Microstructural Analysis of Hot-Compressed Mg-Nd-Zr-Ca Alloy with Low Rare-Earth Content
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedure
3. Results
3.1. Finite Element Simulation
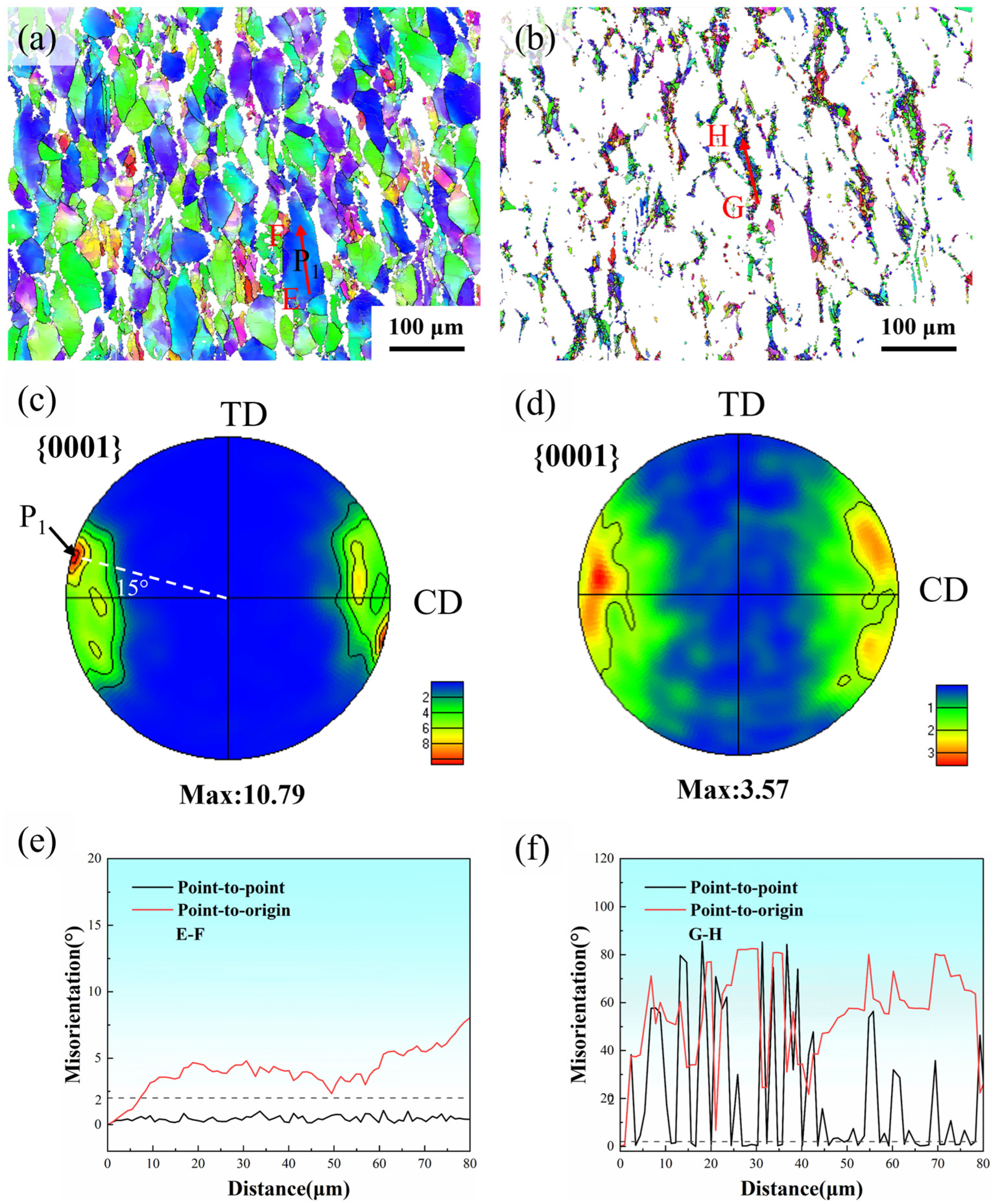
3.2. Microstructure
4. Discussion
4.1. Dynamic Recrystallization Mechanism
4.2. Texture Evolution
4.3. Slip Systems and Dislocation Mechanisms
5. Conclusions
- The distribution of equivalent strain in the hot-compressed specimens exhibited heterogeneity, with strain inhomogeneity increasing progressively with further deformation (Ci = 1.361–1.595). The central region of the specimen exhibited a high equivalent strain due to triaxial compressive stress, accumulating sufficient deformation energy to initiate DRX, which resulted in the formation of a necklace-like microstructure.
- The predominant deformation mechanisms include basal slip, pyramidal slip, twinning, CDRX, TDRX, and PSN, which play critical roles in grain refinement and texture evolution. The deformed grains developed a strong <0001>//CD texture (MPD: 10.79) in the hot-compressed sample, whereas DRX grains effectively weakened the texture, reducing the MPD to 3.57. Basal and pyramidal <c+a> slips were predominantly activated in deformed grains, with average SF of 0.335 and 0.397, respectively. In contrast, DRX grains additionally activated pyramidal <a> slip, exhibiting an average SF of 0.352.
- The high dislocation density in the hot-compressed sample, attributed to the pinning effect of precipitates on dislocations, induces the dynamic precipitation of the Mg41Nd5 phase. Dynamic precipitation promotes nucleation of DRX and inhibits grain growth of DRX grains, resulting in DRX grains with fine size.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RE | Rare earth |
| DRX | Dynamic recrystallization |
| PSN | Particle-stimulated nucleation |
| TDRX | Twin-induced dynamic recrystallization |
| EBSD | Electron back-scattered diffraction |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscope |
| OM | Optical microscope |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscope |
| CD | Compression direction |
| XRD | X-ray diffractometer |
| IPF | Inverse pole figure |
| LAGB | Low-angle grain boundary |
| ET | Extension twin |
| CT | Contraction twin |
| DT | Double twins |
| HAGB | High-angle grain boundary |
| EDS | Energy dispersive spectrometer |
| SF | Schmid factor |
| MPD | maximum pole density |
References
- Yang, Y.; Huo, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, L.; Xiao, Z.; Wang, J.; Hashimoto, A.; Yang, X. Effects of Volume Fraction of Fine Grains on the Tensile Creep Properties of a Hot-Deformed Mg-Gd-Y-Zr Alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 777, 139052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wang, X.; Dang, C.; Zhao, P.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, M.; Wang, J. Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of High-Strength Mg-Gd-Y-Zn-Mn Alloy Processed by Asymmetric Hot Rolling. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 24, 2907–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Yuan, L.; Ma, X.; Zheng, M.; Shan, D.; Guo, B. Strengthening of Low-Cost Rare Earth Magnesium Alloy Mg-7Gd-2Y-1Zn-0.5Zr through Multi-Directional Forging. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 831, 142144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Kim, J.; Li, M.; Gao, Y.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, B.; Pan, F. Effects of Nd Content on the Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of ZK60 Mg Alloy and Corresponding Strengthening Mechanisms. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2024, 901, 146504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Khan, M.A.; Dai, S.; Feng, Y.; Wang, H.; Afifi, M.A.; Li, J. Effect of Double-Extrusion Following by Stepwise-Hot-Rolling on Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Mg-Gd-Y-Zn-Zr Alloy. J. Magnes. Alloys 2025, S221395672500101X. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Pan, H.; Pan, Z.; Zeng, Z.; Xie, D.; Tang, W.; Xie, H.; Li, R.; Qin, G. Unexpectedly High Precipitation Hardening Induced by Supersaturated Solute and Strong Texture in a Mg-13Gd Binary Alloy after Forging. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2023, 872, 144984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minárik, P.; Zemková, M.; Veselý, J.; Bohlen, J.; Knapek, M.; Král, R. The Effect of Zr on Dynamic Recrystallization during ECAP Processing of Mg-Y-RE Alloys. Mater. Charact. 2021, 174, 111033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, J.; Qi, M.; Liao, L.; Gao, Z. Enhanced Mechanical Properties of Mg-Zn-Y-Zr Alloy by Low-Speed Indirect Extrusion. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 9856–9867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Q.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Li, H.; Xia, Z. Effect of Various ca Content on Microstructure and Fracture Toughness of Extruded Mg-2Zn Alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 742, 1019–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Du, Y.; Liu, D.; Jiang, B. Significant Improvement in Mechanical Properties of Mg-Zn-La Alloy by Minor Ca Addition. Mater. Charact. 2020, 160, 110130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, H.; Wang, H.; Niu, X.; Wang, L.; Li, H.; Cheng, W. Revealing the Deformation Behavior and Resultant Texture Evolution in Extruded Dilute Mg-Bi-Sn-Ca Alloy during Hot Compression. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 853, 143788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hou, P.; Wu, Z.; Feng, Z.; Ren, Y.; Choo, H. Dynamic Recrystallization of a Wrought Magnesium Alloy: Grain Size and Texture Maps and Their Application for Mechanical Behavior Predictions. Mater. Des. 2021, 202, 109562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Chen, X.; Li, Q.; Zhu, H.; He, H. Hot Compression Behavior, Simulation Verification and Dynamic Recrystallization Mechanism of Mg-Gd-Y-Zr Alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 31, 3712–3725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.; Lu, L.; Feng, L.; Lu, F.; Gan, C.; Li, X. Effects of Pre-Aging on Microstructure Evolution and Deformation Mechanisms of Hot Extruded Mg-6Zn-1Gd-1Er Mg Alloys. J. Magnes. Alloys 2023, 11, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Tang, A.; Liu, T.; Huang, Y.; Peng, P.; Zhang, J.; Hort, N.; Willumeit-Römer, R.; Pan, F. Development of High Strength-Ductility Mg-Er Extruded Alloys by Micro-Alloying with Mn. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 947, 169669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhao, S.; Li, J.; Feng, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Guo, E. Precipitation Behavior and Mechanical Properties of Mg-Nd-Sm-Zn-Zr Alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 28, 3385–3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Lang, M.; Shi, L.; Li, M.; Zhou, T.; Bao, C.; Yang, M. Study on Hot Deformation Behavior of Homogenized Mg-8.5Gd-4.5Y-0.8Zn-0.4Zr Alloy Using a Combination of Strain-Compensated Arrhenius Constitutive Model and Finite Element Simulation Method. J. Magnes. Alloys 2023, 11, 1016–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amani, S.; Faraji, G.; Abrinia, K. Microstructure and Hardness Inhomogeneity of Fine-Grained AM60 Magnesium Alloy Subjected to Cyclic Expansion Extrusion (CEE). J. Manuf. Process. 2017, 28, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.Z.; Wu, D.; Chen, R.S.; Qi, Y.; Ye, H.Q.; Yang, Z.Q. Revisiting the Role of Zr Micro-Alloying in a Mg-Nd-Zn Alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 832, 155016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Bai, X.; Peng, Q.; Wei, G.; Ma, Z. Hot Deformation Behavior of Ultralight Dual-Phase Mg-6li Alloy: Constitutive Model and Hot Processing Maps. Metals 2021, 11, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, B.-J.; Wang, S.; Xu, T.-W.; Guo, F. Effects of Minor Nd and Er Additions on the Precipitation Evolution and Dynamic Recrystallization Behavior of Mg-6.0Zn-0.5Mn Alloy. J. Magnes. Alloys 2021, 9, 840–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Jin, L.; Dong, J.; Wang, F.; Dong, S. The Texture and Its Optimization in Magnesium Alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2020, 42, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Jin, S.-C.; Jung, J.-G.; Park, S.H. Influence of Undissolved Second-Phase Particles on Dynamic Recrystallization Behavior of Mg-7Sn-1Al-1Zn Alloy during Low- and High-Temperature Extrusions. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 71, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeilpour, H.; Zarei-Hanzaki, A.; Eftekhari, N.; Abedi, H.R.; Ghandehari Ferdowsi, M.R. Strain Induced Transformation, Dynamic Recrystallization and Texture Evolution during Hot Compression of an Extruded Mg-Gd-Y-Zn-Zr Alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 778, 139021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, B.; Khan, F.; Sahoo, B.N.; Panigrahi, S.K. A High Temperature Manufacturability Study of Ultrafine Grained Magnesium Rare-Earth Alloy Using Processing Map and Constitutive Analysis. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 954, 169991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Lu, L.; Zhao, H.; Wu, Z.; Xue, Y.; Wang, W. Effect of Deformation Temperatures on Microstructure of AQ80 Magnesium Alloy under Repeated Upsetting-Extrusion. Acta Metall. Sin. Engl. Lett. 2023, 36, 1649–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Xu, X.; Mansoor, A.; Du, B.; Shi, K.; Liu, K.; Li, S.; Du, W. Precipitate Characteristics and Their Effects on the Mechanical Properties of As-Extruded Mg-Gd-Li-Y-Zn Alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 88, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, H.; Li, Q.; Chen, X.; Chen, P.; Li, X.; Tan, J. Dynamic Recrystallization Mechanism and Precipitation Behavior of Mg-6Gd-3Y-3Sm-0.5Zr Alloy During Hot Compression. Met. Mater. Int. 2023, 29, 390–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Zhu, X.; Wei, D.; Yu, Y.; Wang, G. Construction of an Arrhenius Constitutive Model for Mg-Y-Nd-Zr-Gd Rare Earth Magnesium Alloy Based on the Zener-Hollomon Parameter and Objective Evaluation of Its Accuracy in the Twinning-Rich Intervals. J. Magnes. Alloys 2024, 12, 2890–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Liu, C.; Jiang, S.; Gao, Y.; Wan, Y.; Chen, Z. Analysis of Abnormal Texture and Strengthening Mechanisms of Extruded Mg-Gd-Y-Nd-Zr Alloy. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2023, 25, 2201046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.-Y.; Fang, G. Characterization of Dynamic Precipitation Behaviors Accompanying Dynamic Recrystallization in an Mg-Al-Zn-RE Alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 901, 163745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

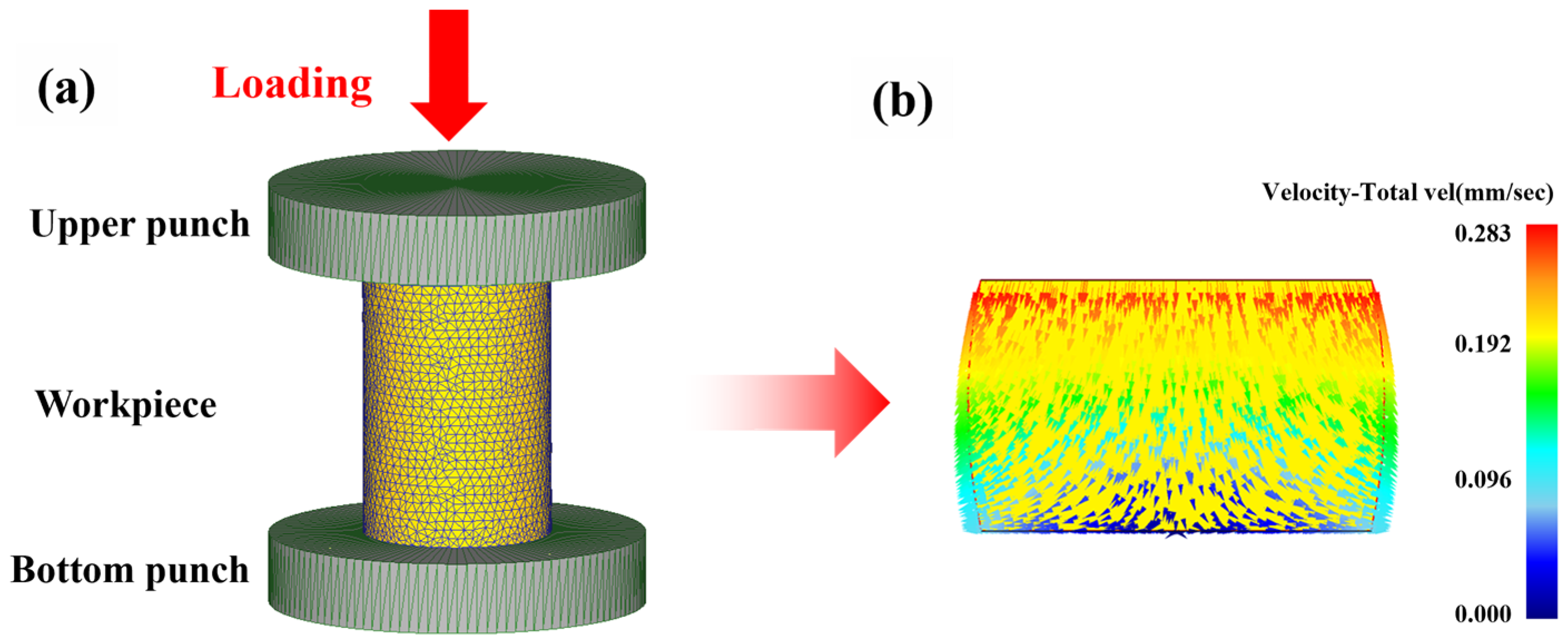

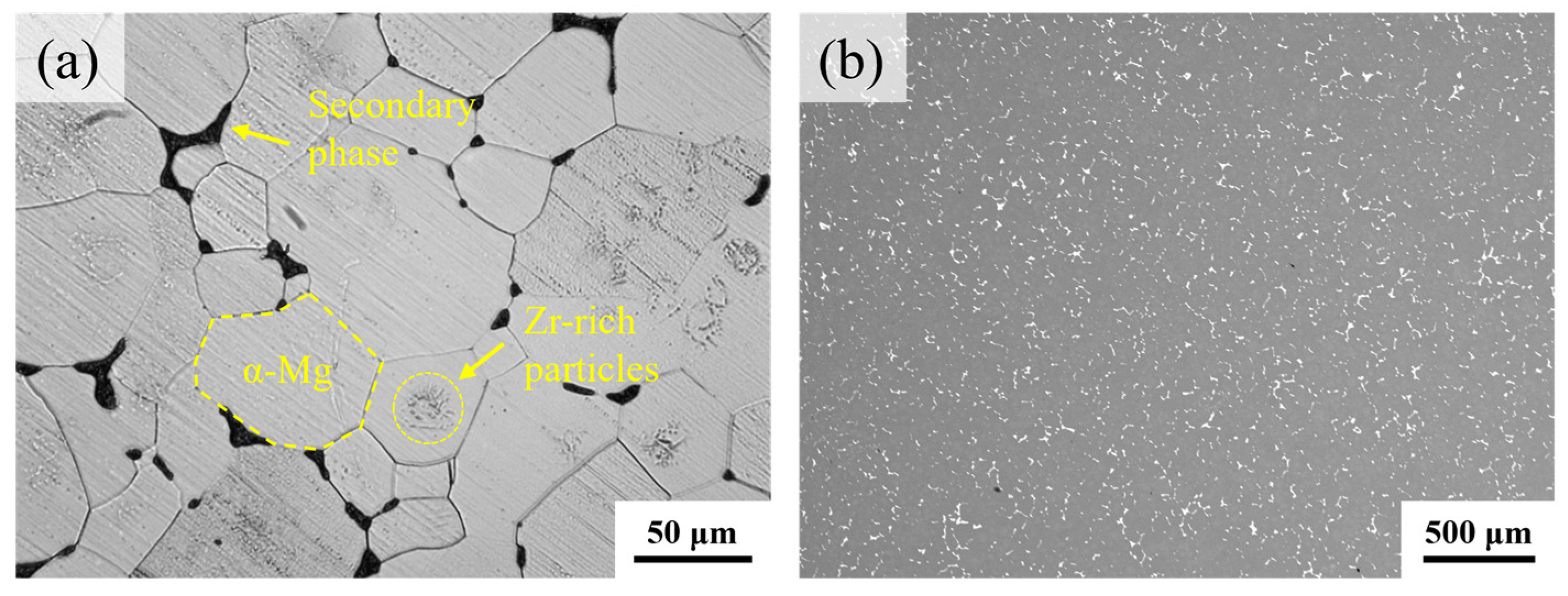
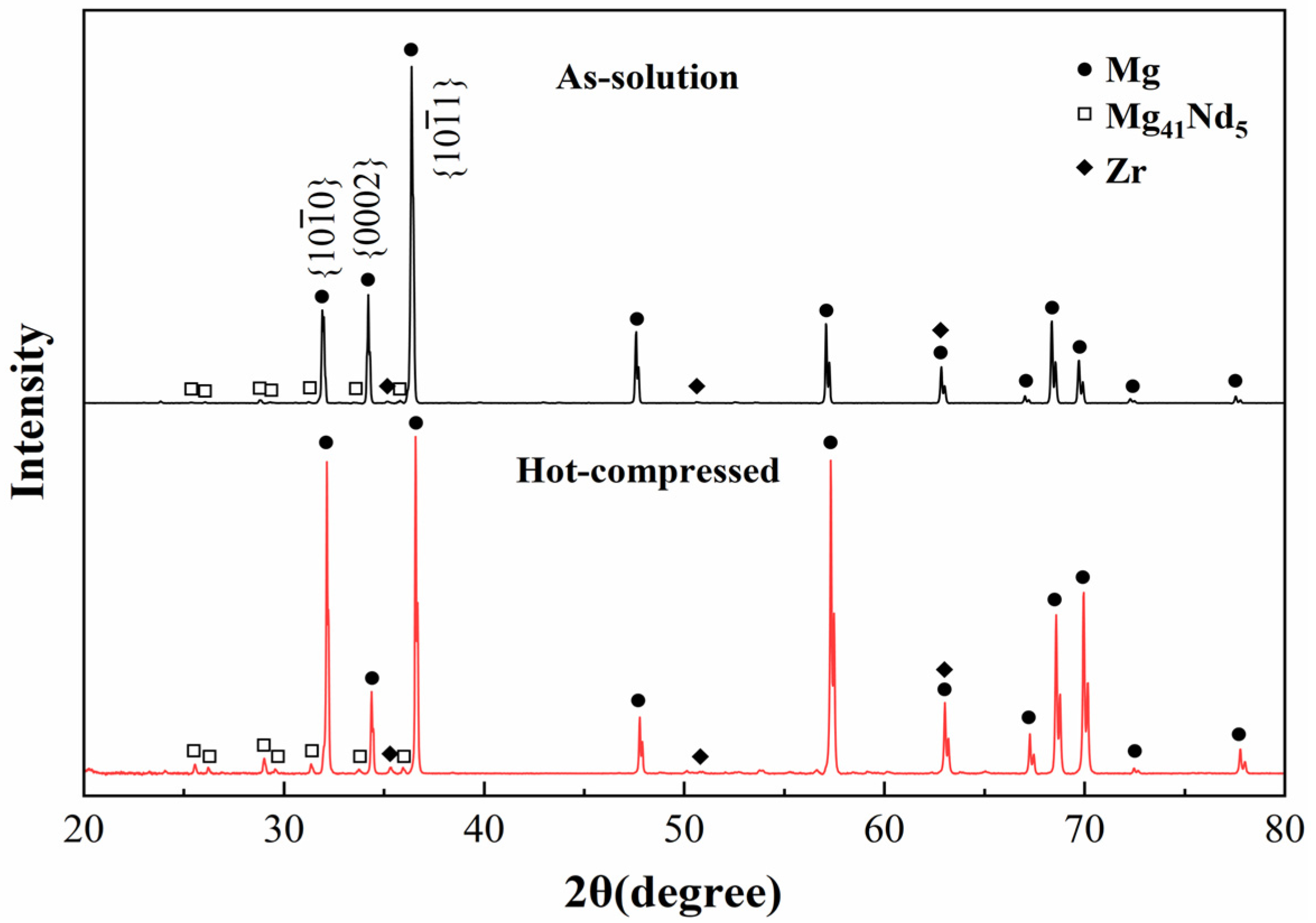
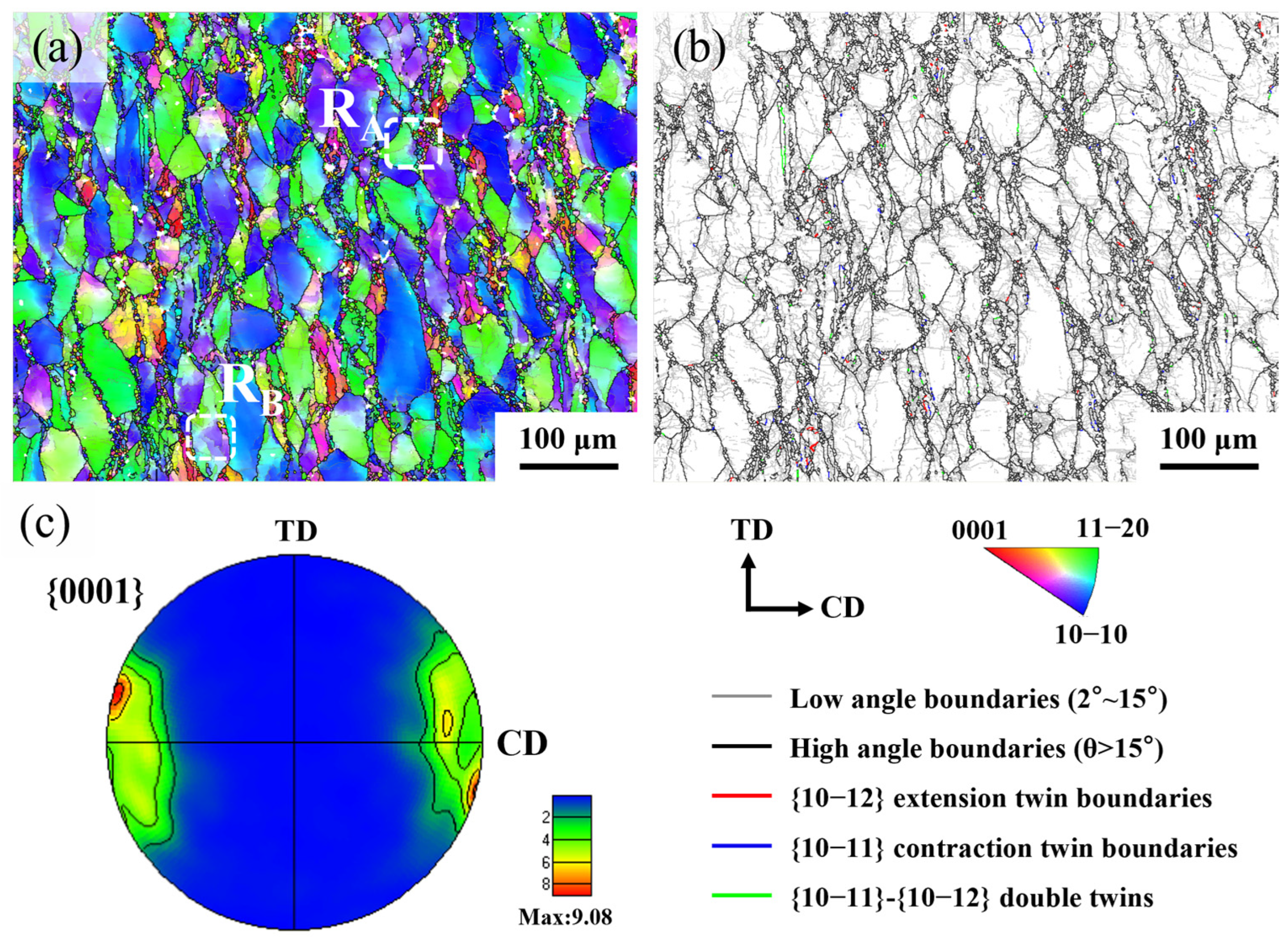





| Simulation and Material Parameters | Parameter Values |
|---|---|
| Workpiece length(mm) | 12 |
| Workpiece diameter(mm) | 8 |
| Poison’s ratio | 0.35 |
| Mesh type | Tetrahedral mesh |
| Total number of elements | 32,000 |
| Relative interference depth | 0.7 |
| Friction coefficient | 0.3 |
| Compression temperature (°C) | 430 |
| Upper punch velocity(mm/s) | 0.27 |
| Step length(mm) | 0.09 |
| Total simulation steps | 60 |
| True Strain | εmin | εmax | εavg | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | 0.018 | 0.150 | 0.097 | 1.361 |
| 0.3 | 0.055 | 0.498 | 0.289 | 1.533 |
| 0.6 | 0.141 | 1.050 | 0.57 | 1.595 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Jiang, B.; Yang, R.; Jing, L.; Lu, L. Microstructural Analysis of Hot-Compressed Mg-Nd-Zr-Ca Alloy with Low Rare-Earth Content. Materials 2025, 18, 4490. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194490
Li Y, Jiang B, Yang R, Jing L, Lu L. Microstructural Analysis of Hot-Compressed Mg-Nd-Zr-Ca Alloy with Low Rare-Earth Content. Materials. 2025; 18(19):4490. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194490
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yiquan, Bingchun Jiang, Rui Yang, Lei Jing, and Liwei Lu. 2025. "Microstructural Analysis of Hot-Compressed Mg-Nd-Zr-Ca Alloy with Low Rare-Earth Content" Materials 18, no. 19: 4490. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194490
APA StyleLi, Y., Jiang, B., Yang, R., Jing, L., & Lu, L. (2025). Microstructural Analysis of Hot-Compressed Mg-Nd-Zr-Ca Alloy with Low Rare-Earth Content. Materials, 18(19), 4490. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194490







