Effect of Mn Content and Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Properties of Laser Cladding of FeCoNiCrTi High-Entropy Alloy Coating
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Mn Content on Coatings
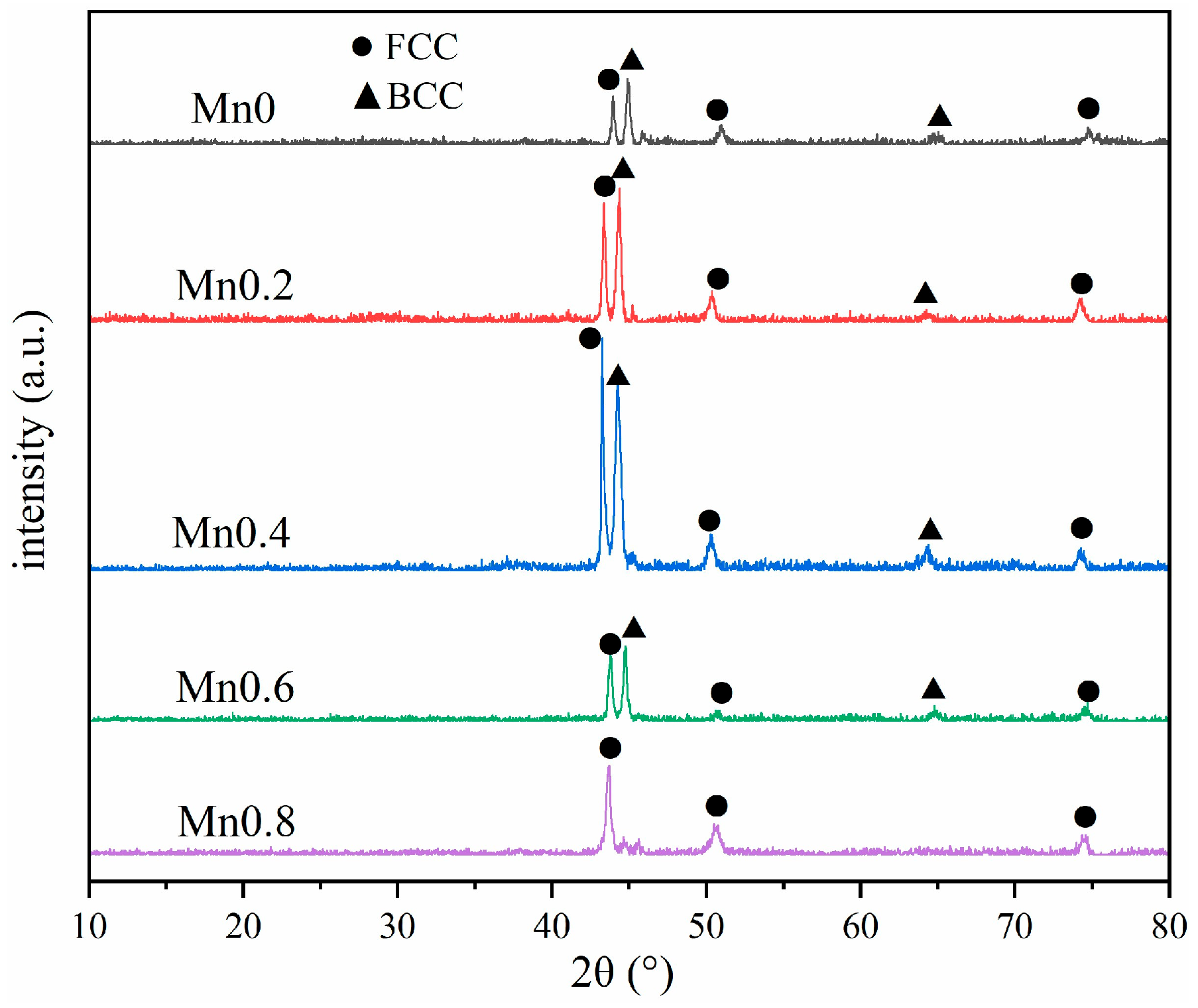
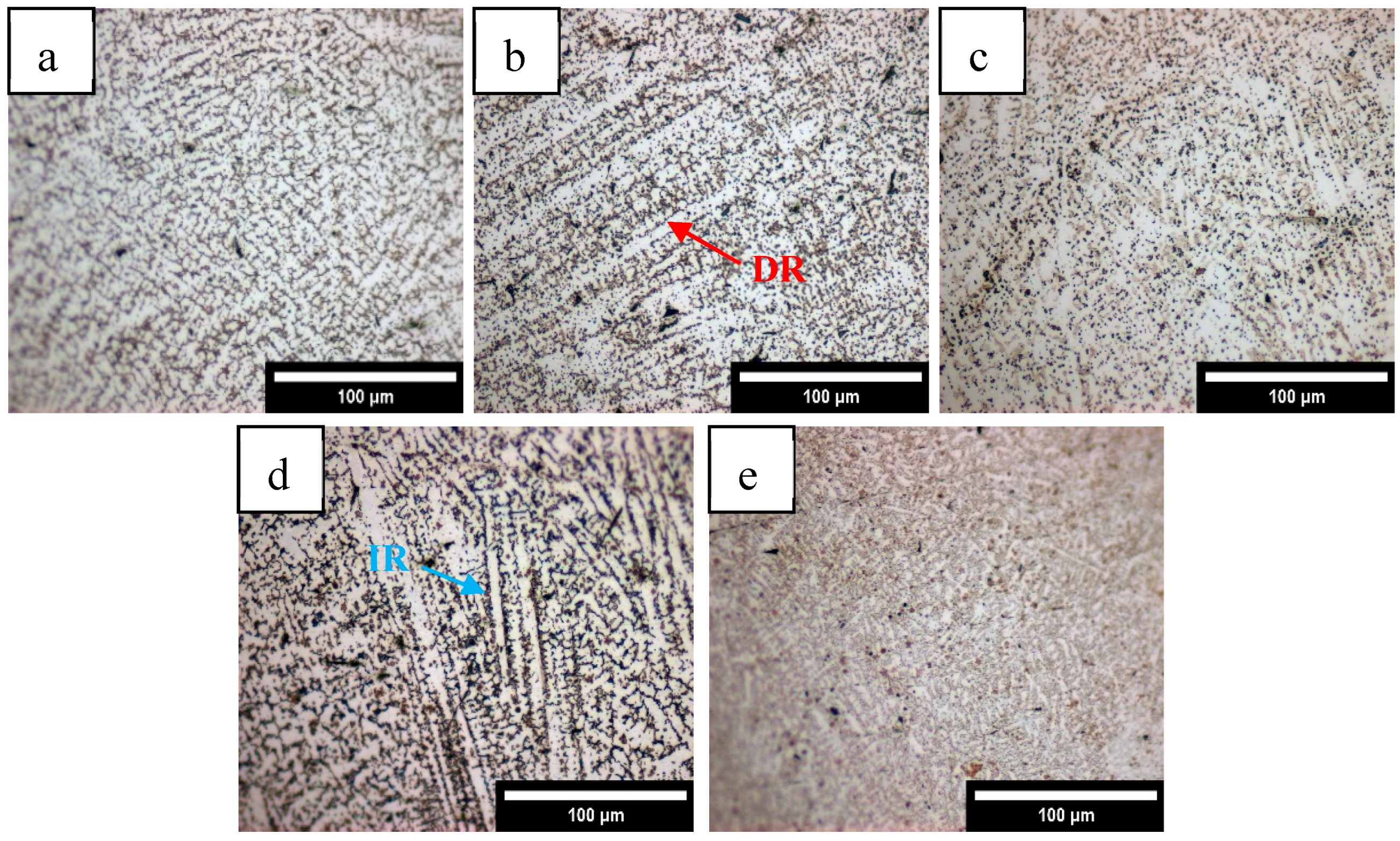
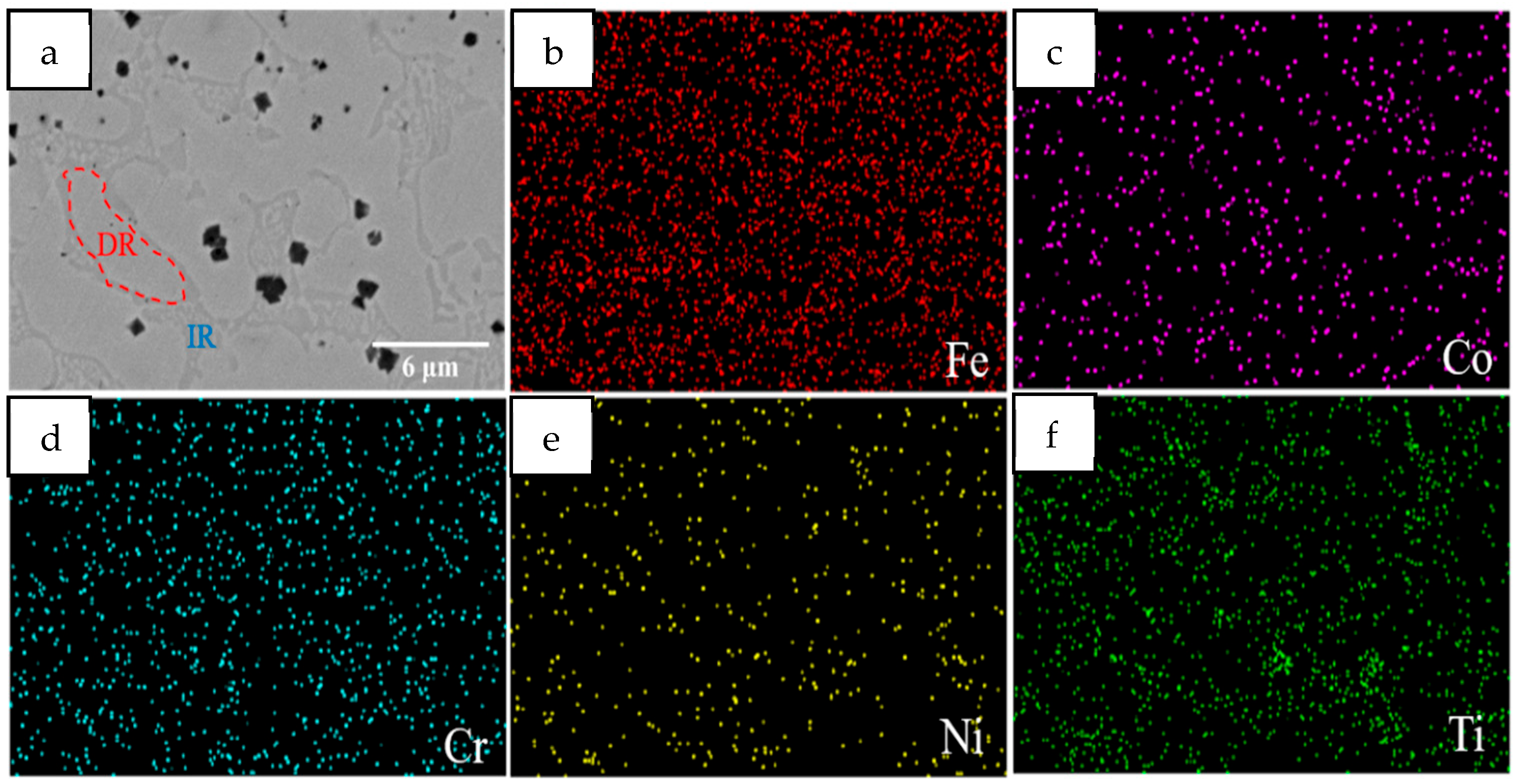
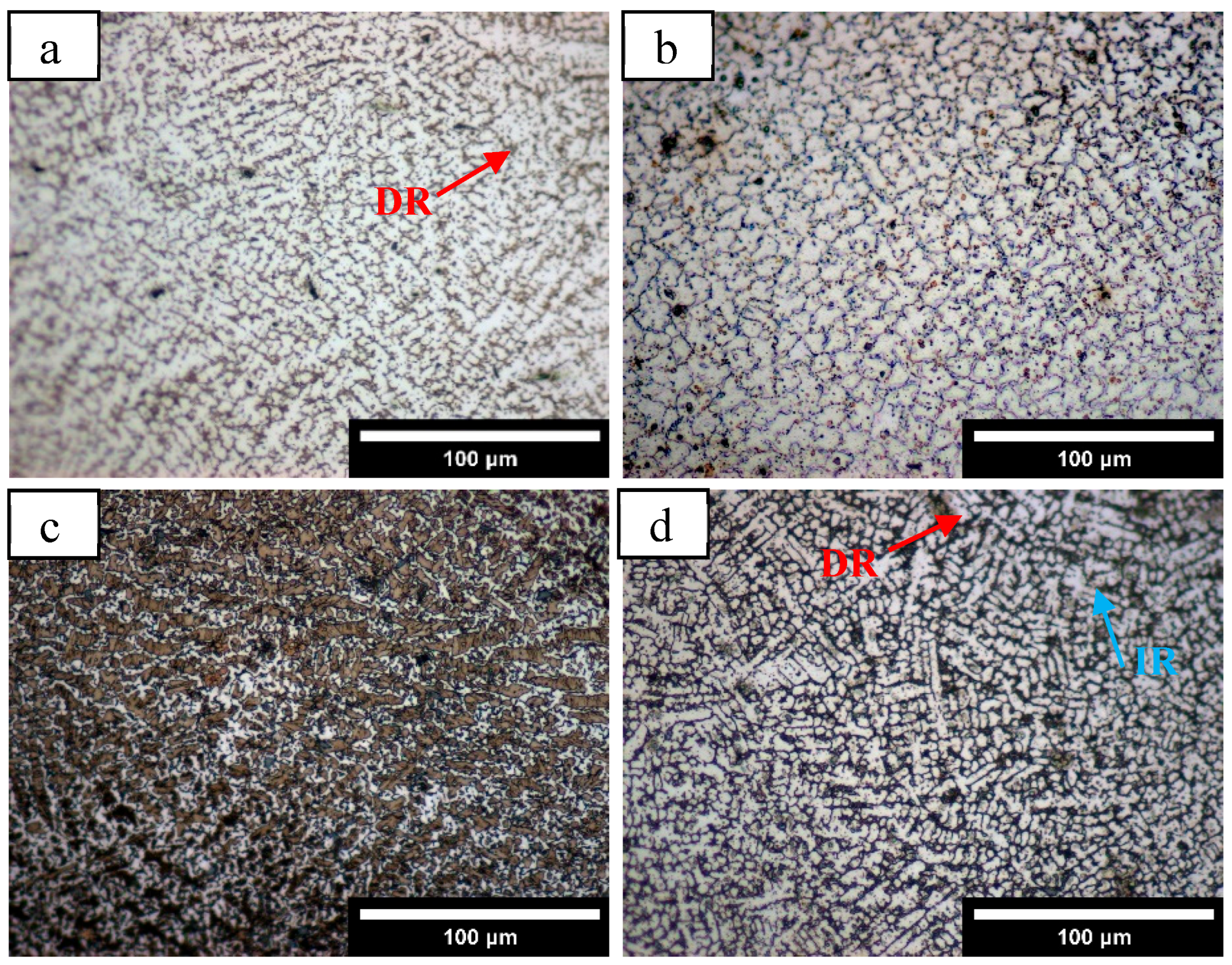
3.1.1. Microstructure Characterization
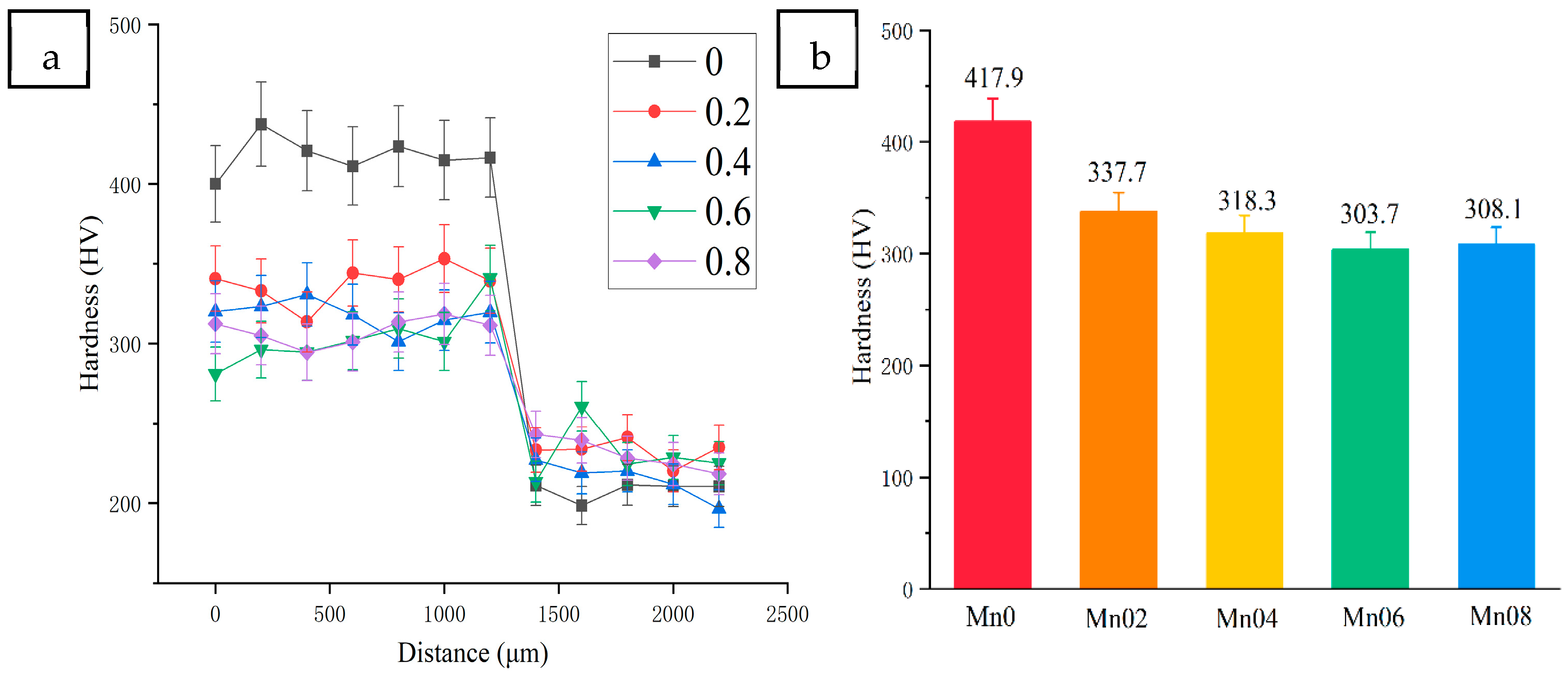
3.1.2. Microhardness
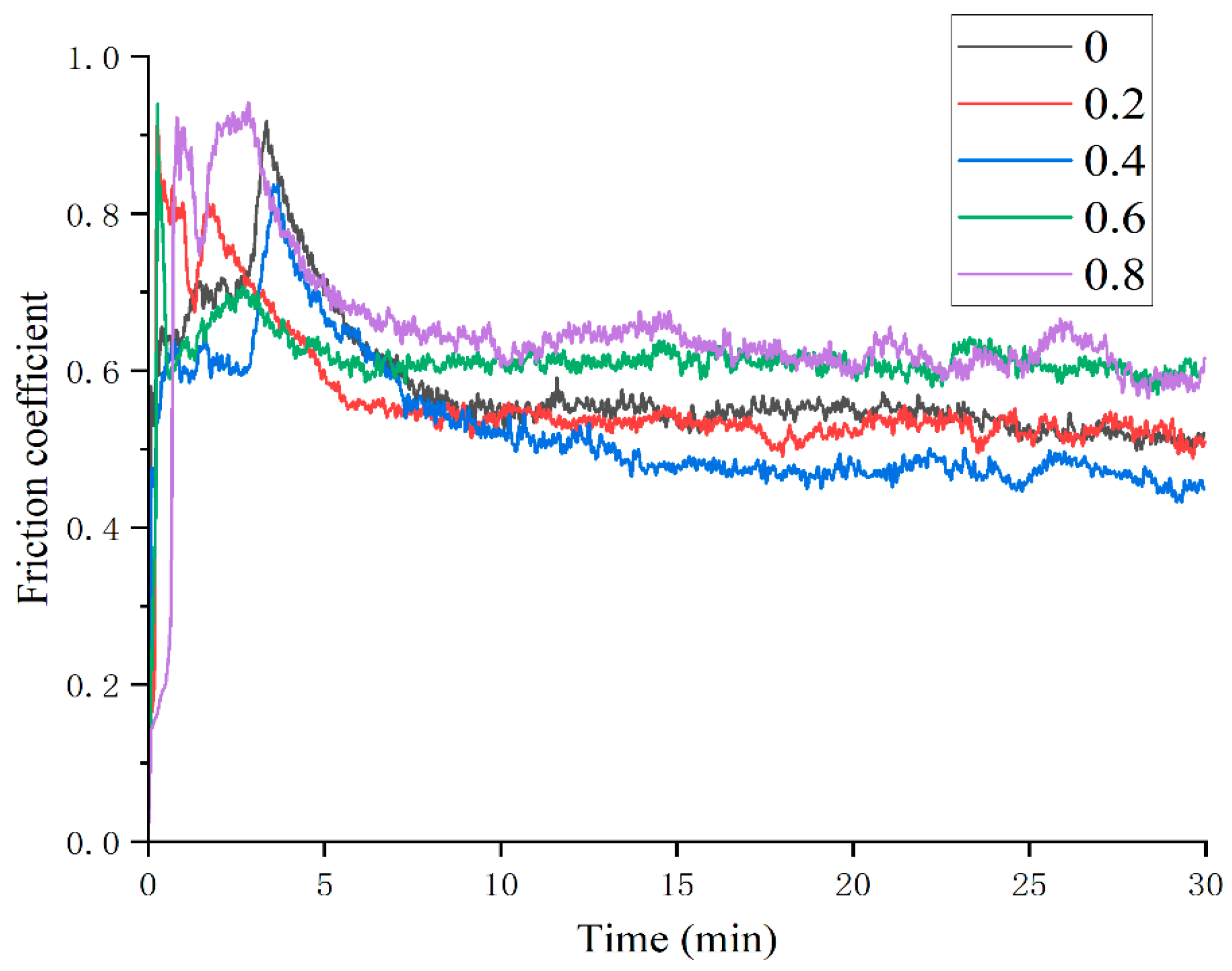
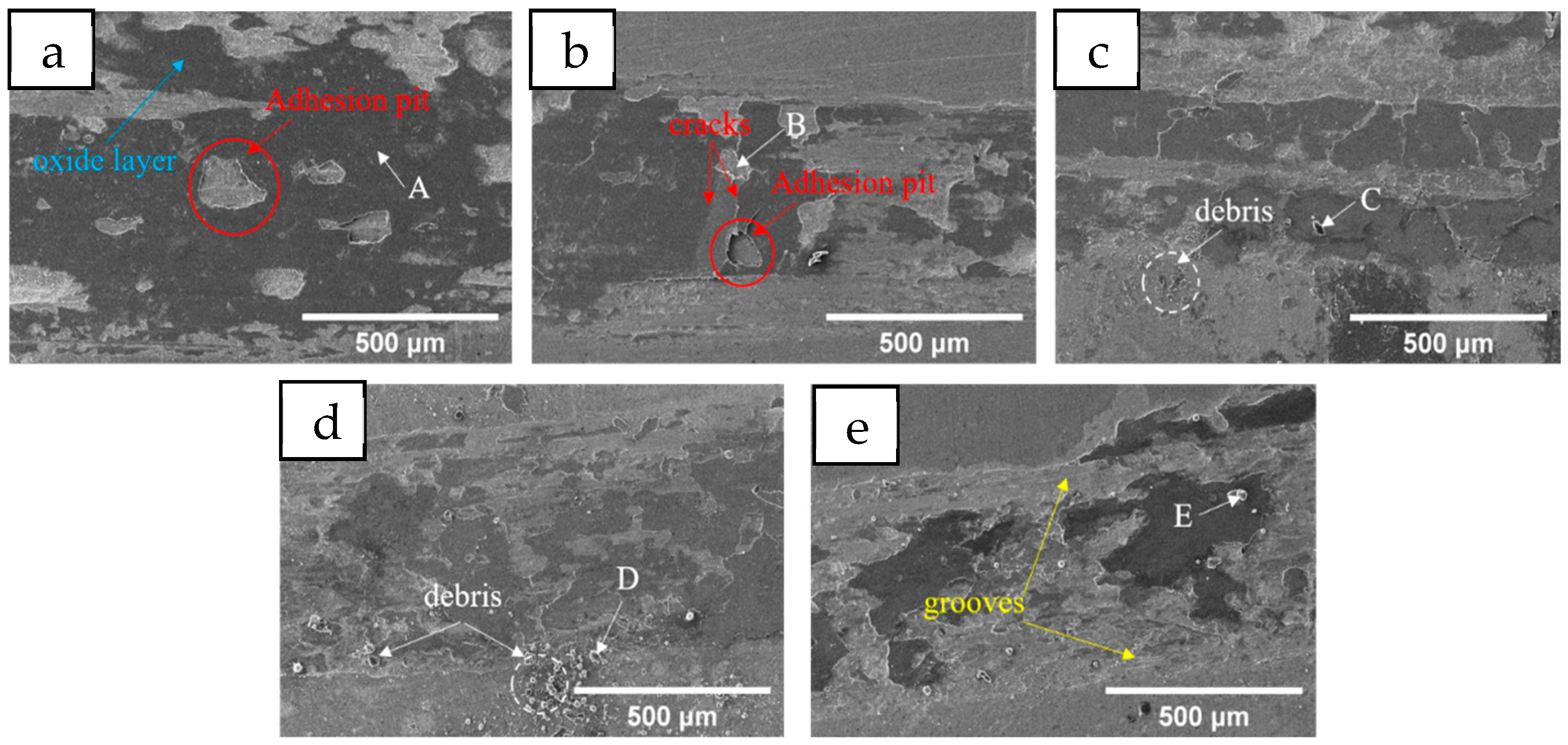
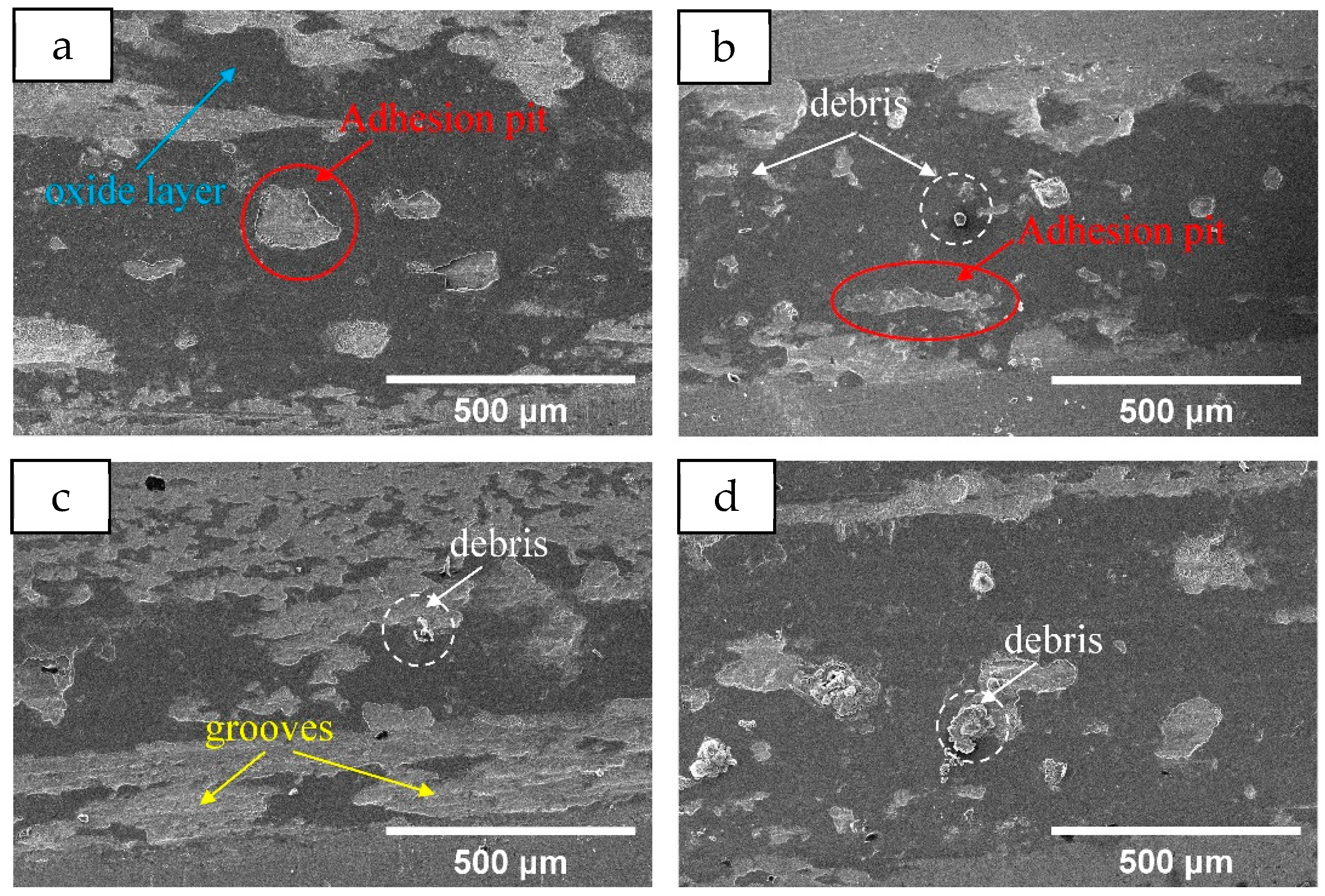
3.1.3. Tribological Properties
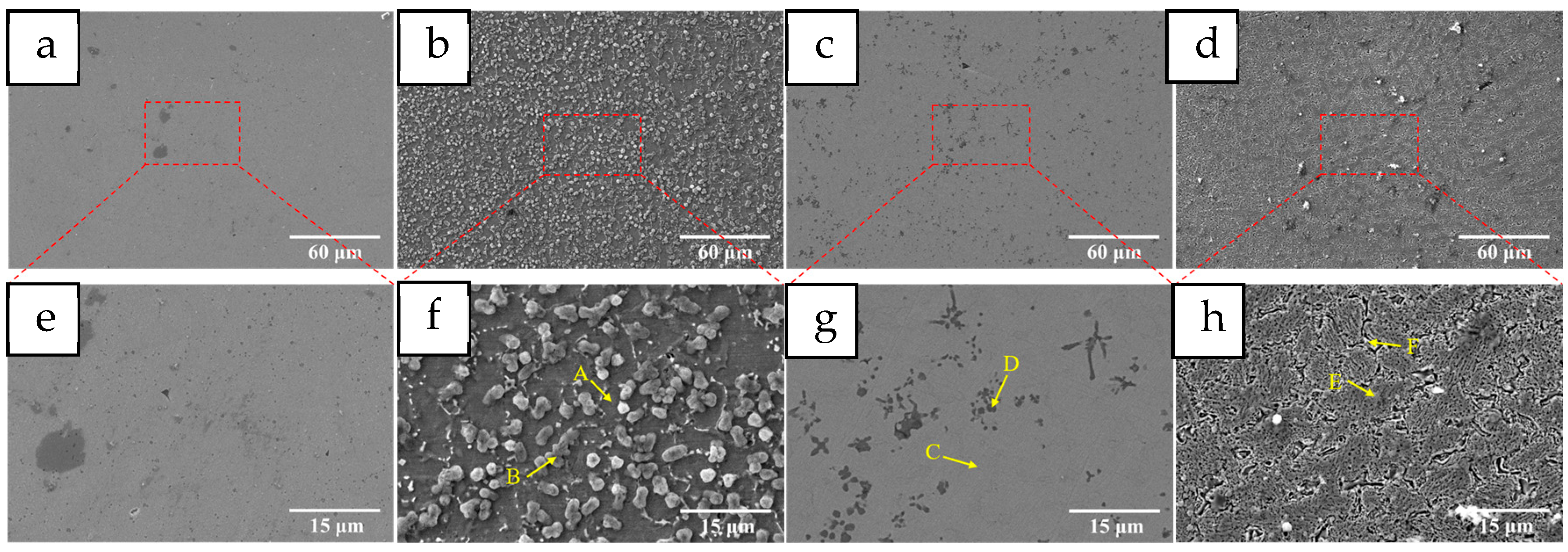
3.2. Effect of Heat Treatment on Coatings
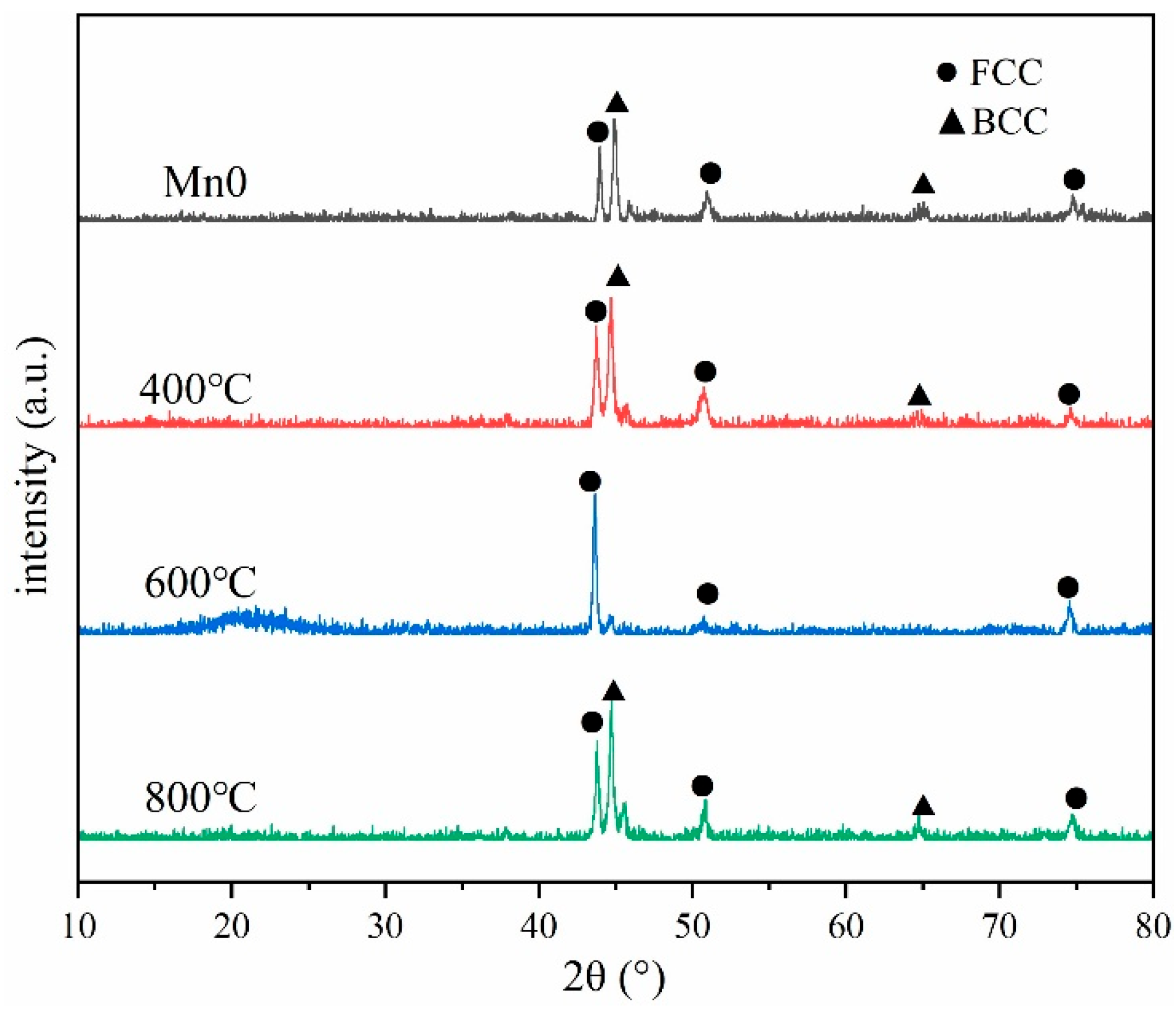
3.2.1. Microstructure Characterization
3.2.2. Microhardness
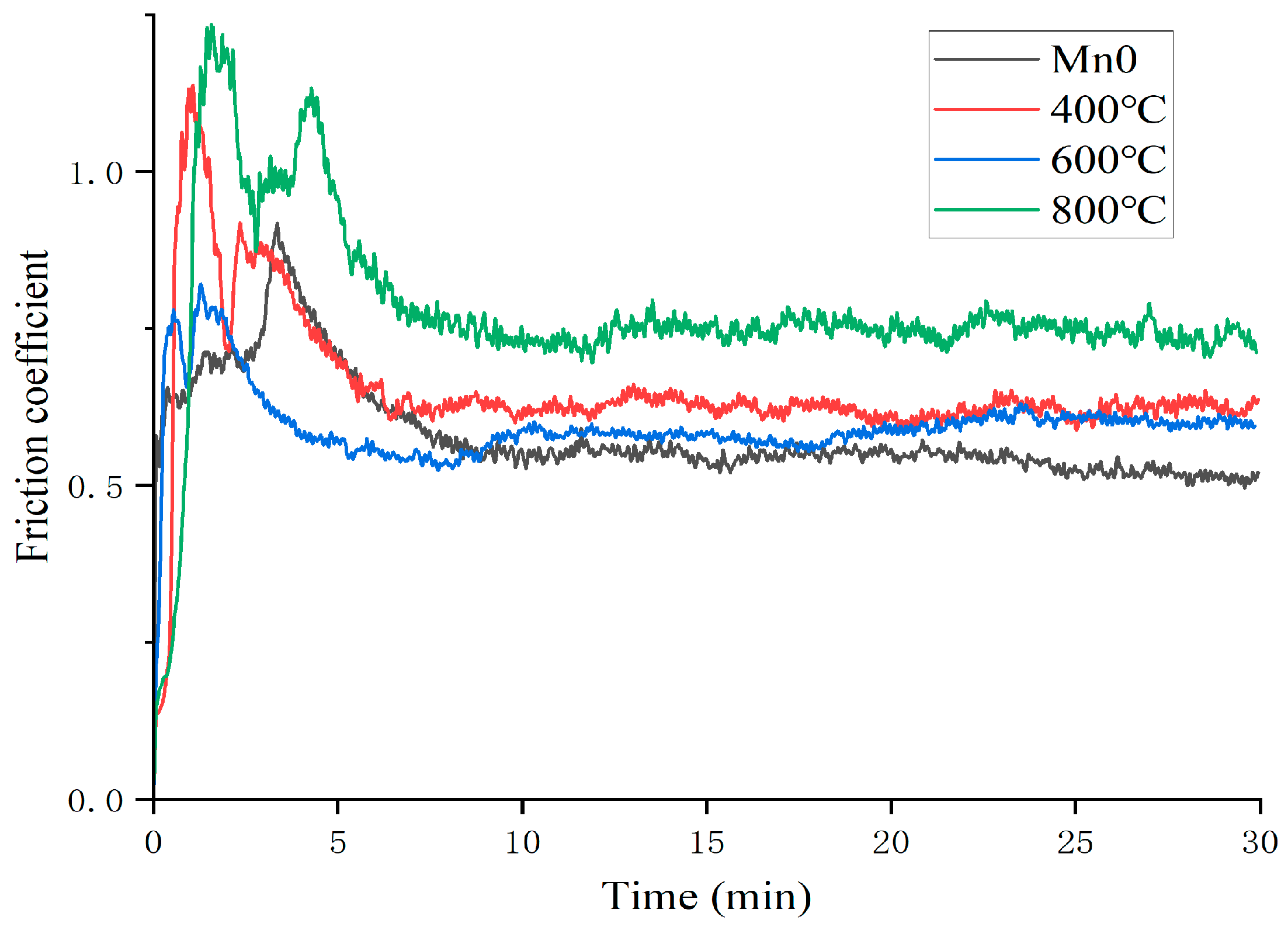
3.2.3. Tribological Properties
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- HEA coatings with different Mn content prepared by laser cladding have a typical dendrite structure. With the increase in Mn content, the microstructure gradually changes from FCC+BCC dual phase to a single FCC structure.
- (2)
- The average microhardness of Mn0 coating is the highest, reaching 415.4 HV. With the increase in Mn content, the coating hardness has a gradual decline, which is related to the transition from FCC+BCC+intermetallic to FCC+BCC and then to FCC single phase. The change trend of the friction coefficient is not completely consistent with that of the coating hardness. In addition to adhesive wear, abrasive wear also occurs, which is the main reason for the significant increase in the friction coefficient of the Mn06 and Mn08 coatings.
- (3)
- After heat treatment at 400 °C and 800 °C, the Mn0 coating exhibits a dual-phase FCC+BCC structure, whereas a single FCC structure is retained following treatment at 600 °C. The HT400 coating surface is primarily decorated with carbides and oxides of various elements, approximately 2.5 μm in size. The HT600 coating maintains a uniform contrast and contains blocky and petal-like Co2Ti-type Laves phases. In the HT800 coating, Ti-rich oxides and carbides are present along the grain boundaries.
- (4)
- Compared with the Mn0 coating, the microhardness of the heat-treated coatings decreases, which is attributed to the release of distortion energy and a corresponding reduction in dislocation density. As the heat treatment temperature increases, more Laves phases, carbides, and oxide precipitates form, leading to a slight increase in hardness. The average friction coefficient increases after heat treatment due to the reduced coating hardness.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yeh, J.W.; Chen, S.K.; Lin, S.J.; Gan, J.Y.; Chin, T.S.; Shun, T.T.; Tsau, C.H.; Chang, S.Y. Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: Novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2004, 6, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huang, Y.; Meng, X.; Xie, Y. A review on high entropy alloys coatings: Fabrication processes and property assessment. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2019, 21, 1900343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.H.; Li, J.S.; Zhang, W.R.; Zhang, Y. A brief review of high-entropy films. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 210, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Cai, Y.; Mu, W.; Guo, W. Precipitation behaviors of the rapidly-solidified CoCrFeNiTi high-entropy alloy during aging treatment. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 970, 172502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Xi, S.; Sun, C. Microstructure and properties of laser cladding and CoCr2.5FeNi2Tix high-entropy alloy composite coatings. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 819, 152986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrakar, R.; Kumar, A.; Chandraker, S.; Rao, K.R.; Chopkar, M. Microstructural and mechanical properties of AlCoCrCuFeNiSix (x = 0 and 0.9) high entropy alloys. Vacuum 2021, 184, 109943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shi, Y. Microhardness, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance of AlxCrFeCoNiCu high-entropy alloy coatings on aluminum by laser cladding. Opt. Laser Technol. 2021, 134, 106632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.C.; Wu, C.L.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, C.H.; Zhang, D.X.; Sun, X.Y. Wear and corrosion of CoCrFeNiMnTix high entropy alloy coatings by laser cladding. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 39, 2811–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Sun, Y.; Chen, N.; Luan, H.; Le, G.; Liu, X.; Ji, Y.; Lu, Y.; Liaw, P.K.; Yang, X.; et al. Simultaneously enhanced strength-ductility of AlCoCrFeNi2.1 eutectic high-entropy alloy via additive manufacturing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 830, 142327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Huang, B.; Tang, J.; Li, T.; Huang, S. Microstructure and properties of argon arc cladded CoCrxFeMoNiAl high entropy alloy coatings on Q235 steel. Mater. Test. 2023, 65, 1465–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.J.; Tian, Y.Z.; Lin, H.R.; Yang, H.J.; Dong, X.G.; Wang, Y.H.; Zhang, Z.F. Achieving high ductility in the 1.7 GPa grade CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy at 77 K. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 740–741, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorobiov, S.I.; Kondrakhova, D.M.; Nepijko, S.A.; Poduremne, D.V.; Shumakova, N.I.; Protsenko, I.Y. Crystalline structure, electrophysical and magnetoresistive properties of high entropy film alloys. J. Nano Elect. Phys. 2016, 8, 03026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, G.M.; Panikar, S.; Ram, G.J.; Kottada, R.S. Additive manufacturing of an aluminum matrix composite reinforced with nanocrystalline high-entropy alloy particles. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 679, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Fu, R.; Liu, J.; Chen, B.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, D.; Yang, Z.; Guo, Y.; Liang, M.; Li, J.; et al. Influence of plasma arc current on the friction and wear properties of CoCrFeNiMn high entropy alloy coatings prepared on CGI through plasma transfer arc cladding. Coatings 2022, 12, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Wen, X.; Huang, B.; Zhuang, J. Microstructure, hardness and corrosion properties of AlCoCrFeNi2.1YHf high-entropy alloy coating prepared by plasma cladding. Mater. Lett. 2023, 330, 133356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Feng, K.; Li, Z.; Lu, F.; Li, R.; Huang, J.; Wu, Y. Microstructure and corrosion properties of CrMnFeCoNi high entropy alloy coating. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 396, 1420–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.L.; Wu, Y.C.; Liaw, P.K.; Luan, J.H.; Jiao, Z.B.; Li, J.; Han, P.D.; Qiao, J.W. Remarkable cryogenic strengthening and toughening in nano-coherent CoCrFeNiTi0.2 high-entropy alloys via energetically-tuning polymorphous precipitates. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 842, 143111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Lau, K.B.; Teh, W.H.; Lee, J.J.; Wei, F.; Lin, M.; Wang, P.; Tan, C.C.; Ramamurty, U. Compositionally graded CoCrFeNiTix high-entropy alloys manufactured by laser powder bed fusion: A combinatorial assessment. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 883, 160825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Gao, W.; Liu, J.; Du, X.; Li, X.; Yang, H. Microstructure and properties of CoCrFeNiTi high-entropy alloy coating fabricated by laser cladding. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2020, 29, 7170–7178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, H.; Xie, J.; Zhang, T.; Yin, L.; Huang, Y. Effect of Ti Content on the Microstructure and Properties of CoCrFeNiMnTix High Entropy Alloy. Entropy 2022, 24, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, K.; Chai, L.; Zhang, C.; Guan, H.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Sun, Q.; Li, Y. Investigation of microstructure and wear resistance of laser-clad CoCrNiTi and CrFeNiTi mediumentropy alloy coatings on Ti sheet. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 145, 107518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Ma, W.; Duan, S.; Wang, Q.; Lin, J. Electrochemical Corrosion Behavior of Ni-Fe-Co-P Alloy Coating Containing Nano-CeO2 Particles in NaCl Solution. Materials 2019, 12, 2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Ma, T.; Jin, Y.; Wang, X.; Dong, D.; Zhu, D. Effect of Sn and Mo on microstructure and electrochemical property of TiZrTaNb high entropy alloys. Crystals 2021, 11, 1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, B.; Zhou, X.; Cheng, G.; Yao, J.; Gong, Y. Microstructure and mechanical properties of thin-wall structure by hybrid laser metal deposition and laser remelting process. Opt. Laser Technol. 2020, 127, 106087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, K.; Ding, H.; Sun, L.; Cao, Y.; Li, X.; Wu, H.; Wang, H. Enhancing high-temperature fretting wear resistance of TC21 titanium alloys by laser cladding self-lubricating composite coatings. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 977, 173360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Cong, W. Laser remelting of CoCrFeNiTi high entropy alloy coatings fabricated by directed energy deposition: Effects of remelting laser power. Opt. Laser Technol. 2023, 158, 108871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shun, T.T.; Chang, L.Y.; Shiu, M.H. Microstructures and mechanical properties of multiprincipal component CoCrFeNiTix alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 556, 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Lu, Y.; Dong, Y.; Wang, T.; Cao, Z.; Li, T. Annealing effects on the microstructure and properties of bulk high-entropy CoCrFeNiTi0.5 alloy casting ingot. Intermetallics 2014, 44, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Vilar, R.; Shen, J. Dry sliding wear behavior of laser clad TiVCrAlSi high entropy alloy coatings on Ti–6Al–4V substrate. Mater Des. 2021, 41, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.S.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, G.L.; Wang, X.H.; Wang, J.F. Microstructure and properties of ceramic particle reinforced FeCoNiCrMnTi high entropy alloy laser cladding coating. Intermetallics 2022, 140, 107402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anoop, S.; Natarajan, S.; Babu, S.K. Analysis of factors influencing dry sliding wear behavior of Al/SiCp–brake pad tribosystem. Mater. Des. 2009, 30, 3831–3838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, D.; Hu, Y.; Cong, W. Laser-directed energy deposition of CoCrFeNiTi high entropy alloy coatings: Effects of powder geometry and laser power. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 126, 3023–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, T.F.J. Review of oxidational wear: Part I: The origins of oxidational wear. Tribol. Int. 1983, 16, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matikainen, V.; Bolelli, G.; Koivuluoto, H.; Sassatelli, P.; Lusvarghi, L.; Vuoristo, P. Sliding wear behaviour of HVOF and HVAF sprayed Cr3C2-based coatings. Wear 2017, 388, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Liu, H.; Hao, J.; Yang, H. Microstructural evolution and corrosion behavior of CoCrFeNiAlxMn(1−x) dual-phase high-entropy alloy coatings prepared by laser cladding. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 886, 161251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Chen, P.; Yang, H.; Hao, J. Effect of heat treatment on phase stability and wear behavior of laser clad AlCoCrFeNiTi0.8 high-entropy alloy coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 392, 125758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Huang, B.; Li, T.; Wu, Y.; Hong, X.; Zheng, J.; Zhu, Y. Effect of heat treatment on microstructure and properties of CrMnFeCoNiMo high entropy alloy coating. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 29, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimzadeh, M.; Malekan, M.; Mirzadeh, H.; Li, L.; Saini, N. Effects of titanium addition on the microstructure and mechanical properties of quaternary CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 856, 143971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, M.; Tsai, M.; Wang, W.; Lin, S.; Yeh, J. Microstructure and wear behavior of AlxCo1.5CrFeNi1.5Tiy high-entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 6308–6317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Ni | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.42–0.5 | 0.17–0.37 | 0.50–0.80 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.25 | ≤0.25 | Bal. |
| Co | Cr | Fe | Ni | Ti | Mn | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CoCrFeNiTi | 20.00 | 20.00 | 20.00 | 20.00 | 20.00 | 0.00 |
| CoCrFeNiTiMn0.2 | 19.23 | 19.23 | 19.23 | 19.23 | 19.23 | 3.85 |
| CoCrFeNiTiMn0.4 | 18.52 | 18.52 | 18.52 | 18.52 | 18.52 | 7.41 |
| CoCrFeNiTiMn0.6 | 17.86 | 17.86 | 17.86 | 17.86 | 17.86 | 10.71 |
| CoCrFeNiTiMn0.8 | 17.24 | 17.24 | 17.24 | 17.24 | 17.24 | 13.79 |
| Elements | Cr | Ni | Co | Ti | Fe | Mn | C | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HEA coating | A | 12.48 | 9.00 | 10.51 | 5.86 | 62.15 | — | — |
| B | 8.01 | 13.84 | 12.03 | 15.06 | 51.05 | — | — | |
| D | 10.91 | 11.33 | 11.68 | 8.67 | 55.20 | 2.22 | — | |
| F | 7.68 | 9.80 | 9.19 | 5.86 | 61.95 | 5.53 | — | |
| H | 8.71 | 11.04 | 12.17 | 15.07 | 46.73 | 6.27 | — | |
| J | 9.02 | 15.48 | 13.34 | 12.67 | 41.92 | 7.57 | — | |
| carbides | C | 3.92 | 3.33 | 3.67 | 14.33 | 17.52 | — | 57.22 |
| E | 2.31 | 2.76 | 2.53 | 16.47 | 11.13 | 0.47 | 64.33 | |
| G | 1.63 | 1.49 | 1.37 | 22.50 | 17.59 | 0.76 | 54.67 | |
| I | 2.80 | 1.80 | 2.42 | 32.42 | 12.40 | 1.28 | 46.88 | |
| K | 1.58 | 2.81 | 2.37 | 31.72 | 13.98 | 1.74 | 45.79 |
| Samples | Mn0 | Mn02 | Mn04 | Mn06 | Mn08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Friction coefficient | 0.5794 | 0.5604 | 0.5236 | 0.6168 | 0.6480 |
| Elements | Cr | Ni | Co | Ti | Fe | Mn | O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 3.24 | 2.51 | 2.68 | 2.94 | 30.99 | — | 57.64 |
| B | 8.23 | 9.32 | 9.06 | 6.46 | 59.16 | 1.95 | 5.82 |
| C | 1.78 | 1.38 | — | 1.10 | 63.25 | 0.78 | 31.70 |
| D | 1.88 | 1.47 | — | 1.32 | 51.41 | 0.96 | 42.95 |
| E | 1.20 | — | — | 0.92 | 54.50 | 1.04 | 42.34 |
| Elements | Cr | Ni | Co | Ti | Fe | C | O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 5.26 | 2.29 | 5.22 | 1.35 | 85.88 | — | — |
| B | 2.42 | 2.03 | 3.09 | 0.65 | 50.43 | 32.40 | 8.97 |
| C | 10.70 | 10.97 | 12.00 | 3.58 | 62.75 | — | — |
| D | 2.87 | 4.67 | 4.80 | 16.56 | 12.59 | 58.50 | — |
| E | 6.18 | 5.24 | 5.11 | 2.14 | 46.83 | 34.49 | — |
| F | 7.16 | 8.34 | 7.52 | 7.81 | 42.96 | 20.38 | 5.83 |
| Mn0 | HT400 | HT600 | HT800 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Friction coefficient | 0.5794 | 0.6524 | 0.5941 | 0.7781 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, S.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, C.; Xu, Z.; Fu, C. Effect of Mn Content and Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Properties of Laser Cladding of FeCoNiCrTi High-Entropy Alloy Coating. Materials 2025, 18, 5160. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18225160
Ma S, Zhou Y, Zhang C, Xu Z, Fu C. Effect of Mn Content and Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Properties of Laser Cladding of FeCoNiCrTi High-Entropy Alloy Coating. Materials. 2025; 18(22):5160. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18225160
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Shibang, Yicheng Zhou, Congzheng Zhang, Zhengchun Xu, and Chengguo Fu. 2025. "Effect of Mn Content and Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Properties of Laser Cladding of FeCoNiCrTi High-Entropy Alloy Coating" Materials 18, no. 22: 5160. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18225160
APA StyleMa, S., Zhou, Y., Zhang, C., Xu, Z., & Fu, C. (2025). Effect of Mn Content and Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Properties of Laser Cladding of FeCoNiCrTi High-Entropy Alloy Coating. Materials, 18(22), 5160. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18225160






