Deep Eutectic Solvents Based on N-Methyltrifluoroacetamide and Lithium Bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide as New Electrolytes with Low Viscosity and High Ionic Conductivity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
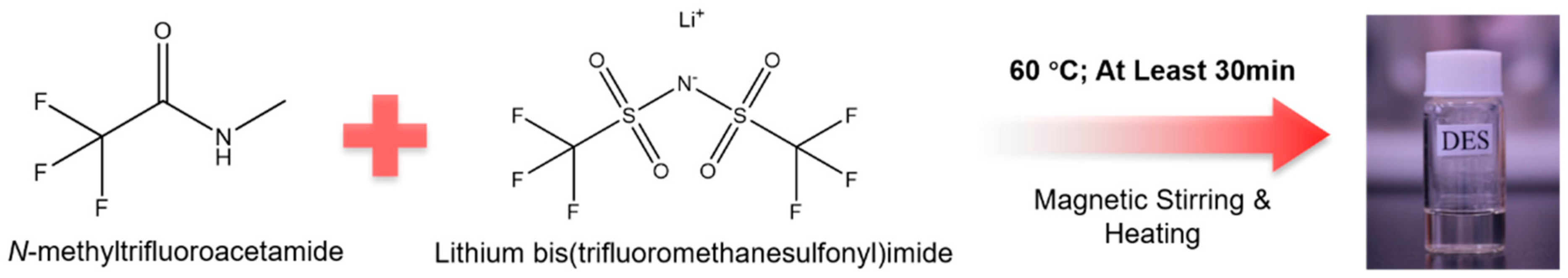
2.2. Preparation of the DESs
2.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
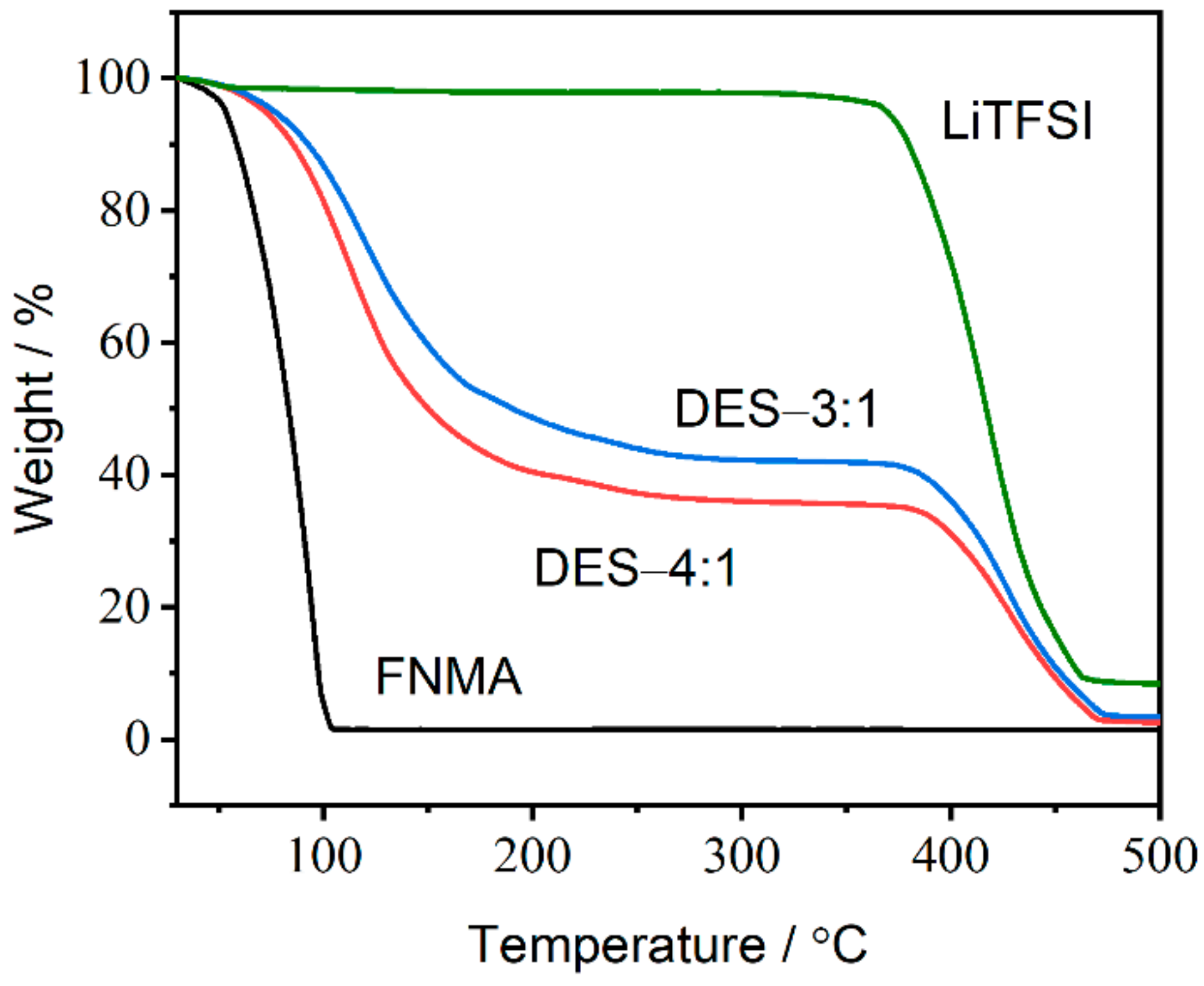
2.4. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
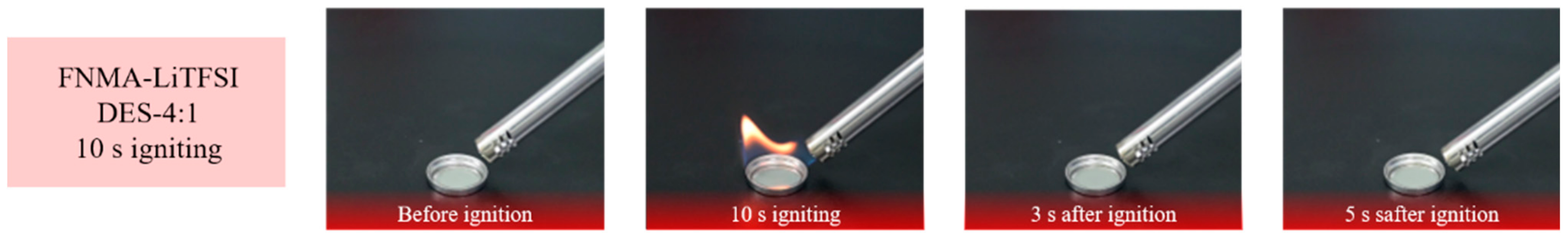
2.5. Flammability Test
2.6. Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Analysis
2.7. Viscosity
2.8. Density
2.9. Ionic Conductivity
3. Results and Discussions
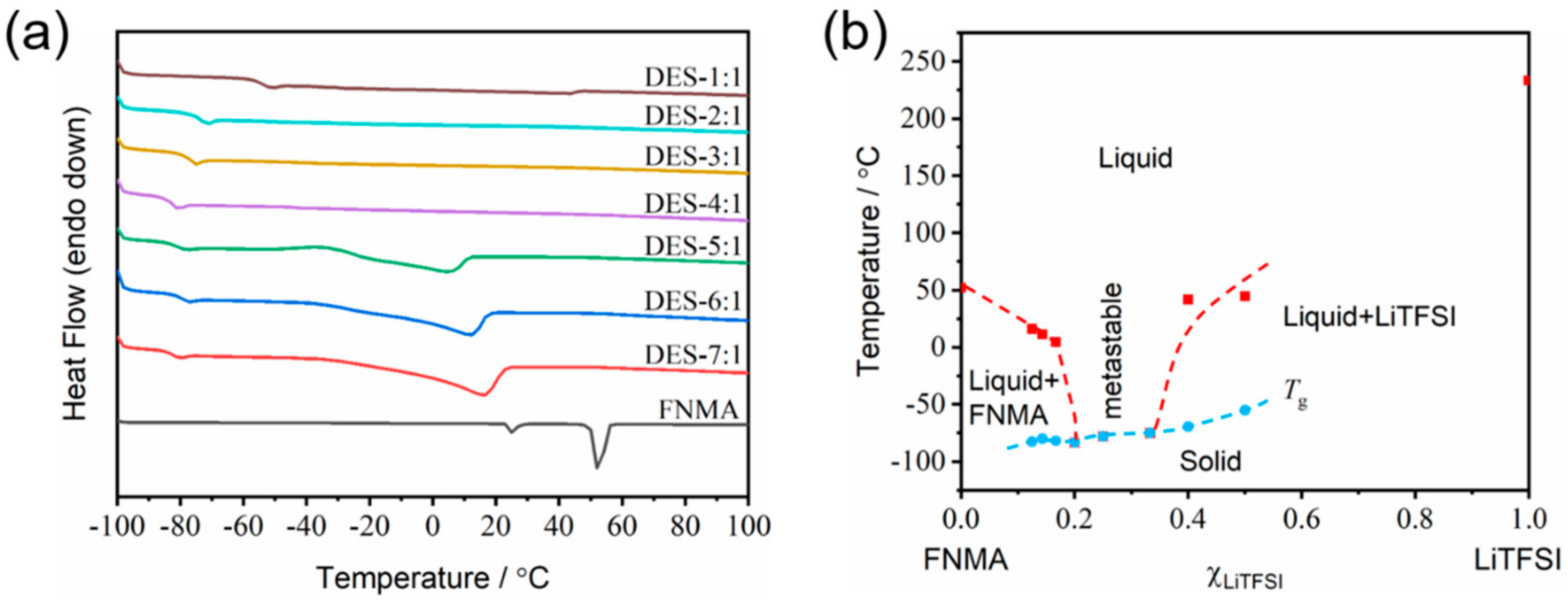
3.1. Thermal Properties
3.2. Flammability Test
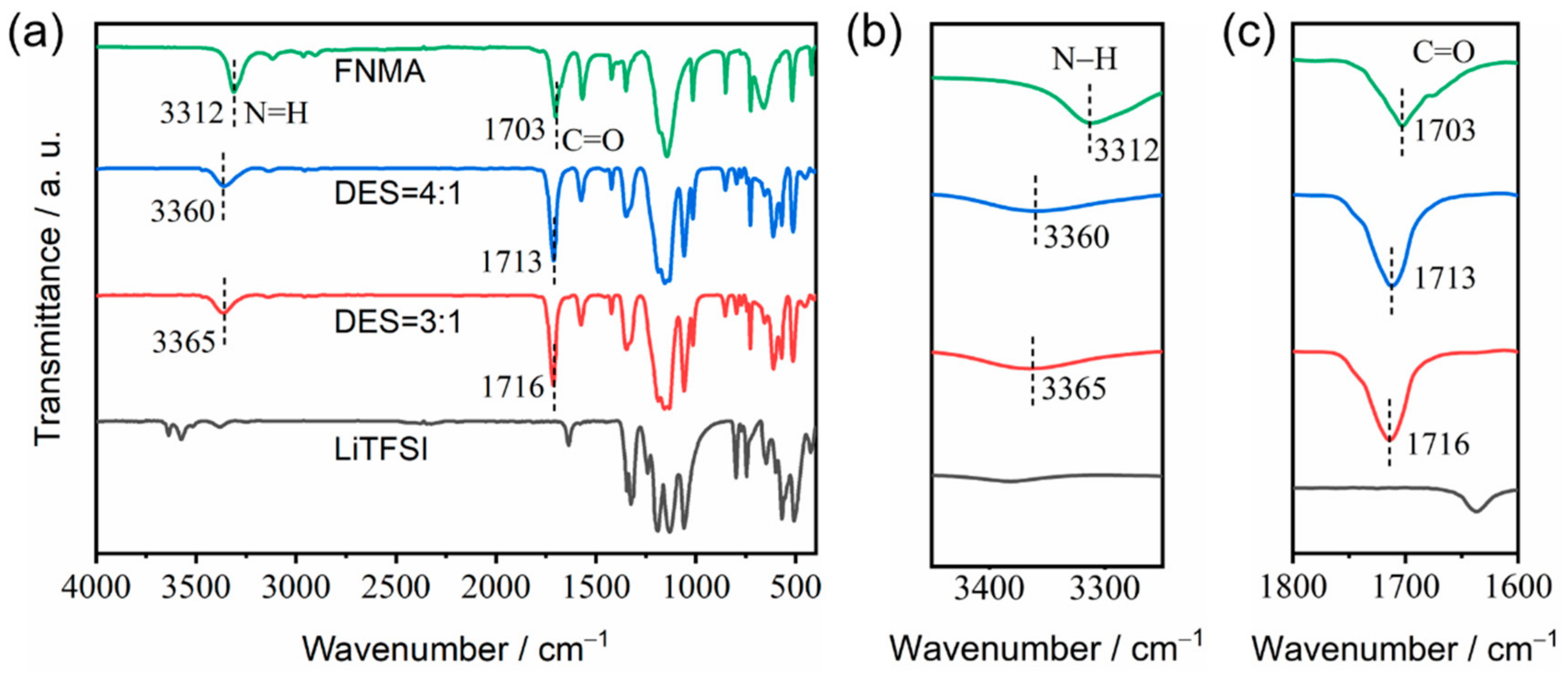
3.3. FT-IR Analysis
3.4. Transport Properties of the As-Prepared DESs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, J.X.; Liang, Q.H.; Yu, X.L.; Lu, Q.F.; Ma, L.B.; Qin, X.Y.; Chen, G.H.; Li, B.H. Deep Eutectic Solvents for Boosting Electrochemical Energy Storage and Conversion: A Review and Perspective. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2011102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Liu, J.; Lu, Z.; Lin, K.; Lyu, Y.-Q.; Li, B.; Ciucci, F.; Kim, J.-K. Non-flammable electrolyte for dendrite-free sodium-sulfur battery. Energy Storage Mater. 2019, 23, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K.; Tambyrajah, V. Novel solvent properties of choline chloride/urea mixtures. Chem. Commun. 2003, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, P.; Bao, Q.; Yao, Y.; Xiao, M.; Xu, Z.; Yang, J.; Liu, W. Environmentally Stable, Robust, Adhesive, and Conductive Supramolecular Deep Eutectic Gels as Ultrasensitive Flexible Temperature Sensor. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2300114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, L.; Yu, G. Eutectic Electrolytes as a Promising Platform for Next-Generation Electrochemical Energy Storage. Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 1648–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, N.; Zengin, H.; Yavuz, A. Electropolymerization of pyrrole from a deep eutectic solvent for supercapacitor applications. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 256, 123645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, H.; Jordão, N.; Amorim, P.; Dionísio, M.; Branco, L.C. Deep Eutectic Solvents as Suitable Electrolytes for Electrochromic Devices. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 2240–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.Q.; Sun, T.J.; Bao, J.Q.; Zheng, S.B.; Du, H.H.; Li, L.; Yuan, X.M.; Ma, T.; Tao, Z.L. “Water-in-Deep Eutectic Solvent” Electrolytes for High-Performance Aqueous Zn-Ion Batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2102035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.L.; Abbott, A.P.; Ryder, K.S. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) and Their Applications. Chem. Rev. 2024, 114, 11060–11082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, H.; Mori, H. Lithium salt/amide-based deep eutectic electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries: Electrochemical, thermal and computational study. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 8853–8863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Xian, F.; Guo, Z.; Lu, C.; Du, X.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, S.; Dong, S.; Cui, G.; Chen, L. Nonflammable Nitrile Deep Eutectic Electrolyte Enables High-Voltage Lithium Metal Batteries. Chem. Mater. 2020, 32, 3405–3413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, H.; Sato, Y.; Mori, H. Tetramethylurea dimer/lithium salt-based deep eutectics as a novel class of eutectic electrolytes. Mater. Chem. Front. 2021, 5, 8078–8085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Si, Y.; Guo, W.; Wang, D.; Fu, Y. Organosulfide-Based Deep Eutectic Electrolyte for Lithium Batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 9881–9885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinh, T.T.A.; Huynh, T.T.K.; Le, L.T.M.; Truong, T.T.T.; Nguyen, O.H.; Tran, K.T.T.; Tran, M.V.; Tran, P.H.; Kaveevivitchai, W.; Le, P.M.L. Deep Eutectic Solvent Based on Lithium Bis[(trifluoromethyl)sulfonyl] Imide (LiTFSI) and 2,2,2-Trifluoroacetamide (TFA) as a Promising Electrolyte for a High Voltage Lithium-Ion Battery with a LiMn2O4 Cathode. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 23843–23853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezzomo, L.; Pianta, N.; Ostroman, I.; Aloni, N.; Golodnitsky, D.; Peled, E.; Mustarelli, P.; Ruffo, R. Deep eutectic solvent electrolytes based on trifluoroacetamide and LiPF6 for Li-metal batteries. J. Power Sources 2023, 561, 232746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, L.; Hu, Y.-S.; Li, H.; Armand, M.; Chen, L. A new class of Solvent-in-Salt electrolyte for high-energy rechargeable metallic lithium batteries. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, B.B.; Spittle, S.; Chen, B.; Poe, D.; Zhang, Y.; Klein, J.M.; Horton, A.; Adhikari, L.; Zelovich, T.; Doherty, B.W.; et al. Deep Eutectic Solvents: A Review of Fundamentals and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 1232–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardin, N.Z.; Duca, Z.; Imel, A.; Ward, P.A. Methyl Carbamate—Lithium Salt Deep Eutectic Electrolyte for Lithium—Ion Batteries. ChemElectroChem 2022, 9, e202200628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Lu, Y.; Li, G.; Fu, L.; Mu, T. Volatility of Deep Eutectic Solvent Choline Chloride: N-Methylacetamide at Ambient Temperature and Pressure. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 7308–7317. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, J.; Van Tan, T.; Conrad, O.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. 1H-1,2,4-Triazole as solvent for imidazolium methanesulfonate. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14, 11441–11447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Hu, J.; Saak, W.; Beckhaus, R.; Wittstock, G.; Vankelecom, I.F.J.; Agert, C.; Conrad, O. Protic ionic liquid and ionic melts prepared from methanesulfonic acid and 1H-1,2,4-triazole as high temperature PEMFC electrolytes. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 10426–10436. [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher, G.S. Analysis of Recent Measurements of the Viscosity of Glasses. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1925, 8, 339–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tammann, G.; Hesse, W. Die Abhängigkeit der Viscosität von der Temperatur bie unterkühlten Flüssigkeiten. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chemie 1926, 156, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, D.H. Das Temperaturabhaengigkeitsgesetz der Viskositaet von Fluessigkeiten. Phys. Z. 1921, 22, 645. [Google Scholar]
- Omar, K.A.; Sadeghi, R. Novel diglycolic acid-based deep eutectic solvents and their applications as a rust remover. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 312, 113380. [Google Scholar]
- Omar, K.A.; Sadeghi, R. Physicochemical properties of deep eutectic solvents: A review. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 360, 119524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.P.; Lipson, J.E.G. Polymer Free Volume and Its Connection to the Glass Transition. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 3987–4007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florindo, C.; Oliveira, F.S.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Fernandes, A.M.; Marrucho, I.M. Insights into the Synthesis and Properties of Deep Eutectic Solvents Based on Cholinium Chloride and Carboxylic Acids. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 2416–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Boothby, D.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K. Deep Eutectic Solvents formed between choline chloride and carboxylic acids: Versatile alternatives to ionic liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 9142–9147. [Google Scholar]
- Abbott, A.P.; Barron, J.C.; Ryder, K.S.; Wilson, D. Eutectic-Based Ionic Liquids with Metal-Containing Anions and Cations. Chem. Eur. J. 2007, 13, 6495–6501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wippermann, K.; Wackerl, J.; Lehnert, W.; Huber, B.; Korte, C. 2-Sulfoethylammonium Trifluoromethanesulfonate as an Ionic Liquid for High Temperature PEM Fuel Cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 136, F25–F37. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Cooper, E.I.; Angell, C.A. Ionic Liquids: Ion Mobilities, Glass Temperatures, and Fragilities. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 6170–6178. [Google Scholar]

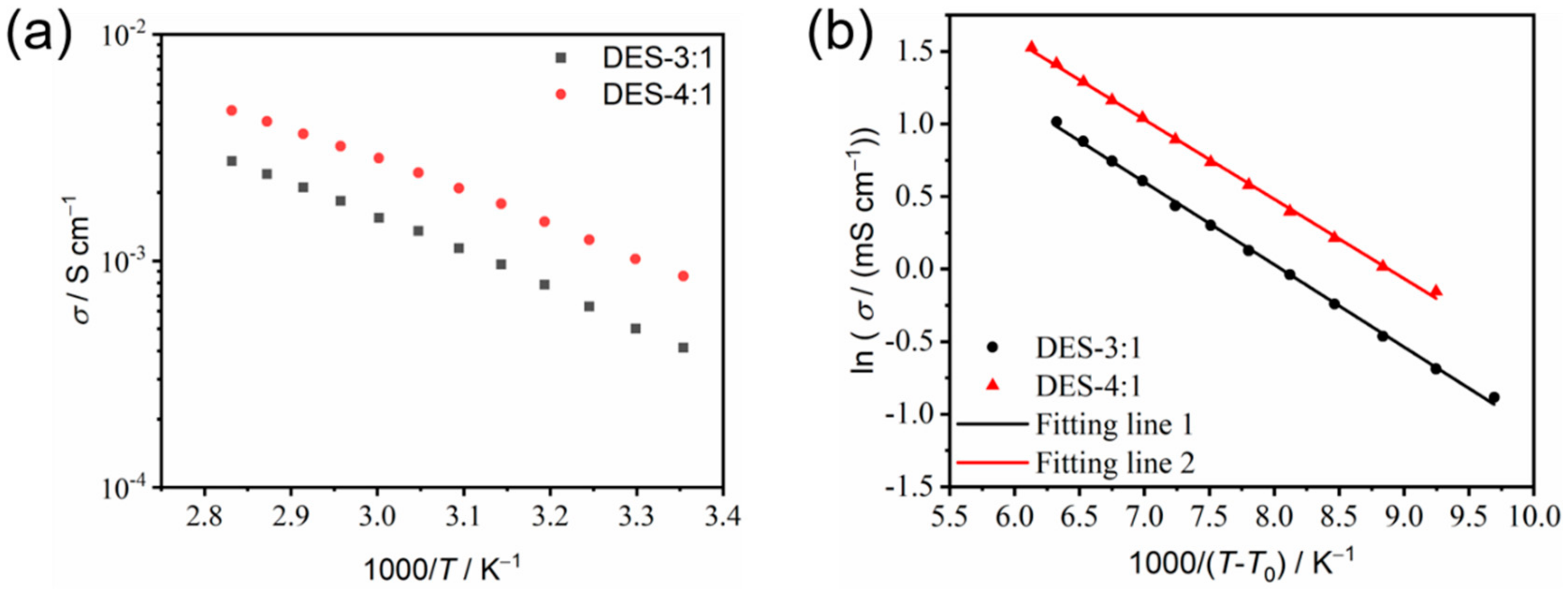
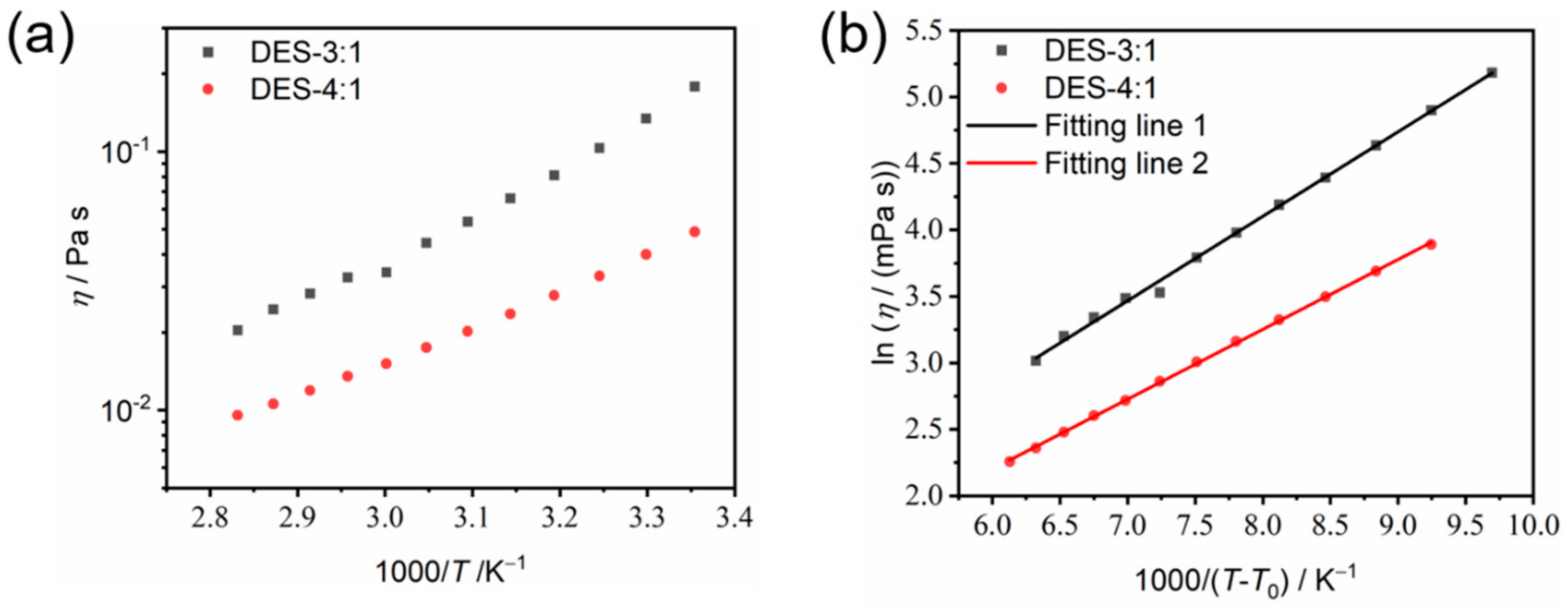
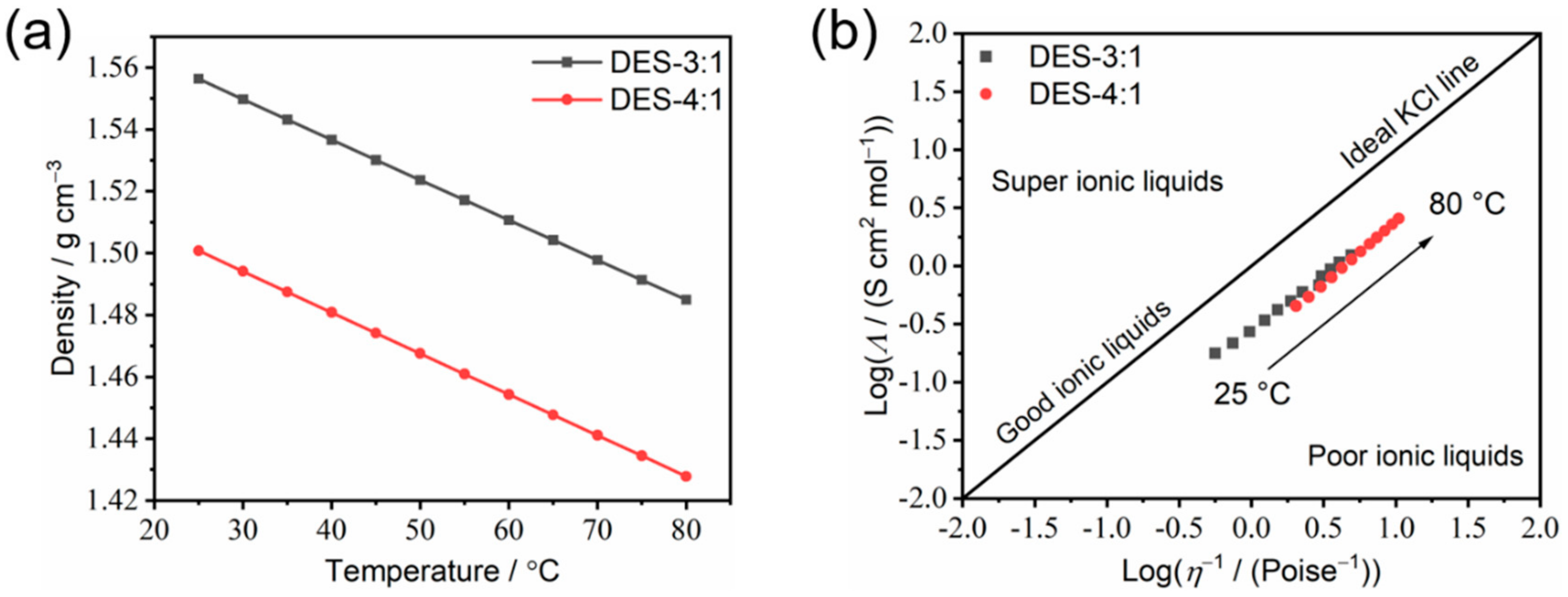
| Component | σ0/mS cm−1 | T0/K | Bσ/K | BσR/kJ mol−1 | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DES-3:1 | 97.51 | 195 | 568.25 | 4.72 | 0.9987 |
| DES-4:1 | 130.32 | 190 | 547.81 | 4.55 | 0.9989 |
| Component | η0/mPa s | T0/K | Bη/K | BηR/kJ mol−1 | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DES-3:1 | 0.38 | 195 | 635.44 | 5.28 | 0.9976 |
| DES-4:1 | 0.39 | 190 | 525.36 | 4.37 | 0.9996 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lyu, G.; Korte, C.; Luo, J. Deep Eutectic Solvents Based on N-Methyltrifluoroacetamide and Lithium Bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide as New Electrolytes with Low Viscosity and High Ionic Conductivity. Materials 2025, 18, 2048. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18092048
Lyu G, Korte C, Luo J. Deep Eutectic Solvents Based on N-Methyltrifluoroacetamide and Lithium Bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide as New Electrolytes with Low Viscosity and High Ionic Conductivity. Materials. 2025; 18(9):2048. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18092048
Chicago/Turabian StyleLyu, Guihong, Carsten Korte, and Jiangshui Luo. 2025. "Deep Eutectic Solvents Based on N-Methyltrifluoroacetamide and Lithium Bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide as New Electrolytes with Low Viscosity and High Ionic Conductivity" Materials 18, no. 9: 2048. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18092048
APA StyleLyu, G., Korte, C., & Luo, J. (2025). Deep Eutectic Solvents Based on N-Methyltrifluoroacetamide and Lithium Bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide as New Electrolytes with Low Viscosity and High Ionic Conductivity. Materials, 18(9), 2048. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18092048







