensors and imaging agents. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 5110–5139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Fluorescent Probe | Linear Range | LOD | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| S, N-CDs | 0.1–50 µM | 92 nM | [31] |
| His-Cu NCs | 0–60 µM | 310 nM | [32] |
| Nitrogen-rich CQDs | 5–100 µM | 700 nM | [33] |
| Fe-doping CDs | 0.25–100 µM | 150 nM | [34] |
| CS-CDs | 10–300 µM | 2830 nM | [35] |
| ZnO QDs | 1–17.5 µM | 1130 nM | [36] |
| D-CDs | 0.5–400 µM | 80 nM | [37] |
| This work | 5–105 μM | 145 nM | This study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, Z.; Liao, J.; Li, X.; Zhou, L. Metal-Free Elemental Selenium Quantum Dots: A Novel and Robust Fluorescent Nanoprobe for Cell Imaging and the Sensitive Detection of Cr(VI). Materials 2025, 18, 2119. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18092119
Gao Z, Liao J, Li X, Zhou L. Metal-Free Elemental Selenium Quantum Dots: A Novel and Robust Fluorescent Nanoprobe for Cell Imaging and the Sensitive Detection of Cr(VI). Materials. 2025; 18(9):2119. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18092119
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Ziyi, Jie Liao, Xia Li, and Li Zhou. 2025. "Metal-Free Elemental Selenium Quantum Dots: A Novel and Robust Fluorescent Nanoprobe for Cell Imaging and the Sensitive Detection of Cr(VI)" Materials 18, no. 9: 2119. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18092119
APA StyleGao, Z., Liao, J., Li, X., & Zhou, L. (2025). Metal-Free Elemental Selenium Quantum Dots: A Novel and Robust Fluorescent Nanoprobe for Cell Imaging and the Sensitive Detection of Cr(VI). Materials, 18(9), 2119. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18092119








