Polydimethylsiloxane-Zinc Oxide Nanorod-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Compression Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Fabrication of PDMS-ZnO NR-Based TENG
3. Results and Discussion
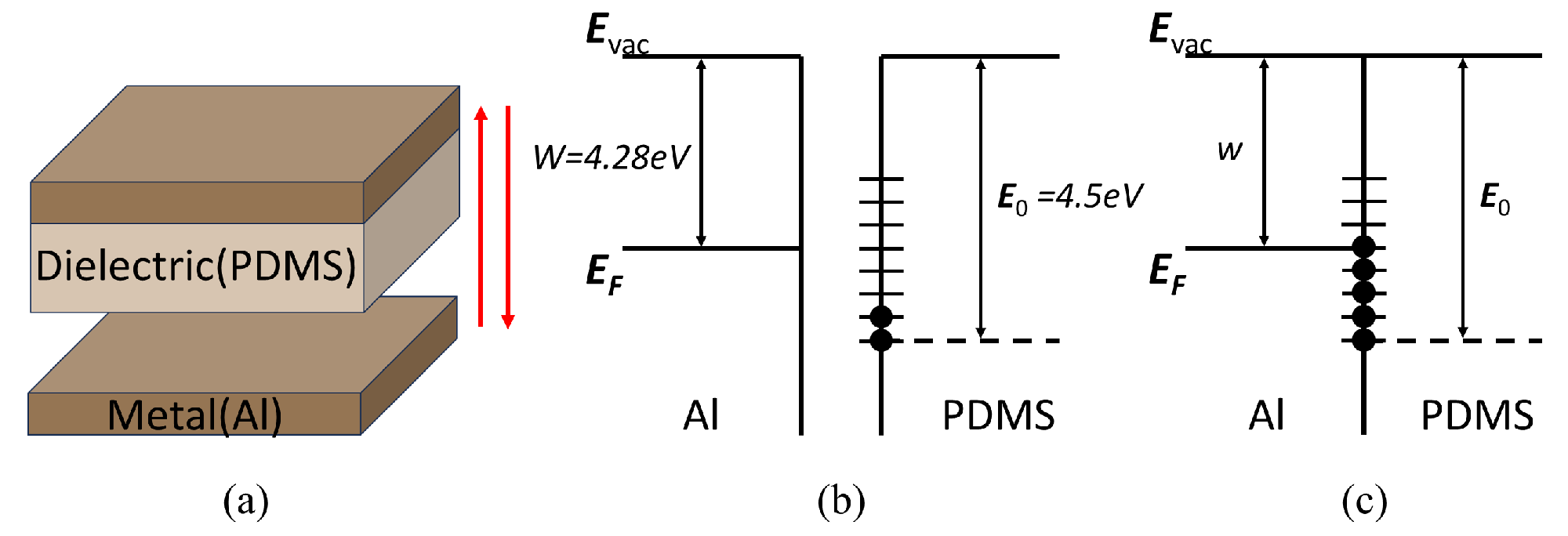
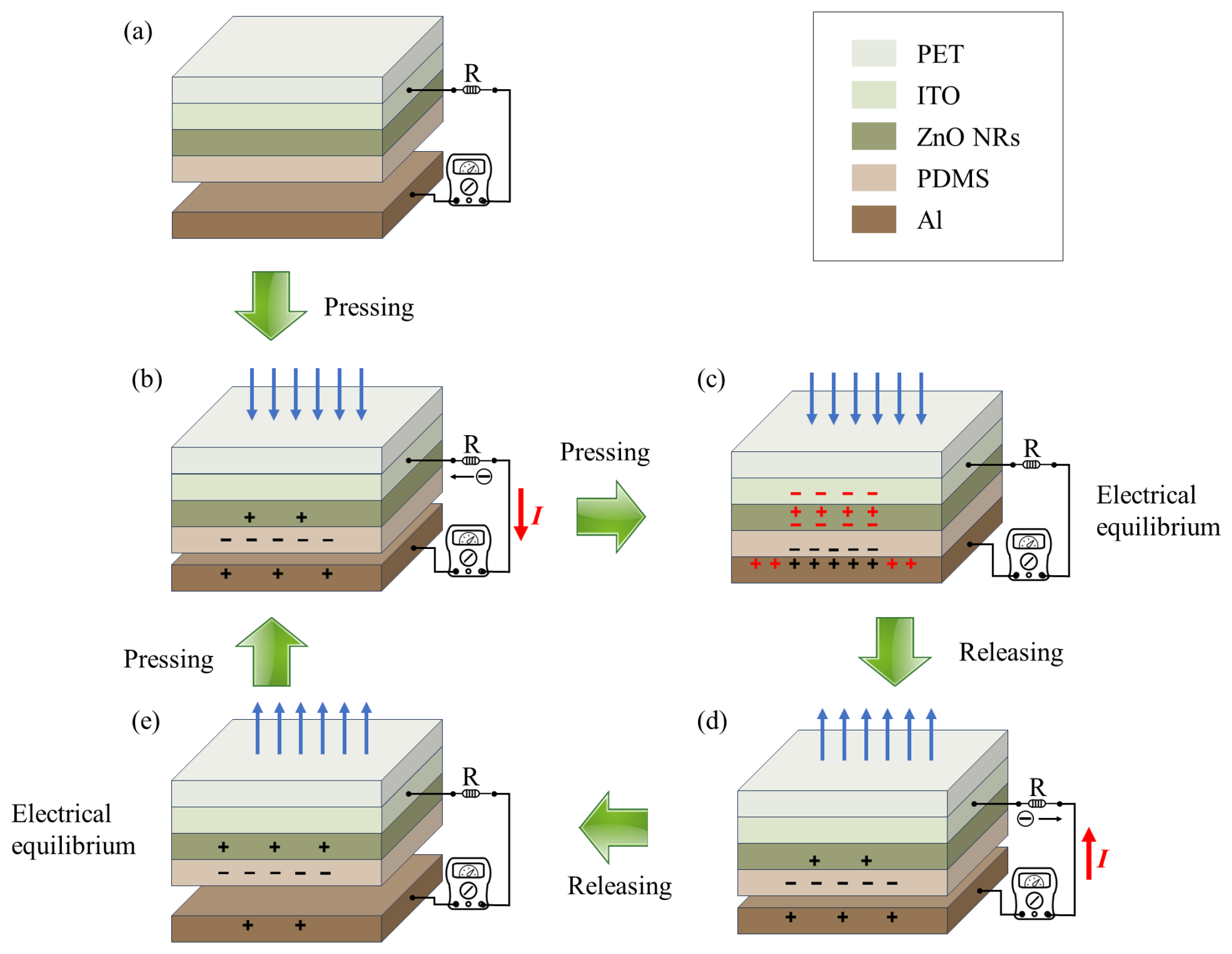
3.1. Operation Mechanism
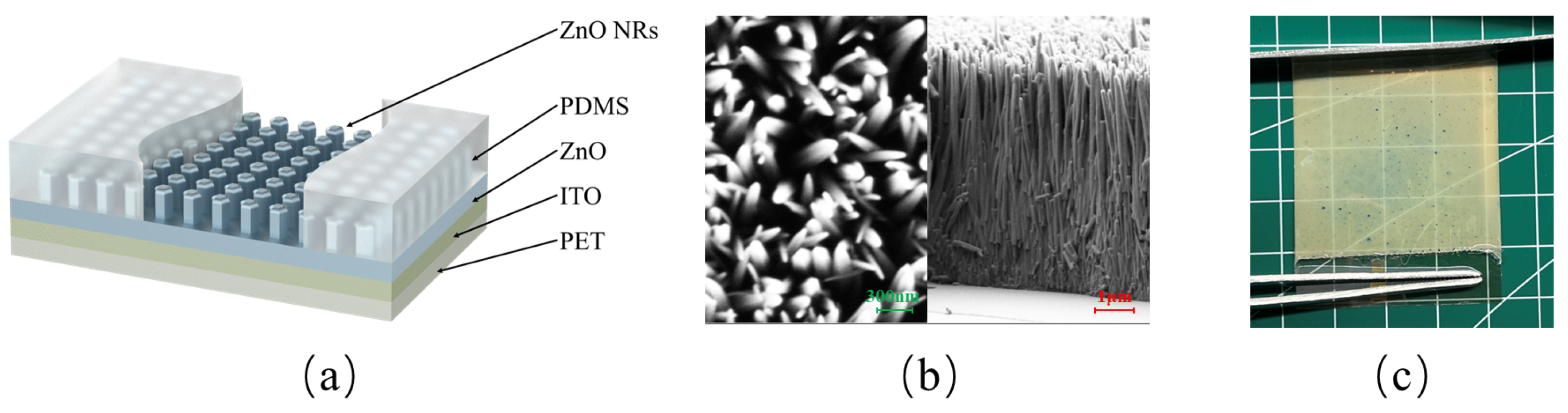
3.2. Fabrication
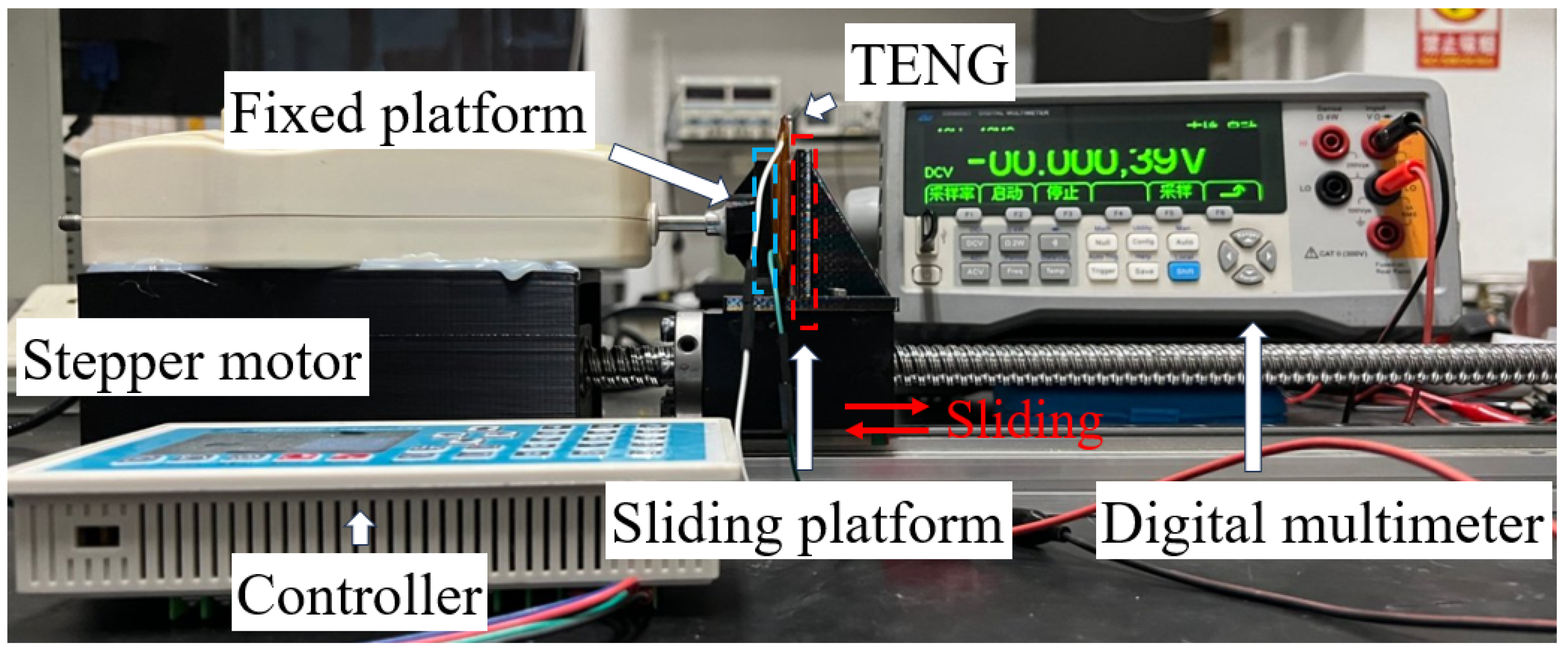
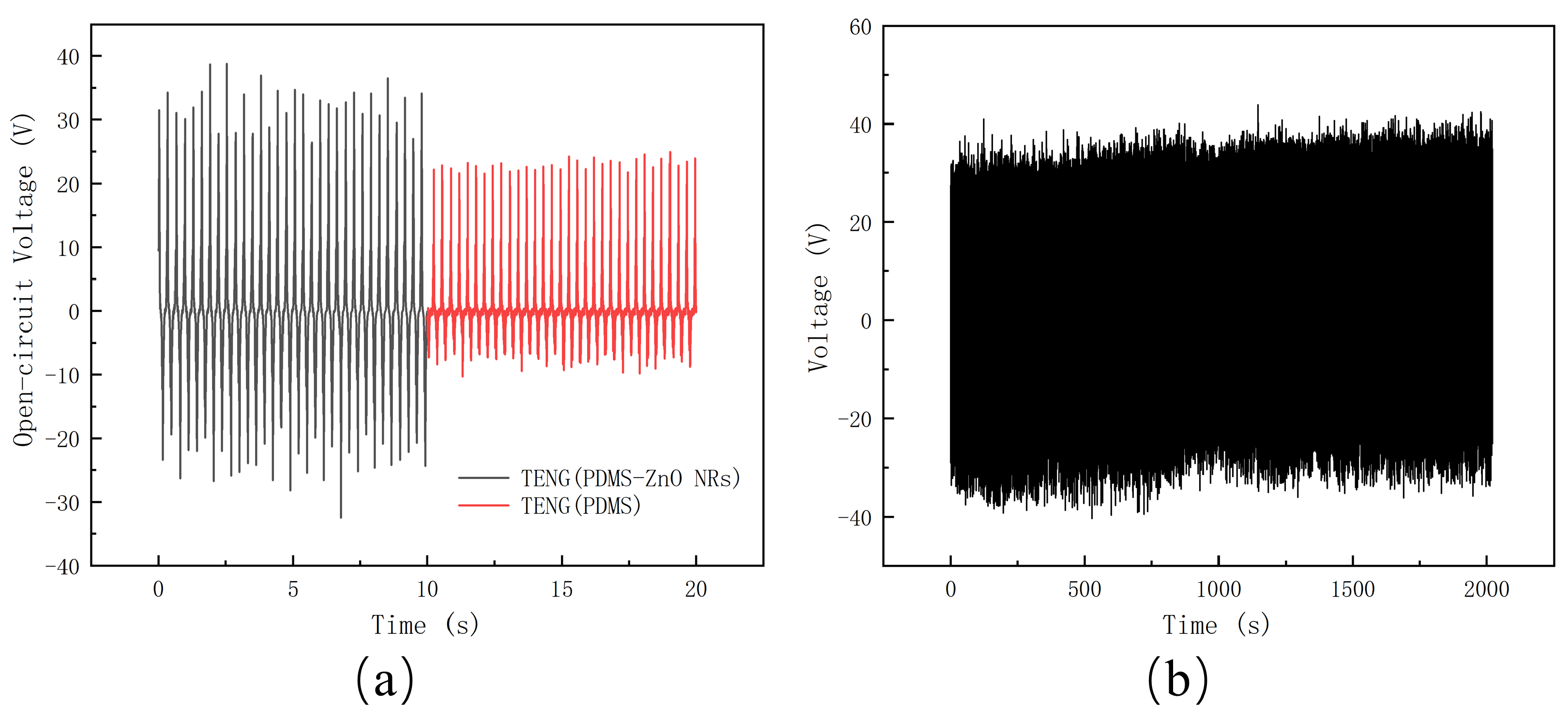
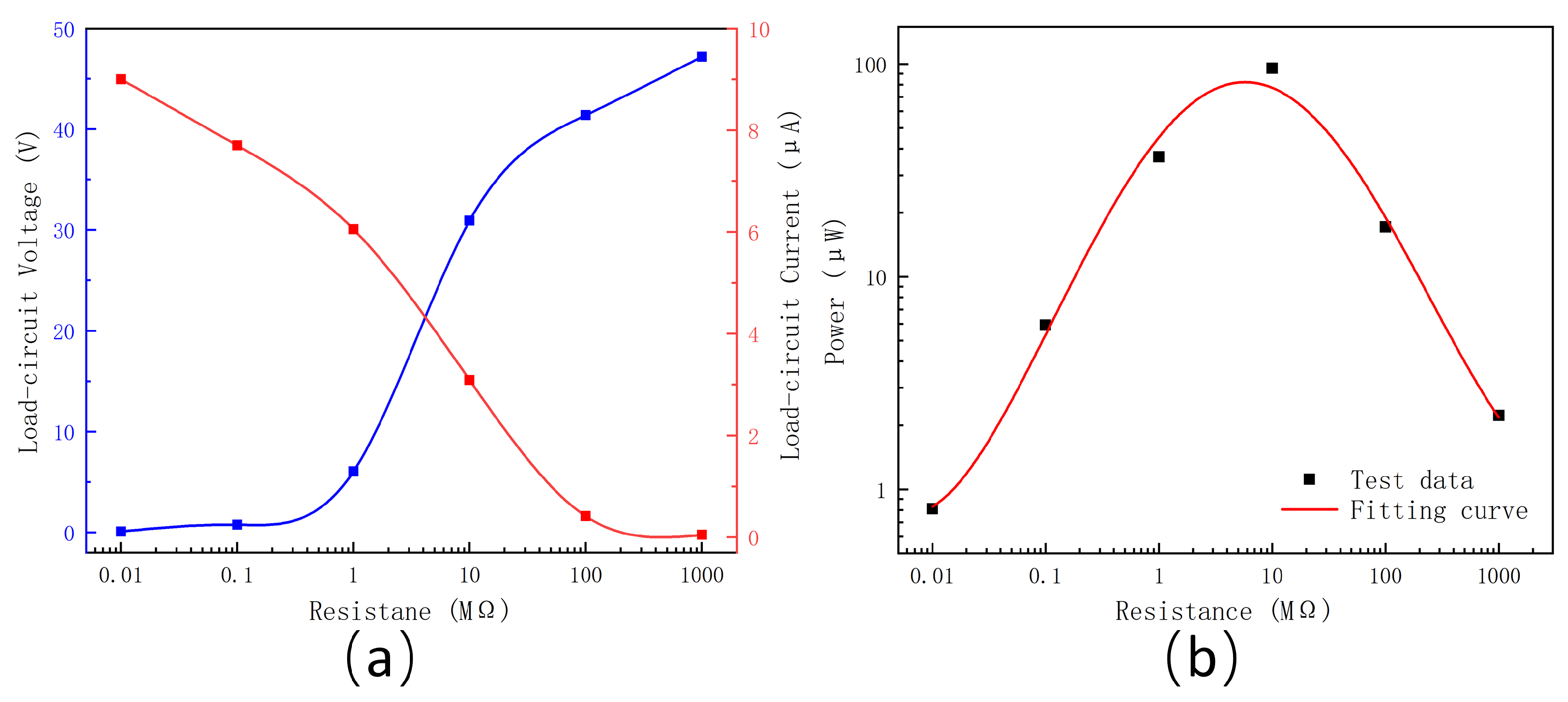
3.3. Electrical Performance
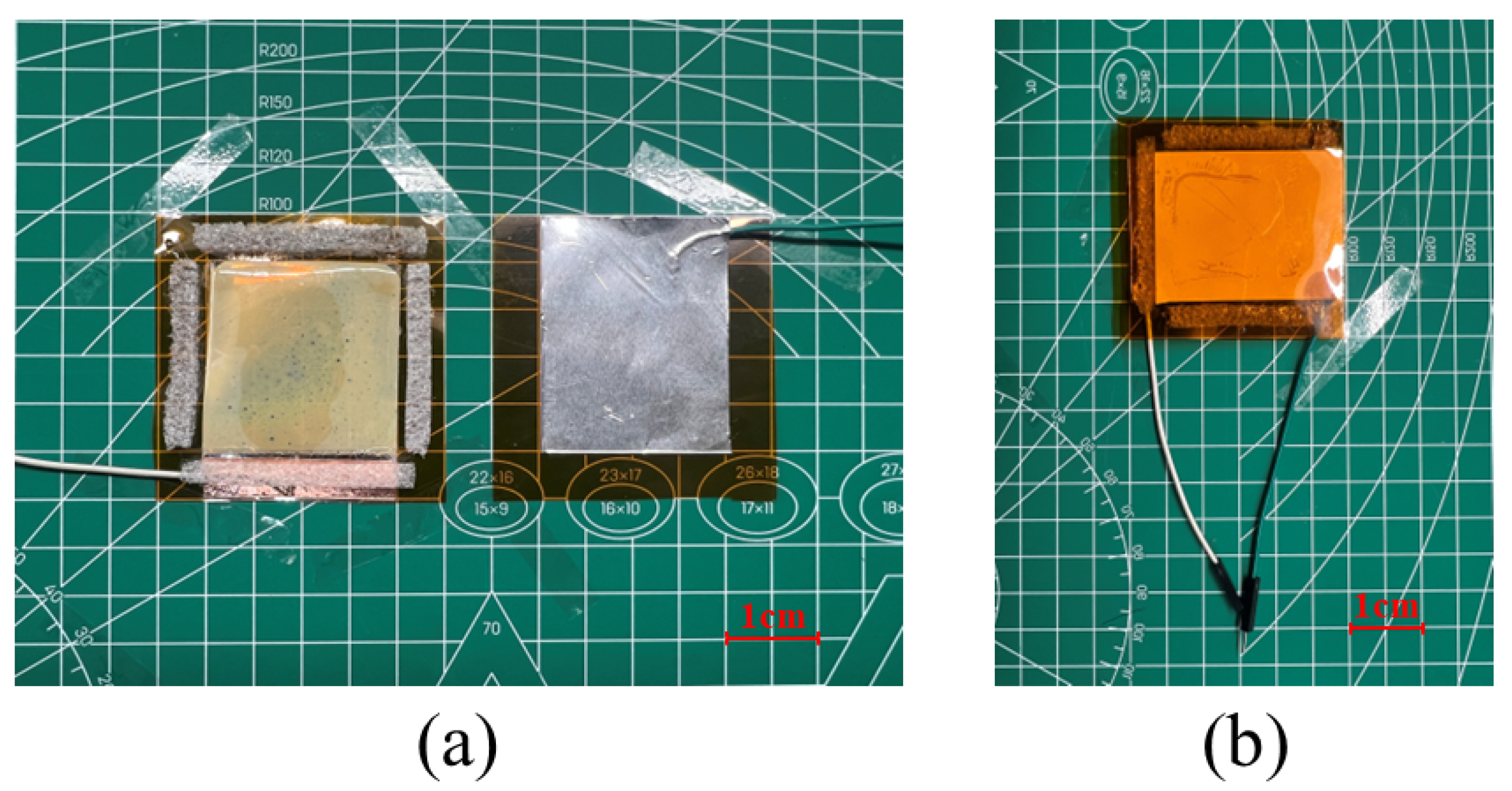
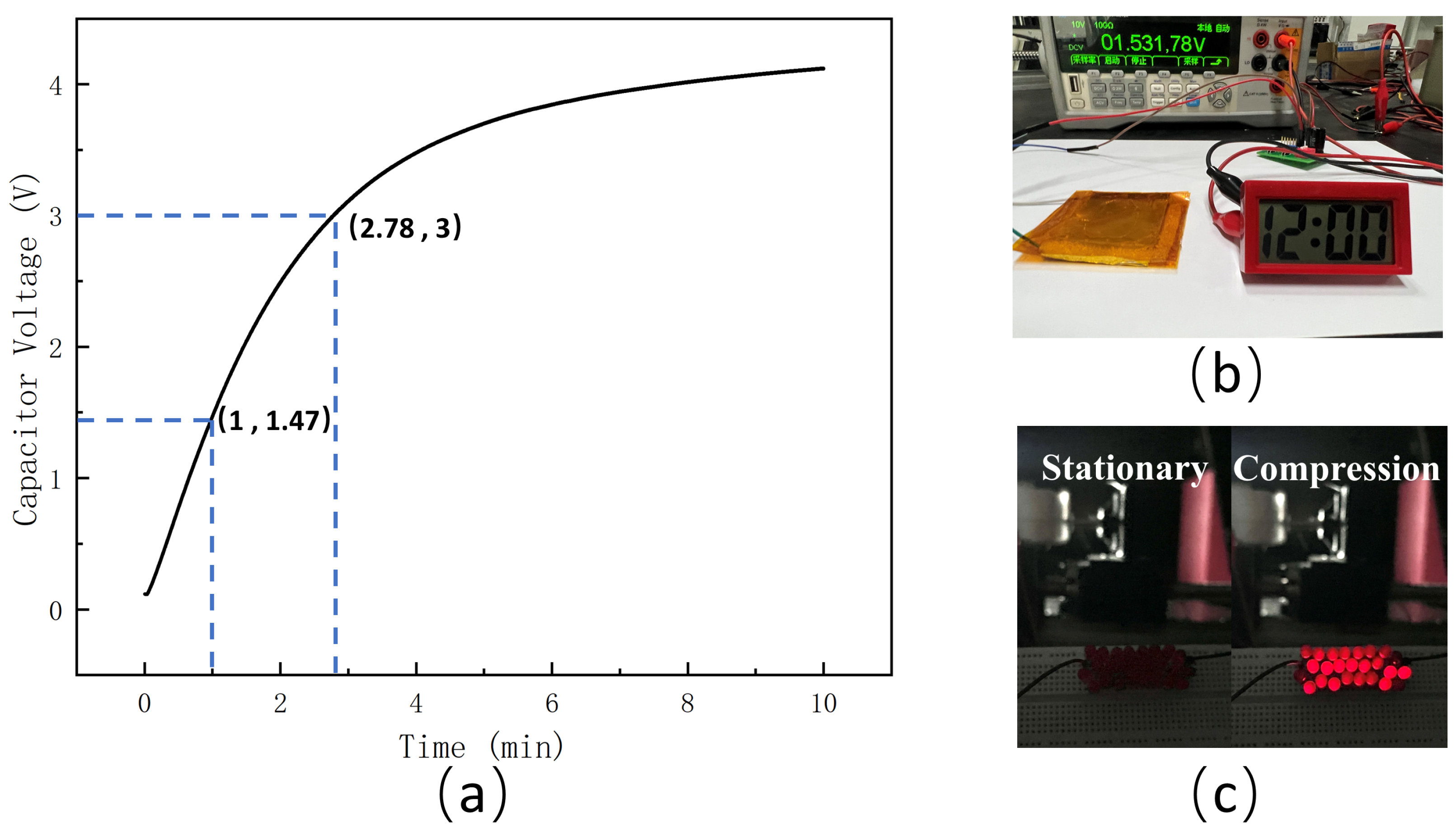
3.4. Application
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Wang, N.; Cao, X. From Triboelectric Nanogenerator to Hybrid Energy Harvesters: A Review on the Integration Strategy toward High Efficiency and Multifunctionality. Materials 2023, 16, 6405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ligęza, P. On Search for Unconventional Energy Sources for Harvesting. Energies 2024, 17, 1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.R.; Tian, Z.Q.; Wang, Z.L. Flexible triboelectric generator. Nano Energy 2012, 1, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L. On Maxwell’s displacement current for energy and sensors: The origin of nanogenerators. Mater. Today 2017, 20, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Chen, J.; Lin, L. Progress in triboelectric nanogenerators as a new energy technology and self-powered sensors. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 2250–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhen, G.; Liu, G.; Bu, T.; Liu, W.; Fu, X.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.L. Remarkable merits of triboelectric nanogenerator than electromagnetic generator for harvesting small-amplitude mechanical energy. Nano Energy 2019, 61, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Lin, L.; Wang, Z.L. Nanoscale triboelectric-effect-enabled energy conversion for sustainably powering portable electronics. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 6339–6346. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Lin, L.; Zhou, Y.S.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Theory of sliding-mode triboelectric nanogenerators. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 6184–6193. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Zhou, Y.S.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Lee, S.; Wang, Z.L. A single-electrode based triboelectric nanogenerator as self-powered tracking system. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 6594–6601. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, N.; Qin, C.; Feng, T.; Li, J.; Yang, Z.; Sun, X.; Liang, E.; Mao, Y.; Wang, X. Non-contact cylindrical rotating triboelectric nanogenerator for harvesting kinetic energy from hydraulics. Nano Res. 2020, 13, 1903–1907. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Li, H.; Shi, B.; Fan, Y.; Wang, Z.L.; Li, Z. Wearable and implantable triboelectric nanogenerators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1808820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Jiang, D.; Qu, X.; Bai, Y.; Cao, Y.; Luo, R.; Li, Z. A Stretchable, Self-Healable Triboelectric Nanogenerator as Electronic Skin for Energy Harvesting and Tactile Sensing. Materials 2021, 14, 1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Xie, Y.; Niu, S.; Lin, L.; Wang, Z.L. Freestanding Triboelectric-Layer-Based Nanogenerators for Harvesting Energy from a Moving Object or Human Motion in Contact and Non-contact Modes. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 2818–2824. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dong, B.; Shi, Q.; Yang, Y.; Wen, F.; Zhang, Z.; Lee, C. Technology evolution from self-powered sensors to AIoT enabled smart homes. Nano Energy 2021, 79, 105414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, P.; Zhu, G.; Lin, Z.H.; Jing, Q.; Chen, J.; Zhang, G.; Ma, J.; Wang, Z.L. Integrated multilayered triboelectric nanogenerator for harvesting biomechanical energy from human motions. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 3713–3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, N.; Zou, H.; Liu, R.; Tao, C.; Fan, X.; Wang, Z.L. Micro-cable structured textile for simultaneously harvesting solar and mechanical energy. Nature Energy 2016, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Gao, L.; Tao, X.; Li, L. Ultra-Flexible and Large-Area Textile-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerators with a Sandpaper-Induced Surface Microstructure. Materials 2018, 11, 2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanakumar, B.; Mohan, R.; Thiyagarajan, K.; Kim, S.J. Fabrication of a ZnO nanogenerator for eco-friendly biomechanical energy harvesting. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 16646–16656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.H.; Shin, S.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Jung, J.Y.; Lee, M.H.; Nah, J. Triboelectric contact surface charge modulation and piezoelectric charge inducement using polarized composite thin film for performance enhancement of triboelectric generators. Nano Energy 2016, 25, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Chen, X.; Yu, B.; Zhang, H. Coupling of piezoelectric and triboelectric effects: From theoretical analysis to experimental verification. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2015, 1, 1500187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Z.L.; Yang, Y. A one-structure-based hybridized nanogenerator for scavenging mechanical and thermal energies by triboelectric–piezoelectric–pyroelectric effects. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 2881–2887. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.L.; Song, J. Piezoelectric Nanogenerators Based on Zinc Oxide Nanowire Arrays. Science 2006, 312, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ko, Y.H.; Nagaraju, G.; Lee, S.H.; Yu, J.S. PDMS-based triboelectric and transparent nanogenerators with ZnO nanorod arrays. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 6631–6637. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yue, X.; Xi, Y.; Hu, C.; He, X.; Dai, S.; Cheng, L.; Wang, G. Enhanced output-power of nanogenerator by modifying PDMS film with lateral ZnO nanotubes and Ag nanowires. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 32566–32571. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Ko, W.; Hong, J. Enhanced performance of triboelectric nanogenerators integrated with ZnO nanowires. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 14, 9319–9322. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, T.; Shao, J.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric nanogenerators. Nat. Rev. Methods Prim. 2023, 3, 39. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.S.; Wang, S.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, G.; Niu, S.; Lin, Z.H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Manipulating Nanoscale Contact Electrification by an Applied Electric Field. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 1567–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, S.; Han, G.; Deng, H.; Ma, M.; Zhong, X. Polydimethylsiloxane-Zinc Oxide Nanorod-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Compression Applications. Materials 2025, 18, 1392. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071392
Zhao S, Han G, Deng H, Ma M, Zhong X. Polydimethylsiloxane-Zinc Oxide Nanorod-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Compression Applications. Materials. 2025; 18(7):1392. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071392
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Shiyu, Guanghui Han, Huaxia Deng, Mengchao Ma, and Xiang Zhong. 2025. "Polydimethylsiloxane-Zinc Oxide Nanorod-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Compression Applications" Materials 18, no. 7: 1392. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071392
APA StyleZhao, S., Han, G., Deng, H., Ma, M., & Zhong, X. (2025). Polydimethylsiloxane-Zinc Oxide Nanorod-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Compression Applications. Materials, 18(7), 1392. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071392







