Influence of Process Parameter and Build Rate Variations on Defect Formation in Laser Powder Bed Fusion SS316L
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fabrication Process
2.2. X-Ray Computed Tomography
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Process Parameter Influence on Defect
3.1.1. Lack of Fusion
3.1.2. Near Dense
3.1.3. Balling
3.2. Build Rate Influence on Defects
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LPBF | Laser Powder Bed Fusion |
| Volumetric Energy Density | |
| AM | Additive Manufacturing |
| LOF | Lack of Fusion |
| OM | Optical Microscopy |
| XCT | X-ray Computed Tomography |
| EDM | Electrical Discharge Machining |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
References
- Conner, B.P.; Manogharan, G.P.; Martof, A.N.; Rodomsky, L.M.; Rodomsky, C.M.; Jordan, D.C.; Limperos, J.W. Making sense of 3-D printing: Creating a map of additive manufacturing products and services. Addit. Manuf. 2014, 1, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafaei, A.; Zhao, C.; He, Y.; Ghiaasiaan, S.R.; Shi, B.; Shao, S.; Shamsaei, N.; Wu, Z.; Kouraytem, N.; Sun, T.; et al. Defects and anomalies in powder bed fusion metal additive manufacturing. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2022, 26, 100974. [Google Scholar]
- DebRoy, T.; Wei, H.; Zuback, J.; Mukherjee, T.; Elmer, J.; Milewski, J.; Beese, A.M.; Wilson-Heid, A.d.; De, A.; Zhang, W. Additive manufacturing of metallic components—Process, structure and properties. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2018, 92, 112–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, J.V.; Narra, S.P.; Cunningham, R.W.; Liu, H.; Chen, H.; Suter, R.M.; Beuth, J.L.; Rollett, A.D. Defect structure process maps for laser powder bed fusion additive manufacturing. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 36, 101552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whip, B.R. Effect of Process Parameters on the Surface Roughness and Mechanical Performance of Additively Manufactured Alloy 718. Master’s Thesis, Wright State University, Dayton, OH, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Young, Z.A.; Coday, M.M.; Guo, Q.; Qu, M.; Hojjatzadeh, S.M.H.; Escano, L.I.; Fezzaa, K.; Sun, T.; Chen, L. Uncertainties induced by processing parameter variation in selective laser melting of Ti6Al4V revealed by in-situ X-ray imaging. Materials 2022, 15, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghouse, S.; Babu, S.; Van Arkel, R.J.; Nai, K.; Hooper, P.A.; Jeffers, J.R. The influence of laser parameters and scanning strategies on the mechanical properties of a stochastic porous material. Mater. Des. 2017, 131, 498–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brika, S.E.; Letenneur, M.; Dion, C.A.; Brailovski, V. Influence of particle morphology and size distribution on the powder flowability and laser powder bed fusion manufacturability of Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 31, 100929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanaei, N.; Fatemi, A. Defects in additive manufactured metals and their effect on fatigue performance: A state-of-the-art review. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2021, 117, 100724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Li, Y.; Bai, Q. Defect formation mechanisms in selective laser melting: A review. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2017, 30, 515–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Pistorius, P.C.; Beuth, J.L. Prediction of lack-of-fusion porosity for powder bed fusion. Addit. Manuf. 2017, 14, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, J.C.; Kartal, M.E.; Carter, L.N.; Attallah, M.M.; Mulvihill, D.M. Classifying shape of internal pores within AlSi10Mg alloy manufactured by laser powder bed fusion using 3D X-ray micro computed tomography: Influence of processing parameters and heat treatment. Mater. Charact. 2020, 163, 110225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifi, M.; Salem, A.; Satko, D.; Shaffer, J.; Lewandowski, J.J. Defect distribution and microstructure heterogeneity effects on fracture resistance and fatigue behavior of EBM Ti–6Al–4V. Int. J. Fatigue 2017, 94, 263–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åkerfeldt, P.; Antti, M.L.; Pederson, R. Influence of microstructure on mechanical properties of laser metal wire-deposited Ti-6Al-4V. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 674, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forien, J.B.; Calta, N.P.; DePond, P.J.; Guss, G.M.; Roehling, T.T.; Matthews, M.J. Detecting keyhole pore defects and monitoring process signatures during laser powder bed fusion: A correlation between in situ pyrometry and ex situ X-ray radiography. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 35, 101336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, M.; Guo, Q.; Escano, L.I.; Clark, S.J.; Fezzaa, K.; Chen, L. Mitigating keyhole pore formation by nanoparticles during laser powder bed fusion additive manufacturing. Addit. Manuf. Lett. 2022, 3, 100068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouraytem, N.; Li, X.; Cunningham, R.; Zhao, C.; Parab, N.; Sun, T.; Rollett, A.D.; Spear, A.D.; Tan, W. Effect of laser-matter interaction on molten pool flow and keyhole dynamics. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2019, 11, 064054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, R.W. Defect Formation Mechanisms in Powder-Bed Metal Additive Manufacturing. P.hD. Thesis, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.; Li, S.; Shi, S.; Li, X.; Hu, X.; Zhu, Q.; Ward, R.M. Effect of processing parameters on surface roughness, porosity and cracking of as-built IN738LC parts fabricated by laser powder bed fusion. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2020, 285, 116788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; DebRoy, T. Toward a unified model to prevent humping defects in gas tungsten arc welding. Weld. J.-N. Y.- 2006, 85, 292. [Google Scholar]
- Parida, R.P.; Senthilkumar, V. Experimental studies of defect generation in selective laser melted Inconel 718 alloy. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 39, 1372–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Liu, J.; Shi, Y.; Wang, L.; Jiang, W. Balling behavior of stainless steel and nickel powder during selective laser melting process. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2012, 59, 1025–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoli, U.S.; Wolfer, A.J.; Matthews, M.J.; Delplanque, J.P.R.; Schoenung, J.M. On the limitations of volumetric energy density as a design parameter for selective laser melting. Mater. Des. 2017, 113, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvish, K.; Chen, Z.; Pasang, T. Reducing lack of fusion during selective laser melting of CoCrMo alloy: Effect of laser power on geometrical features of tracks. Mater. Des. 2016, 112, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Rafi, K.; Gu, H.; Starr, T.; Stucker, B. Analysis of defect generation in Ti–6Al–4V parts made using powder bed fusion additive manufacturing processes. Addit. Manuf. 2014, 1, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucho, W.M.; Lysne, V.H.; Austbø, H.; Sjolyst-Kverneland, A.; Hansen, V. Investigation of effects of process parameters on microstructure and hardness of SLM manufactured SS316L. J. Alloy. Compd. 2018, 740, 910–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Leon Nope, G.; Perez-Andrade, L.; Corona-Castuera, J.; Espinosa-Arbelaez, D.; Muñoz-Saldaña, J.; Alvarado-Orozco, J. Study of volumetric energy density limitations on the IN718 mesostructure and microstructure in laser powder bed fusion process. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 64, 1261–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherry, J.; Davies, H.; Mehmood, S.; Lavery, N.; Brown, S.; Sienz, J. Investigation into the effect of process parameters on microstructural and physical properties of 316L stainless steel parts by selective laser melting. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 76, 869–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliasu, A.; Czekanski, A.; Boakye-Yiadom, S. Effect of laser powder bed fusion parameters on the microstructural evolution and hardness of 316L stainless steel. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 113, 2651–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz Vallejo, N.; Lucas, C.; Ayers, N.; Graydon, K.; Hyer, H.; Sohn, Y. Process optimization and microstructure analysis to understand laser powder bed fusion of 316l stainless steel. Metals 2021, 11, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, T.S.; Collins, D.A.; Le Coq, A.G.; Lach, T.G.; Linton, K.D.; Gussev, M.N.; Werden, J.W.; Mcalister, M.R.; Chen, X.; Joslin, C.B.; et al. Mechanical Properties of Additively Manufactured 316L Stainless Steel Before and After Neutron Irradiation (FY21); Technical Report; Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL): Oak Ridge, TN USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kruth, J.P.; Bartscher, M.; Carmignato, S.; Schmitt, R.; De Chiffre, L.; Weckenmann, A. Computed tomography for dimensional metrology. CIRP Ann. 2011, 60, 821–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragonfly 2022.2; [Computer Software]; Comet Technologies Canada Inc.: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2022.
- Tammas-Williams, S.; Zhao, H.; Léonard, F.; Derguti, F.; Todd, I.; Prangnell, P.B. XCT analysis of the influence of melt strategies on defect population in Ti–6Al–4V components manufactured by Selective Electron Beam Melting. Mater. Charact. 2015, 102, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, T.; Zuback, J.; De, A.; DebRoy, T. Printability of alloys for additive manufacturing. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenthal, D. Mathematical theory of heat distribution during welding and cutting. Weld. J. 1941, 20, 220s–234s. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, S.; Vlasea, M. Melting modes in laser powder bed fusion. Materialia 2020, 9, 100591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masmoudi, A.; Bolot, R.; Coddet, C. Investigation of the laser–powder–atmosphere interaction zone during the selective laser melting process. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2015, 225, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairallah, S.A.; Anderson, A. Mesoscopic simulation model of selective laser melting of stainless steel powder. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2014, 214, 2627–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, W.E.; Barth, H.D.; Castillo, V.M.; Gallegos, G.F.; Gibbs, J.W.; Hahn, D.E.; Kamath, C.; Rubenchik, A.M. Observation of keyhole-mode laser melting in laser powder-bed fusion additive manufacturing. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2014, 214, 2915–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Zhao, C.; Qu, M.; Xiong, L.; Escano, L.I.; Hojjatzadeh, S.M.H.; Parab, N.D.; Fezzaa, K.; Everhart, W.; Sun, T.; et al. In-situ characterization and quantification of melt pool variation under constant input energy density in laser powder bed fusion additive manufacturing process. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 28, 600–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reijonen, J.; Revuelta, A.; Riipinen, T.; Ruusuvuori, K.; Puukko, P. On the effect of shielding gas flow on porosity and melt pool geometry in laser powder bed fusion additive manufacturing. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 32, 101030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapp, J.; Rubenchik, A.M.; Guss, G.; Matthews, M.J. In situ absorptivity measurements of metallic powders during laser powder-bed fusion additive manufacturing. Appl. Mater. Today 2017, 9, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunenthiram, V.; Peyre, P.; Schneider, M.; Dal, M.; Coste, F.; Fabbro, R. Analysis of laser–melt pool–powder bed interaction during the selective laser melting of a stainless steel. J. Laser Appl. 2017, 29, 022303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
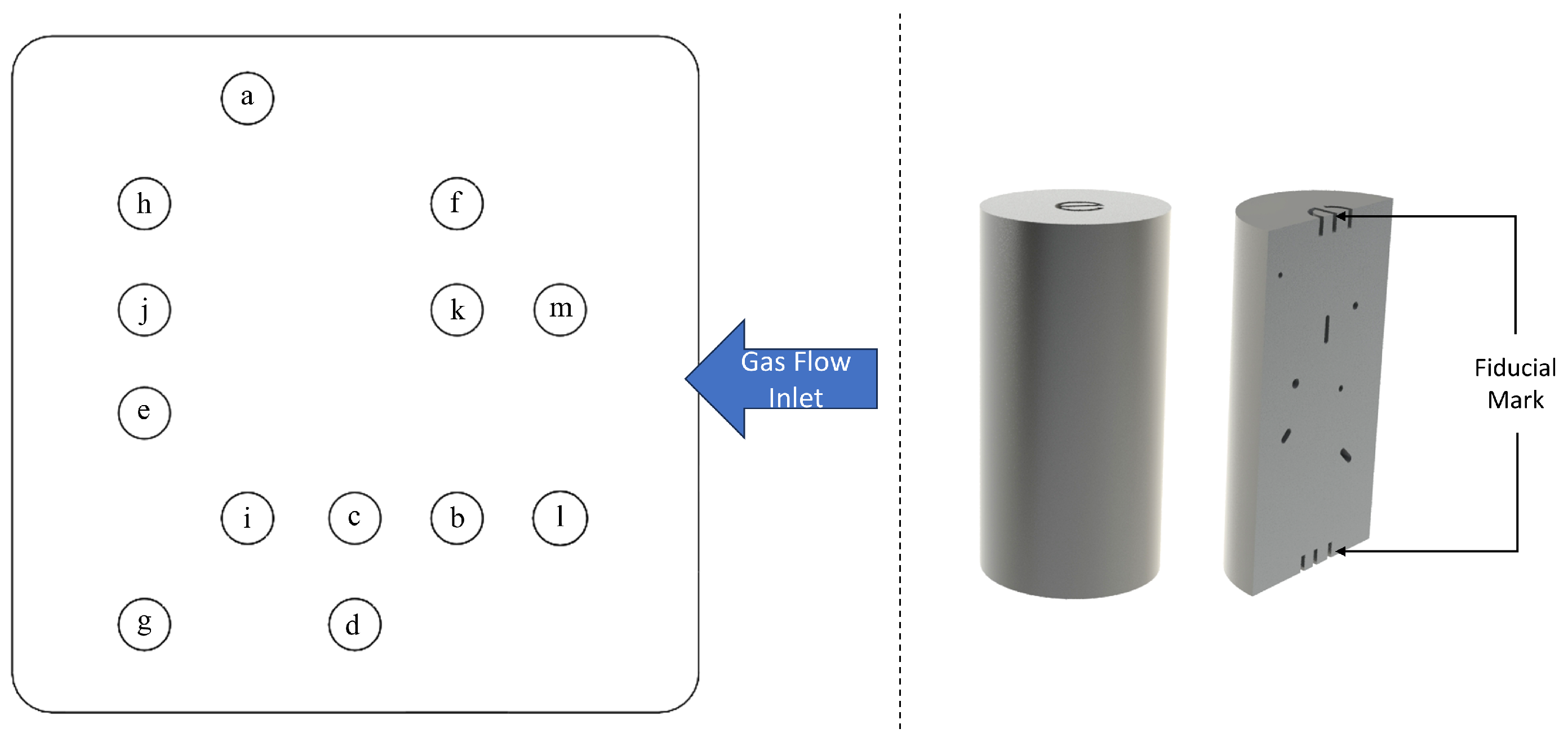
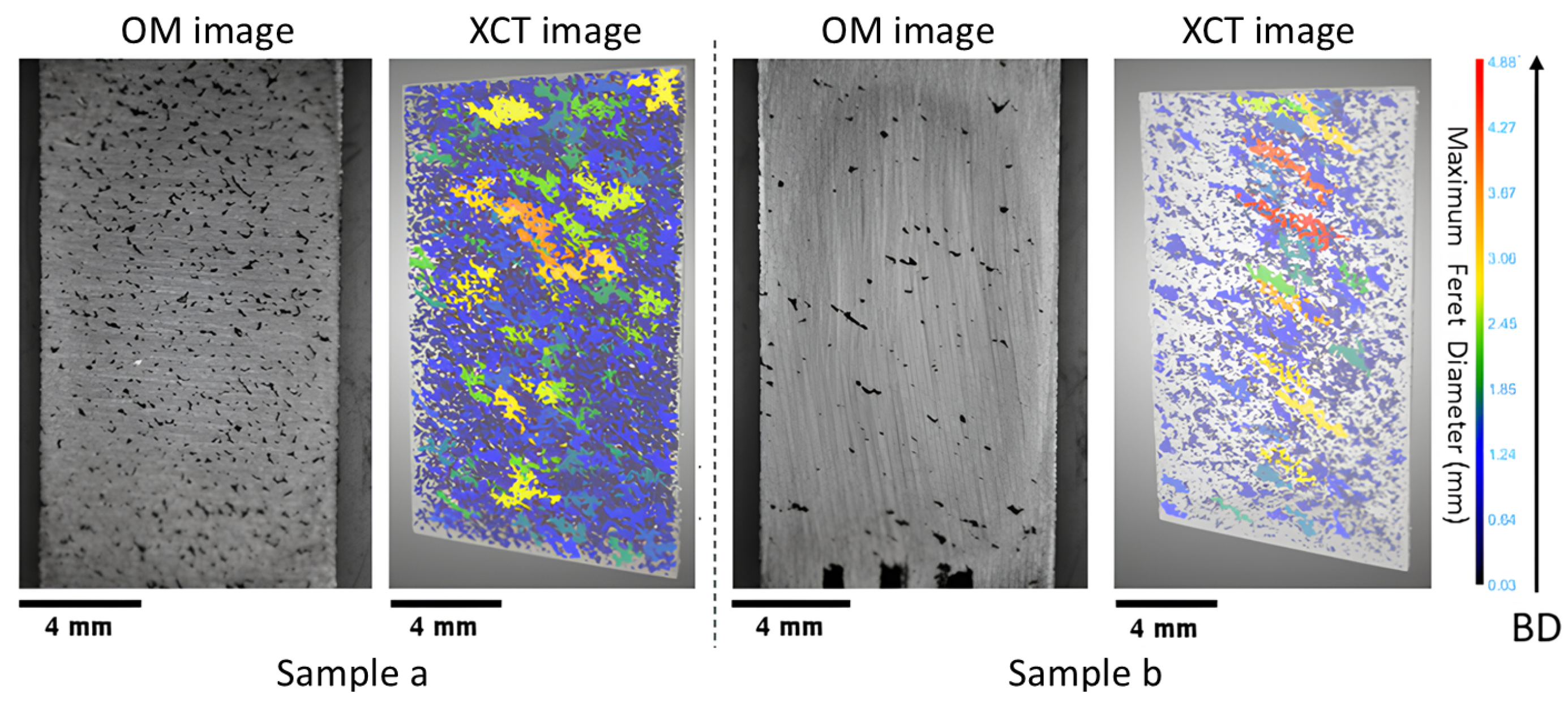


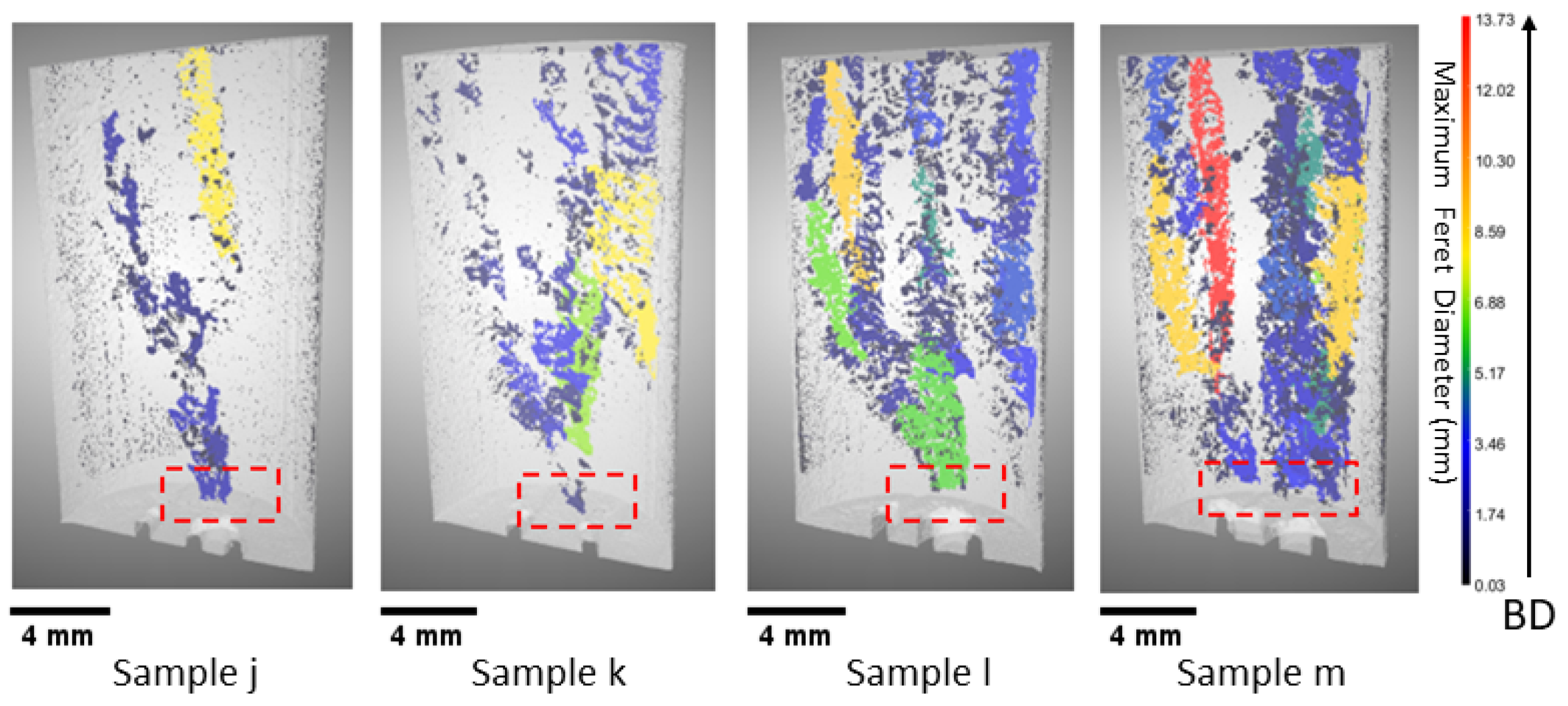
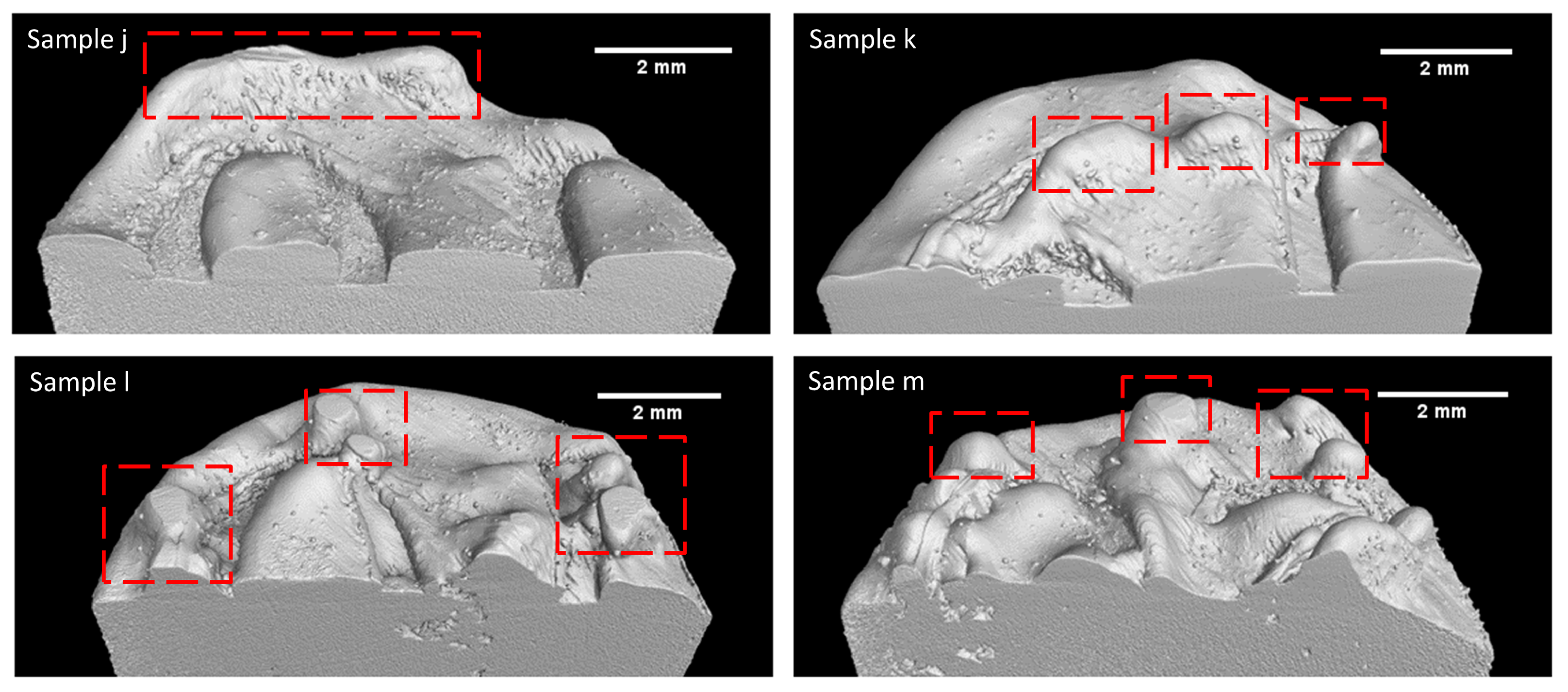
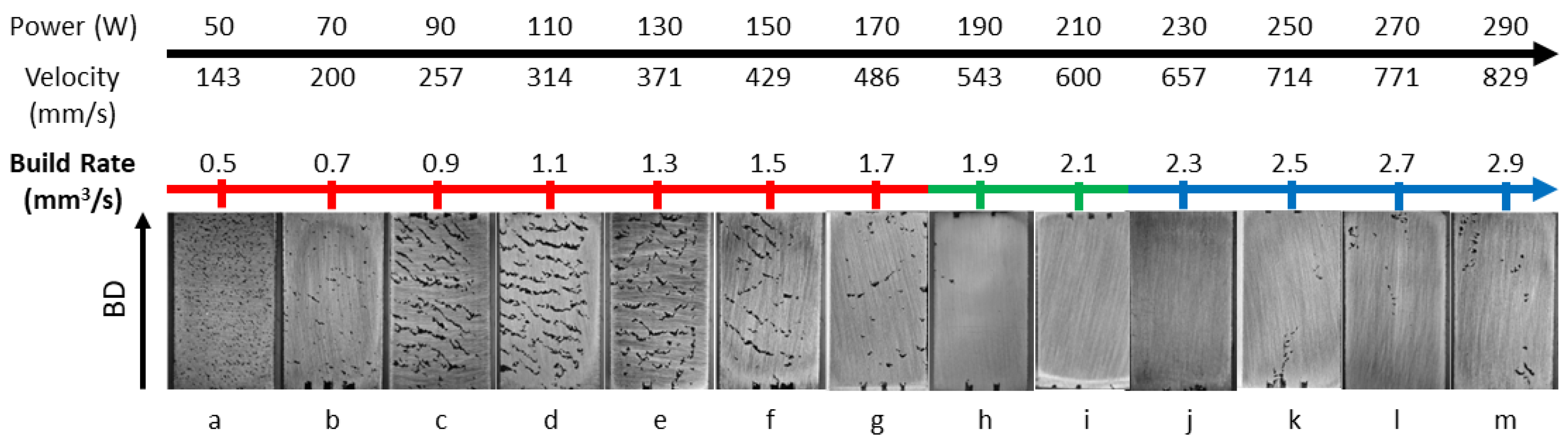
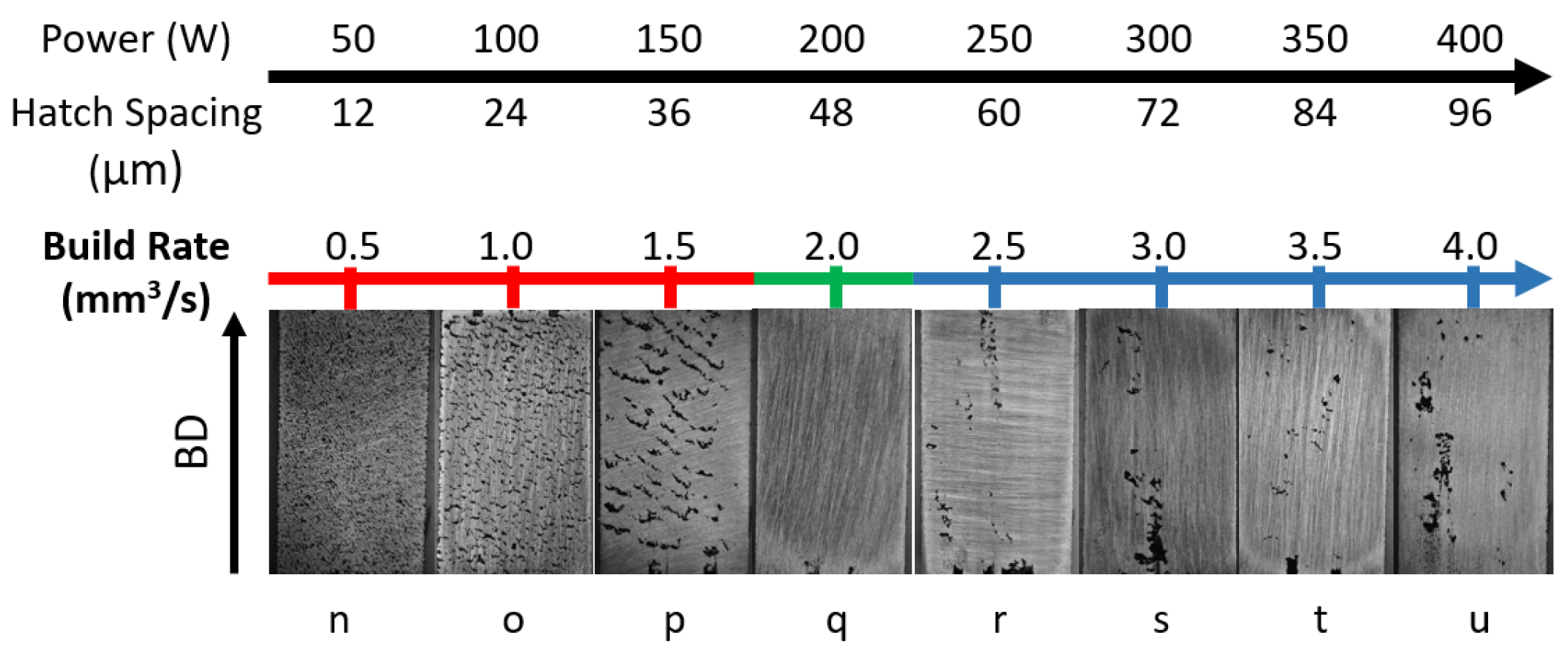
| Sample No | Laser Power (W) | Laser Velocity (mm/s) | Build Rate (mm3/s) | Volume Density * % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | 50 | 143 | 0.5 | 94.71 |
| b | 70 | 200 | 0.7 | 98.80 |
| c | 90 | 257 | 0.9 | 92.57 |
| d | 110 | 314 | 1.1 | 90.36 |
| e | 130 | 371 | 1.3 | 91.17 |
| f | 150 | 429 | 1.5 | 96.61 |
| g | 170 | 486 | 1.7 | 97.81 |
| h | 190 | 543 | 1.9 | 99.88 |
| i | 210 | 600 | 2.1 | 99.75 |
| j | 230 | 657 | 2.3 | 99.63 |
| k | 250 | 714 | 2.5 | 99.38 |
| l | 270 | 771 | 2.7 | 98.41 |
| m | 290 | 829 | 2.9 | 98.06 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anwar, T.U.; Merighe, P.; Kancharla, R.R.; Kombaiah, B.; Kouraytem, N. Influence of Process Parameter and Build Rate Variations on Defect Formation in Laser Powder Bed Fusion SS316L. Materials 2025, 18, 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18020435
Anwar TU, Merighe P, Kancharla RR, Kombaiah B, Kouraytem N. Influence of Process Parameter and Build Rate Variations on Defect Formation in Laser Powder Bed Fusion SS316L. Materials. 2025; 18(2):435. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18020435
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnwar, Tasrif Ul, Patrick Merighe, Rahul Reddy Kancharla, Boopathy Kombaiah, and Nadia Kouraytem. 2025. "Influence of Process Parameter and Build Rate Variations on Defect Formation in Laser Powder Bed Fusion SS316L" Materials 18, no. 2: 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18020435
APA StyleAnwar, T. U., Merighe, P., Kancharla, R. R., Kombaiah, B., & Kouraytem, N. (2025). Influence of Process Parameter and Build Rate Variations on Defect Formation in Laser Powder Bed Fusion SS316L. Materials, 18(2), 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18020435









