Water-Soaking Pretreatment for Enhanced Performance and Heavy Metal Immobilization in Alkali-Activated Pyrolysis MSWIFA Materials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Treatment of Pyrolyzed Fly Ash
2.3. Mix Design
2.4. Tests Methods
2.4.1. Mechanical Strength
2.4.2. Isothermal Calorimetry
2.4.3. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.4.4. TGA
2.4.5. SEM
2.4.6. MIP
2.4.7. Leaching Toxicity of Heavy Metals
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effectiveness of Water-Soaking Treatment for Expansion Control
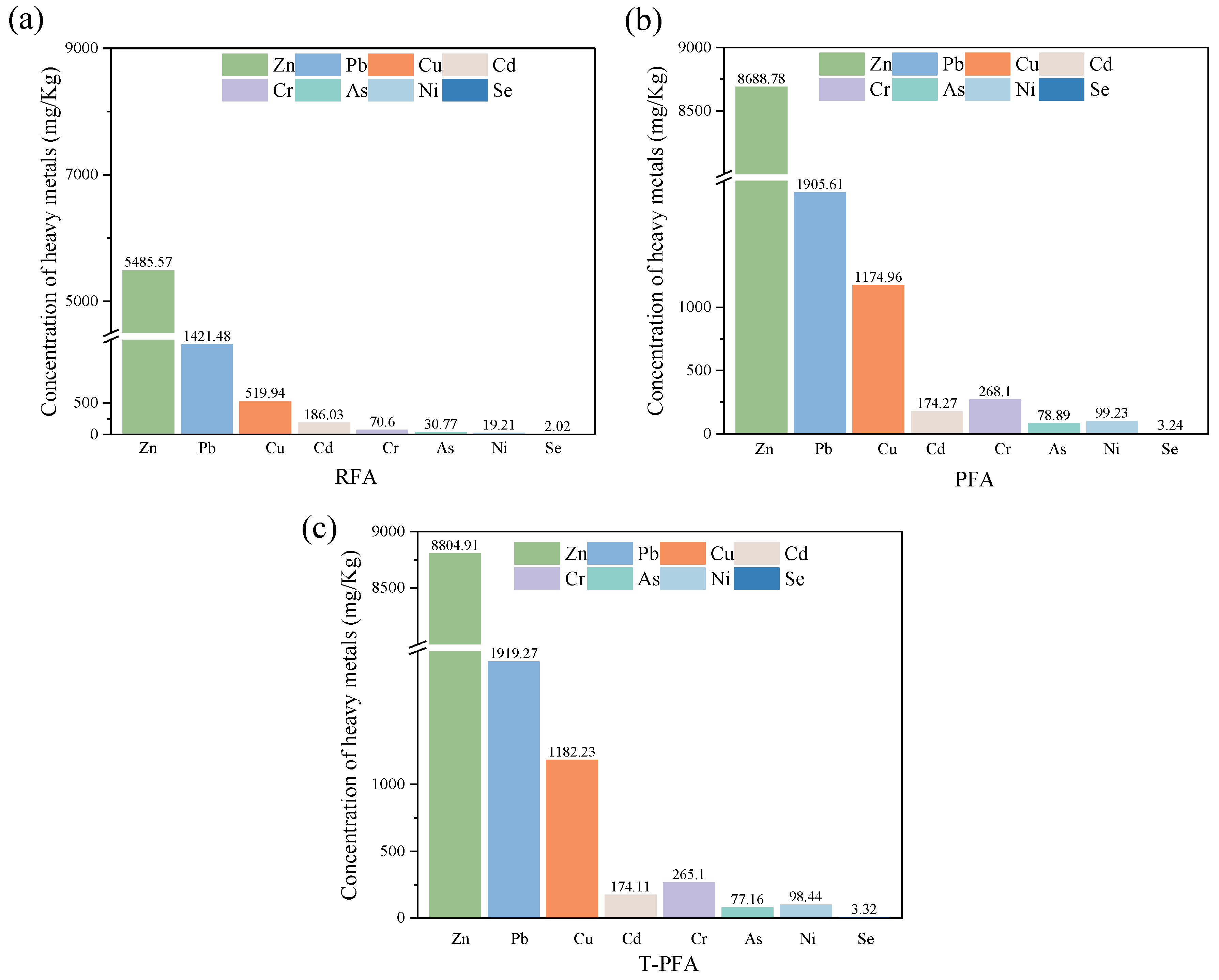
3.2. Physicochemical Characterization of T-PFA
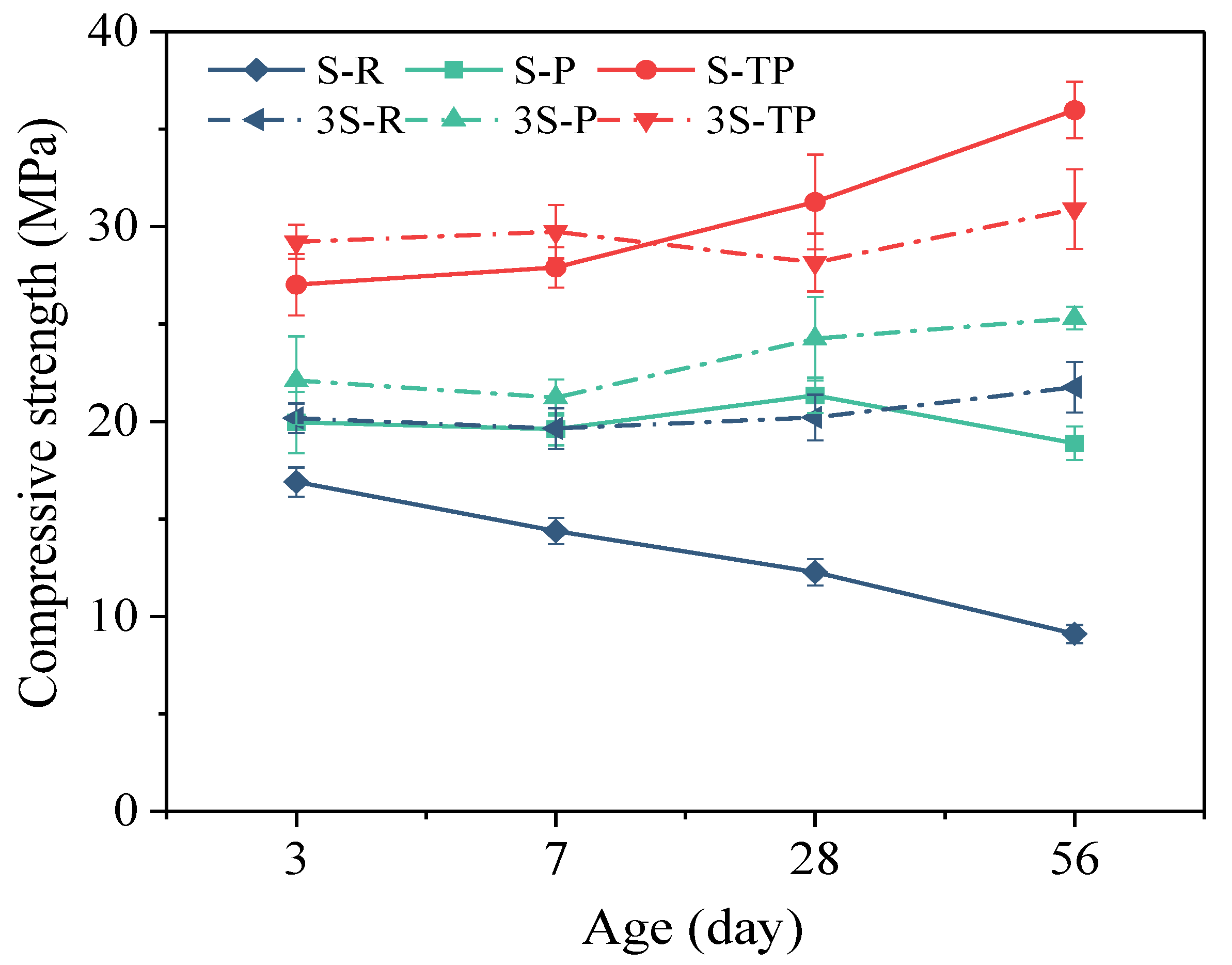
3.3. Compressive Strength Development
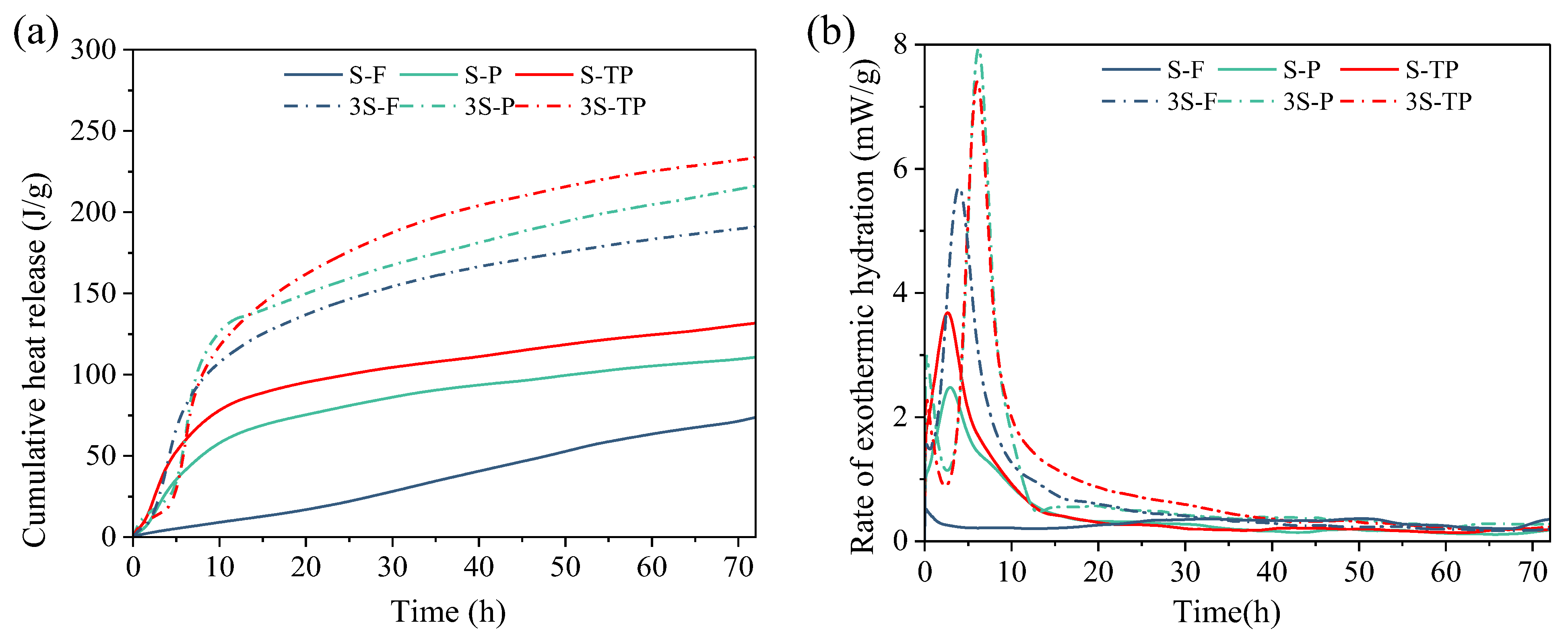
3.4. Hydration Heat Evolution
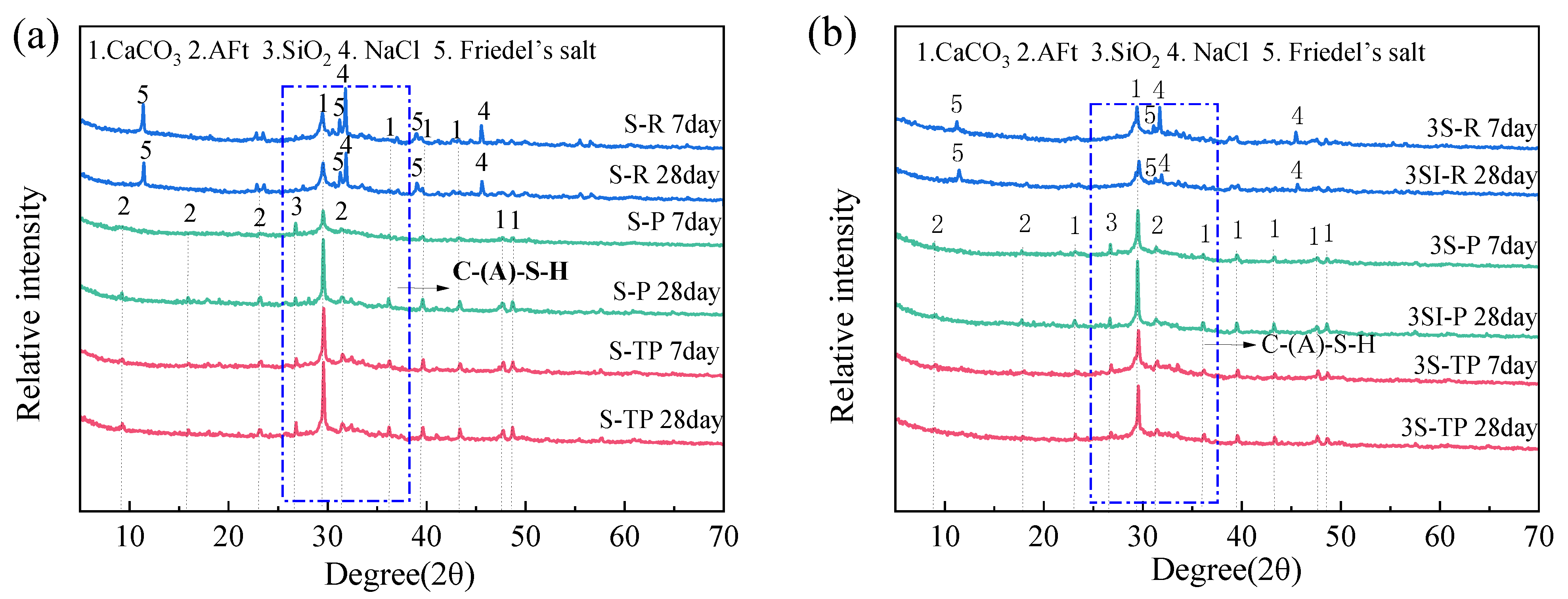
3.5. Phase Evolution and Thermal Analysis of Hydration Products
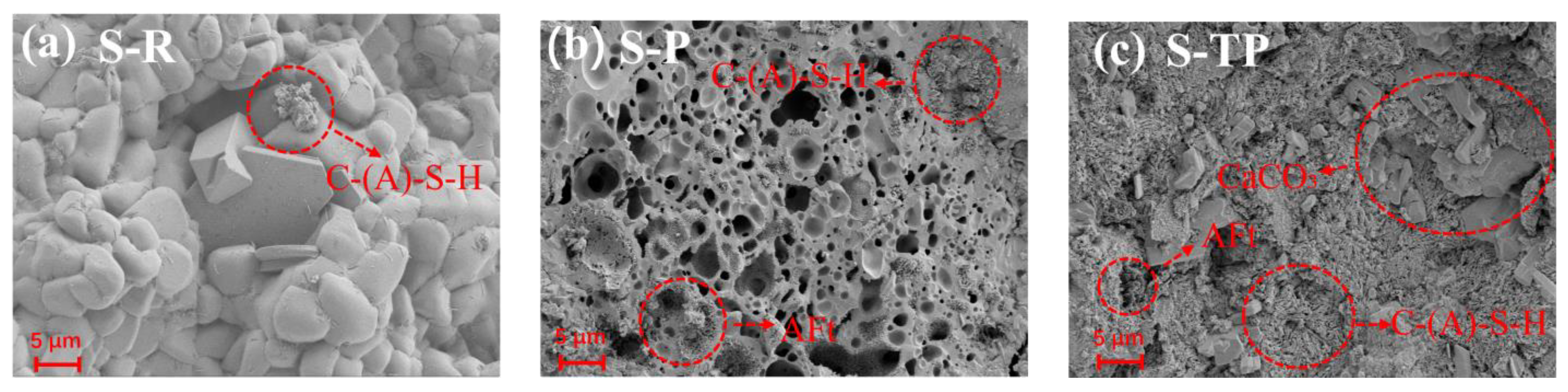
3.6. Microstructural Analysis (SEM)
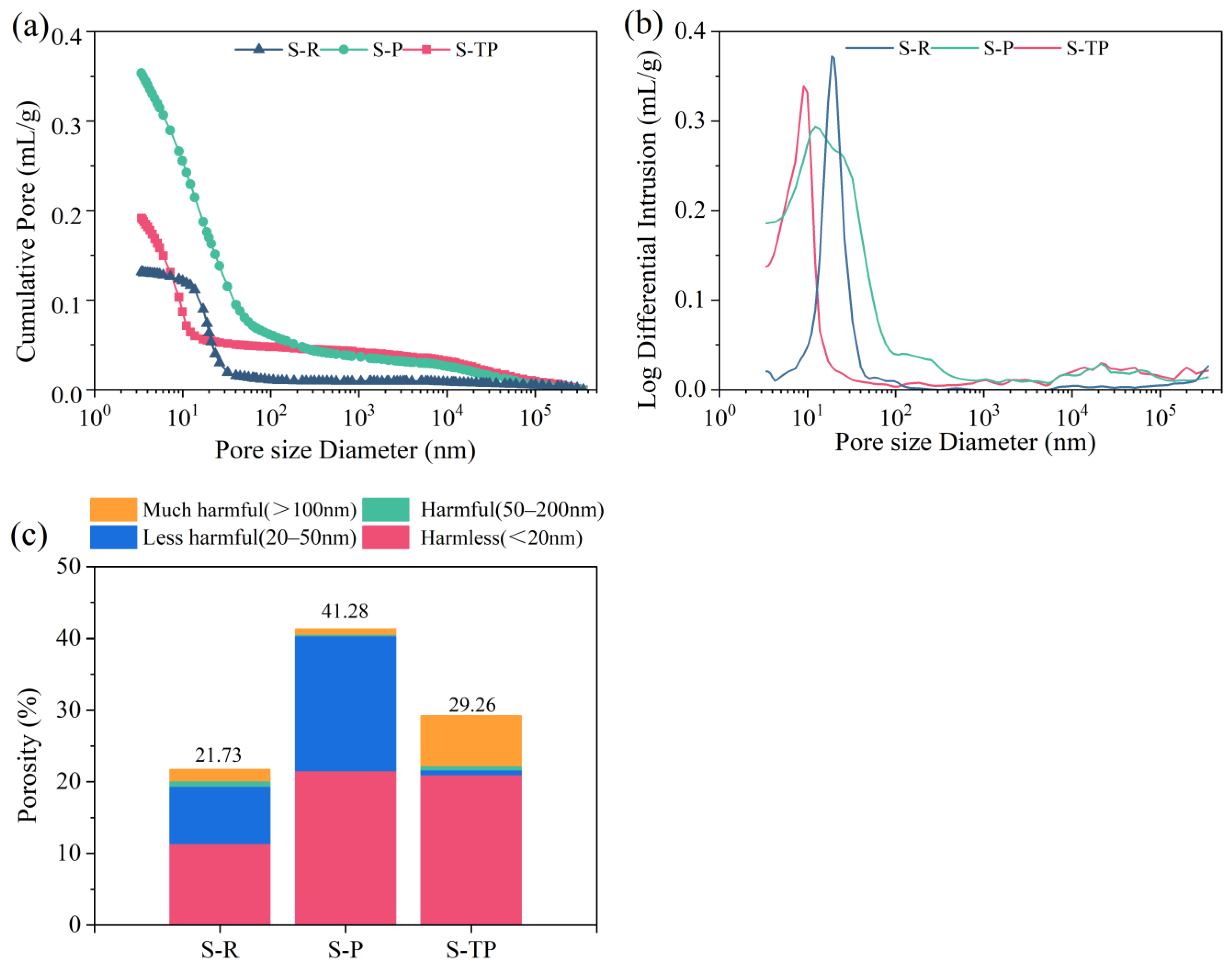
3.7. Pore Structure and Distribution (MIP)
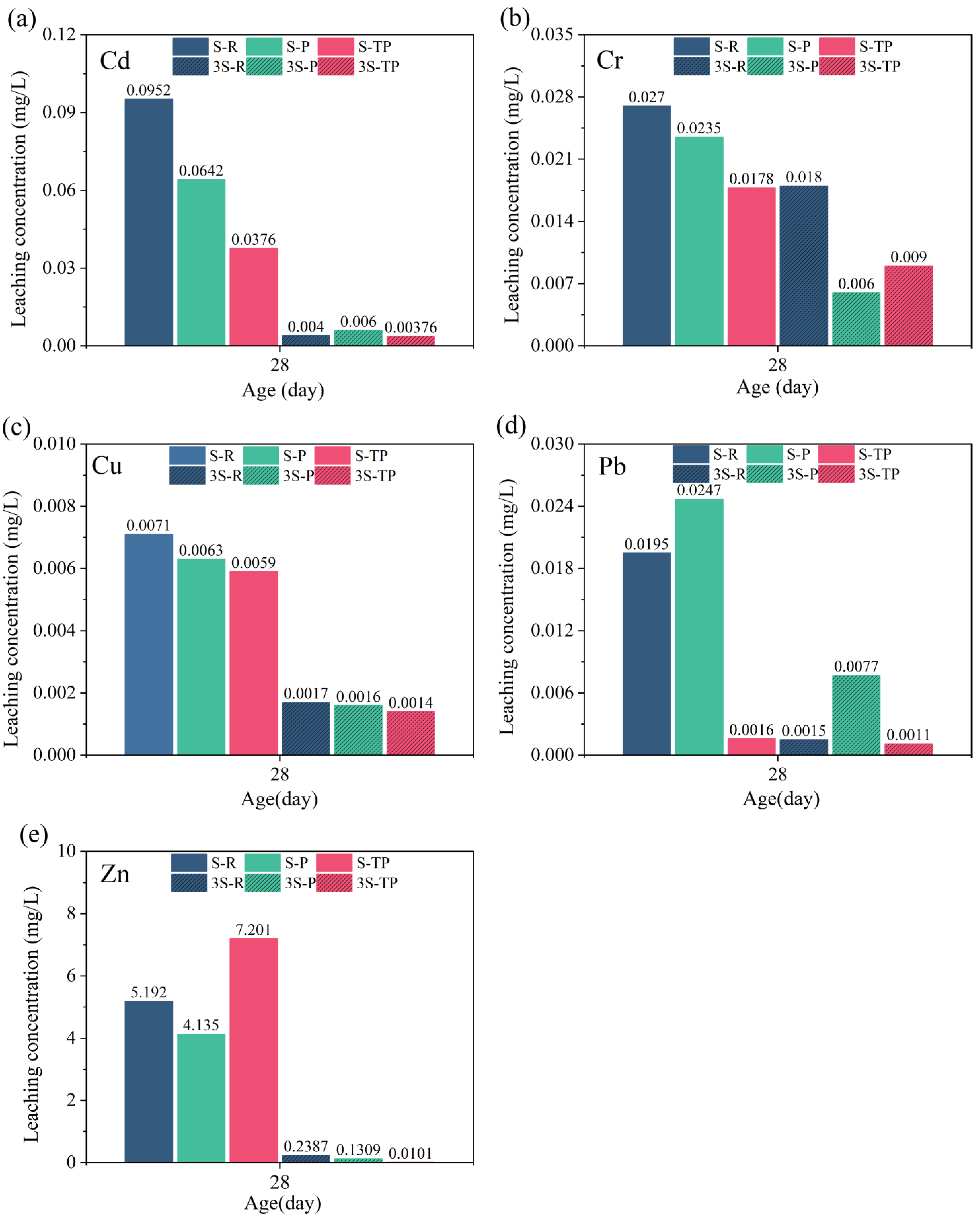
3.8. Heavy Metal Leaching Behavior
4. Conclusions
5. Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bie, R.; Chen, P.; Song, X.; Ji, X. Characteristics of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash with cement solidification treatment. J. Energy Inst. 2016, 89, 704–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Sloot, H.A.; Kosson, D.S.; Hjelmar, O. Characteristics, treatment and utilization of residues from municipal waste incineration. Waste Manag. 2001, 21, 753–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Yao, J.; Masakorala, K.; Li, X.; Li, S.; Li, X. Innovation and prospects of heavy metal solidification/stabilization techniques: A comprehensive review on materials, mechanisms, and evaluation systems. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2025, 37, 104040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Jiménez, A.F.; Palomo, A. New cements for the 21st century: The pursuit of an alternative to Portland cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 750–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, P.; Ling, T.-C. Roles of chlorine and sulphate in MSWIFA in GGBFS binder: Hydration, mechanical properties and stabilization considerations. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 284, 117175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Gehlen, C.; Angst, U.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Yao, Y. Critical chloride content in reinforced concrete—An updated review considering Chinese experience. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 117, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Ding, L.; Zeng, J.; Chen, K.; Peng, Z.; Zhong, L.; Tong, L.; Lan, T.; Wang, H.; Jiang, J.; et al. Investigation of sustainable alkali-activated materials from municipal solid waste incineration fly ash: Insights into the gel system. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 118102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikia, N.; Mertens, G.; Van Balen, K.; Elsen, J.; Van Gerven, T.; Vandecasteele, C. Pre-treatment of municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) bottom ash for utilisation in cement mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 96, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Ji, R.; Liu, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z. Recycling of municipal solid waste incineration by-product for cement composites preparation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 162, 794–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, T.; Meng, Y.; Ju, T.; Chen, Z.; Du, Y.; Deng, Y.; Song, M.; Han, S.; Jiang, J. Synthesis and application of geopolymers from municipal waste incineration fly ash (MSWI FA) as raw ingredient—A review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 182, 106308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Tao, L.; Wang, F.; Lv, G. Synthesis of geopolymers using municipal solid waste incineration fly ash and construction and demolition waste: Mechanical and thermal activation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 111249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provis, J.L.; Palomo, A.; Shi, C. Advances in understanding alkali-activated materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 78, 110–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, I.; Baghban, M.H.; Hashemi, M.; Izadyar, N.; Sajadi, B. Phase change materials incorporated into geopolymer concrete for enhancing energy efficiency and sustainability of buildings: A review. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 17, e01162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labianca, C.; Ferrara, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, X.; De Feo, G.; Hsu, S.-C.; You, S.; Huang, L.; Tsang, D.C.W. Alkali-activated binders—A sustainable alternative to OPC for stabilization and solidification of fly ash from municipal solid waste incineration. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 380, 134963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ślosarczyk, A.; Fořt, J.; Klapiszewska, I.; Thomas, M.; Klapiszewski, Ł.; Černý, R. A literature review of the latest trends and perspectives regarding alkali-activated materials in terms of sustainable development. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 25, 5394–5425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Ding, W.; Fan, C.; Liu, F. Immobilization properties and reaction mechanism of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash with alkali activation technology. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 91, 109559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xie, G.; Wang, Z.; Zeng, C.; Fan, X.; Li, Z.; Ren, J.; Xing, F.; Zhang, W. Manufacture of alkali-activated cementitious materials using municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) ash: Immobilization of heavy metals in MSWI fly ash by MSWI bottom ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 392, 131848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xie, X.; Liu, R.; Lyu, K.; Wang, X.; Yu, J.; Fu, F.; Wu, C.; Zuo, J. Manufacture of alkali-activated cementitious materials using municipal solid waste incineration fly ash (MSWIFA): The effect of the Si/Al molar ratio on fresh and hardened properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 409, 134075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhao, C.; Rao, Y.; Yu, C.; Luo, Z.; Zhao, H.; Wang, X.; Wu, C.; Wang, Q. Solidification/stabilization and risk assessment of heavy metals in municipal solid waste incineration fly ash: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 892, 164451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Li, F.; Xie, H.; Liu, W.; Ouyang, X.; Fu, J.; Wang, H. Self-sensing properties of alkali-activated materials prepared with different precursors. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 409, 134201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Son, J.; Yoo, Y.; Park, S.; Huh, I.-S.; Park, J. Heavy-metal reduction and solidification in municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) fly ash using water, NaOH, KOH, and NH4OH in combination with CO2 uptake procedure. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 380, 122534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.-N.; Luo, J.-J.; Sun, S.-Q. Characteristics of MSWI fly ash with acid leaching treatment. J. Fuel Chem. Technol. 2021, 49, 1208–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Huang, Y.; Jin, X.; Sun, T. Synergistic treatment of heavy metals in municipal solid waste incineration fly ash with geopolymer and chemical stabilizers. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 160, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Hao, Q.; Chen, J.; Hu, M.; Tu, T.; Jiang, C. Distribution characteristics and comparison of chemical stabilization ways of heavy metals from MSW incineration fly ashes. Waste Manag. 2020, 113, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Liu, B. Degradation technologies and mechanisms of dioxins in municipal solid waste incineration fly ash: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 250, 119507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Long, J.; Yue, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Qian, G. Degradation and regeneration inhibition of PCDD/Fs in incineration fly ash by low-temperature thermal technology. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 477, 135315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labaied, I.; Douzane, O.; Promis, G.; Lajili, M. Synthesis of alkali-activated materials blended with fly ash: Optimization of curing conditions and precursor dosage. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 79, 107863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Al-Damad, I.M.A.; Siddika, A.; Kim, T.; Foster, S.; Hajimohammadi, A. Enhancing the workability retention of one-part alkali activated binders by adjusting the chemistry of the activators. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2025, 157, 105928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yu, L.; Zhou, H.; Huang, G.; Yang, C.; Wu, F.; Zhang, Y. An environment-friendly pretreatment process of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash to enhance the immobilization efficiency by alkali-activated slag cement. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 290, 125728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, D.; Poon, C.S. Removal of metallic Al and Al/Zn alloys in MSWI bottom ash by alkaline treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakubu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Ping, D.; Shu, Z.; Chen, Y. Effects of pH dynamics on solidification/stabilization of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 207, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aubert, J.E.; Husson, B.; Vaquier, A. Metallic aluminum in MSWI fly ash: Quantification and influence on the properties of cement-based products. Waste Manag. 2004, 24, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 17671–2021; Method of Testing Cements-Determination of Strength. GB Standard: Beijing, China, 2021.
- Sun, B.B.; Sun, Y.B.; Ye, G.; De Schutter, G. A mix design methodology of blast furnace slag and fly ash-based alkali-activated concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2023, 140, 105076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oinam, Y.; Ju, S.; Shin, M.; Pyo, S. Influence of cellulose micro-fibers on hydration characteristics of cementless UHPC using CaO-activated GGBFS. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 389, 131747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HJ 781-2016; Solid Waste—Determination of 22 Metal Elements—Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometry. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Eckert, J.O.; Guo, Q. Heavy metals in cement and cement kiln dust from kilns co-fired with hazardous waste-derived fuel: Application of EPA leaching and acid-digestion procedures. J. Hazard. Mater. 1998, 59, 55–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Wang, C.; Wang, W.; Shi, Y.; Gao, X. Immobilization of MSWI fly ash through geopolymerization: Effects of water-wash. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, H.J.; Zhang, H.Y.; Xu, H. Resistance of geopolymer mortar to acid and chloride attacks. Procedia Eng. 2017, 210, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, J.-S.; Zhan, B.-J.; Sharma, U.; Poon, C.S. Compressive strength and microstructural properties of dry-mixed geopolymer pastes synthesized from GGBS and sewage sludge ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 182, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chian, S.C.; Ma, T.; Ding, J. Stabilization of dredged clays with ternary alkali-activated materials: Towards sustainable solid wastes recycling. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 426, 139086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, A.N.; Jensen, T.R.; Hanson, J.C. Formation of ettringite, Ca6Al2(SO4)3(OH)12·26H2O, AFt, and monosulfate, Ca4Al2O6(SO4)·14H2O, AFm-14, in hydrothermal hydration of Portland cement and of calcium aluminum oxide—Calcium sulfate dihydrate mixtures studied by in situ synchrotron X-ray powder diffraction. J. Solid State Chem. 2004, 177, 1944–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Song, H.; Cao, S.; Wang, K.; Feng, G. Dual-activated calcined coal gangue for high-performance and eco-friendly cementitious materials. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2025, 36, 8983–8998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamalimoghadam, M.; Vakili, A.H.; Keskin, I.; Totonchi, A.; Bahmyari, H. Solidification and utilization of municipal solid waste incineration ashes: Advancements in alkali-activated materials and stabilization techniques, a review. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 367, 122014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.Y.; Tyrer, M.; Hills, C.D.; Yang, X.M.; Carey, P. Immobilisation of heavy metal in cement-based solidification/stabilisation: A review. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 390–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Liu, Z.; Song, Z.; Zhao, R.; Wu, J.; Wang, L.; Yan, J. Valorization of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash in low-carbon alkali-activated materials. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 495, 153577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Ma, C.; Huang, B.; Lu, X. Development of alkali activated cementitious material from sewage sludge ash: Two-part and one-part geopolymer. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 384, 135547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Provis, J.L.; Feng, D.; van Deventer, J.S.J. Geopolymers for immobilization of Cr6+, Cd2+, and Pb2+. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 157, 587–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, Z.; Cao, Z. Impact of Ni(II) and Cd(II) on the hydration and microstructure of cement pastes for immobilization: C-A-S-H composition and binding characteristic. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 310, 125284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Ding, W.; Fan, C.; Liu, F.; Lu, W.; Yang, H. Solidification performance and mechanism of C-S-H gel for Pb(II), Zn(II), and Cd(II). J. Build. Eng. 2025, 99, 111464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.K.W.; van Deventer, J.S.J. The effects of inorganic salt contamination on the strength and durability of geopolymers. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2002, 211, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, J.; Zha, X.; Dong, L.; Dassekpo, J.-B.M.; Xiao, J. Calcium dissolution-induced porosity increase in cement-solidified MSWIFA: Implications for heavy metal leaching behavior. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2025, 201, 107493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wu, K.; Fang, J.; Ren, C.; Wang, W.; Gao, Y.; Yang, Z. Investigation on the carbonation and heavy metals stabilization of MSWI fly ash by incorporating γ-C2S and Portland cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 445, 137881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, R.; Wu, Z.; Zheng, J.; Sun, H.; Liu, S.; Liu, D. Comparison between physicochemical combined method and conventional cement solidification method for treating heavy metal-contaminated slurry-like mud. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 523, 146460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Zou, S.; Zhou, W.; Huang, Y.; Shao, L.; Yuan, J.; Gou, X.; Jin, W.; Wang, Z.; Chen, X.; et al. Clinically applicable histopathological diagnosis system for gastric cancer detection using deep learning. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabir, H.; Wu, J.; Dahal, S.; Joo, T.; Garg, N. Automated estimation of cementitious sorptivity via computer vision. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 9935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




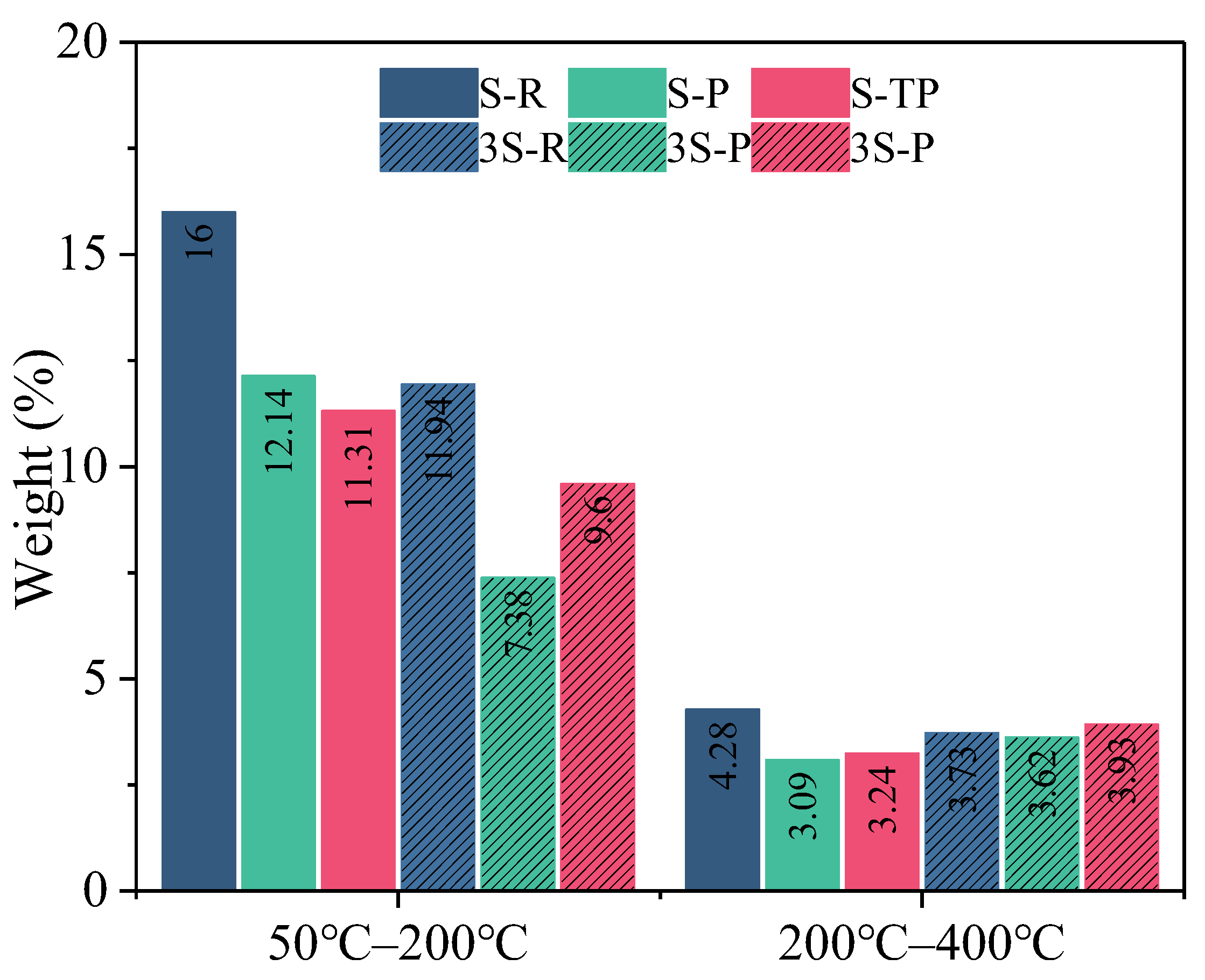
| Oxides | SiO2 | CaO | Al2O3 | MgO | SO3 | TiO2 | Fe2O3 | Na2O | K2O | Cl | ZnO | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GGBS | 31.04 | 40.21 | 15.94 | 7.70 | 2.28 | 0.88 | 0.32 | - | - | - | - | 0.58 |
| PFA | 12.48 | 46.59 | 5.94 | 3.72 | 17.57 | 1.40 | 4.40 | 0.81 | 0.93 | 1.34 | 1.59 | 3.3 |
| RFA | 3.50 | 40.48 | 1.04 | 0.84 | 7.69 | 0.18 | 0.73 | 13.13 | 7.24 | 23.68 | 0.65 | 0.84 |
| Types of Fly Ash | TC | IC | TOC |
|---|---|---|---|
| RFA | 4.883 | 3.254 | 1.629 |
| PFA | 2.529 | 1.909 | 0.62 |
| Mix ID | RFA | PFA | T-PFA | GGBS | Na2SiO3 | NaOH | Water |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S-R | 175.8 | - | - | 175.8 | 57.8 | 16.5 | 92.2 |
| S-P | - | 175.8 | - | 175.8 | |||
| S-TP | - | - | 178.5 | 175.8 | |||
| 3S-R | 89.7- | - | 263.7 | ||||
| 3S-P | - | 89.7 | - | 263.7 | |||
| 3S-TP | - | - | 89.7 | 263.7 |
| Oxides | SiO2 | CaO | Al2O3 | MgO | SO3 | TiO2 | Fe2O3 | Na2O | K2O | Cl | ZnO | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PFA | 12.48 | 46.59 | 5.94 | 3.72 | 17.57 | 1.40 | 4.40 | 0.81 | 0.93 | 1.34 | 1.59 | 3.3 |
| T-PFA | 11.85 | 46.61 | 5.70 | 3.46 | 19.21 | 1.31 | 4.38 | 0.84 | 0.89 | 1.14 | 1.46 | 3.15 |
| HMs | Cu | Cd | Cr | Pb | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Limits | 40 | 0.15 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhong, S.; Shen, L.; Xu, W.; Fang, Y.; Pan, Y. Water-Soaking Pretreatment for Enhanced Performance and Heavy Metal Immobilization in Alkali-Activated Pyrolysis MSWIFA Materials. Materials 2025, 18, 4520. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194520
Zhong S, Shen L, Xu W, Fang Y, Pan Y. Water-Soaking Pretreatment for Enhanced Performance and Heavy Metal Immobilization in Alkali-Activated Pyrolysis MSWIFA Materials. Materials. 2025; 18(19):4520. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194520
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhong, Shengyu, Liang Shen, Wanlan Xu, Yi Fang, and Yunfeng Pan. 2025. "Water-Soaking Pretreatment for Enhanced Performance and Heavy Metal Immobilization in Alkali-Activated Pyrolysis MSWIFA Materials" Materials 18, no. 19: 4520. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194520
APA StyleZhong, S., Shen, L., Xu, W., Fang, Y., & Pan, Y. (2025). Water-Soaking Pretreatment for Enhanced Performance and Heavy Metal Immobilization in Alkali-Activated Pyrolysis MSWIFA Materials. Materials, 18(19), 4520. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194520









