Sn Whisker Growth Mitigation by Modifying the Composition of the Solder Alloys: A Brief Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Early History of Tin Whiskers
1.2. Lead-Free Soldering
2. Sn Whisker Growth
3. Suppressing Whisker Growth in Lead-Free Alloys
3.1. Alloying
3.2. Composite Solder Alloys
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cobb, H.L. Cadmium whiskers. Monthly Rev. Am. Electroplaters Soc. 1946, 33, 28–30. [Google Scholar]
- Compton, K.G.; Mendizza, A.; Arnold, S.M. Filamentary growths on metal surfaces–“whiskers”. Corrosion 1951, 7, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chason, E.; Jadhav, N.; Pei, F.; Buchovecky, E.; Bower, A. Growth of whiskers from Sn surfaces: Driving forces and growth mechanisms. Prog. Surf. Sci. 2013, 88, 103–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NASA NEPP. Available online: https://nepp.nasa.gov/whisker/reference/tech_papers/brusse2003-metal-whisker-discussion.pdf (accessed on 23 January 2025).
- Arnold, S.M. The growth of metal whiskers on electrical components. In Proceedings Electronic Components Conference; Bell Telephone Laboratories, Inc.: Murray Hill, NJ, USA, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham, K.M.; Donahue, M.P. Tin whiskers: Mechanism of growth and prevention. In Proceedings of the 4th International SAMPE Electronics Conference, Albuquerque, NM, 12–14 June 1990; pp. 569–575. [Google Scholar]
- Diehel, R.P. Significant characteristics of tin and tin-lead contact electrodeposits for electronic connectors. Met. Finish. 1993, 91, 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- National Measurement Office (NMO). Available online: www.bis.gov.uk/nmo/enforcement (accessed on 23 January 2025).
- Warwick, M. Implementing lead free soldering-European consortium research. J. Surf. Mt. Technol. 1999, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, C.; Abys, J.; Hopkins, L.; Stevie, F. Understanding whisker phenomenon: The driving force for whisker formation. CircuiTree(USA) 2002, 15, 10. [Google Scholar]
- IPC International. Available online: https://www.ipc.org/system/files/technical_resource/E17%26S36-1.pdf (accessed on 23 January 2025).
- EUR-Lex. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/2002/95/oj/eng (accessed on 23 January 2025).
- Wu, C.M.L.; Yu, D.Q.; Law, C.M.T.; Wang, L. Properties of lead-free solder alloys with rare earth element additions. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2004, 44, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abtew, M.; Selvadury, G. Lead-free solders in microelectronics. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2000, 27, 95–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Shen, J.; Min, D.; Peng, C. Influence of minor Bi additions on the interfacial morphology between Sn–Zn–x Bi solders and a Cu layer. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2009, 20, 1112–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; He, C.; Guo, Y.; Han, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X. Development of Sn–Zn lead-free solders bearing alloying elements. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2010, 21, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, K.; Tu, K.-N. Six cases of reliability study of Pb-free solder joints in electronic packaging technology. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2002, 38, 55–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotadia, H.R.; Howes, P.D.; Mannan, S.H. A review: On the development of low melting temperature Pb-free solders. Microelectron. Reliab. 2014, 54, 1253–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.-C. Getting ready for lead-free solders. Solder. Surf. Mt. Technol. 1997, 9, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, N.M.; Khan, N.B.; Bashir, S.; Khan, A.F.; Quazi, M.M.; Gul, M.; Wakeel, S.; Saad, H.M. Effect of Zn nanoparticle-doped flux on mechanical properties of SAC305 solder joint after electromigration. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2023, 34, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JEITA. Available online: https://home.jeita.or.jp/tss/jisso_eas/english/data/Guidance%202004.6.21.pdf (accessed on 23 January 2025).
- Sharma, M.M.; Kumar, K.; Sang, L.; Wang, X.L.; Awana, V.P.S. Type-II superconductivity below 4K in Sn0.4Sb0.6. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 844, 156140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Sharma, P.; Gurjar, G.; Patnaik, S.; Awana, V.P.S. Structural and superconducting analysis of topologically non-trivial alloy of Sn1-xSbx (x = 0.4, 0.5, 0.6). J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2021, 156, 110136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choquette, S. Liquid-Phase Diffusion Bonding and the Development of a Cu-Ni/Sn Composite Solder Paste for High Temperature Lead-Free Electrical Connections. Ph.D. Thesis, Iowa State University, Ames, IA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.S.; Huh, S.H.; Suganuma, K. Effects of intermetallic compounds on properties of Sn–Ag–Cu lead-free soldered joints. J. Alloys Compd. 2003, 352, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Chang, Y.; Chen, C. Sn-Zn/Ni-Co Interfacial Reactions at 250 °C. J. Electron. Mater. 2014, 43, 3333–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikale, S.; Narayan, P.K. Bond shear strength of Al2O3 nanoparticles reinforced 2220-capacitor/SAC305 solder interconnects reflowed on bare and Ni-coated copper substrate. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2021, 32, 2865–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, C.H.; Suganuma, K.; Lee, J.G.; Mori, H. Interfacial microstructure between Sn-3Ag-xBi alloy and Cu substrate with or without electrolytic Ni plating. J. Electron. Mater. 2003, 32, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, C.; Abys, J.A. Driving force for the formation of Sn whiskers: Compressive stress-pathways for its generation and remedies for its elimination and minimization. IEEE Trans. Electron. Packag. Manuf. 2005, 28, 31–35. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, M.; Su, P.; Chopin, S. Effects of trim and form on the microstructure and whisker growth propensity of Sn finish. In Proceedings Electronic Components and Technology, 2005. ECTC’05; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 452–456. [Google Scholar]
- Smetana, J. Theory of tin whisker growth: “The end game”. IEEE Trans. Electron. Packag. Manuf. 2007, 30, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, T.-H.; Chi, C.-C. Effect of adding Ge on rapid whisker growth of Sn–3Ag–0.5 Cu–0.5 Ce alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 480, 974–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, T.-H.; Jain, C.-C. Morphology of the Tin Whiskers on the Surface of a Sn-3Ag-0.5 Cu-0.5 Nd Alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2011, 42, 684–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanda, I. Electroplating of lead-free solder alloys composed of Sn-Bi and Sn-Ag. In Proceedings of the IPC Printed Circuits Expo, Long Beach, CA, USA, 26–30 April 1998; pp. 457–467. [Google Scholar]
- Illés, B.; Skwarek, A.; Hurtony, T.; Krammer, O.; Medgyes, B.; Szostak, K.; Harsányi, G.; Kovács, A.; Pécz, B. Risk of transition to lead-free in the space sector: Sn whisker growth in thermal vacuum conditions from submicron Sn layer. Mater. Des. 2025, 250, 113637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boettinger, W.J.; Johnson, C.E.; Bendersky, L.A.; Moon, K.-W.; Williams, M.E.; Stafford, G.R. Whisker and hillock formation on Sn, Sn–Cu and Sn–Pb electrodeposits. Acta Mater. 2005, 53, 5033–5050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, H.; Lucas, J.P.; Subramanian, K.N. Micromechanical characterization of thermomechanically fatigued lead-free solder joints. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2002, 13, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Chawla, N.; Chawla, K.K.; Koopman, M. Deformation behavior of (Cu, Ag)–Sn intermetallics by nanoindentation. Acta Mater. 2004, 52, 4291–4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, F.; Jadhav, N.; Buchovecky, E.; Bower, A.F.; Chason, E.; Liu, W.; Tischler, J.Z.; Ice, G.E.; Xu, R. In-situ synchrotron micro-diffraction study of surface, interface, grain structure, and strain/stress evolution during Sn whisker/hillock formation. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 119, 105302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, F.; Chason, E. In Situ Measurement of Stress and Whisker/Hillock Density During Thermal Cycling of Sn Layers. J. Electron. Mater. 2014, 43, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batzill, M.; Diebold, U. The surface and materials science of tin oxide. Prog. Surf. Sci. 2005, 79, 47–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannetier, J.; Denes, G. Tin (II) oxide: Structure refinement and thermal expansion. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. B Struct. Crystallogr. Cryst. Chem. 1980, 36, 2763–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolzan, A.A.; Fong, C.; Kennedy, B.J.; Howard, C.J. Structural studies of rutile-type metal dioxides. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. B Struct. Sci. 1997, 53, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osenbach, J.W.; DeLucca, J.M.; Potteiger, B.D.; Amin, A.; Shook, R.L.; Baiocchi, F.A. Sn corrosion and its influence on whisker growth. IEEE Trans. Electron. Packag. Manuf. 2007, 30, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JEDEC. Current Tin Whisker Theory and Mitigation Practices Guideline; JP002; JEDEC Solid State Technology Association: Arlington, VA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder, V.; Bush, P.; Williams, M.; Vo, N.; Reynolds, H.L. Tin whisker test method development. IEEE Trans. Electron. Packag. Manuf. 2006, 29, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, P.; Howell, J.; Chopin, S. A statistical study of Sn whisker population and growth during elevated temperature and humidity tests. IEEE Trans. Electron. Packag. Manuf. 2006, 29, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, B.; Shinohara, T.; Illés, B. Corrosion properties of tin–copper alloy coatings in aspect of tin whisker growth. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 577, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, J.H.; Pan, S.H.; Chen, X.A. 3D large deformation and nonlinear stress analyses of tin whisker initiation and growth on lead-free components. In Proceedings of the 53rd Electronic Components and Technology Conference, New Orleans, LA, USA, 27–30 May 2003, Proceedings; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2003; pp. 692–697. [Google Scholar]
- Illés, B.; Hurtony, T.; Medgyes, B.; Krammer, O.; Dusek, K.; Busek, D. Sn and Bi whisker growth from SAC0307-Mn07 and SAC0307-Bi1-Mn07 ultra-thin film layers. Vacuum 2021, 187, 110121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Daly, A.A.; El-Taher, A.M.; Gouda, S. Development of new multicomponent Sn–Ag–Cu–Bi lead-free solders for low-cost commercial electronic assembly. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 627, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, B.; Sabri, M.F.M.; Said, S.M.; Sukiman, N.L.; Jauharia, I.; Mahdavifard, M.H. Microstructural and tensile properties of Fe and Bi added Sn-1Ag-0.5 Cu solder alloy under high temperature environment. Microelectron. Reliab. 2018, 82, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavifard, M.H.; Sabri, M.F.M.; Said, S.M.; Rozali, S. High stability and aging resistance Sn-1Ag-0.5 Cu solder alloy by Fe and Bi minor alloying. Microelectron. Eng. 2019, 208, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, S.D.; Majumdar, B.S.; Dutta, I.; Bhassyvasantha, S. Elimination of whisker growth in electroplated tin coatings by indium addition. J. Electron. Mater. 2016, 46, 4062–4075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, S.D.; Dutta, I. Co-electrodeposition of tin with 0.2–20% indium: Implications on tin whisker growth. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 337, 478–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, P.; Liu, P.; Liu, J. Effects of multiple reflows on intermetallic morphology and shear strength of SnAgCu–xNi composite solder joints on electrolytic Ni/Au metallized substrate. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 462, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Yi, D.; Wang, H.; Tu, X.; Wang, B. Microstructure, mechanical properties, and interfacial reaction with Cu substrate of Zr-modified SAC305 solder alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 781, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziami, N.S.M.; Salleh, M.A.A.M.; Sandu, A.V.; Abdullah, M.M.A.B.; Saud, N.; Rahim, S.Z.A.; Vizureanu, P.; Said, R.M.; Ramli, M.I.I. Performance of sn-3.0 ag-0.5 cu composite solder with kaolin geopolymer ceramic reinforcement on microstructure and mechanical properties under isothermal ageing. Materials 2021, 14, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.W.; Kao, C.R. Minor Fe, Co, and Ni additions to SnAgCu solders for retarding Cu3Sn growth. In Proceedings of the 2008 International Conference on Electronic Materials and Packaging, Taipei, Taiwan, 22–24 October 2008; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2008. pp. 76–79.
- Wu, J.; Xue, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, S. Effect of Pr addition on properties and Sn whisker growth of Sn–0.3Ag–0.7Cu low-Ag solder for electronic packaging. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2017, 28, 10230–10244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Xue, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, J. Comparative studies on microelectronic reliability issue of Sn whisker growth in Sn-0.3Ag-0.7Cu-1Pr solder under different environments. Microelectron. Reliab. 2017, 79, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Sun, L.; Han, J.; Guo, Y. Sizes effect of CeSn3 on the whiskers growth of SnAgCuCe solder joints in electronic packaging. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2015, 26, 6194–6197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, T.-H. Rapid whisker growth on the surface of Sn–3Ag–0.5Cu–1.0Ce solder joints. Scr. Mater. 2006, 55, 983–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarobol, P.; Pedigo, A.; Blendell, J.; Handwerker, C.A. Synchrotron micro-diffraction investigation of crystallographic texture of high-Sn alloy films and its effects on whisker growth. In Proceedings of the 2010 Proceedings 60th Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 1–4 June 2010; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 162–169. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, M.E.; Moon, K.W.; Boettinger, W.J.; Josell, D.; Deal, A.D. Hillock and whisker growth on Sn and SnCu electrodeposits on a substrate not forming interfacial intermetallic compounds. J. Electron. Mater. 2007, 36, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, S.H.; Hwang, S.J.; Jung, J.P. Shear strength and aging characteristics of Sn-3.0 Ag-0.5 Cu/Cu solder joint reinforced with ZrO2 nanoparticles. Metals 2020, 10, 1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gain, A.K.; Zhang, L. Microstructure, mechanical and electrical performances of zirconia nanoparticles-doped tin-silver-copper solder alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2016, 27, 7524–7533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, N.; Zhang, L.; Zhong, S. Materials modification of the lead-free solders incorporated with micro/nano-sized particles: A review. Mater. Des. 2021, 197, 109224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, H.; Zhou, Y.; Song, X.; Hu, S.; Shi, B.; Kang, J.; Feng, J. Reactive wetting and interfacial characterization of ZrO2 by SnAgCu-Ti alloy. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 6730–6737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, K.; Wu, Y.; Wang, B. Strengthening mechanism of Ni-modified graphene nanosheets reinforced SnAgCuRE composite solder/Cu joints. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2021, 32, 28695–28707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Liu, Y.C.; Han, Y.J.; Tian, Y.M.; Gao, H.X. Strengthening effects of ZrO2 nanoparticles on the microstructure and microhardness of Sn-3.5 Ag lead-free solder. J. Electron. Mater. 2006, 35, 1672–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wu, Y. Main application limitations of lead-free composite solder doped with foreign reinforcements. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2021, 32, 24644–24660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.J.; Zhang, L.; Chen, C.; Lu, X. Thermal, microstructural, wettability and mechanical properties of Sn1.0Ag0.5Cu composite solder modified with Ti nanoparticles. Mater. Charact. 2024, 212, 113927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salleh, M.A.A.M.; Mcdonald, S.D.; Nogita, K. Effects of Ni and TiO2 additions in as-reflowed and annealed Sn0. 7Cu solders on Cu substrates. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2017, 242, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wodak, I.; Yakymovych, A.; Svec, P.; Orovcik, L.; Khatibil, G. Hybrid solder joints: The effect of nanosized ZrO2 particles on morphology of as-reflowed and thermally aged Sn–3.5 Ag solder joints. Appl. Nanosci. 2023, 13, 7379–7385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, E.A.; Fouda, A.N.; Duraia, E.-S.M. Effect of adding 0.5 wt% ZnO nanoparticles, temperature and strain rate on tensile properties of Sn–5.0 wt% Sb–0.5 wt% Cu (SSC505) lead free solder alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 657, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, R.; Gao, Y.; Wen, J.; Lin, P.; Xu, S.; Tian, Y. Improved shear property of Sn-3.0 Ag-0.5 Cu/Ni micro solder joints under thermal shock between 77 K and 423 K by adding TiO2 nanoparticles. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 29, 5034–5047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Liu, L.; Silberschmidt, V.V.; Chan, Y.; Liu, C.; Wu, F. Retained ratio of reinforcement in SAC305 composite solder joints: Effect of reinforcement type, processing and reflow cycle. Solder. Surf. Mt. Technol. 2016, 28, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Xue, S.; Wang, J.; Xue, P.; Zhong, S.; Long, W. Effect of nanoparticles addition on the microstructure and properties of lead-free solders: A review. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Zhao, X.; Chen, Z.; Gu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, X. Reliability enhancement of Sn-1.0 Ag-0.5 Cu nano-composite solders by adding multiple sizes of TiO2 nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 696, 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Song, L.; Gao, H.; Xiao, Y.; Cao, Y. Microstructure evolution and grain refinement of ultrasonic-assisted soldering joint by using Ni foam reinforced Sn composite solder. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2023, 92, 106244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zuo, Y.; Liu, S.; Guo, F.; Lee, A.; Subramanian, K.N. Whisker growth behaviors in POSS-silanol modified Sn3.0Ag0.5Cu composite solders. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 657, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.; Subramanian, K.N.; Lee, J.-G. Development of nanocomposite lead-free electronic solders. In Proceedings. International Symposium on Advanced Packaging Materials: Processes, Properties and Interfaces, 2005; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 276–281. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.; Peng, C.; Yin, H.G.; Chen, J. Influence of minor POSS molecules additions on the microstructure and hardness of Sn3Ag0.5Cu–xPOSS composite solders. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2012, 23, 1640–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illés, B.; Choi, H.; Hurtony, T.; Dušek, K.; Bušek, D.; Skwarek, A. Suppression of Sn whisker growth from SnAgCu solder alloy with TiO2 and ZnO reinforcement nano-particles by increasing the corrosion resistance of the composite alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 20, 4231–4240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
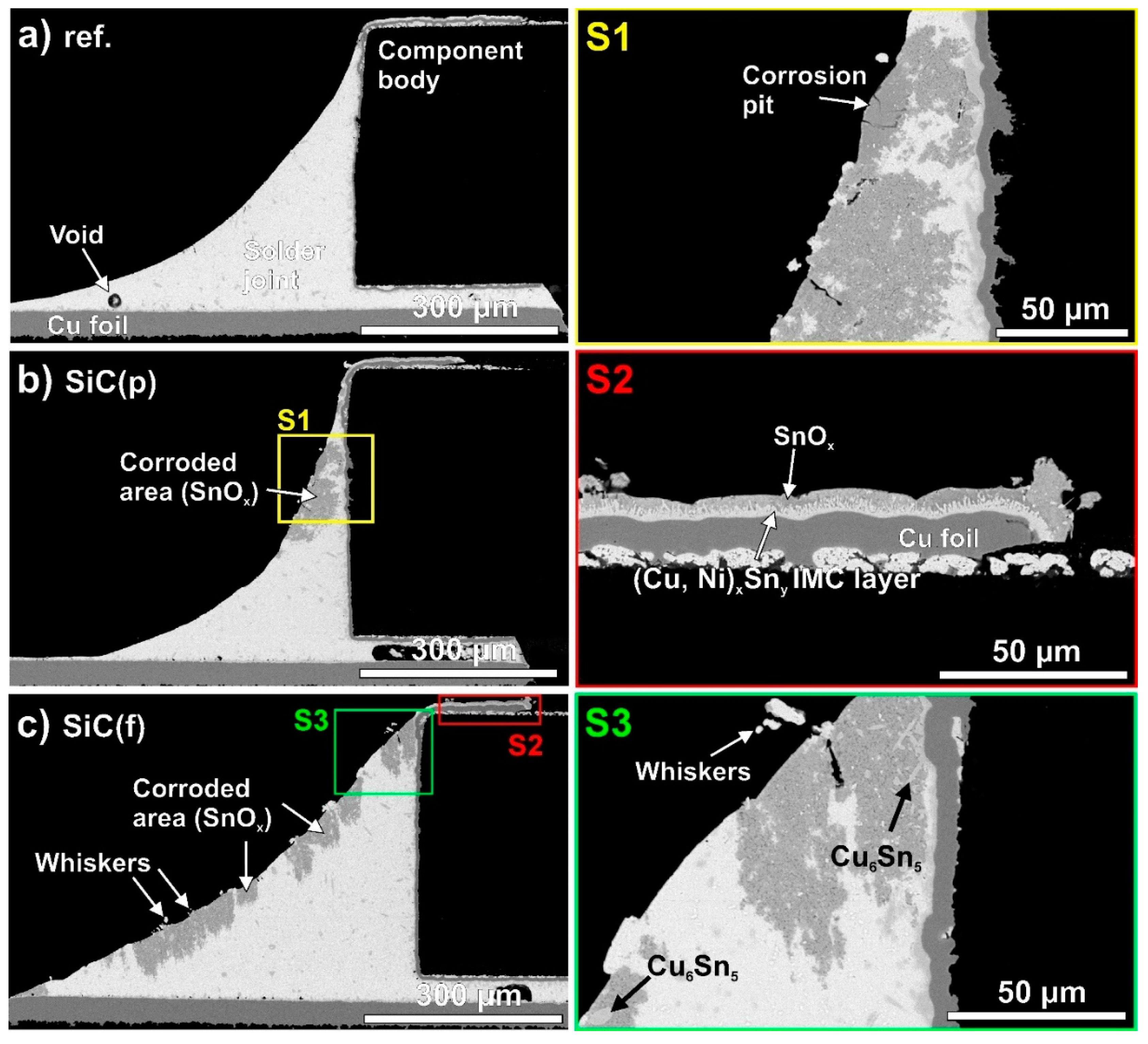
- Choi, H.; Illés, B.; Hurtony, T.; Byun, J.; Géczy, A.; Skwarek, A. Corrosion problems of SAC-SiC composite solder alloys. Corros. Sci. 2023, 224, 111488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illés, B.; Choi, H.; Szostak, K.; Byun, J.; Skwarek, A. Effects of CuO nanoparticles on SAC composite solder joints: Microstructural and DFT study. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 32, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skwarek, A.; Choi, H.; Hurtony, T.; Byun, J.; Mohamad, A.A.; Bušek, D.; Dušek, K.; Illés, B. Effects of ZrO2 Nano-Particles’ Incorporation into SnAgCu Solder Alloys: An Experimental and Theoretical Study. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Xuem, S.; Wang, J.; Wu, M. Coupling effects of rare-earth Pr and Al2O3 nanoparticles on the microstructure and properties of Sn-0.3Ag-0.7Cu low-Ag solder. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 784, 471–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illés, B.; Choi, H.; Byun, J.; Dušek, K.; Bušek, D.; Skwarek, A. Incorporation and corrosion protection mechanism of TiO2 nano-particles in SnAgCu composite alloys: Experimental and density functional theory study. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 23765–23774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nai, S.M.L.; Kuma, J.V.M.; Alam, M.E.; Zhong, X.L.; Babaghorbani, P.; Gupta, M. Using microwave-assisted powder metallurgy route and nano-size reinforcements to develop high-strength solder composites. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2010, 19, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nai, S.M.L.; Wei, J.; Gupte, M. Improving the performance of lead-free solder reinforced with multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 423, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Yang, W.; Song, Q.; Lv, Y.; Jiang, S.; Li, Y.; Zhan, Y. The effects of the addition of CNT@ Ni on the hardness, density, wettability and mechanical properties of Sn-0.7 Cu lead-free solder. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2021, 32, 10843–10854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, S.H.; Seo, S.M.; Juing, J.; Jae, P. Effect of 0D and 1D ZnO nano additive reinforced Sn-3.0 Ag-0.5 Cu solder paste on InGaN LED chip/ENIG joints. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 35, 105795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
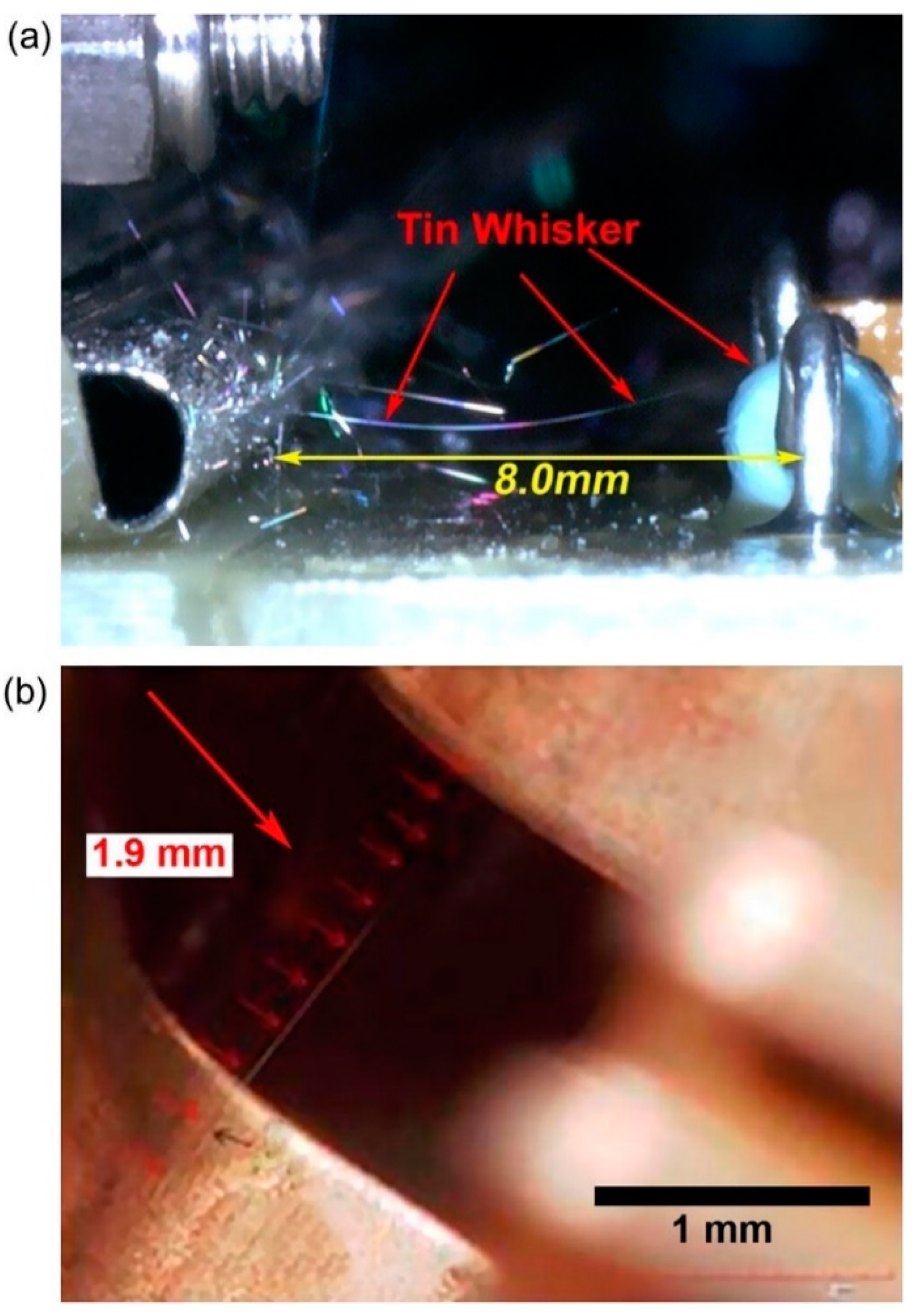
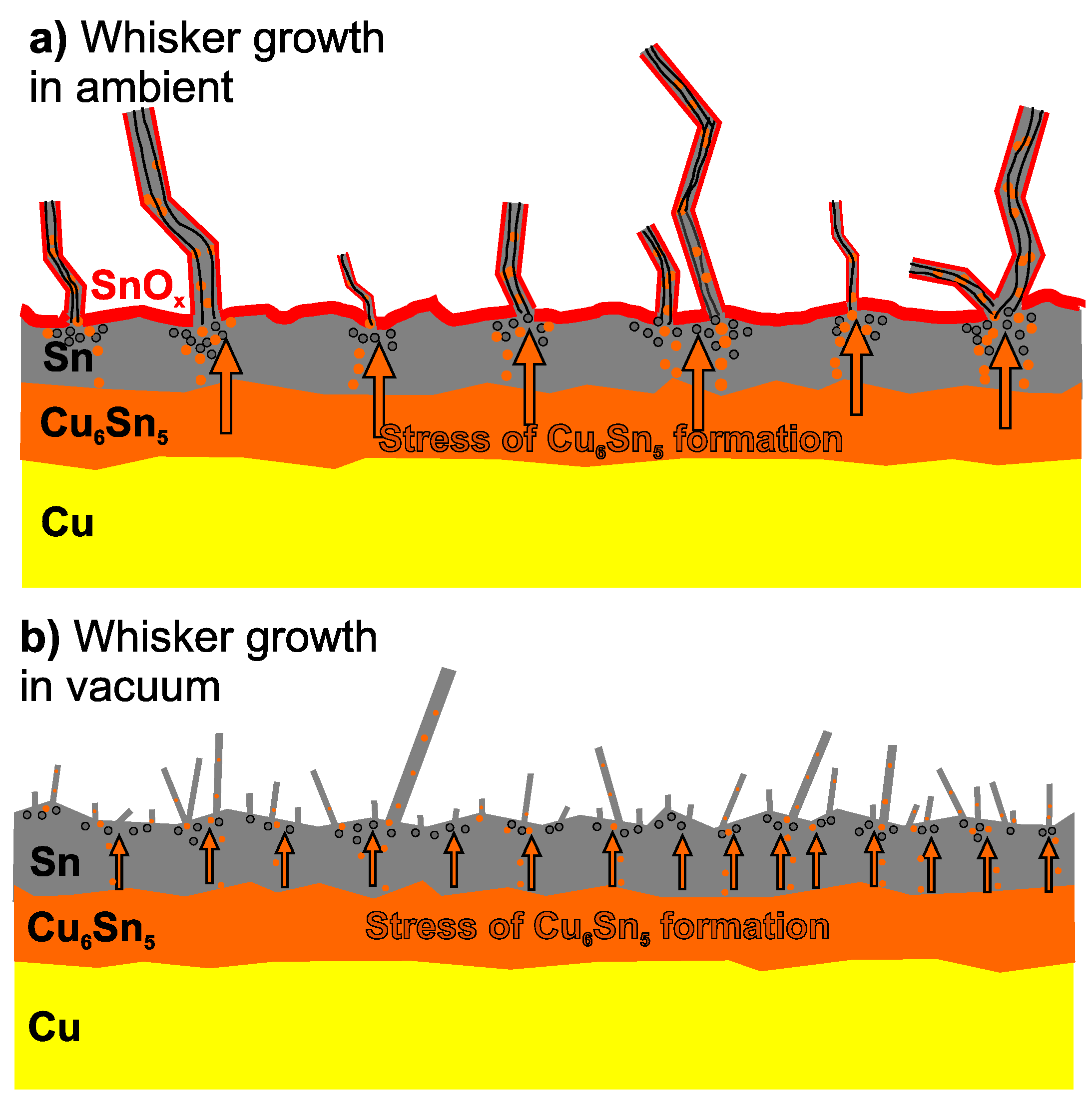

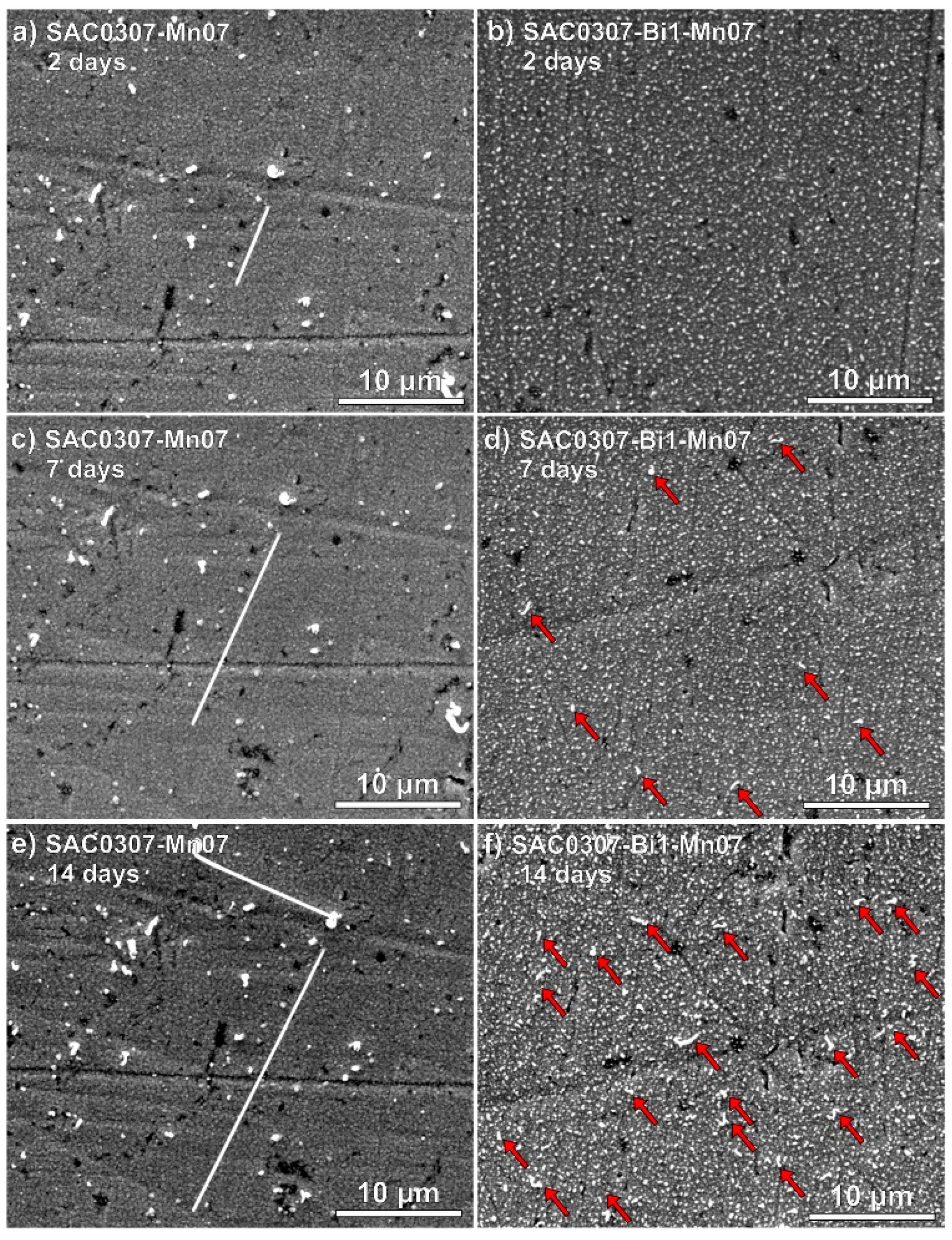





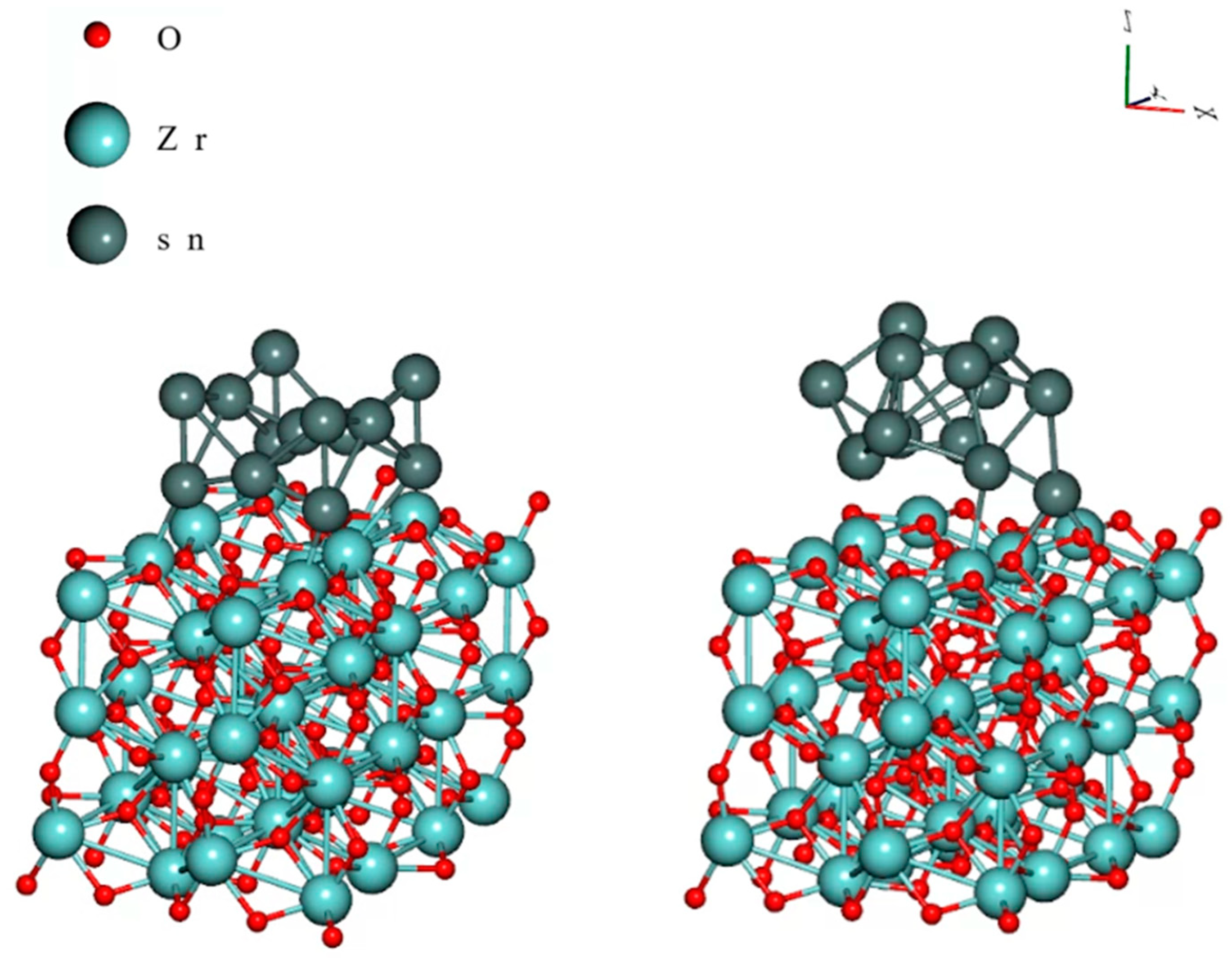
| Year | Application Title 2 | Sector Title 3 | Whisker Place |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1986 | Heart Pacemakers | Medical | Crystal Can |
| 1986 | MIL Aircraft Radar | Military | Hybrid Package Lid |
| 1987 | MI:/Aerospace PWB | MIL/Aerospace | PCB Traces |
| 1988 | Missile Program “B” | Military | Electronic Enclosure |
| 1993 | Govt. Electronics | Govt. Systems | Transistor |
| 1998 | Commercial Satellite | Space | Relays |
| 2000 | Missile Program “D” | Military | Terminals |
| 2000 | Power Mgmt. Modules | Industrial | Connectors |
| 2001 | Hi-Rel | Hi-Rel | Ceramic Chip Cap |
| 2002 | Electric Power Plant | Power | Microcircuit Leads |
| 2002 | GPS Receiver | Aeronautical | RF Enclosure |
| 2003 | Telecom Equipment | Telecom | Ckt Breaker |
| Element | Technology | Effect | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | alloying | Suppressing whisker growth; decreasing the melting temperature | [5,6,7,28,30] |
| Ag | alloying | Neutral effect on whisker growth; forming Ag3Sn IMC, no effect on whiskers | [18,19,20,25] |
| Cu | alloying | Forming Cu6Sn5 (one root cause of whisker growth) and Cu3Sn IMCs | [18,19,20,26,27,28,36,37,38,39] |
| Ni | alloying | Neutral effect on whisker growth; forming Ni3Sn4, Ni3Sn2, and Ni3Sn IMCs; increased shear strength | [56] |
| Bi | alloying | Suppressing whisker growth; decreasing the melting temperature, and improving mechanical parameters | [50,51,52,53] |
| Mn | alloying | Neutral effect on whisker growth; increasing the melting temperature | [50] |
| In | alloying | Suppress whisker growth, decreasing the melting temperature | [54,55] |
| Zr | alloying | Neutral effect on whisker growth; reducingβ-Sn grains | [57] |
| Fe | alloying | Neutral effect on whisker growth; forming Fe2Sn reaction layer | [58,59] |
| Co | alloying | Neutral effect on whisker growth; forming CoSn2 IMC | [59] |
| Cr | alloying | Neutral effect on whisker growth; some mechanical improvements | [44] |
| Pr | alloying | Enhancing wettability, shear force, and ductility; forming PrSn3 causes whisker growth | [60,61] |
| Ce | alloying | Forming CeSn3 and oxidation causes whisker growth | [62,63] |
| POSS-silanol | nanoparticles | Suppressing whisker growth; improving the mechanical parameters | [82,84] |
| TiO2 | nanoparticles | Suppressing whisker growth; improving the mechanical and corrosion parameters | [74,77,80,85,90] |
| ZnO | nanoparticles | Suppressing whisker growth; improving the mechanical and corrosion parameters | [76,85,94] |
| SiC | nanoparticles | Enhancing whisker growth; improving the mechanical but decreasing the corrosion parameters | [86] |
| CuO | nanoparticles | Enhancing whisker growth; improving the mechanical but decreasing the corrosion parameters | [87] |
| ZrO2 | nanoparticles | Enhancing whisker growth; improving the mechanical but decreasing the corrosion parameters | [67,69,71,88] |
| Al2O3 | nanoparticles | Enhancing whisker growth; improving the mechanical and wetting parameters | [27,89] |
| MWCNT | nanoparticles | Neutral effect on whisker growth; improving the mechanical parameters | [91,92] |
| CNT | nanoparticles | Neutral effect on whisker growth; improving the mechanical parameters | [93] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, H.; Illés, B.; Dušek, K. Sn Whisker Growth Mitigation by Modifying the Composition of the Solder Alloys: A Brief Review. Materials 2025, 18, 1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18051130
Choi H, Illés B, Dušek K. Sn Whisker Growth Mitigation by Modifying the Composition of the Solder Alloys: A Brief Review. Materials. 2025; 18(5):1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18051130
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Halim, Balázs Illés, and Karel Dušek. 2025. "Sn Whisker Growth Mitigation by Modifying the Composition of the Solder Alloys: A Brief Review" Materials 18, no. 5: 1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18051130
APA StyleChoi, H., Illés, B., & Dušek, K. (2025). Sn Whisker Growth Mitigation by Modifying the Composition of the Solder Alloys: A Brief Review. Materials, 18(5), 1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18051130






