Exploring the Sound Absorption Potential of Ecoflex™ 00-35 for Soft and Flexible Noise Reduction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experimental Protocol
2.2.1. A/B Ratio
2.2.2. Thinning Agent
2.2.3. Pressure
2.3. Measurement Methods
2.3.1. Microgeometry Analysis
2.3.2. Absorption Coefficient and Surface Impedance
2.3.3. Calculation of NRC and SAA
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Microstructure Characteristics
3.2. Acoustic Behavior
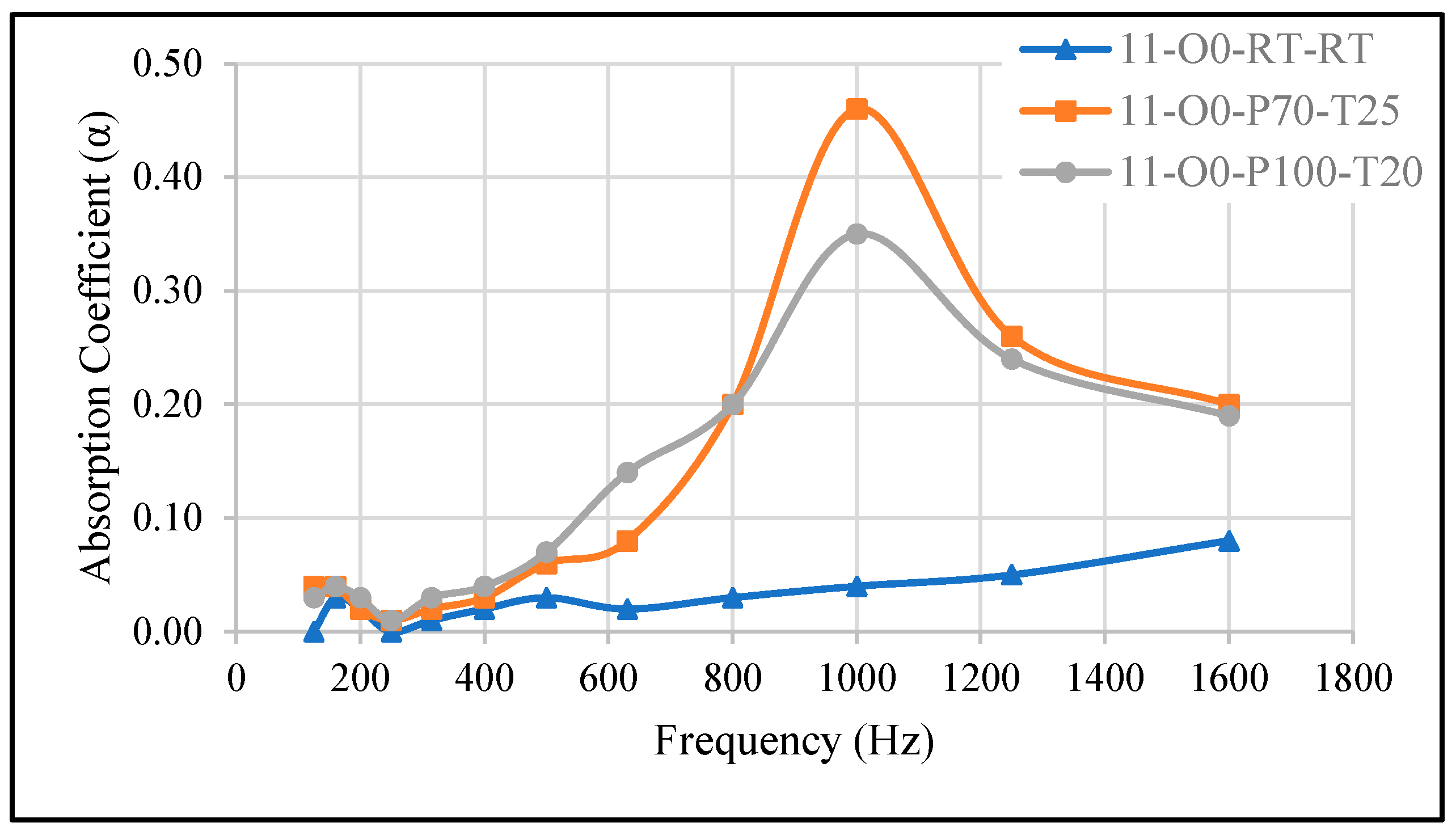
3.2.1. Effect of Pressure Variation at Fixed Curing Time
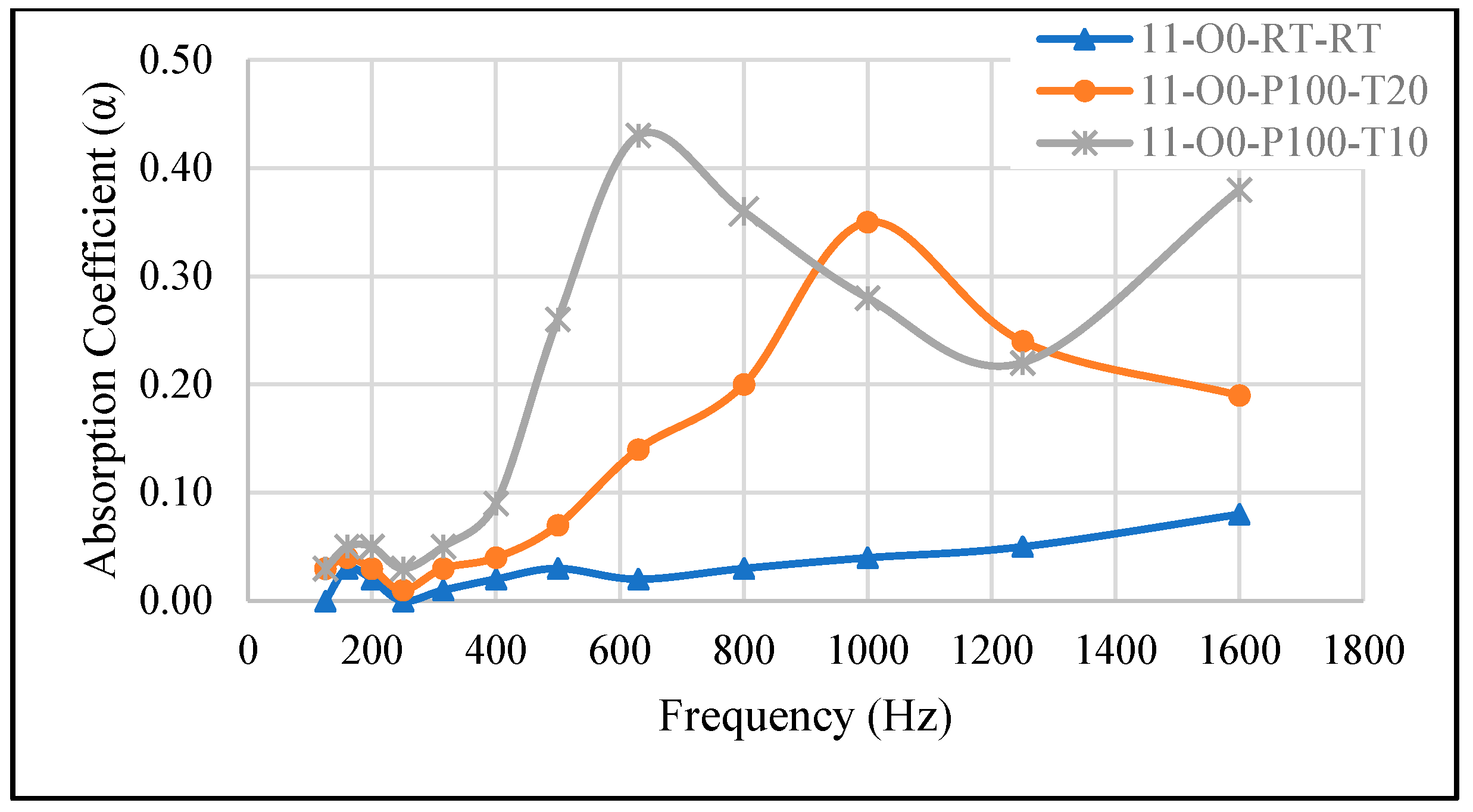
3.2.2. Effect of Time Variation at Fixed Curing Pressure
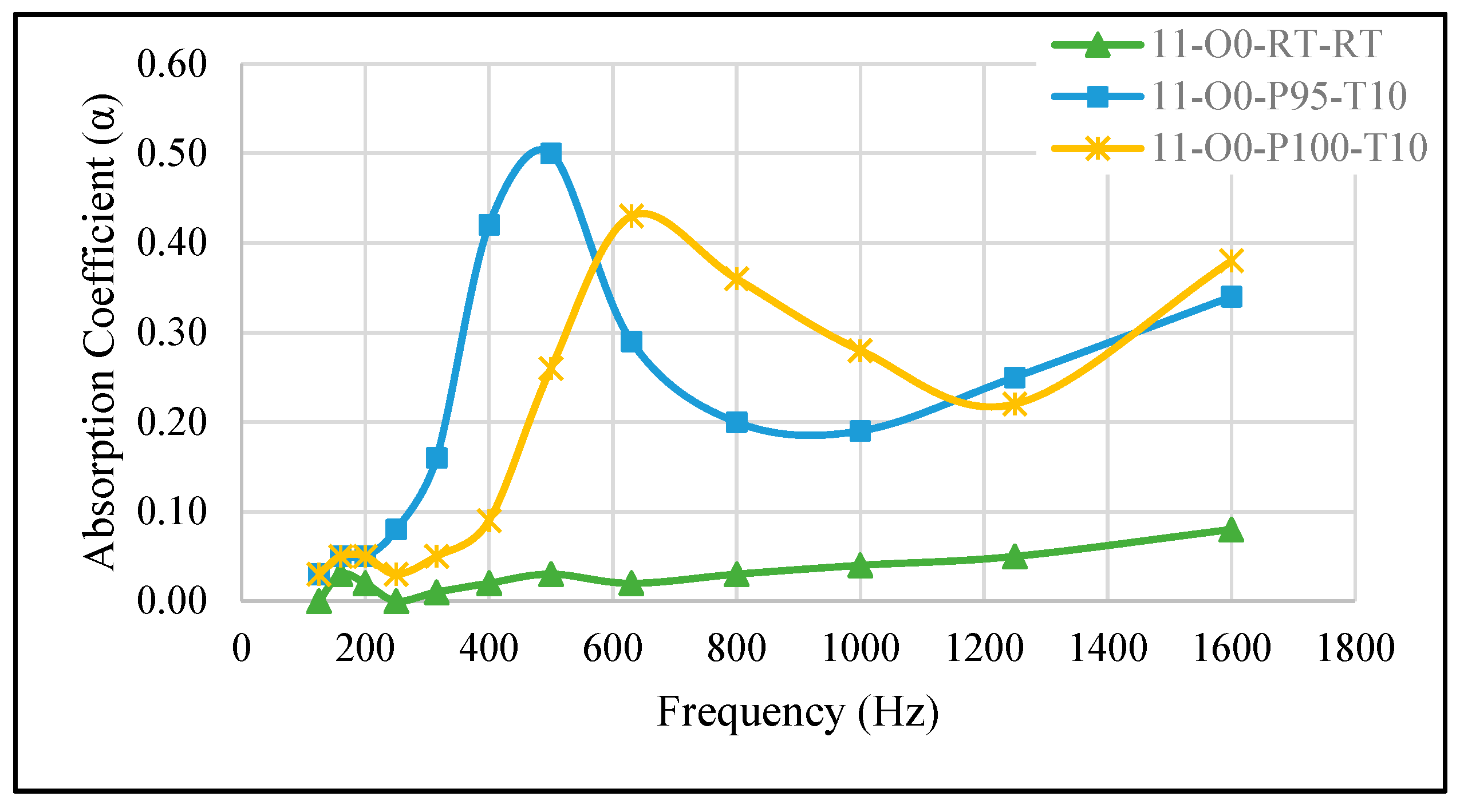
3.2.3. Effect of Minor Pressure Changes and Shorter Curing Time
3.2.4. Combined Effect A/B Ratio and Curing Pressure
3.2.5. Effect of Thinning Agent on Acoustic Performance
3.3. Quantitative Acoustic Performance Assessment
4. Strength, Limitations, and Future Work
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscopy |
| SAC | Sound Absorption Coefficient |
| NRC | Noise Reduction Coefficient |
| SAA | Sound Absorption Average |
References
- Azimi, M. Noise Reduction in Buildings Using Sound Absorbing Materials. J. Archit. Eng. Technol. 2017, 6, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, E.-S.; Lim, Y.-J.; Lee, J.; Moon, J.-B.; Kim, B. Application of Soundproofing Materials for Noise Reduction in Dental CAD/CAM Milling Machines. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, C. Engineering Solutions for Noise Reduction: Development and Optimization of Absorption Models in Urban and Industrial Settings; Research Archive of Rising Scholars (RARS), Polygence: Menlo Park, CA, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodorou, V.; Matysík, M.; Plšková, I.; Kusák, I.; Papaphilippou, P.C.; Krasia-Christoforou, T. Eco-Friendly, Sound Absorbing Materials Based on Cellulose Acetate Electrospun Fibers/Luffa Cylindrica Composites. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2024, 46, e2400863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Sudhakara, P.; Singh, J.; Singh, S.; Singh, G. Emerging progressive developments in the fibrous composites for acoustic applications. J. Manuf. Process. 2023, 102, 443–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Fu, Q.; Si, Y.; Ding, B.; Yu, J. Porous materials for sound absorption. Compos. Commun. 2018, 10, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Ren, M.; Zhang, H.; Peijs, T. Recent progress in acoustic materials and noise control strategies—A review. Appl. Mater. Today 2021, 24, 101141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnova, O. Technology of increase of nanoscale pores volume in protective cement matrix. Int. J. Civ. Eng. Technol. 2018, 9, 1991–2000. [Google Scholar]
- Bušić, R.; Miličević, I.; Šipoš, T.K.; Strukar, K. Recycled Rubber as an Aggregate Replacement in Self-Compacting Concrete-Literature Overview. Materials 2018, 11, 1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazanskaya, L.; Isakovsky, V.; Fadeeva, S. Technological properties of self-compacting concrete mixtures with ground quartz sand. Int. J. Innov. Technol. Explor. Eng. 2019, 8, 799–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Kabir, I.I.; Yeoh, G.H.; Peng, Z. A review on polymer-based materials for underwater sound absorption. Polym. Test. 2021, 96, 107115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Li, B.; Huang, G. Sound absorption characteristics of polymer microparticles. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 101, 2675–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Zhao, C.; Wang, S.; Xuan, S.; Jiang, H.; Gong, X. A novel magnetorheological shear-stiffening elastomer with self-healing ability. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 168, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.A.; Mobarak, M.H.; Rimon, M.I.H.; Al Mahmud, M.Z.; Ghosh, J.; Ahmed, M.M.S.; Hossain, N. Additive manufacturing in polymer research: Advances, synthesis, and applications. Polym. Test. 2024, 132, 108364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilk-Jakubowski, J.L.; Kuchcinski, A.; Pawlik, L.; Wilk-Jakubowski, G. Advanced Sound Insulating Materials: An Analysis of Material Types and Properties. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 6156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smooth-On. Ecoflex™ 00-35 FAST. Available online: https://www.smooth-on.com/products/ecoflex-00-35/ (accessed on 2 April 2022).
- Liao, Z.; Yang, J.; Hossain, M.; Chagnon, G.; Jing, L.; Yao, X. On the stress recovery behaviour of Ecoflex silicone rubbers. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2021, 206, 106624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhou, D.; Xie, Y.; Yang, J.; Kong, J. Tunable sound absorption of silicone rubber materials via mesoporous silica. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 15171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Lei, L.; Liu, Y.; Du, L. Improved Mechanical and Sound Absorption Properties of Open Cell Silicone Rubber Foam with NaCl as the Pore-Forming Agent. Materials 2021, 14, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Liu, Y. The latest research status of porous sound-absorbing materials. J. Polym. Eng. 2025, 45, 207–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Zhao, P.; Cheng, H.; He, Q.; Du, L. Improved low-frequency sound absorption of porous silicone rubber resonance sheet with periodic cavities. J. Low Freq. Noise Vib. Act. Control 2022, 41, 1151–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Zhang, S.; Liu, X.; Du, C.; Dong, H.-W.; Lu, Z. Advances and integration of noise reduction materials and structures: A review of porous materials and acoustic metamaterials. J. Appl. Phys. 2025, 138, 033103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gopalakrishnakone, P. Influence of vacuum on the formation of porous polymer films via water droplets templating. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2009, 287, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.-M.; Guo, Z.-P.; Yang, H.-Z.; Fu, Z.-H.; Pu, Z.-M.; Xiong, S.-M. Effect of vacuum on porosity and mechanical properties of high-pressure die-cast pure copper. China Foundry 2019, 16, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annabi, N.; Nichol, J.W.; Zhong, X.; Ji, C.; Koshy, S.; Khademhosseini, A.; Dehghani, F. Controlling the porosity and microarchitecture of hydrogels for tissue engineering. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2010, 16, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, B.; Wu, Q. Enhanced Low-Frequency Sound Absorption of a Porous Layer Mosaicked with Perforated Resonator. Polymers 2022, 14, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yu, C.; Xin, F. Gradually perforated porous materials backed with Helmholtz resonant cavity for broadband low-frequency sound absorption. Compos. Struct. 2021, 263, 113647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amran, M.; Fediuk, R.; Murali, G.; Vatin, N.; Al-Fakih, A. Sound-Absorbing Acoustic Concretes: A Review. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolli, M.G.; Terracciano, M.; Rea, I.; D’Errico, S.; Placido Mineo, G.; De Stefano, L.; Piccialli, G.; Riela, S.; Oliviero, G.; Borbone, N. Mild-Temperature Catalyzed Hydrosilylation for Simplified Carbohydrate Functionalization of Porous Silicon Nanoparticles. Chemistry 2025, 31, e202402818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietrich, A.; Mejía, E. Investigations on the hydrosilylation of allyl cyanide: Synthesis and characterization of cyanopropyl-functionalized silicones. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 122, 109377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KS F 2814-2:2022; Acoustics—Determination of Sound Absorption Coefficient and Impedance in Impedance Tubes—Part 2: Transfer-Function Method. Korean Agency for Technology and Standards (KATS): Eumseong, Republic of Korea, 2022.
- ASTM C423-23; Standard Test Method for Sound Absorption and Sound Absorption Coefficients by the Reverberation Room Method. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2023.
- Abbad, A.; Jaboviste, K.; Ouisse, M.; Dauchez, N. Acoustic performances of silicone foams for sound absorption. J. Cell. Plast. 2017, 54, 651–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Song, L.; Fang, J.; Li, H.; Luo, M.; Cheng, Q.; Liu, X. Hierarchical porous kapok fiber composite aerogel with Helmholtz resonant cavity for low-frequency sound absorption. Compos. Part B Eng. 2025, 301, 112523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryoo, H.; Yong Lee, K.; Jeon, W. Broadband sound absorption using hybrid resonators with embedded necks and micro-perforations in parallel. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2024, 211, 111205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkunte, S.; Mali, A.; Khan, A.U.; More, N.; Ingle, N.; Nalawade, S.; Sinha, N.; Gupta, M.; Shingare, K.B.; Liao, K.; et al. Porosity in additive manufacturing: Purposeful design, applications, and characterization methods—A review. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2025, 140, 1127–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Chen, G.; Chang, B.P.; Mekonnen, T. Recent progress in the development of porous polymeric materials for oil ad/absorption application. RSC Appl. Polym. 2024, 3, 43–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balsamo, M.; Mistretta, M.C.; Scaffaro, R. Highly porous hollow 3D devices obtained by a combined melt-wet processing for long-term controlled release. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2025, 8, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Qi, Q. Implicit complex topology modeling design method based on Voronoi. Comput.-Aided Des. 2025, 188, 103910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shi, L.; Li, J.; Chen, S.; Yi, Q. Recent Advances in Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Foaming Technology for Thermoplastic Polyurethane Foams: Process Optimization, Property Modulation, and Emerging Applications. J. Polym. Sci. 2025, 63, 3047–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorvath, I.; DeGroot, J.V., Jr.; Dipino, M.; Drake, R.A.; Lawson, D.W.; Robson, S.; Shawl, D.; Tonge, L.M. Fluorosilicone Elastomers For High Temperature. Performance. Patent No. US20100166996A1, 1 July 2010. (Application filed 6 June 2008). [Google Scholar]
- Shafik, E.S. Review on sustainable, eco-friendly novel reinforcing fillers for rubber composites. Pigment Resin Technol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Tian, X.; Wang, H. Modified silicone rubber with super-stretch and high-temperature resistance for liquid metal/elastomer composites with electrical insulation and strain-invariant electromagnetic shielding. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2025, 230, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
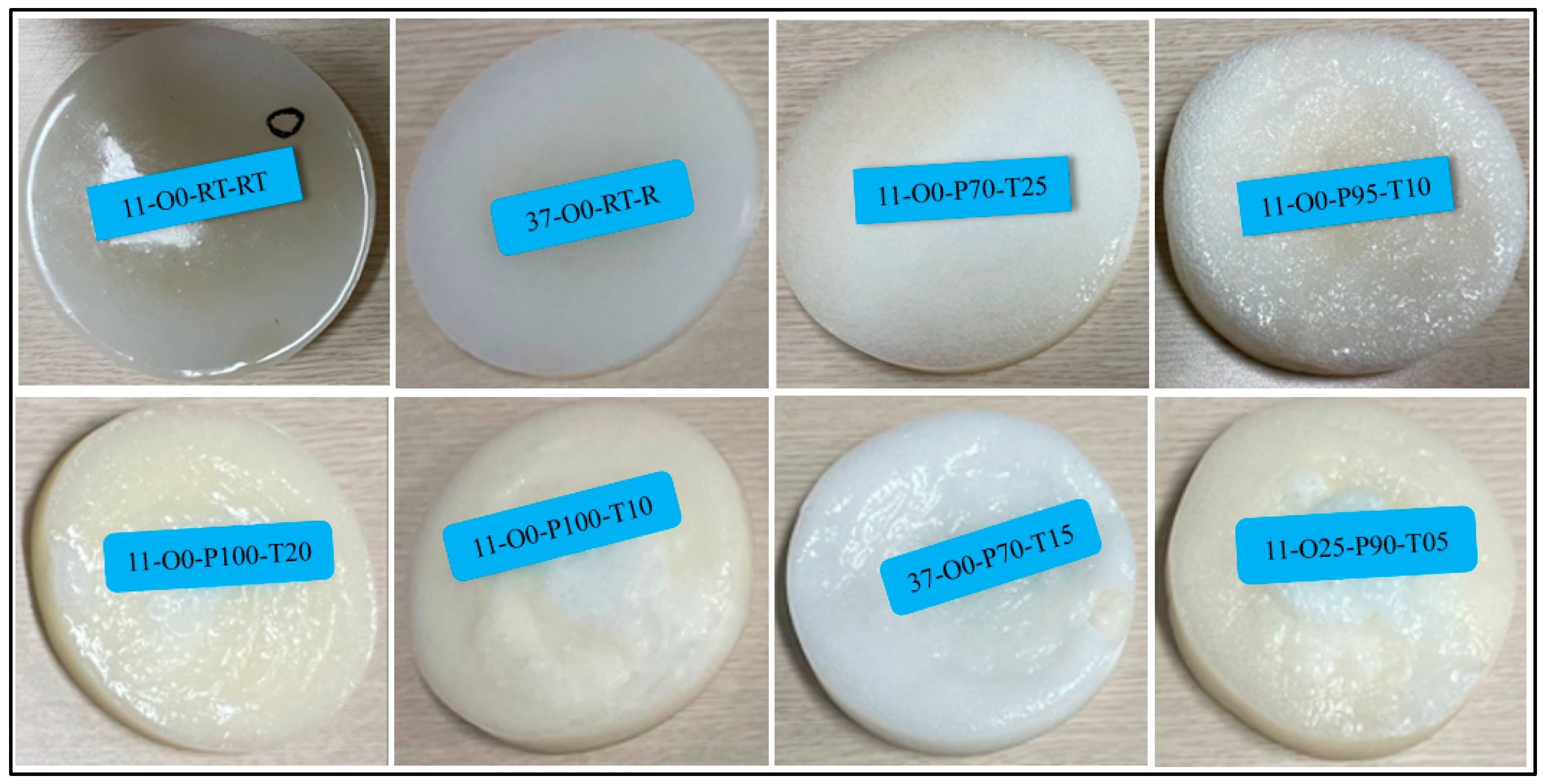

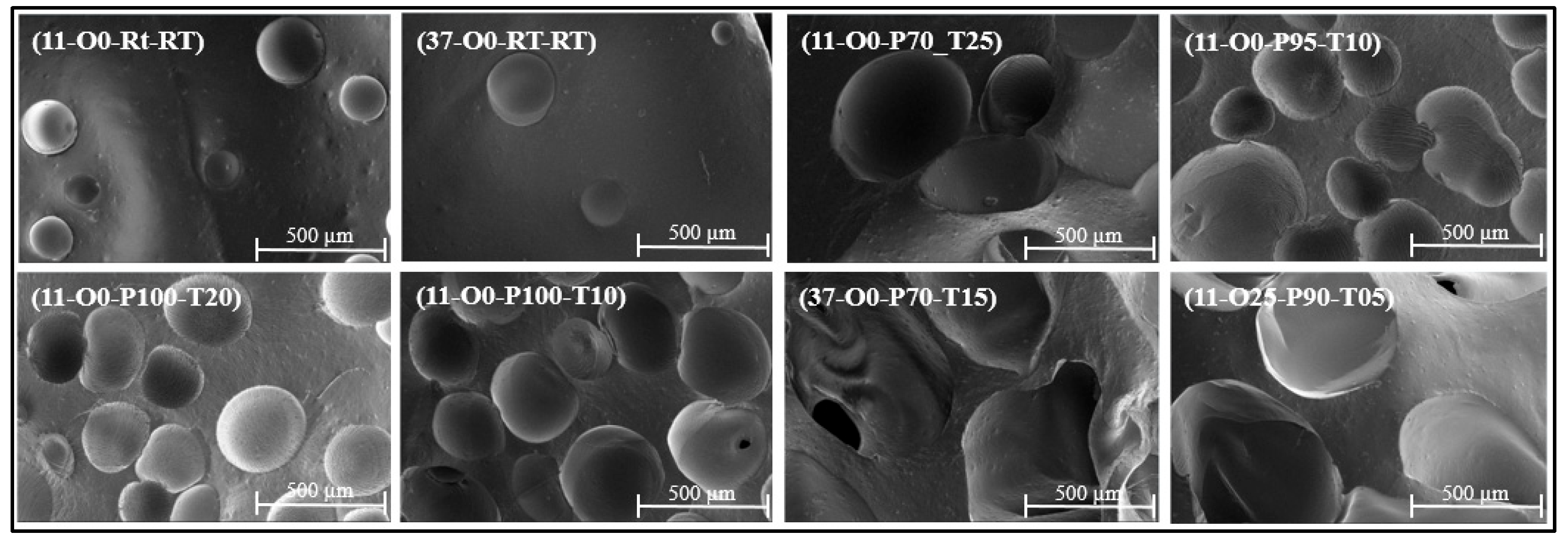
| Sample | %A | %B | %Oil | Curing Temp. | Pressure (kPa) | Time in Vacuum (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
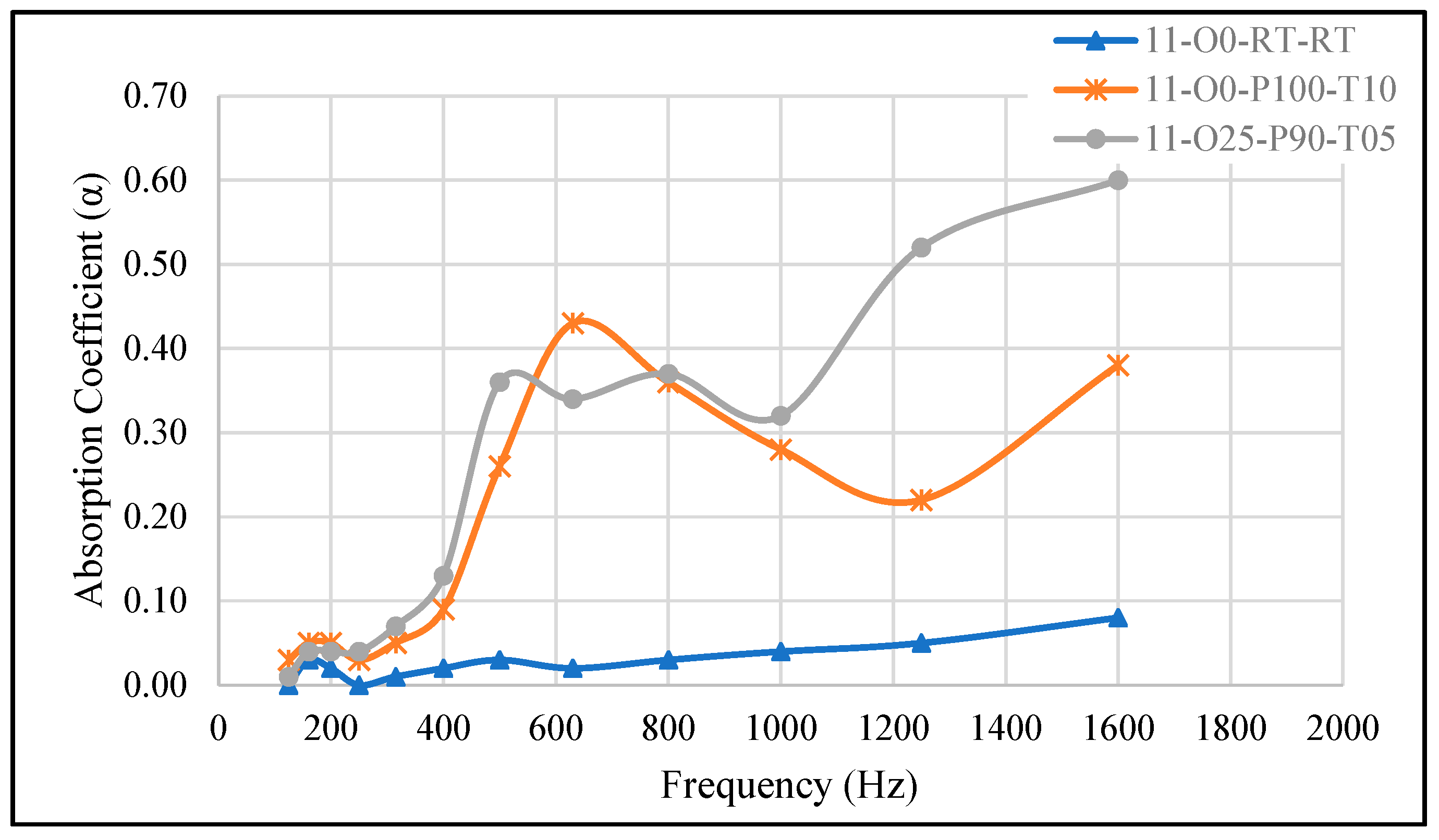
| 11-O0-RT-RT(ref) | 50 | 50 | - | Room | - | - |
| 11-O0-P70-T25 | 50 | 50 | - | - | –70 | 25 |
| 11-O0-P100-T20 | 50 | 50 | - | - | –100 | 20 |
| 11-O0-P95-T10 | 50 | 50 | - | - | –95 | 10 |
| 11-O0-P100-T10 | 50 | 50 | - | - | –100 | 10 |
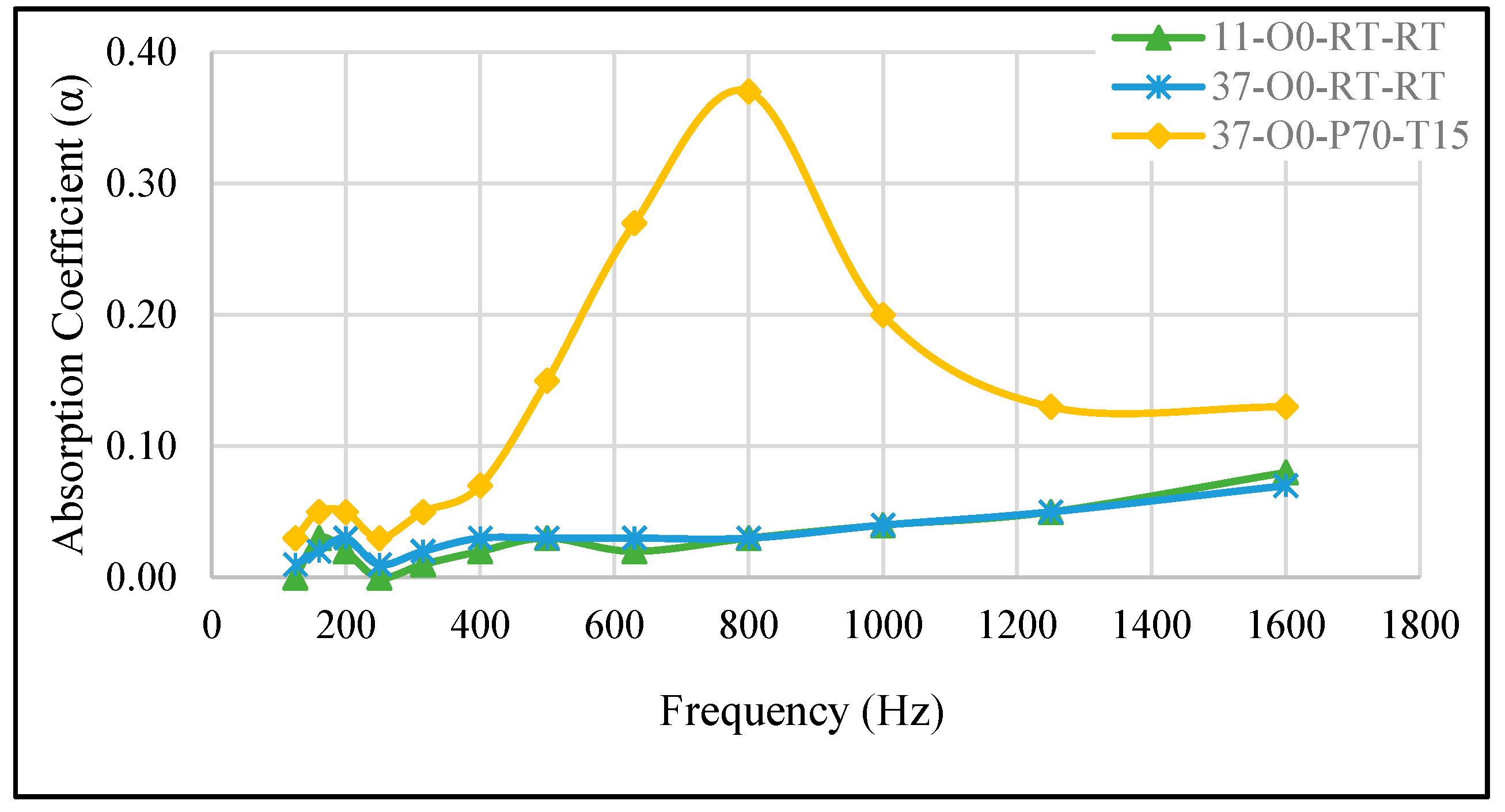
| 37-O0-RT-RT | 30 | 70 | - | Room | - | - |
| 37-O0-P70-T15 | 30 | 70 | - | - | –70 | 15 |
| 11-O25-P90-T05 | 50 | 50 | 25 | - | –90 | 5 |
| Sample | 11-O0-RT-RT | 37-O0-RT-RT | 11-O0-P70-T25 | 11-O0-P95-T10 | 11-O0-P100-T20 | 11-O0-P100-T10 | 37-O0-P70-T15 | 11-O25-P90-T05 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average cell diameter (mm) | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.72 | 0.35 | 0.38 | 0.46 | 0.93 | 0.85 |
| SD cell diameter (mm) | 0.06 | 0.11 | 0.15 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.13 | 0.25 |
| Sample | Description | Peak SAC | Peak Freq. (Hz) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 11-O0-RT-RT | A/B = 1:1, no oil, cured at room temperature, no vacuum | 0.07 | 1600 |
| 11-O0-P70-T25 | A/B = 1:1, no oil, cured at –70 kPa for 25 min | 0.46 | 1000 |
| 11-O0-P100-T20 | A/B = 1:1, no oil, cured at –100 kPa for 20 min | 0.35 | 1000 |
| 11-O0-P95-T10 | A/B = 1:1, no oil, cured at –95 kPa for 10 min | 0.50 | 500 |
| 11-O0-P100-T10 | A/B = 1:1, no oil, cured at –100 kPa for 10 min | 0.43 | 630 |
| 37-O0-RT-RT | A/B = 3:7, no oil, cured at room temperature, no vacuum | 0.08 | 1600 |
| 37-O0-P70-T15 | A/B = 3:7, no oil, cured at –70 kPa for 15 min | 0.37 | 800 |
| 11-O25-P90-T05 | A/B = 1:1, 25% silicone oil, cured at –90 kPa for 5 min | 0.60 | 1600 |
| This Study Performance | Comparable Literature Performance | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| 11-O0-RT-RT, SAC = 0.08 at 1.6 kHz | Dense unmodified silicone rubber, SAC < 0.15 | [33] |
| 11-O0-P70-T25, SAC = 0.46 at 1 kHz | Open-cell silicone foam, SAC 0.45–0.55 at 1–1.5 kHz | [33] |
| 11-O0-P100-T20, SAC = 0.35 at 1 kHz | NaCl-templated silicone foam, SAC~0.35–0.40 at 1–1.2 kHz | [19] |
| 11-O0-P95-T10, SAC = 0.50 at 500 Hz | Porous silicone with irregular pores, SAC 0.48–0.53 at 800–1000 Hz | [33] |
| 11-O0-P100-T10, SAC = 0.43 at 630 Hz | Large-pore silicone foam, SAC~0.40–0.45 at 600–800 Hz | [19] |
| 37-O0-RT-RT, SAC = 0.07 at 1.6 kHz | Low-porosity silicone, SAC < 0.15 | [33] |
| 37-O0-P70-T15, SAC = 0.37 at 800 Hz | High-pressure cured silicone foam, SAC~0.35–0.40 at 800 Hz | [19] |
| 11-O25-P90-T05, SAC = 0.60 at 1.6 kHz | Mesoporous silica–silicone composite, SAC 0.58–0.62 at 1.4–1.6 kHz | [18] |
| Sample | NRC | SAA |
|---|---|---|
| 11-O0-RT-RT | 0.04 | 0.03 |
| 11-O0-P70-T25 | 0.18 | 0.13 |
| 11-O0-P100-T20 | 0.15 | 0.13 |
| 11-O0-P95-T10 | 0.28 | 0.25 |
| 11-O0-P100-T10 | 0.24 | 0.21 |
| 37-O0-RT-RT | 0.04 | 0.03 |
| 37-O0-P70-T15 | 0.13 | 0.14 |
| 11-O25-P90-T05 | 0.33 | 0.28 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohamed, N.; Mohamed, M.; Kim, J.G. Exploring the Sound Absorption Potential of Ecoflex™ 00-35 for Soft and Flexible Noise Reduction. Materials 2025, 18, 4481. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194481
Mohamed N, Mohamed M, Kim JG. Exploring the Sound Absorption Potential of Ecoflex™ 00-35 for Soft and Flexible Noise Reduction. Materials. 2025; 18(19):4481. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194481
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohamed, Nourelhuda, Manal Mohamed, and Jae Gwan Kim. 2025. "Exploring the Sound Absorption Potential of Ecoflex™ 00-35 for Soft and Flexible Noise Reduction" Materials 18, no. 19: 4481. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194481
APA StyleMohamed, N., Mohamed, M., & Kim, J. G. (2025). Exploring the Sound Absorption Potential of Ecoflex™ 00-35 for Soft and Flexible Noise Reduction. Materials, 18(19), 4481. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194481







