Anaerobic Biodegradation of Polylactic Acid-Based Items: A Specific Focus on Disposable Tableware Products
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Feedstock Materials
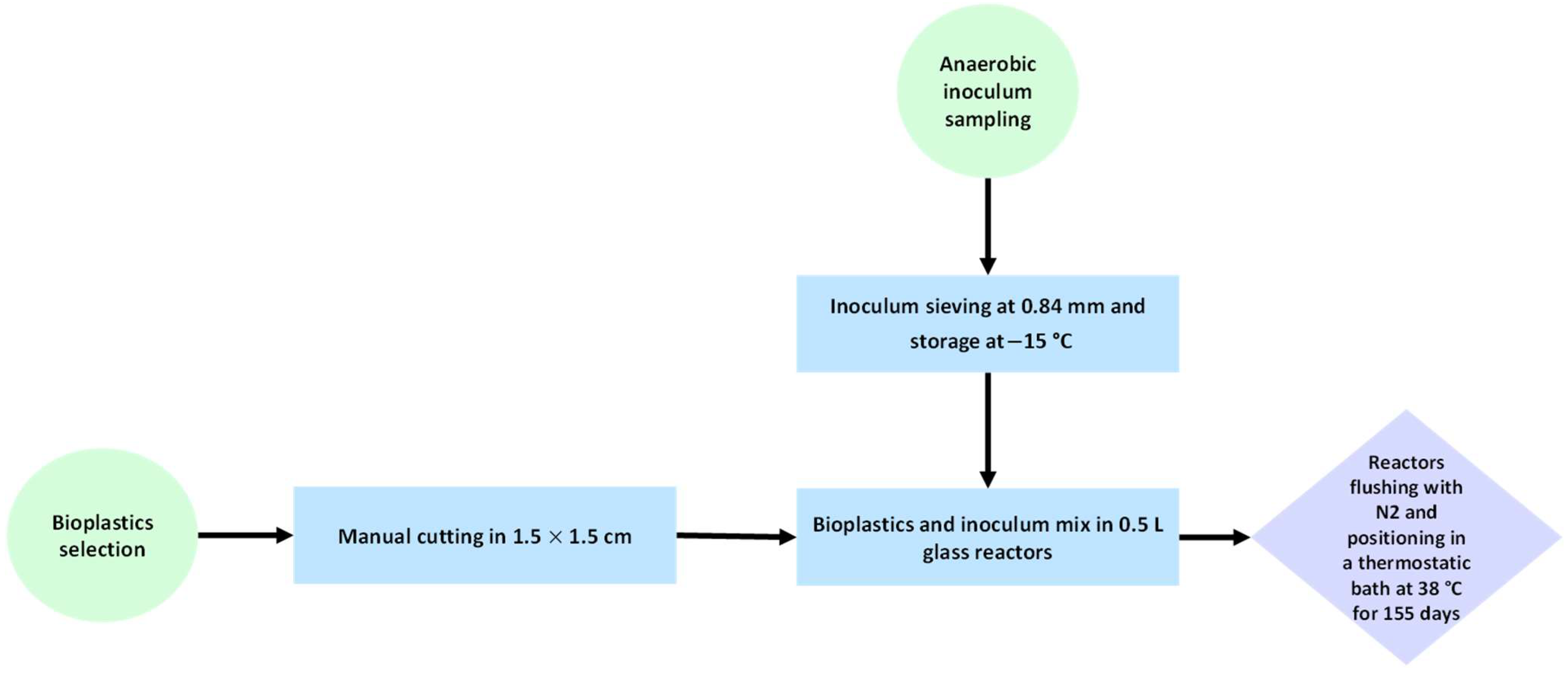
2.2. Anaerobic Biodegradation Tests
2.3. Statistical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Mesophilic Anaerobic Biodegradation Tests
3.2. Comparison of Mesophilic and Previous Thermophilic Experimental Campaigns
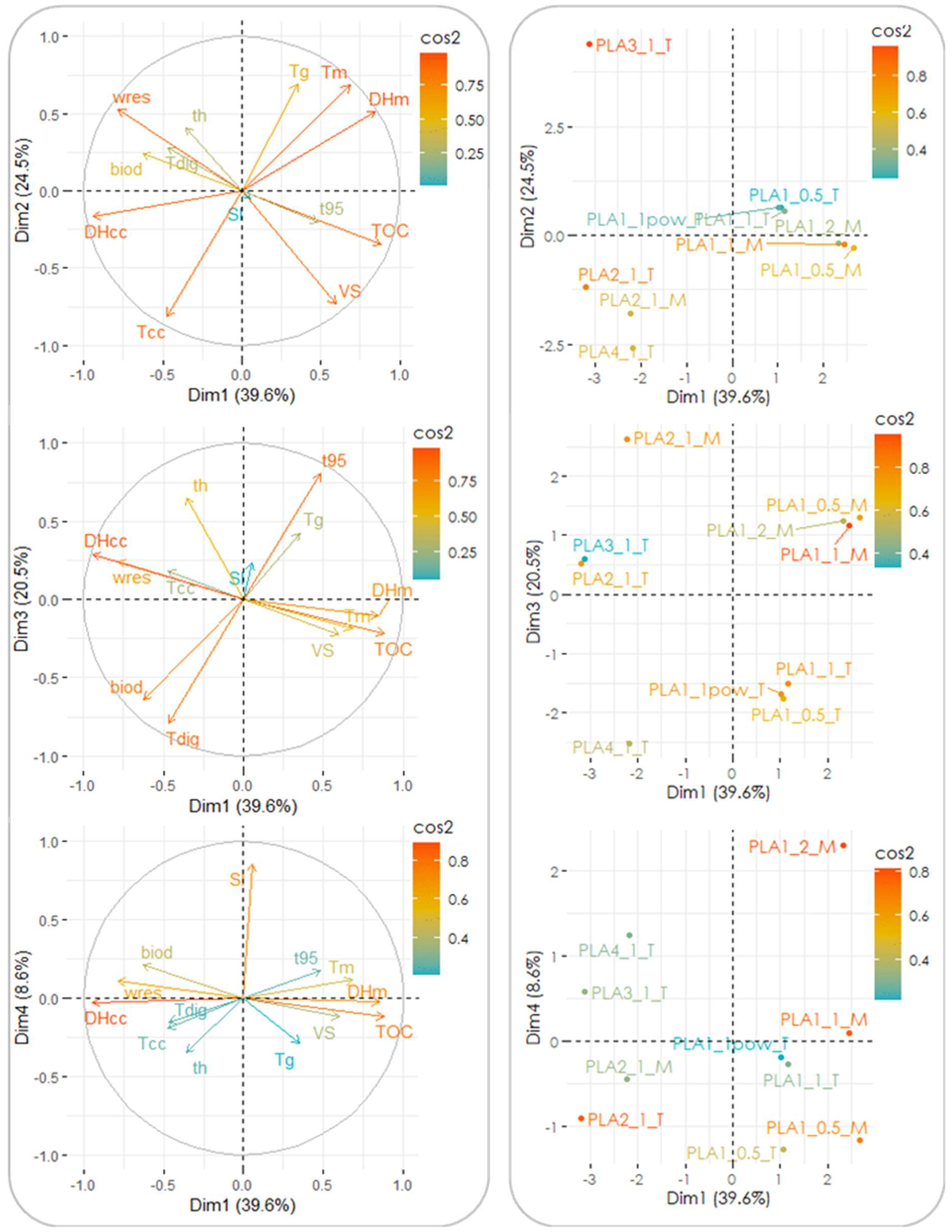
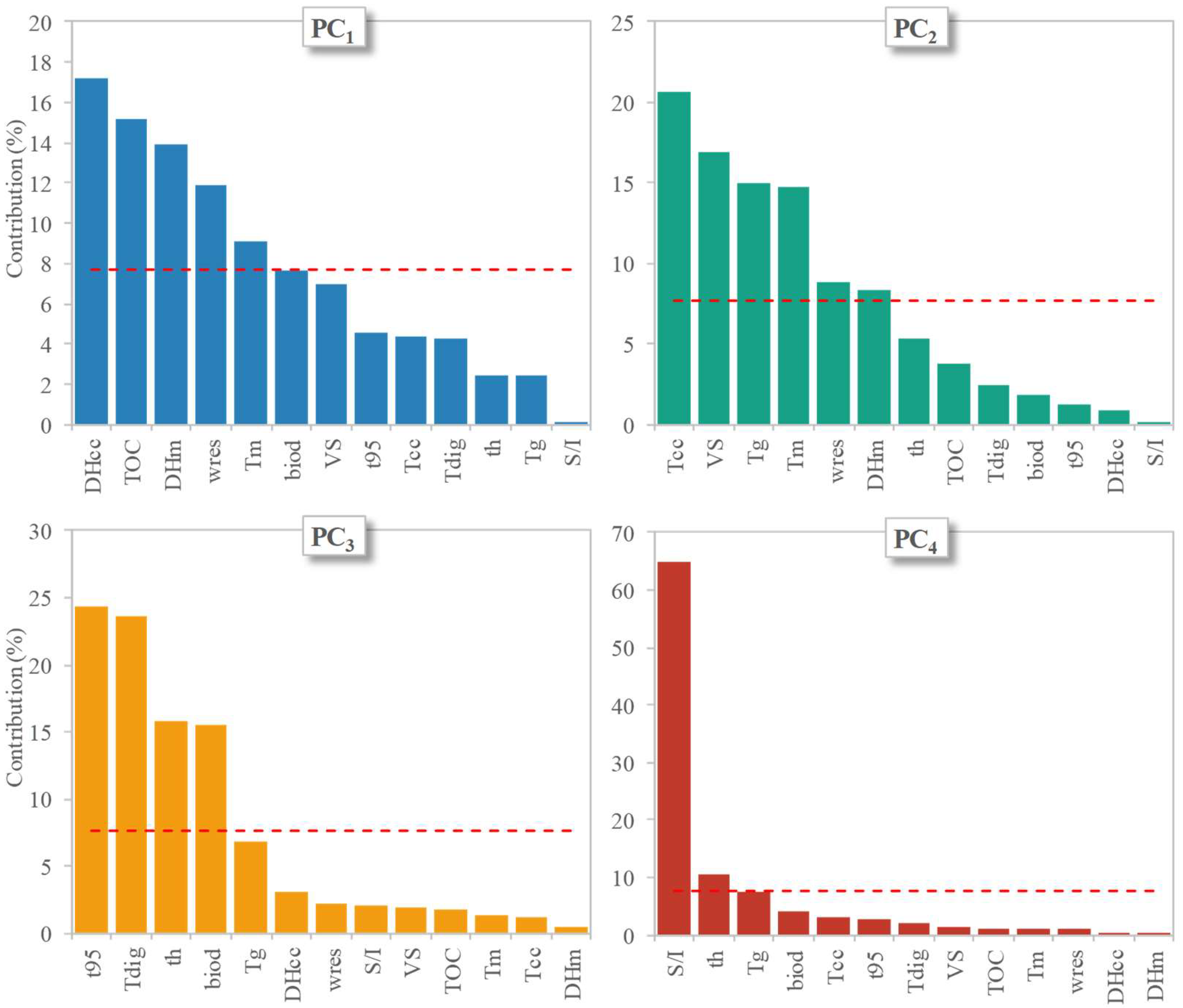
3.3. Statistical Analysis of Parameter Effects on Biodegradation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- European Bioplastics. Bioplastic Market Development Update 2024. Available online: http://www.european-bioplastics.org/news/publications (accessed on February 2025).
- Mehmood, A.; Raina, N.; Phakeenuya, V.; Wonganu, B.; Cheenkachorn, K. The Current Status and Market Trend of Polylactic Acid as Biopolymer: Awareness and Needs for Sustainable Development. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 72, 3049–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandakumar, A.; Chuah, J.A.; Sudesh, K. Bioplastics: A Boon or Bane? Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 147, 111237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, W.L.; Barbir, J.; Abubakar, I.R.; Paço, A.; Stasiskiene, Z.; Hornbogen, M.; Fendt, M.T.C.; Voronova, V.; Klõga, M. Consumer Attitudes and Concerns with Bioplastics Use: An International Study. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0266918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farah, S.; Anderson, D.G.; Langer, R. Physical and Mechanical Properties of PLA, and Their Functions in Widespread Applications—A Comprehensive Review. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 107, 367–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soodergard, A.; Stolt, M. Properties of Lactic Acid Based Polymers and Their Correlation with Composition. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2002, 27, 1123–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasal, R.M.; Janorkar, A.V.; Hirt, D.E. Poly(Lactic Acid) Modifications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2010, 35, 338–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Ma, P.; Hoch, M.; Arnoldi, E.; Cai, X.; Dong, W.; Chen, M. Transparent Blown Films from Poly(Lactide) and Poly(Ethylene-Co-Vinyl Acetate) Compounds: Structure and Property. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2016, 129, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangeetha, V.H.; Deka, H.; Varghese, T.O.; Nayak, S.K. State of the Art and Future Prospectives of Poly(Lactic Acid) Based Blends and Composites. Polym. Compos. 2018, 39, 81–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosli, N.A.; Karamanlioglu, M.; Kargarzadeh, H.; Ahmad, I. Comprehensive Exploration of Natural Degradation of Poly(Lactic Acid) Blends in Various Degradation Media: A Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 187, 732–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorrasi, G.; Pantani, R. Hydrolysis and Biodegradation of Poly(Lactic Acid). Adv. Polym. Sci. 2018, 279, 119–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husárová, L.; Pekařová, S.; Stloukal, P.; Kucharzcyk, P.; Verney, V.; Commereuc, S.; Ramone, A.; Koutny, M. Identification of Important Abiotic and Biotic Factors in the Biodegradation of Poly(l-Lactic Acid). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 71, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karamanlioglu, M.; Preziosi, R.; Robson, G.D. Abiotic and Biotic Environmental Degradation of the Bioplastic Polymer Poly(Lactic Acid): A Review. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2017, 137, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, N.; Bienaime, C.; Belloy, C.; Queneudec, M.; Silvestre, F.; Nava-Saucedo, J.E. Polymer Biodegradation: Mechanisms and Estimation Techniques—A Review. Chemosphere 2008, 73, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mistry, A.N.; Kachenchart, B.; Wongthanaroj, A.; Somwangthanaroj, A.; Luepromchai, E. Rapid Biodegradation of High Molecular Weight Semi-Crystalline Polylactic Acid at Ambient Temperature via Enzymatic and Alkaline Hydrolysis by a Defined Bacterial Consortium. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2022, 202, 110051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decorosi, F.; Exana, M.L.; Pini, F.; Adessi, A.; Messini, A.; Giovannetti, L.; Viti, C. The Degradative Capabilities of New Amycolatopsis Isolates on Polylactic Acid. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarerat, A.; Pranamuda, H.; Tokiwa, Y. Poly (l-Lactide)-Degrading Activity in Various Actinomycetes. Macromol. Biosci. 2002, 2, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhtar, S.; Zaheer, A.; Aiysha, D.; Abdulla Malik, K.; Mehnaz, S. Actinomycetes: A Source of Industrially Important Enzymes. J. Proteom. Bioinform. 2017, 10, 316–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emadian, S.M.; Onay, T.T.; Demirel, B. Biodegradation of Bioplastics in Natural Environments. Waste Manag. 2017, 59, 526–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, T.P.; Völker, C.; Kramm, J.; Landfester, K.; Wurm, F.R. Plastics of the Future? The Impact of Biodegradable Polymers on the Environment and on Society. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falzarano, M.; Marìn, A.; Cabedo, L.; Polettini, A.; Pomi, R.; Rossi, A.; Zonfa, T. Alternative End-of-Life Options for Disposable Bioplastic Products: Degradation and Ecotoxicity Assessment in Compost and Soil. Chemosphere 2024, 362, 142648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrò, P.S.; Grosso, M. Bioplastics and Waste Management. Waste Manag. 2018, 78, 800–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cazaudehore, G.; Guyoneaud, R.; Evon, P.; Martin-Closas, L.; Pelacho, A.M.; Raynaud, C.; Monlau, F. Can Anaerobic Digestion Be a Suitable End-of-Life Scenario for Biodegradable Plastics? A Critical Review of the Current Situation, Hurdles, and Challenges. Biotechnol. Adv. 2022, 56, 107916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falzarano, M.; Polettini, A.; Pomi, R.; Rossi, A.; Zonfa, T. Anaerobic Biodegradability of Commercial Bioplastic Products: Systematic Bibliographic Analysis and Critical Assessment of the Latest Advances. Materials 2023, 16, 2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, A.J.; Ávila, M.; Saenz, G.; Salazar, J. Crystallization of PLA-Based Materials. In Poly(lactic acid) Science and Technology: Processing, Properties, Additives and Applications; Jiménez, A., Peltzer, M., Ruseckaite, R., Eds.; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2015; ISBN 9781782624806. [Google Scholar]
- Kolstad, J.J.; Vink, E.T.H.; De Wilde, B.; Debeer, L. Assessment of Anaerobic Degradation of IngeoTM Polylactides under Accelerated Landfill Conditions. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2012, 97, 1131–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasmara, C.; Marchetti, R. Biogas Production from Biodegradable Bioplastics. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2016, 15, 2041–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazaudehore, G.; Monlau, F.; Gassie, C.; Lallement, A.; Guyoneaud, R. Active Microbial Communities during Biodegradation of Biodegradable Plastics by Mesophilic and Thermophilic Anaerobic Digestion. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 443, 130208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernat, K.; Kulikowska, D.; Wojnowska-Baryła, I.; Zaborowska, M.; Pasieczna-Patkowska, S. Thermophilic and Mesophilic Biogas Production from PLA-Based Materials: Possibilities and Limitations. Waste Manag. 2021, 119, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narancic, T.; Verstichel, S.; Reddy Chaganti, S.; Morales-Gamez, L.; Kenny, S.T.; De Wilde, B.; Babu Padamati, R.; O’Connor, K.E. Biodegradable Plastic Blends Create New Possibilities for End-of-Life Management of Plastics but They Are Not a Panacea for Plastic Pollution. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 10441–10452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaborowska, M.; Bernat, K.; Pszczółkowski, B.; Cydzik-Kwiatkowska, A.; Kulikowska, D.; Wojnowska-Baryła, I. Multi-Faceted Analysis of Thermophilic Anaerobic Biodegradation of Poly(Lactic Acid)-Based Material. Waste Manag. 2023, 155, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucina, M.; Soggia, G.; De Nisi, P.; Giordano, A.; Adani, F. Assessing the Anaerobic Degradability and the Potential Recovery of Biomethane from Different Biodegradable Bioplastics in a Full-Scale Approach. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 354, 127224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, A.; van-Eerten Jansen, M.C.A.A.; Acharya, B. Biodegradation of Bioplastic Using Anaerobic Digestion at Retention Time as per Industrial Biogas Plant and International Norms. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, S.R. Strategic Sustainability Assessment of Enhanced Anaerobic Digestion of Food and Bioplastic Waste for Municipalities. Ph.D. Thesis, Clemson University, Clemson, SC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Pantani, R.; Sorrentino, A. Influence of Crystallinity on the Biodegradation Rate of Injection-Moulded Poly(Lactic Acid) Samples in Controlled Composting Conditions. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2013, 98, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucina, M.; De Nisi, P.; Trombino, L.; Tambone, F.; Adani, F. Degradation of Bioplastics in Organic Waste by Mesophilic Anaerobic Digestion, Composting and Soil Incubation. Waste Manag. 2021, 134, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bracciale, M.P.; De Gioannis, G.; Falzarano, M.; Muntoni, A.; Polettini, A.; Pomi, R.; Rossi, A.; Sarasini, F.; Tirillò, J.; Zonfa, T. Anaerobic Biodegradation of Disposable PLA-Based Products: Assessing the Correlation with Physical, Chemical and Microstructural Properties. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 452, 131244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EN 13432; Packaging—Requirements for Packaging Recoverable Through Composting and Biodegradation—Test Scheme and Evaluation Criteria for the Final Acceptance of Packaging. European Committee for Standardisation (CEN): Brussels, Belgium, 2000.
- ISO 565:1990; Test Sieves—Metal Wire Cloth, Perforated Metal Plate and Electroformed Sheet; Nominal Sizes of Openings. International Organization for Standardization: London, UK, 2016.
- ISO 3310-1:2016; Test Sieves—Technical Requirements and Testing. Part 1: Test Sieves of Metal Wire Cloth. International Organization for Standardization: London, UK, 2016.
- ISO 14853:2016; Plastics—Determination of the Ultimate Anaerobic Biodegradation of Plastic Materials in an Aqueous System—Method by Measurement of Biogas Production. International Organization for Standardization: London, UK, 2016.
- American Public Health Association (APHA), American Water Works Association (AWWA), Water Environment Federation (WEF). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. In Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 24th ed.; APHA Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Beltrán, F.R.; Arrieta, M.P.; Moreno, E.; Gaspar, G.; Muneta, L.M.; Carrasco-Gallego, R.; Yáñez, S.; Hidalgo-Carvajal, D.; de la Orden, M.U.; Urreaga, J.M. Evaluation of the Technical Viability of Distributed Mechanical Recycling of PLA 3D Printing Wastes. Polymers 2021, 13, 1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, S.; Kamruddin, M.; Ajikumar, P.K.; Tyagi, A.K.; Raj, B. Nanocrystalline and Metastable Phase Formation in Vacuum Thermal Decomposition of Calcium Carbonate. Thermochim. Acta 2000, 363, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deghiche, A.; Haddaoui, N.; Zerriouh, A.; Fenni, S.E.; Cavallo, D.; Erto, A.; Benguerba, Y. Effect of the Stearic Acid-Modified TiO2 on PLA Nanocomposites: Morphological and Thermal Properties at the Microscopic Scale. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, Z.; Javadi, A.; Mohammadzadeh, F.; Alavi, K. Investigation on the Role of Nanoclay and Nano Calcium Carbonate on Morphology, Rheology, Crystallinity and mechanical properties of binary and ternary nanocomposites based on PLA. Int. J. Polym. Anal. Charact. 2020, 26, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomai, J.; Suksut, B.; Karl Schlarb, A. Crystallization Behavior of Poly(Lactic Acid)/Titanium Dioxide Nanocomposites. Appl. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2015, 8, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Harris, A.M.; Lee, E.C. Improving Mechanical Performance of Injection Molded PLA by Controlling Crystallinity. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 107, 2246–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrieta, M.P.; López, J.; Rayón, E.; Jiménez, A. Disintegrability under Composting Conditions of Plasticized PLA-PHB Blends. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2014, 108, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siracusa, V.; Blanco, I.; Romani, S.; Tylewicz, U.; Rocculi, P.; Rosa, M.D. Poly(Lactic Acid)-Modified Films for Food Packaging Application: Physical, Mechanical, and Barrier Behavior. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 125, E390–E401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrán, F.R.; de la Orden, M.U.; Lorenzo, V.; Pérez, E.; Cerrada, M.L.; Martínez Urreaga, J. Water-Induced Structural Changes in Poly(Lactic Acid) and PLLA-Clay Nanocomposites. Polymer 2016, 107, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kervran, M.; Vagner, C.; Cochez, M.; Ponçot, M.; Saeb, M.R.; Vahabi, H. Thermal Degradation of Polylactic Acid (PLA)/Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) Blends: A Systematic Review. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2022, 201, 109995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buswell, A.M.; Mueller, H.F. Mechanism of Methane Fermentation. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1952, 44, 550–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelidaki, I.; Alves, M.; Bolzonella, D.; Borzacconi, L.; Campos, J.L.; Guwy, A.J.; Kalyuzhnyi, S.; Jenicek, P.; Van Lier, J.B. Defining the Biomethane Potential (BMP) of Solid Organic Wastes and Energy Crops: A Proposed Protocol for Batch Assays. Water Sci. Technol. 2009, 59, 927–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holliger, C.; Alves, M.; Andrade, D.; Angelidaki, I.; Astals, S.; Baier, U.; Bougrier, C.; Buffière, P.; Carballa, M.; De Wilde, V.; et al. Towards a Standardization of Biomethane Potential Tests. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 74, 2515–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lê, S.; Josse, J.; Husson, F. FactoMineR: An R Package for Multivariate Analysis. J. Stat. Softw. 2008, 25, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassambara, A.; Mundt, F. Factoextra: Extract and Visualize the Results of Multivariate Data Analyses. R Package Version 1.0.7. 2020. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=factoextra (accessed on January 2024).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021; Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on January 2024).
- Cazaudehore, G.; Guyoneaud, R.; Lallement, A.; Gassie, C.; Monlau, F. Biochemical Methane Potential and Active Microbial Communities during Anaerobic Digestion of Biodegradable Plastics at Different Inoculum-Substrate Ratios. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 324, 116369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Ueda, T.; Ishigami, A.; Ito, H. Changes in Crystal Structure and Accelerated Hydrolytic Degradation of Polylactic Acid in High Humidity. Polymers 2021, 13, 4324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Castell, O.; Badia, J.D.; Ingles-Mascaros, S.; Teruel-Juanes, R.; Serra, A.; Ribes-Greus, A. Polylactide-Based Self-Reinforced Composites Biodegradation: Individual and Combined Influence of Temperature, Water and Compost. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2018, 158, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagi, H.; Ninomiya, F.; Funabashi, M.; Kunioka, M. Thermophilic Anaerobic Biodegradation Test and Analysis of Eubacteria Involved in Anaerobic Biodegradation of Four Specified Biodegradable Polyesters. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2013, 98, 1182–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Méndez, S.J.; Ramos-Suárez, J.L.; Ritter, A.; Mata González, J.; Camacho Pérez, Á. Anaerobic Digestion of Commercial PLA and PBAT Biodegradable Plastic Bags: Potential Biogas Production and 1H NMR and ATR-FTIR Assessed Biodegradation. Heliyon 2023, 9, e16691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Material | Type of Item | Thickness [μm] | TS (1) [%ww] | VS (2) [%ww] | TOC (3) [gC (kgTS)−1] | Hydrogen (4) [gH (kgTS)−1] | ThCH4 (5) [ml (gTOC)−1] | ThCO2 (5) [ml (gTOC)−1] | χ (6) [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inoculum | --- | --- | 6.4 ± 0.0 | 4.2 ± 0.0 | 29.1 ± 2.4 | n.a. (7) | --- | --- | --- |
| PLA1 | Cup | 205 | 99.6 ± 0.0 | 99.6 ± 0.0 | 530 ± 1.4 | 55.4 ± 0.1 | 952.8 | 915 | 37.5 |
| PLA2 | Plate | 257 | 99.6 ± 0.0 | 97 ± 0.0 | 484.4 ± 0.2 | 54.1 ± 0.2 | 913.4 | 954 | 0.5 |
| LACT | --- | --- | 77.5 ± 0.3 | 42.3 ± 0.3 | 317.9 ± 1.1 | 45.8 ± 0.7 | 933.9 | 933.9 | --- |
| Material | Mn [Da] | Mw [Da] | PDI |
|---|---|---|---|
| PLA1 | 81,500 | 165,200 | 2.028 |
| PLA2 | 66,200 | 145,000 | 2.204 |
| Run | Material Size [cm] | S/I Ratio [gVSsubstrate (gVSinoculum)−1] | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| PLA1_0.5_M | 1.5 × 1.5 | 0.5 | This study |
| PLA1_1_M | 1 | ||
| PLA1_2_M | 2 | ||
| PLA2_1_M | 1 | ||
| PLA1_ABIO_M | --- (abiotic) | ||
| PLA2_ABIO_M | --- (abiotic) | ||
| LACT_0.5_M | --- | 0.5 | This study |
| LACT_1_M | 1 | ||
| LACT_2_M | 2 | ||
| PLA1_0.5_T | 1.5 × 1.5 | 0.5 | [37] |
| PLA1_1_T | 1.5 × 1.5 | 1 | |
| PLA1_1pow_T | <0.1 | 1 | |
| PLA2_1_T | 1.5 × 1.5 | 1 | |
| PLA3_1_T | 1.5 × 1.5 | 1 | |
| PLA4_1_T | 1.5 × 1.5 | 1 |
| Run | Vnet [mL (gTOCPLA)−1] | BDbiogas [%] | BDTOC [%] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 38 °C a | 55 °C b | 38 °C a | 55 °C b | 38 °C a | 55 °C b | |
| PLA1_0.5 | 1162.9 ± 13.8 | 1654.8 ± 1.6 | 62.4 ± 0.7 | 93.1 ± 0.1 | 80.5 ± 1.3 | 91.7 ± 0.4 |
| PLA1_1 | 1281.0 ± 32.5 | 1638.8 ± 7.9 | 68.7 ± 1.7 | 89.1 ± 0.4 | 84.9 ± 0.6 | 90.7 ± 0.3 |
| PLA1_2 | 1404.1 ± 6.5 | --- | 75.2 ± 0.3 | --- | 87.8 ± 0.3 | --- |
| PLA2_1 | 1369.8 ± 2.7 | 1659.1 ± 24.8 | 73.4 ± 0.1 | 90.3 ± 1.3 | 88.9 ± 0.1 | 89.9 ± 0.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Falzarano, M.; Polettini, A.; Pomi, R.; Rossi, A.; Zonfa, T.; Bracciale, M.P.; Gabrielli, S.; Sarasini, F.; Tirillò, J. Anaerobic Biodegradation of Polylactic Acid-Based Items: A Specific Focus on Disposable Tableware Products. Materials 2025, 18, 1186. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18051186
Falzarano M, Polettini A, Pomi R, Rossi A, Zonfa T, Bracciale MP, Gabrielli S, Sarasini F, Tirillò J. Anaerobic Biodegradation of Polylactic Acid-Based Items: A Specific Focus on Disposable Tableware Products. Materials. 2025; 18(5):1186. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18051186
Chicago/Turabian StyleFalzarano, Marica, Alessandra Polettini, Raffaella Pomi, Andreina Rossi, Tatiana Zonfa, Maria Paola Bracciale, Serena Gabrielli, Fabrizio Sarasini, and Jacopo Tirillò. 2025. "Anaerobic Biodegradation of Polylactic Acid-Based Items: A Specific Focus on Disposable Tableware Products" Materials 18, no. 5: 1186. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18051186
APA StyleFalzarano, M., Polettini, A., Pomi, R., Rossi, A., Zonfa, T., Bracciale, M. P., Gabrielli, S., Sarasini, F., & Tirillò, J. (2025). Anaerobic Biodegradation of Polylactic Acid-Based Items: A Specific Focus on Disposable Tableware Products. Materials, 18(5), 1186. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18051186










