Effect of Adding Molybdenum on Microstructure, Hardness, and Corrosion Resistance of an AlCoCrFeNiMo0.25 High-Entropy Alloy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Microstructure Analysis
2.3. Hardness and Nanoindentation Testing
2.4. Corrosion Testing
3. Results and Discussion
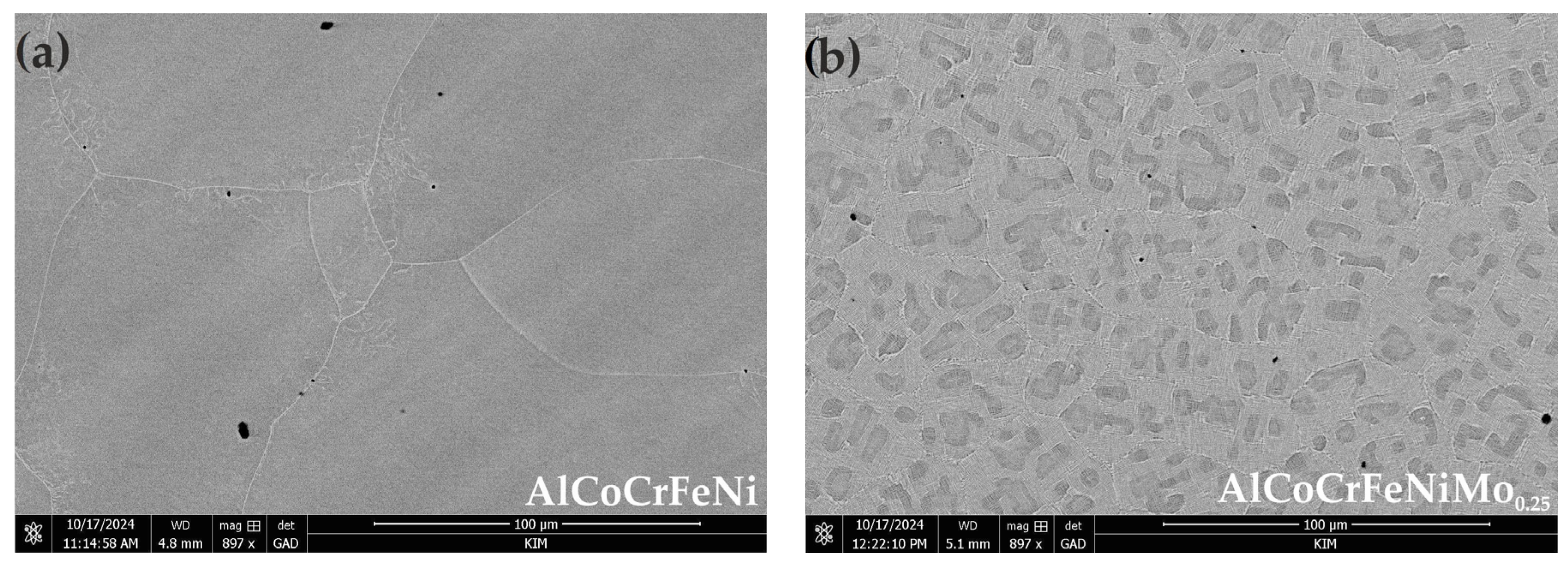
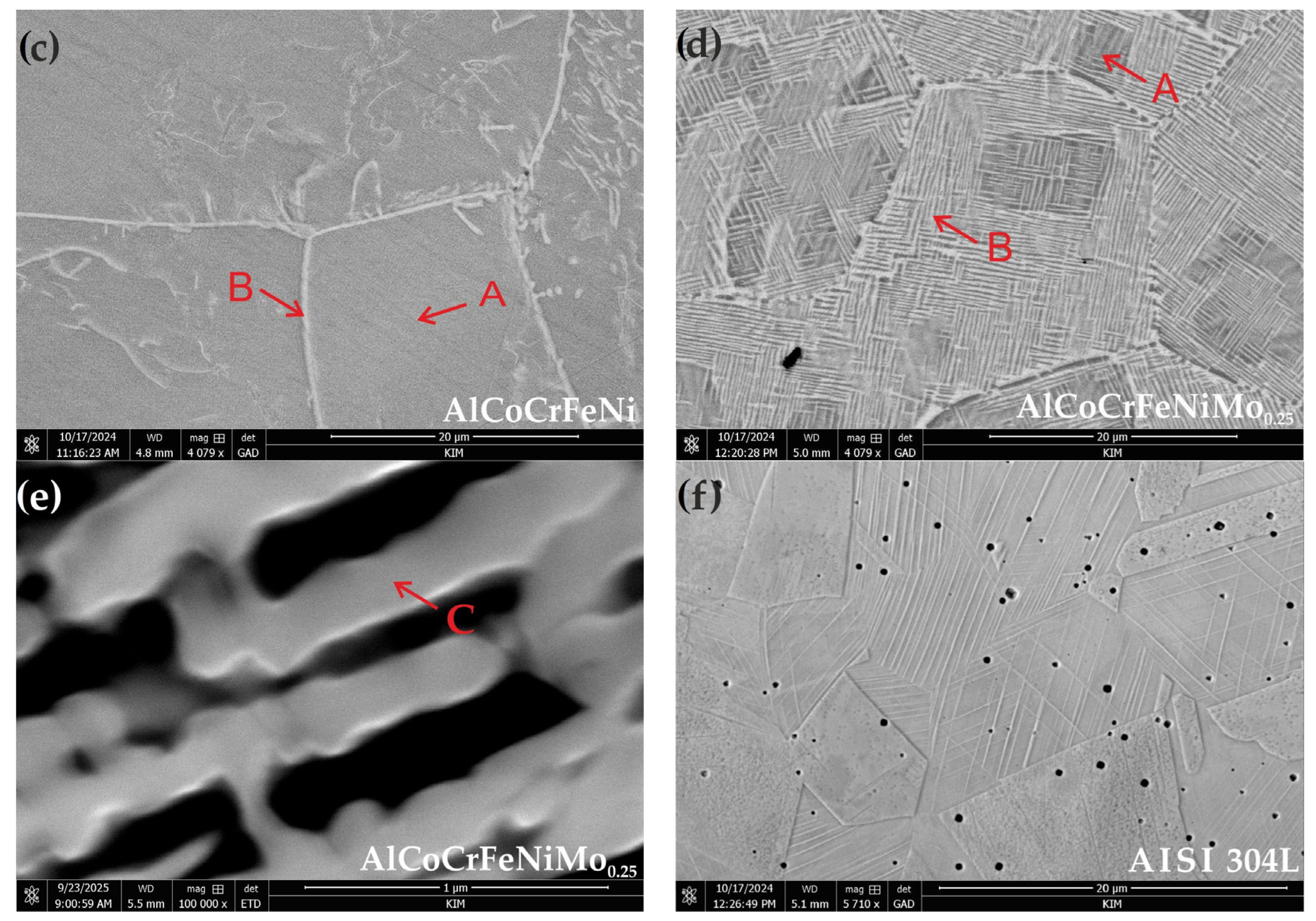
3.1. Microstructure Characteristics
3.2. Mechanical Properties
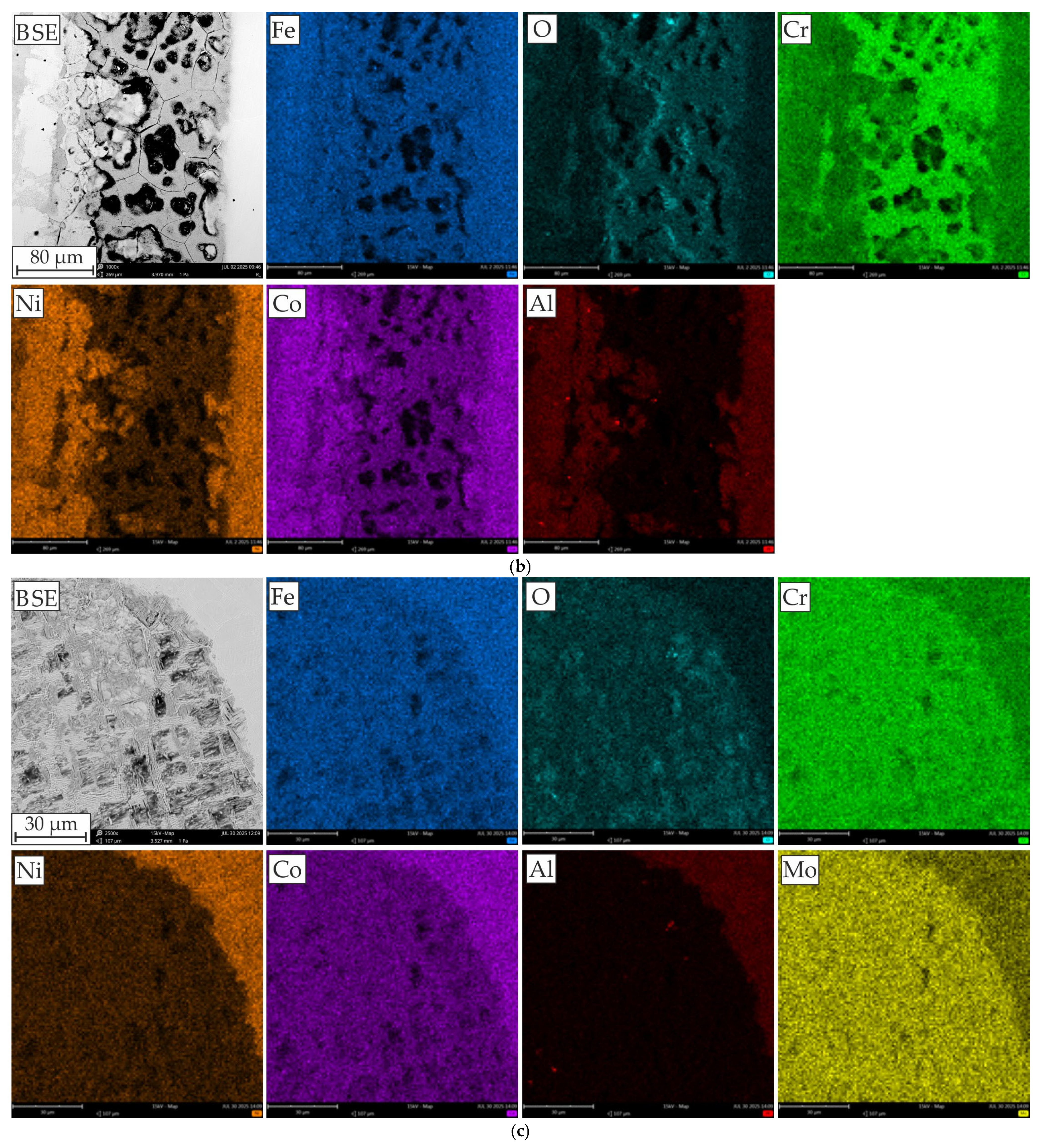
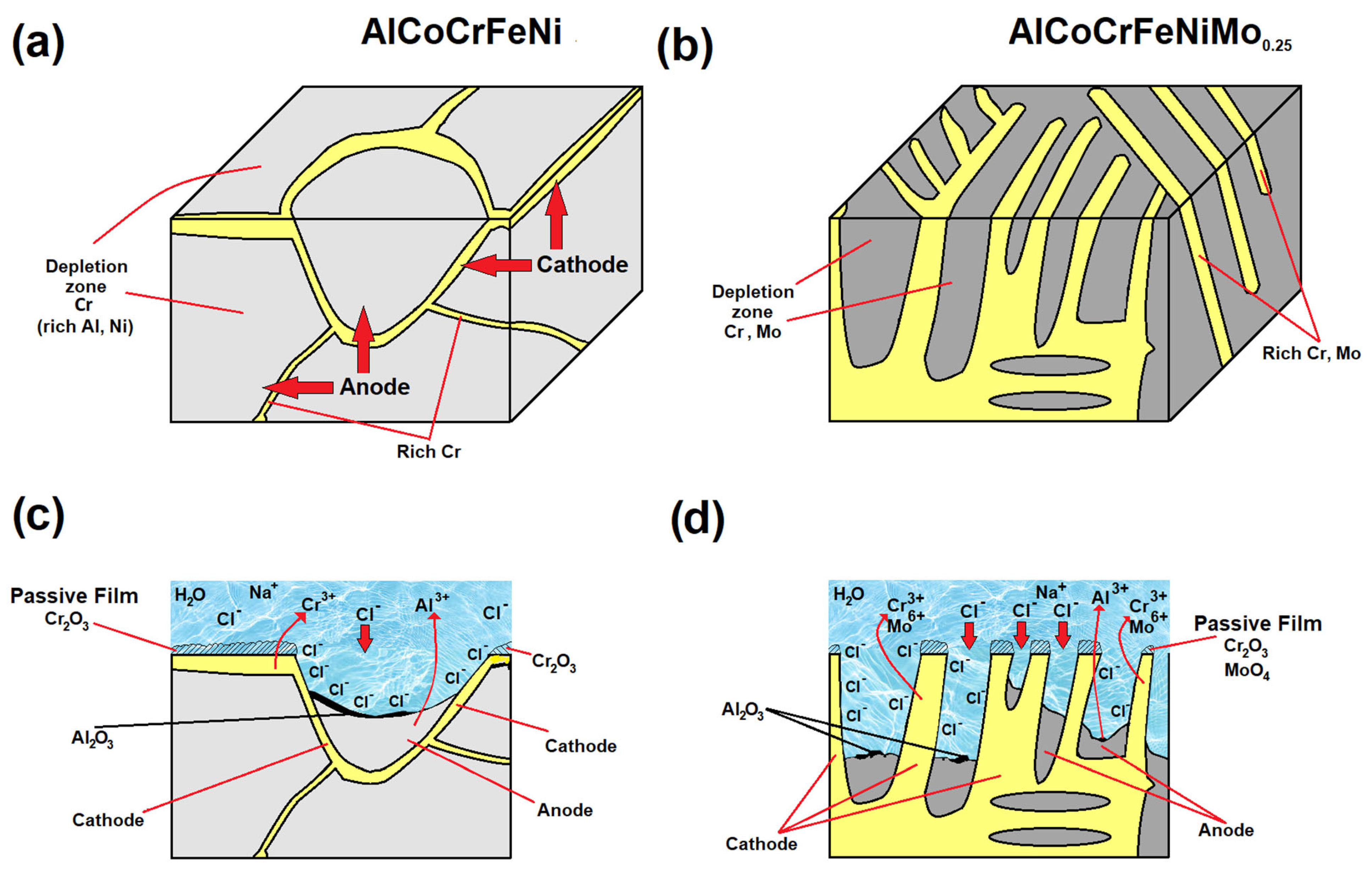
3.3. Corrosion Behavior
4. Conclusions
- The addition of Mo creates a mosaic-patterned microstructure, and XRD analysis indicated the presence of the σ phase, whereby the XRD analysis showed that the average grain sizes for B2/BCC phases have a smaller size after Mo addition.
- Based on Vickers hardness tests, the surface of the HEA alloy with Mo showed a more than 3-fold-increase in hardness compared to AISI 304L, with an increase of nearly 50% compared to the reference HEA, which can be attributed to lattice distortion by Mo, grain refinement, and the presence of a hard and brittle σ phase.
- Nanoidentification tests have shown that the addition of Mo increases hardness (H) and elastic modulus (E) and improves the H/E and H3/E2 ratios, also causing an increase in the elastic recovery index with a decreasing plasticity index. This indicates an improvement in anti-wear properties with resistance to impact loading.
- Polarization tests in 3.5% NaCl showed that the addition of Mo improves the corrosion resistance of HEA alloys, manifested by a decrease in corrosion current density and, thus, a decrease in corrosion rate and a shift in the corrosion potential towards higher values.
- EIS corrosion tests showed that the phase angle and impedance modulus values for AlCoCrFeNiMo0.25 were higher in the low-frequency range, indicating the formation of a more stable passive layer. Furthermore, in the low-frequency range, all tested surfaces were characterized by high impedance above 105 Ω·cm2, indicating that these surfaces have adequate corrosion resistance in a 0.9% NaCl solution, making them suitable for medical applications in this respect. All tested materials behaved almost like an ideal capacitor.
- SEM-EDS analysis of the surface after the corrosion tests revealed that in the case of the AlCoCrMFeNi equivalent alloy, corrosion occurs due to Cr segregation, where the Cr-depleted grain interiors are predisposed to the formation of corrosion pits, and the Al- and Ni-rich grain interiors are subject to corrosion. Areas rich in Al and Ni form the anode, while areas rich in Cr form the cathode. In the case of HEA with Mo, pits developed at the boundaries of areas enriched in Cr and Mo, leading to galvanic corrosion with an adjacent matrix (rich in Al and Ni).
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krella, A.K.; Zakrzewska, D.E.; Buszko, M.H.; Marchewicz, A. Effect of Thermal Treatment and Erosion Aggressiveness on Resistance of S235JR Steel to Cavitation and Slurry. Materials 2021, 14, 1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, R.B.; Arora, H.S.; Boyana, A.V.; Saiteja, P.; Grewal, H.S. Tribological Behavior of Microwave Synthesized High Entropy Alloy Claddings. Wear 2019, 436–437, 203028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, A.; Merino, M.C.; Coy, A.E.; Viejo, F.; Arrabal, R.; Matykina, E. Pitting Corrosion Behaviour of Austenitic Stainless Steels—Combining Effects of Mn and Mo Additions. Corros. Sci. 2008, 50, 1796–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Duval, T.; Hung, U.D.; Yeh, J.W.; Shih, H.C. Microstructure and Electrochemical Properties of High Entropy Alloys—A Comparison with Type-304 Stainless Steel. Corros. Sci. 2005, 47, 2257–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walczak, M.; Nowak, W.J.; Szala, M.; Grądzka-Dahlke, M.; Maciaszek, N.; Vališ, D.; Pasierbiewicz, K. Effect of Molybdenum Addition on Microstructure and Behavior of AlCoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloys in Wet Environments. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2025, 25, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.-H.; Yeh, J.-W. High-Entropy Alloys: A Critical Review. Mater. Res. Lett. 2014, 2, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, Z.U.; Khalid, M.Y.; Ur Rehman, E.; Ullah, S.; Atif, M.; Tariq, A. A Review on Laser Cladding of High-Entropy Alloys, Their Recent Trends and Potential Applications. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 68, 225–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.-W.; Chen, S.-K.; Lin, S.-J.; Gan, J.-Y.; Chin, T.-S.; Shun, T.-T.; Tsau, C.-H.; Chang, S.-Y. Nanostructured High—Entropy Alloys with Multiple Principal Elements: Novel Alloy Design Concepts and Outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2004, 6, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, G.L.; Davies, H.A. Cooling Rate and Size Effect on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of AlCoCrFeNi High Entropy Alloy. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 2009, 131, 034501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.-C.; Chen, J.-H.; Stadler, S.; Chen, S.-H. Properties of Atomized AlCoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloy Powders and Their Phase-Adjustable Coatings Prepared via Plasma Spray Process. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 478, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, J.; Jarvis, T.; Wu, X.; Stanford, N.; Hodgson, P.; Fabijanic, D.M. Comparative Study of the Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Direct Laser Fabricated and Arc-Melted AlxCoCrFeNi High Entropy Alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 633, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, Y.-F.; Chen, T.-J.; Chen, S.-K.; Yeh, J.-W. Microstructure and Mechanical Property of As-Cast, -Homogenized, and -Deformed AlxCoCrFeNi (0 ≤ x ≤ 2) High-Entropy Alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 488, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokarewicz, M.; Grądzka-Dahlke, M. Review of Recent Research on AlCoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloy. Metals 2021, 11, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, G.L. Atomic Packing Efficiency and Phase Transition in a High Entropy Alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 478, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogura, M.; Fukushima, T.; Zeller, R.; Dederichs, P.H. Structure of the High-Entropy Alloy Al CrFeCoNi: Fcc versus Bcc. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 715, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Gao, M.C.; Diao, H.; Yang, T.; Liu, J.; Zuo, T.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Aluminum Alloying Effects on Lattice Types, Microstructures, and Mechanical Behavior of High-Entropy Alloys Systems. JOM 2013, 65, 1848–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Yang, B.; Xie, X.; Brechtl, J.; Dahmen, K.A.; Liaw, P.K. Corrosion of Al CoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloys: Al-Content and Potential Scan-Rate Dependent Pitting Behavior. Corros. Sci. 2017, 119, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-M.; Tsai, H.-L. Evolution of Microstructure, Hardness, and Corrosion Properties of High-Entropy Al0.5CoCrFeNi Alloy. Intermetallics 2011, 19, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, Y.-F.; Lee, T.-D.; Chen, S.-K.; Chang, Y.-S. Electrochemical Passive Properties of AlxCoCrFeNi (x = 0, 0.25, 0.50, 1.00) Alloys in Sulfuric Acids. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 1026–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Sun, S.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, G.; Yang, H.; Hao, J. Effect of Si Addition on Microstructure and Wear Behavior of AlCoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloy Coatings Prepared by Laser Cladding. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 405, 126522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.G.; Zhang, Y. Effect of Nb Addition on the Microstructure and Properties of AlCoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 532, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokarewicz, M.; Gradzka-Dahlke, M.; Nowak, W.J.; Gradzik, A.; Szala, M.; Walczak, M. Effect of Vanadium Addition on the Wear Resistance of Al0.7CoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloy. Materials 2024, 17, 6021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lu, Y. Microstructure and Properties of AlCoCrFeNiBx(x = 0, 0.1, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1.0) High Entropy Alloys. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2017, 46, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Niu, P.; Liu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wang, X.; Peng, Y.; Liu, J. Effect of Zr Content on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of AlCoCrFeNi High Entropy Alloy. Mater. Des. 2016, 94, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.A.; Yehia, H.M.; Mohamed, A.S.A.; El-Nikhaily, A.E.; Elkady, O.A. Effect of Copper Addition on the AlCoCrFeNi High Entropy Alloys Properties via the Electroless Plating and Powder Metallurgy Technique. Crystals 2021, 11, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, W.J.; Kubaszek, T.; Gradzik, A.; Grądzka-Dahlke, M.; Perkowski, D.; Tokarewicz, M.; Walczak, M.; Szala, M. Effect of Ti Doping of Al0.7CoCrFeNi-Based High Entropy Alloys on Their Erosion Resistance by Solid Particles. Materials 2025, 18, 3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Li, Q.; Sun, R.; Chang, C.; Liu, B.; Ma, X. Effect of Mn Addition on Microstructure and Corrosion Behavior of AlCoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloy. Intermetallics 2024, 167, 108236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.M.; Fu, H.M.; Zhang, H.F.; Wang, A.M.; Li, H.; Hu, Z.Q. Microstructures and Compressive Properties of Multicomponent AlCoCrFeNiMox Alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 6975–6979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.; Zhao, T.; Du, C.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, D. Effect of Molybdenum Content on the Microstructure and Corrosion Behavior of FeCoCrNiMox High-Entropy Alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2020, 46, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.X.; Zhang, X.L.; Gu, X.Y. Effect of Molybdenum on Phases, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Al0.5CoCrFeMo Ni High Entropy Alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 743, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.-L.; Wang, Z.-J.; Wu, Q.-F.; Wang, J.-C.; Li, J.-J.; Yu, J.-K. Effect of Mo Addition on Corrosion Behavior of High-Entropy Alloys CoCrFeNiMox in Aqueous Environments. Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 2019, 32, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, W.C.; Pharr, G.M. Measurement of Hardness and Elastic Modulus by Instrumented Indentation: Advances in Understanding and Refinements to Methodology. J. Mater. Res. 2004, 19, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PN-EN ISO 14577-1:2015; Metallic Materials—Instrumented Indentation Test for Hardness and Materials Parameters—Part 1: Test Method. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015.
- ASTM Standard G 102–89; Standard Practice for Calculation of Corrosion Rates and Related Information from Electrochemical Measurements. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2004.
- Shi, X.; Wang, C.; Huang, M.; Cui, H. Microstructure and Wear Resistance Property of AlFeCrNiMox Coatings by Plasma Cladding. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 106537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, W.J.; Jopek, J.; Maciaszek, N. Effect of Mo Addition on the Oxidation Behavior of the AlCoCrFeNi High Entropy Alloy. Adv. Sci. Technol. Res. J. 2026; 20, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Salas, D.; Sahu, B.; Xiang, S.; Skokan, M.; Butler, B.; Arroyave, R.; Karaman, I. Enhanced Strain Hardening Response of Multi-Principal Element Alloys with L12 Nanodomains Designed for Multiple Objectives and Constraints. Mater. Today Commun. 2025, 48, 113265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, R.; Li, Y. Recent Advances in the Performance and Mechanisms of High-Entropy Alloys Under Low- and High-Temperature Conditions. Coatings 2025, 15, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chudoba, T.; Richter, F. Investigation of Creep Behaviour under Load during Indentation Experiments and Its Influence on Hardness and Modulus Results. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2001, 148, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Jiao, Z.M.; Yuan, G.Z.; Ma, S.G.; Wang, Z.H.; Yang, H.J.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, J.W. Effect of Strain Rate on Deformation Behavior of AlCoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloy by Nanoindentation. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2016, 25, 2255–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Z.-M.; Ma, S.-G.; Yuan, G.-Z.; Wang, Z.-H.; Yang, H.-J.; Qiao, J.-W. Plastic Deformation of Al0.3CoCrFeNi and AlCoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloys Under Nanoindentation. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2015, 24, 3077–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoro, A.M.; Lephuthing, S.S.; Rasiwela, L.; Olubambi, P.A. Nondestructive Measurement of the Mechanical Properties of Graphene Nanoplatelets Reinforced Nickel Aluminium Bronze Composites. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyen, M.L.; Cook, R.F. A Practical Guide for Analysis of Nanoindentation Data. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2009, 2, 396–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szala, M.; Walczak, M.; Pasierbiewicz, K.; Kamiński, M. Cavitation Erosion and Sliding Wear Mechanisms of AlTiN and TiAlN Films Deposited on Stainless Steel Substrate. Coatings 2019, 9, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walczak, M.; Pasierbiewicz, K.; Szala, M. Effect of Ti6Al4V Substrate Manufacturing Technology on the Properties of PVD Nitride Coatings. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2022, 142, 723–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Bor, B.; Plunkett, A.; Domènech, B.; Schneider, G.A.; Giuntini, D. Nanoindentation of Supercrystalline Nanocomposites: Linear Relationship Between Elastic Modulus and Hardness. JOM 2022, 74, 2261–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyagari, A.; Barthelemy, C.; Gwalani, B.; Banerjee, R.; Scharf, T.W.; Mukherjee, S. Reciprocating Sliding Wear Behavior of High Entropy Alloys in Dry and Marine Environments. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 210, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orazem, M.E.; Tribollet, B. A Tutorial on Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy. ChemTexts 2020, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walczak, M.; Okuniewski, W.; Nowak, W.J.; Chocyk, D.; Pasierbiewicz, K. Corrosion Behavior of Shot Peened Ti6Al4V Alloy Fabricated by Conventional and Additive Manufacturing. Materials 2025, 18, 2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żebrowski, R.; Walczak, M. The Effect of Shot Peening on the Corrosion Behaviour of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Made by DMLS. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2018, 18, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meghwal, A.; Anupam, A.; Luzin, V.; Schulz, C.; Hall, C.; Murty, B.S.; Kottada, R.S.; Berndt, C.C.; Ang, A.S.M. Multiscale Mechanical Performance and Corrosion Behaviour of Plasma Sprayed AlCoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloy Coatings. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 854, 157140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.P.; Chang, C.C.; Chen, Y.Y.; Yeh, J.W.; Shih, H.C. Effect of the Aluminium Content of AlxCrFe1.5MnNi0.5 High-Entropy Alloys on the Corrosion Behaviour in Aqueous Environments. Corros. Sci. 2008, 50, 2053–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, Y.L.; Yeh, J.W.; Shih, H.C. Effect of Molybdenum on the Pitting Resistance of Co1.5CrFeNi1.5Ti0.5Mox Alloys in Chloride Solutions. Corrosion 2011, 67, 085002–1–085002–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, Y.L.; Yeh, J.W.; Shih, H.C. The Effect of Molybdenum on the Corrosion Behaviour of the High-Entropy Alloys Co1.5CrFeNi1.5Ti0.5Mox in Aqueous Environments. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 2571–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Ren, W.; Yang, J.; Tian, A.; Du, Y.; Liu, G.; Wei, R.; Zhang, G.; Chen, Y. The Corrosion Behavior of Ultra-Fine Grained CoNiFeCrMn High-Entropy Alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 816, 152583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudalia, M.; Guenbour, A.; Bellaouchou, A.; Fernandez-Domene, R.M.; Garcia-Anton, J. Corrosion Behaviour of a Highly Alloyed Austenitic Alloy UB6 in Contaminated Phosphoric Acid. Int. J. Corros. 2013, 2013, 363826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radojković, B.; Jegdić, B.; Pejić, J.; Eraković Pantović, S.; Marunkić, D.; Simović, A.; Milošević, M.; Alić, B. Passive Film Properties and Corrosion Resistance of AISI 304L Stainless Steel. Corros. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. Corros. Process. Corros. Control 2025, 60, 233–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stainless Steels; Davis, J.R., Ed.; ASM Specialty Handbook; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 1994; ISBN 978-0-87170-503-7. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Lan, A.D.; Qiao, J.W. Corrosion Behavior of Al0.1CoCrFeNi High Entropy Alloy in Various Chloride-Containing Solutions. Front. Mater. 2021, 7, 533843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Collins, L.; Balke, N.; Liaw, P.K.; Yang, B. In-Situ Electrochemical-AFM Study of Localized Corrosion of Al CoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloys in Chloride Solution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 439, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargel, C. Introducton to The Corrosion of Aluminium. In Corrosion of Aluminium; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 81–109. ISBN 978-0-08-044495-6. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, S.; Zheng, Z.; Qiao, Y.; Duan, Y.; Cui, J.; Mekkey, S.D.; Amin, M.A.; Melhi, S.; Yang, H.; Zhou, H.; et al. Corrosion Behavior of As-Cast Al0.75CoCr1.25FeNi High Entropy Alloy in 0.5 mol/L Sulfuric Acid. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2024, 7, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Projected | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alloy | Al | Co | Cr | Fe | Ni | Mo |
| AlCoCrFeNi | 20.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | − |
| AlCoCrFeNiMo0.25 | 19.0 | 19.0 | 19.0 | 19.0 | 19.0 | 5.0 |
| Measured | ||||||
| Alloy | Al | Co | Cr | Fe | Ni | Mo |
| AlCoCrFeNi | 18.2 | 20.2 | 20.3 | 20.4 | 20.8 | − |
| AlCoCrFeNiMo0.25 | 18.1 | 19.3 | 18.5 | 19.0 | 18.7 | 5.4 |
| C | Mn | Si | P | S | Cr | Ni | N | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.028 | 1.541 | 0.341 | 0.045 | <0.001 | 18.23 | 8.756 | 0.041 | bal. |
| Sample/Phase | Average Grain Size (nm) | Microstrain (%) |
|---|---|---|
| AlCoCrFeNi—B2/BCC | 90.69 | 0.096 |
| AlCoCrFeNiMo0.25—B2/BCC | 73.35 | 0.057 |
| AlCoCrFeNiMo0.25—σ | 93.82 | 0.126 |
| Sample | Spot | Phase | Al | Co | Cr | Fe | Ni | Mo |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AlCoCrFeNi | A | B2/BCC | 20.87 | 20.17 | 18.25 | 19.16 | 21.55 | − |
| B | B2/BCC | 17.89 | 19.86 | 21.57 | 22.99 | 22.64 | − | |
| AlCoCrFeNiMo0.25 | A | B2/BCC | 19.27 | 19.18 | 18.03 | 18.41 | 19.0 | 5.40 |
| B | B2/BCC | 15.13 | 20.19 | 20.62 | 19.83 | 17.48 | 6.75 | |
| C | σ | 4.06 | 19.95 | 34.75 | 25.41 | 7.40 | 8.44 |
| Sample | Average Hardness HV1 | SD (−) |
|---|---|---|
| AISI 304L | 240 | ±3.62 |
| AlCoCrFeNi | 495 | ±17.07 |
| AlCoCrFeNiMo0.25 | 772 | ±27.22 |
| Material | H (GPa) | E (GPa) | H/E | H3/E2 (×10−3) | Welast (pJ) | Wplast (pJ) | Wtotal (pJ) | Index ERI | Index PI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AISI 304L | 5.0 ± 0.4 | 226.4 ± 24.3 | 0.022 | 2.37 | 180.8 ± 11.2 | 860.4 ± 31.5 | 1041.7 ± 31.1 | 0.17 | 0.83 |
| AlCoCrFeNi | 6.2 ± 0.7 | 194.4 ± 18.8 | 0.032 | 6.51 | 219.1 ± 6.7 | 652.8 ± 36.2 | 871 ± 37.0 | 0.25 | 0.75 |
| AlCoCrFeNiMo0.25 | 13.3 ± 4.1 | 261.4 ± 35.9 | 0.050 | 37.37 | 252.2 ± 12.4 | 361.7 ± 99.1 | 613.8 ± 100 | 0.41 | 0.59 |
| Sample No. | Rs | R1 | CPE1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qdl1 | n1 | |||
| Ω·cm2 | ×105 Ω·cm2 | ×10−5 Ω−1·Sn·cm−2 | ||
| AISI 304L | 9.95 | 2.57 | 3.16 | 0.90 |
| AlCoCrFeNi | 10.49 | 5.01 | 1.89 | 0.88 |
| AlCoCrFeNiMo0.25 | 10.51 | 6.63 | 2.09 | 0.92 |
| Sample No. | icorr | Ecorr | Epit | CR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [µA·cm−2] | [mV] | [mV] | ×10−3 [mm·Year−1] | |
| AISI 304L | 0.74 ± 0.04 | −352 ± 13 | 255 ± 17 | 7.75 ± 0.42 |
| AlCoCrFeNi | 2.31 ± 0.06 | −252 ± 19 | 159 ± 10 | 19.68 ± 0.51 |
| AlCoCrFeNiMo0.25 | 0.18 ± 0.03 | −202 ± 2 | 128 ± 22 | 1.52 ± 0.25 |
| Sample | Spot | Al | Co | Cr | Fe | Ni | Mo | O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AlCoCrFeNi | C | 16.47 | 19.36 | 18.19 | 19.31 | 19.66 | − | 7.00 |
| D | 21.02 | 23.20 | 18.28 | 19.42 | 19.86 | − | 1.95 | |
| AlCoCrFeNiMo0.25 | C | 0.83 | 19.54 | 29.87 | 22.94 | 13.07 | 10.00 | 3.74 |
| D | 6.04 | 16.94 | 22.61 | 19.34 | 13.45 | 12.27 | 9.35 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Walczak, M.; Nowak, W.J.; Okuniewski, W.; Chocyk, D. Effect of Adding Molybdenum on Microstructure, Hardness, and Corrosion Resistance of an AlCoCrFeNiMo0.25 High-Entropy Alloy. Materials 2025, 18, 4566. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194566
Walczak M, Nowak WJ, Okuniewski W, Chocyk D. Effect of Adding Molybdenum on Microstructure, Hardness, and Corrosion Resistance of an AlCoCrFeNiMo0.25 High-Entropy Alloy. Materials. 2025; 18(19):4566. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194566
Chicago/Turabian StyleWalczak, Mariusz, Wojciech J. Nowak, Wojciech Okuniewski, and Dariusz Chocyk. 2025. "Effect of Adding Molybdenum on Microstructure, Hardness, and Corrosion Resistance of an AlCoCrFeNiMo0.25 High-Entropy Alloy" Materials 18, no. 19: 4566. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194566
APA StyleWalczak, M., Nowak, W. J., Okuniewski, W., & Chocyk, D. (2025). Effect of Adding Molybdenum on Microstructure, Hardness, and Corrosion Resistance of an AlCoCrFeNiMo0.25 High-Entropy Alloy. Materials, 18(19), 4566. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194566








