Cellular Automaton Simulation of Corrosion in 347H Steel Exposed to Molten Solar Salt at Pilot-Plant Scale
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology: Experimental Procedure and Modeling
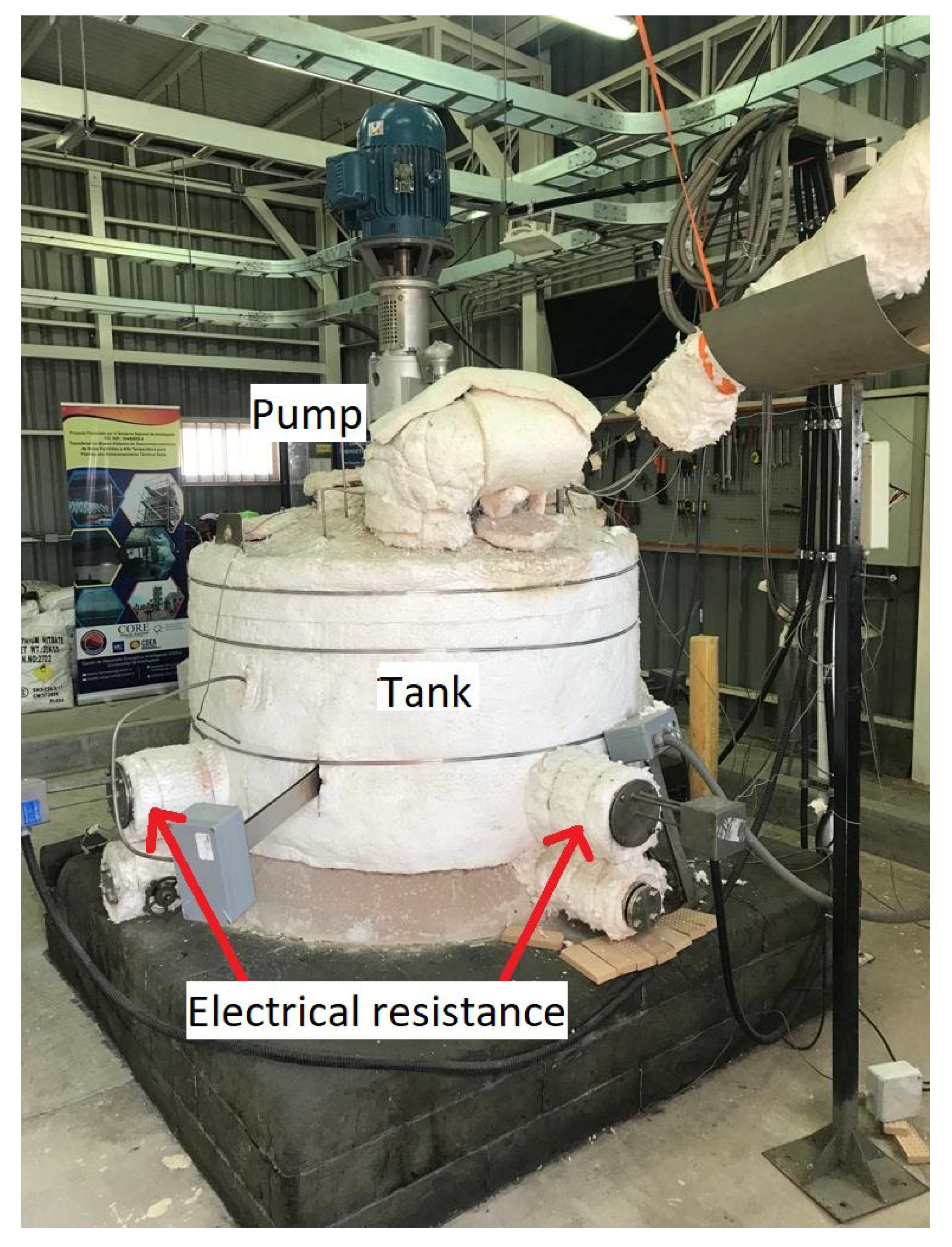
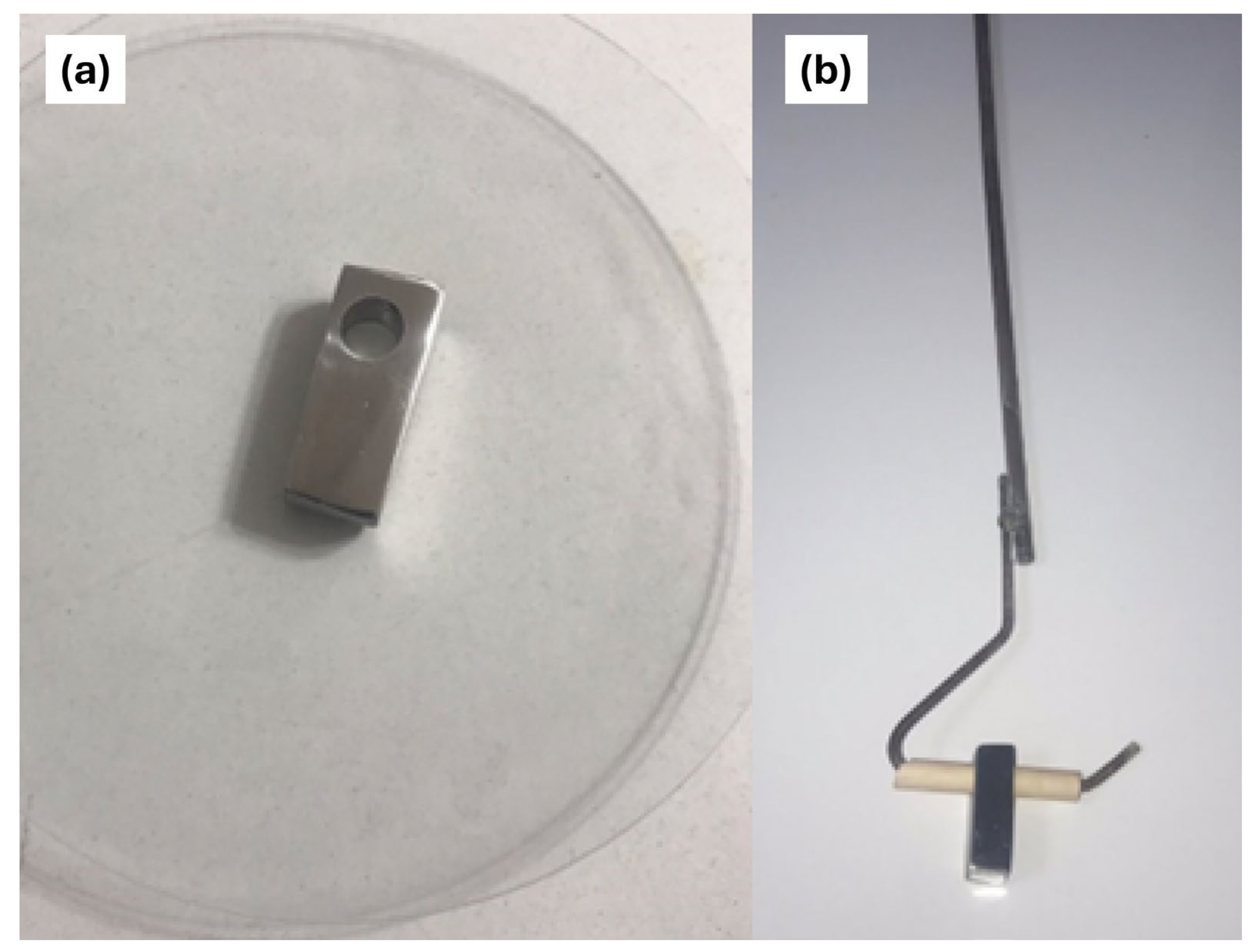
2.1. Immersion Test
2.2. Modeling
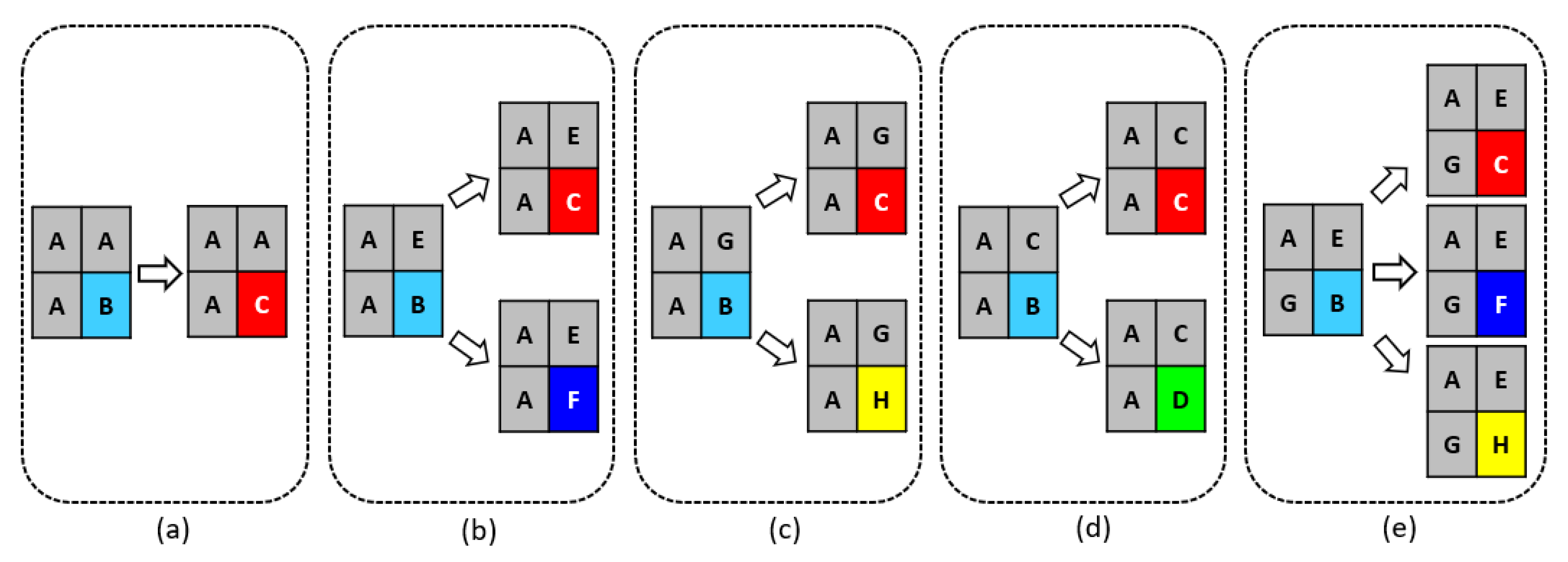
2.3. Corrosion Mechanism
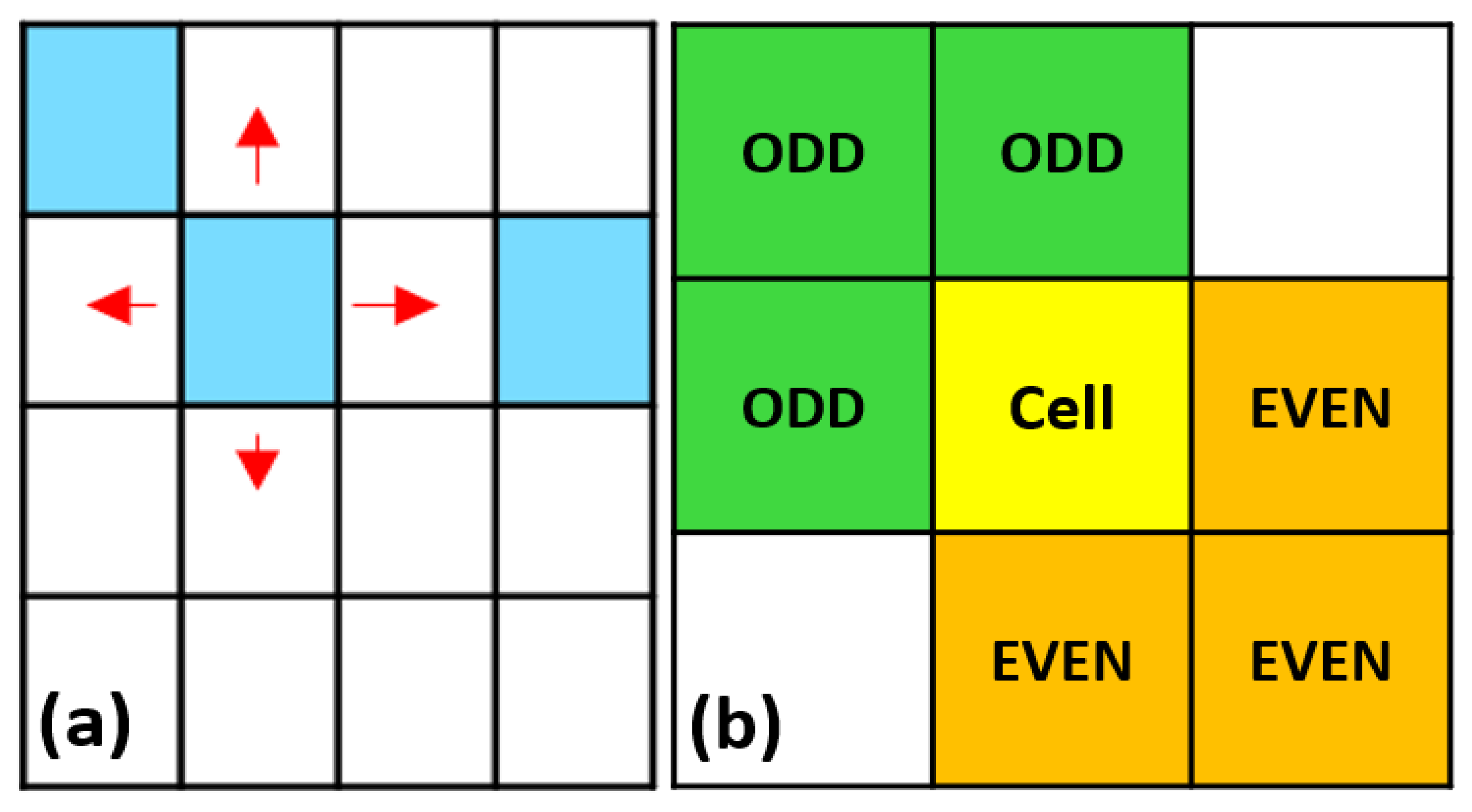
2.4. Site Definition
2.5. Model Parameters
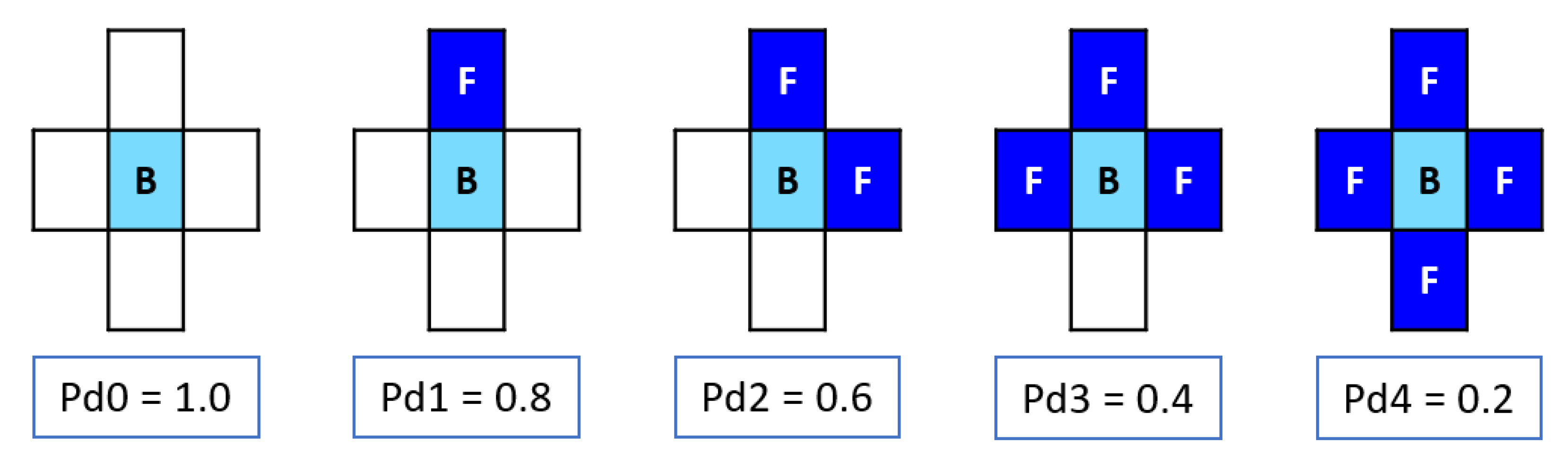
2.6. Transformation Rules
3. Results
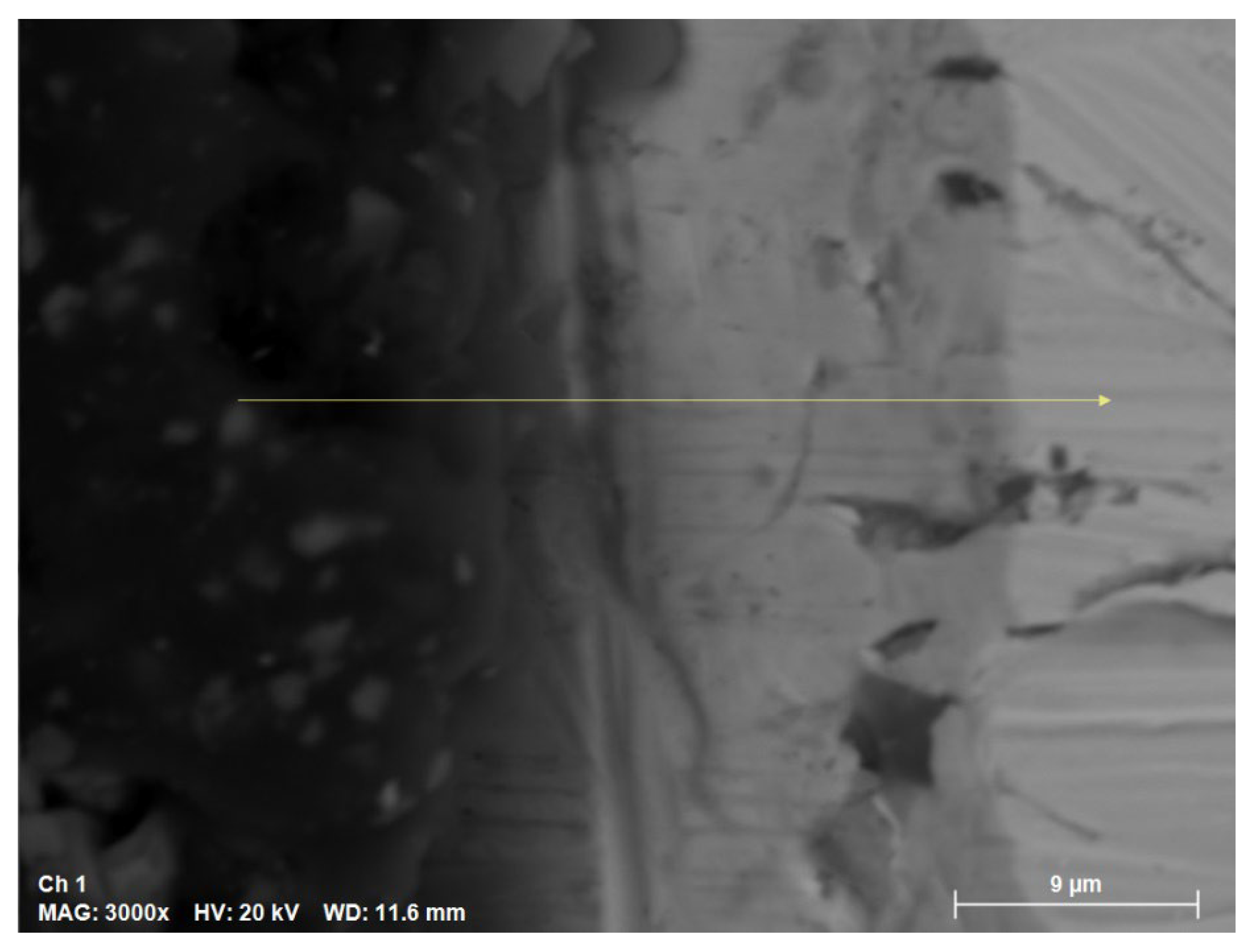
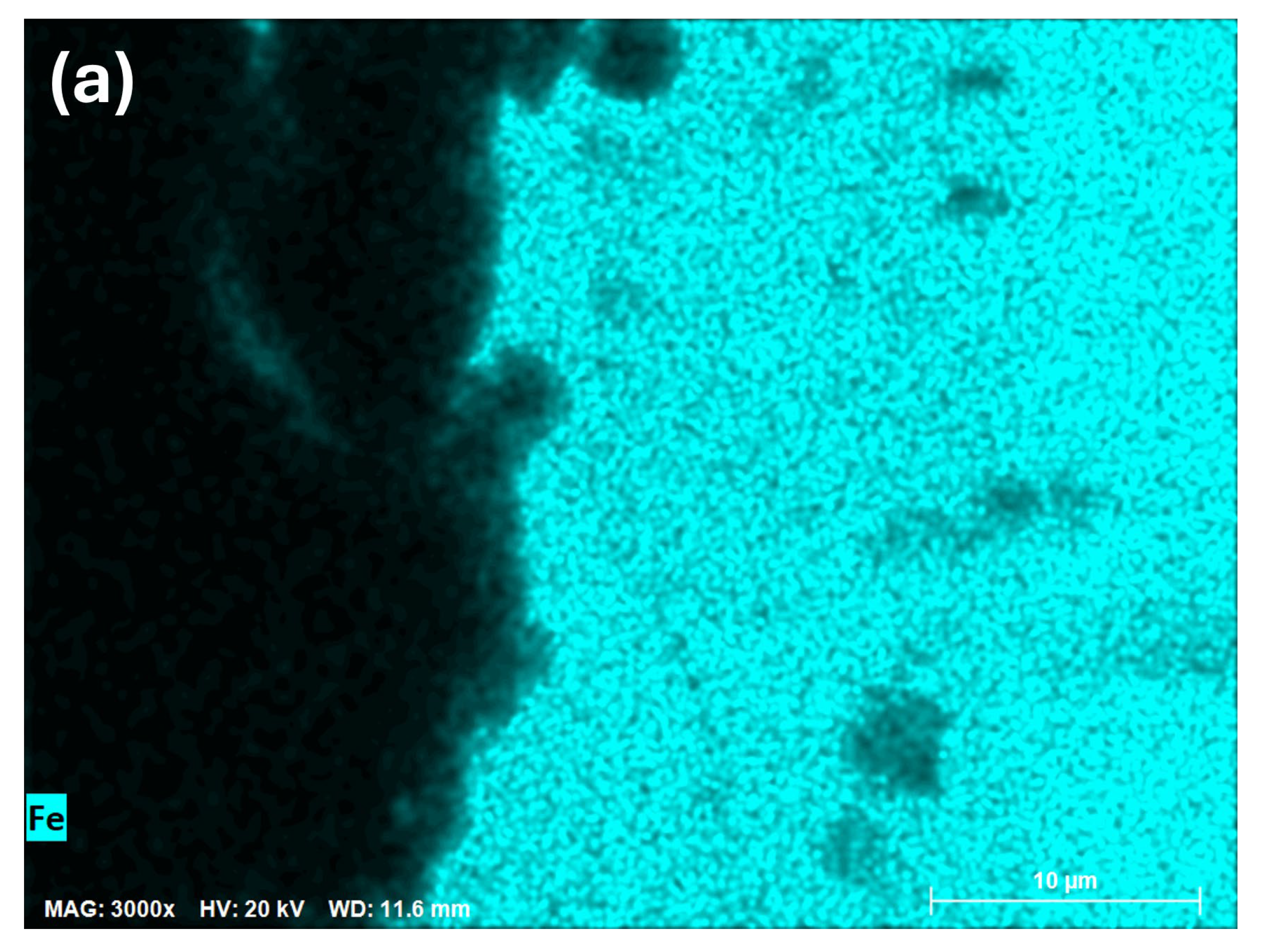
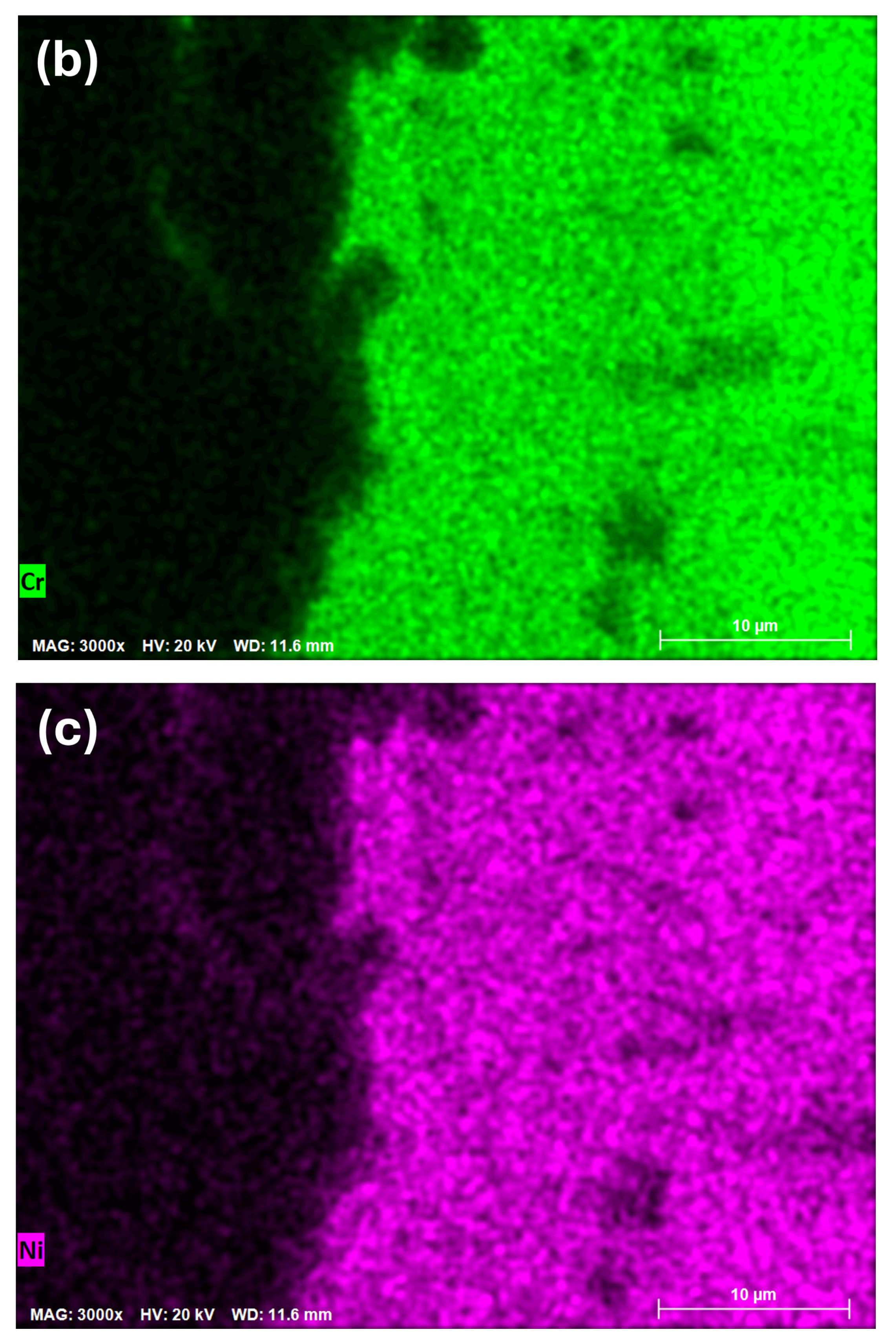
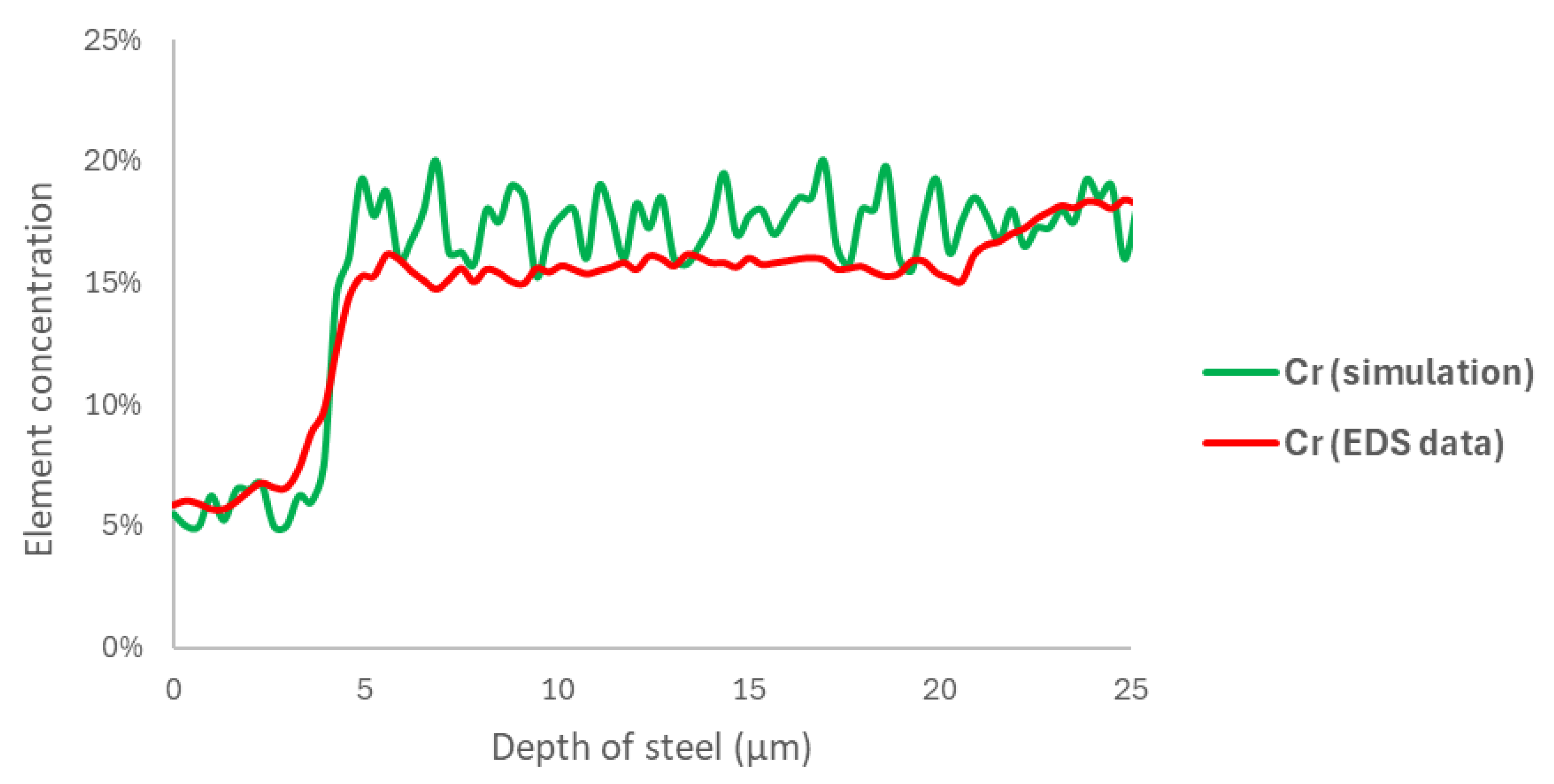
3.1. SEM/EDS
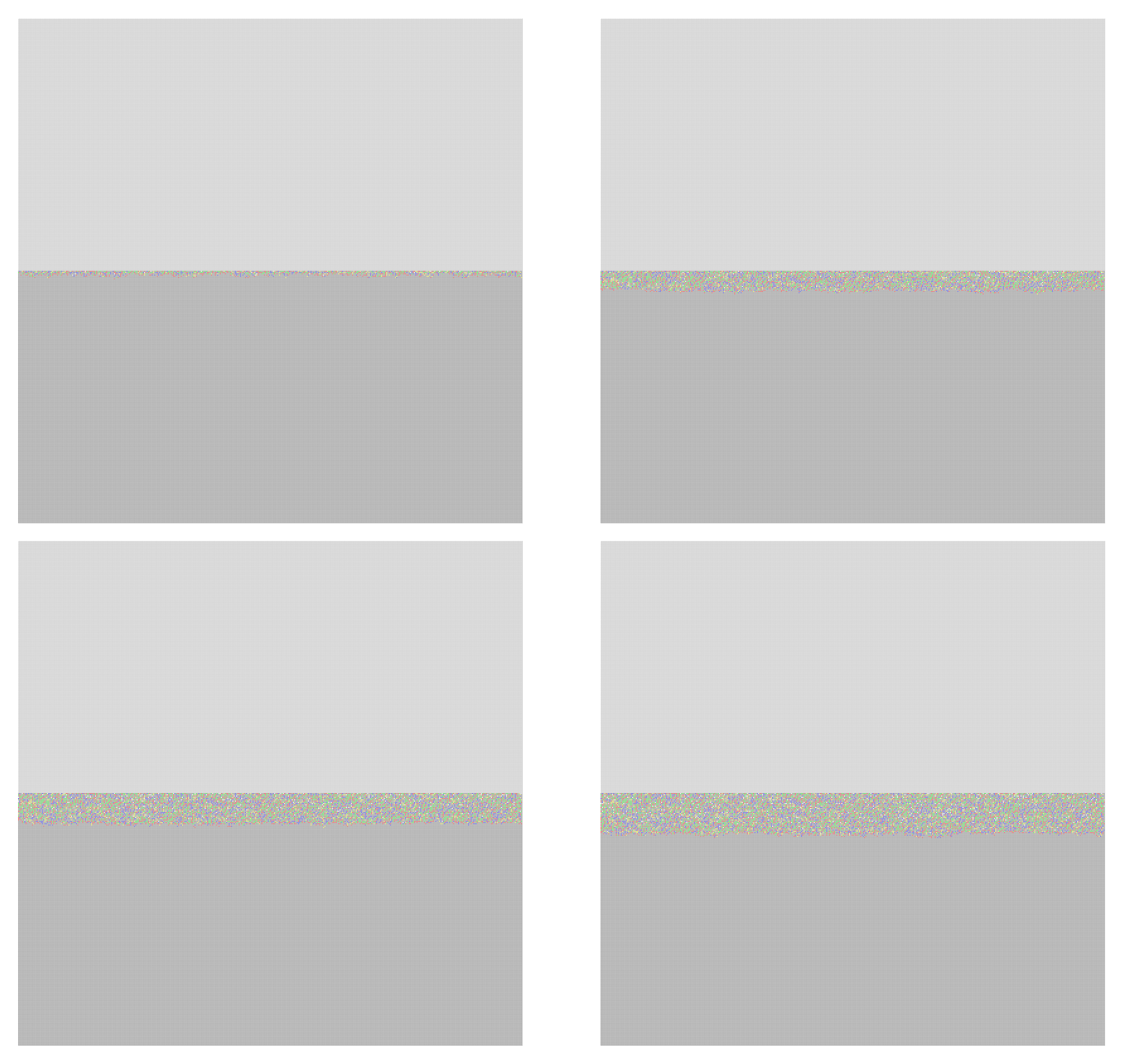
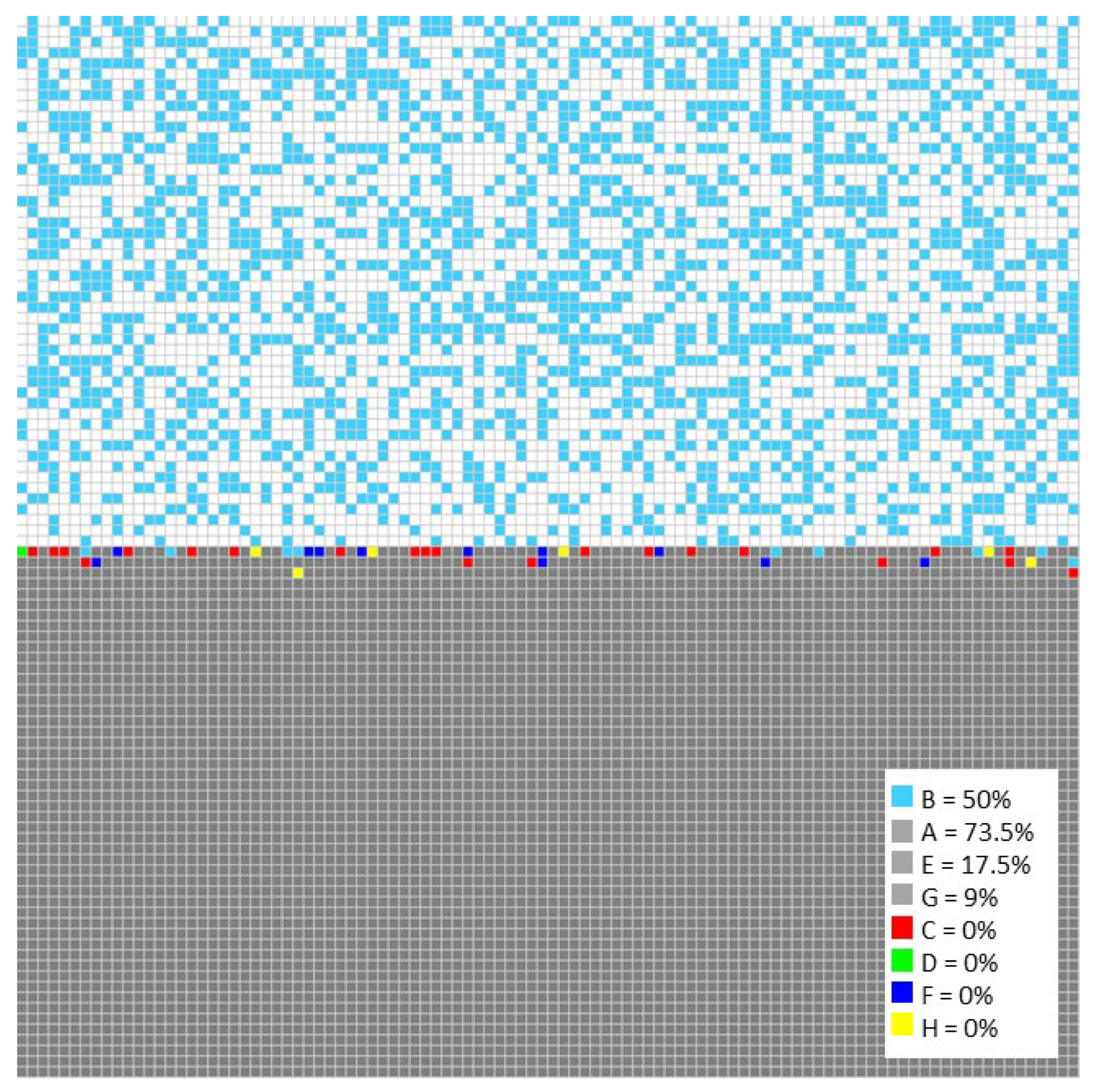
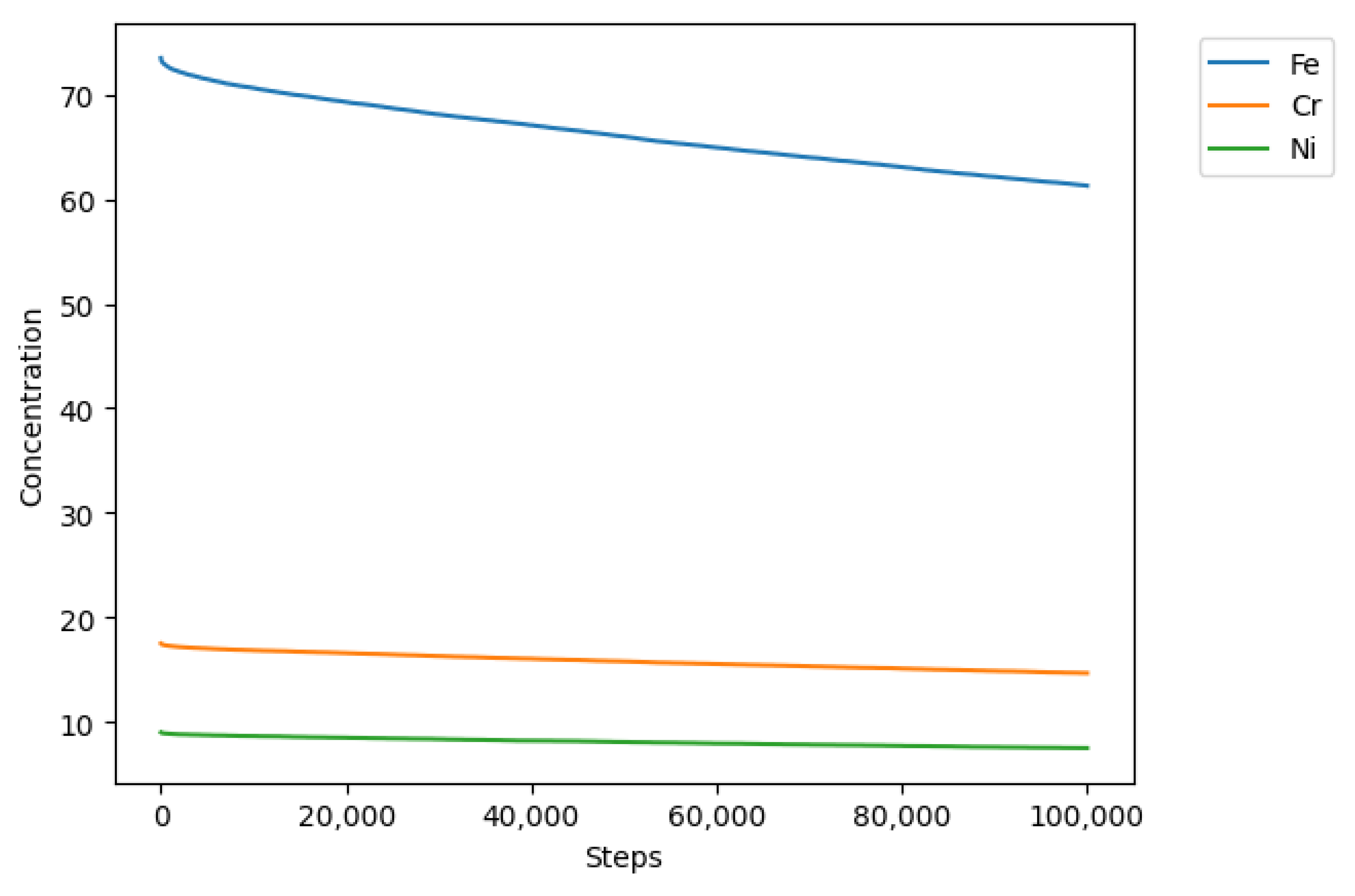
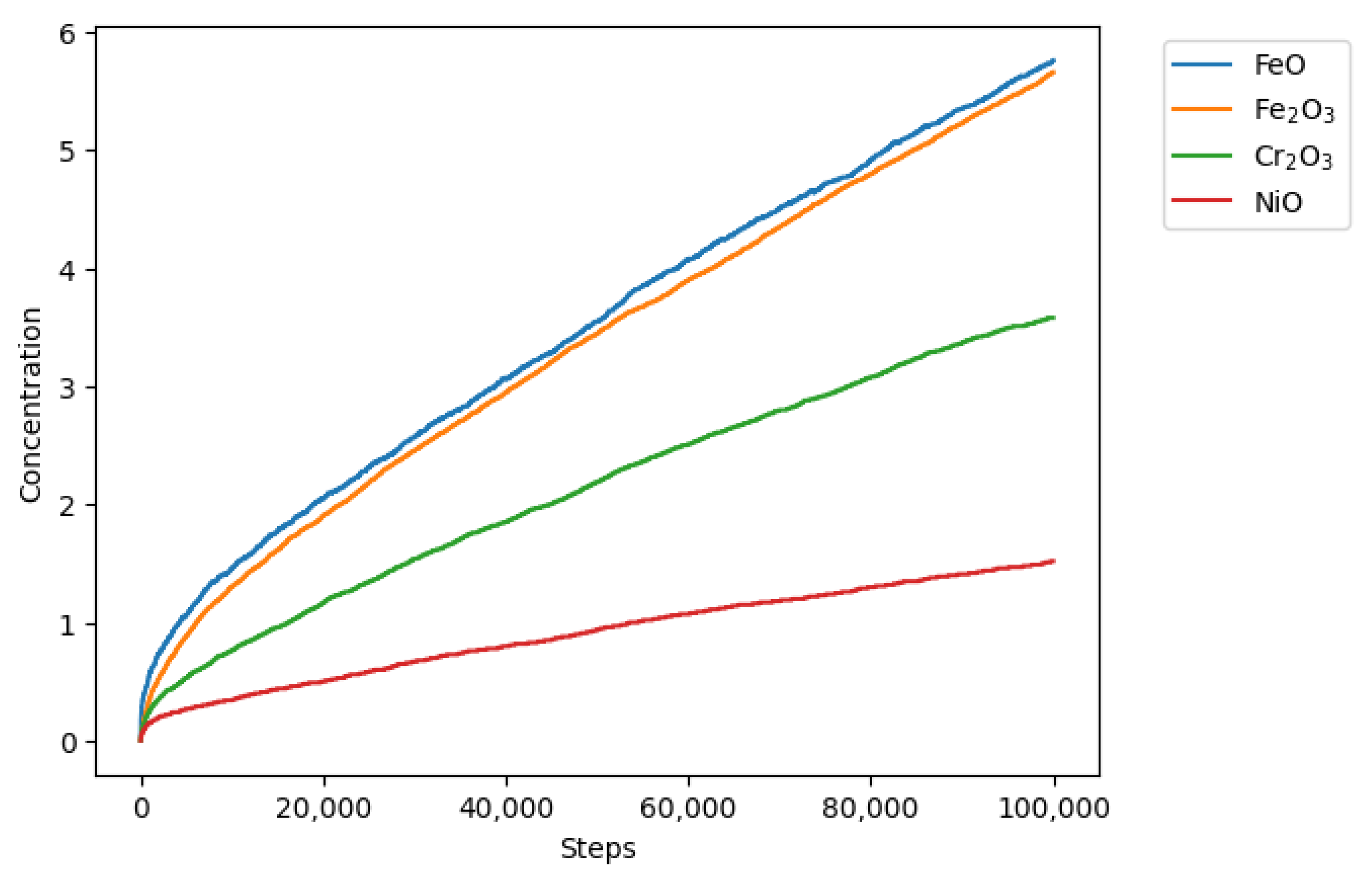
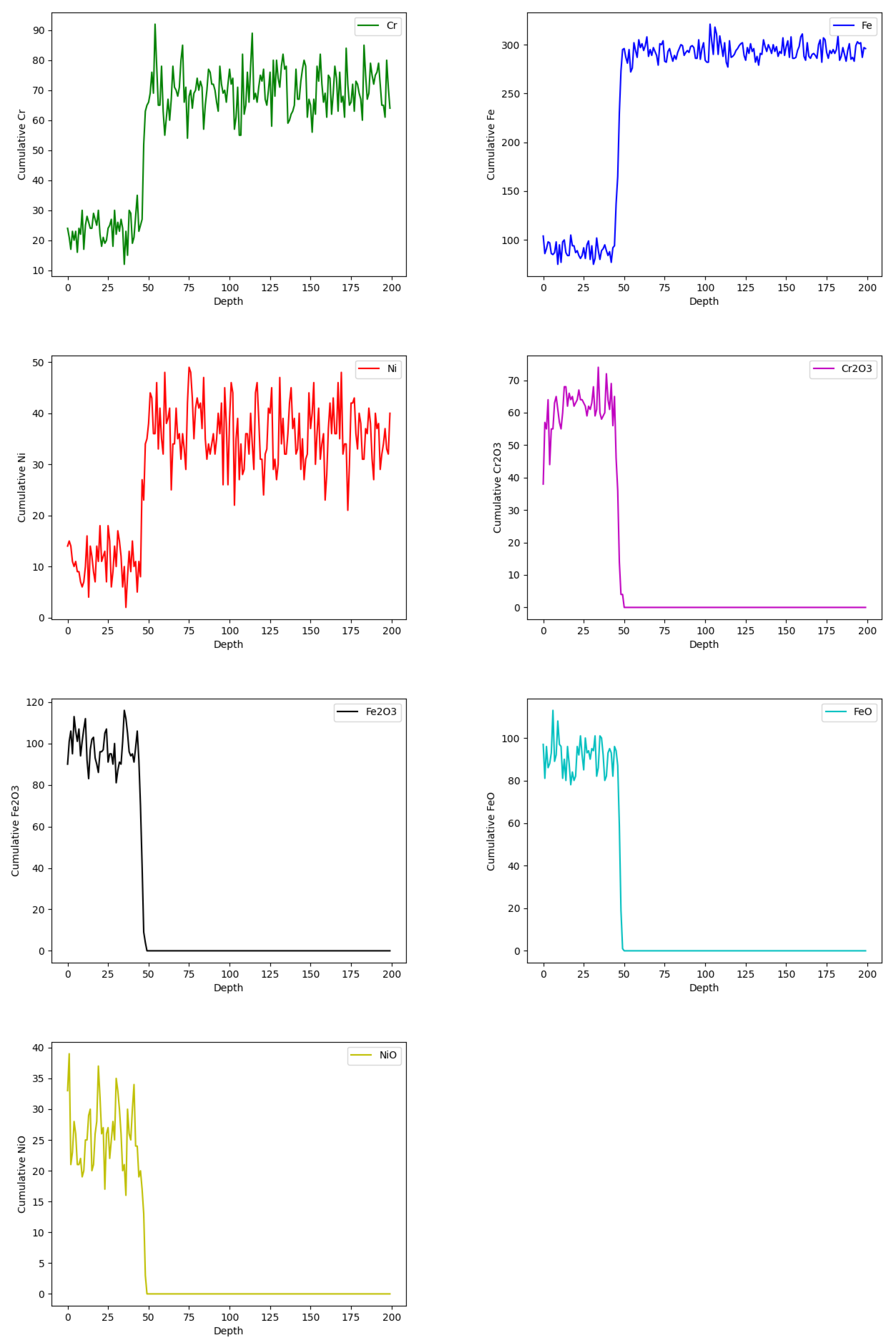
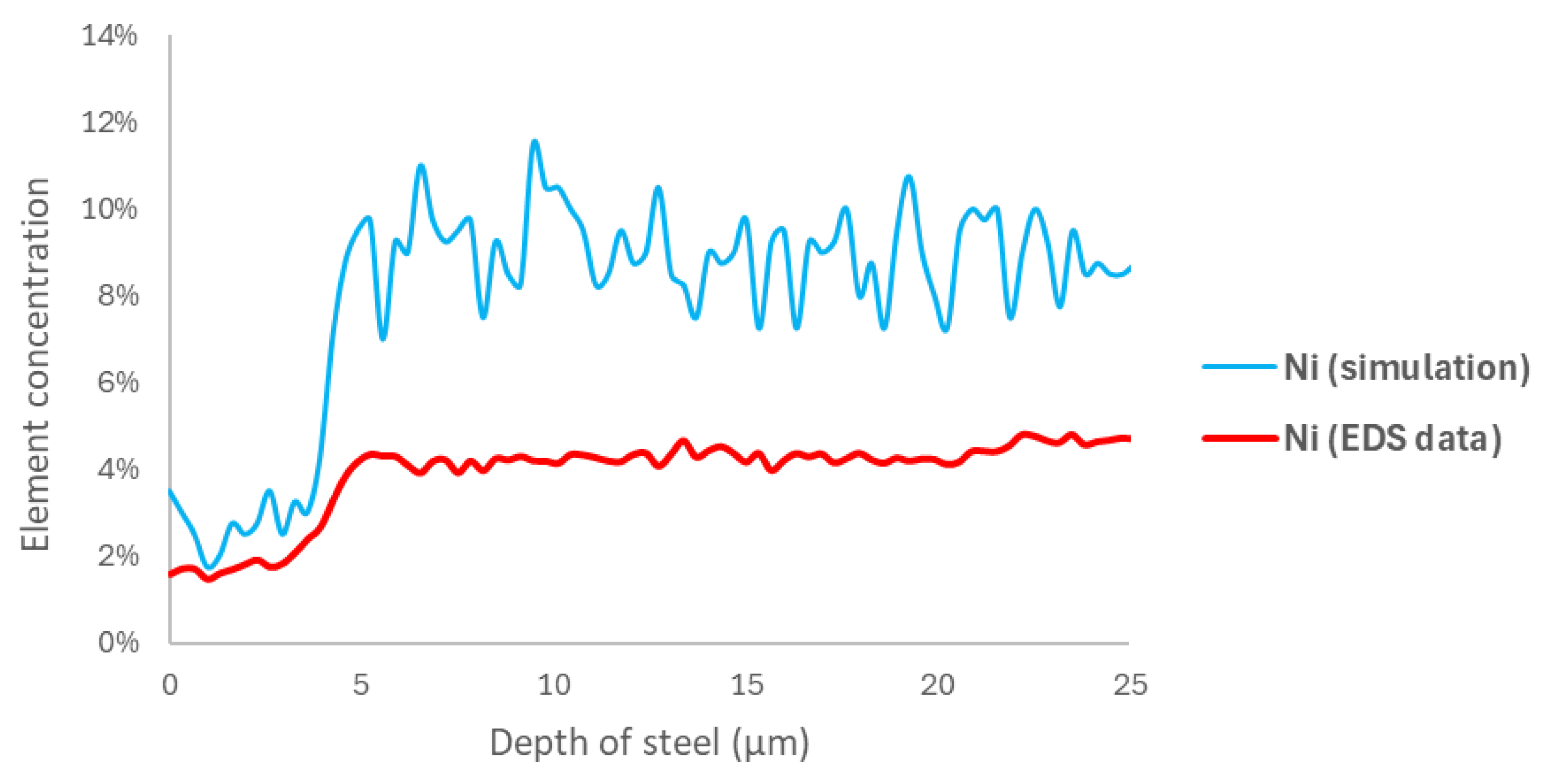
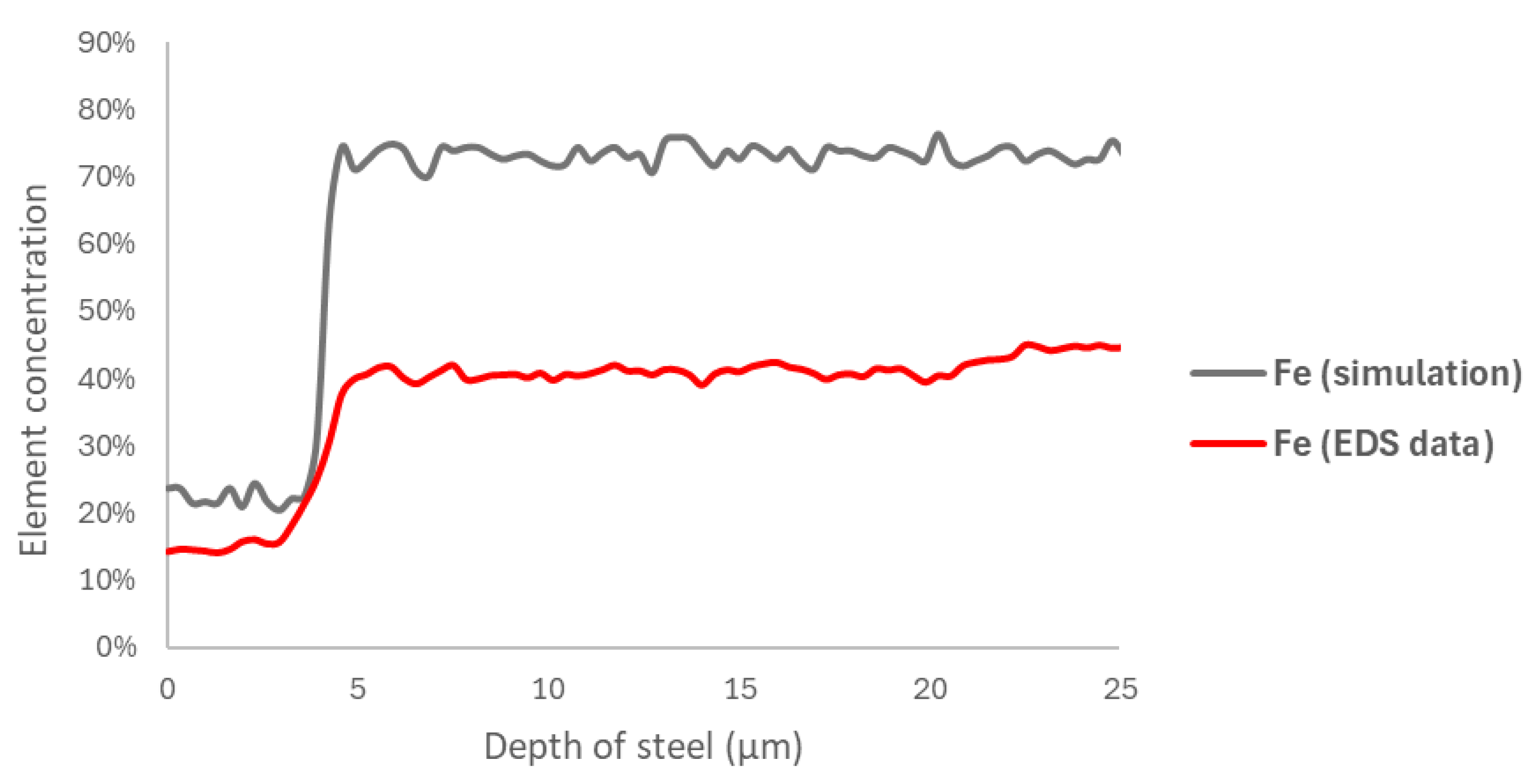
3.2. Modeling
3.3. Data Processing
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Palacios, A.; Barreneche, C.; Navarro, M.E.; Ding, Y. Thermal energy storage technologies for concentrated solar power—A review from a materials perspective. Renew. Energy 2020, 156, 1244–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walczak, M.; Pineda, F.; Fernández, Á.G.; Mata-Torres, C.; Escobar, R.A. Materials corrosion for thermal energy storage systems in concentrated solar power plants. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 86, 22–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilchez, F.; Pineda, F.; Walczak, M.; Ramos-Grez, J. The effect of laser surface melting of stainless steel grade AISI 316L welded joint on its corrosion performance in molten Solar Salt. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2020, 213, 110576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorio, J.D.; Mehos, M.; Imponenti, L.; Kelly, B.; Price, H.; Torres-Madronero, J.; Rivera-Alvarez, A.; Nieto-Londono, C.; Ni, C.; Yu, Z.; et al. Failure Analysis for Molten Salt Thermal Energy Storage Tanks for In-Service CSP Plants. 2024. Available online: www.nrel.gov/publications (accessed on 25 November 2024.).
- Granados, B.L.; Granados, B.L.; Tovar, R.S. Corrosion. Editorial de la Universidad Politecnica de Valencia, 2018. Available online: https://elibro.net/es/lc/uantof/titulos/57467 (accessed on 27 November 2024).
- Sarvghad, M.; Steinberg, T.A.; Will, G. Corrosion of stainless steel 316 in eutectic molten salts for thermal energy storage. Sol. Energy 2018, 172, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, S.; Steinberg, T.; Will, G. Corrosion mechanisms in molten salt thermal energy storage for concentrating solar power. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 114, 109328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, C.; Gallardo-González, J.; Ruiz-Cabañas, F.J.; Barreneche, C.; Martínez, M.; Segarra, M.; Fernández, A.I. Study of corrosion by Dynamic Gravimetric Analysis (DGA) methodology. Influence of chloride content in solar salt. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2016, 157, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, A.G.; Rey, A.; Lasanta, I.; Mato, S.; Brady, M.P.; Pérez, F.J. Corrosion of alumina-forming austenitic steel in molten nitrate salts by gravimetric analysis and impedance spectroscopy. Mater. Corros. 2014, 65, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Encinas-Sánchez, V.; de Miguel, M.T.; Lasanta, M.I.; García-Martín, G.; Pérez, F.J. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS): An efficient technique for monitoring corrosion processes in molten salt environments in CSP applications. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2019, 191, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Guan, B.; Wei, X.; Lu, J.; Ding, J. Cellular automata simulation on the corrosion behavior of Ni-base alloy in chloride molten salt. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2019, 203, 110170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wei, X.; Lu, J.; Ding, J.; Wang, W. Simulation of corrosion behavior of Fe–Cr–Ni alloy in binary NaCl–CaCl2 molten salt using a cellular automata method. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2021, 231, 111301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Lu, J.; Wei, X.; Ding, J.; Wang, W. 2D and 3D cellular automata simulation on the corrosion behaviour of Ni-based alloy in ternary molten salt of NaCl–KCl–ZnCl2. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2022, 240, 111694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stafiej, J.; Di Caprio, D.; Bartosik, Ł. Corrosion-passivation processes in a cellular automata based simulation study. J. Supercomput. 2013, 65, 697–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiso, S.; di Caprio, D.; de Lamare, J.; Gwinner, B. Intergranular corrosion: Comparison between experiments and cellular automata. Corros. Sci. 2020, 177, 108953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Brokate, C.F.; di Caprio, D.; Féron, D.; de Lamare, J.; Chaussé, A. Probabilistic cellular automata model of generalised corrosion, transition to localised corrosion. Corros. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2017, 52, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J. Cellular automaton modeling on the corrosion/oxidation mechanism of steel in liquid metal environment. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2008, 50, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinoso-Burrows, J.C.; Toro, N.; Cortés-Carmona, M.; Pineda, F.; Henriquez, M.; Madrid, F.M.G. Cellular Automata Modeling as a Tool in Corrosion Management. Materials 2023, 16, 6051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallco, A.; Portillo, C.; Kogan, M.J.; Galleguillos, F.; Fernández, A.G. A materials screening test of corrosion monitoring in LiNO3 containing molten salts as a thermal energy storage material for CSP plants. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorcheh, A.S.; Durham, R.N.; Galetz, M.C. High temperature corrosion in molten solar salt: The role of chloride impurities. Mater. Corros. 2017, 68, 943–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, Á.G.; Cabeza, L.F. Molten salt corrosion mechanisms of nitrate based thermal energy storage materials for concentrated solar power plants: A review. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2019, 194, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong, J.M.; Broers, G.H.J. A Reversible Oxygen Electrode in an Equimolar KNO,-NANO, Melt Saturated with Sodium Peroxide-II. A Voltammetric Study. Electrochim. Acta 1976, 21, 893–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 17245; Corrosion of metals and alloys—Test method for high temperature corrosion testing of metallic materials by immersing in molten salt or other liquids under static conditions. ISO/FDIS 17245:2015. ISO TC156 (High Temperature Corrosion). International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015.


| Chemical Composition of AISI 347H Stainless Steel [%p/p] | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe | C | Si | Mn | Cr | Mo | Ni | Al | Co | Cu | Nb | W |
| 70.5 | 0.04565 | 0.1885 | 1.735 | 17.05 | 0.396 | 8.96 | 0.0068 | 0.114 | 0.4195 | 0.4015 | 0.0378 |
| Chemical Composition of Solar Salt | |
|---|---|
| Compound | [%p/p] |
| NaNO3 | 60.2 |
| KNO3 | 39.8 |
| Fe | O2− | Fe3O4 | Fe2O3 | Cr | Cr2O3 | Ni | NiO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H |
| Site | Element | E° (V) | P.ox_rel | P.rel₁ (%) | P.rel₂ (%) | P.rel₃ (%) | P.rel₄ (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Fe | −0.44 | 1.55 | 31.4 | 57.4 | - | 54.6 |
| E | Cr | −0.74 | 2.09 | 42.4 | 42.6 | 61.8 | - |
| G | Ni | −0.25 | 1.29 | 26.2 | - | 38.2 | 45.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reinoso-Burrows, J.C.; Cortés-Carmona, M.; Henríquez, M.; Fuentealba, E.; Alvear, A.; Soto, C.; Durán, C.; Pastén, R.; Guerreiro, L.; Madrid, F.M.G. Cellular Automaton Simulation of Corrosion in 347H Steel Exposed to Molten Solar Salt at Pilot-Plant Scale. Materials 2025, 18, 713. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18030713
Reinoso-Burrows JC, Cortés-Carmona M, Henríquez M, Fuentealba E, Alvear A, Soto C, Durán C, Pastén R, Guerreiro L, Madrid FMG. Cellular Automaton Simulation of Corrosion in 347H Steel Exposed to Molten Solar Salt at Pilot-Plant Scale. Materials. 2025; 18(3):713. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18030713
Chicago/Turabian StyleReinoso-Burrows, Juan C., Marcelo Cortés-Carmona, Mauro Henríquez, Edward Fuentealba, Andrés Alvear, Carlos Soto, Carlos Durán, Raúl Pastén, Luis Guerreiro, and Felipe M. Galleguillos Madrid. 2025. "Cellular Automaton Simulation of Corrosion in 347H Steel Exposed to Molten Solar Salt at Pilot-Plant Scale" Materials 18, no. 3: 713. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18030713
APA StyleReinoso-Burrows, J. C., Cortés-Carmona, M., Henríquez, M., Fuentealba, E., Alvear, A., Soto, C., Durán, C., Pastén, R., Guerreiro, L., & Madrid, F. M. G. (2025). Cellular Automaton Simulation of Corrosion in 347H Steel Exposed to Molten Solar Salt at Pilot-Plant Scale. Materials, 18(3), 713. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18030713








