Thermal Stability and Irradiation Resistance of (CrFeTiTa)70W30 and VFeTiTaW High Entropy Alloys
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
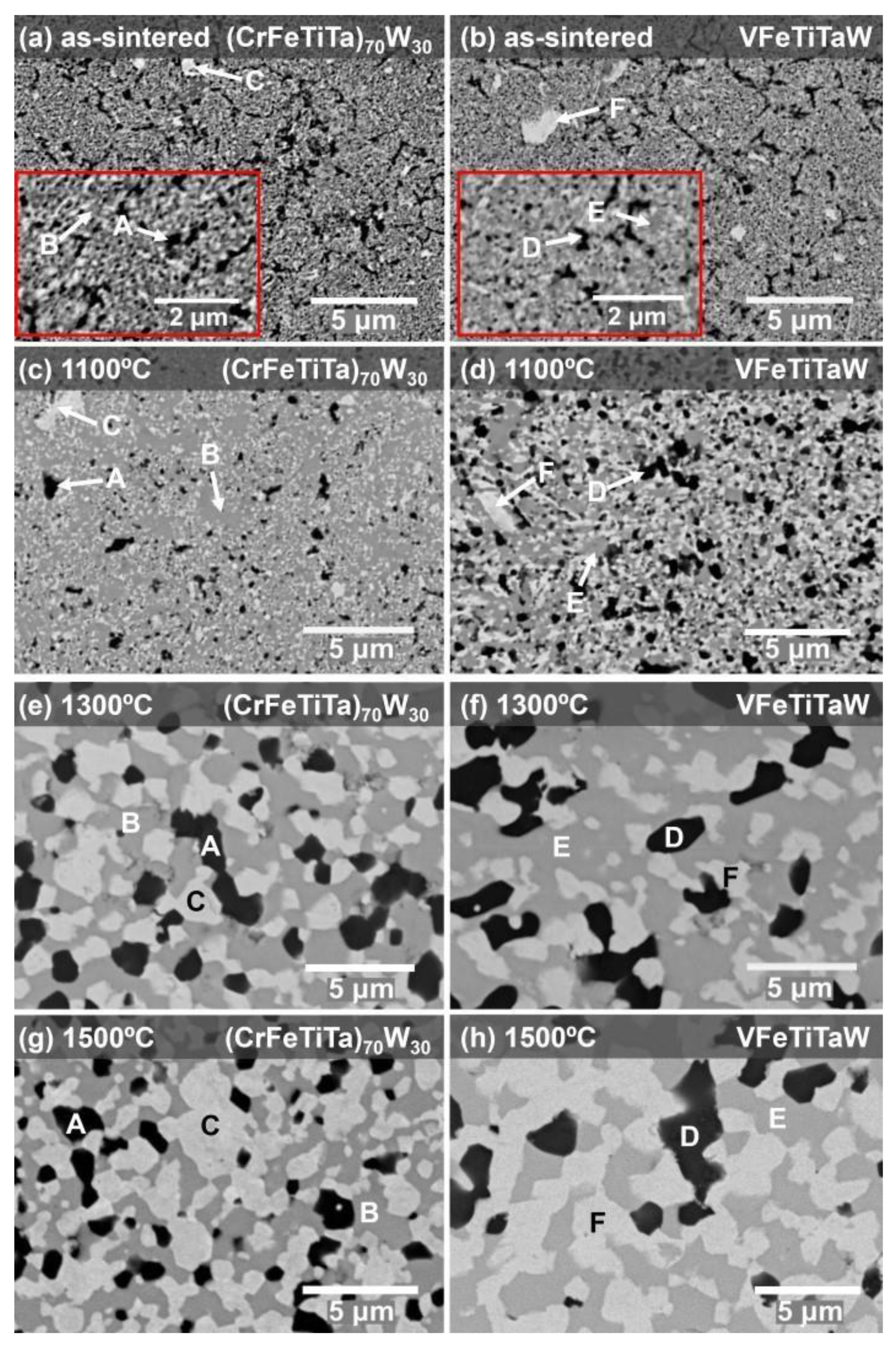
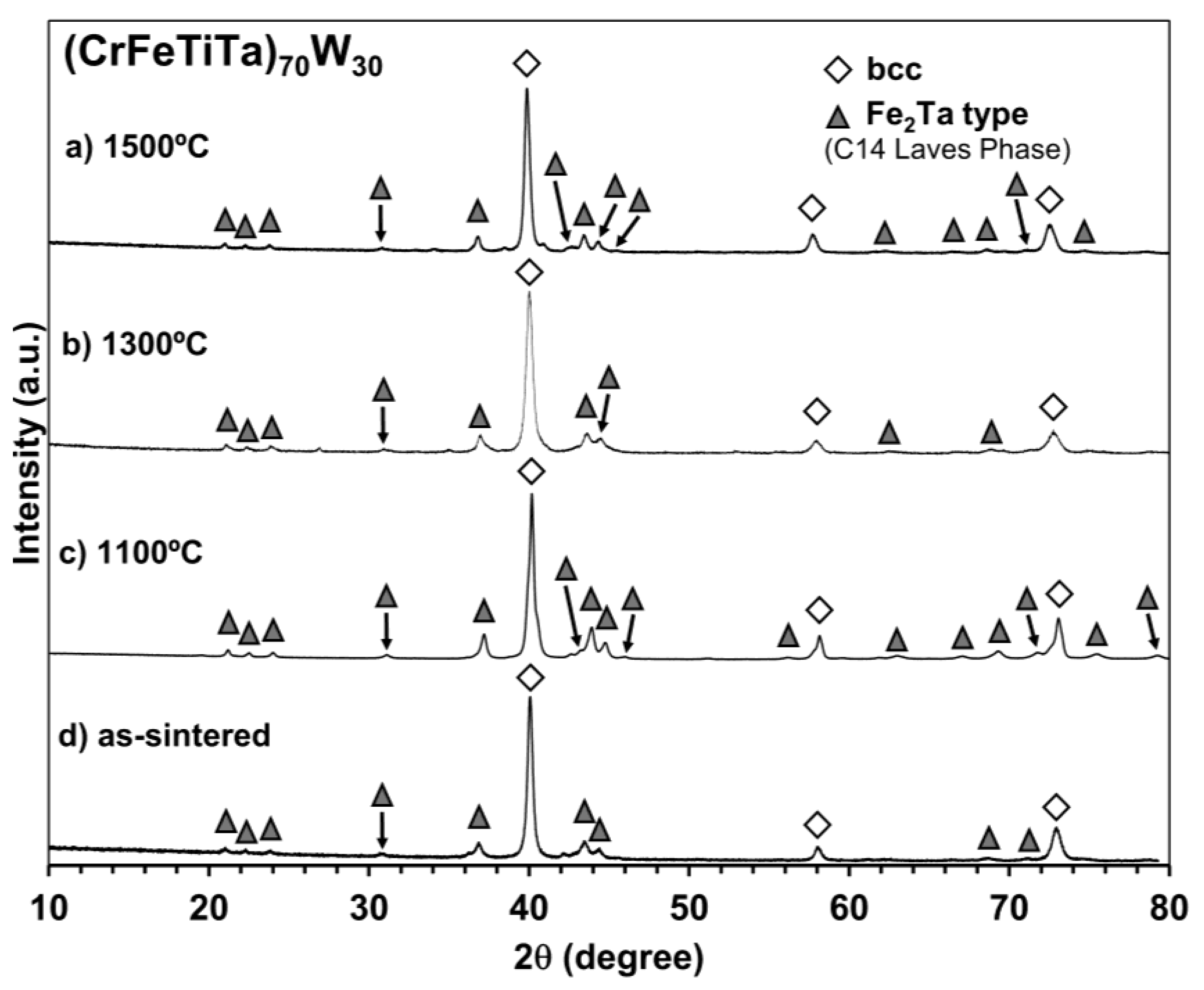
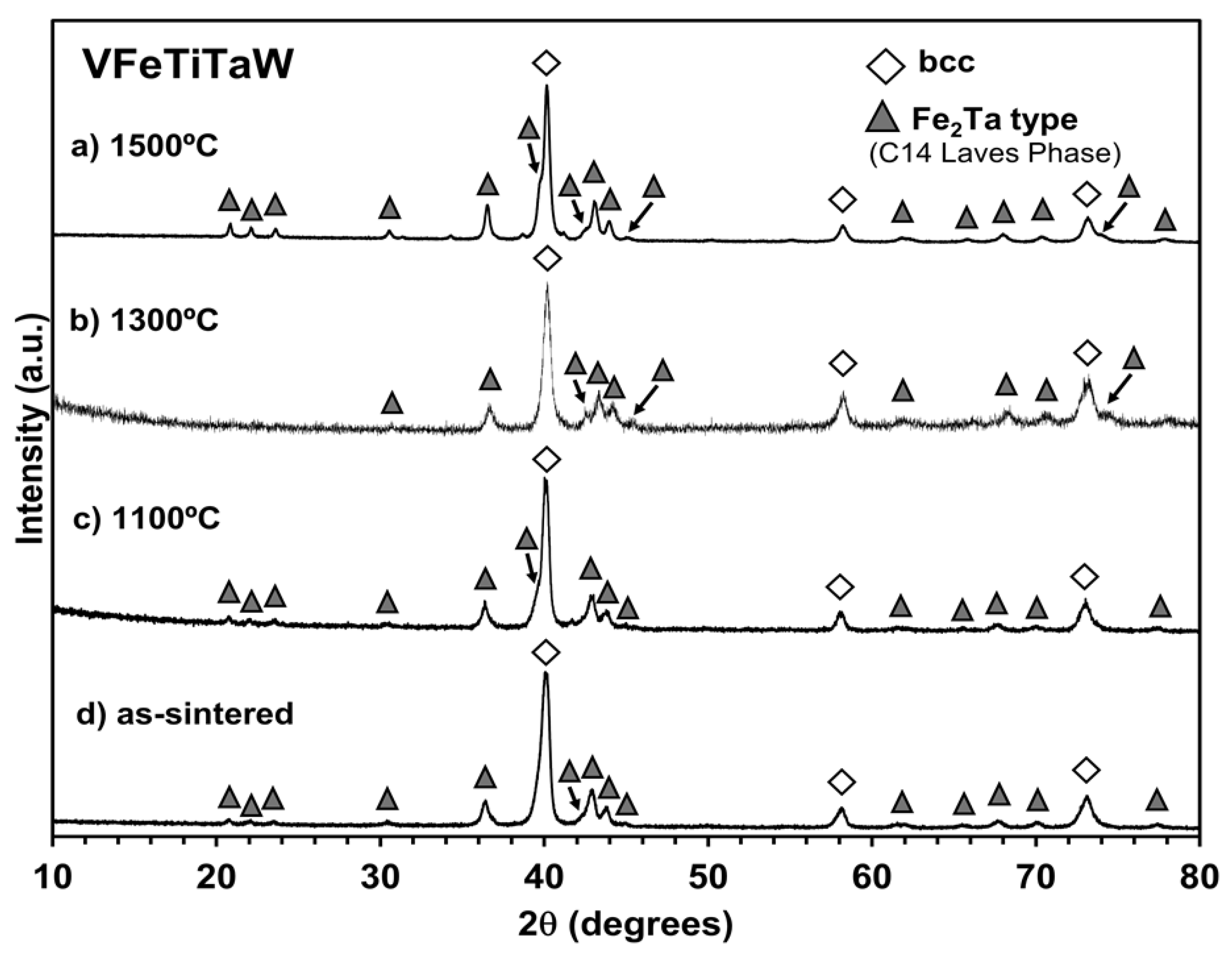
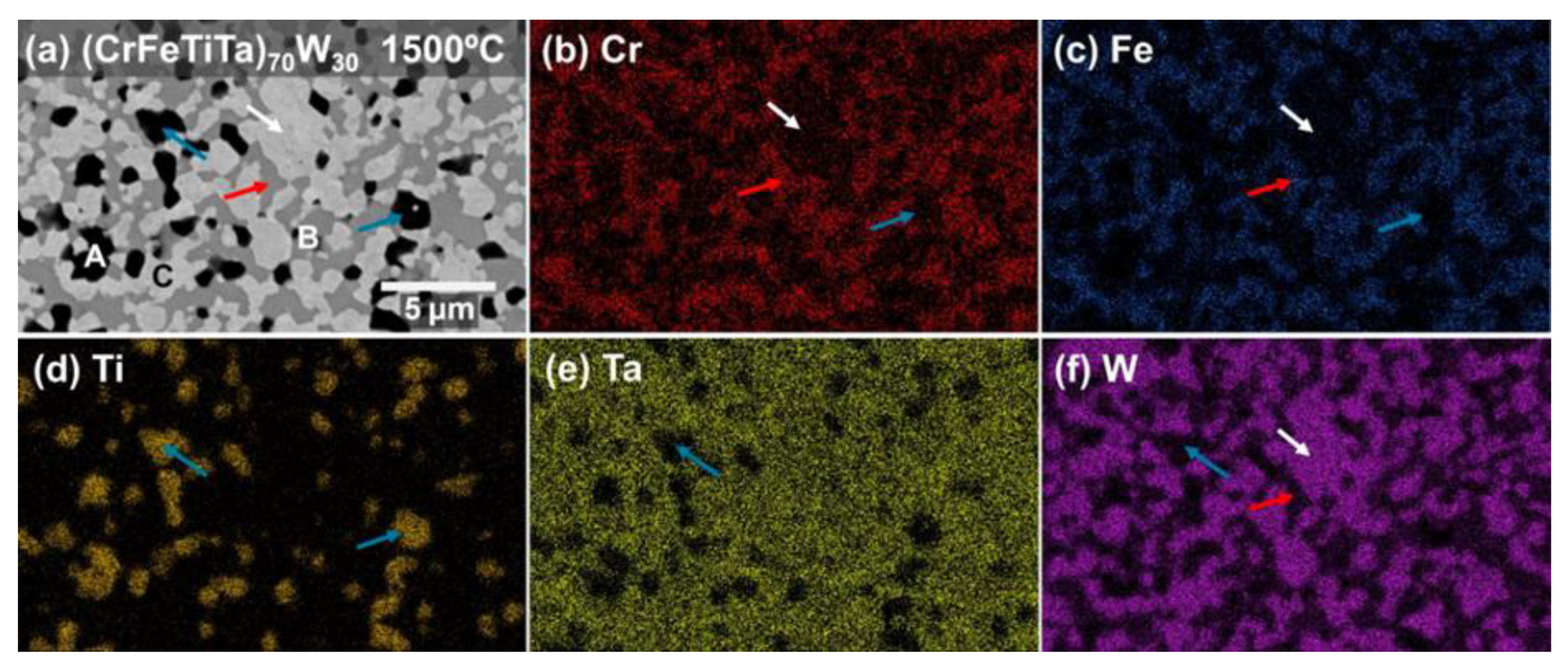
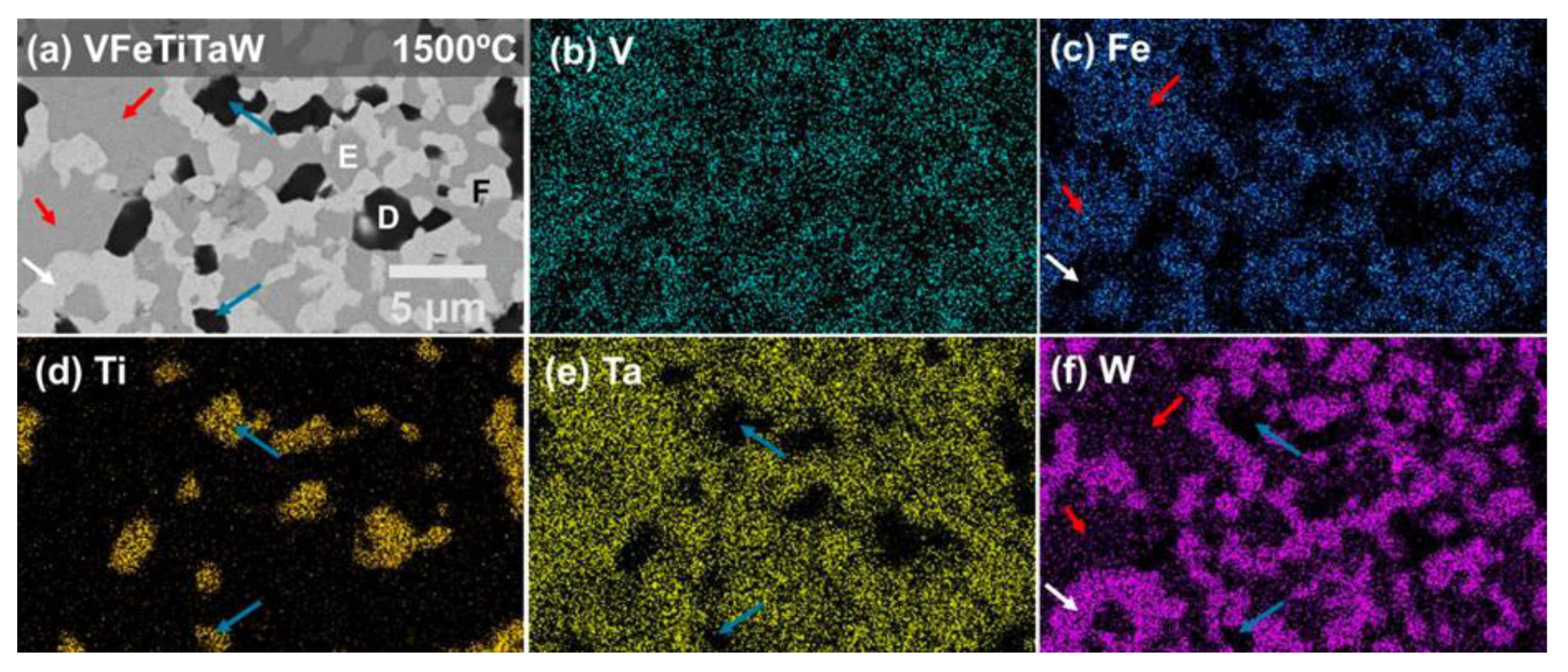
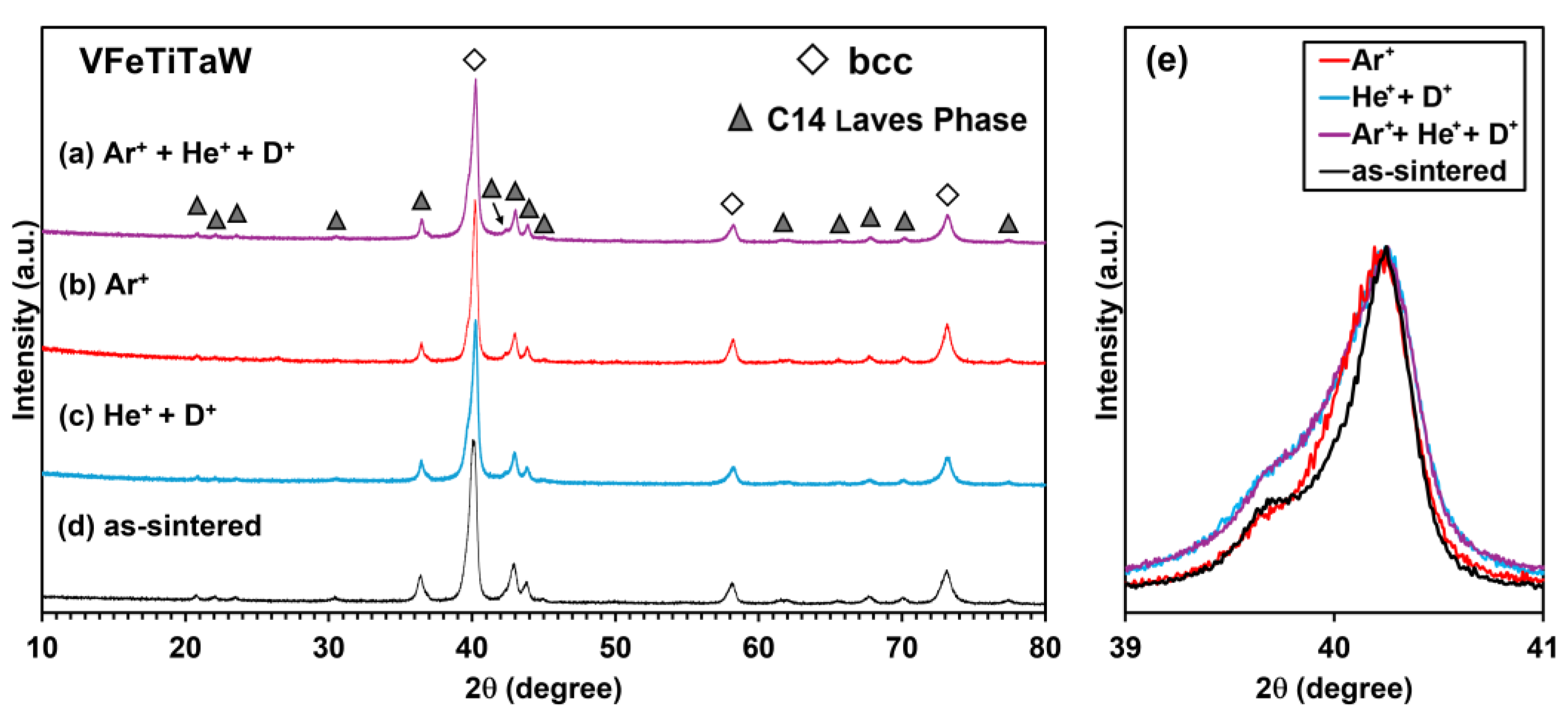
3.1. Structural Characterization
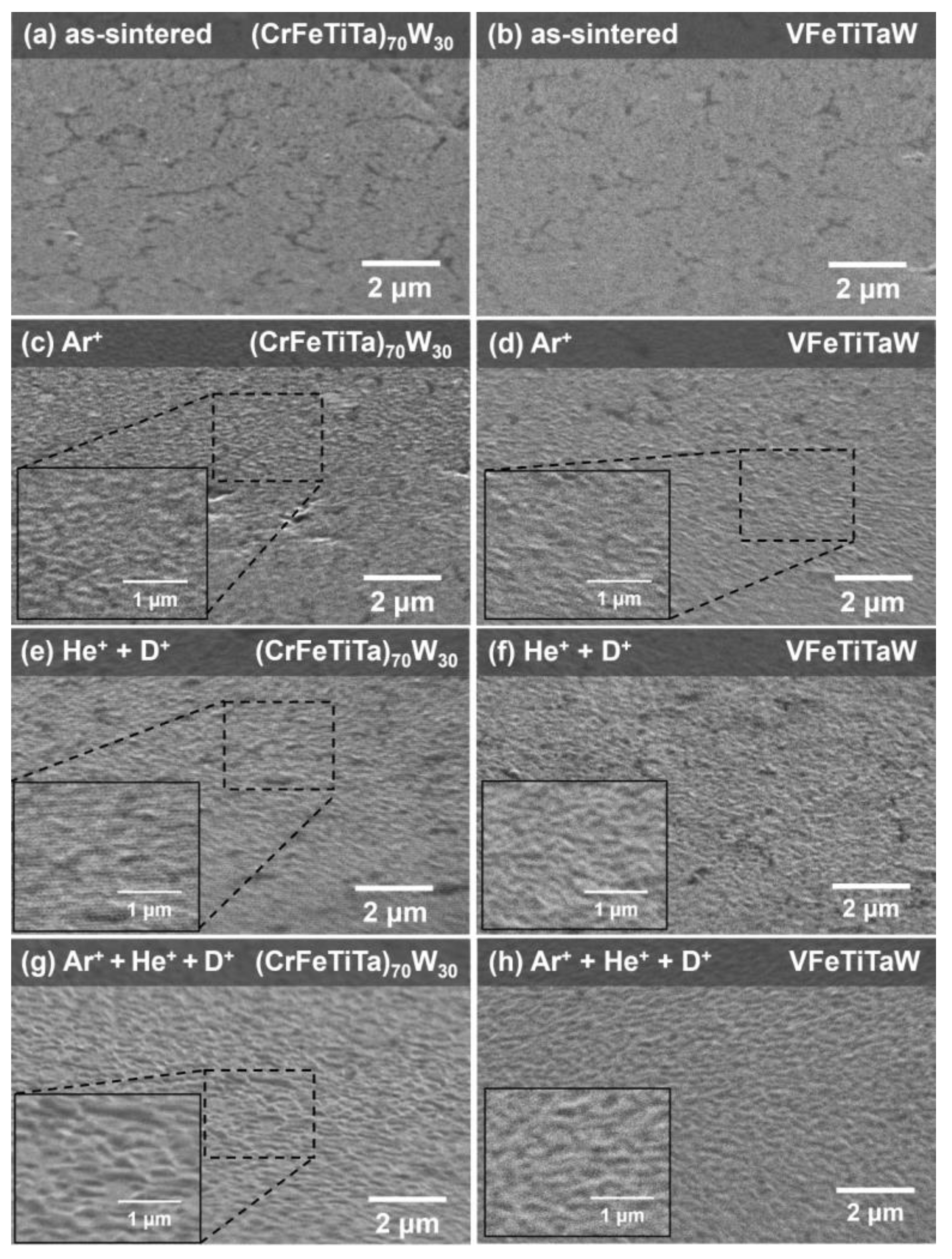
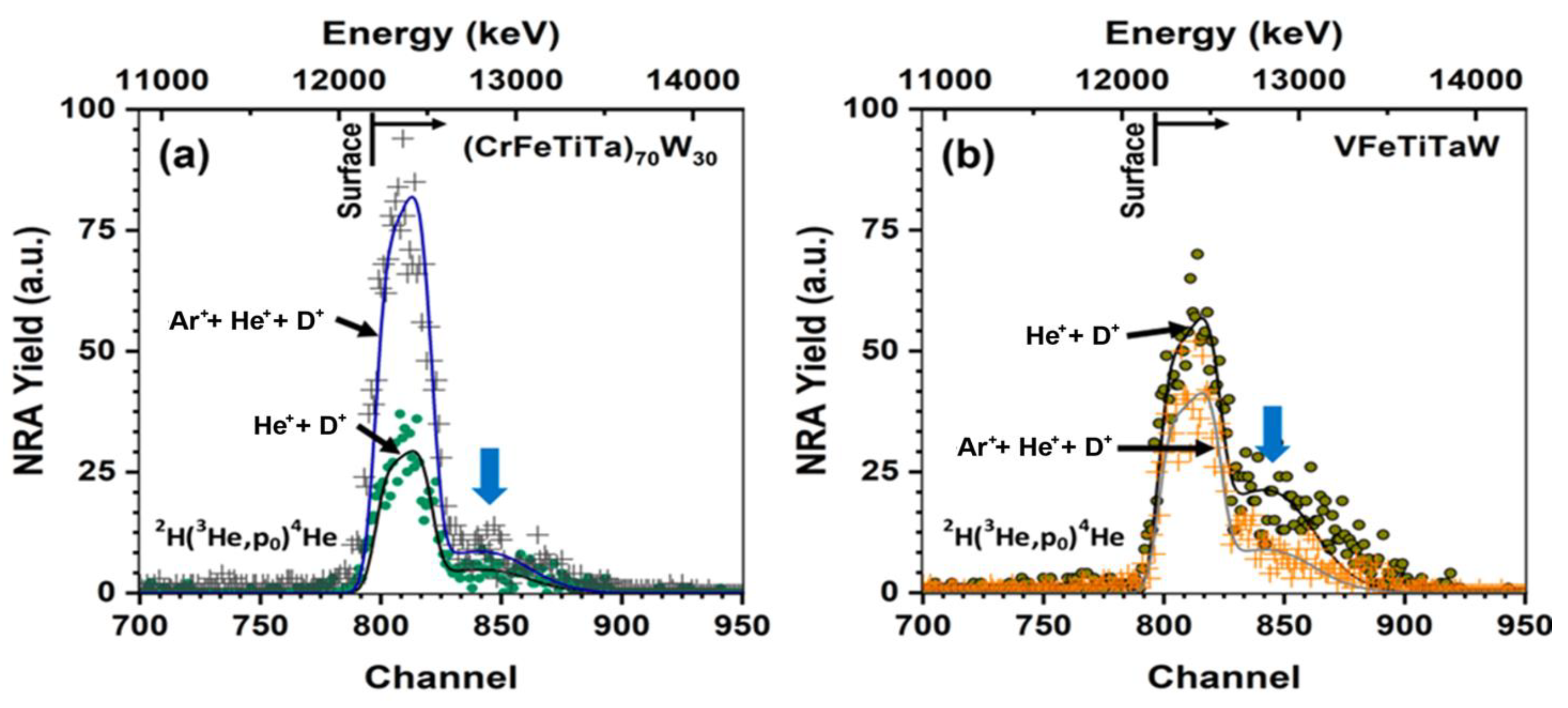
3.2. Irradiation Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mathew, M.D. Nuclear Energy: A Pathway towards Mitigation of Global Warming. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2022, 143, 104080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kembleton, R. Nuclear Fusion, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; ISBN 9780081028865. [Google Scholar]
- ITER Organization. What Is ITER? Available online: https://www.iter.org/proj/inafewlines (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Wu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Hu, L.; Jin, M.; Li, Y.; Jiang, J.; Yu, J.; Alejaldre, C.; Stevens, E.; Kim, K.; et al. Identification of Safety Gaps for Fusion Demonstration Reactors. Nat. Energy 2016, 1, 16154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ITER Organization. Making It Work. Available online: https://www.iter.org/fusion-energy/making-it-work (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Stork, D.; Agostini, P.; Boutard, J.L.; Buckthorpe, D.; Diegele, E.; Dudarev, S.L.; English, C.; Federici, G.; Gilbert, M.R.; Gonzalez, S.; et al. Developing Structural, High-Heat Flux and Plasma Facing Materials for a near-Term DEMO Fusion Power Plant: The EU Assessment. J. Nucl. Mater. 2014, 455, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li-Puma, A.; Richou, M.; Magaud, P.; Missirlian, M.; Visca, E.; Ridolfini, V.P. Potential and Limits of Water Cooled Divertor Concepts Based on Monoblock Design as Possible Candidates for a DEMO Reactor. Fusion Eng. Des. 2013, 88, 1836–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wang, T.; Yang, C.; Ge, C. Effect of Hot Working Process on the Mechanical Properties of Tungsten Materials. J. Nucl. Mater. 2013, 442, S233–S236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.H. Copper Matrix Composites as Heat Sink Materials for Water-Cooled Divertor Target. Nucl. Mater. Energy 2015, 5, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kareer, A.; Waite, J.C.; Li, B.; Couet, A.; Armstrong, D.E.J.; Wilkinson, A.J. Short Communication: ‘Low Activation, Refractory, High Entropy Alloys for Nuclear Applications’. J. Nucl. Mater. 2019, 526, 151744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, R.; Correia, B.; Galatanu, A.; Alves, E.; Tejado, E.; Pastor, Y.; Dias, M. Simulation, Structural, Thermal and Mechanical Properties of the FeTiTaVW High Entropy Alloy. Metals 2024, 14, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carruthers, A.W.; Li, B.S.; Rigby, M.; Raquet, L.C.; Mythili, R.; Ghosh, C.; Dasgupta, A.; Armstrong, D.E.J.; Gandy, A.S.; Pickering, E.J. Novel Reduced-Activation TiVCrFe Based High Entropy Alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 856, 157399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waseem, O.A.; Ryu, H.J. Powder Metallurgy Processing of a Wx TaTiVCr High-Entropy Alloy and Its Derivative Alloys for Fusion Material Applications. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdi, H.; Abedi, H.R.; Zhang, Y. A Review Study on Thermal Stability of High Entropy Alloys: Normal/Abnormal Resistance of Grain Growth. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 960, 170826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O.N.; Wilks, G.B.; Scott, J.M.; Miracle, D.B. Mechanical Properties of Nb25Mo25Ta 25W25 and V20Nb20Mo 20Ta20W20 Refractory High Entropy Alloys. Intermetallics 2011, 19, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.D.; Luan, H.W.; Liu, X.; Chen, N.; Li, X.Y.; Shao, Y.; Yao, K.F. Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of TixNbMoTaW Refractory High-Entropy Alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 712, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.Q.; Wang, Z.; Yang, T.F.; Zhang, Y. Irradiation Behavior in High Entropy Alloys. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2015, 22, 879–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, E.J.; Carruthers, A.W.; Barron, P.J.; Middleburgh, S.C.; Armstrong, D.E.J.; Gandy, A.S. High-Entropy Alloys for Advanced Nuclear Applications. Entropy 2021, 23, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraus, W.; Nolze, G. POWDER CELL—A Program for the Representation and Manipulation of Crystal Structures and Calculation of the Resulting X-Ray Powder Patterns. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1996, 29, 301–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villars, P.; Cenzual, K.; Pearson, W.B. Pearson’s Crystal Data: Crystal Structure Database for Inorganic Compounds. In Chemistry, Materials Science; ASM International: Almere, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kulcinski, G.L.; Wittkower, A.B.; Ryding, G. Use of heavy ions from a tandem accelerator to simulate high fluence, fast neutron damage in metals. Nucl. Instrum. Methods 1971, 94, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Was, G.S. Challenges to the use of ion irradiation for emulating reactor irradiation. J. Mater. Res. 2015, 30, 1158–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, M.R.; Dudarev, S.L.; Nguyen-Manh, D.; Zheng, S.; Packer, L.W.; Sublet, J.C. Neutron-Induced Dpa, Transmutations, Gas Production, and Helium Embrittlement of Fusion Materials. J. Nucl. Mater. 2013, 442, S755–S760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, J.F.; Ziegler, M.D.; Biersack, J.P. SRIM—The Stopping and Range of Ions in Matter (2010). Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 2010, 268, 1818–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, M. SIMNRA, a Simulation Program for the Analysis of NRA, RBS and ERDA. AIP Conf. Proc. 1999, 475, 541–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IAEA. IBANDL Database. Available online: http://nds.iaea.org/ibandl/ (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Senkov, O.N.; Miracle, D.B.; Chaput, K.J.; Couzinie, J.P. Development and Exploration of Refractory High Entropy Alloys—A Review. J. Mater. Res. 2018, 33, 3092–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coury, F.G.; Butler, T.; Chaput, K.; Saville, A.; Copley, J.; Foltz, J.; Mason, P.; Clarke, K.; Kaufman, M.; Clarke, A. Phase Equilibria, Mechanical Properties and Design of Quaternary Refractory High Entropy Alloys. Mater. Des. 2018, 155, 244–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zareipour, F.; Shahmir, H.; Huang, Y. Formation and Significance of Topologically Close-Packed Laves Phases in Refractory High-Entropy Alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 986, 174148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murty, B.S.; Yeh, J.W.; Ranganathan, S.; Bhattacharjee, P.P. Special Subgroups of High-Entropy Alloys. In High-Entropy Alloys; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 145–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O.N.; Senkova, S.V.; Woodward, C.; Miracle, D.B. Low-Density, Refractory Multi-Principal Element Alloys of the Cr-Nb-Ti-V-Zr System: Microstructure and Phase Analysis. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 1545–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, A.; Inoue, A. Classification of Bulk Metallic Glasses by Atomic Size Difference, Heat of Mixing and Period of Constituent Elements and Its Application to Characterization of the Main Alloying Element. Mater. Trans. 2005, 46, 2817–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.J.; Lin, J.P.; Chen, G.L.; Liaw, P.K. Solid-Solution Phase Formation Rules for Multi-Component Alloys. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2008, 10, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catarino, N.; Dias, M.; Lopes, J.; Jepu, I.; Alves, E. Helium and Deuterium Irradiation Effects in Tungsten-Based Materials with Titanium. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 355, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogorodnikova, O.V.; Roth, J.; Mayer, M. Ion-Driven Deuterium Retention in Tungsten. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 103, 034902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waseem, O.A.; Woller, K.B.; Sweidan, F.B.; Ryu, H.J. Effects of F3+ Ion Implantation on the Properties of W and W0.5(TaTiVCr)0.5 for Depth Marker-Based Plasma Erosion Analysis. Nucl. Mater. Energy 2020, 25, 100806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Composition | Implanted Ions | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ar+ | He+ | D+ | |
| (CrFeTiTa)70W30 | x | ||
| (CrFeTiTa)70W30 | x | x | |
| (CrFeTiTa)70W30 | x | x | x |
| VFeTiTaW | x | ||
| VFeTiTaW | x | x | |
| VFeTiTaW | x | x | x |
| (CrFeTiTa)70W30 | Cr (at.%) | Fe (at.%) | Ti (at.%) | Ta (at.%) | W (at.%) |
| Phase B | 22.5 ± 0.5 | 49.0 ± 0.3 | - | 20.8 ± 0.1 | 7.7 ± 0.3 |
| Phase C | - | - | 2.6 ± 1.9 | 21.1 ± 0.1 | 76.3 ± 1.8 |
| VFeTiTaW | V (at.%) | Fe (at.%) | Ti (at.%) | Ta (at.%) | W (at.%) |
| Phase E | 27.3 ± 0.2 | 40.6 ± 0.3 | - | 25.4 ± 0.1 | 6.7 ± 0.4 |
| Phase F | 17.8 ± 0.4 | - | - | 17.2 ± 0.4 | 65.1 ± 0.4 |
| Implanted with He+ + D+ | Implanted with Ar+ + He+ + D+ | |
|---|---|---|
| (CrFeTiTa)70W30 | 5.47% | 14.41% |
| VFeTiTaW | 13.20% | 8.58% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pereira, A.; Martins, R.; Monteiro, B.; Correia, J.B.; Galatanu, A.; Catarino, N.; Belec, P.J.; Dias, M. Thermal Stability and Irradiation Resistance of (CrFeTiTa)70W30 and VFeTiTaW High Entropy Alloys. Materials 2025, 18, 1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18051030
Pereira A, Martins R, Monteiro B, Correia JB, Galatanu A, Catarino N, Belec PJ, Dias M. Thermal Stability and Irradiation Resistance of (CrFeTiTa)70W30 and VFeTiTaW High Entropy Alloys. Materials. 2025; 18(5):1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18051030
Chicago/Turabian StylePereira, André, Ricardo Martins, Bernardo Monteiro, José B. Correia, Andrei Galatanu, Norberto Catarino, Petra J. Belec, and Marta Dias. 2025. "Thermal Stability and Irradiation Resistance of (CrFeTiTa)70W30 and VFeTiTaW High Entropy Alloys" Materials 18, no. 5: 1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18051030
APA StylePereira, A., Martins, R., Monteiro, B., Correia, J. B., Galatanu, A., Catarino, N., Belec, P. J., & Dias, M. (2025). Thermal Stability and Irradiation Resistance of (CrFeTiTa)70W30 and VFeTiTaW High Entropy Alloys. Materials, 18(5), 1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18051030








