Study on the Dynamic Mechanical Response of Orthotropic Materials Under Biaxial Impact Loading
Abstract
1. Introduction
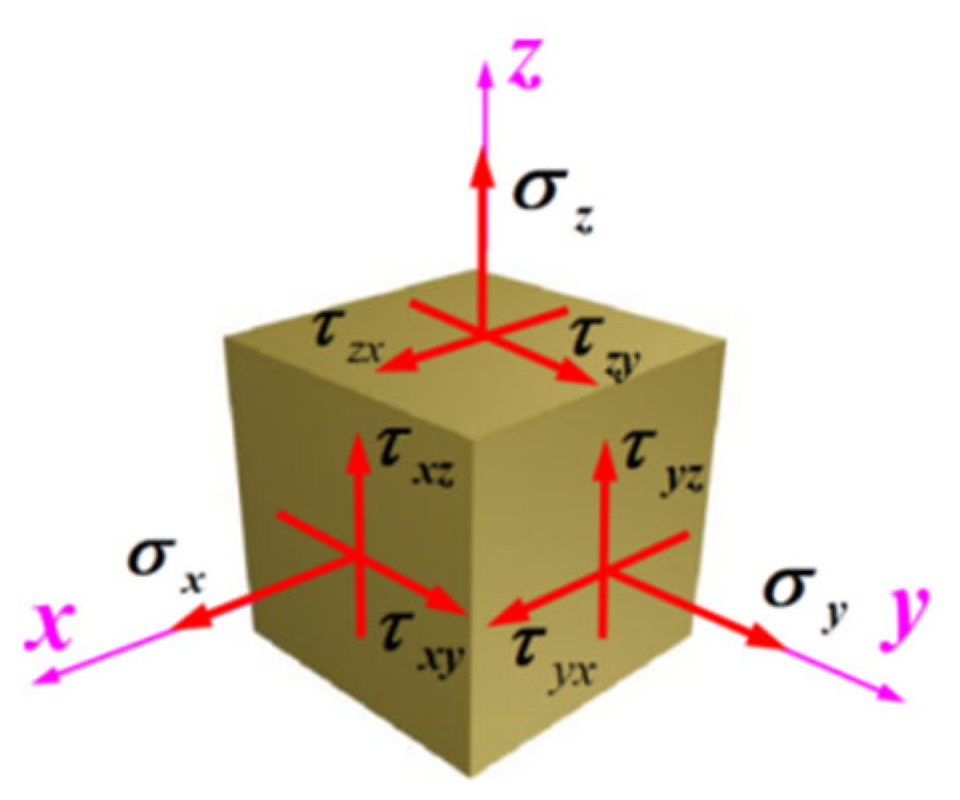
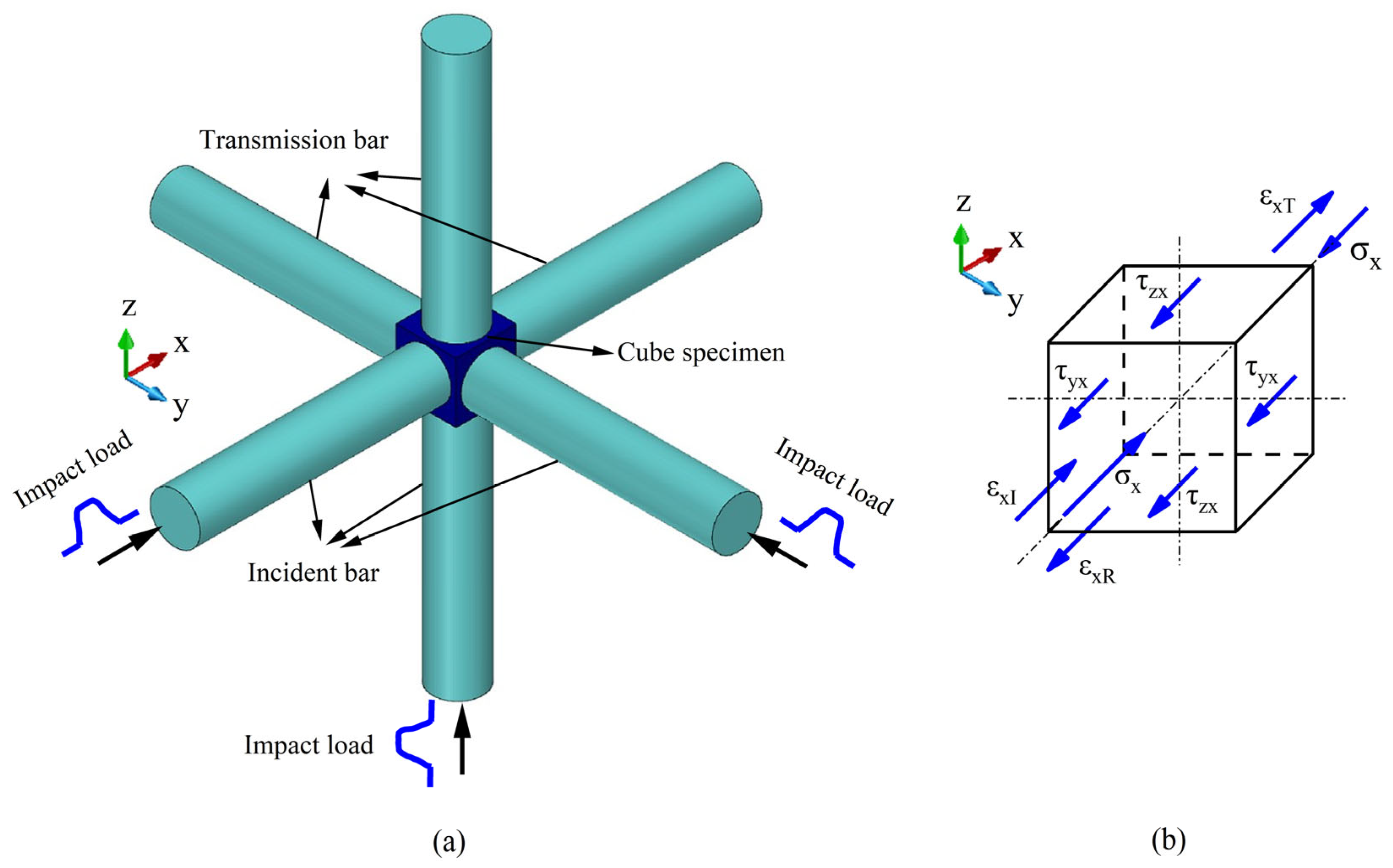
2. Theory Derivation of Specimen Under Complex Impact Loading
3. Materials and Methods
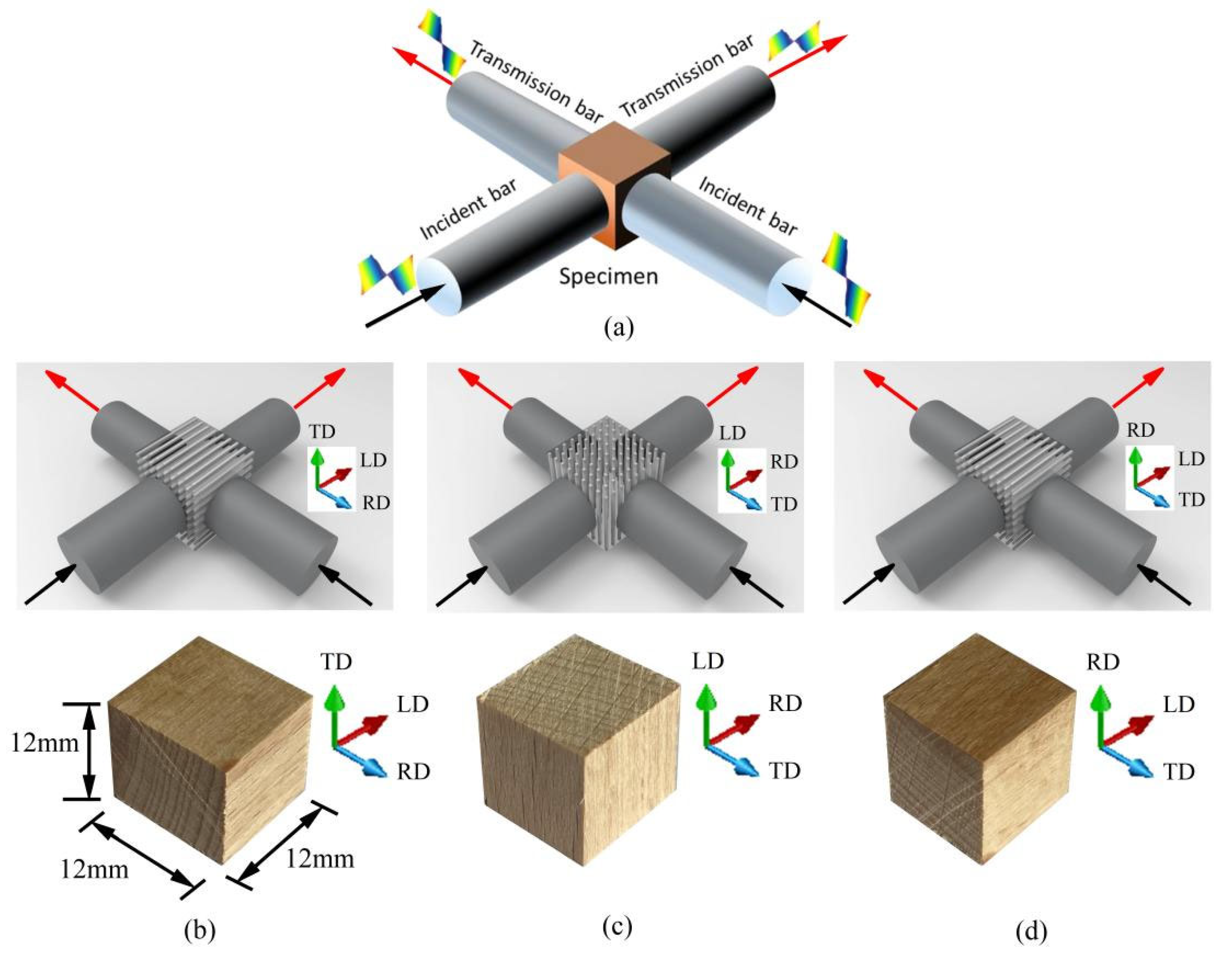
3.1. Test Materials
3.2. Experimental Apparatus
4. Results and Discussion
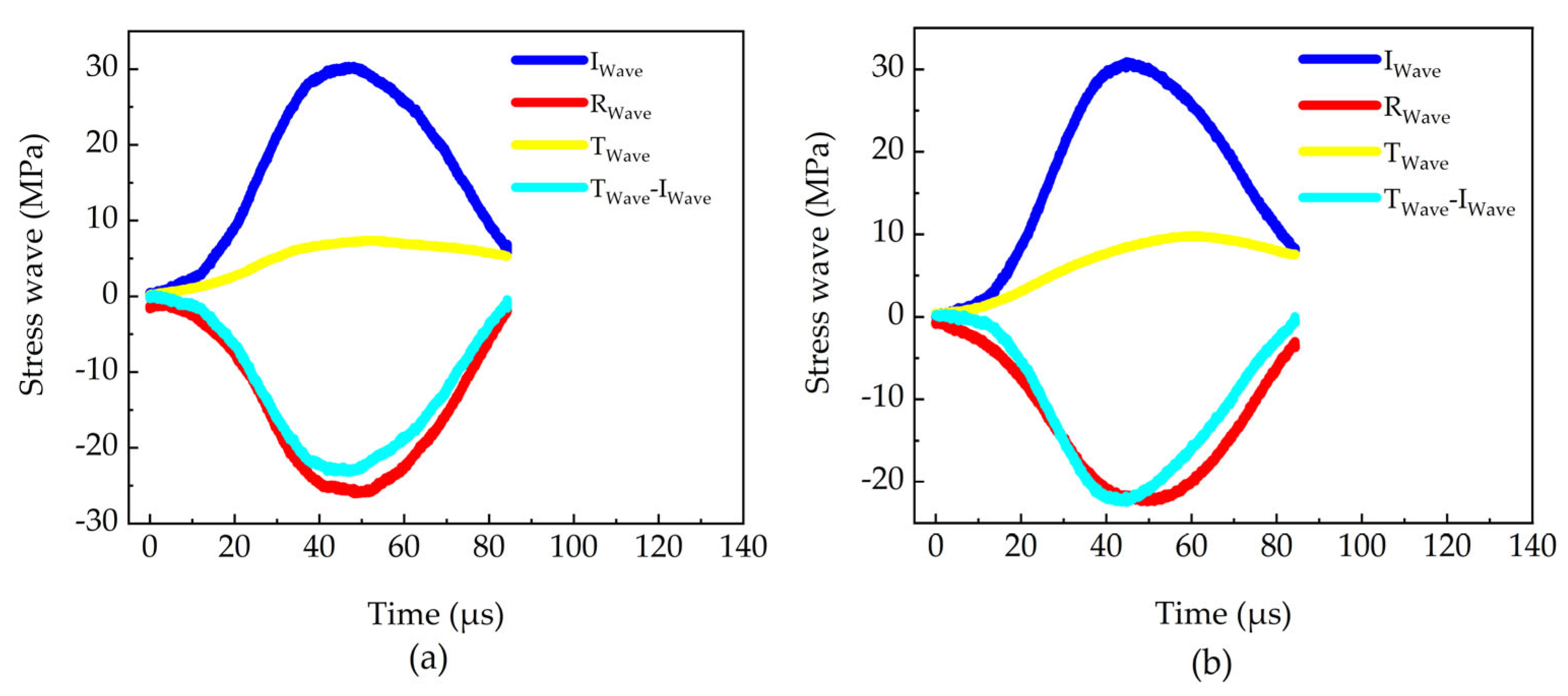
4.1. Experimental Validation
4.2. Analysis and Discussion of Test Data
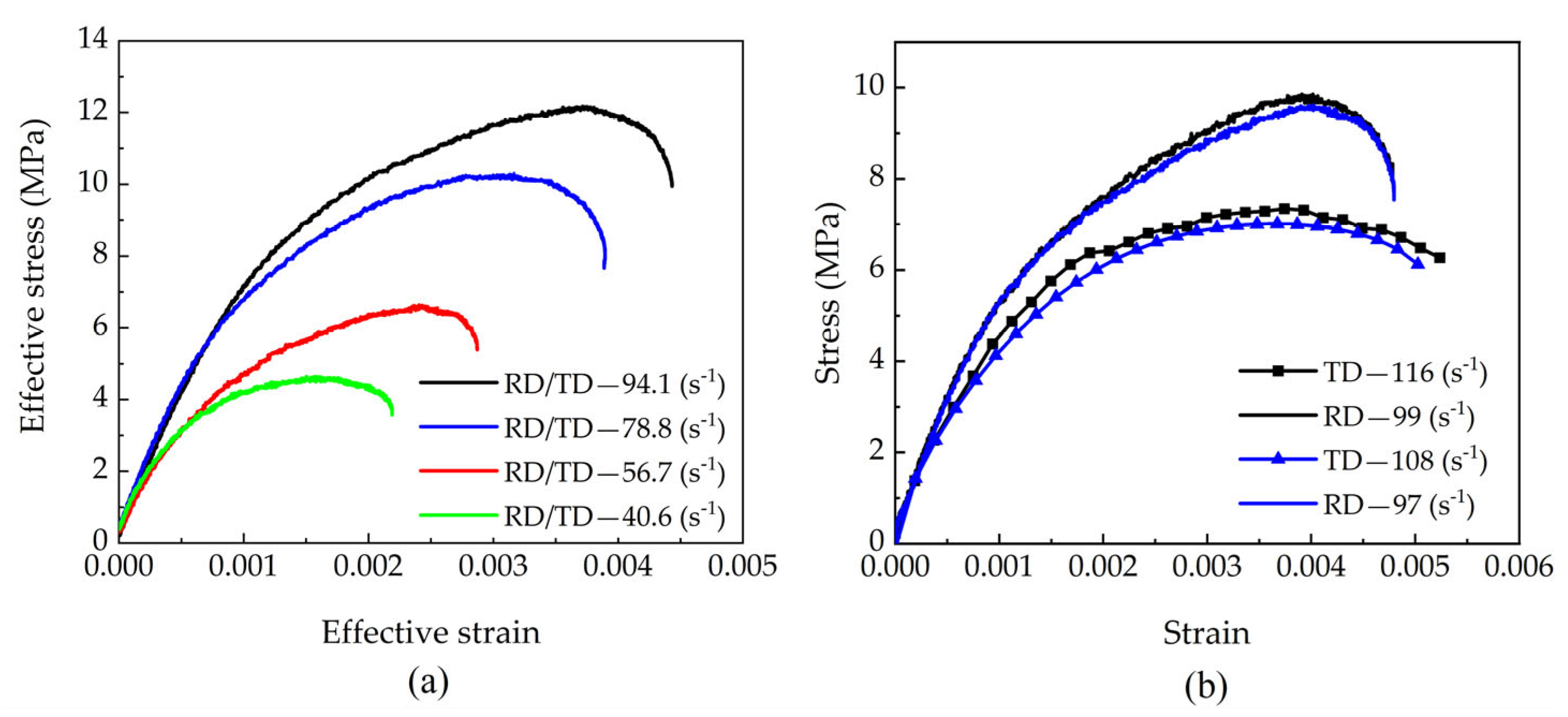
4.2.1. Impact Loading Tests on Beech Specimens in RD and TD
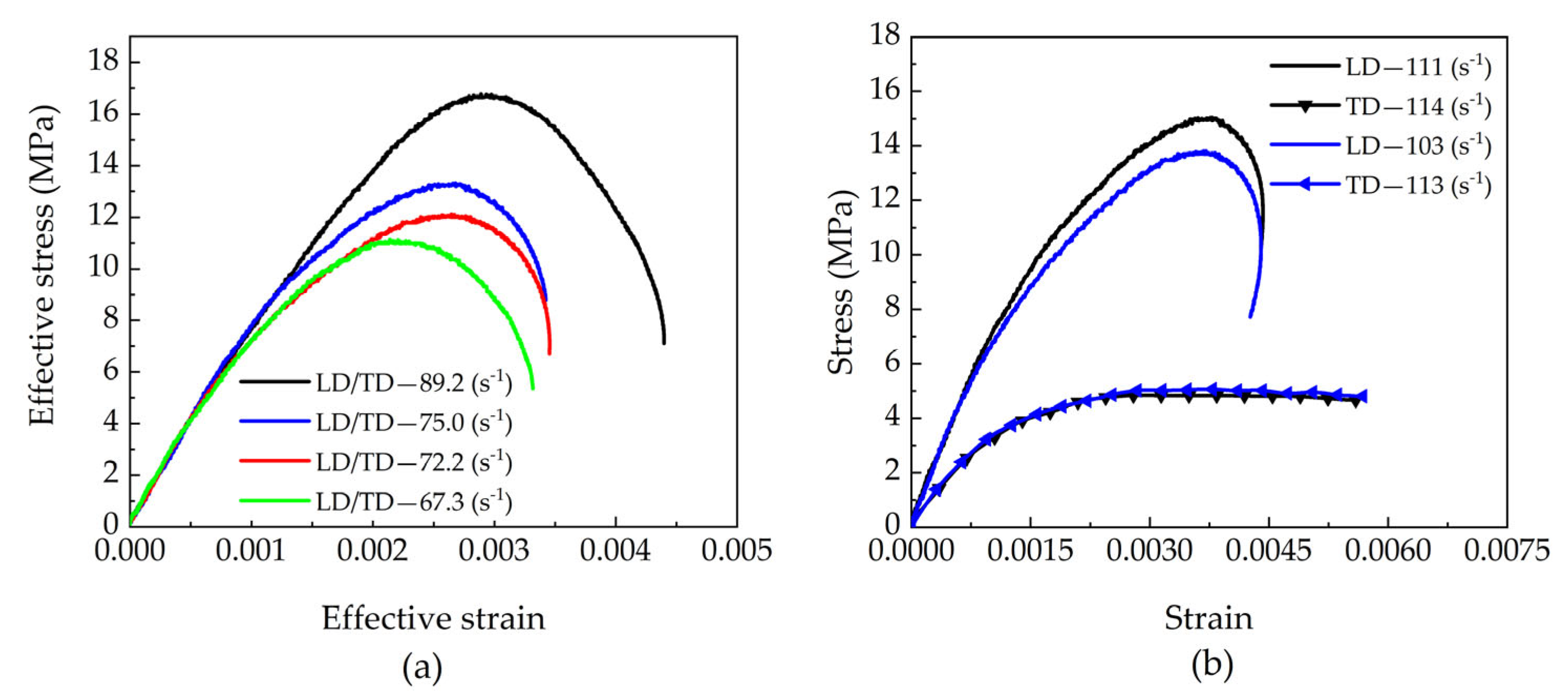
4.2.2. Impact Loading Tests on Beech Specimens in LD and RD
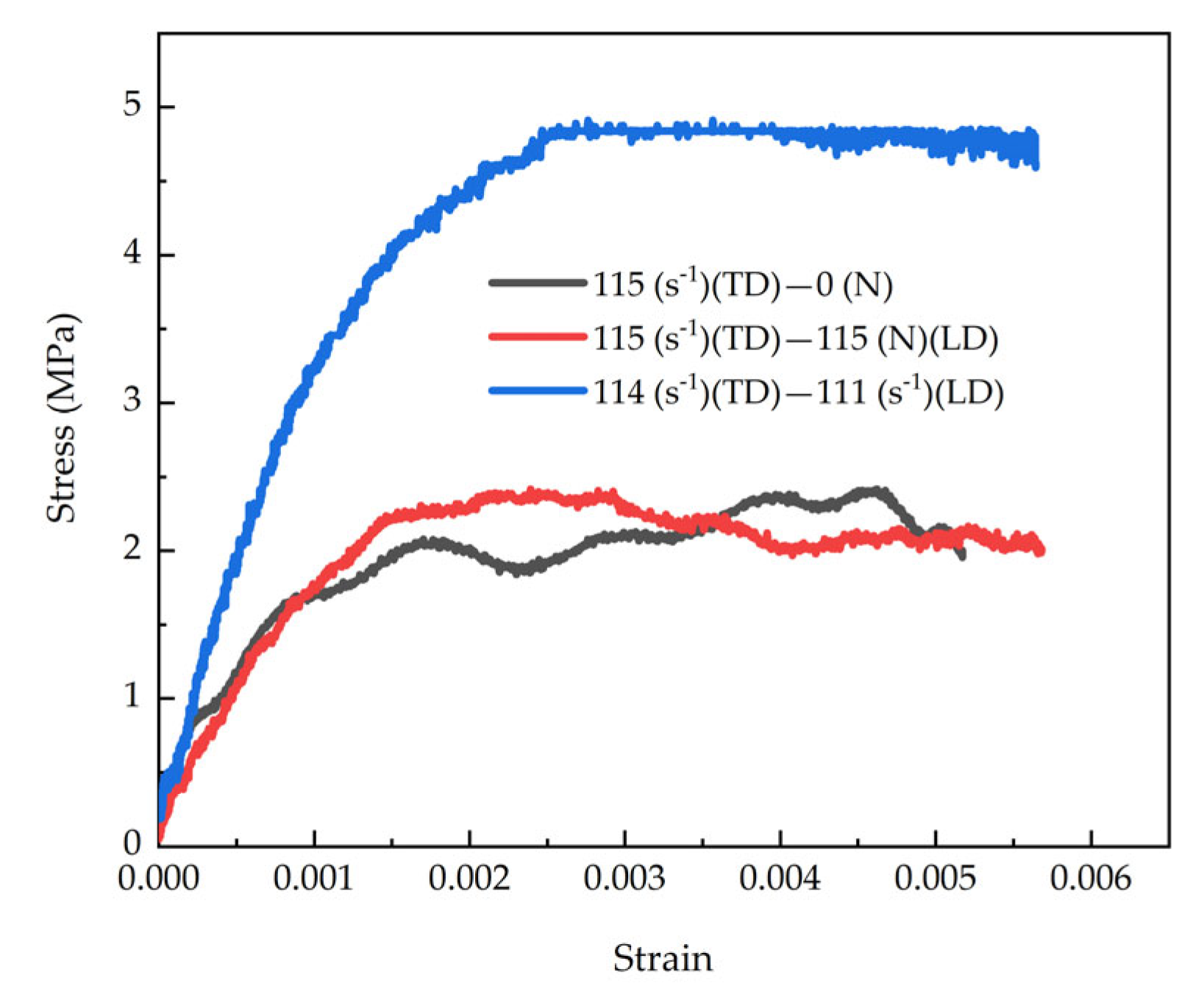
4.2.3. Impact Loading Tests on Beech Specimens in LD and TD
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The direction-dependent dynamic response mechanism of beech wood under biaxial impact was elucidated. Under different combined loading conditions (radial-tangential, radial-longitudinal and longitudinal-tangential), the material exhibits significantly different dynamic strength and deformation behaviors across different orientations, following the consistent strength hierarchy: longitudinal > radial > tangential. This reveals the heterogeneous and direction-coupled characteristics of orthotropic materials under complex stress states.
- (2)
- The synergistic effect of biaxial stress states on the dynamic mechanical behavior was revealed. Experimental results demonstrate that biaxial loading not only significantly enhances the equivalent Stress–Strain response, resulting in overall curve elevation, but also alters the material’s deformation mechanisms and energy absorption modes through the coupled effects of strain rate strengthening and multiaxial stresses, thereby extending beyond the traditional mechanical understanding framework under uniaxial impact.
- (3)
- The coupling mechanism between lateral confinement and multiaxial loading on the dynamic response was discovered. Under identical strain rate conditions, the tangential stress amplitude induced by biaxial loading is significantly higher than that under uniaxial or laterally confined uniaxial conditions, indicating that the interaction of multiaxial stress states plays a decisive role in the material’s dynamic performance. This finding demonstrates that conventional dynamic constitutive models based on isotropic assumptions are inadequate for describing the response of orthotropic materials under multiaxial impact.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.; Hao, H.; Lu, Y. Anisotropic dynamic damage and fragmentation of rock materials under explosive loading. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 2003, 41, 917–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniou, A.; Daudeville, L.; Marin, P.; Potapov, S. Extending the discrete element method to account for dynamic confinement and strain-rate effects for simulating hard impacts on concrete targets. J. Dyn. Behav. Mater. 2025, 11, 119–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Z.; Lok, T.S.; Hong, L.; Yin, T. Innovative testing technique of rock subjected to coupled static and dynamic loads. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. 2008, 45, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Chawla, K.; Maheswaran, B.; Syrlybayev, D.; Thevamaran, R. Embracing nonlinearity and geometry: A dimensional analysis guided design of shock absorbing materials. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 7148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, S.; Tao, W.; Liang, Y.; Huan, S.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J. Development of a true-biaxial split Hopkinson pressure bar device and its application. Materials 2021, 14, 7298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolsky, H. An investigation of the mechanical properties of materials at very high rates of loading. Proc. Phys. Soc. 1949, B62, 676–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Song, W.; Zhao, W.; Tan, X. An experimental study on dynamic mechanical properties of fiber-reinforced concrete under different strain rates. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Han, R.; Tang, S.; Sun, G.; Wang, H. Dynamic mechanical properties and energy analysis of argillaceous siltstone and quartzite under impact loading. J. Appl. Geophys. 2025, 243, 105934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forquin, P.; Gary, G.; Gatuingt, F. A testing technique for concrete under confinement at high rates of strain. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2008, 35, 425–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Lu, H.; Cooper, W.L.; Komanduri, R. Effect of mass density on the compressive behavior of dry sand under confinement at high strain rates. Exp. Mech. 2011, 51, 1499–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, F.; Si, X.; Li, X.; Wang, S. Dynamic triaxial compression tests on sandstone at high strain rates and low confining pressures with split Hopkinson pressure bar. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2019, 113, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Mao, J.; Yu, X.; Zhou, B.; Wang, L. Study on the Dynamic Mechanical Properties of ultrahigh-performance concrete under triaxial constraints. Materials 2023, 16, 6591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, S.; Yu, B.; Wang, L. The dynamic impact experiments under active confining pressure and the constitutive equation of PP/PA blends at multi-axial compressive stress state. Macromol. Symp. 2009, 286, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Shan, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, L.; Gao, G.; Hu, S.; Wang, P. Dynamic compression behaviors of concrete under true triaxial confinement: An experimental technique. Mech. Mater. 2019, 140, 103220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Zhang, Q.B.; Wu, G.; Li, J.C.; Zhao, J. Dynamic mechanical and fracture behaviour of sandstone under multiaxial loads using a triaxial hopkinson bar. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2019, 52, 2175–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummeltenberg, A.; Curbach, M. Entwurf und Aufbau eines zweiaxialen Split-Hopkinson-Bars. Beton Und Stahlbetonbau 2012, 107, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, H.; Suo, T.; Wu, B.; Li, Y.; Zhao, H. A versatile split Hopkinson pressure bar using electromagnetic loading. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2018, 116, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, K.; Qi, L.; Kang, H.; Guo, Y.; Li, Y. A novel technique to measure the biaxial properties of materials at high strain rates by electromagnetic Hopkinson bar system. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2022, 167, 104286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Liang, J.; Li, Y.; Cui, H.; Li, Y. Dynamic biaxial compression of CFRP laminates using electromagnetic loading. Acta Mech. Solida Sin. 2022, 35, 891–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Lu, J.; Li, C.; Li, M.; Gao, M. Experimental study on the mechanical and failure behaviors of deep rock subjected to true triaxial stress: A review. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2022, 32, 915–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Zhu, J.; Zhou, T.; Zhao, J. Novel three-dimensional rock dynamic tests using the true triaxial electromagnetic Hopkinson bar system. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2021, 54, 2079–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, B.; Zouari, A.; Zhao, H. Biaxial compression tests on Hopkinson bars. Proceedings 2018, 2, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, B.; Quillery, P.; Zouari, A.; Zhao, H. Exploratory tests on a biaxial compression Hopkinson bar set-up. Exp. Mech. 2021, 61, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Hao, H.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Huan, S. Volumetric properties of concrete under true triaxial dynamic compressive loadings. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2019, 31, 04019126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quillery, P.; Durand, B.; Huang, M.; Seck, K.; Zhao, H. Dynamic biaxial compression tests using 4 symmetric input Hopkinson bars. Exp. Mech. 2024, 64, 729–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Pang, Z.; Li, Z.; Wen, G.; Su, Z.; He, J.; Liu, K.; Jiang, D.; Li, Z.; Chen, S.; et al. An origami-wheeled robot with variable width and enhanced sand walking versatility. Thin-Walled Struct. 2025, 206, 112645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benvenuti, E.; Orlando, N.; Gebhardt, C.; Kaliske, M. An orthotropic multi-surface damage-plasticity FE-formulation for wood: Part I—Constitutive model. Comput. Struct. 2020, 240, 106350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Pang, S.; Chen, S.; Liu, Y.; Aiyiti, W.; Chen, Z. Design and application of hybrid lattice metamaterial structures with high energy absorption and compressive resistance. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 33, 7100–7112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, L.; He, J.; Wen, G.; Wang, Z.; Yang, J.; Xie, Y.; Liu, J. Multifunctional TPMS-based metastructures. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2025, 293, 110208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, S.; Liang, Y.; Tao, W.; Liu, Y.; Huan, S.; Qin, H. Effect of the strain rate and fiber direction on the dynamic mechanical properties of beech wood. Forests 2019, 10, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xia, K. High strength biocomposites consolidated from hardwood particles by severe plastic deformation. Cellulose 2019, 26, 1067–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Tian, Q.; Nie, J.; Cao, P.; Tan, Z. Mechanical properties and damage mechanisms of woods under extreme environmental conditions. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 20, e03146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Musawi, H.; Huber, C.; Gusenbauer, C.; Ungerer, B.; Grabner, M.; Ploszczanski, L.; Schönbauer, B.; Painer, J.; Krenke, T.; Müller, U. The compressive behaviour of beech and birch at different moisture and temperature conditions along the grain. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2024, 159, 108017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambarelli, S.; Bošnjak, J.; Platas, R.N.F.; Jin, K. Experimental study on mechanical properties of European oak and Norway spruce clear wood. Materials 2025, 18, 3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Z.; Lu, Y.; Wu, G.; Bai, L.; Barker-Rothschild, D.; Lyu, J.; Liu, S.; Rojas, O.J. Wood elasticity and compressible wood-based materials: Functional design and applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2025, 147, 101354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Li, W.; Li, L.; Li, T.; Ma, C. Crashworthiness design and multi-objective optimization for bio-inspired hierarchical thin-walled structures. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2022, 131, 929–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Xiao, J. Crashworthiness design and multi-objective optimization of bionic thin-walled hybrid tube structures. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2024, 139, 999–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, G.; Zhang, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; He, J.; Chen, Z.; Liu, J.; Xie, Y. Origami-based acoustic metamaterial for tunable and broadband sound attenuation. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2023, 239, 107872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moilanen, C.; Björkqvist, T.; Engberg, B.; Salminen, L.; Saarenrinne, P. High strain rate radial compression of Norway spruce earlywood and latewood. Cellulose 2016, 23, 873–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wouts, J.; Haugou, G.; Oudjene, M.; Coutellier, D.; Morvan, H. Strain rate effects on the compressive response of wood and energy absorption capabilities—Part A: Experimental investigations. Compos. Struct. 2016, 149, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Song, B.; Dang, L.; Zhang, Z. Effect of strain rate on mechanical properties of the bamboo material under quasi-static and dynamic loading condition. Compos. Struct. 2018, 200, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wouts, J.; Haugou, G.; Oudjene, M.; Morvan, H.; Coutellier, D. Strain rate effects on the compressive response of wood and energy absorption capabilities—Part B: Experimental investigation under rigid lateral confinement. Compos. Struct. 2018, 204, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walley, S.; Perry, J. The high-rate mechanical properties of wood mostly obtained using the kolsky bar: A review. J. Dyn. Behav. Mater. 2025, 11, 284–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

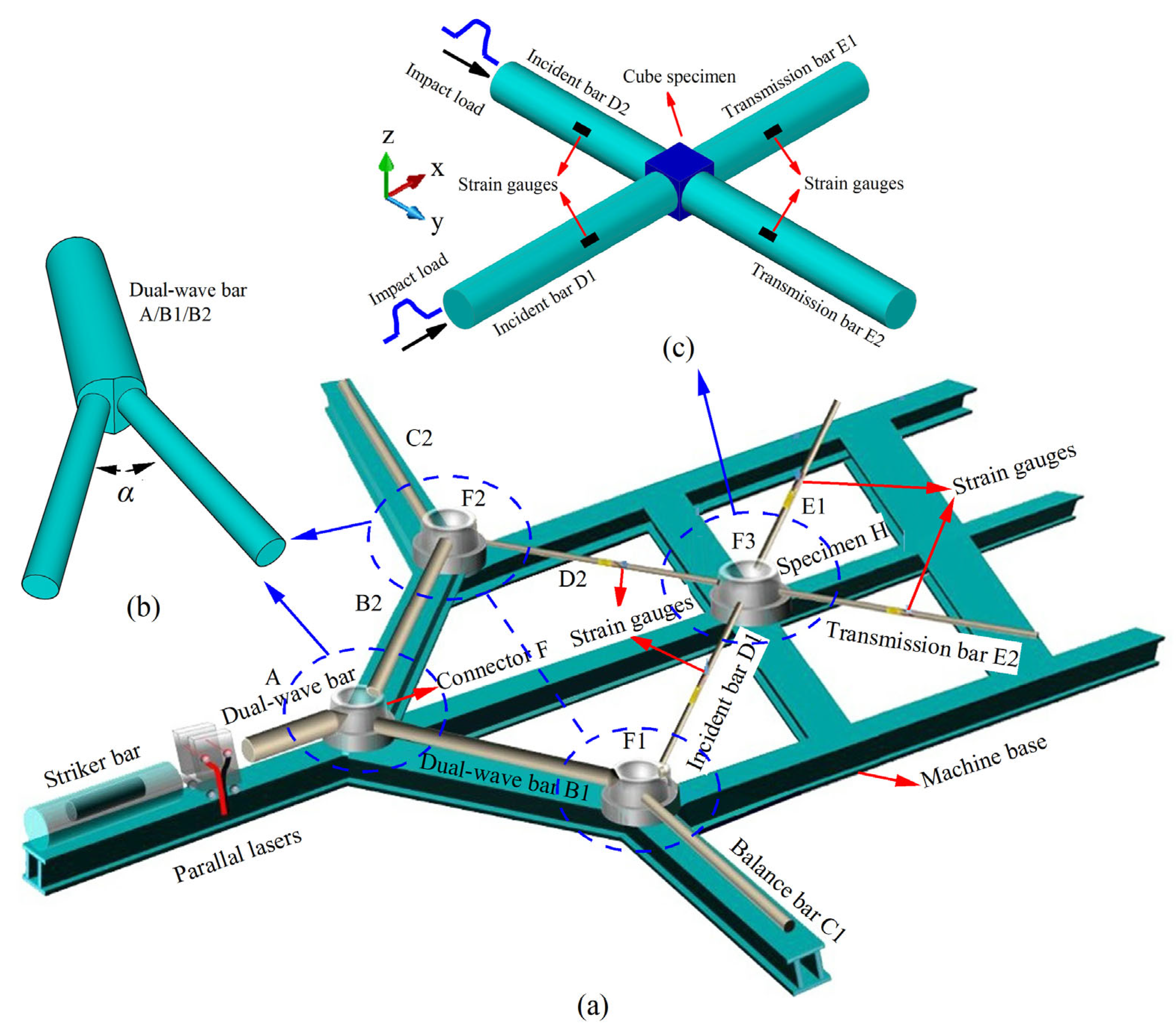






| Material | Density [g/cm3] | Elasticity Modulus [GPa] | Poisson Ratio | Diameter × Length [mm × mm] | Angle [°] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Striker bar | SUS304 | 7.93 | 193 | 0.3 | Ø50 × 200 | - |
| DWB A | SUS304 | 7.93 | 193 | 0.3 | Ø40 × 1514.14 | 70 |
| DWB B1/B2 | SUS304 | 7.93 | 193 | 0.3 | Ø20 × 1499.61 | 160 |
| Balance bar C1/C2 | SUS304 | 7.93 | 193 | 0.3 | Ø10 × 1210 | - |
| Incident bar D1/D2 | SUS304 | 7.93 | 193 | 0.3 | Ø10 × 1210 | - |
| Transmission bar E1/E2 | SUS304 | 7.93 | 193 | 0.3 | Ø10 × 1210 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pang, S.; Tao, W.; Ou, H.; Liu, J.; Chen, J.; Liu, L.; Huan, S.; Pan, Z.; Huang, Y. Study on the Dynamic Mechanical Response of Orthotropic Materials Under Biaxial Impact Loading. Materials 2025, 18, 5634. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18245634
Pang S, Tao W, Ou H, Liu J, Chen J, Liu L, Huan S, Pan Z, Huang Y. Study on the Dynamic Mechanical Response of Orthotropic Materials Under Biaxial Impact Loading. Materials. 2025; 18(24):5634. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18245634
Chicago/Turabian StylePang, Shumeng, Weijun Tao, Haifeng Ou, Jie Liu, Jiangping Chen, Liangkun Liu, Shi Huan, Zhaodong Pan, and Yiquan Huang. 2025. "Study on the Dynamic Mechanical Response of Orthotropic Materials Under Biaxial Impact Loading" Materials 18, no. 24: 5634. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18245634
APA StylePang, S., Tao, W., Ou, H., Liu, J., Chen, J., Liu, L., Huan, S., Pan, Z., & Huang, Y. (2025). Study on the Dynamic Mechanical Response of Orthotropic Materials Under Biaxial Impact Loading. Materials, 18(24), 5634. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18245634






