AlNiCo Magnet with NdFeB-Nanocrystalline Phase Prepared by Spark Plasma Sintering
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
- AlNiCo powder with a spinodal structure and NdFeB powder with a nanocrystalline structure, which exhibit shape anisotropy and magnetocrystalline anisotropy, respectively, are sintered by SPS. The AlNiCo magnet with an NdFeB-nanocrystalline phase is prepared, in which the microstructure consists mainly of AlNiCo regions with a spinodal structure, NdFeB regions with a nanocrystalline structure, and an unavoidable transition region approximately 1~7 µm wide between them.
- The hysteresis loop of the AlNiCo magnet with the NdFeB-nanocrystalline phase shows single-phase magnetization behavior, in contrast with the double-phase magnetization observed in simple mixed powders. With the high coercivity and excellent coupling effect of the NdFeB-nanocrystalline phase, the coercivity of the AlNiCo magnet with the NdFeB-nanocrystalline phase increased from 1250 Oe of the AlNiCo powder to 2490 Oe.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SPS | spark plasma sinter |
| H | magnetic field |
| M | moment |
| Hc | coercivity |
| Mr | remanent magnetism |
| Ms | saturation magnetism |
References
- Cui, J.; Kramer, M.; Zhou, L.; Liu, F.; Gabay, A.; Hadjipanayis, G.; Balasubramanian, B.; Sellmyer, D. Current progress and future challenges in rare-earth-free permanent magnets. Acta Mater. 2018, 158, 118–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, M.J.; McCallum, R.W.; Anderson, I.A. Constantinides, Prospects for Non-Rare Earth Permanent Magnets for Traction Motors and Generators. JOM 2012, 64, 752–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Sun, J.B.; Feng, J.H.; Ji, P.G.; Zhang, Y. Deformation mechanism of highly textured Alnico magnets. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 94, 169334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.L.; Zhao, J.T.; Liu, Z.; Xia, W.X.; Zhu, S.M.; Lee, D.; Yan, A.R. The phase and microstructure analysis of Alnico magnets with high coercivity. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 379, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, M.; Johnson, F.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, Q.; Rutkowski, S.F.; Zhou, L.; Kramer, M.J. Processing of alnico permanent magnets by advanced directional solidification methods. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 420, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Miller, M.K.; Lu, P.; Ke, L.Q.; Skomski, R.; Dillon, H.; Xing, Q.; Palasyuk, A.; McCartney, M.R.; Smith, D.J.; et al. Architecture and magnetism of alnico. Acta Mater. 2014, 74, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, H.Y.; Zhao, Z.H.; Liu, Y.Q.; Liu, L.; Huang, M.; Zhou, B.; Ding, Y.; Zhao, J.T.; Sun, Y.L.; Yan, A.R. Effect of grain structure on the magnetic properties of AlNiCo 8 magnets, Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 40, 109844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.M.; Zhao, J.T.; Xia, W.X.; Sun, Y.L.; Peng, Y.; Fu, J.C. Magnetic structure and coercivity mechanism of AlNiCo magnets studied by electron holography. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 720, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Q.; Miller, M.K.; Zhou, L.; Dillon, H.M.; McCallum, R.W.; Anderson, I.E.; Constantinides, S.; Kramer, M.J. Phase and elemental distributions in alnico magnetic materials. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2013, 49, 3314–3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, Z.; Liu, Z.; Haq, A.u. Synthesis, magnetic and microstructural properties of Alnico magnets with additives. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 428, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, S.U.; Ahmad, Z.; Haq, A.U.; Akhtar, S. Effects of Zr magneting on the microstructure and magnetic properties of Alnico permanent magnets. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 44, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, R.; Murty, B.S.; Srinivas, V. Study of microstructure and magnetic properties of AlNiCo(CuFe) high entropy alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 746, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Tang, W.; Ke, L.Q.; Guo, W.; Poplawsky, J.D.; Anderson, I.E.; Kramer, M.J. Microstructural and magnetic property evolution with different heat-treatment conditions in an Alnico magnet. Acta Mater. 2017, 133, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, S.U.; Jiang, Q.Z.; Lei, W.K.; Liu, K.; Zeng, L.L.; Ghazanfar, M.; Ahmad, T.; Liu, R.H.; Ma, S.C.; Zhong, Z.C. Microstructures and magnetic properties of cast alnico 8 permanent magnets under various heat treatment conditions. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2019, 552, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skomski, R.; Coey, J.M.D. Magnetic anisotropy—How much is enough for a permanent magnet? Scr. Mater. 2016, 112, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.Y.; Valloppilly, S.; Li, X.Z.; Yue, L.P.; Skomski, R.; Anderson, I.; Kramer, M.; Tang, W.; Shield, J.; Sellmyer, D.J. Texture development and coercivity enhancement in cast alnico 9 magnets. AIP Adv. 2018, 8, 056215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Q.; Zhao, J.T.; Zhao, Z.H.; Liu, L.; Huang, M.; Zhou, B.; Ding, Y.; Sun, Y.L.; Yan, A.R. Microstructure and magnetic properties of Dy-added Alnico magnets. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 973, 172894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saheb, N.; Iqbal, Z.; Khalil, A.; Hakeem, A.S.; Al Aqeeli, N.; Laoui, T.; Al-Qutub, A.; Kirchner, R. Spark Plasma Sintering of Metals and Metal Matrix Nanocomposites: A Review. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madugundo, R.; Rao, N.V.R.; Schönhöbel, A.M.; Salazar, D.; El-Gendy, A.A. Recent Developments in Nanostructured Permanent Magnet Materials and Their Processing Methods. In Magnetic Nanostructured Materials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 157–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.Y.; Liu, X.M.; Zhang, J.X. Neck Formation and Self-Adjusting Mechanism of Neck Growth of Conducting Powders in Spark Plasma Sintering. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2005, 89, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shichalin, O.O.; Buravlev, I.Y.; Portnyagin, A.S.; Dvornik, M.I.; Mikhailenko, E.A.; Golub, A.V.; Zakharenko, A.M.; Sukhorada, A.E.; Talskikh, K.Y.; Buravleva, A.A.; et al. SPS hard metal alloy WC-8Ni-8Fe fabrication based on mechanochemical synthetic tungsten carbide powder. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 816, 152547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papynov, E.K.; Portnyagin, A.S.; Modin, E.B.; Mayorov, V.Y.; Shichalin, O.O.; Golikov, A.P.; Pechnikov, V.S.; Gridasova, E.A.; Tananaev, I.G.; Avramenko, V.A. A complex approach to assessing porous structure of structured ceramics obtained by SPS technique. Mater. Charact. 2018, 145, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Kang, N.-H.; Feng, L.; Lee, S.-H.; Yu, J.-H.; Lee, J.-G. Anisotropic Nanocrystalline Nd-Fe-B-Based Magnets Produced by Spark Plasma Sintering Technique. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samardak, V.Y.; Samardak, A.Y.; Borisov, S.A.; Antonov, V.A.; Mushtuk, P.S.; Shtarev, D.S.; Shichalin, O.O.; Belov, A.A.; Azon, S.A.; Rogachev, K.A.; et al. Investigation of the composition, structure and magnetic properties of the Nd2Fe14B ceramics dependence on the initial powder characteristics and spark plasma sintering modes. Vacuum 2023, 215, 112206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.J.; Wang, J.M.; Yuan, Z.K.; Liu, R.J.; Zhu, M.G.; Liu, Z.; Chen, X.; Li, W.; Guo, Z.H. High cerium content (Nd-Pr-Ce)2Fe14B melt-spun ribbons with high coercivity. J. Rare Earths 2024, 42, 690–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

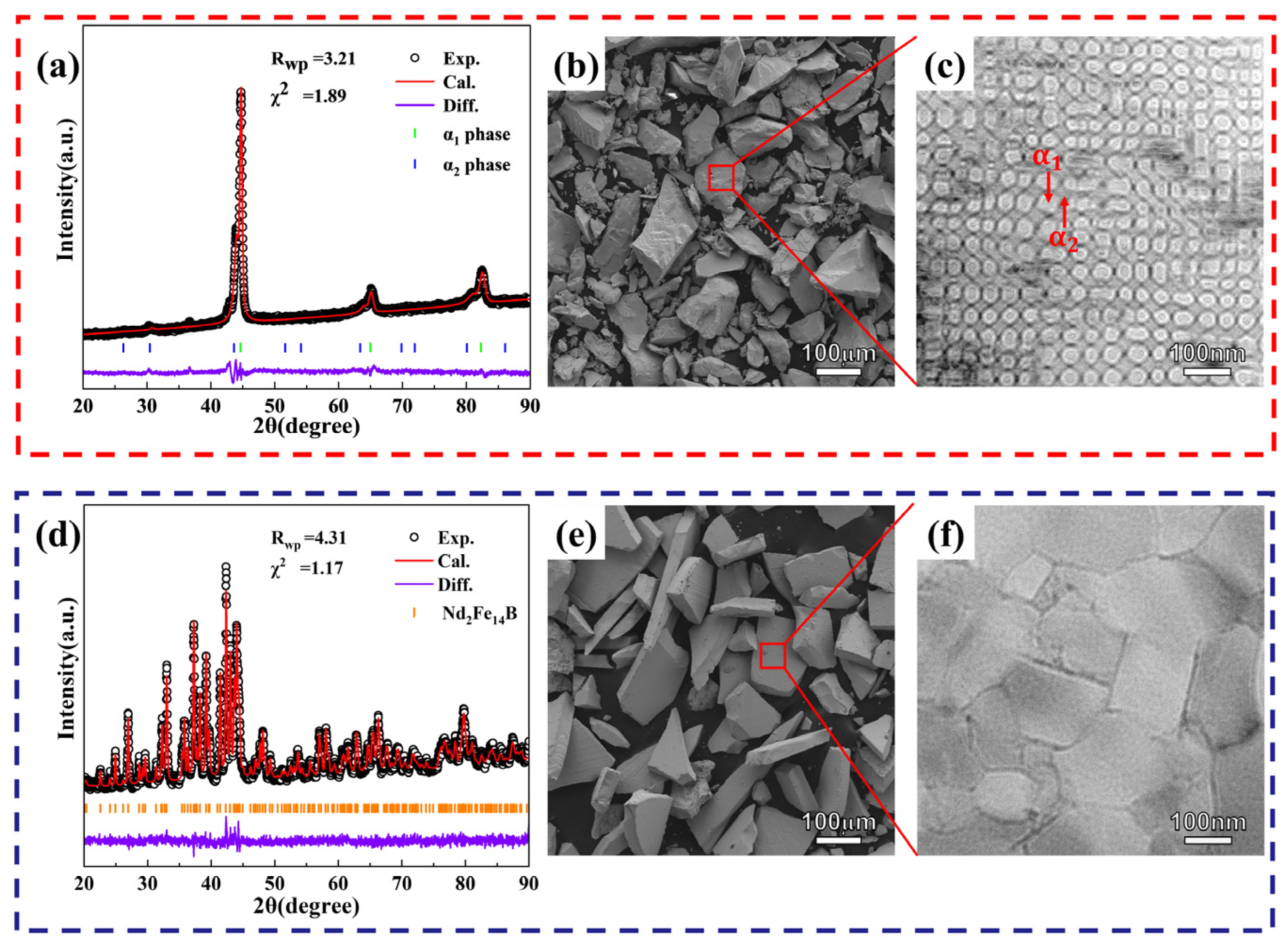

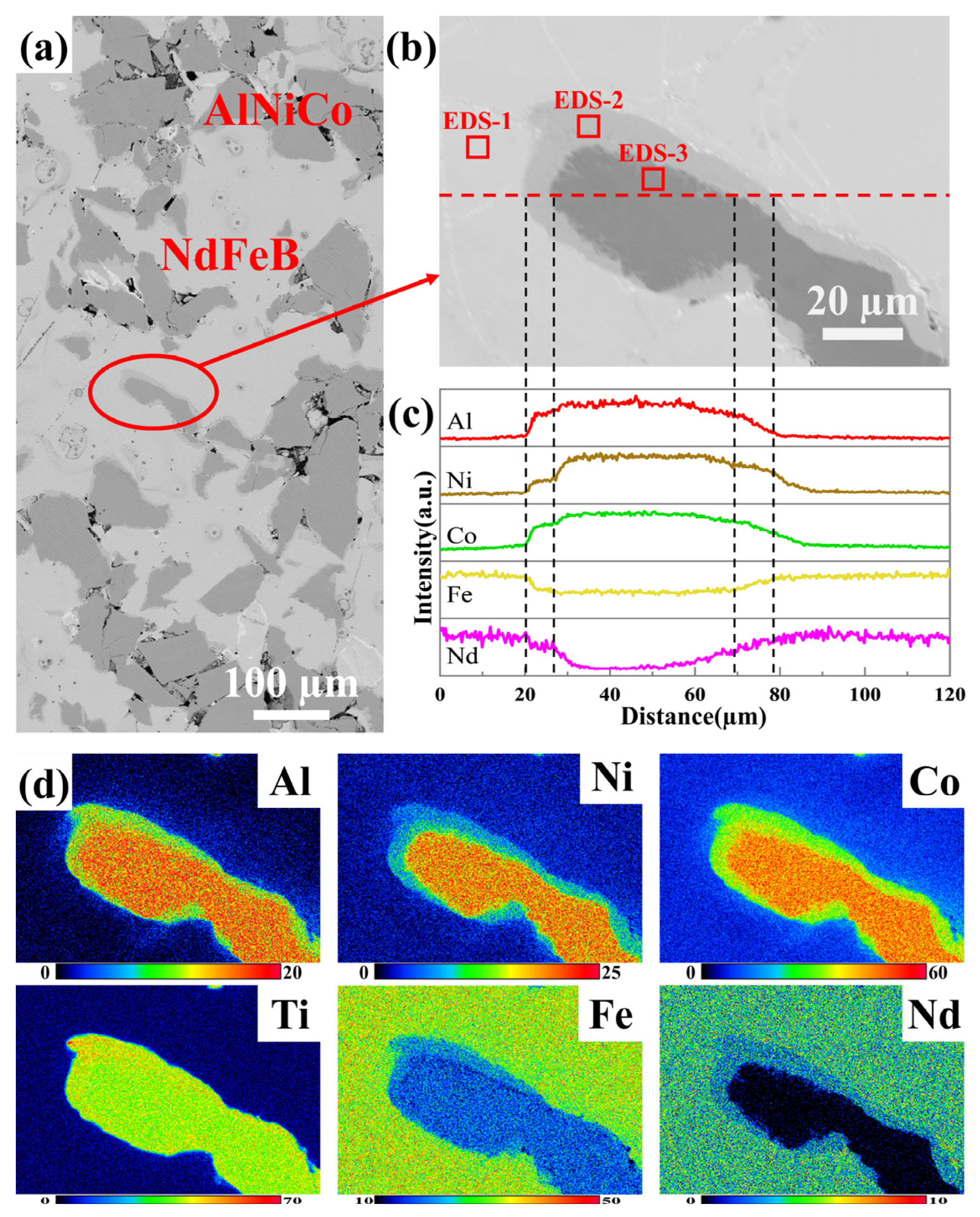

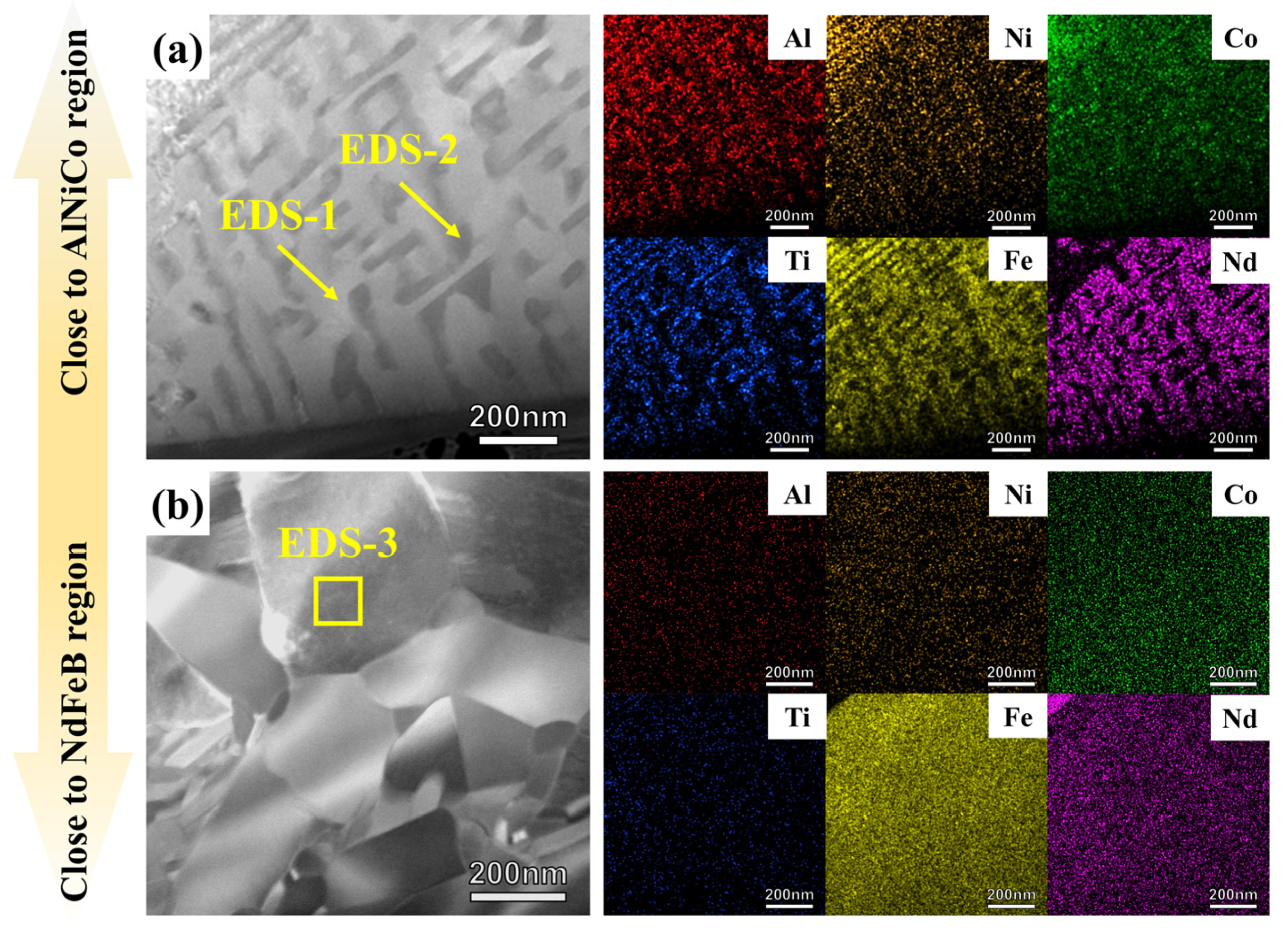
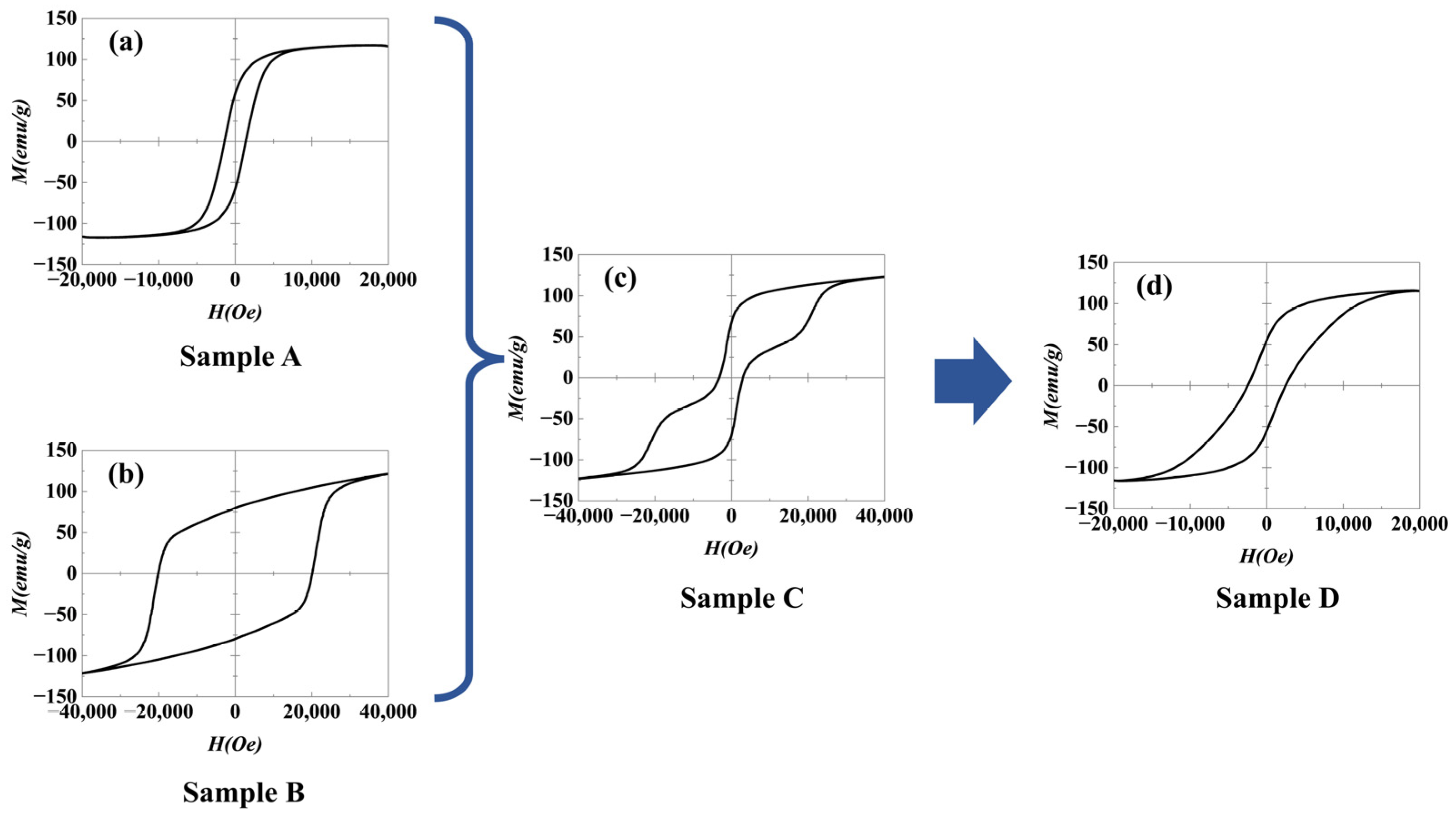


| Phase | Parameters | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a (Å) | c (Å) | Volume (Å3) | Content (wt%) | |
| α1 | 2.78 | 2.78 | 21.5 | 26.0 |
| α2 | 6.02 | 6.02 | 218.5 | 19.9 |
| Nd2Fe14B | 8.5 | 12.6 | 115.0 | 54.1 |
| Al | Ni | Co | Ti | Cu | Fe | Nd | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EDS-1 | - | - | 6.5 | - | - | 65.6 | 27.8 |
| EDS-2 | 2.3 | 6.0 | 27.6 | 4.3 | 1.9 | 37.7 | 20.3 |
| EDS-3 | 6.2 | 13.1 | 37.9 | 5.3 | 2.8 | 34.7 | - |
| Phase | Al | Ni | Co | Ti | Cu | Fe | Nd |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α1 | 2.5 | 7.6 | 38.6 | 1.6 | 1.7 | 48.0 | - |
| α2 | 10.1 | 25.2 | 34.9 | 8.9 | 4.1 | 16.8 | - |
| Nd2Fe14B | - | - | 6.4 | - | - | 69.5 | 24.1 |
| Al | Ni | Co | Ti | Cu | Fe | Nd | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EDS-1 | 1.7 | 3.2 | 20.8 | 1.5 | 1.0 | 50.9 | 20.7 |
| EDS-2 | 6.8 | 6.6 | 45.6 | 16.6 | 0.5 | 19.4 | 4.6 |
| EDS-3 | 0.6 | - | 9.2 | 0.2 | - | 68.5 | 21.5 |
| Sample | Hc (Oe) | Mr (emu/g) | Ms (emu/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 1250 | 39 | 110 |
| B | 21,000 | 79 | 123 |
| C | 3250 | 67 | 119 |
| D | 2490 | 55 | 116 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lan, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liu, L.; Yu, X.; Hu, T.; Sun, Y.; Ding, Y.; Yan, A. AlNiCo Magnet with NdFeB-Nanocrystalline Phase Prepared by Spark Plasma Sintering. Materials 2025, 18, 1847. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081847
Lan H, Liu Y, Zhao J, Liu L, Yu X, Hu T, Sun Y, Ding Y, Yan A. AlNiCo Magnet with NdFeB-Nanocrystalline Phase Prepared by Spark Plasma Sintering. Materials. 2025; 18(8):1847. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081847
Chicago/Turabian StyleLan, Haifeng, Yueqing Liu, Jiangtao Zhao, Lei Liu, Xiaoqiang Yu, Tianyu Hu, Yingli Sun, Yong Ding, and Aru Yan. 2025. "AlNiCo Magnet with NdFeB-Nanocrystalline Phase Prepared by Spark Plasma Sintering" Materials 18, no. 8: 1847. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081847
APA StyleLan, H., Liu, Y., Zhao, J., Liu, L., Yu, X., Hu, T., Sun, Y., Ding, Y., & Yan, A. (2025). AlNiCo Magnet with NdFeB-Nanocrystalline Phase Prepared by Spark Plasma Sintering. Materials, 18(8), 1847. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081847







