Thermodynamic Evaluation and Optimization of the CaO-TiO2-SiO2 Ternary System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Review of Literature Data
2.1. CaO-TiO2 System
2.2. CaO-SiO2 System
2.3. SiO2-TiO2 System
2.4. CaO-TiO2-SiO2 System
3. Thermodynamic Modeling
3.1. Unary Components
3.2. Liquid Phase
3.3. Binary Intermediate Compounds
3.4. Ternary Intermediate Compound
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tulyaganov, D.U.; Dimitriadis, K.; Agathopoulos, S.; Fernandes, H.R. Glasses and glass-ceramics in the CaO–MgO–SiO2 system: Diopside containing compositions—A brief review. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2023, 612, 122351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, A.Q.; Zhang, W.J.; Cheng, X.Y.; Liu, Z.F. Effects of B2O3 contents on crystallization behaviors and dielectric properties of CaO-B2O3-SiO2 glass ceramics. Key Eng. Mater. 2016, 680, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, D.P.; Das, S.K. The influence of TiO2 content on the properties of glass ceramics: Crystallization, microstructure and hardness. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 4127–4134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.; Kim, K. Effect of TiO2 content on crystallization behavior of CaO–Al2O3–SiO2–ZnO glass-ceramic glaze. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 13677–13686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.; Kim, K.; Han, K.-S. Effect of SiO2/TiO2 ratio on the crystallization behavior of CaO-TiO2-SiO2 glass-ceramic system for opaque white glaze. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2024, 629, 122863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Ding, H.; Ao, W.; Liu, Y.; Chang, L.; Zhang, J. Preparation of a CaCO3-TiO2 composite based opaque glaze: Insight into the mechanism of opacification and glaze yellowing inhibition. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2020, 40, 6171–6180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yan, L.; Ye, L.; Xiao, G.; Wang, K.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, L.; Du, Y. Thermodynamic evaluation and optimization of the K2O-Al2O3-SiO2 system. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2024, 107, 8732–8745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Li, C.; Yang, J.; Xiao, G.; Deng, Z.; Liu, L.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, Y. Thermodynamic Assessment of the P2O5-Na2O and P2O5-MgO Systems. Materials 2024, 17, 2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kattner, U.R. The CALPHAD method and its role in material and process development. Tecnol. Metal. Mater. Min. 2016, 13, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umezu, S. Investigation on the iron blast furnace slag containing titanium. J. Min. Metall. Inst. Jpn. 1930, 46, 867. [Google Scholar]
- Fukusima, M. The systems SiO2-CaO-TiO2, CaO·SiO2-CaO·SiO2·TiO2, CaO·SiO2·TiO2-TiO2, CaO·SiO2-CaO·TiO2, and CaO·TiO2-TiO2. Kinsoku No Kenkyu Tokyo 1934, 11, 377–395. [Google Scholar]
- Von Wartenberg, H.; Reusch, H. Melting point diagrams of highly fireproof oxides. VII. systems with CaO and BeO. Z. Fuer Anorg. Chem. 1937, 230, 257–276. [Google Scholar]
- Devries, R.; Roy, R.; Osborn, E. Phase Equilibria in the System CaO-TiO2. J. Phys. Chem. 1954, 58, 1069–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coughanour, L.; Roth, R.; Deprosse, V. Phase equilibrium relations in the systems Lime-Titania. J. Res. Natl. Bur. Stand. 1954, 52, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, R.S. Revision of the phase equilibrium diagram of the binary system calcia-titania, showing the compound Ca4Ti3O10. J. Res. Natl. Bur. Stand. 1958, 61, 437–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongejan, A.; Wilkins, A. A re-examination of the system CaO-TiO2 at liquidus temperatures. J. Less Common Met. 1970, 20, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, S.; Muan, A. Phase relations in the system CaO-iron oxide-TiO2 in air. Am. Mineral. J. Earth Planet. Mater. 1971, 56, 1332–1346. [Google Scholar]
- Tulgar, H. Solid state relationships in the system calcium oxide-titanium dioxide. Istanbul Tech. Univ. Bul. 1976, 29, 111–129. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, W.; Wu, L.; Navrotsky, A. Combined experimental and computational investigation of thermodynamics and phase equilibria in the CaO-TiO2 system. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2018, 101, 1361–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylor, B.; Cook, O. High-temperature heat contents of the metatitanates of calcium, iron and Magnesium. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1946, 68, 1003–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, E. Low-Temperature Heat Capacities and Entropies at 298.16K. of Some Titanates of Aluminum, Calcium, Lithium and Zinc. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1955, 77, 2150–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.; Schmalzried, H. The free energy of formation of some titanates, silicates, and magnesium aluminate from measurements made with galvanic cells involving solid electrolytes. J. Phys. Chem. 1964, 68, 2444–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takayama-Muromachi, E.; Navrotsky, A. Energetics of compounds (A2+B4+O3) with the perovskite structure. J. Solid State Chem. 1988, 72, 244–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyot, F.; Richet, P.; Courtial, P.; Gillet, P. High-temperature heat capacity and phase transitions of CaTiO3 perovskite. Phys. Chem. Miner. 1993, 20, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodfield, B.F.; Shapiro, J.L.; Stevens, R.; Boerio-Goates, J.; Putnam, R.L.; Helean, K.B.; Navrotsky, A. Molar heat capacity and thermodynamic functions for CaTiO3. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 1999, 31, 1573–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putnam, R.L.; Navrotsky, A.; Woodfield, B.F.; Boerio-Goates, J.; Shapiro, J.L. Thermodynamics of formation for zirconolite (CaZrTi2O7) from T = 298.15K to T = 1500K. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 1999, 31, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, R.; Yashima, M. Space group and crystal structure of the perovskite CaTiO3 from 296 to 1720K. J. Solid State Chem. 2005, 178, 2867–2872. [Google Scholar]
- Yashima, M.; Ali, R. Structural phase transition and octahedral tilting in the calcium titanate perovskite CaTiO3. Solid State Ion. 2009, 180, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, K.; Abraham, K. Thermodynamic properties of calcium titanates: CaTiO3, Ca4Ti3O10, and Ca3Ti2O7. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2009, 41, 816–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navi, N.U.; Shneck, R.Z.; Shvareva, T.Y.; Kimmel, G.; Zabicky, J.; Mintz, M.H.; Navrotsky, A. Thermochemistry of (CaxSr1-x)TiO3, (BaxSr1-x)TiO3, and (BaxCa1-x)TiO3 perovskite solid solutions. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2012, 95, 1717–1726. [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman, L. Calculation of multicomponent ceramic phase diagrams. Physica B+C 1988, 150, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschen, M.; Decapitani, C. Experimental determination and computation of the liquid miscibility gap in the system CaO-MgO-SiO2-TiO2. J. Phase Equilib. 1999, 20, 593–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daněk, V.; Nerád, I. Phase Diagram and Structure of Melts of the System CaO-TiO2-SiO2. Chem. Pap. 2002, 56, 241–246. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, L.; Li, C.; Yang, J.; Xiao, G.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, L.; Masset, P.J. Critical evaluation and thermodynamic assessment of the Al2O3–TiO2–CaO ternary system. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 41349–41363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rankin, G. The Ternary System CaO-Al2O3-SiO2. Am. J. Sci. 1915, 39, 1–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greig, J. Immiscibility in silicate melts; Part I. Am. J. Sci. 1927, 5, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborn, E.F. The compound merwinite (3CaO·MgO·2SiO2) and its stability relations within the system CaO-MgO-SiO2 (preliminary report). J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1943, 26, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troemel, G.; Fix, W.; Heinke, R. Hochtemperaturuntersuchungen bis 1900 °C an Calciumorthosilikat und Tricalciumsilikat. Tonind.-Ztg. Ker. Rundsch. 1969, 93, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Tewhey, J.D.; Pc, H. The two phase region in the CaO-SiO2 system: Experimental data and thermodynamic analysis. Phys. Chem. Glas. 1979, 20, 41–53. [Google Scholar]
- Kay, D.; Taylor, J. Activities of silica in the lime+alumina+silica system. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1960, 56, 1372–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Richardson, F. Solubility of calcium sulphide and activities in lime-silica melts. J. Iron Steel Inst. 1962, 200, 373. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, J.; Dinsdale, A. Thermodynamic and phase diagram data for the CaO-SiO2 system. Calphad 1990, 14, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillert, M.; Sundman, B.; Wang, X. An assessment of the CaO-SiO2 system. Metall. Trans. B 1990, 21, 303–312. [Google Scholar]
- Hillert, M.; Sundman, B.; Wang, X.; Barry, T. A reevaluation op the rankinite phase in the CaO-SiO2 system. Calphad 1991, 15, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, G.; Wu, P.; Blander, M.; Pelton, A.D. Critical evaluation and optimization of the thermodynamic properties and phase diagrams of the MnO-SiO2 and CaO-SiO2 systems. Can. Metall. Q. 1994, 33, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Q.; Chou, K.C. Thermodynamic Modeling of CaO-CaF2 and CaO-SiO2 Systems. High Temp. Mater. Process. 2015, 34, 95–100. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.; Hillert, M.; Wang, X. Thermodynamic assessment of the CaO-MgO-SiO2 system. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1995, 26, 2293–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunting, E.N. Phase equilibria in the systems TiO2, TiO2-SiO2 and TiO2-Al2O3. Bur. Stand. J. Res. 1933, 11, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricker, R.W.; Hummel, F. Reactions in the System TiO2-SiO2; revision of the phase diagram. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1951, 34, 271–279. [Google Scholar]
- Agamawi, Y.; White, J. The System Al2O3-TiO2-SiO2. Br. Ceram. Trans. 1952, 51, 293–325. [Google Scholar]
- Devries, R.; Roy, R.; Osborn, E. The System TiO2-SiO2. Br. Ceram. Trans. 1954, 53, 525–540. [Google Scholar]
- Don Mctaggart, G.; Andrews, A. Immiscibility area in the system TiO2-ZrO2-SiO2. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1957, 40, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirillova, S.; Almjashev, V.; Gusarov, V. Phase relationships in the SiO2-TiO2 system. Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 56, 1464–1471. [Google Scholar]
- Ilatovskaia, M.; Fabrichnaya, O. Liquid Immiscibility and Thermodynamic Assessment of the Al2O3-TiO2-SiO2 System. J. Phase Equilib. Diffus. 2022, 43, 15–31. [Google Scholar]
- Decapitani, C.; Kirschen, M. A generalized multicomponent excess function with application to immiscible liquids in the system CaO-SiO2-TiO2. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1998, 62, 3753–3763. [Google Scholar]
- Boulay, E.; Nakano, J.; Turner, S.; Idrissi, H.; Schryvers, D.; Godet, S. Critical assessments and thermodynamic modeling of BaO-SiO2 and SiO2-TiO2 systems and their extensions into liquid immiscibility in the BaO-SiO2-TiO2 system. Calphad 2014, 47, 68–82. [Google Scholar]
- Devries, R.; Roy, R.; Osborn, E. Phase equilibria in the system CaO-TiO2-SiO2. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1955, 38, 158–171. [Google Scholar]
- PÁnek, Z.; KanclÍř, E.; Staroň, J.; Kozlovský, M.; Palčo, Š. The effect of TiO2 on phase transformations of periclase-spinellitic systems in the presence of silicates. Ceram.-Silik. 1976, 20, 13–22. [Google Scholar]
- Kirschen, M.; De Capitani, C. Immiscible silicate liquids in the CaO-SiO2-TiO2-Al2O3 system. Schweiz. Mineral. Petrogr. Mitt. 1998, 78, 175–178. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, X.; Shi, J.; Klemettinen, L.; Chen, M.; Taskinen, P.; Jokilaakso, A. Equilibrium phase relations of CaO-SiO2-TiO2 system at 1400 °C and oxygen partial pressure of 10−10 atm. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 847, 156472. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, X.; Chen, M.; Qiu, Y.; Shi, J.; Li, J.; Liu, C.; Taskinen, P.; Jokilaakso, A. Influence of manganese oxide on the liquid-perovskite equilibrium in the CaO-SiO2-TiO2 system at 1400 °C in air. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 11176–11182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, E.; Orr, R.; Bonnickson, K. Low temperature heat capacity, entropy at 298.16K., and high temperature heat content of sphene (CaTiSiO5). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1954, 76, 4320–4321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, S.; Kelley, K. Heat and Free-Energy Data for Tricalcium Dititanate, Sphene, Lithium Metatitanate, and Zinc-Titanium Spinel; US Department of Energy, Bureau of Mines: Washington, DC, USA, 1956.
- Zhang, M.; Salje, E.; Bismayer, U.; Unruh, H.-G.; Wruck, B.; Schmidt, C. Phase transition(s) in titanite CaTiSiO5: An infrared spectroscopic, dielectric response and heat capacity study. Phys. Chem. Miner. 1995, 22, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xirouchakis, D.; Fritsch, S.; Putnam, R.L.; Navrotsky, A.; Lindsley, D.H. Thermochemistry and the enthalpy of formation of synthetic end-member (CaTiSiO5) titanite. Am. Mineral. 1997, 82, 754–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiéblot, L.; Tequi, C.; Richet, P. High-temperature heat capacity of grossular (Ca3Al2Si3O12), enstatite (MgSiO3), and titanite (CaTiSiO5). Am. Mineral. 1999, 84, 848–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowe, M.; Greedan, J.; Garrett, J.; Burke, N.; Vance, E.; George, I. Melt-grown sphene (CaTiSiO5) crystals. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 1986, 5, 979–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangeman, J.; Xirouchakis, D. High-temperature heat capacity and thermodynamic properties for end-member titanite (CaTiSiO5). Phys. Chem. Miner. 2001, 28, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.; Brown, G. High-temperature structural study of the P21/a↔A2/a phase transition in synthetic titanite, CaTiSiO5. Am. Mineral. 1976, 61, 435–447. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, H.; Zhang, M.; Bismayer, U.; Salje, E.; Schmidt, C.; Kek, S.; Morgenroth, W.; Bleser, T. Phase transformation of natural titanite: An infrared, Raman spectroscopic, optical birefringence and X-ray diffraction study. Phase Transit. A Multinatl. J. 1996, 59, 39–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrosch, J.; Bismayer, U.; Salje, E.K. Anti-phase boundaries and phase transitions in titanite: An X-ray diffraction study. Am. Mineral. 1997, 82, 677–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bismayer, U.; Zhang, M.; Groat, L.; Salje, E.; Meyer, H.-W. The β-γ phase transition in titanite and the isosymmetric analogue in malayaite. Phase Transit. 1999, 68, 545–556. [Google Scholar]
- Pelton, A.; Wu, P. Thermodynamically Optimised Phase Diagrams of Oxide Systems; Technical Report for Phase Diagrams far Ceramists; American Ceramic Society: Westerville, OH, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Kohler, F. Estimation of the thermodynamic data for a ternary system from the corresponding binary systems. Monatshefte Fuer Chem. 1960, 91, 738–740. [Google Scholar]
- Hampl, M.; Schmid-Fetzer, R. Thermodynamic description of the Ti-O system. Int. J. Mater. Res. 2015, 106, 439–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, R.G.; Brown, T.H. Heat capacity of minerals in the system Na2O-K2O-CaO-MgO-FeO-Fe2O3-Al2O3-SiO2-TiO2-H2O-CO2: Representation, estimation, and high temperature extrapolation. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1985, 89, 168–183. [Google Scholar]
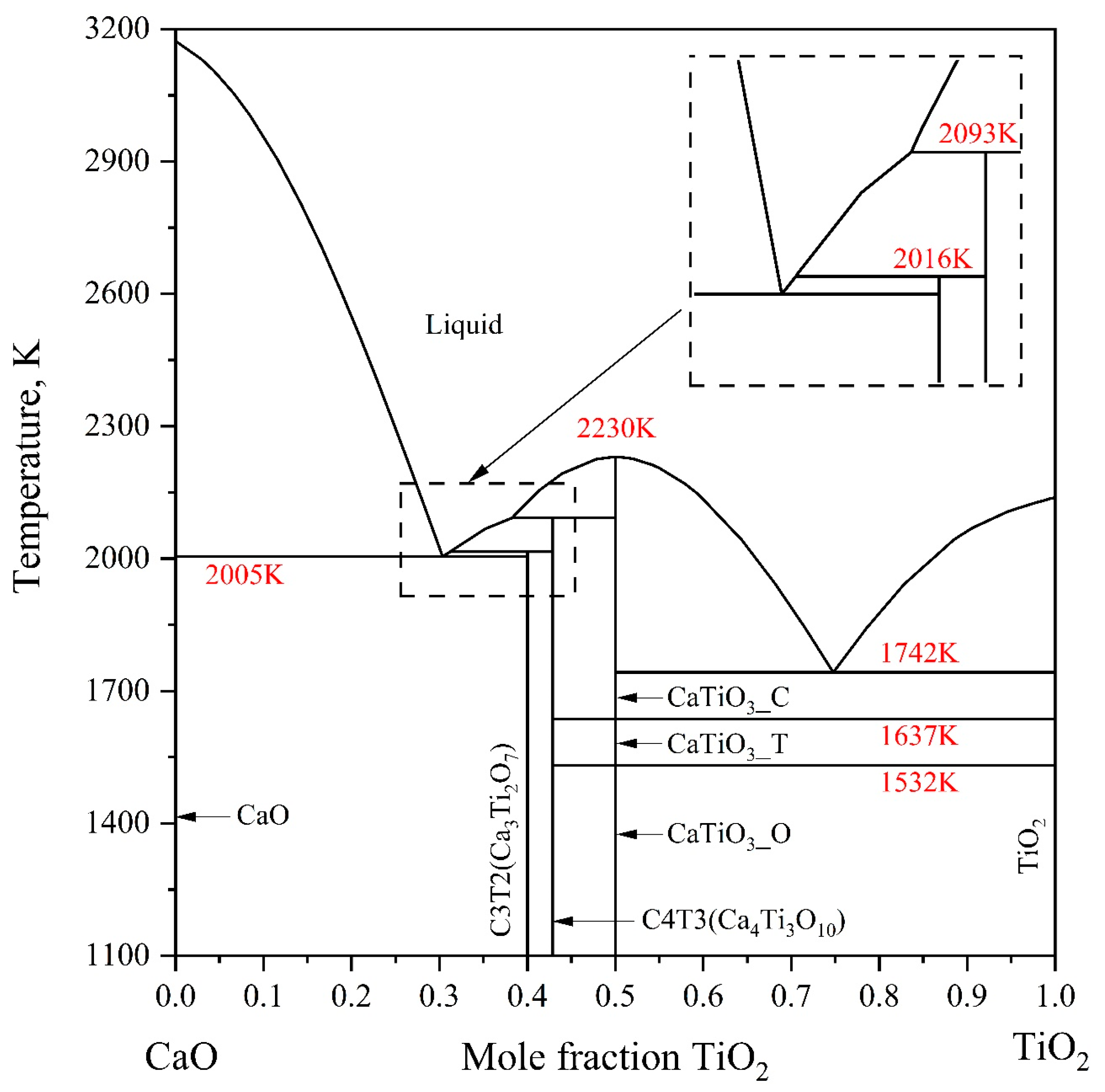
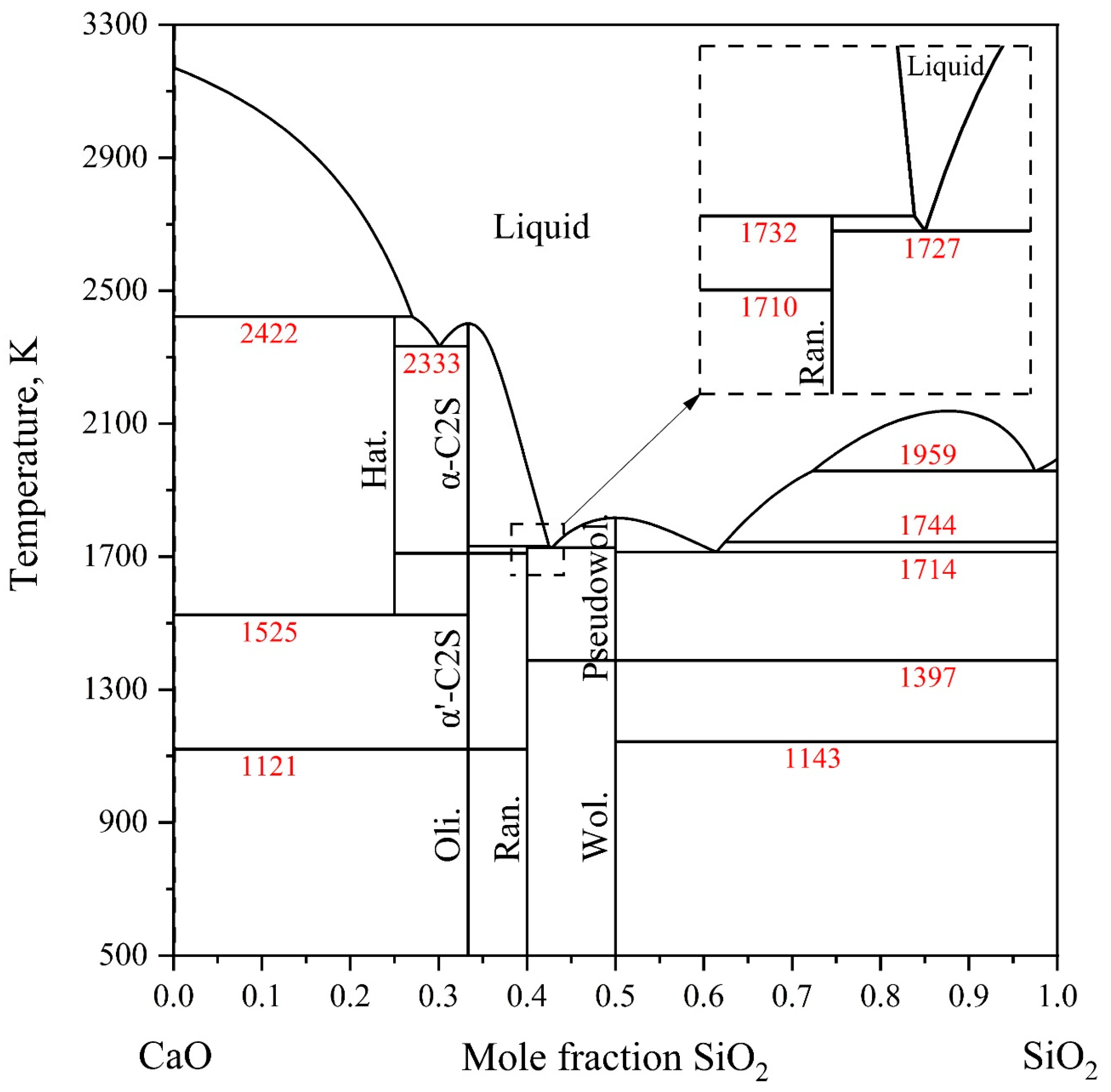

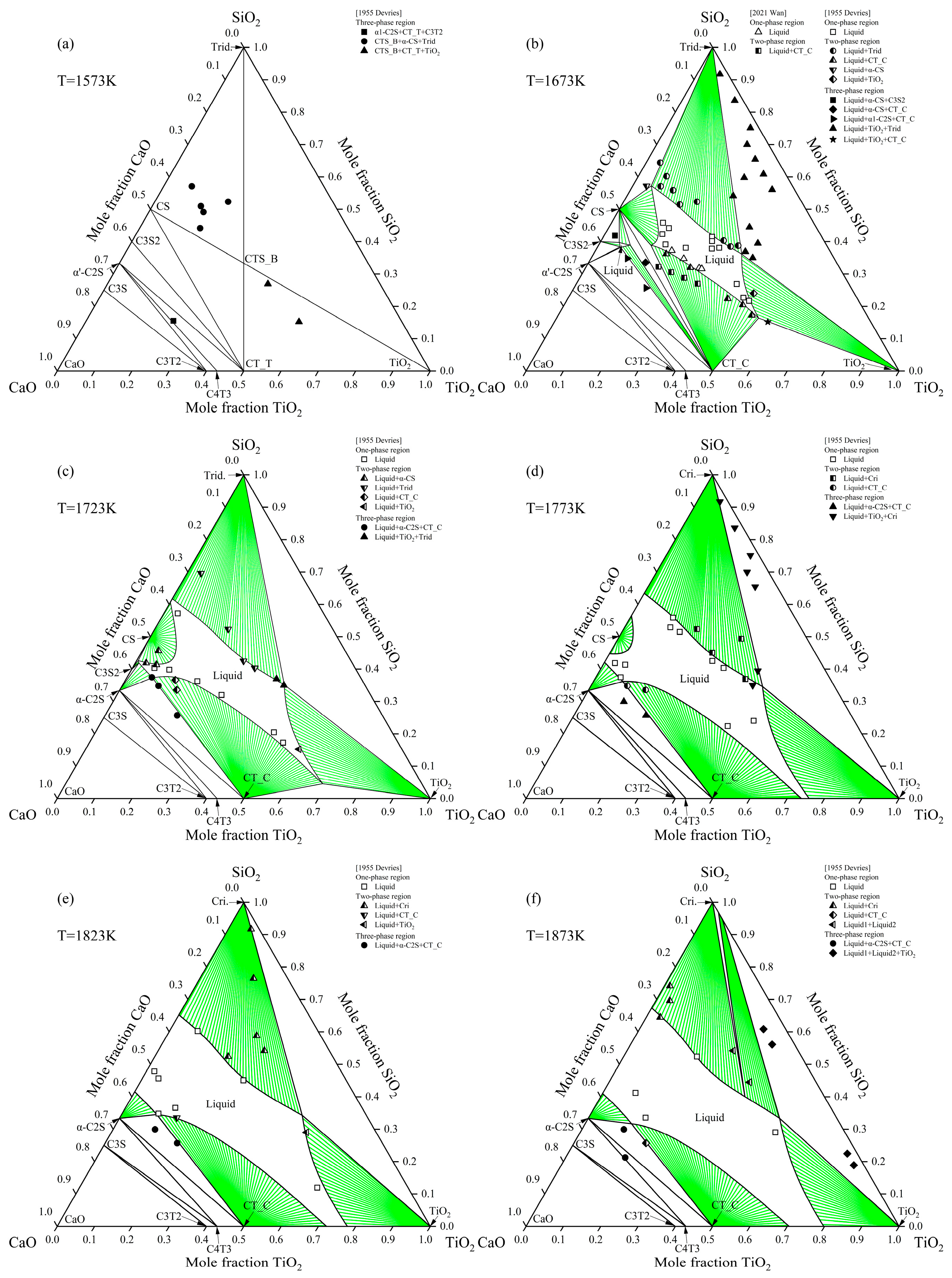
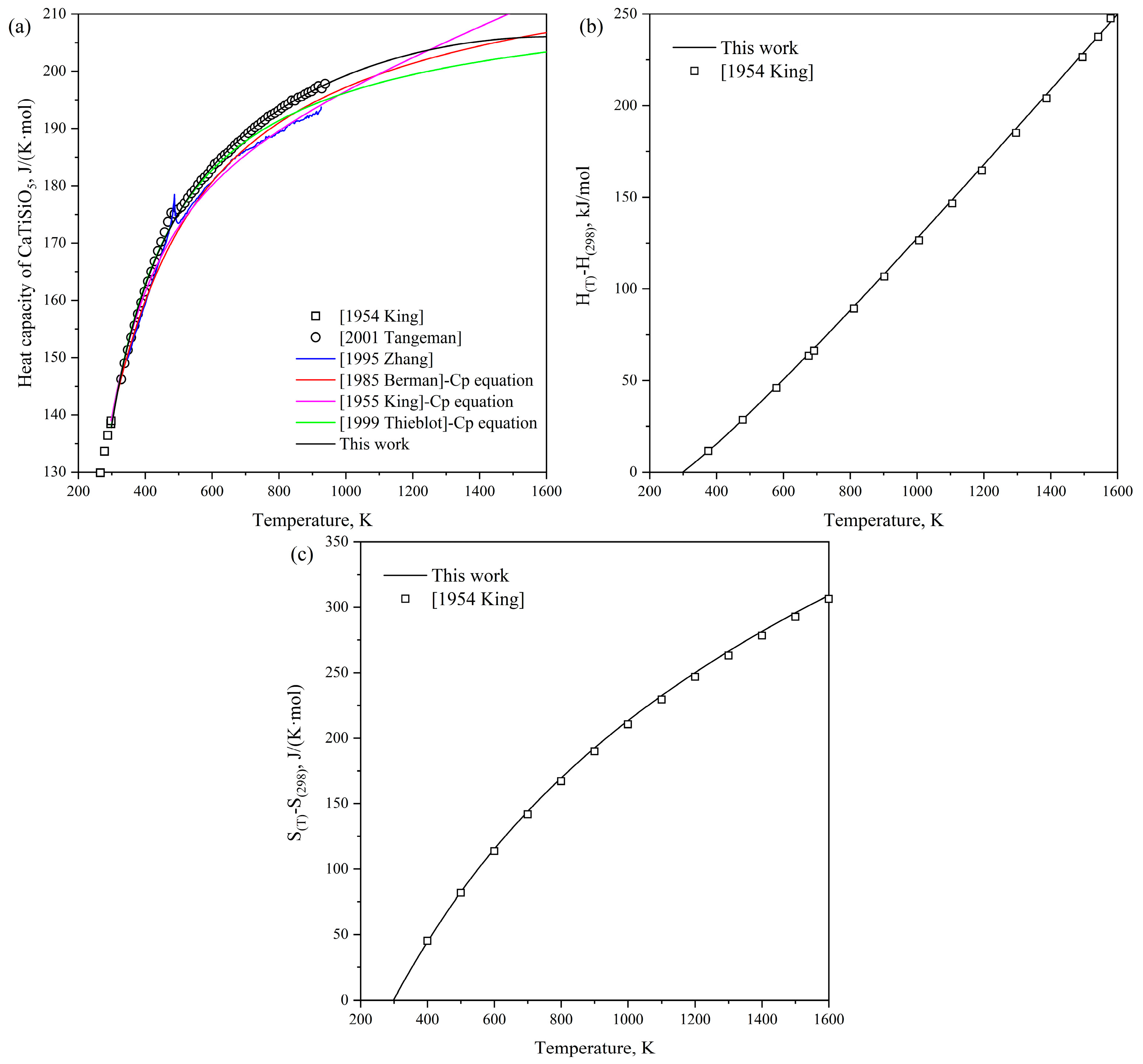
| Phase Name | Model | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Liquid | (Ca+2,Ti+2,Ti+3)P(O−2,Va,O,TiO2,SiO2,SiO4−4)Q | This work |
| Periclase (CaO) | (Ca+2)1(O−2)1 | [34] |
| Rutile (TiO2) | (Ti+4)1(O−2)2 | [34] |
| Quartz (Qua.) | (SiO2)1 | [47] |
| Tridymite (Tri.) | (SiO2)1 | [47] |
| Cristobalite (Cri.) | (SiO2)1 | [47] |
| Olivine (Oli.) | (Ca+2)2(Si+4)1(O−2)4 | [47] |
| α′-Ca2SiO4 (α′-C2S) | (Ca+2)2(Si+4)1(O−2)4 | [47] |
| α-Ca2SiO4 (α-C2S) | (Ca+2)2(Si+4)1(O−2)4 | [47] |
| Larnite (Lar.) | (Ca+2)2(Si+4)1(O−2)4 | [47] |
| Pseudowollastonite (Pseudowol.) | (Ca+2)1(Si+4)1(O−2)3 | [47] |
| Wollastonite (Wol.) | (Ca+2)1(Si+4)1(O−2)3 | [47] |
| Hatruite (Hat.) | (Ca+2)3(Si+4)1(O−2)5 | [47] |
| Rankinite (Ran.) | (Ca+2)3(Si+4)2(O−2)7 | [47] |
| CaTiO3_O (CT_O) | (Ca+2)1(Ti+4)1(O−2)3 | [34] |
| CaTiO3_T (CT_T) | (Ca+2)1(Ti+4)1(O−2)3 | [34] |
| CaTiO3_C (CT_C) | (Ca+2)1(Ti+4)1(O−2)3 | [34] |
| Ca3Ti2O7 (C3T2) | (Ca+2)3(Ti+4)2(O−2)7 | [34] |
| Ca4Ti3O10 (C4T3) | (Ca+2)4(Ti+4)3(O−2)10 | [34] |
| CaTiSiO5 (α-Sph.) | (Ca+2)1(Ti+4)1(Si+4)1(O−2)5 | This work |
| CaTiSiO5 (β-Sph.) | (Ca+2)1(Ti+4)1(Si+4)1(O−2)5 | This work |
| Phase | Model | Thermodynamics Parameter |
|---|---|---|
| Liquid | (Ca+3,Ti+2,Ti+3)P(O−2,Va, O,TiO2,SiO2,SiO4−4)Q | |
| α-Sph. | (Ca+2)1(Ti+4)1(Si+4)1(O−2)5 | |
| β-Sph. | (Ca+2)1(Ti+4)1(Si+4)1(O−2)5 | |
| FUNCTIONS | ||
| Properties | T, K | Calculated Value (This Work) | Experimental Value | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| , kJ·mol−1 | 298.15 | −2598.21 | −2601.4 ± 2.38 | [62] |
| 298.15 | −2602.84 ± 2.07 | [63] | ||
| 298.15 | −2610.13 ± 2.9 | [65] | ||
| , kJ·mol−1 | 298.15 | −107.17 | −110.86 ± 1.52 | [62] |
| 298.15 | −112.34 ± 1.05 | [63] | ||
| 298.15 | −119.59 ± 2.24 | [65] | ||
| , J·mol−1·K−1 | 298.15 | 126.31 | 129.2856 ± 0.8368 | [62] |
| , kJ·mol−1 | - | 0.199 (486 K) | 0.196 ± 0.007 (483 ± 5 K) | [68] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, L.; Li, C.; Wang, Z.; Wu, J.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, L.; Liu, L. Thermodynamic Evaluation and Optimization of the CaO-TiO2-SiO2 Ternary System. Materials 2025, 18, 4448. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194448
Ye L, Li C, Wang Z, Wu J, Zhao W, Zhang L, Liu L. Thermodynamic Evaluation and Optimization of the CaO-TiO2-SiO2 Ternary System. Materials. 2025; 18(19):4448. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194448
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Lideng, Chenbo Li, Ziqian Wang, Junfeng Wu, Wenqing Zhao, Ligang Zhang, and Libin Liu. 2025. "Thermodynamic Evaluation and Optimization of the CaO-TiO2-SiO2 Ternary System" Materials 18, no. 19: 4448. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194448
APA StyleYe, L., Li, C., Wang, Z., Wu, J., Zhao, W., Zhang, L., & Liu, L. (2025). Thermodynamic Evaluation and Optimization of the CaO-TiO2-SiO2 Ternary System. Materials, 18(19), 4448. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194448







