Structural Characterization, Cytotoxicity and Microbiological Activity of One-Step-Synthesized RGO/AuNPs Nanocomposites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
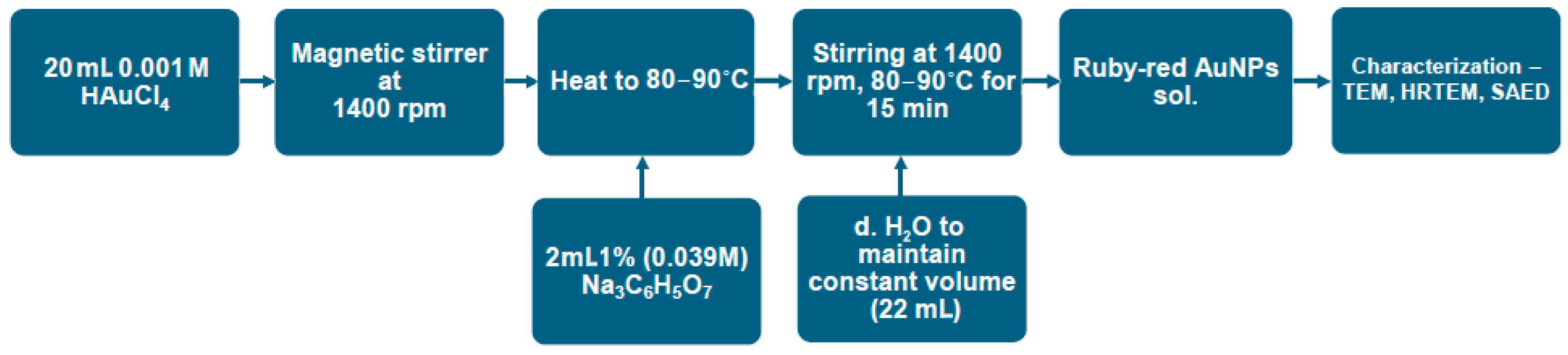
2.1. Synthesis of Au Nanoparticles
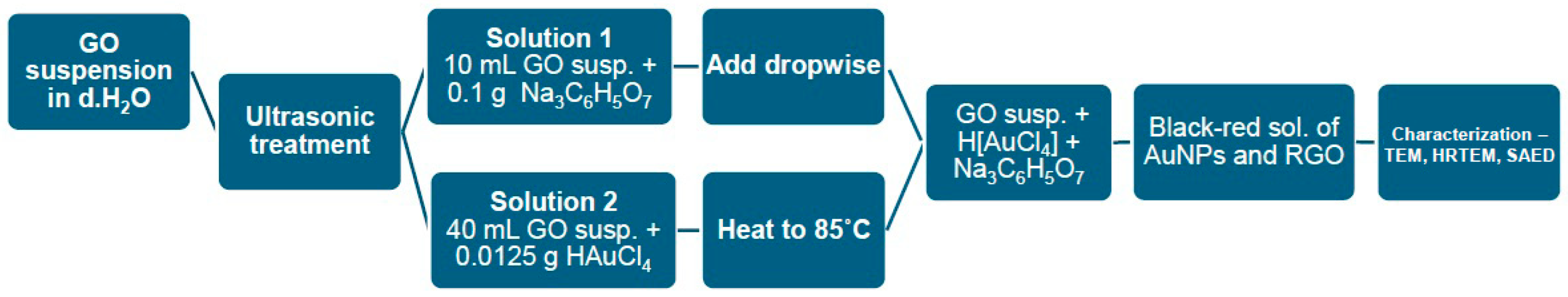
2.2. Synthesis of RGO/AuNPs Composites
- Solution 1. To 10 mL of the GO suspension, add 0.1 g of Na3C6H5O7.
- Solution 2. To 40 mL of the GO suspension, add 0.0125 g of HAuCl4. Heat to 85 °C on a magnetic stirrer.
2.3. Characterization Techniques
2.3.1. TEM Analysis
2.3.2. Dynamic Light Scattering
2.4. Cytotoxicity and Biocompatibility
2.5. Antimicrobial Activity
2.5.1. Broth Dilution Method (Saline-D. Water)
2.5.2. Agar Diffusion and Modified Spot-Test Methods
- Surface inoculation (100 µL in Petri dishes on Nutrient Broth agar (NB-agar));
- Incubation at 30 °C for 30 min;
- Loading of filter discs with 20 μL of synthesized solutions.
- Drying at 30 °C for 30 min;
- Incubation of the Petri dishes at 30 °C for 24 h.
- All antibacterial experiments were performed in triplicate.
2.6. Statistical Analysis Method
3. Results
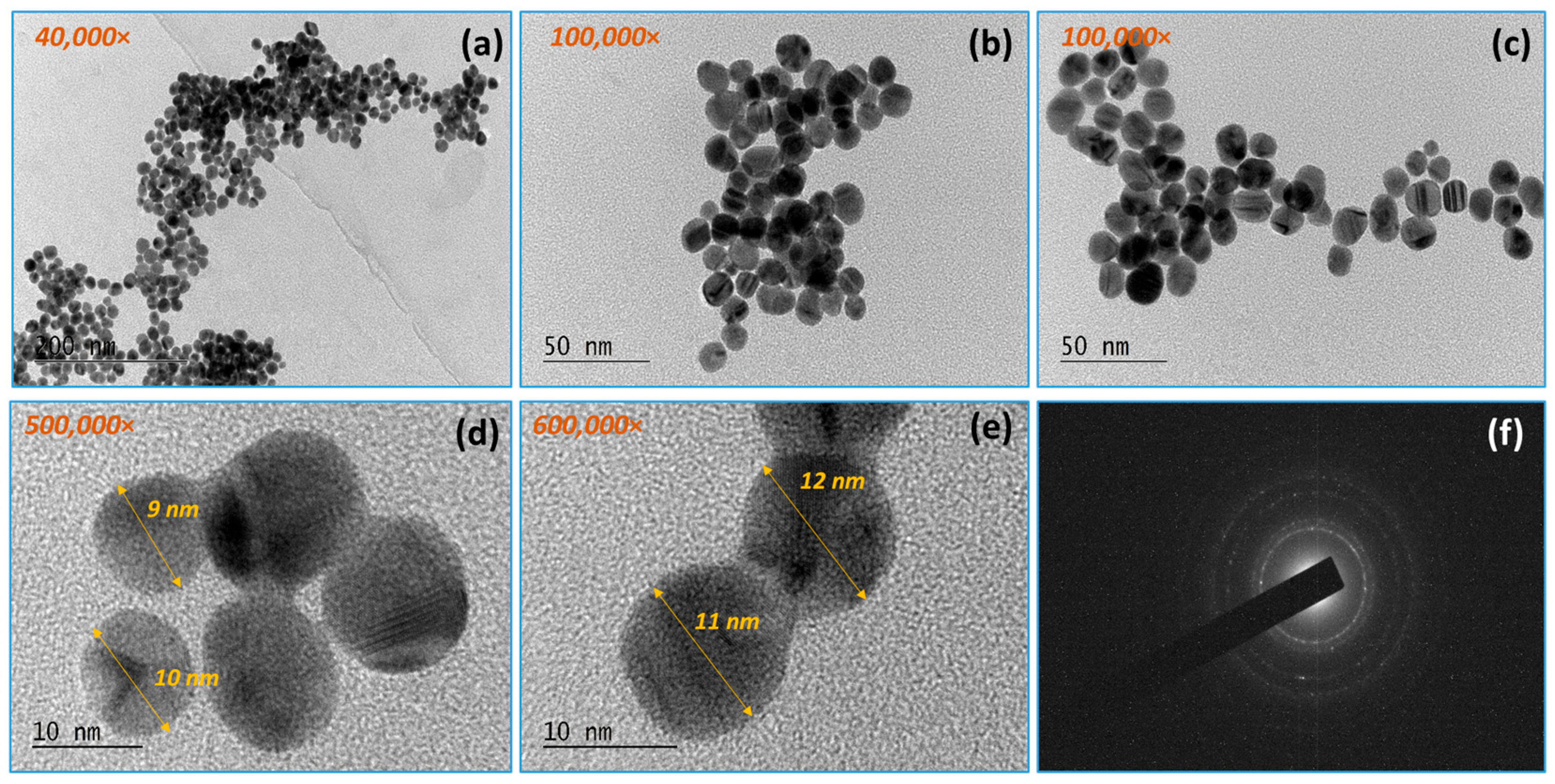
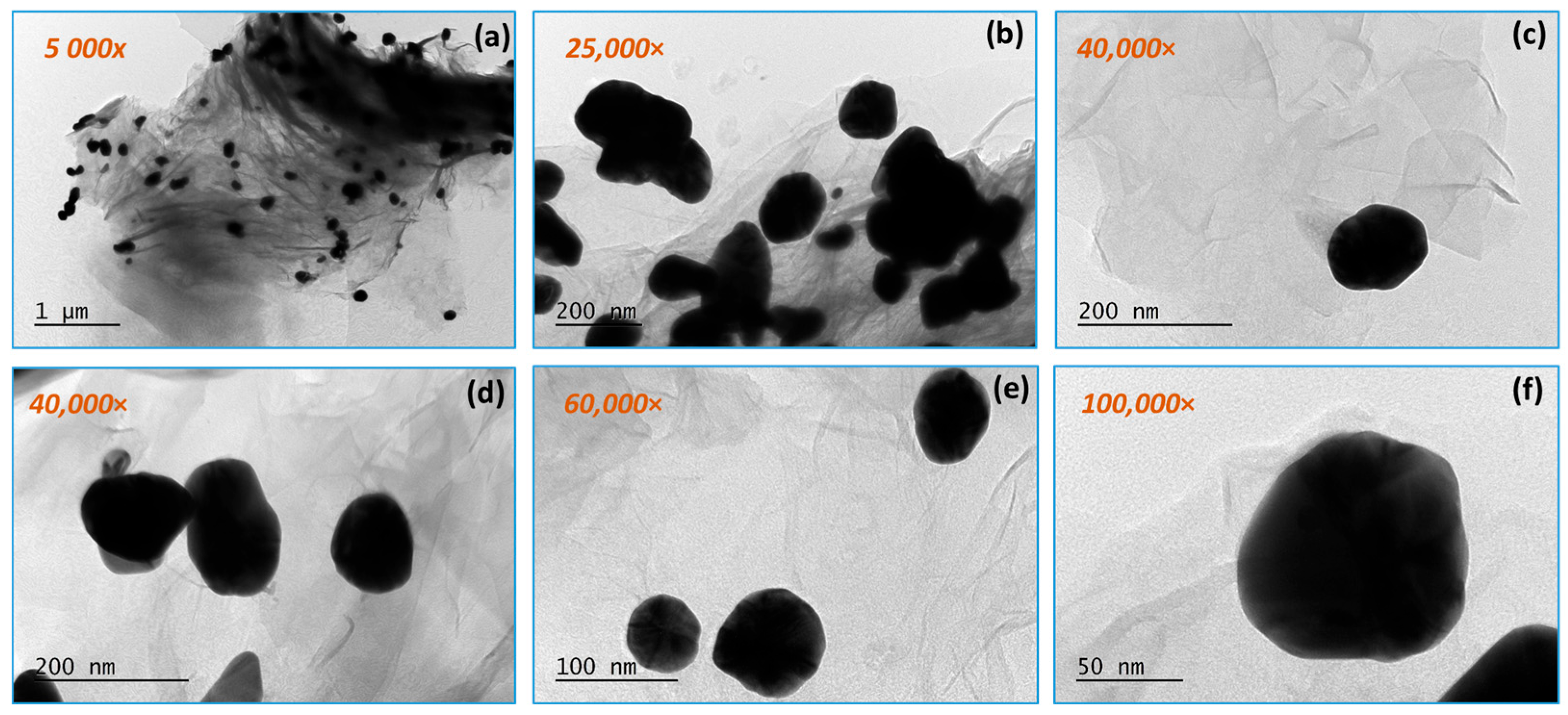
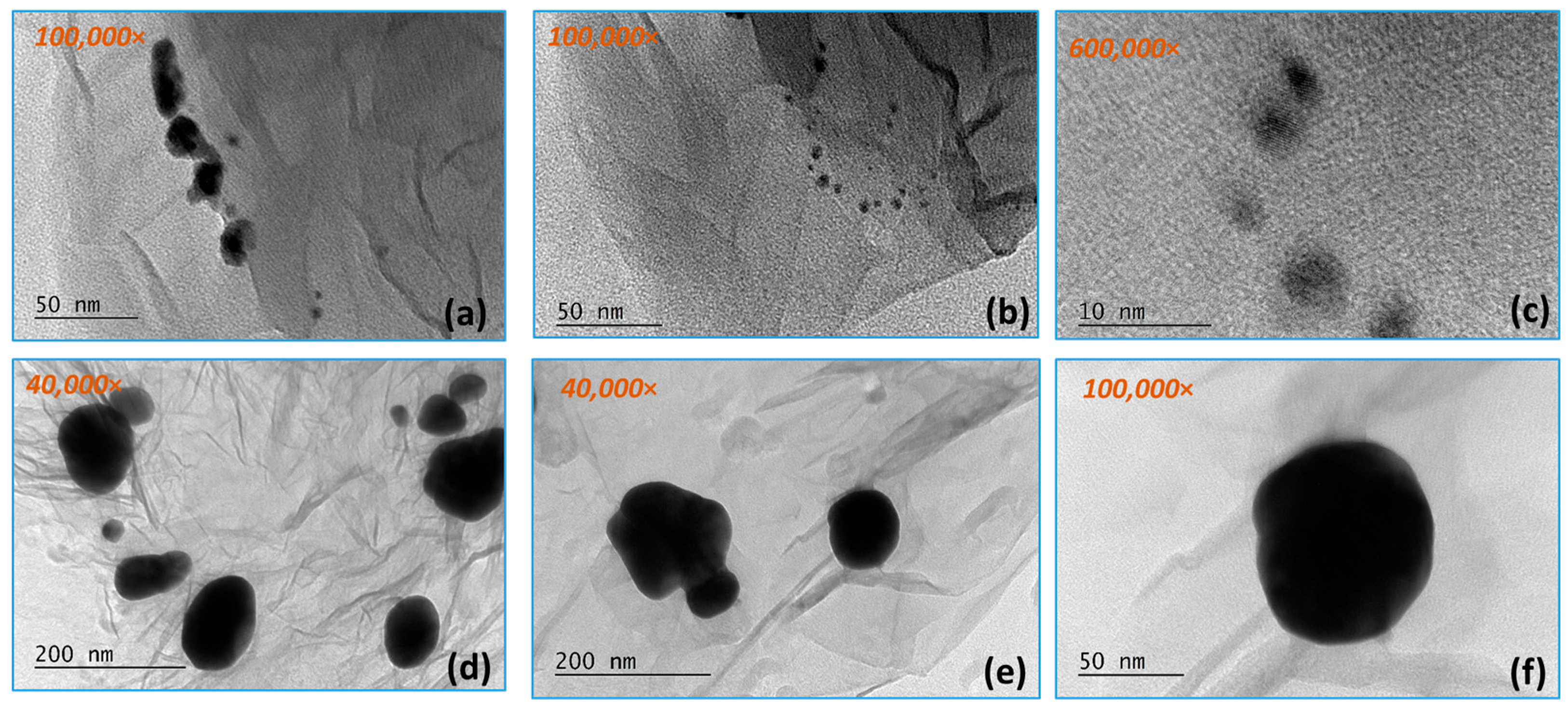
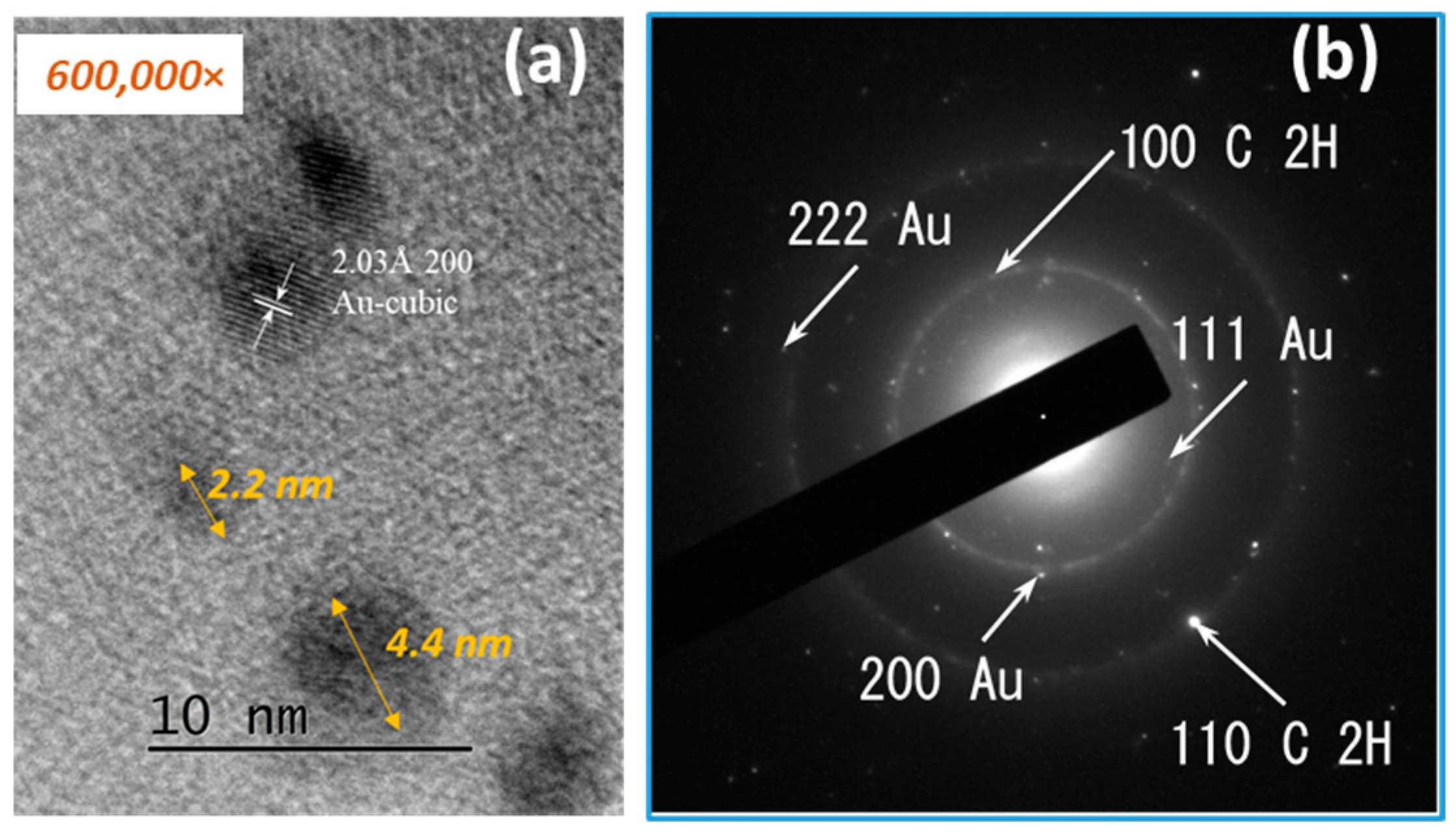
3.1. TEM Analysis Results
3.1.1. Gold Nanoparticles
3.1.2. RGO/AuNPs
3.2. Particle Size Distribution and Surface Charge Results
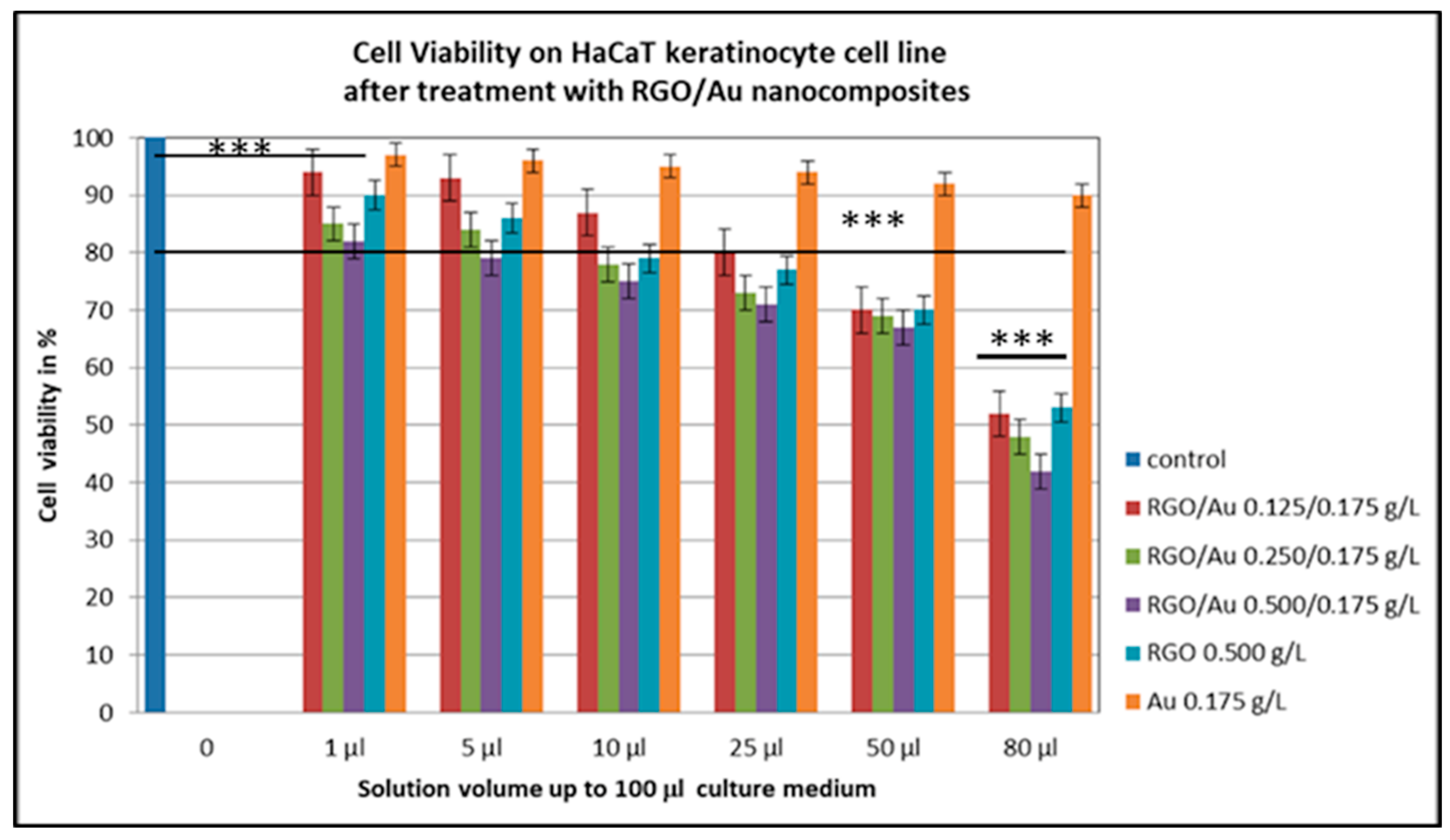
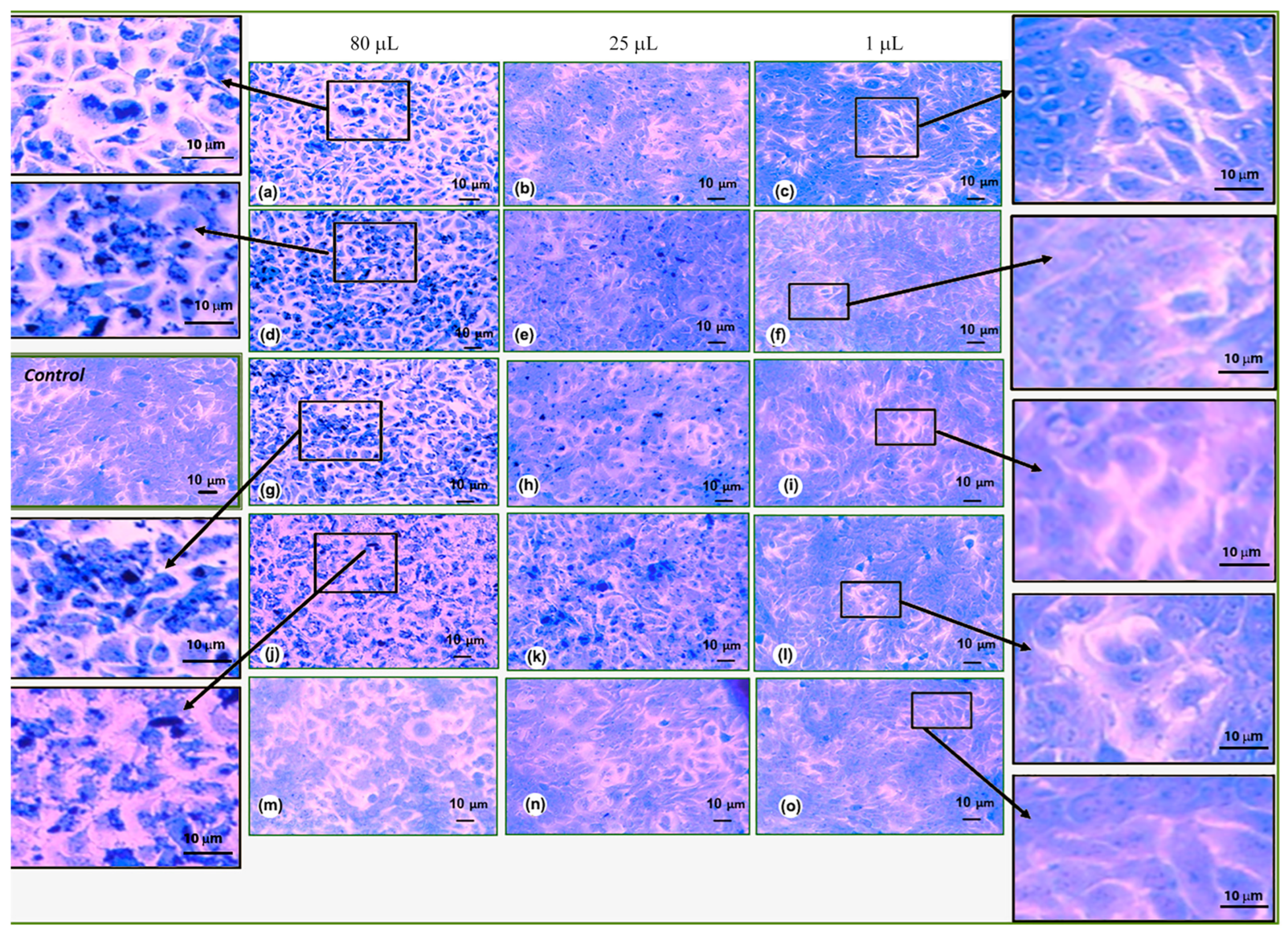
3.3. Cytotoxicity and Biocompatibility Assay
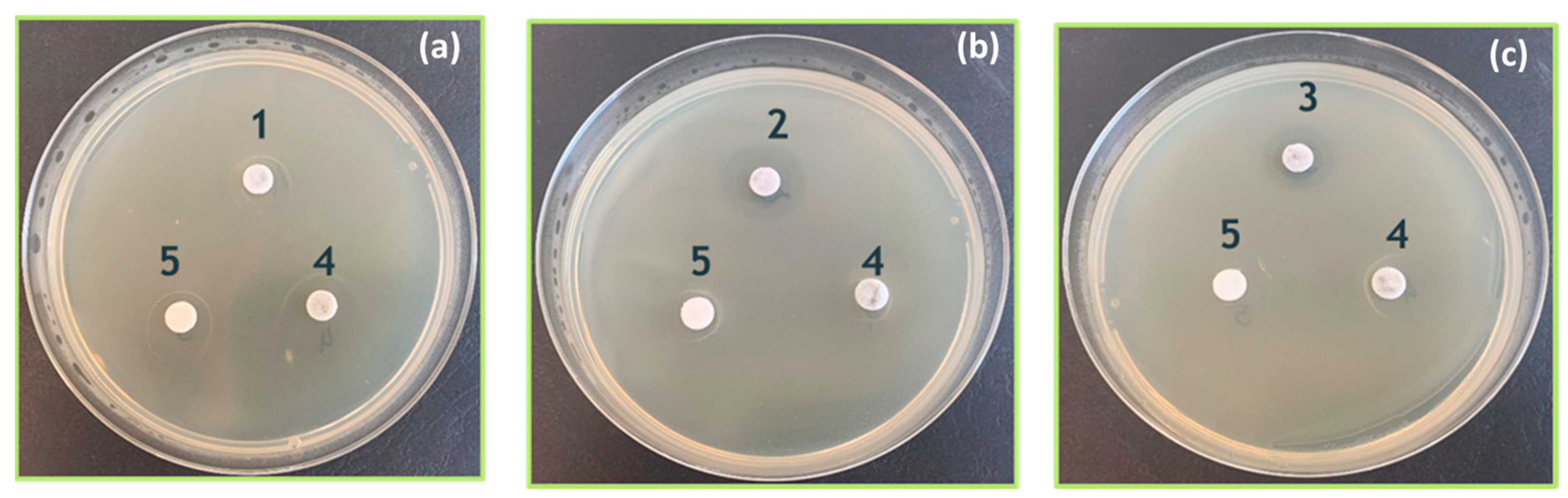
3.4. Antimicrobial Testing
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- use lower metal content and are synthesized through a simpler, scalable, and greener one-step method;
- exhibit equal or superior biological performance, and are suitable for multifunctional biomedical applications, including antibacterial coatings and targeted therapies.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GO | Graphene Oxide |
| RGO | Reduced Graphene Oxide |
| AuNPs | Gold nanoparticles |
| MPB | Meat-peptone broth |
| McF | McFarland standard |
| DLS | Dynamic Light Scattering |
| PDI | Polydispersity index |
| TEM | Transmission Electron Microscopy |
| HRTEM | High Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy |
| SAED | Selected Area Electron Diffraction |
| HaCaT | Human keratinocyte cell culture |
| NBIMCC | Bulgarian national collection for microorganisms and cell cultures |
| FBS | Fetal Bovine Serum |
References
- Novoselov, K.S.; Geim, A.K.; Morozov, S.V.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Dubonos, S.V.; Grigorieva, I.V.; Firsov, A.A. Electric Field Effect in Atomically Thin Carbon Films. Science 2004, 306, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreyer, D.R.; Park, S.; Bielawski, C.W.; Ruoff, R.S. The chemistry of graphene oxide. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarangi, M.K.; Sasmita Padhi, S.; Rath, G.; Nanda, S.S.; Yi, D.K. Advances in immunological and theranostic approaches of gold nanoparticles—A review. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2023, 153, 110858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dykman, L.; Khlebtsov, B.; Khlebtsov, N. Drug delivery using gold nanoparticles. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2025, 216, 115481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Lin, Y. Graphene and graphene oxide: Biofunctionalization and applications in biotechnology. Trends Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniel, M.C.; Astruc, D. Gold Nanomolecular Chemistry, Quantum-Size-Related Properties, and Applications toward Biology, Catalysis, and Nanotechnology. Chem. Rev. 2003, 104, 293–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turcheniuk, K.; Hage, C.-H.; Spadavecchia, J.; Serrano, A.Y.; Larroulet, I.; Pesquera, A.; Zurutuza, A.; Gonzalez, M.; Héliot, L.; Boukaert, J.; et al. Plasmonic photothermal destruction of uropathogenic E. coli with reduced graphene oxide and core/shell nanocomposites of gold nanorods/reduced graphene oxide. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehdipour-Ataei, S.; Aram, E. Nanomaterials for biosensing and imaging applications: Graphene and its derivatives. Microchem. J. 2025, 208, 112479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkevich, J.; Stevenson, P.C.; Hillier, J.A. Study of the Nucleation and Growth Processes in the Synthesis of Colloidal Gold. Discuss. Faraday Soc. 1951, 11, 55–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreaden, E.C.; Alkilany, A.M.; Huang, X.; Murphy, C.J.; El-Sayed, M.A. The golden age: Gold nanoparticles for biomedicine. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2740–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; El-Sayed, I.H.; Qian, W.; El-Sayed, M.A. Cancer cell imaging and photothermal therapy in the near-infrared region by using gold nanorods. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 2115–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.; Wang, S.; Guo, Q.; Zhong, R.; Chen, X.; Xia, X. Anti-Tumor Strategies of Photothermal Therapy Combined with Other Therapies Using Nanoplatforms. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, S.; Wu, X.; Xing, Y.; Lilak, S.; Wu, M.; Zhao, J.X. Enhanced synergetic antibacterial activity by a reduce graphene oxide/Ag nanocomposite through the photothermal effect. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 185, 110616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Zeng, T.H.; Hofmann, M.; Burcombe, E.; Wei, J.; Jiang, R.; Kong, J.; Chen, Y. Antibacterial activity of graphite, graphite oxide, graphene oxide, and reduced graphene oxide: Membrane and oxidative stress. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 6971–6980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podsiadlo, P.; Sinani, V.A.; Bahng, J.H.; Kam, N.W.; Lee, J.; Kotov, N.A. Layer-by-layer assembly of nanoscale polyelectrolytes and reduced graphene oxide for biomedical applications. Langmuir 2008, 24, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammar, M.M.; Ali, R.; Elaziz, N.A.A.; Habib, H.; Abbas, F.M.; Yassin, M.T.; Maniah, K.; Abdelaziz, R. Nanotechnology in oncology: Advances in biosynthesis, drug delivery, and theranostics. Discov. Oncol. 2025, 16, 1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, G. Large Clusters and Colloids: Metals in the Embryonic State. Chem. Rev. 1992, 92, 1709–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuy, P.T.; Hue, B.T.C.; Sang, N.X.; Thuy, L.T.T.; Lieu, P.L. Synthesis of zinc oxide-doped reduced graphene oxide (rGO) nanocomposites on visible light-driven photocatalytic and antibacterial activity applications. Nano Express 2024, 5, 045018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, W.; Zhao, Z.; Hu, H.; Gogotsi, Y.; Qiu, J. Highly controllable and green reduction of graphene oxide to flexible graphene film with high strength. Mater. Res. Bull. 2013, 48, 4797–4803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| No. | Composition | RGO [g/L] | AuNPs [g/L] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sample 1 | RGO/Au 0.125/0.175 g/L | 0.125 | 0.175 |
| Sample 2 | RGO/Au 0.250/0.175 g/L | 0.250 | 0.175 |
| Sample 3 | RGO/Au 0.500/0.175 g/L | 0.5 | 0.175 |
| Sample 4 | RGO 0.500 g/L | 0.5 | - |
| Sample 5 | Au 0.175 g/L | - | 0.175 |
| COD | Spac. Gr. | Phase | hkl | D [Å] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| #96-101-1061 | P63mc | C 2H | 100 | 2.1391 |
| C 2H | 110 | 1.2350 | ||
| #96-900-8464 | Fm-3m | Au | 111 | 2.3546 |
| Au | 200 | 2.0391 | ||
| Au | 222 | 1.1773 |
| PDI | Zeta Potential [mV] | Size [nm] | Composition |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.850 ± 0.007 | –35.03 ± 0.67 | 248.5 ± 18.3 | RGO/Au 0.125/0.175 g/L |
| 0.240 ± 0.099 | –36.96± 0.59 | 589.7 ± 25.7 | RGO/Au 0.250/0.175 g/L |
| 0.300 ± 0.117 | –38.50 ± 1.18 | 564.8 ± 54.1 | RGO/Au 0.500/0.175 g/L |
| 0.433 ± 0.036 | –36.84 ± 1.16 | 835.6 ± 45.9 | RGO 0.500 g/L |
| 0.402 ± 0.147 | –27.72 ± 0.22 | 277.5 ± 7.5 | Au 0.175 g/L |
| 16× | 8× | 4× | 2× | Composition |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Staphylococcus aureus | ||||
| - | - | 8.1 × 106 | 1.72 × 107 | RGO/Au 0.125/0.175 g/L |
| 1 × 109 | 1 × 109 | 1 × 109 | 3 × 10 | RGO/Au 0.250/0.175 g/L |
| 4 × 101 | 3 × 101 | 2 × 101 | 1 × 10 | RGO/Au 0.500/0.175 g/L |
| 1 × 109 | 1 × 109 | 1 × 109 | 1 × 109 | RGO 0.500 g/L |
| - | - | 1.39 × 107 | 1.31 × 107 | Au 0.175 g/L |
| Escherichia coli | ||||
| - | - | 1.22 × 107 | 1.76 × 107 | RGO/Au 0.125/0.175 g/L |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | RGO/Au 0.250/0.175 g/L |
| 3 × 101 | 0 | 0 | 0 | RGO/Au 0.500/0.175 g/L |
| 1 × 109 | 1 × 109 | 1 × 109 | 1 × 109 | RGO 0.500 g/L |
| - | - | 1.48 × 107 | 1.67 × 107 | Au 0.175 g/L |
| 16× | 8× | 4× | 2× | Composition |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Staphylococcus aureus | ||||
| 1 × 109 | 1 × 109 | 1 × 109 | 1 × 109 | RGO/Au 0.125/0.175 g/L |
| 1 × 109 | 1 × 109 | 1 × 109 | 1 × 109 | RGO/Au 0.250/0.175 g/L |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | RGO/Au 0.500/0.175 g/L |
| 1 × 109 | 1 × 109 | 1 × 109 | 1 × 109 | RGO 0.500 g/L |
| 1 × 109 | 1 × 109 | 1 × 109 | 1 × 109 | Au 0.175 g/L |
| Escherichia coli | ||||
| 1 × 109 | 1 × 109 | 1 × 109 | 1 × 109 | RGO/Au 0.125/0.175 g/L |
| 1 × 109 | 1 × 109 | 1 × 109 | 1 × 109 | RGO/Au 0.250/0.175 g/L |
| 5.7 × 106 | 0 | 0 | 0 | RGO/Au 0.500/0.175 g/L |
| 1 × 109 | 1 × 109 | 1 × 109 | 1 × 109 | RGO 0.500 g/L |
| 1 × 109 | 1 × 109 | 1 × 109 | 1 × 109 | Au 0.175 g/L |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martinov, B.; Dimitrov, D.; Foteva, T.; Kostadinova, A.; Staneva, A. Structural Characterization, Cytotoxicity and Microbiological Activity of One-Step-Synthesized RGO/AuNPs Nanocomposites. Materials 2025, 18, 4464. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194464
Martinov B, Dimitrov D, Foteva T, Kostadinova A, Staneva A. Structural Characterization, Cytotoxicity and Microbiological Activity of One-Step-Synthesized RGO/AuNPs Nanocomposites. Materials. 2025; 18(19):4464. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194464
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartinov, Boris, Dimitar Dimitrov, Tsvetelina Foteva, Aneliya Kostadinova, and Anna Staneva. 2025. "Structural Characterization, Cytotoxicity and Microbiological Activity of One-Step-Synthesized RGO/AuNPs Nanocomposites" Materials 18, no. 19: 4464. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194464
APA StyleMartinov, B., Dimitrov, D., Foteva, T., Kostadinova, A., & Staneva, A. (2025). Structural Characterization, Cytotoxicity and Microbiological Activity of One-Step-Synthesized RGO/AuNPs Nanocomposites. Materials, 18(19), 4464. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194464







