Effects of the Addition of Iron and Chromium on the Structure and Properties of the Ni-Co-Mn-In Alloy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
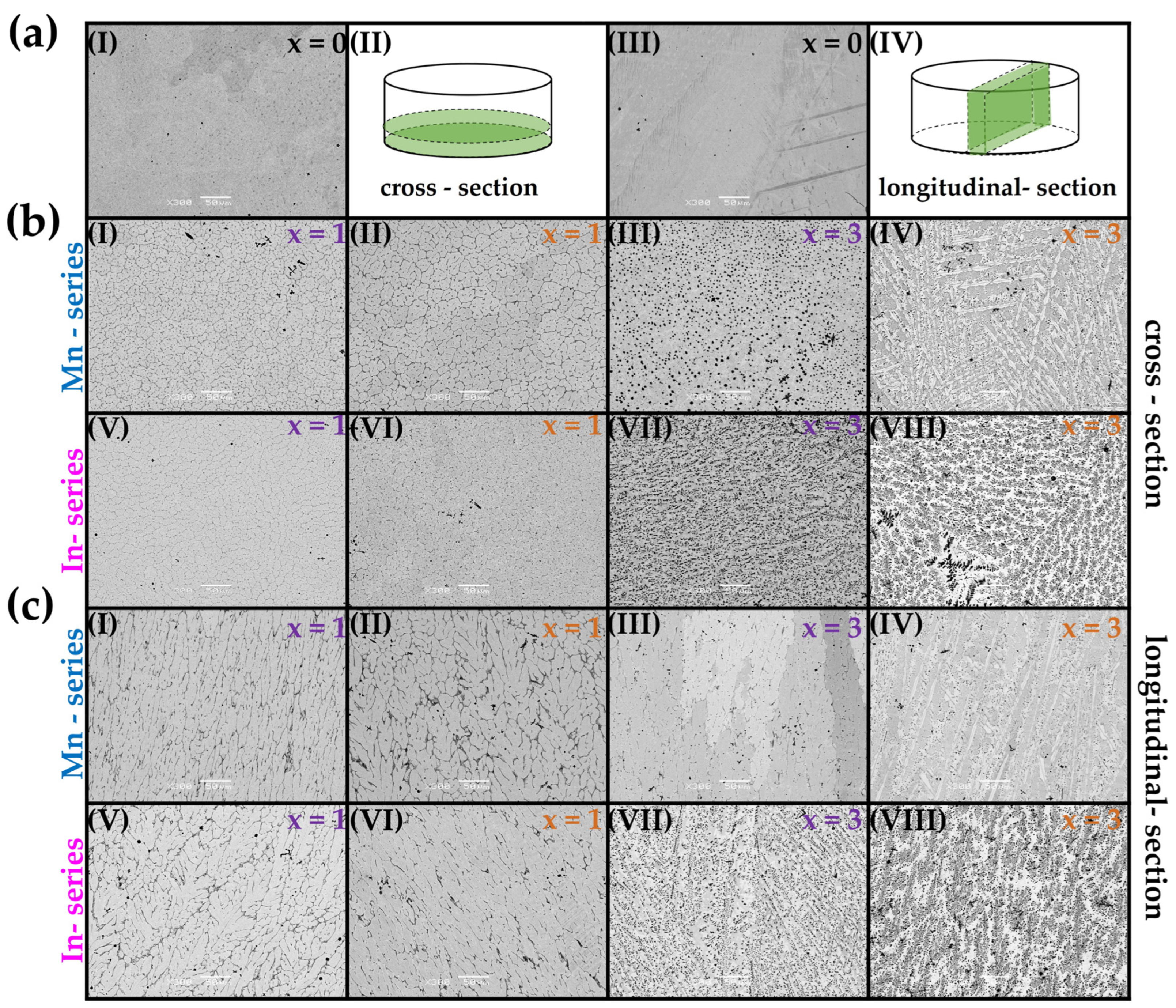
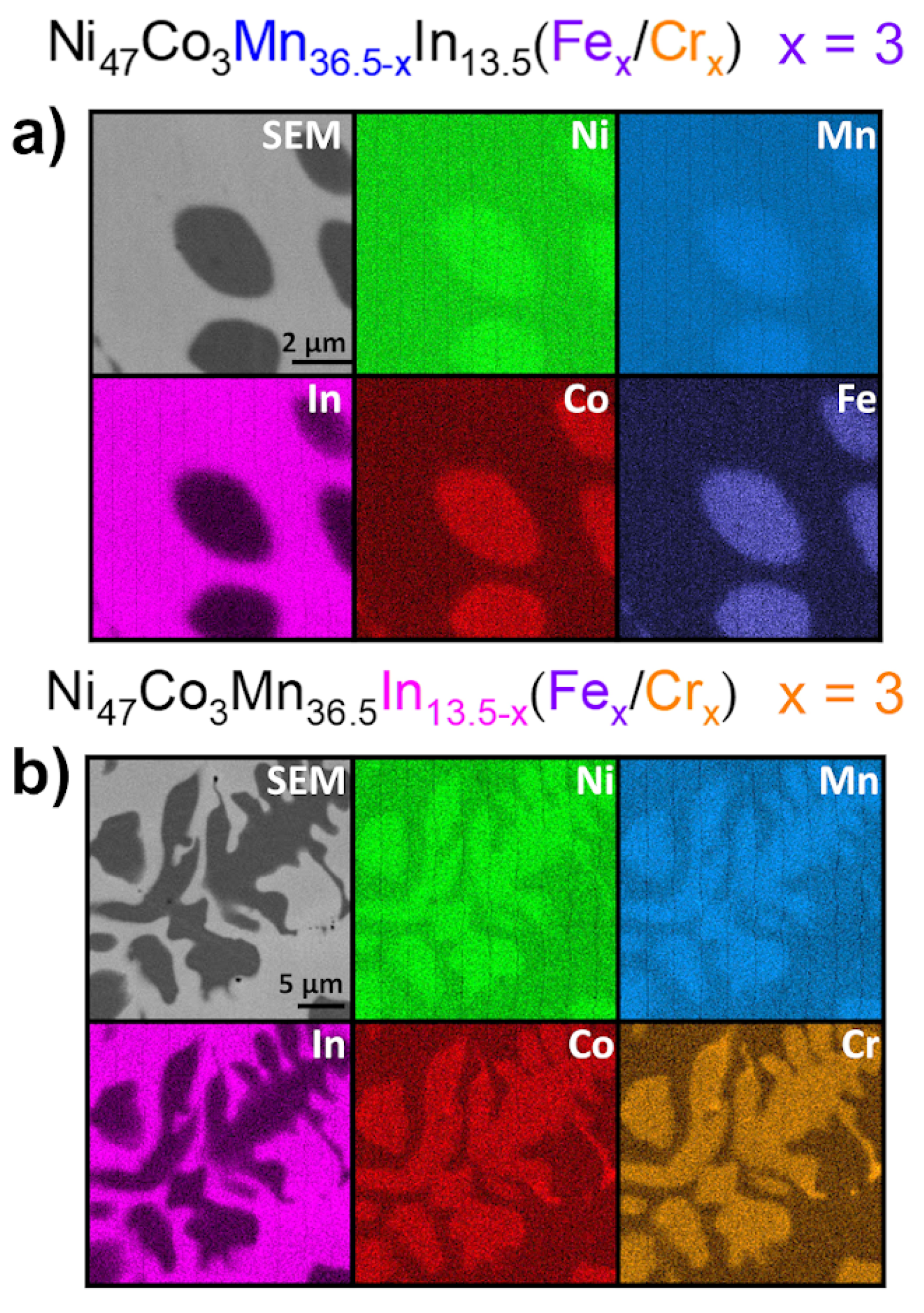
3.2. Microstructure (SEM) and Chemical Composition (EDS)
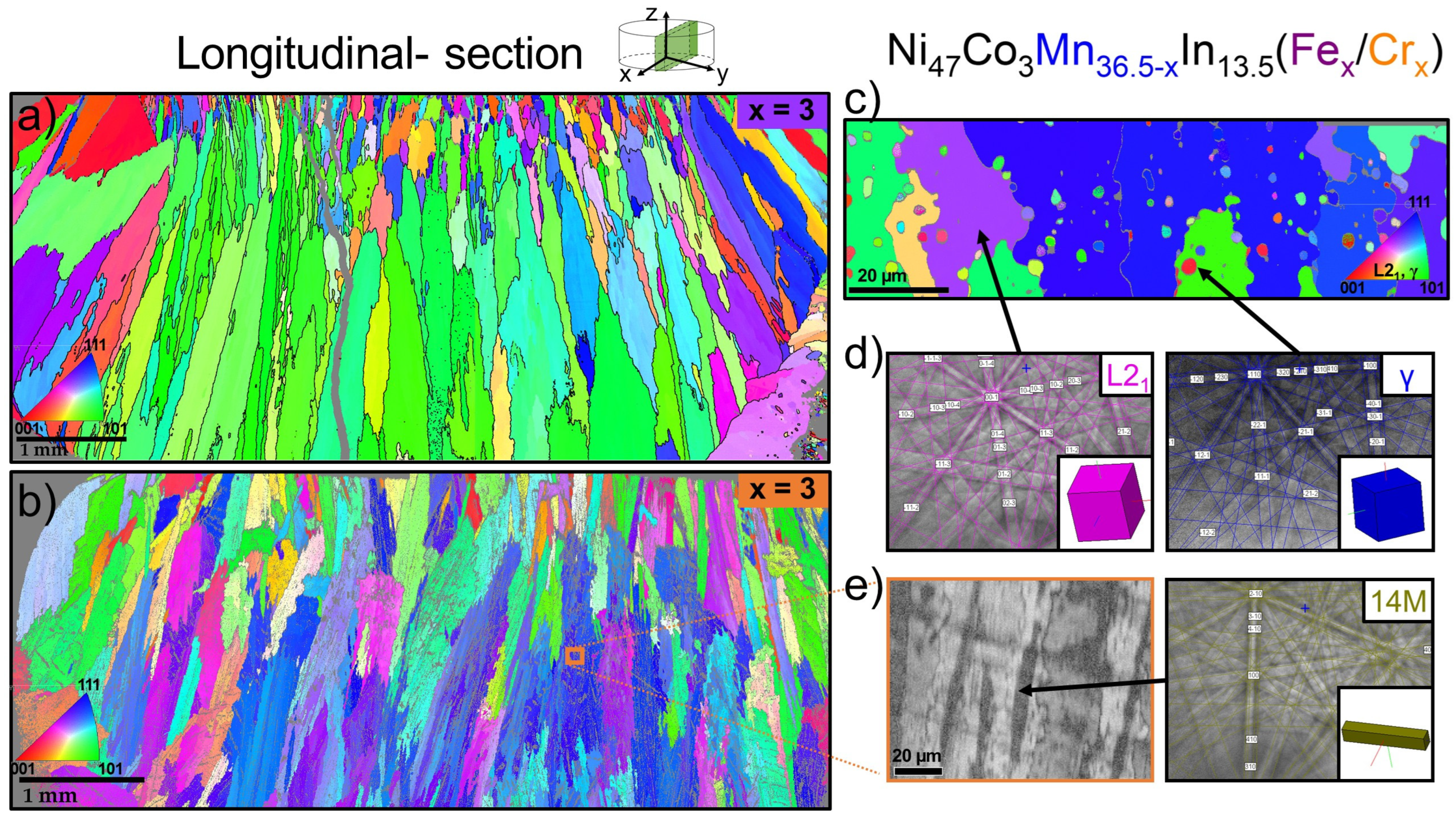
3.3. Electron Backscatter Diffraction (EBSD)
3.4. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
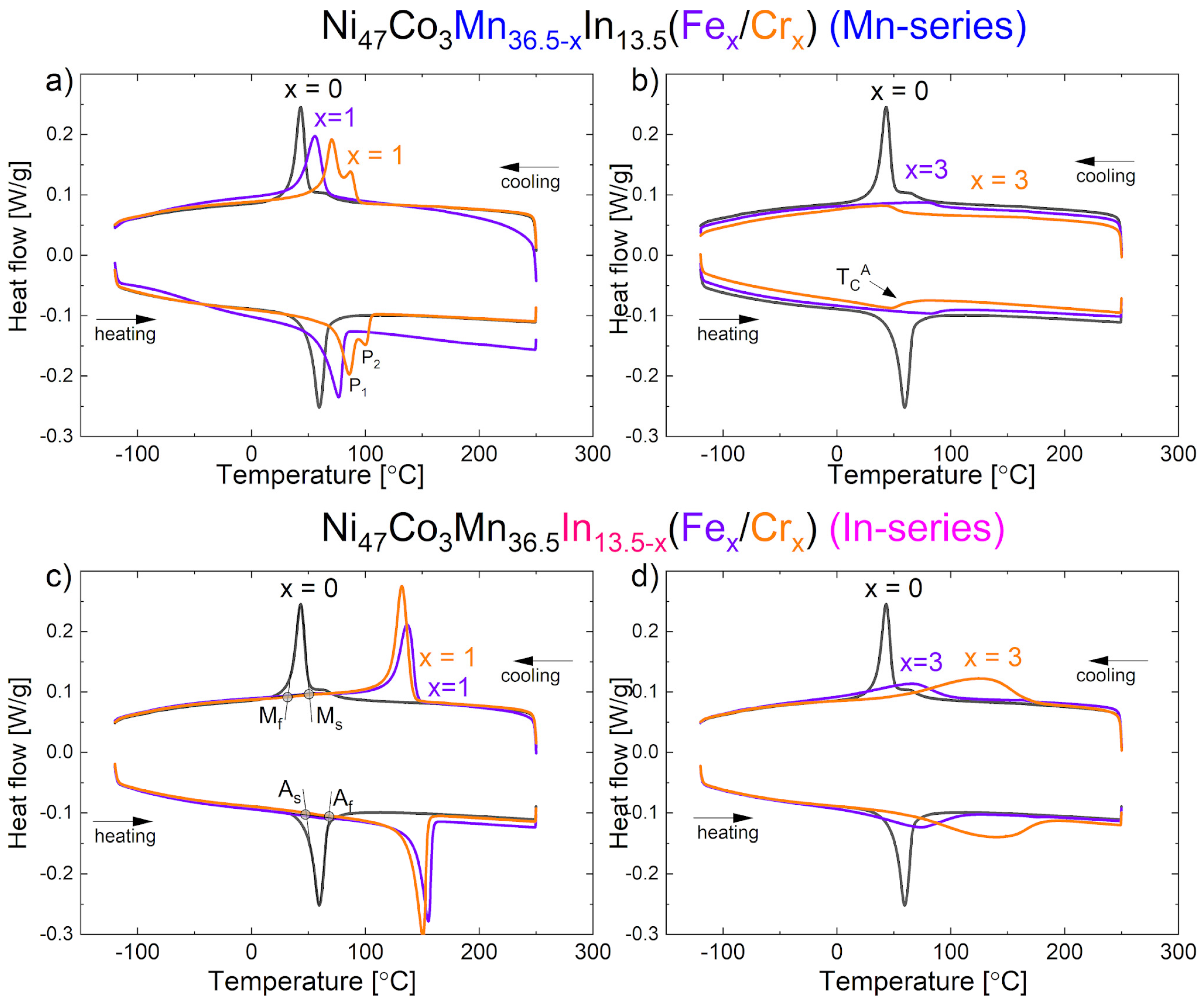
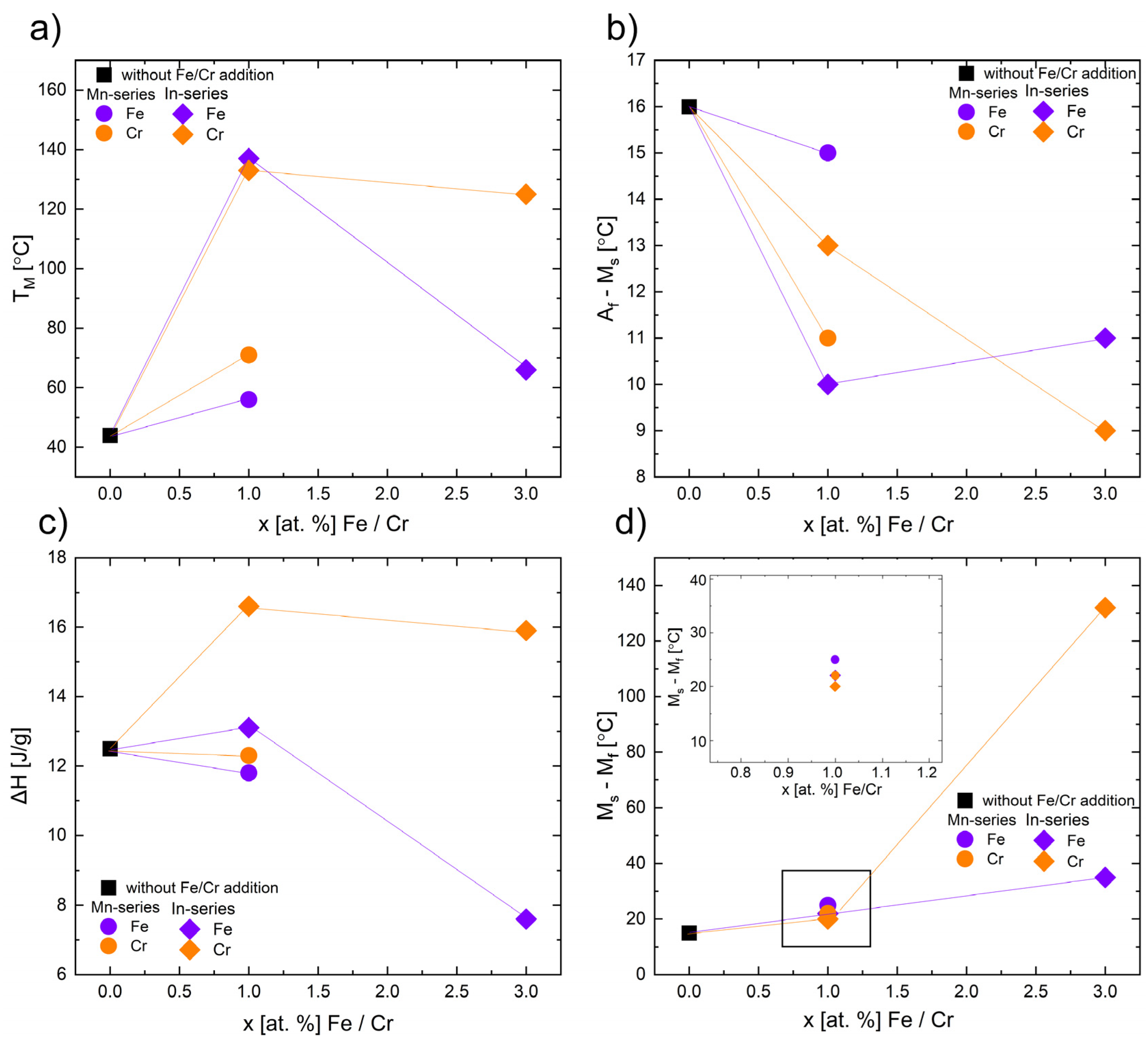
3.5. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
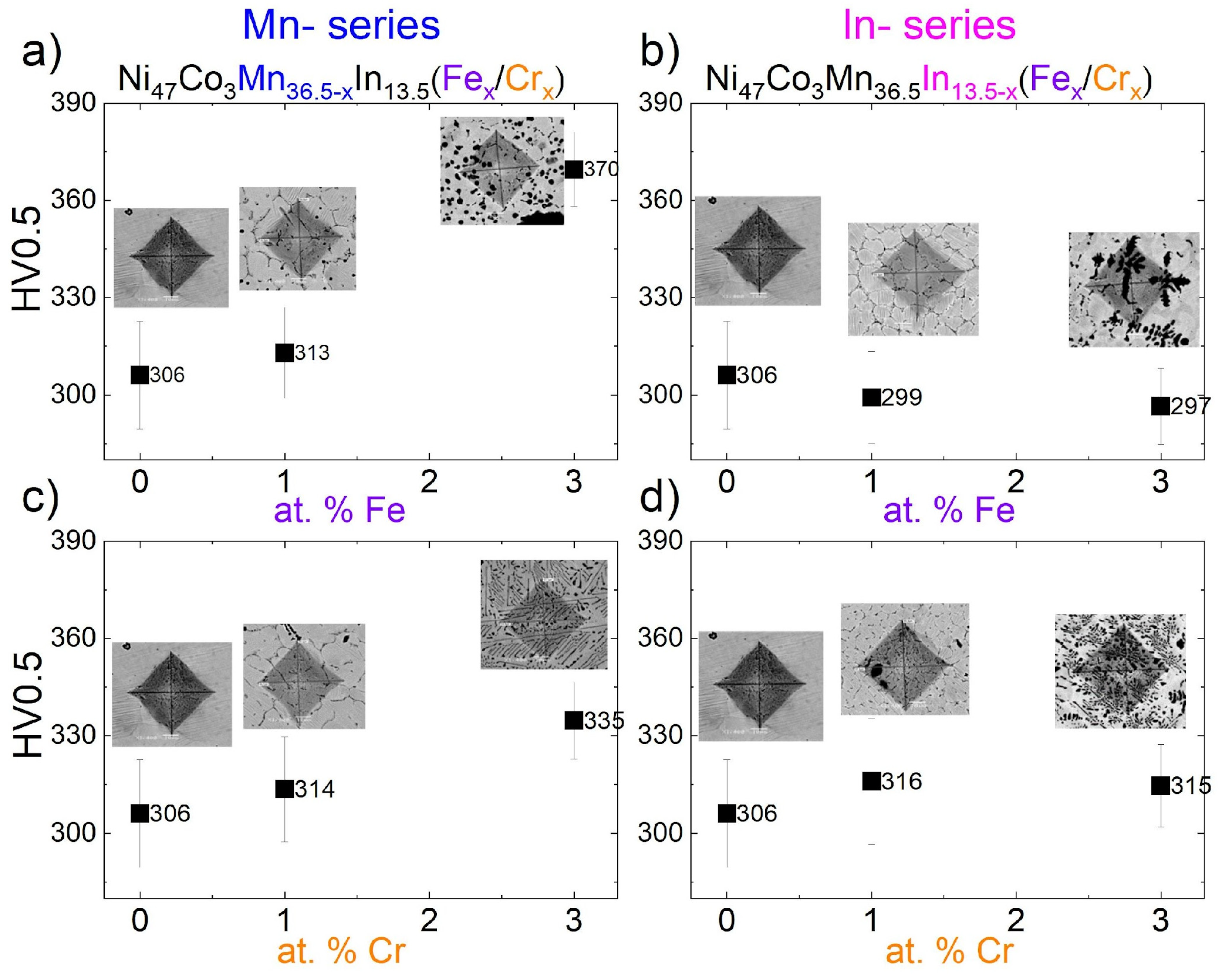
3.6. Microhardness
4. Conclusions
- 1.
- Changes in the microstructure and phase composition:
- The Ni47Co3Mn36.5−xIn13.5 quaternary alloy exhibits a coarse-grained martensitic structure (monoclinic, P2/m), while 1% Fe- and Cr-doped alloys exhibit a mixture of austenite (L21, Fmm), martensite (monoclinic, P2/m), and γ particles enriched in Co and Fe/Cr, respectively, with a specific distribution in the matrix.
- The addition of 1% Fe caused higher microstructure refinement compared to the 1% Cr addition.
- Increasing the addition to 3 at.% caused an increase in the volume fraction of γ particles and their distribution, as well as changed their morphology (dendritic-like shape).
- 2.
- Changes in the martensitic transformation (MT) behavior:
- An increase in martensitic transformation (MT) temperatures was observed, which was higher in the In-series than in the Mn-series.
- This weakened or arrested the martensitic transformation in alloys containing additions of 3 at.% Fe or 3 at.% Cr, resulting in a total of 6 at.% of alloying elements when the 3 at.% Co already present in the alloy was included.
- 3.
- Changes in microhardness:
- An increase in microhardness from 306 HV0.5 (x = 0) to 370 HV0.5 (x = 3 at.% of Fe) and 335 HV0.5 (x = 3 at.% of Cr) in the Ni47Co3Mn36.5−xIn13.5 (Fex/Crx) series was observed.
- The microhardness in the In-series and in the 1 at.%-doped (Fe/Cr) Mn-series remained at a similar level, irrespective of the morphology and γ particle size.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BSE | Backscattered Electron |
| DSC | Differential Scanning Calorimetry |
| EBSD | Electron Backscatter Diffraction |
| EDM | Electric Discharge Machine |
| EDS | Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy |
| FSMA | Ferromagnetic Shape Memory Alloy |
| MCE | Magnetocaloric Effect |
| MT | Martensitic Transformation |
| RC | Refrigeration Capacity |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscopy |
| TEM | Transmission Electron Microscopy |
| VAR | Vacuum Arc Melting |
| XRD | X-Ray Diffraction |
References
- O’Handley, R.C.; Murray, S.J.; Marioni, M.; Nembach, H.; Allen, S.M. Phenomenology of Giant Magnetic-Field-Induced Strain in Ferromagnetic Shape-Memory Materials (Invited). J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 87, 4712–4717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Yang, J.; Li, D.; Yang, B.; Yan, H.; Nie, Z.; Hou, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Large Elastocaloric Effect in a Polycrystalline Ni45.7Co4.2Mn37.3Sb12.8 Alloy with Low Transformation Strain. Scr. Mater. 2019, 162, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sozinov, A.; Likhachev, A.A.; Lanska, N.; Ullakko, K. Giant Magnetic-Field-Induced Strain in NiMnGa Seven-Layered Martensitic Phase. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 80, 1746–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephan, J.M.; Pagounis, E.; Laufenberg, M.; Paul, O.; Ruther, P. A Novel Concept for Strain Sensing Based on the Ferromagnetic Shape Memory Alloy NiMnGa. IEEE Sens. J. 2011, 11, 2683–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sozinov, A.; Lanska, N.; Soroka, A.; Zou, W. 12% Magnetic Field-Induced Strain in Ni-Mn-Ga-Based Non-Modulated Martensite. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 021902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Gottschall, T.; Skokov, K.P.; Moore, J.D.; Gutfleisch, O. Giant Magnetocaloric Effect Driven by Structural Transitions. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kainuma, R.; Imano, Y.; Ito, W.; Sutou, Y.; Morito, H.; Okamoto, S.; Kitakami, O.; Oikawa, K.; Fujita, A.; Kanomata, T.; et al. Magnetic-Field-Induced Shape Recovery by Reverse Phase Transformation. Nature 2006, 439, 957–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, W.; Imano, Y.; Kainuma, R.; Sutou, Y.; Oikawa, K.; Ishida, K. Martensitic and Magnetic Transformation Behaviors in Heusler-Type NiMnIn and NiCoMnIn Metamagnetic Shape Memory Alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2007, 38, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planes, A.; Mañosa, L.; Moya, X.; Krenke, T.; Acet, M.; Wassermann, E.F. Magnetocaloric Effect in Heusler Shape-Memory Alloys. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2007, 310, 2767–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Yang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Esling, C.; Zhao, X.; Zuo, L. Large low-field magnetocaloric effect in a directionally solidified Ni50Mn18Cu7Cu25 alloy. Intermetallics 2017, 88, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Xie, L.; Yu, Q.; Wang, J.; Jiang, C. Toughening the Grain Boundaries by Introducing a Small Amount of the Second Phase: Ni-Cu-Mn-Ga Shape Memory Alloys as an Example. Acta Mater. 2024, 263, 119469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhu, J.; Ding, Z. Preparation and Characterization of Ni-Mn-Ga-Cu Shape Memory Alloy with Micron-Scale Pores. Metals 2024, 14, 1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheibel, F.; Liu, W.; Pfeuffer, L.; Shayanfar, N.; Taubel, A.; Skokov, K.P.; Riegg, S.; Wu, Y.; Gutfleisch, O. Influence of Gd-Rich Precipitates on the Martensitic Transformation, Magnetocaloric Effect, and Mechanical Properties of Ni-Mn-In Heusler Alloys—A Comparative Study. J. Appl. Phys. 2023, 133, 075104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeuffer, L.; Lemke, J.; Shayanfar, N.; Riegg, S.; Koch, D.; Taubel, A.; Scheibel, F.; Kani, N.A.; Adabifiroozjaei, E.; Molina-Luna, L.; et al. Microstructure Engineering of Metamagnetic Ni-Mn-Based Heusler Compounds by Fe-Doping: A Roadmap towards Excellent Cyclic Stability Combined with Large Elastocaloric and Magnetocaloric Effects. Acta Mater. 2021, 221, 117390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Zhang, P.; Xu, Y.; Sun, W.; Liu, J. Elastocaloric Effect in Ni45Mn36.4In13.6Co5 Metamagnetic Shape Memory Alloys under Mechanical Cycling. Mater. Lett. 2015, 148, 110–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, A.; Sun, W.; Zhao, D.; Liu, J. Influence of Cr on Microstructure and Elastocaloric Effect in Ni–Mn–In–Co–Cr Polycrystalline Alloys. Phys. Lett. Sect. A Gen. At. Solid. State Phys. 2018, 382, 2876–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Villa, P.O.; Mañosa, L.; Planes, A.; Soto-Parra, D.E.; Sánchez-Llamazares, J.L.; Flores-Zúñiga, H.; Frontera, C. Elastocaloric and Magnetocaloric Effects in Ni-Mn-Sn(Cu) Shape-Memory Alloy. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 113, 053506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, P.; Zhang, G.; Li, Z.; Yang, B.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, D.; Du, Y. Combining Magnetocaloric and Elastocaloric Effects to Achieve a Broad Refrigeration Temperature Region in Ni43Mn41Co5Sn11 Alloy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2022, 550, 169082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Checa, A.; Porro, J.M.; Feuchtwanger, J.; Lázpita, P.; Hansen, T.C.; Mondelli, C.; Sozinov, A.; Barandiarán, J.M.; Ullakko, K.; Chernenko, V. Role of Fe Addition in Ni–Mn–Ga–Co–Cu–Fe Ferromagnetic Shape Memory Alloys for High-Temperature Magnetic Actuation. Acta Mater. 2020, 196, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Sui, J.H.; Gao, Z.Y.; Zhang, J.; Cai, W. Investigation on Martensitic Transformation Behavior, Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Fe-Doped Ni-Mn-In Alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 507, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.-L.; Feng, Z.-C.; Zhang, K.; Wu, M.-Y.; Tian, X.-H.; Guo, E.-J. Microstructure, Martensitic Transformation and Mechanical Properties of Ni–Mn–Sn Alloys by Substituting Fe for Ni. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China Engl. Ed. 2017, 27, 2234–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Tai, Z.; Zhang, K.; Tian, X.; Cai, W. Simultaneous Enhancement of Magnetic and Mechanical Properties in Ni-Mn-Sn Alloy by Fe Doping. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halder, M.; Suresh, K.G. Effect of Fe Substitution at the Ni and Mn Sites on the Magnetic Properties of Ni50Mn35In15 Heusler Alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 647, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Fang, Y.; Feng, S.; Zhai, Q.; Luo, Z.; Zheng, H. Magnetostructural Transition Behavior in Fe-Doped Heusler Mn-Ni-In Ribbon Materials. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 417, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Sui, J.H.; Wang, H.B.; Cai, W. Reversible Magnetic-Field-Induced Phase Transformation and Magnetocaloric Effect above Room Temperature in a NiMnInFe Polycrystal. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2012, 324, 1982–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Qian, M.; Zhang, X.; Wei, L.; Cao, F.; Xing, D.; Cui, X.; Sun, J.; Geng, L. Martensite Transformation and Magnetic Properties of Fe-Doped Ni-Mn-Sn Alloys with Dual Phases. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 689, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkera, H.S.; Kaur, D. Effect of Cr Addition on the Structural, Magnetic and Mechanical Properties of Magnetron Sputtered Ni–Mn–In Ferromagnetic Shape Memory Alloy Thin Films. J. Phys. A 2016, 122, 996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkera, H.S.; Singh, I.; Kaur, D. Room Temperature Magnetocaloric Effect in Ni-Mn-In-Cr Ferromagnetic Shape Memory Alloy Thin Films. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 424, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Quetz, A.; Aryal, A.; Saleheen, A.U.; Rodionov, I.; Blinov, M.; Prudnikova, M.; Dubenko, I.; Prudnikov, V.; Mazumdar, D.; et al. Effects of the Partial Substitution of Ni by Cr on the Transport, Magnetic, and Magnetocaloric Properties of Ni50Mn37In13. AIP Adv. 2017, 7, 056433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar-Mejía, C.; Devi, P.; Singh, S.; Felser, C.; Wosnitza, J. Influence of Cr Substitution on the Reversibility of the Magnetocaloric Effect in Ni-Cr-Mn-In Heusler Alloys. Phys. Rev. Mater. 2021, 5, 104406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.M.; Wang, L.-D.; Liu, H.X.; Yan, H.L.; Jia, N.; Yang, B.; Li, Z.-B.; Zhang, Y.D.; Esling, C.; Zhao, X.; et al. Correlation between Microstructure and Martensitic Transformation, Mechanical Properties and Elastocaloric Effect in Ni–Mn-Based Alloys. Intermetallics 2019, 113, 106579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matyja, E.; Prusik, K.; Zubko, M.; Dercz, G. Microstructure Refinement and Mechanical Properties of the NiCoMnIn Alloy Obtained by Arc Melting Technique from Mechanically Alloyed Powder. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 859, 157841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, N.M.; Salas, D.; Wang, S.; Roshchin, I.V.; Santamarta, R.; Arroyave, R.; Duong, T.; Chumlyakov, Y.I.; Karaman, I. On the Microstructural Origins of Martensitic Transformation Arrest in a NiCoMnIn Magnetic Shape Memory Alloy. Acta Mater. 2018, 142, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Liu, J.; Chen, X.; Sun, W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, M.; Shao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yan, A. Giant Caloric Effect of Low-Hysteresis Metamagnetic Shape Memory Alloys with Exceptional Cyclic Functionality. Acta Mater. 2017, 133, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Brock, J.; Sugerman, I. Anomalous Transport Properties of Ni2Mn1-XCrxGa Heusler Alloys at the Martensite-Austenite Phase Transition. Phys. Rev. B 2016, 93, 054419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picornell, C.; Pons, J.; Paulsen, A.; Frenzel, J.; Kaminskii, V.; Sapozhnikov, K.; Van Humbeeck, J.; Kustov, S. Burst-like Reverse Martensitic Transformation during Heating, Cooling and under Isothermal Conditions in Stabilized Ni-Ti-Nb. Scr. Mater. 2020, 180, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Alarcos, V.; Recarte, V.; Pérez-Landazábal, J.I.; Cesari, E.; Rodríguez-Velamazán, J.A. Long-Range Atomic Order and Entropy Change at the Martensitic Transformation in a Ni-Mn-In-Co Metamagnetic Shape Memory Alloy. Entropy 2014, 16, 2756–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recarte, V.; Pérez-Landazábal, J.I.; Sánchez-Alarcos, V.; Rodríguez-Velamazán, J.A. Dependence of the Martensitic Transformation and Magnetic Transition on the Atomic Order in Ni-Mn-In Metamagnetic Shape Memory Alloys. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 1937–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Zhong, M.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Yang, H. Grain Size Effect of the γ Phase Precipitation on Martensitic Transformation and Mechanical Properties of Ni-Mn-Sn-Fe Heusler Alloys. Materials 2021, 14, 2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, K.; Li, L.; Li, Z.; Bi, X.; Wang, J. Grain Boundary Decohesion by Nanoclustering Ni and Cr Separately in CrMnFeCoNi High-Entropy Alloys. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaay0639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, K.; Kozlowski, M.; Lukaszkiewicz, N.; Kobus, M.; Bielecki, J.; Jurczyk, M. Effect of Indium on the Properties of Mg-Zn-Based Alloys. Metals 2023, 13, 1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
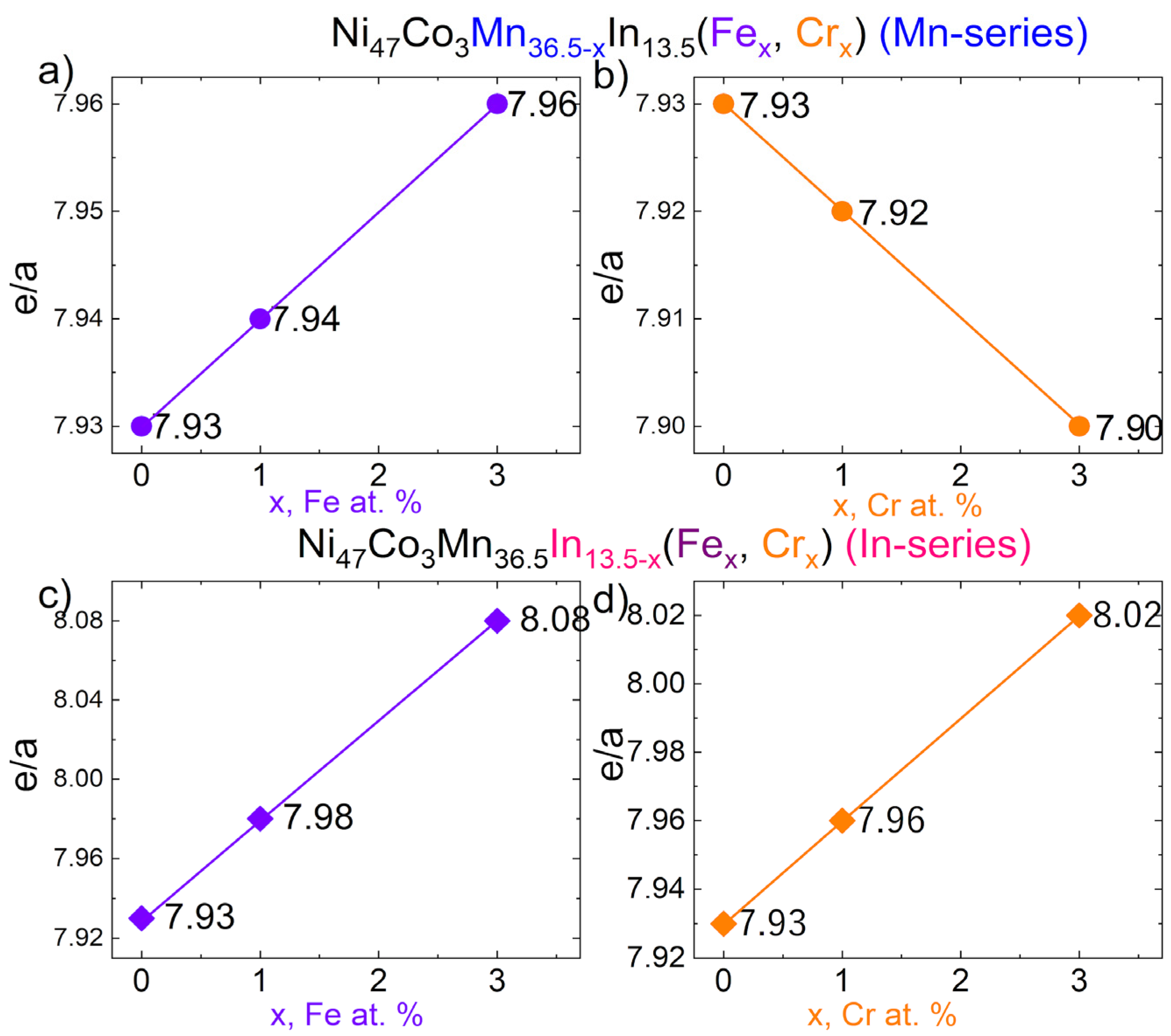


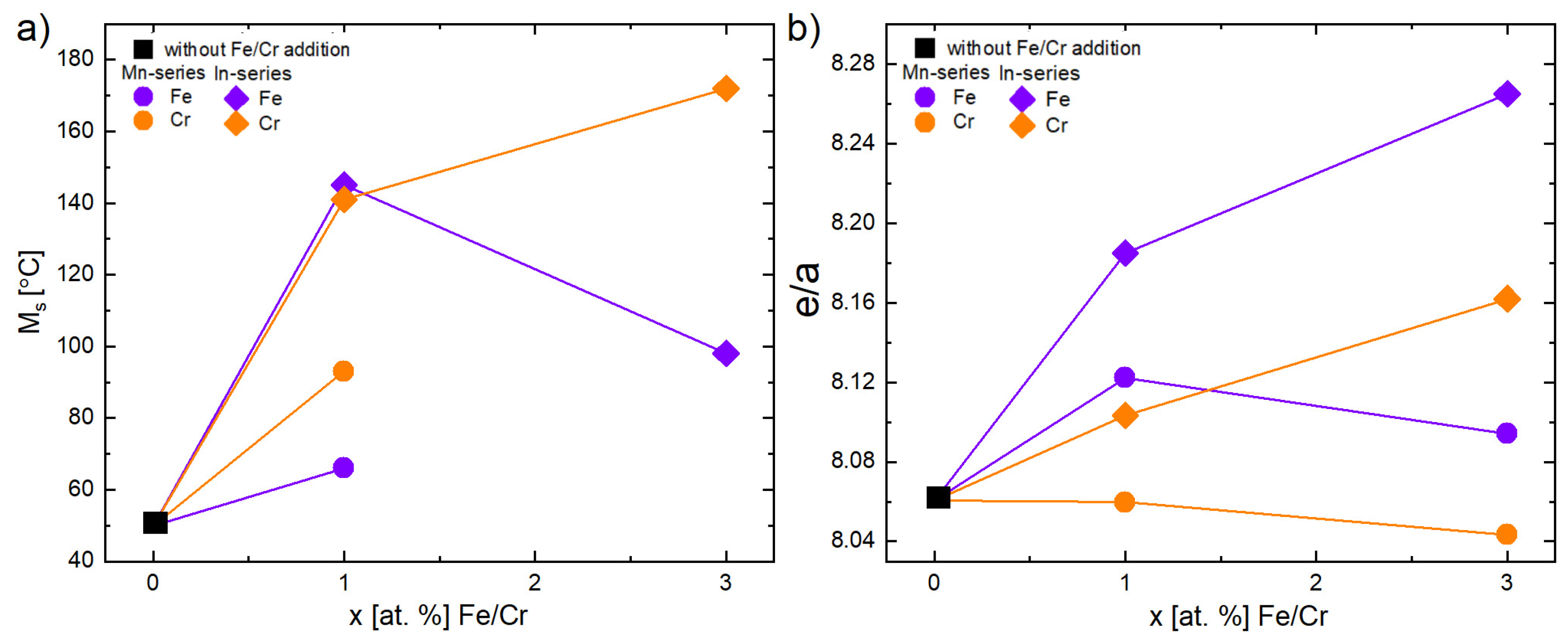
| Ni | Mn | Co | In | Fe | Cr | e/a | Short Name | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 47.0 | 36.5 | 3.0 | 13.5 | - | - | 7.93 | x = 0 | |
| Mn-series | 47.0 | 35.5 | 3.0 | 13.5 | 1.0 | - | 7.94 ↑ | x = 1 |
| 47.0 | 33.5 | 3.0 | 13.5 | 3.0 | - | 7.96 ↑ | x = 3 | |
| 47.0 | 35.5 | 3.0 | 13.5 | - | 1.0 | 7.92 ↓ | x = 1 | |
| 47.0 | 33.5 | 3.0 | 13.5 | - | 3.0 | 7.90 ↓ | x = 3 | |
| In-series | 47.0 | 36.5 | 3.0 | 12.5 | 1.0 | - | 7.98 ↑ | x = 1 |
| 47.0 | 36.5 | 3.0 | 10.5 | 3.0 | - | 8.08 ↑ | x = 3 | |
| 47.0 | 36.5 | 3.0 | 12.5 | - | 1.0 | 7.96 ↑ | x = 1 | |
| 47.0 | 36.5 | 3.0 | 10.5 | - | 3.0 | 8.02 ↑ | x = 3 |
| Ni | Mn | Co | In | Fe | Cr | e/a | Short Name | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn-series | 51.1 | 34.0 | 2.1 | 12.8 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 8.06 | x = 0 |
| 52.2 | 33.2 | 1.7 | 12.1 | 0.8 | 0.0 | 8.12 | x = 1 | |
| 51.3 | 31.5 | 1.9 | 12.7 | 2.6 | 0.0 | 8.09 | x = 3 | |
| 51.3 | 33.8 | 1.7 | 12.7 | 0.0 | 0.5 | 8.06 | x = 1 | |
| 50.7 | 32.3 | 2.3 | 12.5 | 0.0 | 2.3 | 8.04 | x = 3 | |
| In-series | 52.6 | 33.9 | 2.0 | 11.0 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 8.18 | x = 1 |
| 51.9 | 34.0 | 2.2 | 9.1 | 2.8 | 0.0 | 8.26 | x = 3 | |
| 51.8 | 33.9 | 1.8 | 12.1 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 8.10 | x = 1 | |
| 51.1 | 34.8 | 2.0 | 9.8 | 0.0 | 2.3 | 8.16 | x = 3 |
| Ms [°C] | TM [°C] | Mf [°C] | Ms–Mf | ΔH [J/g] | TCA [°C] | As [°C] | TA [°C] | Af [°C] | Af–As [°C] | Af–Ms [°C] | ΔH [J/g] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x = 0 | 50 | 44 | 35 | 15 | −11.2 | 68 | 49 | 58 | 66 | 17 | 16 | 12.5 |
| Ni47Co3Mn36.5−xIn13.5(Fex/Crx) (Mn-series) | ||||||||||||
| x = 1 | 66 | 56 | 41 | 25 | −10.4 | - | 59 | 75 | 81 | 22 | 15 | 11.8 |
| x = 1 | 93 | P1 71 P2 88 | 61 | 22 | −12.3 | - | 72 | P1 85 P2 100 | 104 | 32 | 11 | 12.3 |
| x = 3 | - | - | - | - | 87 | - | - | - | - | |||
| x = 3 | - | - | - | - | 51 | - | - | - | - | |||
| Ni47Co3Mn36.5In13.5−x(Fex/Crx) (In-series) | ||||||||||||
| x = 1 | 145 | 137 | 123 | 22 | −12.5 | - | 142 | 154 | 158 | 16 | 10 | 13.1 |
| x = 1 | 141 | 133 | 121 | 20 | −17.1 | - | 137 | 149 | 154 | 17 | 13 | 16.6 |
| x = 3 | 98 | 66 | 7 | 35 | −7.9 | 168 | 10 | 73 | 109 | 99 | 11 | 7.6 |
| x = 3 | 172 | 125 | 40 | 132 | −20.4 | - | 60 | 134 | 181 | 121 | 9 | 15.9 |
| at.% | Mn-Series | Phase | γ Fraction | In-Series | Phase | γ Fraction | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| at.% Fe | x = 0 | 306 (17) | M | 0% | 306 (17) | M | 0% |
| x = 1 | 313 (14) | M + A + γ | 5.0% | 299 (14) | M + A + γ | 7.0% | |
| x = 3 | 370 (11) | A + γ | 6.4% | 297 (12) | M + A + γ | 12.9% | |
| at.% Cr | x = 0 | 306 (17) | M | 0% | 306 (17) | M + A + γ | 0% |
| x = 1 | 314 (16) | M + A + γ | 6.7% | 316 (19) | M + A + γ | 6.8% | |
| x = 3 | 335 (12) | M + A + γ | 15.4% | 315 (13) | M + A + γ | 19% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matyja, E.; Prusik, K. Effects of the Addition of Iron and Chromium on the Structure and Properties of the Ni-Co-Mn-In Alloy. Materials 2025, 18, 4597. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194597
Matyja E, Prusik K. Effects of the Addition of Iron and Chromium on the Structure and Properties of the Ni-Co-Mn-In Alloy. Materials. 2025; 18(19):4597. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194597
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatyja, Edyta, and Krystian Prusik. 2025. "Effects of the Addition of Iron and Chromium on the Structure and Properties of the Ni-Co-Mn-In Alloy" Materials 18, no. 19: 4597. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194597
APA StyleMatyja, E., & Prusik, K. (2025). Effects of the Addition of Iron and Chromium on the Structure and Properties of the Ni-Co-Mn-In Alloy. Materials, 18(19), 4597. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194597







