Efficacious Removal of Cd2+ and Pb2+ Ions from Wastewater Using a Novel Fe3O4/SiO2/PANI-SDBS Nanocomposite
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
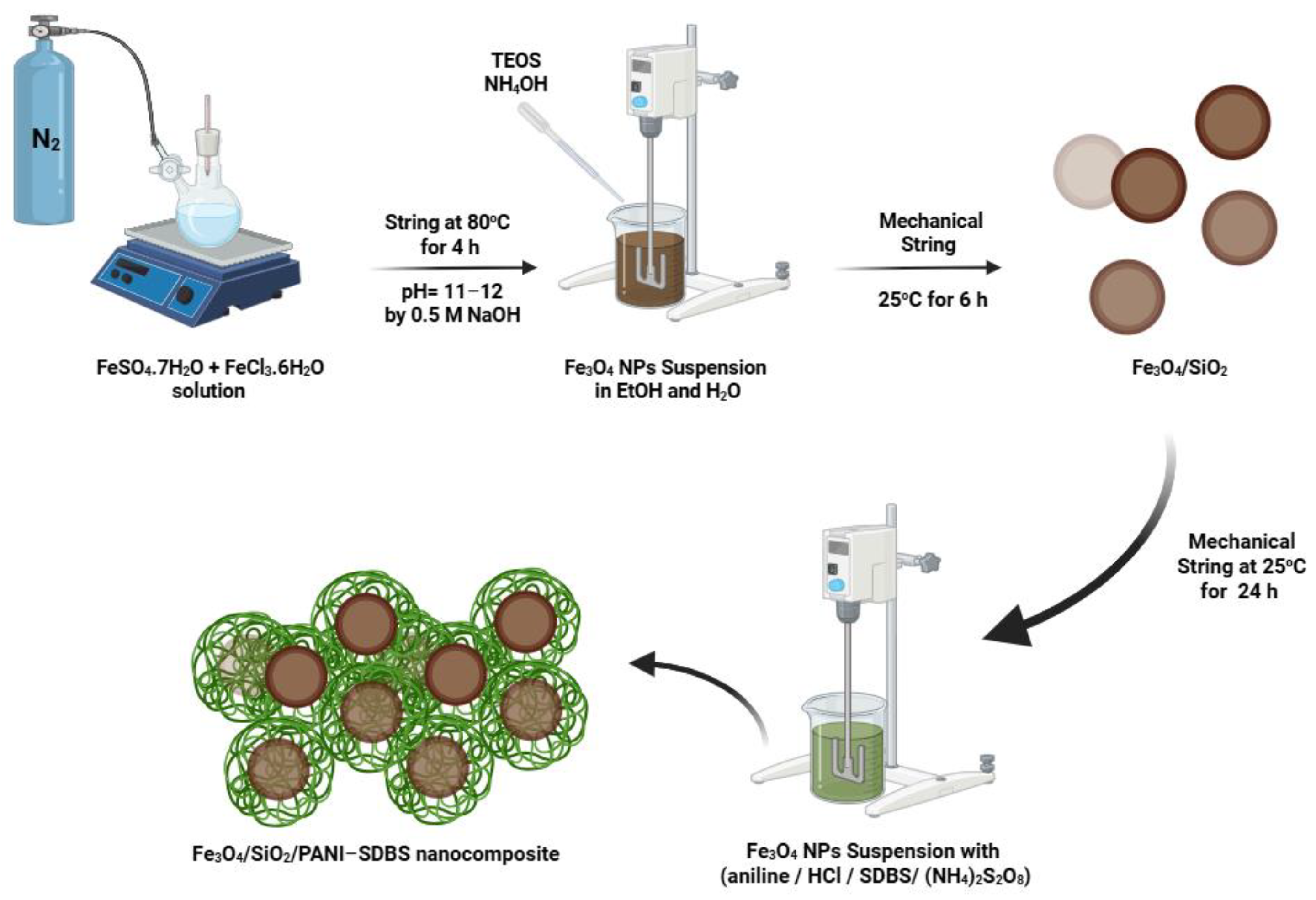
2.1. Synthesis of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles
2.2. Synthesis of Fe3O4/SiO2 Nanocomposite
2.3. Synthesis of Fe3O4/ SiO2/PANI-SDBS Nanocomposite
2.4. Characterization and Tools
2.5. Adsorption Experiments
2.5.1. Batch Experiment
2.5.2. Reusability Study
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Adsorbent
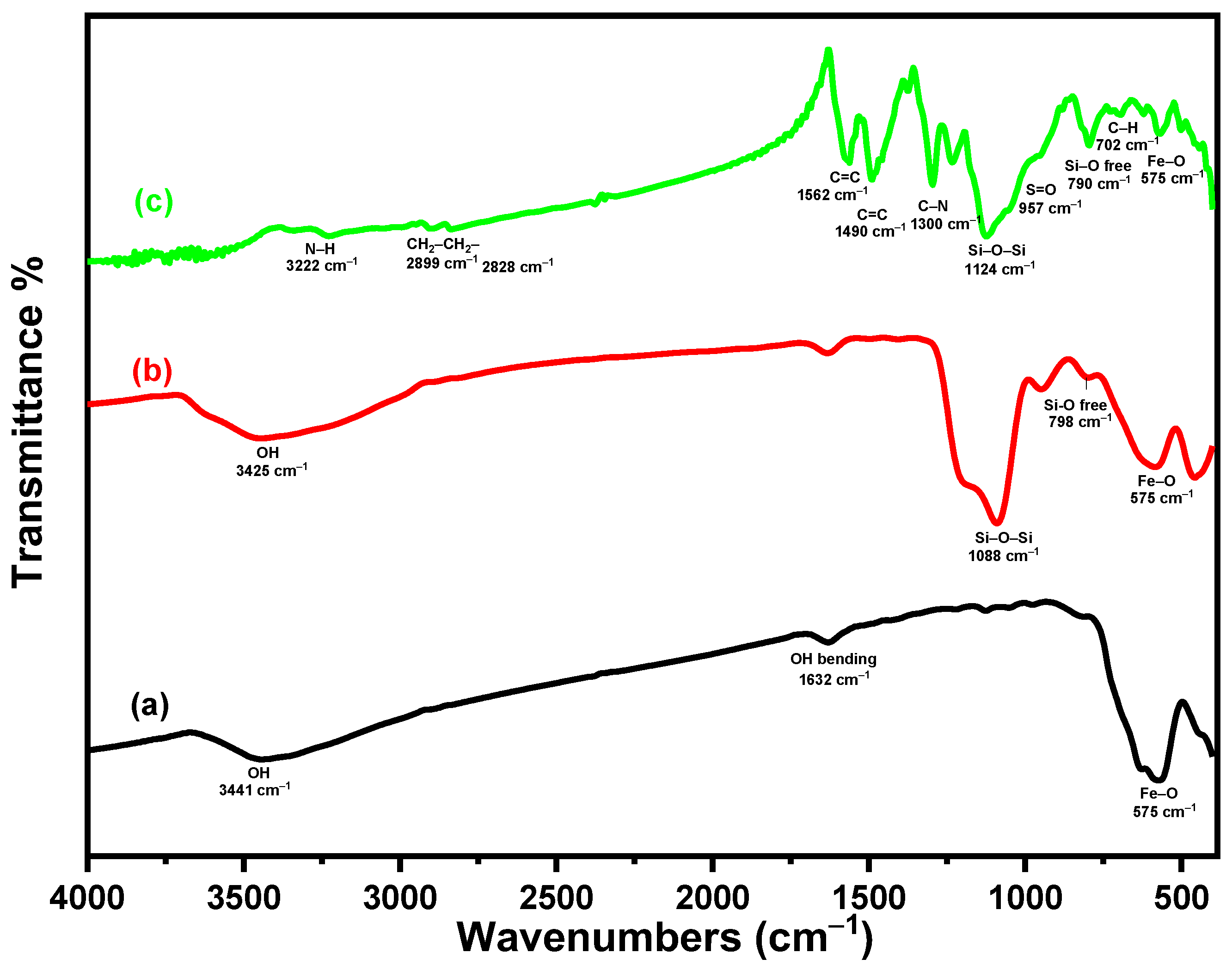
3.1.1. FTIR Study
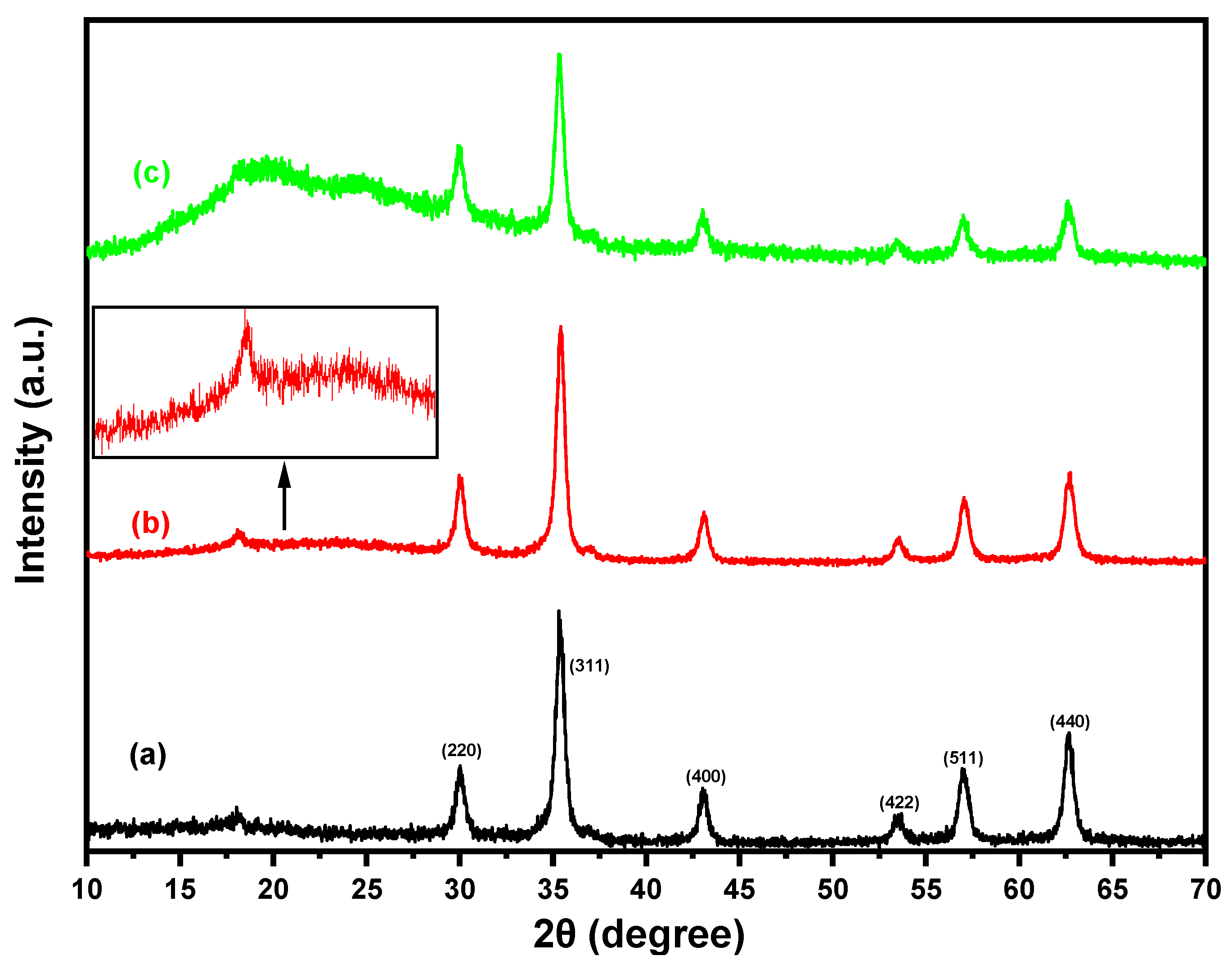
3.1.2. XRD Study
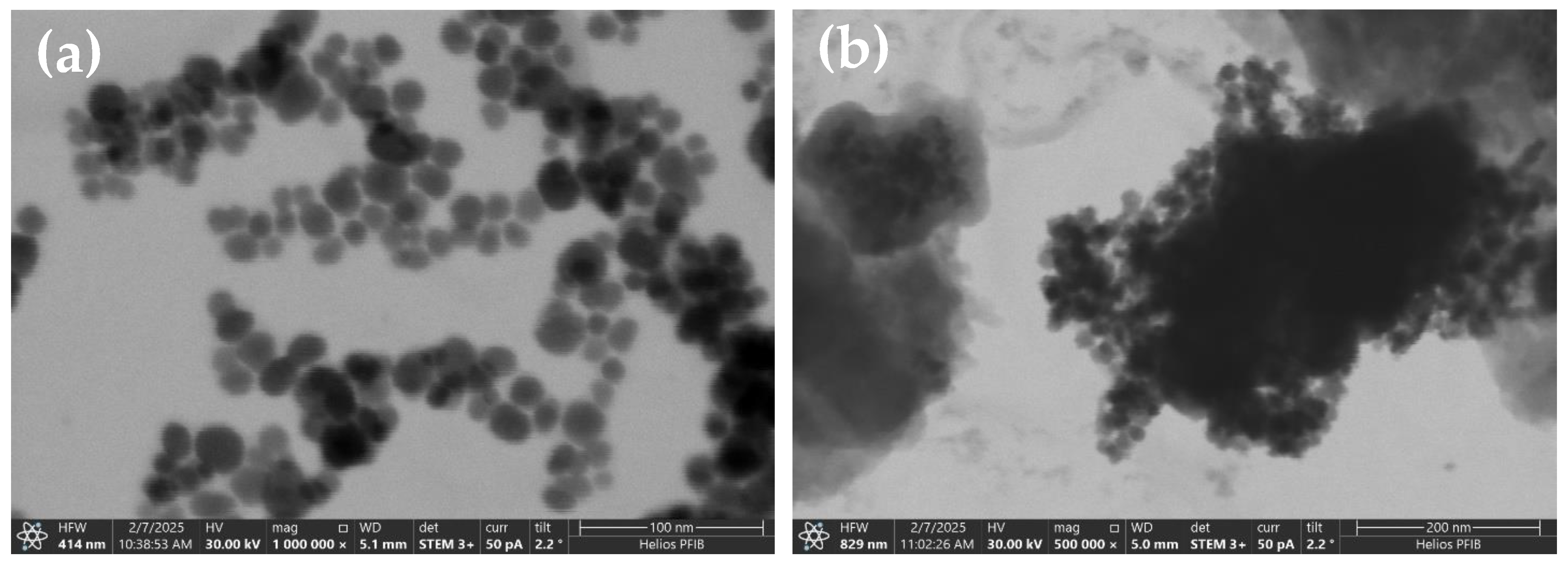
3.1.3. TEM and Elemental Analysis
3.1.4. BET Measurement
3.1.5. TGA Study
3.2. Adsorption Studies for Cd2+ and Pb2+ Ions
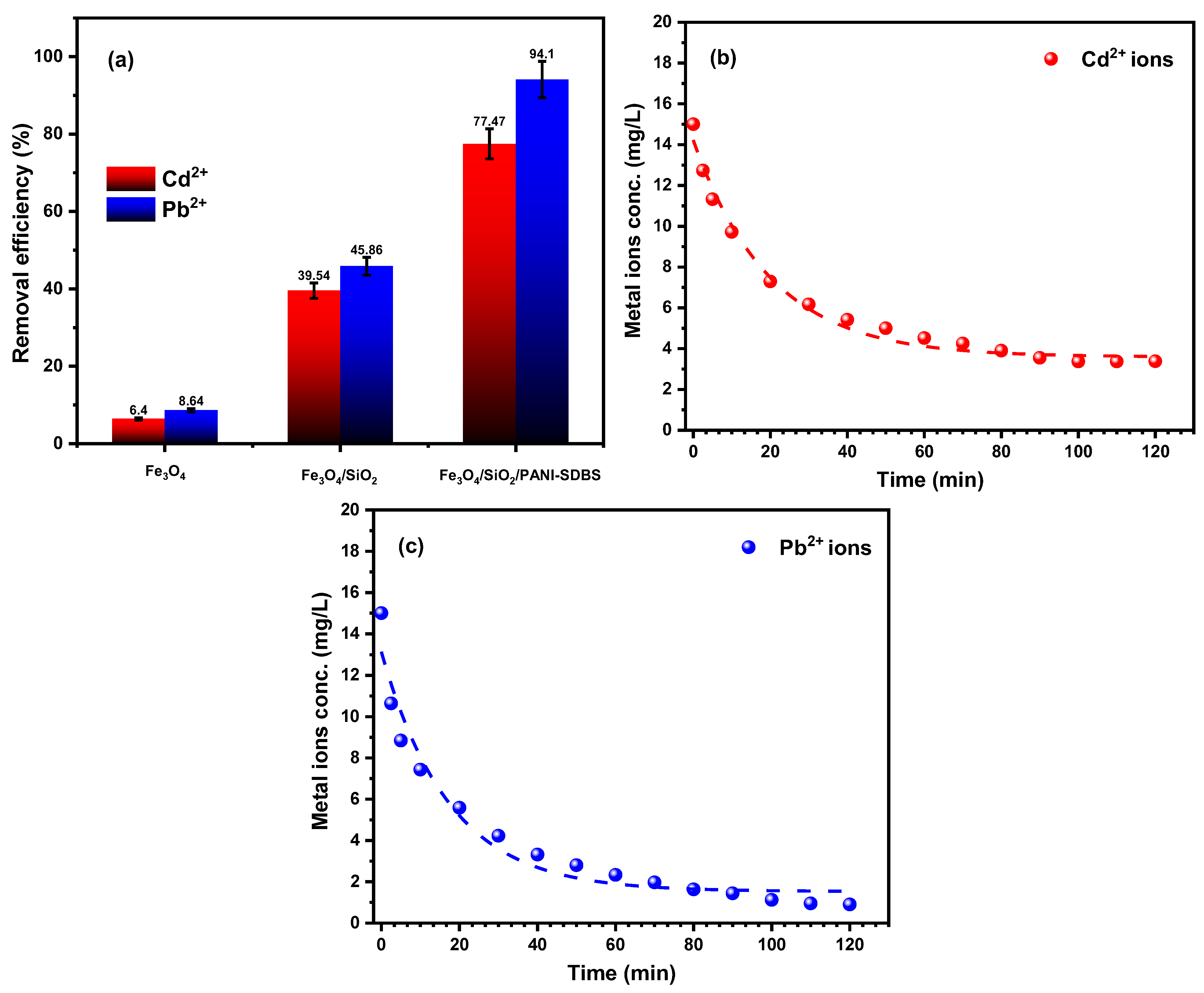
3.2.1. Adsorbent Type
3.2.2. Contact Time
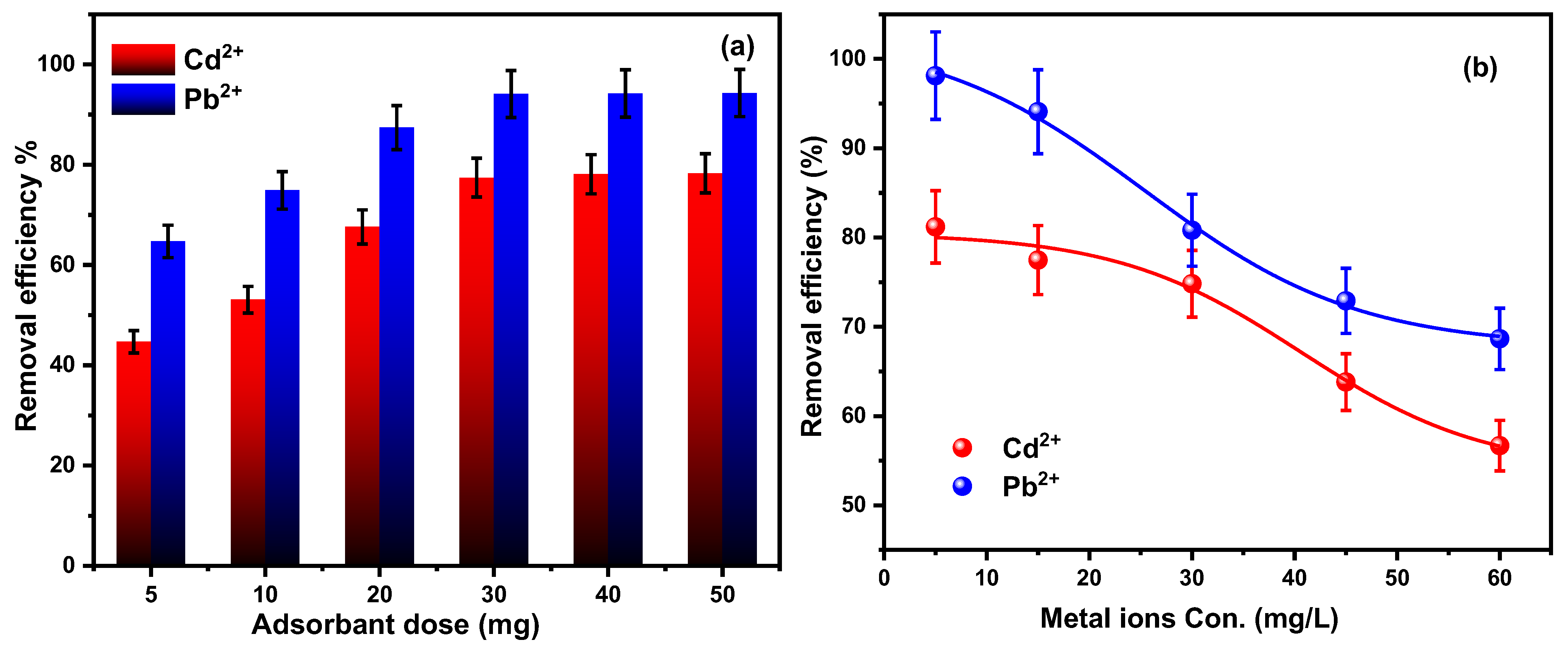
3.2.3. Nanocomposite Dose
3.2.4. Metal Ion Concentration
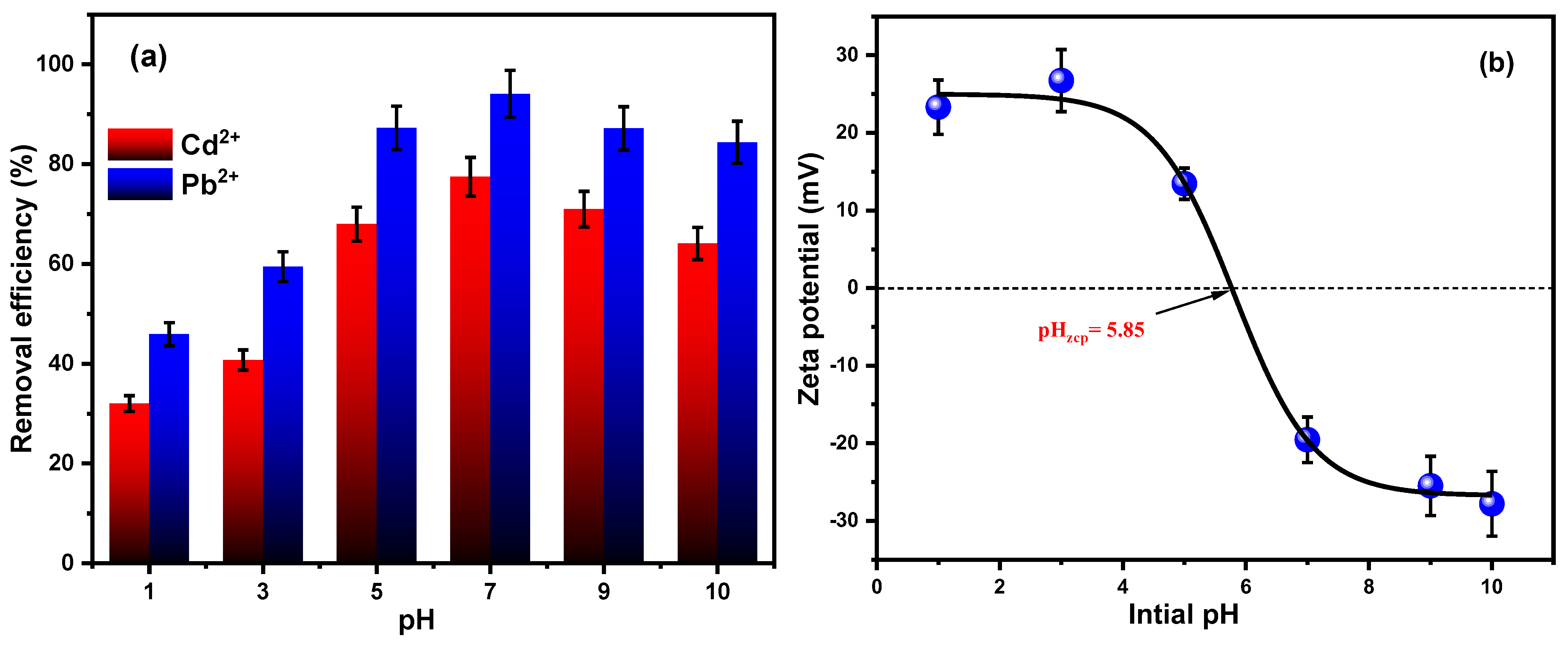
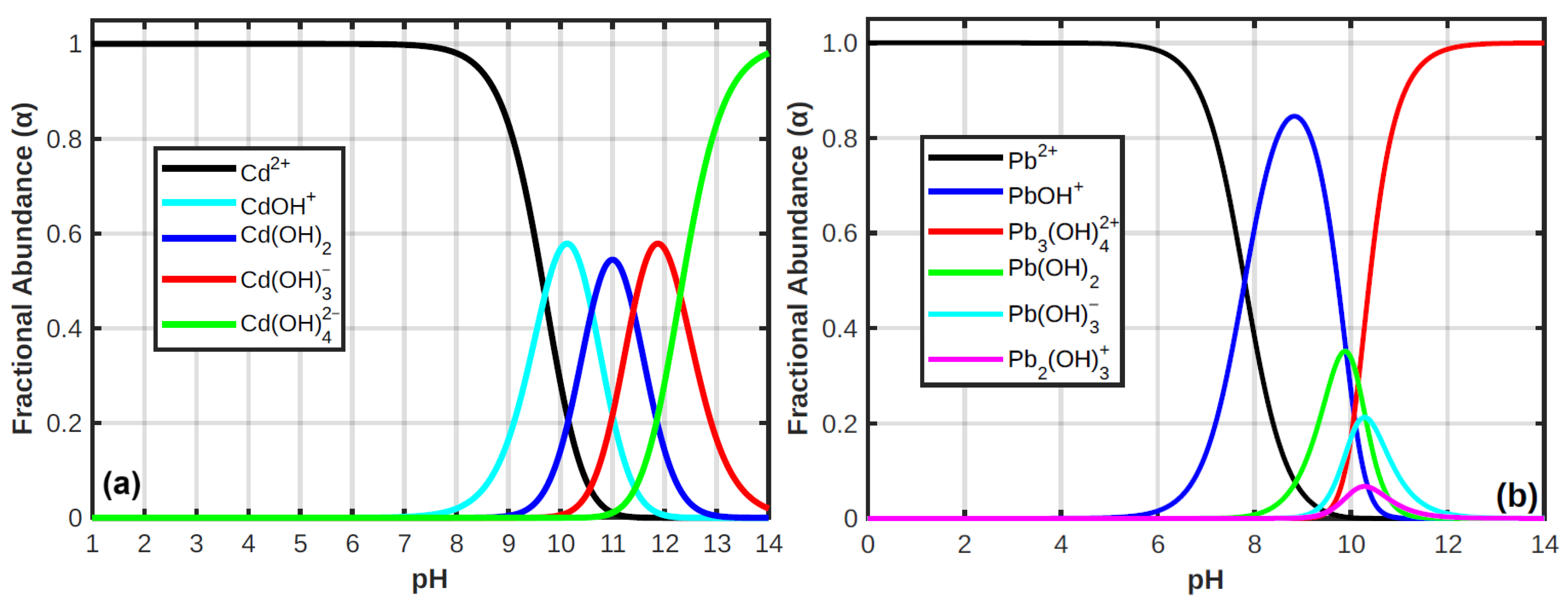
3.2.5. pH and Zeta Potential
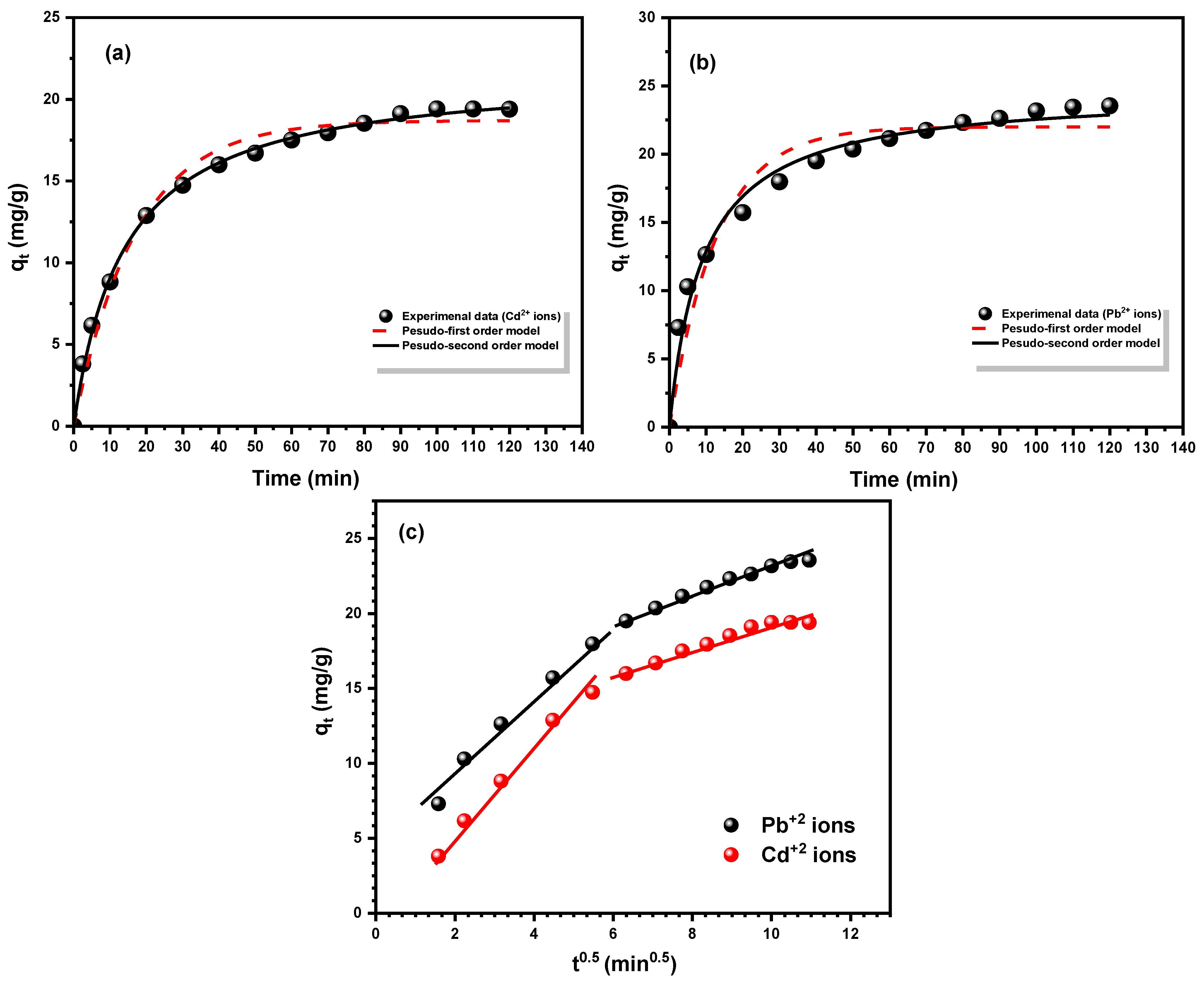
3.3. Kinetics of Adsorption Studies
3.4. Isotherm Studies
3.5. Thermodynamic Study
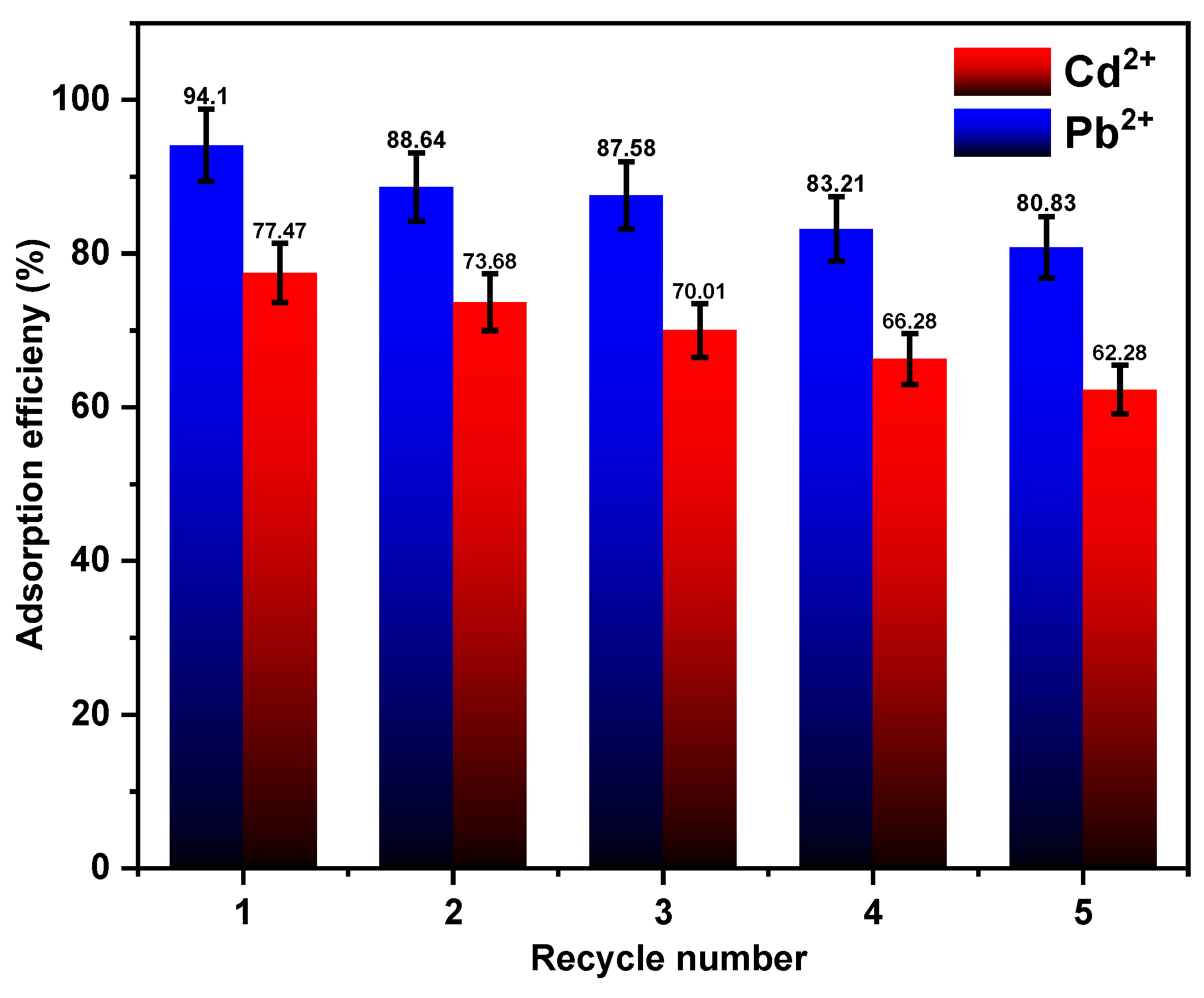
3.6. Adsorbent Reusability and Regeneration Study
3.7. Comparison Studies
3.8. Characterization of the Nanocomposite After Metal Ions Adsorption
3.8.1. FTIR Analysis
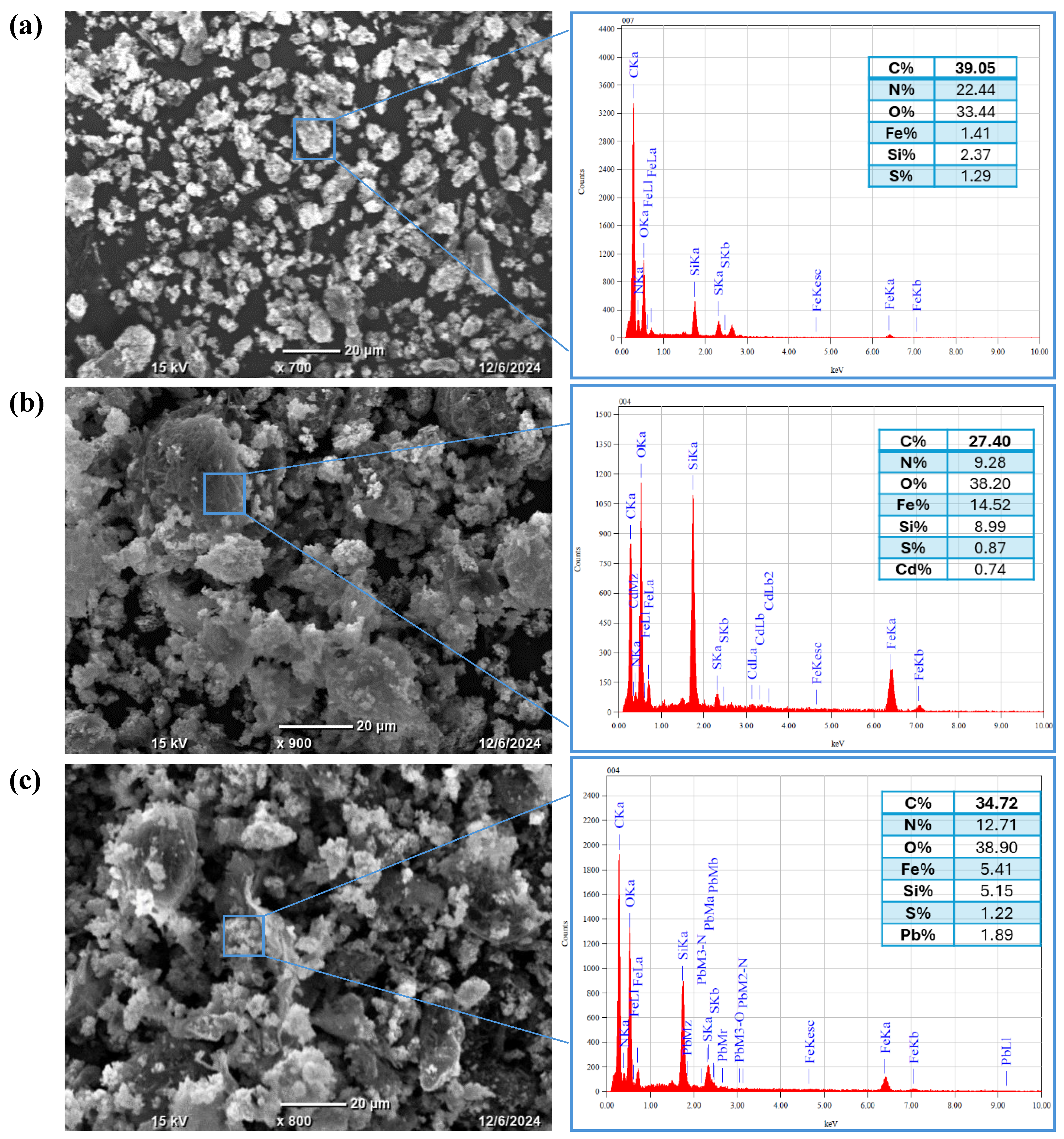
3.8.2. SEM and EDS Analysis
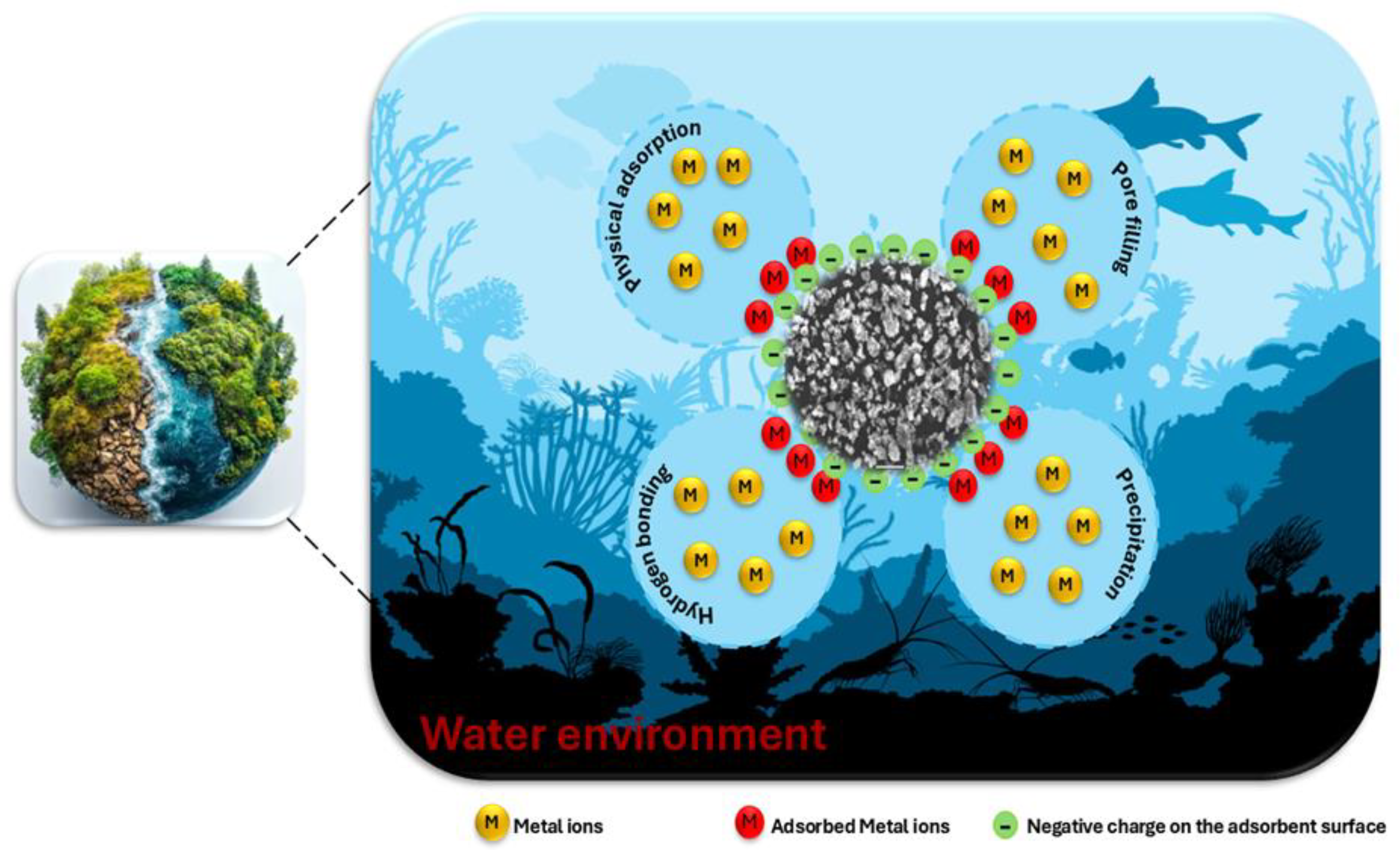
3.9. The Proposed Adsorption Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rahman, Z.; Singh, V.P. The relative impact of toxic heavy metals (THMs) (arsenic (As), cadmium (Cd), chromium (Cr)(VI), mercury (Hg), and lead (Pb)) on the total environment: An overview. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raj, D.; Maiti, S.K. Sources, bioaccumulation, health risks and remediation of potentially toxic metal(loid)s (As, Cd, Cr, Pb and Hg): An epitomised review. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.S.; Aslam, A.A.; Iftikhar, R.; Junaid, M.; Imran, S.M.; Nazir, M.S.; Ali, Z.; Zafar, M.; Kanwal, A.; Kamil Othman, N.; et al. The potential of functionalized graphene-based composites for removing heavy metals and organic pollutants. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 53, 103809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Shi, Y.; Ma, N.L.; Ye, H.; Verma, M.; Ng, H.S.; Ge, S. Utilizing adsorption of wood and its derivatives as an emerging strategy for the treatment of heavy metal-contaminated wastewater. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 340, 122830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, D.; Pittman, C.U. Arsenic removal from water/wastewater using adsorbents—A critical review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 142, 1–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, I.; Gupta, V.K. Advances in water treatment by adsorption technology. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2661–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. National Primary Drinking Water Regulations: EPA Limits on Cadmium and Lead. USA Environmental Protection Agency. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/ground-water-and-drinking-water/national-primary-drinking-water-regulations (accessed on 30 March 2025).
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality: Lead and Cadmium; World Health Organization: Geneve, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Naushad, M.u.; Vasudevan, S.; Sharma, G.; Kumar, A.; Alothman, Z.A. Adsorption kinetics, isotherms, and thermodynamic studies for Hg2+ adsorption from aqueous medium using alizarin red-S-loaded amberlite IRA-400 resin. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 18551–18559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, A.; Malik, L.A.; Ahad, S.; Manzoor, T.; Bhat, M.A.; Dar, G.N.; Hussain Pandith, A. Removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous system by ion-exchange and biosorption methods. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 729–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wu, D.; Wang, X.; Huang, W.; Lawless, D.; Feng, X. Removal of heavy metals from water using polyvinylamine by polymer-enhanced ultrafiltration and flocculation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 158, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssif, M.M.; El-Attar, H.G.; Hessel, V.; Wojnicki, M. Recent Developments in the Adsorption of Heavy Metal Ions from Aqueous Solutions Using Various Nanomaterials. Materials 2024, 17, 5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, K.G.; Gupta, S. Adsorption of a few heavy metals on natural and modified kaolinite and montmorillonite: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 140, 114–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, S.; Priya, A.K.; Senthil Kumar, P.; Hoang, T.K.A.; Sekar, K.; Chong, K.Y.; Khoo, S.K.; Ng, H.S.; Show, P.L. A critical and recent developments on adsorption technique for removal of heavy metals from wastewater-A review. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 135146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamboj, V.; Tiwari, D.P. Removal of heavy metal (Cu, Cr, and Ni) ions from aqueous solution using derived activated carbon from water hyacinth. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2024, 14, 5075–5083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzukashvili, S.; Sommerville, R.; Hu, W.; Brooks, O.; Kökkılıç, O.; Ouzilleau, P.; Rowson, N.A.; Waters, K.E. Zeolite synthesis from coal fly ash and its application to heavy metals remediation from water contaminated with Pb, Cu, Zn and Ni ions. Miner. Eng. 2024, 209, 108619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, D.; Tang, Y.; Zou, B.; Wang, Y. Mesoporous Magnetic/Polymer Hybrid Nanoabsorbent for Rapid and Efficient Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Wastewater. Langmuir 2024, 40, 2773–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheraz, N.; Shah, A.; Haleem, A.; Iftikhar, F.J. Comprehensive assessment of carbon-, biomaterial- and inorganic-based adsorbents for the removal of the most hazardous heavy metal ions from wastewater. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 11284–11310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgharinezhad, A.A.; Esmaeilpour, M.; Afshar, M.G. Synthesis of magnetic Fe3O4@SiO2 nanoparticles decorated with polyvinyl alcohol for Cu(II) and Cd(II) ions removal from aqueous solution. Chem. Pap. 2024, 78, 3799–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, A.; Kumar, A.; Singh, A. Adsorptive removal of heavy metals, dyes, and pharmaceuticals: Carbon-based nanomaterials in focus. Carbon 2024, 217, 118621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomathi, T.; Susi, S.; Alam, M.M.; Al-Sehemi, A.G.; Radha, E.; Pazhanisamy, P.; Vijayakumar, S. Copper(II) ion removal from aqueous solutions using alginate nanoparticles/ carboxymethyl cellulose/ polyethylene glycol ternary blend: Characterization, isotherm and kinetic studies. Polym. Test. 2024, 130, 108321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zohrabi, Y. Synthesis and application of magnetic ferrites (MFe2O4) in the removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions: An updated review. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2024, 299, 117024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin Md, J.; Jeong, Y.-K. Adsorptive removal of pollutants from water using magnesium ferrite nanoadsorbent: A promising future material for water purification. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 9422–9447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourens, A.; Falch, A.; Malgas-Enus, R. Magnetite immobilized metal nanoparticles in the treatment and removal of pollutants from wastewater: A review. J. Mater. Sci. 2023, 58, 2951–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, S.; Sherino, B.; Suppiah, D.D.; Sagadevan, S.; Julkapli, N.M. Prospective and potential of magnetic nanoparticles in advanced and sustainable wastewater treatment. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 63, 105540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Zhang, G.; Zhu, J.; Wu, Z. Adsorption of heavy metal ions in water by surface functionalized magnetic composites: A review. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2022, 8, 907–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi Pasandideh, E.; Kakavandi, B.; Nasseri, S.; Mahvi, A.H.; Nabizadeh, R.; Esrafili, A.; Rezaei Kalantary, R. Silica-coated magnetite nanoparticles core-shell spheres (Fe3O4@SiO2) for natural organic matter removal. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2016, 14, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Xie, S.; Zheng, S.; Xu, Y.; Sun, Y. Two-step modification (sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate composites acid-base) of sepiolite (SDBS/ABsep) and its performance for remediation of Cd contaminated water and soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 433, 128760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, L.; Xie, Q.; Chi, L.; Gu, W.; Wu, D. Adsorption of phosphate from water by easily separable Fe3O4@SiO2 core/shell magnetic nanoparticles functionalized with hydrous lanthanum oxide. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 465, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wu, W.; Yang, S.; Zhou, J.; Hong, M.; Xiao, X.; Ren, F.; Jiang, C. Template and Silica Interlayer Tailorable Synthesis of Spindle-like Multilayer α-Fe2O3 /Ag/SnO2 Ternary Hybrid Architectures and Their Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abkenar, S.D.; Khoobi, M.; Tarasi, R.; Hosseini, M.; Shafiee, A.; Ganjali, M.R. Fast Removal of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solution Using Magnetic-Modified Fe3O4 Nanoparticles. J. Environ. Eng. 2015, 141, 04014049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Lai, X.; Zou, Y.; Zhou, X.; Liu, D.; Wan, J.; Xin, H. Chestnut-like CoFe2O4@SiO2@In2O3 nanocomposite microspheres with enhanced acetone sensing property. Sens. Actuators B. Chem. 2018, 255, 3364–3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandaruwan, C.; Herath, H.M.P.C.K.; Karunarathne, T.S.E.F.; Ratnayake, S.P.; Amaratunga, G.A.J.; Dissanayake, D.P. Polyaniline/palladium nanohybrids for moisture and hydrogen detection. Chem. Cent. J. 2018, 12, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noby, H.; El-Shazly, A.H.; Elkady, M.F.; Ohshima, M. Novel preparation of self-assembled HCl-doped polyaniline nanotubes using compressed CO2-assisted polymerization. Polymer. 2018, 156, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.G.; Cho, S.K.; Oh, S.G.; Im, S.S. Preparation and characterization of polyaniline nanoparticles synthesized from DBSA micellar solution. Synth. Met. 2002, 126, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Zhai, J.; Wan, M.; Wang, D.; Jiang, L. Layered nanostructures of polyaniline with graphene oxide as the dopant and template. Synth. Met. 2010, 160, 1617–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; He, J.; Li, Y.; Cai, X.; Zhang, K.; Liu, T.; Hu, Y.; Lin, D.; Kong, L.; Liu, J. Removal of cadmium and lead ions from water by sulfonated magnetic nanoparticle adsorbents. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 494, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hozhabr Araghi, S.; Entezari, M.H. Amino-functionalized silica magnetite nanoparticles for the simultaneous removal of pollutants from aqueous solution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 333, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssif, M.M.; El-Attar, H.G.; Małecki, S.; Włoch, G.; Czapkiewicz, M.; Kornaus, K.; Wojnicki, M. Mercury Ion Selective Adsorption from Aqueous Solution Using Amino-Functionalized Magnetic Fe2O3/SiO2 Nanocomposite. Materials 2024, 17, 4254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Huang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yan, J.; Zhang, X. Sandwich structures of graphene@Fe3O4@PANI decorated with TiO2 nanosheets for enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 662, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, N.; Zhong, M.; Fei, P.; Lei, Z.; Su, B. Magnetic and electrochemical properties of PANI-CoFe2O4 nanocomposites synthesized via a novel one-step solvothermal method. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 660, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavi, M.; Ahmad, M.; Haron, M.; Namvar, F.; Nadi, B.; Rahman, M.; Amin, J. Synthesis, Surface Modification and Characterisation of Biocompatible Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications. Molecules 2013, 18, 7533–7548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanzadeh, M.; Simchi, A.; Shahriyari Far, H. Nanoporous composites of activated carbon-metal organic frameworks for organic dye adsorption: Synthesis, adsorption mechanism and kinetics studies. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020, 81, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.-H.; Huang, S.-Z.; Chen, L.-H.; Li, Y.; Yang, X.-Y.; Yuan, Z.-Y.; Su, B.-L. Applications of hierarchically structured porous materials from energy storage and conversion, catalysis, photocatalysis, adsorption, separation, and sensing to biomedicine. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 3479–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, C.; Zhang, Y.; Kong, Q.; Wang, Q.; Chen, G.; Guam, H.; Dong, C. Soft-template synthesis of mesoporous NiFe2O4 for highly sensitive acetone detection. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2020, 31, 6000–6007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Peng, K.; Dou, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; An, G. Facile Synthesis of Wormhole-Like Mesoporous Tin Oxide via Evaporation-Induced Self-Assembly and the Enhanced Gas-Sensing Properties. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Luo, J.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yang, S. Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solutions by an adsorbent based on metal-organic framework and polyoxometalate. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 648, 986–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Salman, M.; Youngblood, J.P.; Farooq, U.; Yasmeen, S.; Al-Ahmary, K.M.; Ahmed, M. Enhanced adsorption of Congo red dye by CS/PEG/ZnO composite hydrogel: Synthesis, characterization, and performance evaluation. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 411, 125704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, D.; Zhu, R.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, M.; Wang, S.; Wu, Y.; Luo, J.; Fu, L. Preparation of amidoxime modified covalent organic framework for efficient adsorption of lead ions in aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 492, 152292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi, U.R.; Srivastava, V.C.; Mall, I.D.; Lataye, D.H. Rice husk ash as an effective adsorbent: Evaluation of adsorptive characteristics for Indigo Carmine dye. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 710–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdurahim, A.A.; Yahya, M.D.; Abdulkareem, A.S.; Garba, U.; Mustapha, L.S.; Zahir, A.; Obayomi, K.S. Insightful performance analysis of fluoride ion adsorption onto graphene-zinc oxide composite beads and its prediction by Artificial Neural Network (ANN) modeling. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2024, 39, 101288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, S.; Luo, J.; An, Q.; Xiao, Z.; Wang, H.; Cai, W.; Zhai, S.; Li, Z. Efficiently selective adsorption of Pb(II) with functionalized alginate-based adsorbent in batch/column systems: Mechanism and application simulation. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 250, 119585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Guo, H.; Xue, R.; Wang, M.; Cao, Y.; Wang, X.; Xu, M.; Jang, W. A free nitrogen-containing Sm-MOF for selective detection and facile removal of mercury(II). Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 618, 126484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, W.; Jingjing, L.; Wei, L.; Jiangtao, F.; Wei, Y. Synthesis of polyaniline/TiO2 composite with excellent adsorption performance on acid red G. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 21132–21141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salahshour, R.; Shanbedi, M.; Esmaeili, H. Methylene Blue Dye Removal from Aqueous Media Using Activated Carbon Prepared by Lotus Leaves: Kinetic, Equilibrium and Thermodynamic Study. Acta Chim. Slov. 2021, 68, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, B.; Deng, Q.; Shao, H.; Cao, B.; Fan, Y.; Li, W.; Huang, M. Fe3O4 @Mesoporous-SiO2 @Chitosan@Polyaniline Core–Shell Nanoparticles as Recyclable Adsorbents and Reductants for Hexavalent Chromium. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 1831–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changwei, X.; Xijian, L.; Shimin, M.; Lijuan, Z.; Jie, L. Sub-micron-sized polyethylenimine-modified polystyrene/Fe3O4/chitosan magnetic composites for the efficient and recyclable adsorption of Cu(II) ions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 394, 378–385. [Google Scholar]
- El-Sayed, M.M.H.; Elsayed, R.E.; Attia, A.; Farghal, H.H.; Azzam, R.A.; Madkour, T.M. Novel nanoporous membranes of bio-based cellulose acetate, poly(lactic acid) and biodegradable polyurethane in-situ impregnated with catalytic cobalt nanoparticles for the removal of Methylene Blue and Congo Red dyes from wastewater. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2021, 2, 100123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.K.; Aggarwal, I.; Kumar, H.; Prasad, L.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, A.; Dai-Viet, N.V.; Van Thuan, D.; Mishra, V. Magnetite nanoparticles as sorbents for dye removal: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 2487–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, L.; Gao, F.; Shuangbao; Bian, Y.; Liu, Z.; Dai, Y. A novel adsorbent Auricularia Auricular for the removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution: Isotherm and kinetics studies. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 23, 101576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temkin, M.J.; Pyzhev, V. Recent Modifications to Langmuir Isotherms. Acta. Phys. Chim. 1940, 12, 217–222. [Google Scholar]
- Saeed, M.; Munir, M.; Nafees, M.; Shah, S.S.A.; Ullah, H.; Waseem, A. Synthesis, characterization and applications of silylation based grafted bentonites for the removal of Sudan dyes: Isothermal, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2020, 291, 109697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popoola, L.T. Nano-magnetic walnut shell-rice husk for Cd(II) sorption: Design and optimization using artificial intelligence and design expert. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, W.J.; Morris, J.C. Kinetics of Adsorption on Carbon from Solution. J. Sanit. Eng. Div. 1963, 89, 31–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H. Über die Adsorption in Lösungen. Zeitschrift für Physikalische Chemie. J. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 1907, 57, 385–470. [Google Scholar]
- Belhaj, A.F.; Elraies, K.A.; Alnarabiji, M.S.; Abdul Kareem, F.A.; Shuhli, J.A.; Mahmood, S.M.; Belhaj, H. Experimental investigation, binary modelling and artificial neural network prediction of surfactant adsorption for enhanced oil recovery application. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 406, 127081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubinin, M.M. Fundamentals of the theory of adsorption in micropores of carbon adsorbents: Characteristics of their adsorption properties and microporous structures. Carbon 1989, 27, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandiyanto, A.B.D.; Santiuly Girsang, G.C.; Maryanti, R.; Ragadhita, R.; Anggraeni, S.; Fauzi, F.M.; Sakinah, P.; Puji Astuti, A.; Usdiyana, D.; Fiandini, M.; et al. Isotherm adsorption characteristics of carbon microparticles prepared from pineapple peel waste. Commun. Sci. Technol. 2020, 5, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özcan, A.; Öncü, E.M.; Özcan, A.S. Kinetics, isotherm and thermodynamic studies of adsorption of Acid Blue 193 from aqueous solutions onto natural sepiolite. Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2006, 277, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassimi, A.E.; Achour, Y.; El Himri, M.; Laamari, M.R.; El Haddad, M. High Efficiency of Natural Safiot Clay to Remove Industrial Dyes from Aqueous Media: Kinetic, Isotherm Adsorption and Thermodynamic Studies. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2021, 11, 12717–12731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Wang, T.; Zhai, L.; Wu, W.; Dong, S.; Gao, S.; Mao, L. Adsorption behavior and mechanism of Fe-Mn binary oxide nanoparticles: Adsorption of methylene blue. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 539, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.; Naidu, R.; Du, J.; Qi, F.; Ahsan, M.A.; Liu, Y. Magnetic responsive mesoporous alginate/β-cyclodextrin polymer beads enhance selectivity and adsorption of heavy metal ions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 207, 826–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.T.; Khandaker, S.; Bashar, M.M.; Islam, A.; Ahmed, M.; Akter, R.; Alsukaibi, A.K.D.; Hasan, M.M.; Alshammari, H.M.; Kuba, T. Simultaneous toxic Cd(II) and Pb(II) encapsulation from contaminated water using Mg/Al-LDH composite materials. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 368, 120810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Meng, Y.; Qiu, X.; Zhou, F.; Wang, H.; Zhou, S.; Yan, C. Novel porous phosphoric acid-based geopolymer foams for adsorption of Pb(II), Cd(II) and Ni(II) mixtures: Behavior and mechanism. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 7030–7039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, S.T.; Beigi, P.; Babamoradi, M. Synthesis of pectin hydrogel /Fe3O4/Bentonite and its use for the adsorption of Pb (II), Cu (II), and Cd (II) heavy metals from aqueous solutions. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2023, 298, 116899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Qu, J.; Yuan, Y.; Song, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Tao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Z. Simultaneous scavenging of Cd(II) and Pb(II) from water by sulfide-modified magnetic pinecone-derived hydrochar. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 341, 130758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takanlou, L.K.; Farzadkia, M.; Mahvi, A.H.; Esrafili, A. Heavy metal adsorption efficiency magnetic porous composites Fe3O4–SiO2–APTES. Desalination Water Treat. 2020, 184, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maneechakr, P.; Mongkollertlop, S. Investigation on adsorption behaviors of heavy metal ions (Cd2+, Cr3+, Hg2+ and Pb2+) through low-cost/active manganese dioxide-modified magnetic biochar derived from palm kernel cake residue. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šolić, M.; Maletić, S.; Isakovski, M.K.; Nikić, J.; Watson, M.; Kónya, Z.; Rončević, Z. Removing low levels of Cd(II) and Pb(II) by adsorption on two types of oxidized multiwalled carbon nanotubes. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Liu, X.; Ren, P.; Gao, J.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Z. Removal behavior and mechanism of amino/carboxylate-functionalized Fe@SiO2 for Cr(VI) and Cd(II) from aqueous solutions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 72058–72073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yin, Q.; Ji, X.; Wang, F.; Gao, X.; Zhao, M. High and fast adsorption of Cd(II) and Pb(II) ions from aqueous solutions by a waste biomass based hydrogel. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastgerdi, Z.H.; Meshkat, S.S.; Esrafili, M.D. Enhanced adsorptive removal of Indigo carmine dye performance by functionalized carbon nanotubes based adsorbents from aqueous solution: Equilibrium, kinetic, and DFT study. J. Nanostructure Chem. 2019, 9, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humelnicu, D.; Valentin Soroaga, L.; Arsene, C.; Humelnicu, I.; Iulian Olariu, R. Adsorptive Performance of Soy Bran and Mustard Husk Towards Arsenic (V) Ions from Synthetic Aqueous Solutions. Acta Chim. Slov. 2019, 66, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
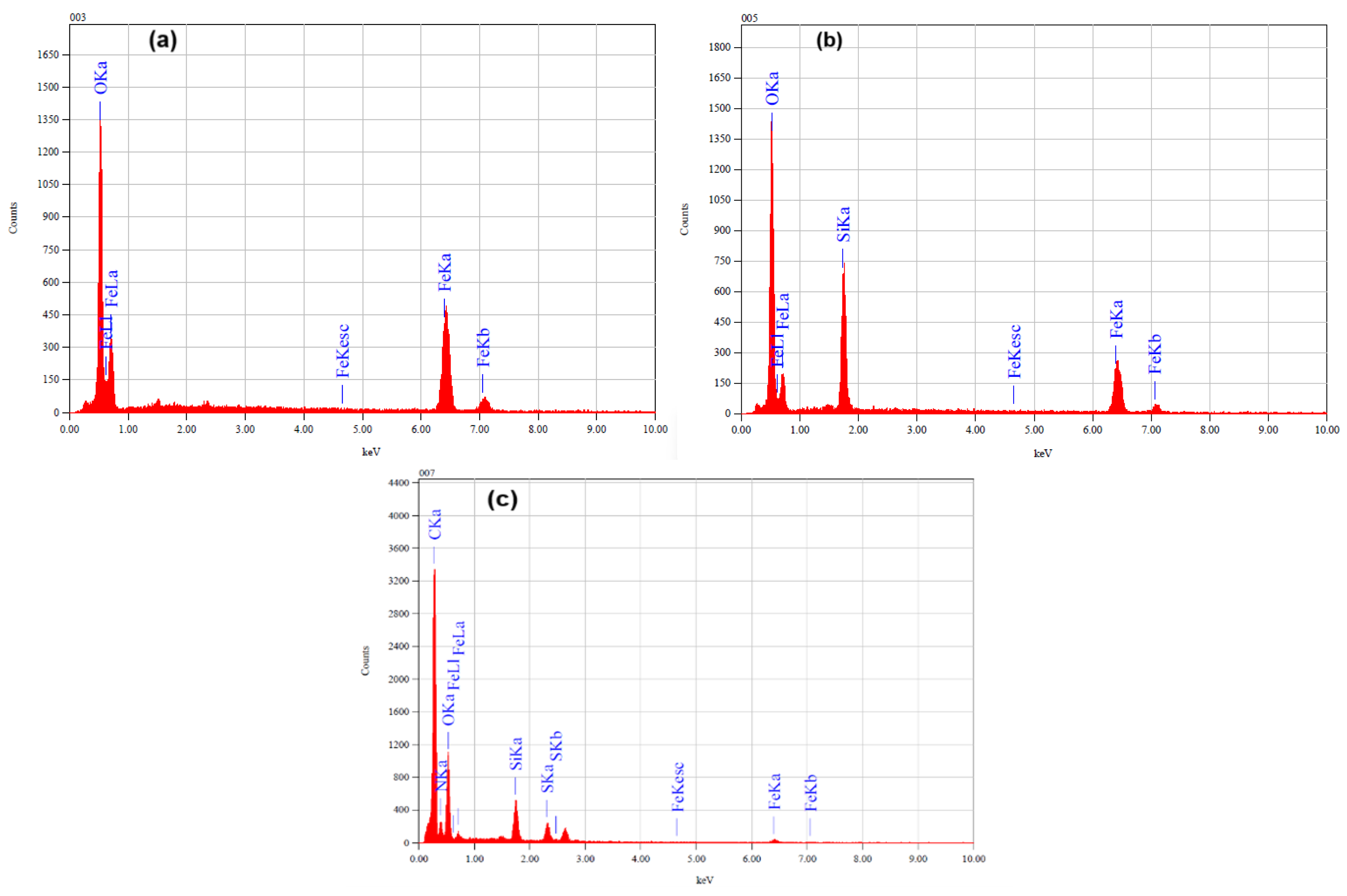




| Sample | Fe (%) | O (%) | Si (%) | N (%) | C (%) | S (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe3O4 nanoparticles | 37.46 | 62.54 | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Fe3O4/SiO2 | 35.86 | 48.50 | 15.64 | -- | -- | -- |
| Fe3O4/SiO2/PANI-SDBS | 39.05 | 33.44 | 2.37 | 22.44 | 39.05 | 1.29 |
| Adsorbents | Specific Surface Area (m² g⁻¹) |
|---|---|
| Fe3O4 | 28.71 |
| Fe3O4/SiO2 | 63.92 |
| Fe3O4/SiO2/PANI-SDBS | 116.67 |
| Models | Form of an Equation | Equation |
|---|---|---|
| Linear pseudo-first order (PFO) | (5) | |
| Nonlinear pseudo-first order (PFO) | (6) | |
| Linear pseudo-second order (PSO) | (7) | |
| Nonlinear pseudo-second order (PSO) | (8) | |
| Intraparticle diffusion | (9) |
| Model | Form | Parameter | Pb2+ Ion | Cd2+ Ion |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudo-first order | ||||
| Linear form | ||||
| qe.exp (mg/g) qe.cal (mg/g) K1 (min−1) R2 | 23.53 19.55 0.091 0.937 | 19.39 16.82 0.091 0.956 | ||
| Nonlinear form | ||||
| qe.exp (mg/g) qe.cal (mg/g) K1 (min−1) R2 | 23.53 22.99 0.078 0.938 | 19.39 18.70 0.058 0.983 | ||
| Pseudo-second order | ||||
| Linear form | ||||
| qe.exp (mg/g) qe.cal (mg/g) K2 (g/mg min) R2 | 23.53 24.15 0.004 0.998 | 19.39 21.80 0.003 0.996 | ||
| Nonlinear form | ||||
| qe.exp (mg/g) qe.cal (mg/g) K2 (g/mg min) R2 | 23.53 24.59 0.004 0.981 | 19.39 21.74 0.003 0.998 | ||
| Intraparticle diffusion | ||||
| Kp1 (mg/g/min) C (mg/g) R2 Kp2 (mg/g/min) C (mg/g) R2 | 2.64 3.87 0.98 0.88 14.13 0.978 | 2.85 0.136 0.988 0.78 11.27 0.944 | ||
| Isotherm | Applicability Criteria | Form | Parameter | Pb2+ | Cd2+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Langmuir | Single-layer or homogeneous adsorption | Linear form | KL (L/mg) | 0.426 | 0.237 |
| qmax (mg/g) | 72.20 | 67.84 | |||
| R2 | 0.939 | 0.974 | |||
| Nonlinear form | KL (L/mg) | 0.340 | 0.228 | ||
| qmax (mg/g) | 72.88 | 66.92 | |||
| R2 | 0.913 | 0.956 | |||
| Freundlich | Non-uniform distribution or multilayer adsorption | Linear form | N | 2.74 | 2.20 |
| KF (mg/g) | 22.66 | 14.76 | |||
| R2 | 0.994 | 0.995 | |||
| Nonlinear form | N | 2.64 | 2.41 | ||
| KF (mg/g) | 22.18 | 16.15 | |||
| R2 | 0.993 | 0.987 | |||
| Temkin | Uniform distribution or heterogeneous surface | Linear form | BT (J/mol) | 14.68 | 14.83 |
| K (L/mg) | 10.79 | 2.41 | |||
| R2 | 0.901 | 0.966 | |||
| Nonlinear form | BT (J/mol) | 14.43 | 13.07 | ||
| K (L/mg) | 10.92 | 3.10 | |||
| R2 | 0.904 | 0.974 | |||
| Dubinin–Radushkevich (D-R) | Differentiate between chemical and physical absorption | Linear form | qs (mg/g) | 46.27 | 42.11 |
| E (J/mol) | 101.8 | 50.61 | |||
| R2 | 0.801 | 0.804 | |||
| Nonlinear form | qs (mg/g) | 64.34 | 61.26 | ||
| E (J/mol) | 711.96 | 135.88 | |||
| R2 | 0.884 | 0.946 |
| Metal Ions | ΔH° (kJ mol−1) | ΔS° (J mol−1 K−1) | ΔG° (kJ mol−1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 298 | 303 | 308 | 313 | 318 | |||
| Cd2+ | 25.28 | 97.90 | −3.89 | −4.37 | −4.86 | −5.35 | −5.84 |
| Pb2+ | 33.57 | 131.96 | −5.76 | −6.42 | −7.08 | −7.74 | −8.40 |
| Adsorbents | pH Medium | Adsorption Capacity (mg g−1) | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd2+ | Pb2+ | |||
| Mesoporous alginate/β-cyclodextrin polymer beads | 5 | 2.47 | 21.09 | [73] |
| LDH-SHMP | 5 | 24.34 | 45.66 | [74] |
| PAG | 7 | 6.29 | 12.49 | [75] |
| Pectin hydrogel/Fe3O4/Bentonite | 7 | 35.52 | 40.13 | [76] |
| Sulfide-modified magnetic hydrochar described as MHC-S4 | 5.5 | 62.49 | 149.33 | [77] |
| Fe3O4@SiO2–APTES | 6 | 18.88 | - | [78] |
| MnO2-modified magnetic biochar | - | 18.60 | 49.64 | [79] |
| Oxidized multiwalled carbon nanotubes (Ox-MWCNTs) | 5 | 10.50 | 23.40 | [80] |
| Amino/carboxylate-functionalized Fe@SiO2 | 6 | 62.04 | -- | [81] |
| Soybean residue–poly (acrylic acid) (SR–PAA) | 6 | 25.76 | 36.75 | [82] |
| Fe3O4/SiO2/PANI-SDBS | 7 | 67.84 | 72.20 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Youssif, M.M.; Wojnicki, M. Efficacious Removal of Cd2+ and Pb2+ Ions from Wastewater Using a Novel Fe3O4/SiO2/PANI-SDBS Nanocomposite. Materials 2025, 18, 2083. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18092083
Youssif MM, Wojnicki M. Efficacious Removal of Cd2+ and Pb2+ Ions from Wastewater Using a Novel Fe3O4/SiO2/PANI-SDBS Nanocomposite. Materials. 2025; 18(9):2083. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18092083
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoussif, Mahmoud M., and Marek Wojnicki. 2025. "Efficacious Removal of Cd2+ and Pb2+ Ions from Wastewater Using a Novel Fe3O4/SiO2/PANI-SDBS Nanocomposite" Materials 18, no. 9: 2083. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18092083
APA StyleYoussif, M. M., & Wojnicki, M. (2025). Efficacious Removal of Cd2+ and Pb2+ Ions from Wastewater Using a Novel Fe3O4/SiO2/PANI-SDBS Nanocomposite. Materials, 18(9), 2083. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18092083








