Research Progress on the Utilization of Semi-Dry Calcium-Based Desulfurization Dross in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Physical and Chemical Properties of Desulfurization Dross of Semi-Dry Method
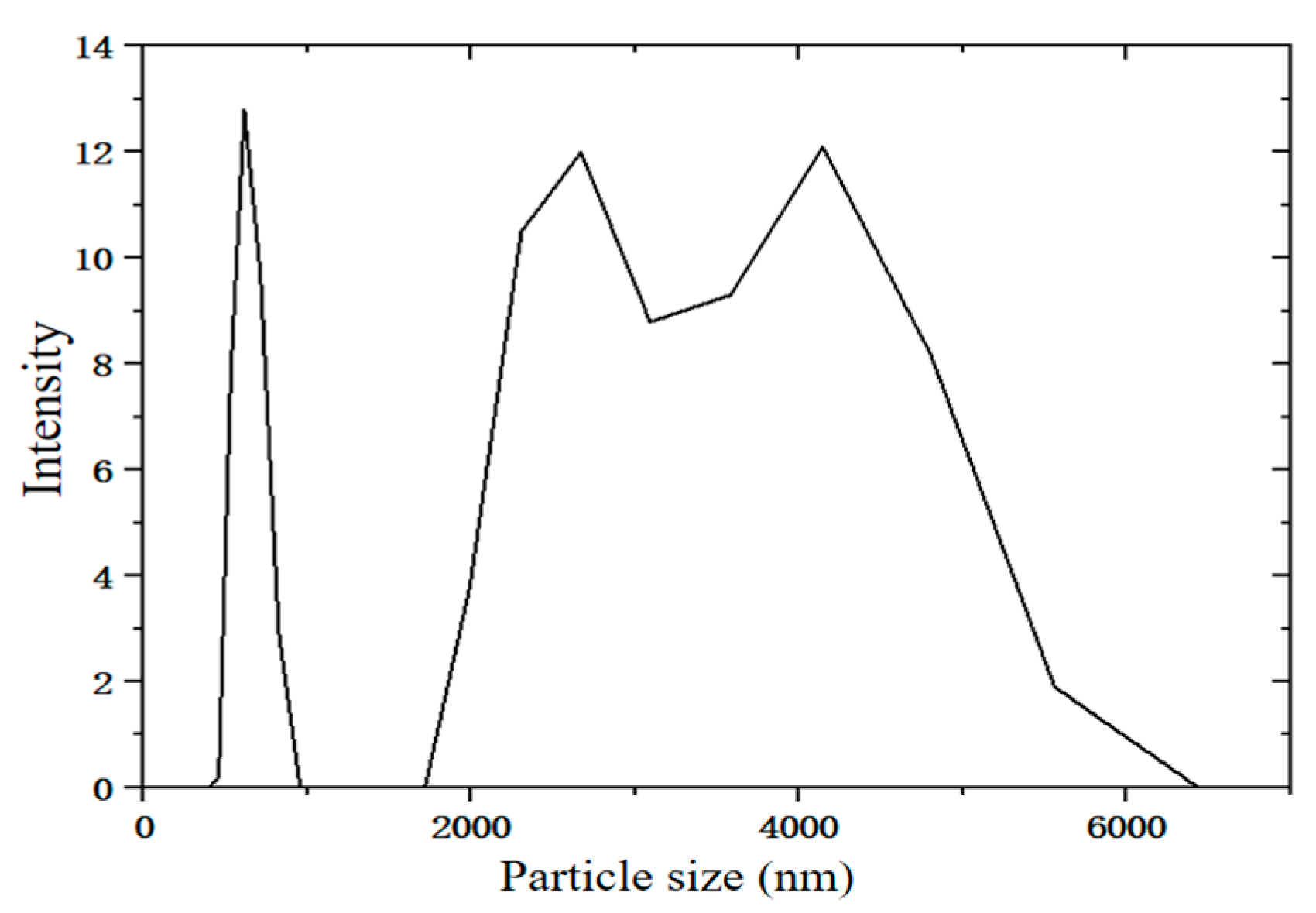
2.1. Analysis of Particle Size of Desulfurization Dross Provided by a Company in Ma’anshan
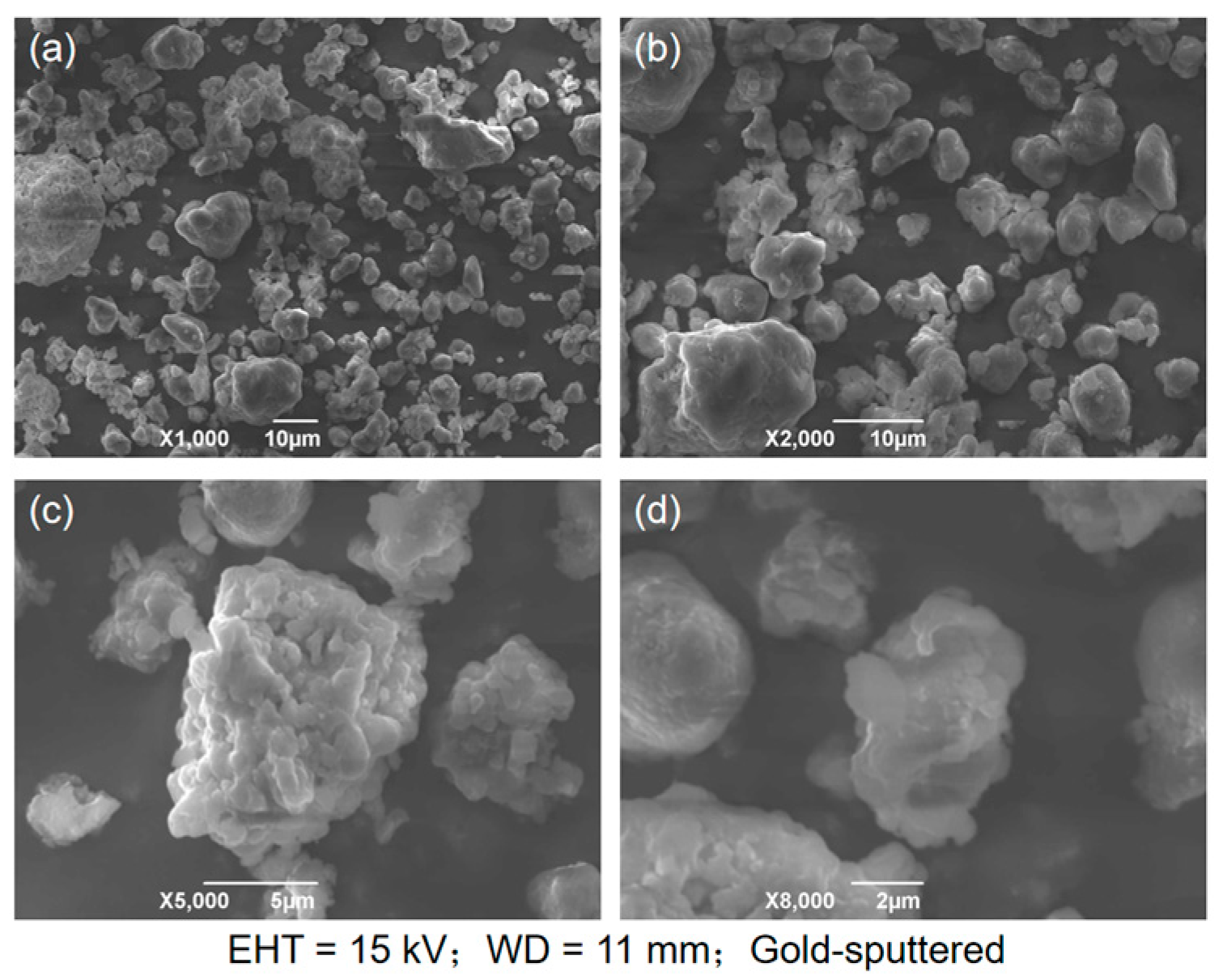
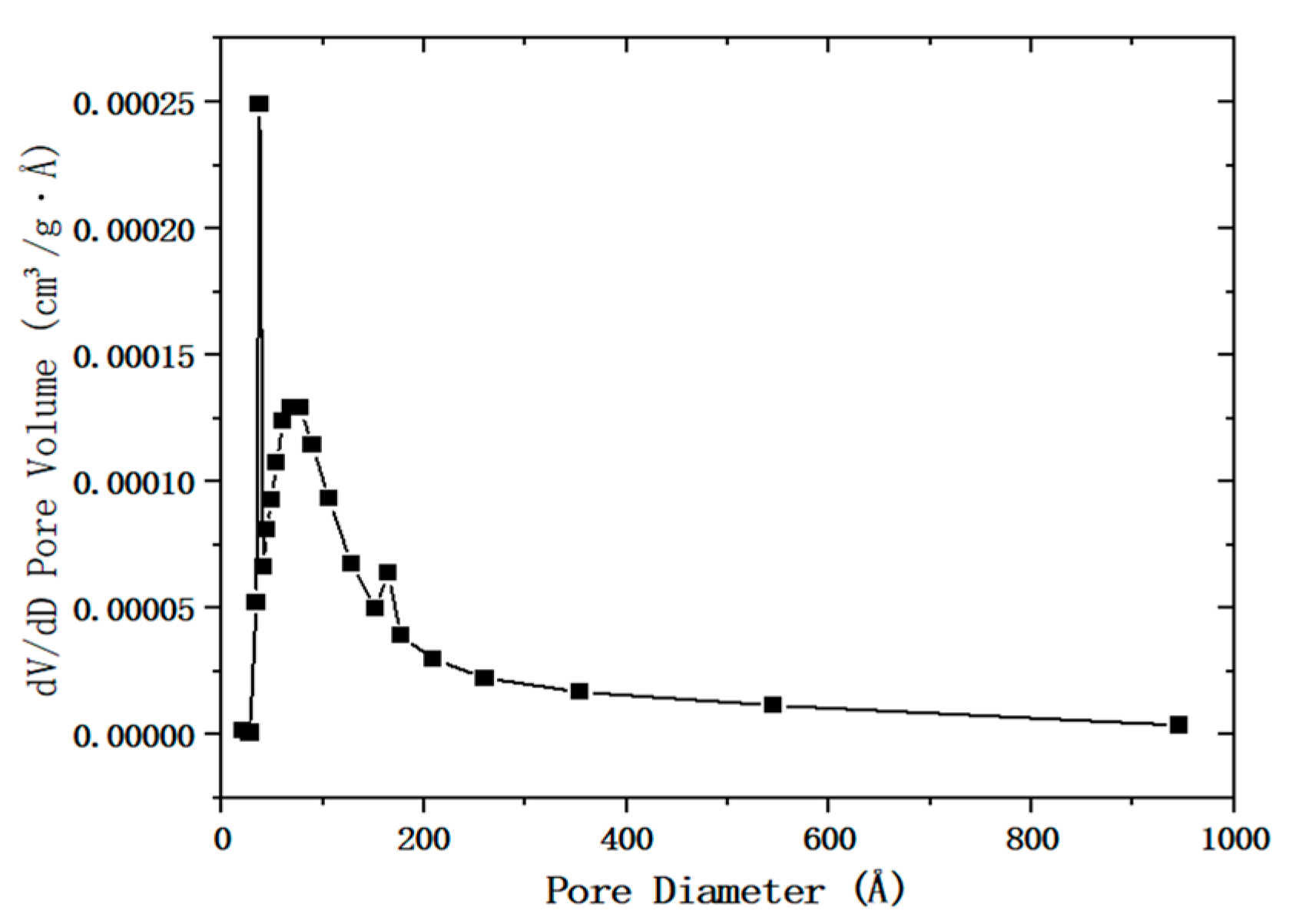
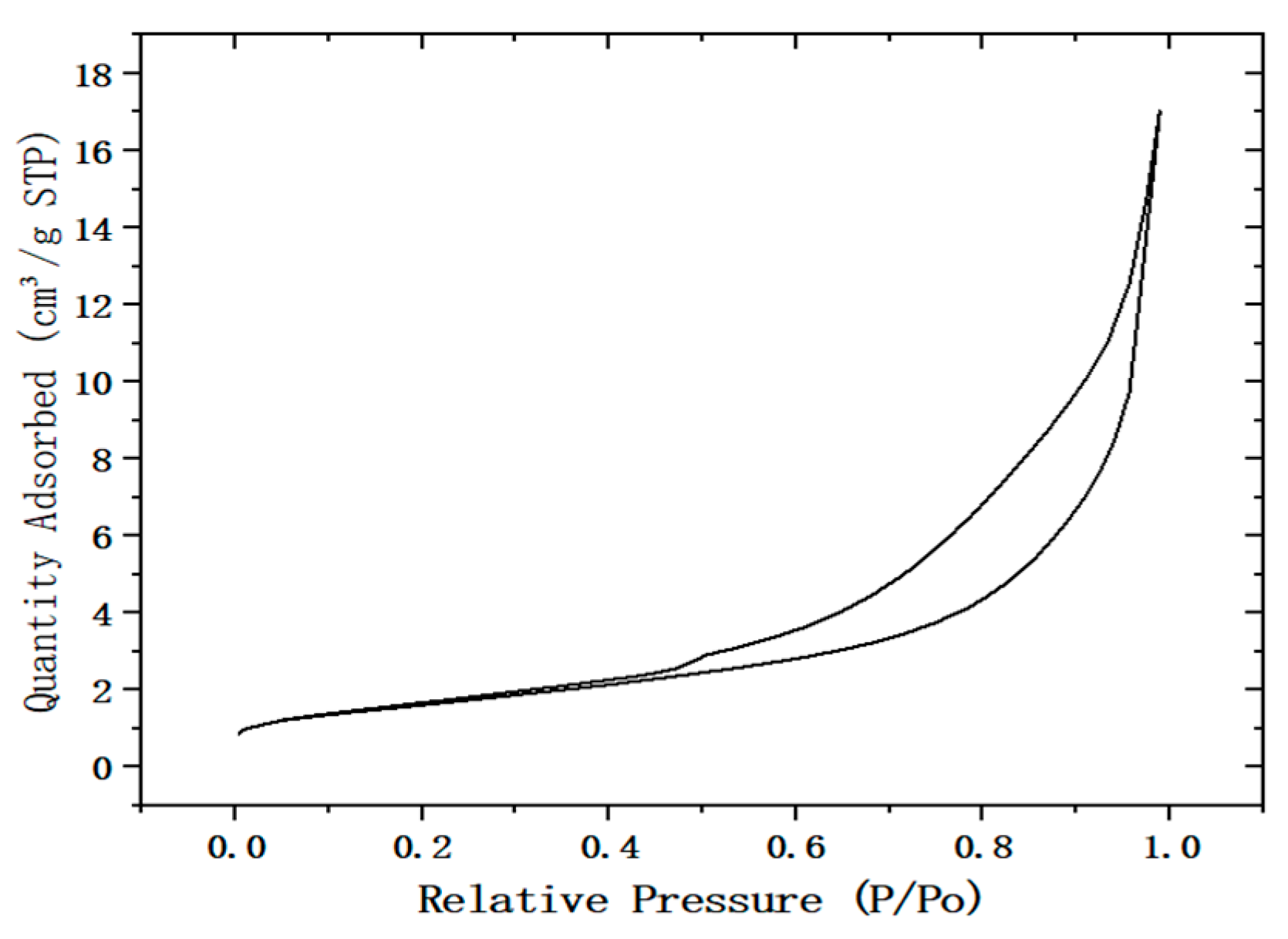
2.2. Shape Analysis of Desulfurization Dross
2.3. Component Analysis of Desulfurization Dross Provided by a Company in Ma’anshan
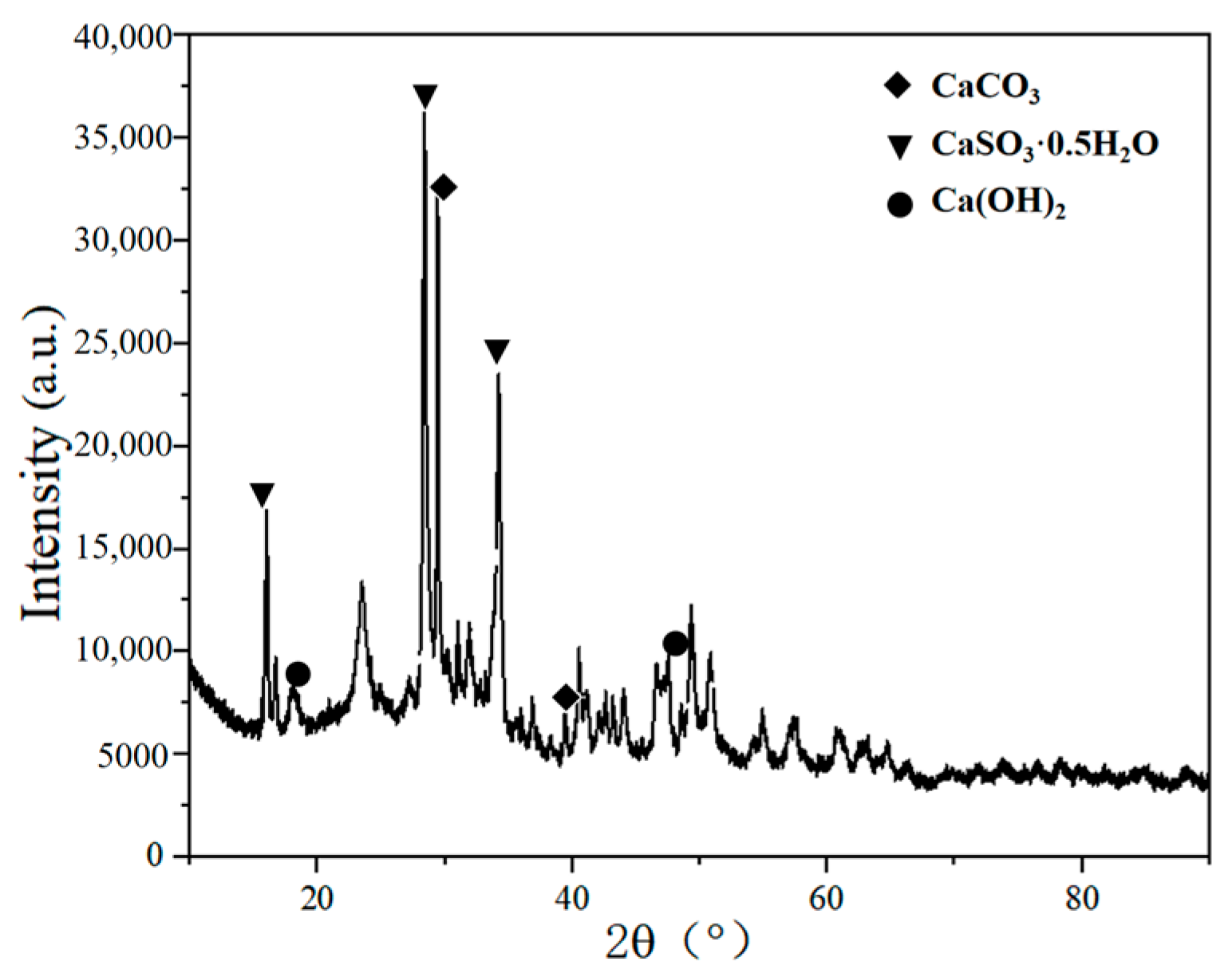
3. Resource Utilization for Semi-Dry Desulfurization Dross
3.1. Building Material Field

3.2. Agricultural Field
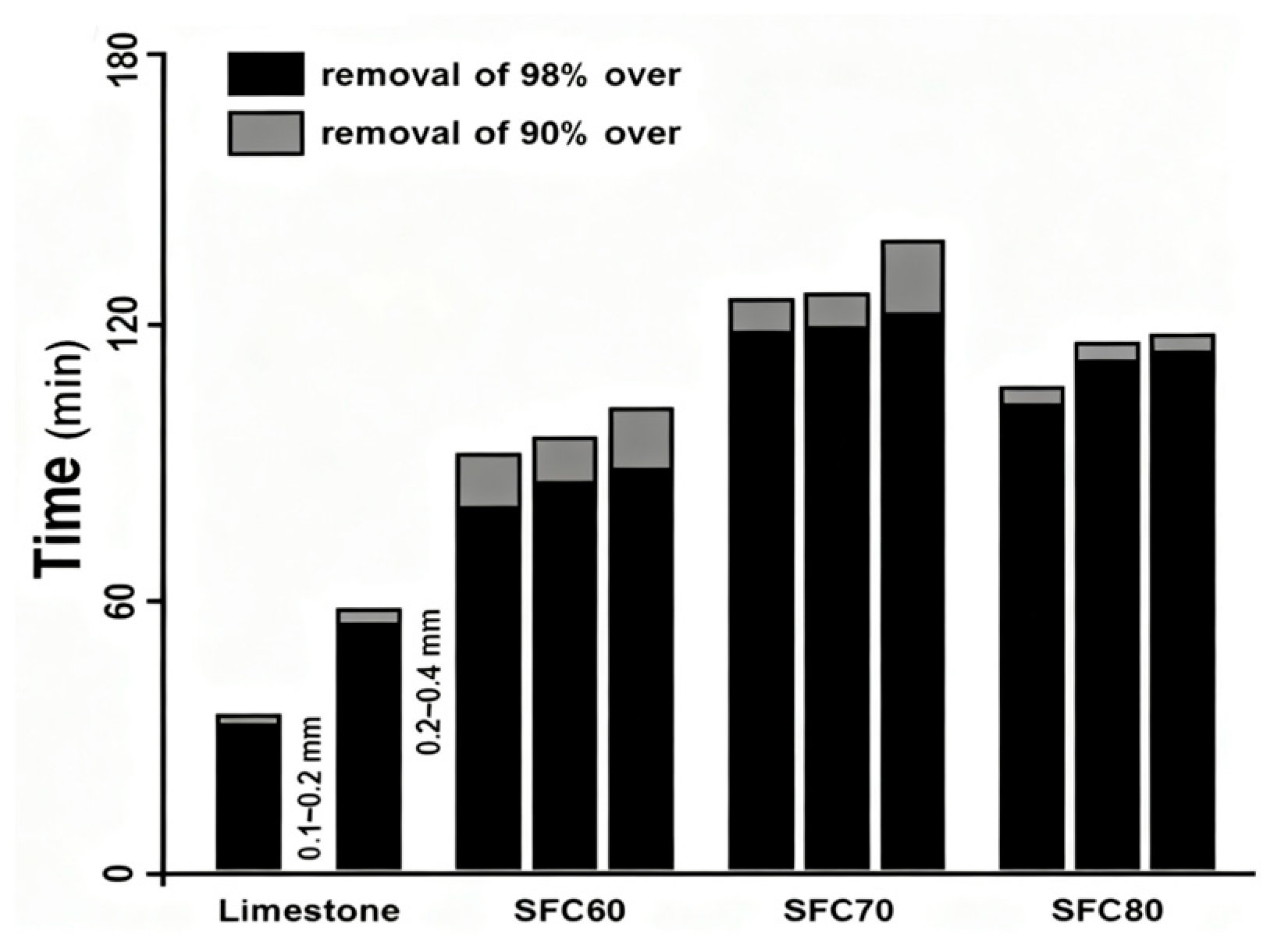
3.3. Wet Flue Gas Desulfurization
3.4. Treatment for Sludge and Wastewater
3.5. High-Value-Added Utilization
3.6. Environmental Risk
4. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qian, H.Q.; Xu, S.D.; Cao, J.; Ren, F.Z.; Wei, W.D.; Meng, J.; Wu, L.B. Air pollution reduction and climate co-benefits in China’s industries. Nat. Sustain. 2021, 4, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, B.F. Spatial characteristics of carbon dioxide emission in Chinese cities and analysis of synergistic control with sulfur dioxide. China’s Energy 2012, 34, 33–37. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.X.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zhang, H. Spatial and temporal distribution of sulfur dioxide and main emission sources in China. China Environ. Sci. 2023, 43, 5678–5686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenpeace Environment Trust (GET). 2020. Ranking the World’s Sulfur Dioxide (SO2) Hotspots: 2019–2020. Available online: https://storage.googleapis.com/planet4-international-stateless/2020/10/fa64275b-so2report.pdf (accessed on 20 July 2025).
- China’s Environmental Bulletin. 2022. Available online: https://www.cnemc.cn/jcbg/zghjzkgb/202206/P020220624327755600688.pdf (accessed on 20 September 2025).
- McLinden, C.A.; Fioletov, V.; Shephard, M.W.; Krotkov, N.; Li, C.; Martin, R.V.; Moran, M.D.; Joiner, J. Space-based detection of missing sulfur dioxide sources of global air pollution. Nat. Geosci. 2016, 9, 496–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.C.; Liu, M.W. Evolution and Governance of Urban Air Pollution in China: Perspectives from Environmental Sociology. J. Minzu Univ. China (Philos. Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2020, 475, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Analysis of current situation and improvement suggestions for sulfur dioxide monitoring in ambient air. Clean. World 2024, 40, 108–110. [Google Scholar]
- Ai, Y.; Chu, X.Y.; Liu, Y.H.; Li, M.; Wu, P.F.; Ma, X.Q. Effects of acid rain on soil microorganisms during decomposition of Chinese fir litter. J. For. Environ. 2025, 45, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.K.; Hou, Q.Y.; Yang, Z.F.; Yu, T.; Wang, J.X. Distribution characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metal elements in sediments of Pearl River Delta water system. Chin. J. Ecol. 2025, 44, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Y.Y.; Zhang, X.; Jin, Y.B.; Zhao, B.N.; Li, J. Effects of simulated acid rain and freeze–thaw cycles on compressive/flexural strength and heavy metal solidification of geopolymer mortar. J. South-Cent. Minzu Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.W. Acid rain erosion resistance of steel slag pervious pavement. Shandong Jiaotong Keji 2025, 2, 106–109+116. [Google Scholar]
- National Bureau of Statistics. Statistical Communiqué of the People’s Republic of China on National Economic and Social Development for 2021 [EB/OL]. (2022-02-28). Available online: https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1726005152208486329&wfr=spider&for=pc (accessed on 19 July 2025).
- Liu, X. Interpretation of the “Law of the People’s Republic of China on the Prevention and Control of Environmental Pollution by Solid Waste”. Rural. Pract. Technol. 2022, 1, 19–20. [Google Scholar]
- Du, J.Z.; Cao, S.A. Current status and progress of wet flue gas desulfurization technology. Appl. Chem. Ind. 2019, 48, 1495–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Han, J.; Liu, Y.; Dou, Z.; Zhang, T.A. Summary of research progress on industrial flue gas desulfurization technology. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 281, 119849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.L.; Chen, H.; You, Y.F.; Cao, C.L.; Luo, Y.J.; Yang, S.W. Study on physical and chemical properties of three typical dry desulfurization ashes. Mod. Chem. Ind. 2022, 42, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.J.; Lu, G.; Zhao, R.Z.; Zhang, Q.L.; Peng, J.M. High-efficiency conversion and resource utilization technology of semi-dry desulfurization ash. New Technol. New Process 2024, 10, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, D.Y.; Wang, Y.; Ye, K.H.; Xing, Y.; Su, W.; Duan, S.Y. Progress in resource utilization of calcium-based semi-dry desulfurization ash from iron and steel industry. Chin. J. Eng. 2024, 46, 567–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.P.; Cheng, Q. Comparison of CFB and SDA semi-dry desulfurization technologies. Petrochem. Equip. 2022, 25, 14–16. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.H.; Wang, D.; Zhu, F.; Qiu, M.Y.; Dong, Y.P.; Shi, G. Treatment and disposal of flue gas desulfurization by-products. Hebei Metall. 2020, 7, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.P. Exploration on comprehensive utilization of semi-dry sintering flue gas desulfurization ash. Resour. Econ. Environ. Prot. 2016, 9, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Ren, A.L.; Cui, S.L.; Guo, B.; Gong, L.P.; Guo, L. Leaching Characteristics of Trace Elements in Calcium-Based Desulfurization Ash from Sintering Flue Gas. J. Saf. Environ. 2010, 10, 36–40. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.L. Analysis of Thallium Pollution and Control Measures in the Iron and Steel Industry. Fujian Metall. 2024, 53, 71–74. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Huang, Y.J.; Li, Z.Y.; Gao, J.W.; Liu, J.; Qi, S.J.; Zhao, J.Q. Physicochemical properties of two kinds of desulfurization ashes and their application tests in wet desulfurization. Sinter. Pelletizing 2024, 49, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.L.; Cheng, L.M.; Shi, Z.L.; Zhang, W.G. Experimental study on preparation of sulphoaluminate cement clinker from CFB high-calcium desulfurization ash and slag. Energy Eng. 2021, 42, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.S.; Wang, D.S.; Zhang, D.K.; Ma, G.Y.; Yu, S.J.; Yang, D.Z. Study on comprehensive utilization of desulfurization ash in sintering flue gas by Angang. Angang Technol. 2011, 6, 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.J. Sulfur dioxide emissions in China and their environmental impacts (continued). Sulphur Phosphorus Bulk Mater. Handl. Relat. Eng. 2021, 5, 43–48+6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Dong, Q.G.; Chen, N.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Z.Y. Effects of semi-dry desulfurization ash with different pretreatment methods on properties of autoclaved aerated concrete. New Build. Mater. 2022, 49, 115–119. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.L.; Jin, Y.C. Study on Technology of Recycling Semi-Dry Sintering Flue Gas Desulfurization Ash into Sintering Process. In Proceedings of the 11th China Iron and Steel Annual Conference, Beijing, China, 21–22 November 2017; pp. 275–279. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, G.W.; Liu, M.; Duan, Y.F.; Hu, P.; Li, T.; Li, Y.S. Effect of flue gas components on the NO removal and element mercury oxidation performance of Mn-modified low-temperature catalyst. Int. J. Chem. React. Eng. 2021, 19, 1031–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Bian, J.F.; Ren, A.L.; Ren, P.; Zhang, Z. Physical and chemical properties of semi-dry desulfurization ash from sintering flue gas. J. Cent. South Univ. (Sci. Technol.) 2010, 41, 387–392. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, L.; Liu, Q.C.; Fang, S.H.; Ren, S.; Liu, L.; Kong, M.; Zhu, B.H. Oxidative modification of semi-dry sintering flue gas desulfurization ash. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2016, 10, 3147–3151. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; You, R.R.; Clark, M.; Yu, Y. Pb(Ⅱ) removal from aqueous solution by a low-cost adsorbent dry desulfurization slag. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 314, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, N.X. Resource utilization based on characteristics of desulfurization ash. Fujian Build. Mater. 2025, 2, 89–91+100. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, J.P. Research on current situation of comprehensive utilization of desulfurization ash and slag. Metall. Manag. 2021, 5, 150–151. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.L.; Cui, L.; Ma, C.Y.; Dong, Y.; Xu, X.R. Study on characteristics and comprehensive utilization of dry and semi-dry desulfurization ash. Power Syst. Eng. 2005, 21, 27–29. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.Y.F.; Li, Z.Y.; Hu, Y.M. Study on shrinkage performance of cement-stabilized macadam pavement base with composite desulfurization ash expansive agent in cold regions. Transp. Sci. Technol. 2023, 2, 46–50. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.S.; Chen, J.H.; Su, Q.F.; Zhang, L.B. Analysis of desulfurization ash properties and its influence on asphalt pavement performance. Shanxi Archit. 2021, 47, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, X.; Zuo, S.; Li, J.; Hou, N.; Zuo, H.; Zhou, T. Study of the Design and Mechanical Properties of the Mix Proportion for Desulfurization Gypsum–Fly Ash Flowable Lightweight Soil. Coatings 2023, 13, 1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Xia, Y.H.; Zhang, T.T.; Yang, L.X.; Qian, Y.L. Study on effect of desulfurization ash-based soil stabilizer on properties of stabilized soil. Build. Technol. 2021, 5, 53–58+63. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; La, R.T.; Gao, Y.X.; Li, S.; Ma, P.F. Study on effect of limestone powder on properties of machine-sprayed lightweight plastering gypsum mortar. New Build. Mater. 2020, 47, 41–44. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Y.; Zeng, R.; Tao, C.X.; Lao, L.L.; Xie, Z.F.; Qin, F.A. Research and industrial application of desulfurization ash as substitute for cement raw meal. Cem. Eng. 2023, 1, 1–6+47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.X.; Zhang, S.J.; Du, Q. Practical study on adding desulfurization ash to slag powder admixture. Shanxi Metall. 2023, 46, 15–16+39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- State Administration for Market Regulation. Ground Granulated Blast Furnace Slag Used for Cement, Mortar and Concrete (GB/T 18046-2017) [EB/OL]. (2017-12-29). Available online: https://openstd.samr.gov.cn/bzgk/gb/newGbInfo?hcno=92B4CAB43B6EF6AEE4CCF38DB60C6FB9 (accessed on 23 September 2025).
- Song, Y.M.; Qian, J.S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z. Self-cementing mechanism of CFBC coal ashes at early ages. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. 2008, 23, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carro-López, D.; González-Fonteboa, B.; Eiras-López, J.; Seara-Paz, S. Comparing circulating fluidised bed fly ash and limestone as additions for cement. Mag. Concr. Res. 2019, 71, 1302–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, M. Synthesis and Characterization of Mortars with Circulating Fluidized Bed Combustion Fly Ash and Ground Granulated Blast-Furnace Slag. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 123, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.L.; Wang, D.M.; Ren, F.; Rui, Y. Investigation of Rheological Properties of Fresh Cement Paste Containing Ultrafine Circulating Fluidized Bed Fly Ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 188, 1007–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, L. Feasibility study on using sintered dry desulfurization ash as admixture. Build. Technol. 2022, 6, 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.J.; Yu, L.F.; Kang, M. Research on pretreatment technology of desulfurization ash and slag for concrete. Build. Technol. 2022, 6, 25–28. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Tan, S.Y.; Yu, F.; Qin, Y.; Cui, K.R.; Fang, Y.; Memet·Nurmemet. Experimental study on mix proportion of desulfurization ash concrete based on pseudo-level method. China Concr. Cem. Prod. 2023, 1, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, P. Effect of dry desulfurization ash on properties of cement-stabilized recycled aggregate mixture. China Concr. Cem. Prod. 2023, 7, 95–98+102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Lin, S.H.; Su, Q.F.; Wang, J.C.; Lai, Y.Q.; Lu, M.Y.; Shang, Q.Y. Application research of dry desulfurization ash in lightweight plastering gypsum mortar. New Build. Mater. 2022, 49, 71–74. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, B.; Dong, Q.G. Pilot application study of Baosteel sintering desulfurization ash in autoclaved aerated concrete. Baosteel Technol. 2023, 5, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.S.; Li, J.C.; Zuo, Z.M.K.; Wang, Q.Z.; Lei, G.Y. Study on preparation of lightweight wall materials with high content of semi-dry sintering desulfurization ash. Sinter. Pelletizing 2023, 48, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Huang, Z.; Ding, Y.; Xu, W.; Zhang, M.; Wei, L.B.; Yang, H.R. Feasibility study of grinding circulating fluidized bed ash as cement admixture. Materials 2022, 15, 5610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- State Administration for Market Regulation. Fly Ash Used for Cement and Concrete (GB/T 1596-2017) [EB/OL]. (2017-07-12). Available online: https://openstd.samr.gov.cn/bzgk/gb/newGbInfo?hcno=55F3B96AC1260FCD3C9452FF47C087E5 (accessed on 23 September 2025).
- Hui, C.X.; Li, H.; Lang, M.S.; Luo, L. Resource utilization ways of sintering desulfurization ash. Hebei Metall. 2023, 4, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phoungthong, K.; He, P.J.; Shao, L.M.; Zhang, H. Leachate phytotoxicity of flue gas desulfurization residues from coal-fired power plant. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 19808–19817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, C.J.; Zhang, Y.L.; Tian, J.L.; Wang, Q.; Sun, B.B. Application of by-products from sintering flue gas desulfurization and denitrification in cement. Hebei Metall. 2022, 6, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.J.; Zheng, H.P.; Huang, X.; Xie, K.Z.; Xu, P.Z.; Zhang, R.Z. Effects of soil amendments on root activity and yield of rice in cold waterlogged paddy fields. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2013, 29, 182–187. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Luo, Z.C.; Xiao, X.P.; Qu, D.M.; Luo, X.S.; Luo, Z.Y.; Sun, G.; Hong, X.; Yu, C.X. Effects of soil conditioners on soil properties and rice growth in cold waterlogged paddy fields. Soils 2016, 48, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.T.; Feng, X.X.; Xie, Y.T.; Li, Q.L.; Liu, Z.G. Study on preparation of non-fired planting ceramsite from fly ash and desulfurization ash. Cem. Technol. 2020, 5, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.X.; Han, F.; Liu, C.T. Application of calcium-based desulfurization ash in limestone-gypsum wet desulfurization system. Sinter. Pelletizing 2024, 49, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.Y.; Huang, Y.J.; Gu, L.Q.; Lin, H.Y.; Wang, X.Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.R.; Cao, G.H.; Li, Z.Y. Experimental study on semi-dry desulfurization ash in wet desulfurization. Appl. Chem. Ind. 2022, 51, 3580–3585+3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.S.; Liu, G.Z.; Zhang, Q.X.; Guo, M.G. Dissolution characteristics of pellet desulfurization ash in wet desulfurization. Appl. Chem. Ind. 2021, 50, 2148–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.W.; Jiang, X.Y. Study on adding desulfurization ash for wet desulfurization of sintering flue gas. Shandong Chem. Ind. 2024, 53, 229–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, C.; Seo, J.; Choi, M.; Cho, J.; Ahn, J.; Cho, K. Utilization of CFBC fly ash as a binder to produce in-furnace desulfurization sorbent. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yu, N.; Fang, A.; Liu, B.F.; Ren, N.Q.; Xing, D.F. Co-treatment of potassium ferrate and ultrasonication enhances degradability and dewaterability of waste activated sludge. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 361, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, B.Y.; Yang, J.K.; Shi, Y.F.; Song, J.; Shi, Y.; Xiao, J.; Li, C.; Xu, X.Y.; He, S.; Liang, S.; et al. Roles of iron species and pH optimization on sewage sludge conditioning with Fenton’s reagent and lime. Water Res. 2016, 95, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, M.Q.; Dong, K. Study on the Improvement of Sludge Dewatering Performance by PUWU, Potassium Ferrate and Desulfurization Ash. J. Nanyang Inst. Technol. 2020, 12, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, L.; Tian, Z.M.; Wang, J.G.; Gao, J.P.; Ding, B.; Li, X.J. Study on preparation of ceramsite from desulfurization ash and oily sludge. Fly Ash Compr. Util. 2020, 34, 82–86+90. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, Y.D. Experimental study on treatment of mine water by combined modified desulfurization ash and polyacrylamide. Energy Environ. Prot. 2019, 33, 26–28. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, Y.D. Experimental study on treatment of coal mine water with modified desulfurization ash. Resour. Econ. Environ. Prot. 2018, 11, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, D.A.; Liao, X.; Zhang, X.F.; Teng, A.; Xue, X. A novel resource utilization of the calcium-based semi-dry flue gas desulfurization ash: As a reductant to remove chromium and vanadium from vanadium industrial wastewater. Hazard Mater. 2018, 342, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, G.D.; Wan, X.X.; Liu, X.P.; Shen, F.X.; Wu, Z.G. Experimental study on preparation of high-purity calcium sulfate from dry desulfurization ash. Henan Chem. Ind. 2024, 41, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.Y. Study on the Preparation of High-Value-Added Calcium Carbonate and Calcium Sulfate from Desulfurization Ash. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2020, 40, 616–621. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, W.F.; Zhuang, W.; Lin, T.F.; Chen, H.; Su, Q.F.; Wang, J.C. Preparation and Properties of Natural Rubber/ Flue Gas Desulfurization Ash Composites. Spec. Purp. Rubber Prod. 2023, 44, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.L.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, J.N.; Li, C. Composite catalytic thermal decomposition effect based on boilingfurnace roasting desulfurization ash. Sinter. Pelletizing 2024, 49, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, S.D.; Su Hg Wang, F.; Mao, R. Process analysis of SO2 released by reduction calcination experiment of sintering semi-dry desulfurization ash. J. Iron Steel Res. 2020, 32, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.; Tang, C.Y.; An, X.Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, S.K.; Huang, C.H.; Wang, Z.Q. Study on catalytic upgrading of biomass pyrolysis gas with desulfurization ash based on model compound method. Renew. Energy Resour. 2023, 41, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- State Administration for Market Regulation. Recycled Coarse Aggregate for Concrete (GB/T 25177-2010) [EB/OL]. (2010-09-26). Available online: https://openstd.samr.gov.cn/bzgk/gb/newGbInfo?hcno=408BB2760FDF20C93184F94B53BFC95A (accessed on 23 September 2025).
- Ministry of Transport of the People’s Republic of China. Recycled Coarse Aggregate for Concrete (JTG/T 3650-2020) [EB/OL]. (2020-06-18). Available online: https://www.doc88.com/p-70887883675124.html (accessed on 23 September 2025).
- Standards Policy and Strategy Committee of British. Recycled Coarse Aggregate for Concrete (BS ISO 17318:2015) [EB/OL]. (2015-06-01). Available online: https://img.antpedia.com/standard/files/pdfs_ora/20230612/bs/BS ISO/BS ISO 17318-2015.pdf (accessed on 23 September 2025).
- Lai, J.L.; Yin, P.J.; Wang, X.Y.; Li, H.Q.; Tian, G.; Ren, X.L. Research on the current standard system of soil conditioners in China. China Stand. 2024, 12, 69–72. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Huang, X. Interpretation of the new National Food Safety Standard—Limits of Contaminants in Foods. China Food Saf. Mag. 2023, 5, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Classification of Desulfurization Dross | Wet Flue Gas Desulfurization Dross | Semi-Dry Desulfurization Dross | Dry Desulfurization Dross |
|---|---|---|---|
| Desulfurization process source | Lime-dross method | CFB; SDA | Activated carbon adsorption; dry shot blasting; dense-phase tower (DFA) |
| Comparison Dimension | SDA | DFA |
|---|---|---|
| Key Equipment | Lime slurry is atomized and contacts flue gas in parallel flow; after reaction, dry desulfurization dross is formed through drying | Powdered Ca(OH)2 desulfurizer is fully mixed with flue gas in countercurrent flow in a dense-phase tower. The reaction is enhanced by means of a high-concentration bed |
| Process Limitations | Rotary atomizer | Dense-phase reaction tower + high-efficiency dust collector |
| Process Limitations | Wear of the atomizer leads to high operating costs | Local wall sticking is prone to occur in the dense-phase bed, requiring control of wind speed and bed concentration |
| Chemical Composition | CaO | SO3 | Cl | Fe2O3 | K2O | MgO | SiO2 | TiO2 | Na2O | Al2O3 | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content (%) | 55.49 | 31.33 | 4.10 | 3.47 | 1.82 | 0.87 | 0.82 | 0.59 | 0.51 | 0.49 | 0.51 |
| Standard error | 0.25 | 0.23 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.043 | 0.041 | 0.03 | 0.025 | 0.025 | 0.025 |
| Group | A | B | C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compressive Strength Before Freeze–thaw Cycles/MPa | 6.3 | 5.4 | 6.6 |
| Tensile Strength | 0.42 | 0.30 | 0.40 |
| Compressive Strength After Freeze–thaw Cycles (5 Freeze–thaw Cycles) | 5.8 | - | 5.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, M.; Wang, R.; Yan, S.; Du, X.; Yin, Z.; Wu, G.; Li, J.; Li, C. Research Progress on the Utilization of Semi-Dry Calcium-Based Desulfurization Dross in China. Materials 2025, 18, 4455. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194455
Pan M, Wang R, Yan S, Du X, Yin Z, Wu G, Li J, Li C. Research Progress on the Utilization of Semi-Dry Calcium-Based Desulfurization Dross in China. Materials. 2025; 18(19):4455. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194455
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Min, Ruiying Wang, Shejiao Yan, Xiangqian Du, Zhenxing Yin, Guangchao Wu, Jiamao Li, and Canhua Li. 2025. "Research Progress on the Utilization of Semi-Dry Calcium-Based Desulfurization Dross in China" Materials 18, no. 19: 4455. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194455
APA StylePan, M., Wang, R., Yan, S., Du, X., Yin, Z., Wu, G., Li, J., & Li, C. (2025). Research Progress on the Utilization of Semi-Dry Calcium-Based Desulfurization Dross in China. Materials, 18(19), 4455. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194455








