Mechanical Performance and Energy Absorption of Ti6Al4V I-WP Lattice Metamaterials Manufactured via Selective Laser Melting
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Structural Design
2.2. Sample Preparation
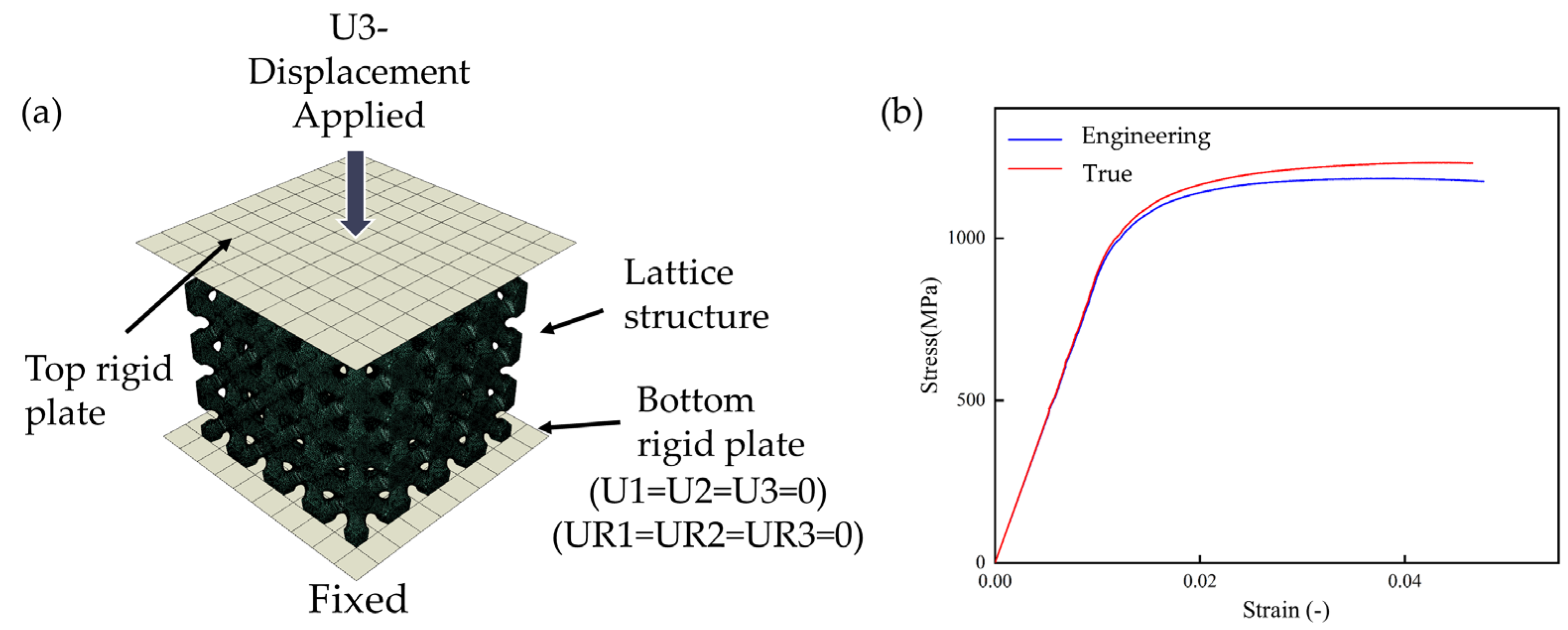
2.3. Finite Element Simulation
2.4. Mechanical Performance Test
2.5. Characterization Test
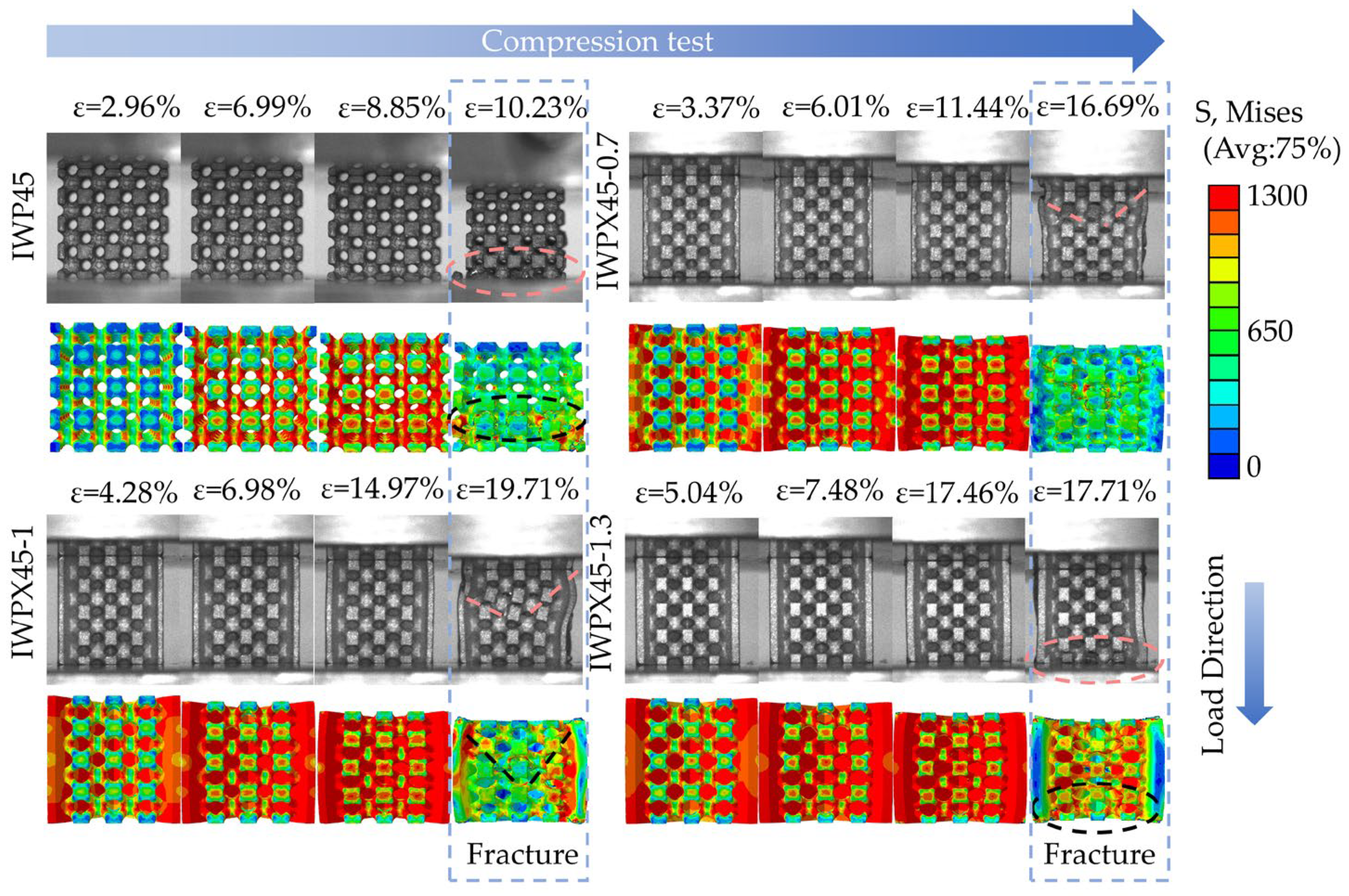
3. Results
3.1. Print Quality
3.2. Analysis of Mechanical Properties
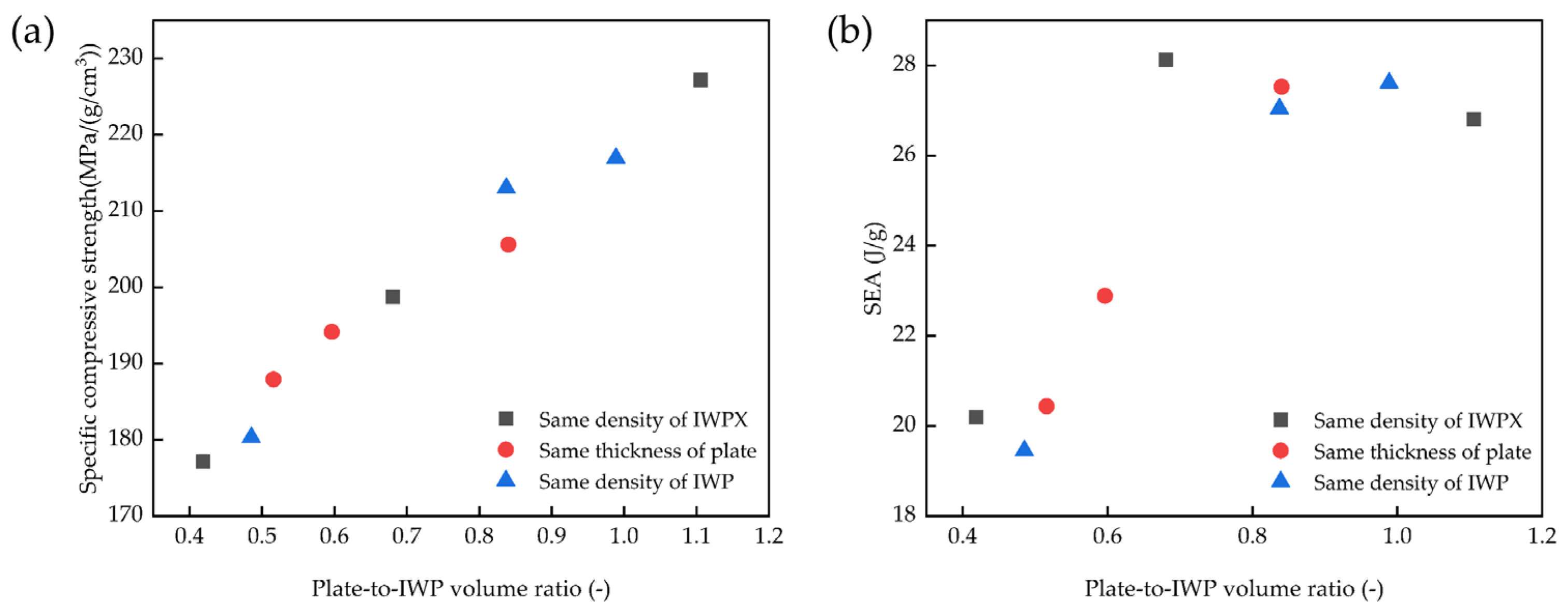
3.3. Mechanical Properties of Structures with Different Volume Ratios
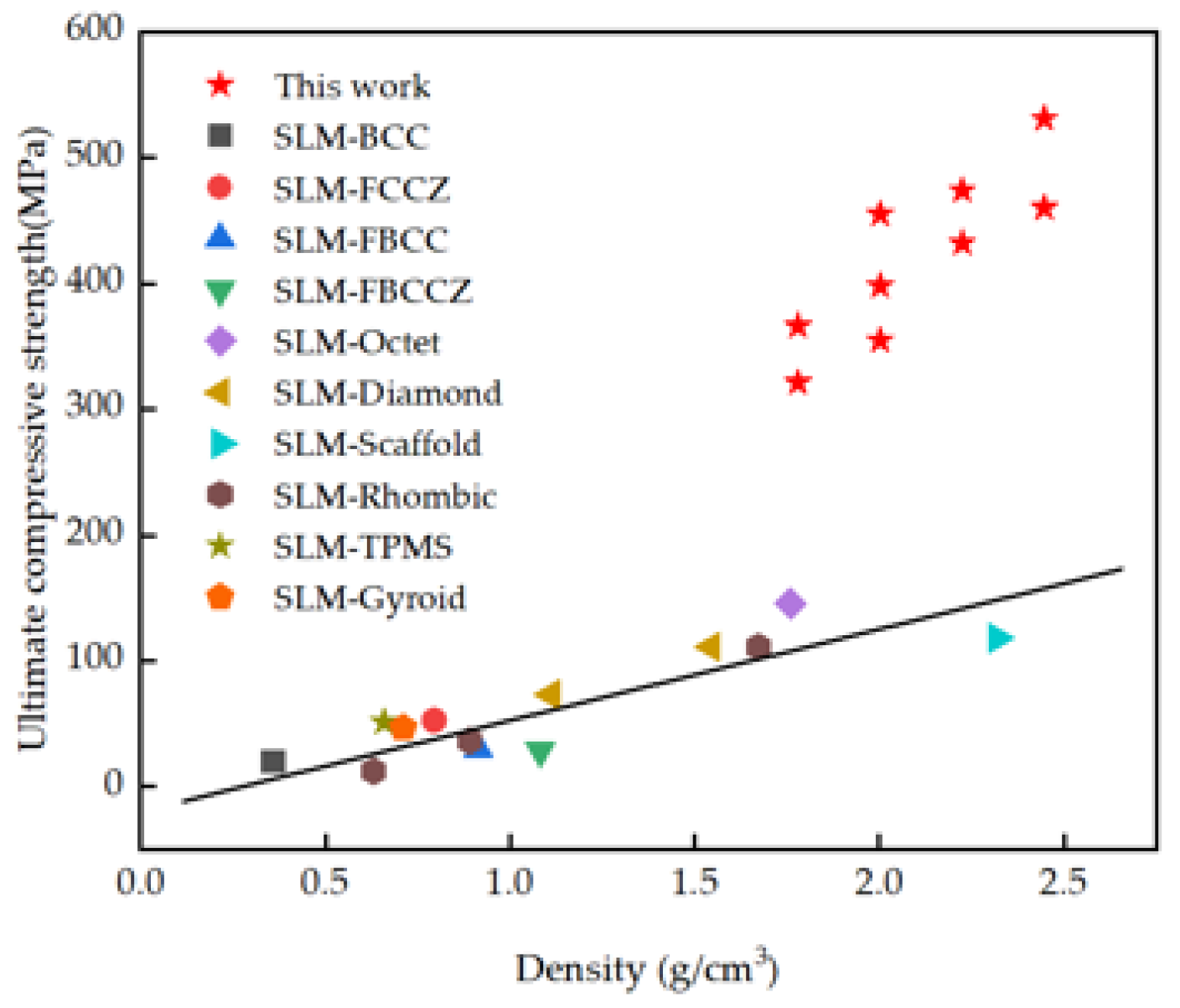
3.4. Comparison with Other Lattice Structures
4. Conclusions
- The specific strength of the titanium alloy IWP-X lattice structure reaches 227.22 MPa/(g/cm3), which is 1.26 times that of the titanium alloy block (180 MPa/(g/cm3)). Compared with the IWP45 structure of the same density, the ultimate compressive strength of IWPX45-1.3 increased by 455.23 MPa (122.06% improvement), and the energy absorption increased by 54.28 MJ/m3 (265.03% improvement).
- The finite element simulation tests effectively predicted the stress distribution and fracture failure site of the structure during the compression test. With the incorporation of the plate structure, the structure transformed from the layer-by-layer fracture of IWP to the V-shaped fracture.
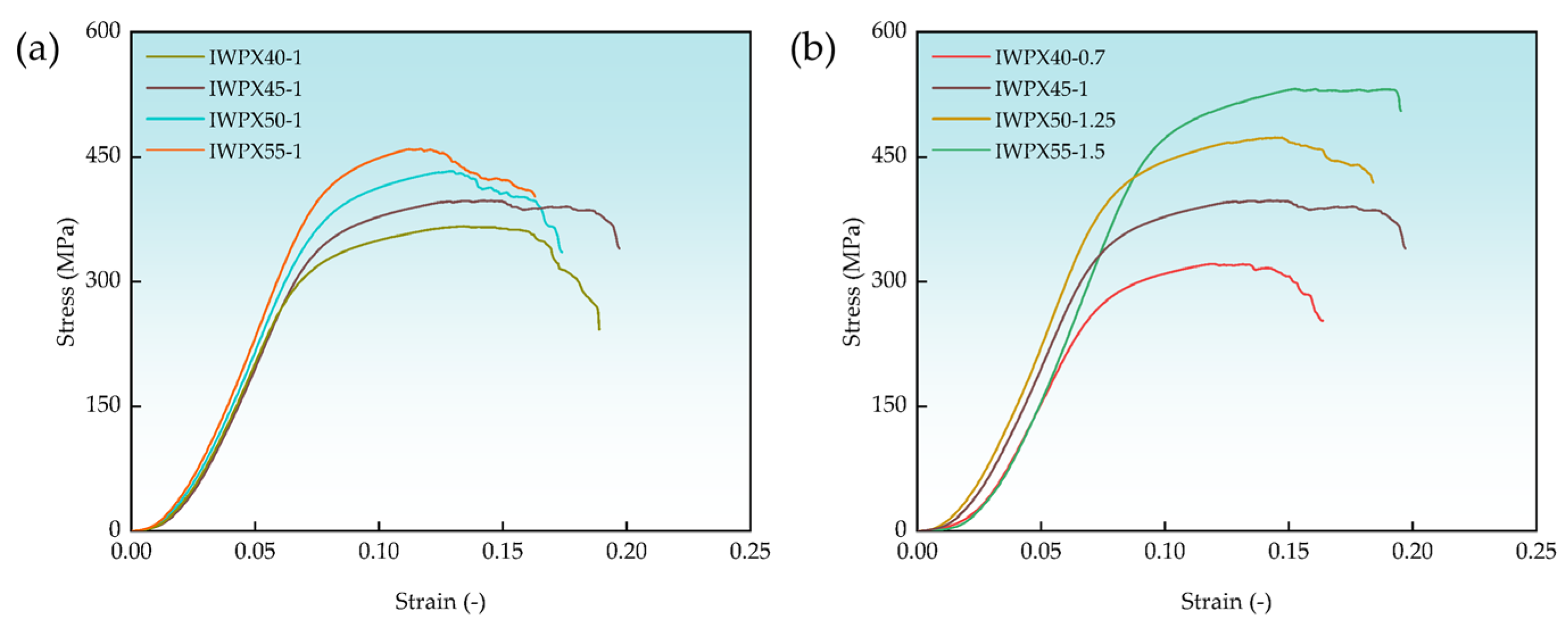
- As the volume ratio of plate-to-IWP increases, the structural mechanical properties and deformation resistance are enhanced. The SEA reaches its maximum value in the ratio of 0.7 to 0.8. The energy absorption of IWPX45-1 increased by 56.96 MJ/m3 (282.03% improvement), which is the largest increase.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, J.; Hu, L.; Wu, J.; Yan, Z.; Chen, Y.; He, C.; Ai, S. Bilayer Lattice Structure Integrated with Phase Change Material for Innovative Thermal Protection System Design. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2023, 141, 108576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.; He, P.; Yang, Y.; Sang, L. Crashworthiness Optimization of Crash Box with 3D-Printed Lattice Structures. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2023, 247, 108198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Jiang, F.; Yang, S. Advanced Honeycomb Designs for Improving Mechanical Properties: A Review. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 227, 109393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlmann, E.; Kersting, R.; Klein, T.B.; Cruz, M.F.; Borille, A.V. Additive Manufacturing of Titanium Alloy for Aircraft Components. Procedia CIRP 2015, 35, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, L.; He, J.; Wen, G.; Wang, Z.-P.; Yang, J.; Xie, Y.M.; Liu, J. Multifunctional TPMS-Based Metastructures. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2025, 293, 110208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Hong, R.; Mai, D.; Lu, Y.; Lin, J. Exploring Construction of Biomedical Ti6Al4V-Ti5Cu Composite Alloy with Interpenetrating Structure: Microstructure and Corrosion Resistance. Materials 2025, 18, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Wu, S.; Yang, L.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Cai, C.; Yan, C.; Shi, Y. Ni–Ti Multicell Interlacing Gyroid Lattice Structures with Ultra-High Hyperelastic Response Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2024, 195, 104099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Bai, J.; To, A.C. Functionally Graded Lattice Structure Topology Optimization for the Design of Additive Manufactured Components with Stress Constraints. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2019, 344, 334–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Gu, D.; Liu, H.; Zhang, H.; Shan, J.; Zhang, Y. Lightweight Load-Bearing Heat Dissipation Multifunctional Pomelo Peel-Inspired Structures Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion. Int. J. Bioprinting 2023, 9, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yu, C.; Ren, G.; Shen, S.; Yi, H. Laser Additive Manufacturing of Three-Dimensional Porous Structures: Structural Design, Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Applications. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2025, 36, 3684–3725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, X.; Guo, A.; Guo, S.; Sui, S.; Yang, W.; Tang, R.; Li, X.; Qu, P.; Wang, M.; Lin, X. Laser Powder Bed Fusion for the Fabrication of Triply Periodic Minimal Surface Lattice Structures: Synergistic Macroscopic and Microscopic Optimization. J. Manuf. Process. 2024, 119, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Cao, J.; Zheng, Z.; Zhao, R.; Xu, G.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Hur, B.; Yue, X. Deformation Behavior of Inconel 625 Alloy with TPMS Structure. Materials 2025, 18, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Jiang, X.; Yang, G.; Song, B.; Sha, H. Design and Mechanical Performance Analysis of T-BCC Lattice Structures. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 32, 1538–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; He, J.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, D.; Wu, H.; Xiao, L.L.; Xi, S. Ultra Strong FCC Structured Ni8Cr4Co4Fe6W2 High Entropy Alloys with High Strength and Ductility by Laser Powder Bed Fusion. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 992, 174580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Long, Y.; Ge, J.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, P.; Yuan, S.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, T. A Novel Approach for Mechanical Regulation of Thin-Walled Crystal Plate Lattices: Experimental Characterization and Simulation. Mater. Des. 2022, 223, 111122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Fu, J.; Shang, C.; Lin, Z.; Li, B. Porous Scaffold Design by Solid T-Splines and Triply Periodic Minimal Surfaces. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2018, 336, 333–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Nguyen, N.V.; Nguyen-Xuan, H.; Lee, J. Isogeometric 3D Optimal Designs of Functionally Graded Triply Periodic Minimal Surface Plates. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2024, 277, 109406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Gao, S.; Pokkalla, D.K.; Zhang, S.; Han, C.; Liu, F.; Xiao, Z.; Kandukuri, S.Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, K. Additive Manufacturing of Metallic Metamaterials with Enhanced Mechanical Properties Enabled by Microstructural and Structural Design. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2024, 199, 104172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Gao, Z.; Dai, M.; Song, B.; Yang, B.; Zhang, T.; Yuan, S.; Liu, G.; Zhao, M. Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer Performances of Aluminum Alloy Lattices with Triply Periodic Minimal Surfaces. Materials 2025, 18, 1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Cao, X.; Yang, H.; Wang, S.; Cao, W.; He, C. Dual-Material TPMS Metamaterial with High Load-Bearing Capacity and Performance Stability. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2025, 303, 110613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Li, X.; Zhang, D.Z.; Zhai, W. TPMS-Based Interpenetrating Lattice Structures: Design, Mechanical Properties and Multiscale Optimization. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2023, 244, 108092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naji, M.M.; Alagha, A.N.; Sheikh-Ahmad, J.Y.; Abu Al-Rub, R.K. Hybrid Plate-TPMS Lattice Metamaterials with Exceptional Stiffness and Strength. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2025, 20, e2536560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Gao, K.; Liu, J.; Zou, Z.; Yang, J.; Qian, M.; Zhai, W.; Wu, Z. Breaking Stiffness-Tunability Trade-offs in Metamaterials: A Minimal Surface Guided Hybrid Lattice Strategy. Adv. Sci. 2025, e10586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaber, A.; Singh, A.; Rodopoulos, D.C.; Karathanasopoulos, N. Hybrid Manufacturing and Mechanics of Copper-Based Architected Materials and Copper–Aluminum Interpenetrating Phase Composites. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2025, 38, 674–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Tang, Q.; Song, J.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, Q.; Ma, S.; Setchi, R.; Zhao, M. TPMS-Based Strut-Shell Interpenetrating Lattice Metamaterial with Wide-Range Customizable Mechanical Properties and Superior Energy Absorption. Compos. Struct. 2024, 349–350, 118555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirupathi, S.; Reddy, K.U.; Rao, A.U.; Reddy, P.V. Machine Learning-Based Yield Strength Prediction in 3D Printed Ti6Al4V Lattice Structures: A Combined Simulation and Experimental Approach. Next Mater. 2025, 9, 101190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Sun, J.; Guo, K.; Wang, L. Compressive Mechanical Properties and Energy Absorption Characteristics of SLM Fabricated Ti6Al4V Triply Periodic Minimal Surface Cellular Structures. Mech. Mater. 2022, 166, 104241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.; Sun, J.; Kong, N.; Han, Z.; Zhao, H.; Ren, L.; Ma, Z. Enlarged Cell Size Induces Ultra-High Specific Strength in Octahedral Lattice Structure. Compos. Struct. 2025, 371, 119472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eren, Z.; Gokcekaya, O.; Nakano, T.; Mecitoğlu, Z. In-Plane Quasi-Static Compression Deformation of Ti6Al4V Double Arrow-Headed Lattice Structures Fabricated by Electron Beam Powder Bed Fusion Process: Build Orientation, Scan Speed and Failure Mechanism. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 27, 6192–6210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, X.; Guo, Y.; Chang, H.; Sun, Z.; Zhou, L.; Alexandrov, I.V. Effects of Plasma Electrolytic Polishing on Surface Finish and Mechanical Properties of Ti6Al4V Diamond Lattices with a Specific Relative Density. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2025, 496, 131659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, N.; Zhang, J.; Li, C.; Shen, Y.; Fang, J. Mechanical Properties of Three-Dimensional Functionally Graded Triply Periodic Minimum Surface Structures. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2023, 246, 108118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Gu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Yin, Y.; Tan, Q.; Li, M.; Zhang, M.-X. Mechanical Performance of a Node Reinforced Body-Centred Cubic Lattice Structure Manufactured via Selective Laser Melting. Scr. Mater. 2020, 189, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasingh, C.G.G.D.; Palaniyandi, K.; Moganraj, A. Investigation of Energy Absorption and Deformation Behaviour of Novel Nested Hybrid Lattice Structure during Uniaxial Compression under High-Strain-Rate Loading in Multiple Directions. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2025, 36, 9906–9923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, B.; Zhou, S.; Luo, M.; Han, F.; Chai, C.; Wang, J.; Yang, X. Superior Energy Absorption Characteristics of Additively-Manufactured Hollow-Walled Lattices. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2024, 264, 108834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daynes, S.; Feih, S. Functionally Graded Lattice Structures with Tailored Stiffness and Energy Absorption. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2025, 285, 109861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Chen, X.; He, S.; Zhang, J.; Hu, J.; Bai, L.; Wang, C.H. Bionic Spiderweb Lattice Metamaterials for Energy Absorption and Vibration Isolation. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2025, 300, 110386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Mao, Y.; Heng, Y.; Tao, J.; Xiang, L.; Qin, X.; Wei, Q. Mechanical Responses of Triply Periodic Minimal Surface Gyroid Lattice Structures Fabricated by Binder Jetting Additive Manufacturing. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2025, 35, 2803–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezapourian, M.; Jasiuk, I.; Saarna, M.; Hussainova, I. Selective Laser Melted Ti6Al4V Split-P TPMS Lattices for Bone Tissue Engineering. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2023, 251, 108353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Ma, W.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, S.; Tang, H. Ultra-High Specific Strength Ti6Al4V Alloy Lattice Material Manufactured via Selective Laser Melting. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 840, 142956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazur, M.; Leary, M.; Sun, S.; Vcelka, M.; Shidid, D.; Brandt, M. Deformation and Failure Behaviour of Ti-6Al-4V Lattice Structures Manufactured by Selective Laser Melting (SLM). Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 84, 1391–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zhang, D.Z.; Liu, F.; Li, Z.; Ma, Z.; Ren, Z. Mechanical and Energy Absorption Characteristics of Additively Manufactured Functionally Graded Sheet Lattice Structures with Minimal Surfaces. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2020, 167, 105262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Hu, S.; Chen, R.; Gu, Y.; Kong, X.; Tao, J.; Jiang, Y. Mechanical Properties Tailoring of Topology Optimized and Selective Laser Melting Fabricated Ti6Al4V Lattice Structure. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2019, 99, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, K.; Blok, A.; Weber, L.; Ahmadi, S.M.; Petrov, R.; Nikolic, K.; Borisov, E.V.; Leeflang, S.; Ayas, C.; Zadpoor, A.A.; et al. Continuous and Pulsed Selective Laser Melting of Ti6Al4V Lattice Structures: Effect of Post-Processing on Microstructural Anisotropy and Fatigue Behaviour. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 36, 101433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yan, C.; Han, C.; Chen, P.; Yang, S.; Shi, Y. Mechanical Response of a Triply Periodic Minimal Surface Cellular Structures Manufactured by Selective Laser Melting. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2018, 148, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
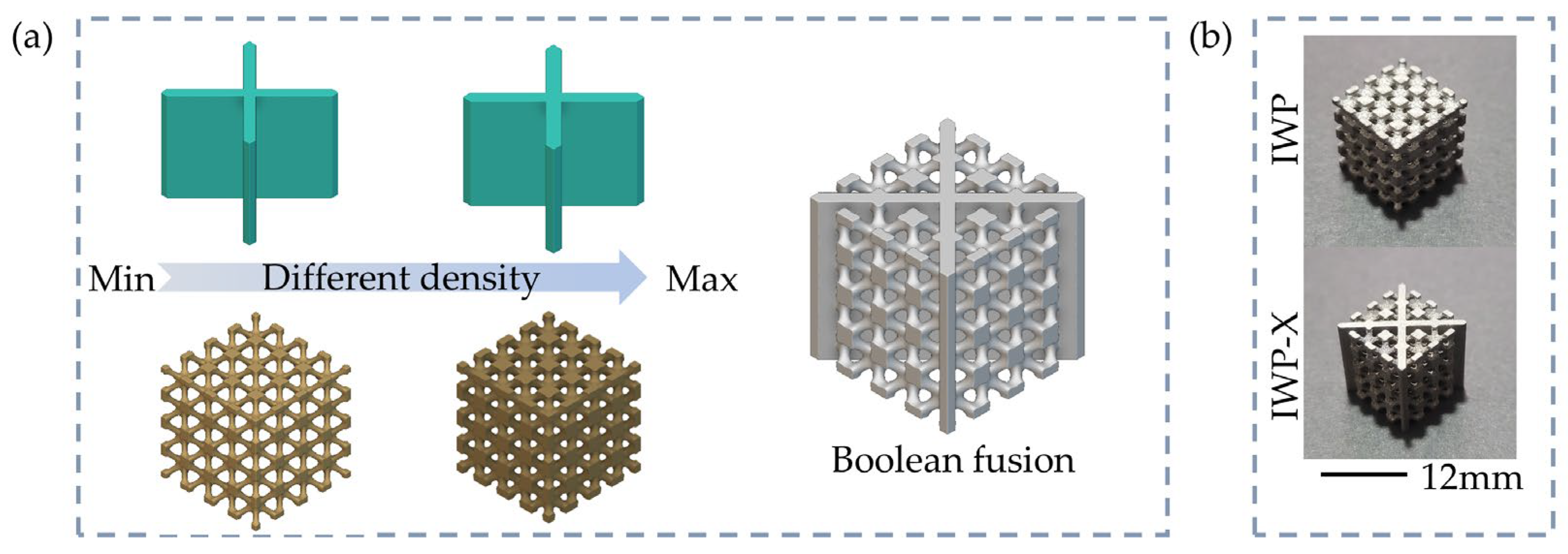
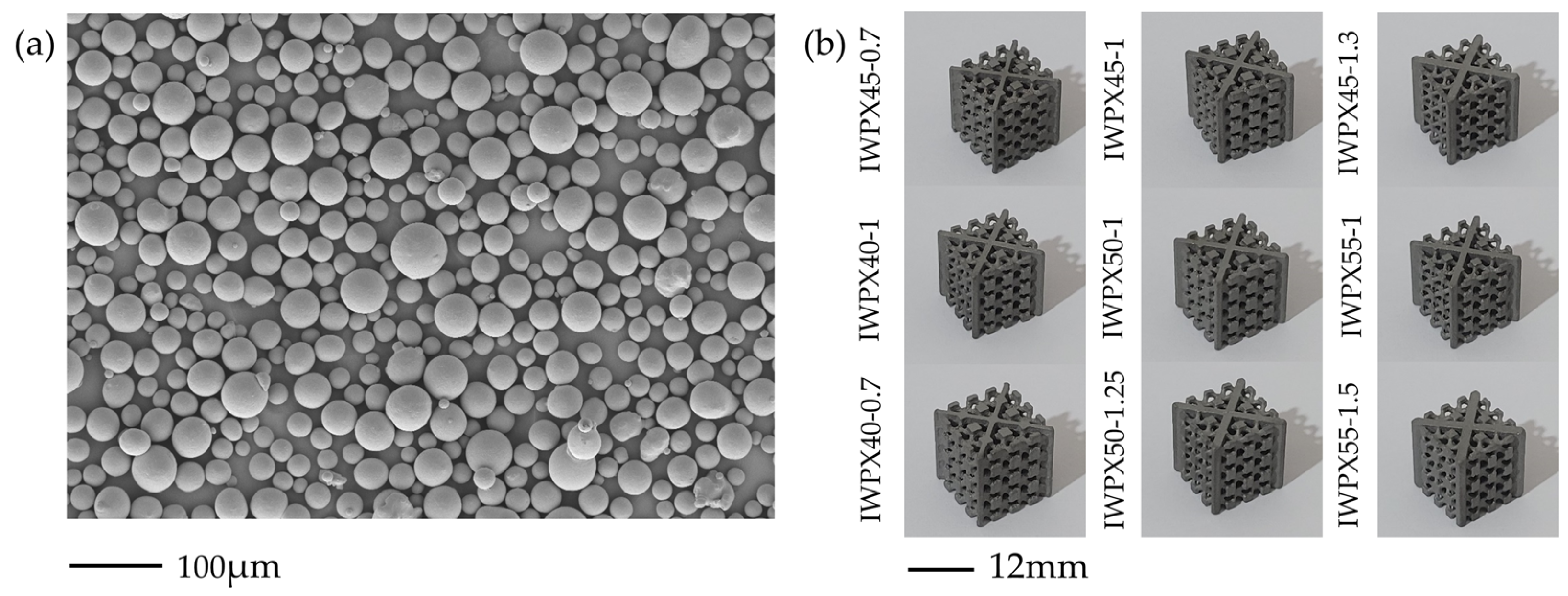
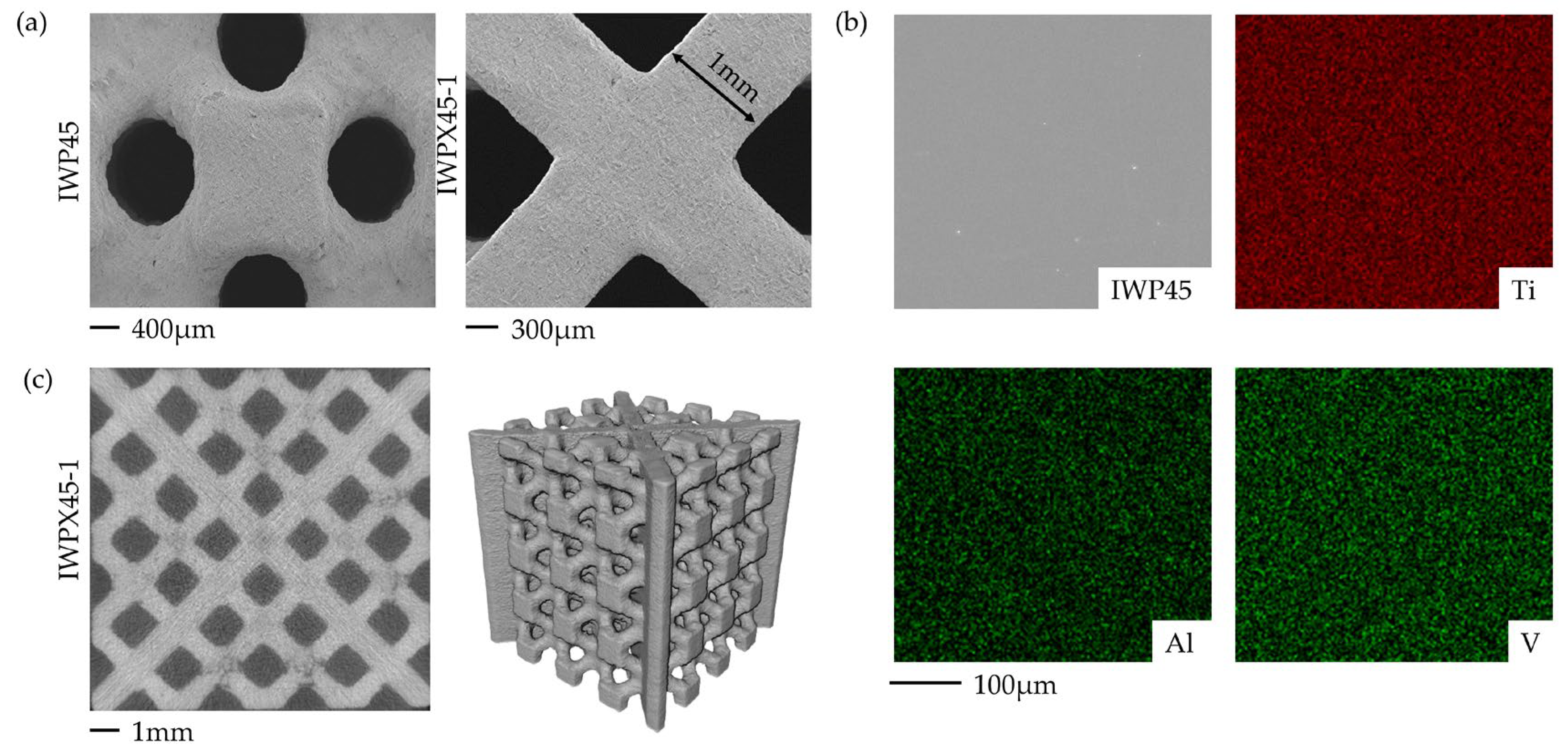

| Structure | Relative Density of I-WP (%) | Thickness of Plate t (mm) | Relative Density (%) | Vt/VIWP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IWP45 | 45.00 | None | 45 | None |
| IWPX45-0.7 | 37.80 | 0.7 | 45 | 0.42 |
| IWPX45-1 | 32.60 | 1 | 45 | 0.68 |
| IWPX45-1.3 | 25.60 | 1.3 | 45 | 1.11 |
| IWPX40-1 | 26.40 | 1 | 40 | 0.84 |
| IWPX50-1 | 37.80 | 1 | 50 | 0.60 |
| IWPX55-1 | 43.00 | 1 | 55 | 0.52 |
| IWPX40-0.7 | 32.60 | 0.7 | 40 | 0.49 |
| IWPX50-1.25 | 32.60 | 1.25 | 50 | 0.84 |
| IWPX55-1.5 | 32.60 | 1.5 | 55 | 1.00 |
| Laser Power | Laser Spot Size | Hatch Distance | Scanning Speed | Layer Thickness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 280 W | 0.1 mm | 0.1 mm | 1000 mm/s | 0.03 mm |
| Element | Ti | Al | V | Fe | O | C | H | N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mass fraction (%) | Bal | 5.5–6.5 | 3.5–4.5 | ≤0.25 | ≤0.2 | ≤0.08 | ≤0.012 | ≤0.05 |
| Power | Yield Strength (MPa) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation After Break (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ti6Al4V | 1050 ± 50 | 1230 ± 50 | 7 ± 3 |
| Structure | Number of Nodes | Number of Elements |
|---|---|---|
| IWP45 | 1,562,279 | 959,832 |
| IWPX45-0.7 | 1,649,300 | 1,019,071 |
| IWPX45-1 | 1,432,624 | 874,278 |
| IWPX45-1.3 | 1,390,934 | 852,106 |
| Structure | Relative Density (%) | Actual Relative Density (%) | Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| IWP45 | 45.00 | 46.64 ± 0.52 | 3.64 ± 1.16 |
| IWPX45-0.7 | 45.00 | 46.60 ± 0.36 | 3.56 ± 0.80 |
| IWPX45-1 | 45.00 | 46.85 ± 0.35 | 4.11 ± 0.78 |
| IWPX45-1.3 | 45.00 | 46.82 ± 0.35 | 4.04 ± 0.78 |
| IWPX40-1 | 40.00 | 41.34 ± 0.43 | 3.35 ± 1.08 |
| IWPX50-1 | 50.00 | 51.55 ± 0.85 | 3.10 ± 1.70 |
| IWPX55-1 | 55.00 | 56.45 ± 0.35 | 2.64 ± 0.63 |
| IWPX40-0.7 | 40.00 | 41.13 ± 0.64 | 2.83 ± 1.60 |
| IWPX50-1.25 | 50.00 | 51.95 ± 0.43 | 3.90 ± 0.86 |
| IWPX55-1.5 | 55.00 | 56.55 ± 0.86 | 2.82 ± 1.56 |
| Structure | Elastic Modulus (GPa) | Yield Strength (MPa) | Ultimate Compressive Strength (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| IWP45 | 3.81 ± 0.55 | 178.01 ± 5.52 | 205.01 ± 9.12 |
| IWPX45-0.7 | 6.56 ± 0.68 | 269.35 ± 7.23 | 354.79 ± 13.25 |
| IWPX45-1 | 6.85 ± 0.72 | 317.77 ± 9.32 | 398.95 ± 15.82 |
| IWPX45-1.3 | 7.43 ± 0.85 | 359.12 ± 11.23 | 455.23 ± 17.92 |
| IWPX40-1 | 6.72 ± 0.51 | 287.25 ± 8.12 | 366.36 ± 14.52 |
| IWPX50-1 | 7.20 ± 0.79 | 339.28 ± 10.52 | 432.25 ± 16.72 |
| IWPX55-1 | 7.58 ± 0.88 | 372.27 ± 11.92 | 460.65 ± 18.32 |
| IWPX40-0.7 | 5.86 ± 0.42 | 250.58 ± 6.82 | 321.78 ± 11.32 |
| IWPX50-1.25 | 7.19 ± 0.63 | 370.24 ± 11.82 | 474.45 ± 19.12 |
| IWPX55-1.5 | 7.64 ± 0.32 | 431.48 ± 11.98 | 531.36 ± 19.82 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, L.; Xiao, X.; Zhu, X.; Liu, J.; Sun, G.; Xu, Y.; Yang, S.; Jiang, C.; Geng, D. Mechanical Performance and Energy Absorption of Ti6Al4V I-WP Lattice Metamaterials Manufactured via Selective Laser Melting. Materials 2025, 18, 4626. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194626
Yu L, Xiao X, Zhu X, Liu J, Sun G, Xu Y, Yang S, Jiang C, Geng D. Mechanical Performance and Energy Absorption of Ti6Al4V I-WP Lattice Metamaterials Manufactured via Selective Laser Melting. Materials. 2025; 18(19):4626. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194626
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Le, Xiong Xiao, Xianyong Zhu, Jiaan Liu, Guangzhi Sun, Yanheng Xu, Song Yang, Cheng Jiang, and Dongni Geng. 2025. "Mechanical Performance and Energy Absorption of Ti6Al4V I-WP Lattice Metamaterials Manufactured via Selective Laser Melting" Materials 18, no. 19: 4626. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194626
APA StyleYu, L., Xiao, X., Zhu, X., Liu, J., Sun, G., Xu, Y., Yang, S., Jiang, C., & Geng, D. (2025). Mechanical Performance and Energy Absorption of Ti6Al4V I-WP Lattice Metamaterials Manufactured via Selective Laser Melting. Materials, 18(19), 4626. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194626






