Microstructure and Corrosion Behaviors of Gas Tungsten Arc Welds for Borated Stainless Steel Using Various Filler Metals
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Welding Methods
2.2. Microstructure Analysis
2.3. Corrosion Test
2.3.1. Sensitization Test
2.3.2. Pitting Corrosion Test
2.3.3. Cyclic Polarization Test
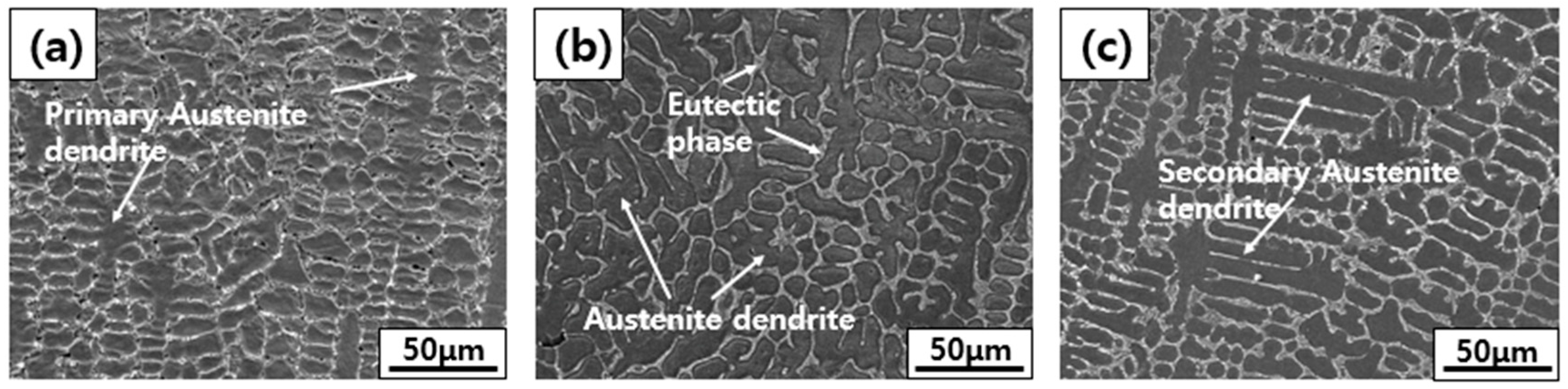
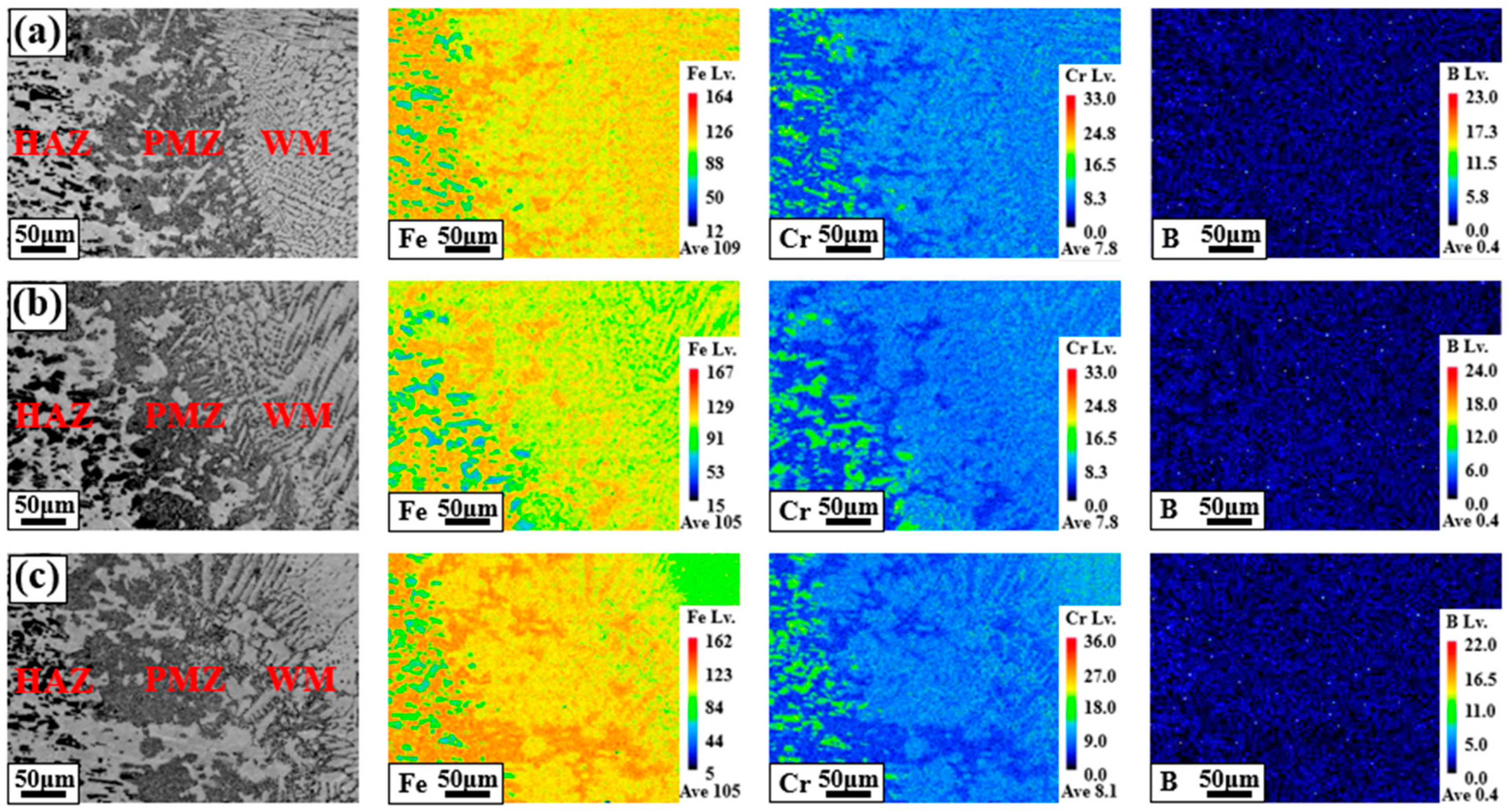
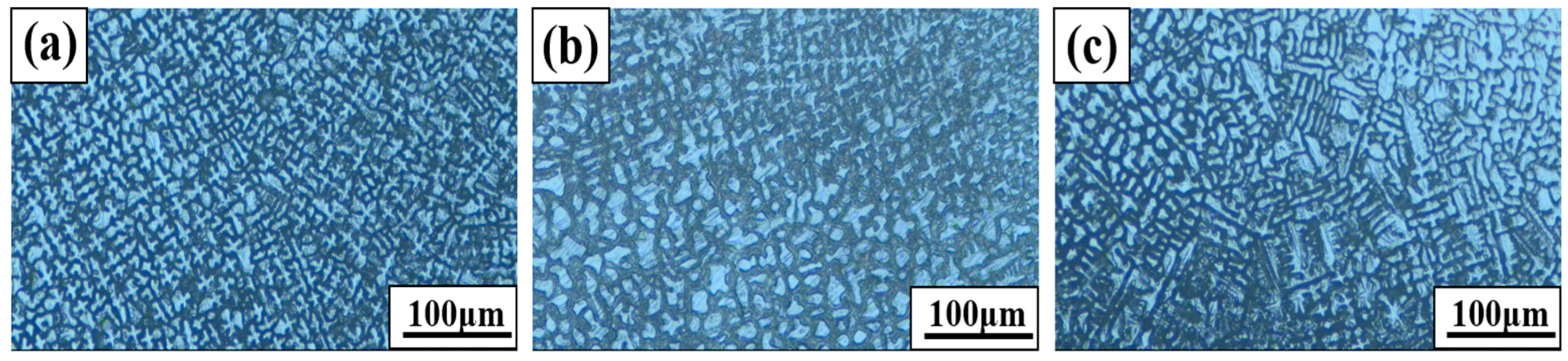
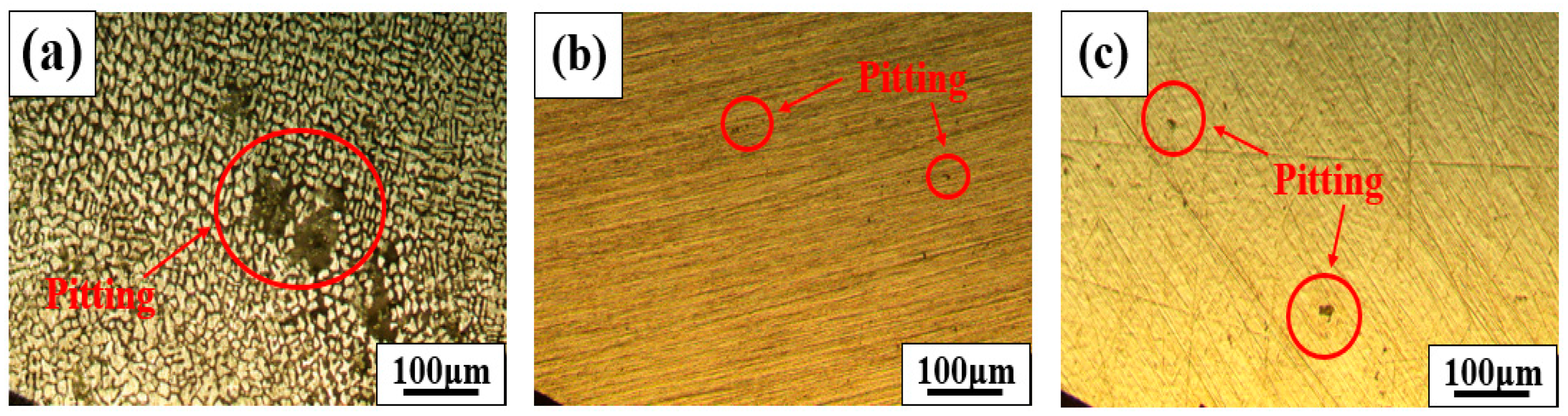
3. Results and Discussion
Microstructure and Component Behavior
4. Conclusions
- (1)
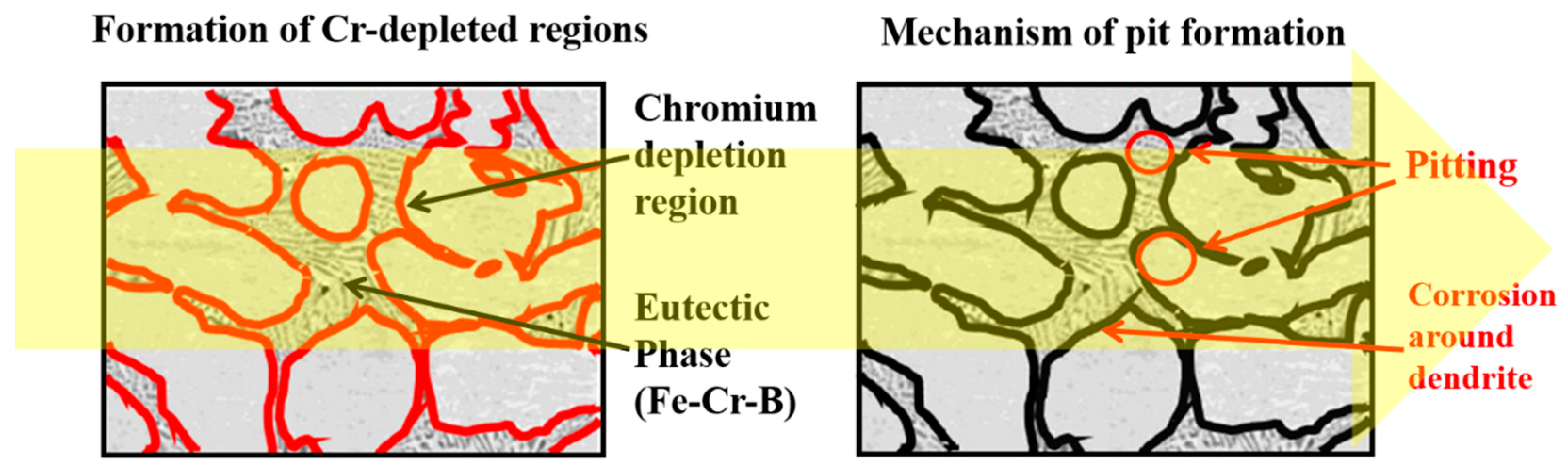
- Eutectic reactions involving the B component were observed in the ID regions of all WMs, resulting from the dilution of the B component of the BM into the WM during welding.
- (2)
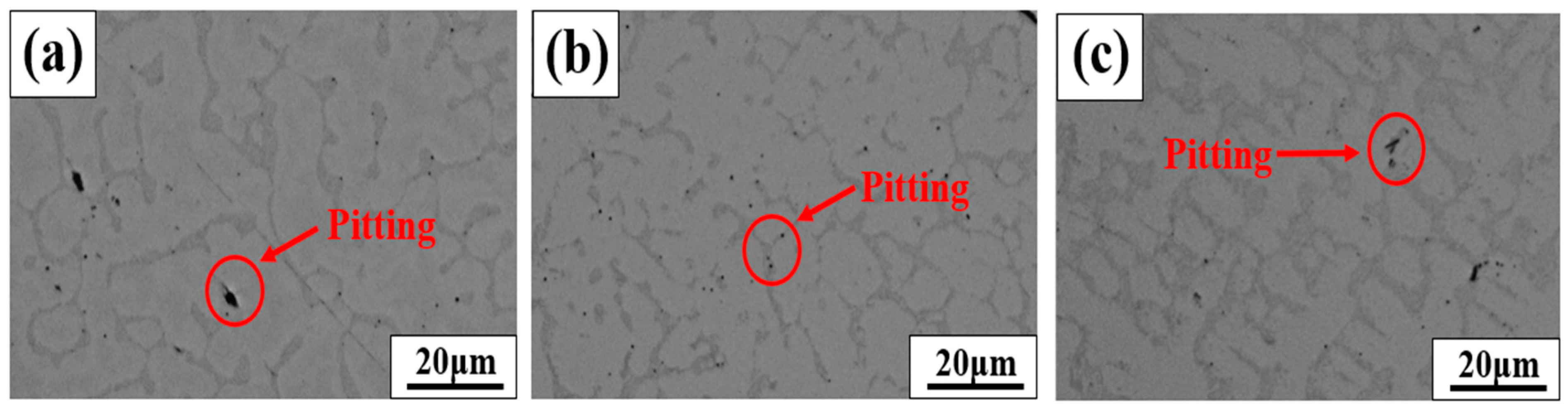
- As a result of the pitting corrosion sensitivity, 308L WM with a high fraction of B components (0.64 wt.%) showed the highest corrosion sensitivity.
- (3)
- As a result of the polarization test, 309L WM with a low fraction of B components (0.20 wt.%) exhibited the highest corrosion resistance (Epit; 0.87 V and Erp; 0.45 V), indicating the fastest repassivation after pitting formation.
- (4)
- Component segregation of boron in the WM has a negative impact on the corrosion resistance of welded specimens because it causes Cr-depleted areas.
- (5)
- Using a filler metal with a low boron content is expected to effectively improve the weldability and corrosion resistance of BSS materials.
- (6)
- When using BSS as a nuclear material, it is essential to carefully evaluate and control the boron content to ensure optimal weldability and corrosion resistance.
- (7)
- These research results can serve as a basis for developing filler wires and corrosion evaluation technologies for BSS welding.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wiss, T.; Hiernaut, J.-P.; Roudil, D.; Colle, J.-Y.; Maugeri, E.; Talip, Z.; Janssen, A.; Rondinella, V.; Konings, R.J.; Matzke, H.-J.; et al. Evolution of spent nuclear fuel in dry storage conditions for millennia and beyond. J. Nucl. Mater. 2014, 451, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilip, J.J.S.; Ram, G.D.J. Microstructures and Properties of Friction Freeform Fabricated Borated Stainless Steel. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2013, 22, 3034–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-W.; Wang, Z.-J.; Fu, D.-G.; Li, G.; Liu, H.-T.; Zhang, X.-M. Fabrication of high borated austenitic stainless steel thick plates with enhanced ductility and toughness using a hot-roll-bonding method. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 799, 140212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Moon, B.M.; Sohn, D.-S. Fabrication of Gd containing duplex stainless steel sheet for neutron absorbing structural materials. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2013, 45, 689–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, C.; Bai, J.; Liu, Y.; Huang, X.; Wu, H. Method research and engineering application of the B10-abundance correction for PWR. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2021, 378, 111250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesquita, A.Z.; Reis, I.C.; de Almeida, V.F.; Rodrigues, R.R. Boron-10 effect on the reactivity of the IPR-R1 Triga research reactor. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2019, 132, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovecký, M.; Závorka, J.; Jiřičková, J.; Ondráček, Z.; Škoda, R. Fixed neutron absorbers for improved nuclear safety and better economics in nuclear fuel storage, transport and disposal. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2023, 55, 2288–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, C.-H.; Jang, J.H.; Kim, S.-D.; Moon, J.; Ha, H.-Y.; Kang, J.-Y.; Lee, C.-H.; Lee, T.-H.; Kang, N. Effect of annealing on mechanical properties and microstructure evolution of borated stainless steels. J. Nucl. Mater. 2019, 515, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Cui, J.; Ma, A.; Ji, B.; Shi, J.; Liu, Z.; Yu, B.; Chen, X.; Ma, H.; Zhang, S.; et al. Unveiling the pitting corrosion mechanism of borated stainless steel in the wet storage environment of spent nuclear fuels. Acta Mater. 2024, 263, 119477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.; Ahn, J.-H.; Jung, R.; Kim, H.-J.; Chu, Y.; Choi, D.H.; Lee, H.; Jung, H.-D. Characterization of Various Stainless Steels Containing Gadolinium as Thermal Neutron Absorbing and Shielding Materials. Metals 2024, 14, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.D.; Nascimento, A.R.; Koga, G.Y.; Zepon, G.; Kiminami, C.S.; Botta, W.J.; Bolfarini, C. Alloy design for microstructural-tailored boron-modified ferritic stainless steel to ensure corrosion and wear resistance. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 24, 418–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM A887-89; Standard Specification for Borated Stainless Steel Plate, Sheet, and Strip for Nuclear Application. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2014.
- Moon, J.; Jang, J.H.; Kim, S.-D.; Lee, T.-H.; Ha, H.-Y.; Lee, C.-H.; Hong, H.-U. Different aspect of solidification cracking susceptibility and hot ductility behavior of borated stainless steels and the effects of boron content. Mater. Charact. 2020, 164, 110319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, H.-Y.; Kim, S.-D.; Jang, J.H.; Lee, T.-H.; Lee, C.-H.; Moon, J. Pitting Corrosion and Passive Behavior of Type AISI 304-based Borated Stainless Steels in a Boric Acid Solution. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 101506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-J.; Yin, F.-J.; Li, Y.-W.; Xie, G.-M.; Wang, G.-D.; Liu, H.-T. Investigation on joining high borated stainless steels through electron beam welding technology. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2022, 302, 117489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM A262-15; Standard Practices for Detecting Susceptibility to Intergranular Attack in Austenitic Stainless Steels. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021.
- ASTM G48-11; Standard Test Methods for Pitting and Crevice Corrosion Resistance of Stainless Steels and Related Alloys by Use of Ferric Chloride Solution. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.
- Bouchard, D.; Kirkaldy, J.S. Prediction of Dendrite Arm Spacings in Unsteadyand Steady-State Heat Flow of Unidirectionally Solidified Binary Alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. 1997, 28, 651–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbach, I.; Diepers, H.-J.; Beckermann, C. Transient growth and interaction of equiaxed dendrites. Cryst. Growth 2005, 275, 624–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seah, K.H.W.; Hemanth, J.; Sharma, S.C. Effect of the cooling rate on the dendrite arm spacing and the ultimate tensile strength of cast iron. J. Mater. Sci. 1998, 33, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorio, W.R.; Goulart, P.R.; Garcia, A.; Santos, G.A.; Neto, C.M. Effect of Dendritic Arm Spacing on Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Resistance of Al 9 Wt Pct Si and Zn 27 Wt Pct Al Alloys. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2006, 37, 2525–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, A.R.; Clayton, C.R.; Doss, K.; Lu, Y.C. On the Role of Cr in the Passivity of Stainless Steel. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1986, 133, 2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Composition (wt.%) | C | Mn | Si | Cr | Ni | B | N | Co | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Base metal | 304B6 | 0.08 | 2.00 | 0.75 | 19.00 | 13.50 | 1.62 | 0.10 | - |
| Filler wire | 308L | 0.022 | 1.84 | 0.39 | 19.75 | 9.66 | - | 0.027 | 0.164 |
| 309L | 0.011 | 1.54 | 0.47 | 23.12 | 13.78 | - | 0.055 | 0.184 | |
| 310 | 0.091 | 1.56 | 0.48 | 26.63 | 21.06 | - | 0.019 | 0.236 | |
| Pass | Current (A) | Voltage (V) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 50 (base current)—20 (pulse current) | 11 |
| 2~3 | 70 | 11 |
| WM | C | Mn | Si | Cr | Ni | B | N | Co |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 308L | 0.016 | 1.67 | 0.41 | 19.51 | 11.26 | 0.649 | 0.046 | 0.044 |
| 309L | 0.010 | 1.99 | 0.42 | 22.53 | 13.51 | 0.202 | 0.046 | 0.120 |
| 310 | 0.069 | 1.45 | 0.47 | 24.47 | 19.04 | 0.482 | 0.024 | 0.177 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seo, M.; Nam, H.; Yoon, Y.; Kang, N.; Park, C. Microstructure and Corrosion Behaviors of Gas Tungsten Arc Welds for Borated Stainless Steel Using Various Filler Metals. Materials 2025, 18, 550. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18030550
Seo M, Nam H, Yoon Y, Kang N, Park C. Microstructure and Corrosion Behaviors of Gas Tungsten Arc Welds for Borated Stainless Steel Using Various Filler Metals. Materials. 2025; 18(3):550. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18030550
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeo, Minseok, Hyunbin Nam, Yongju Yoon, Namhyun Kang, and Cheolho Park. 2025. "Microstructure and Corrosion Behaviors of Gas Tungsten Arc Welds for Borated Stainless Steel Using Various Filler Metals" Materials 18, no. 3: 550. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18030550
APA StyleSeo, M., Nam, H., Yoon, Y., Kang, N., & Park, C. (2025). Microstructure and Corrosion Behaviors of Gas Tungsten Arc Welds for Borated Stainless Steel Using Various Filler Metals. Materials, 18(3), 550. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18030550








