Effect of Post-Weld Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Hardness Evolution of the Martensitic Hardfacing Layers for Hot Forging Tools Repair
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Problem Statement
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Hardfacing Proces
3.2. Post-Weld Heat Treatment (PWHT)
4. Experimental
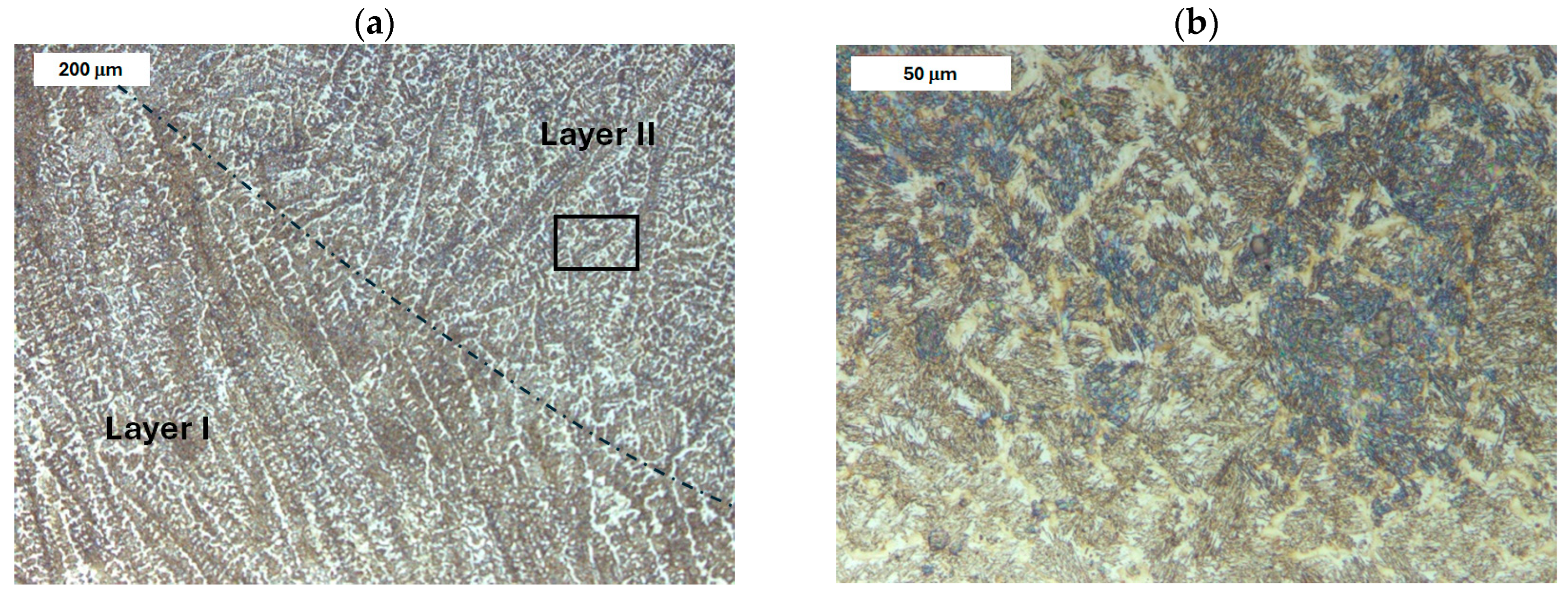
4.1. Examination of Modified X38CrMoV5-3 Steel
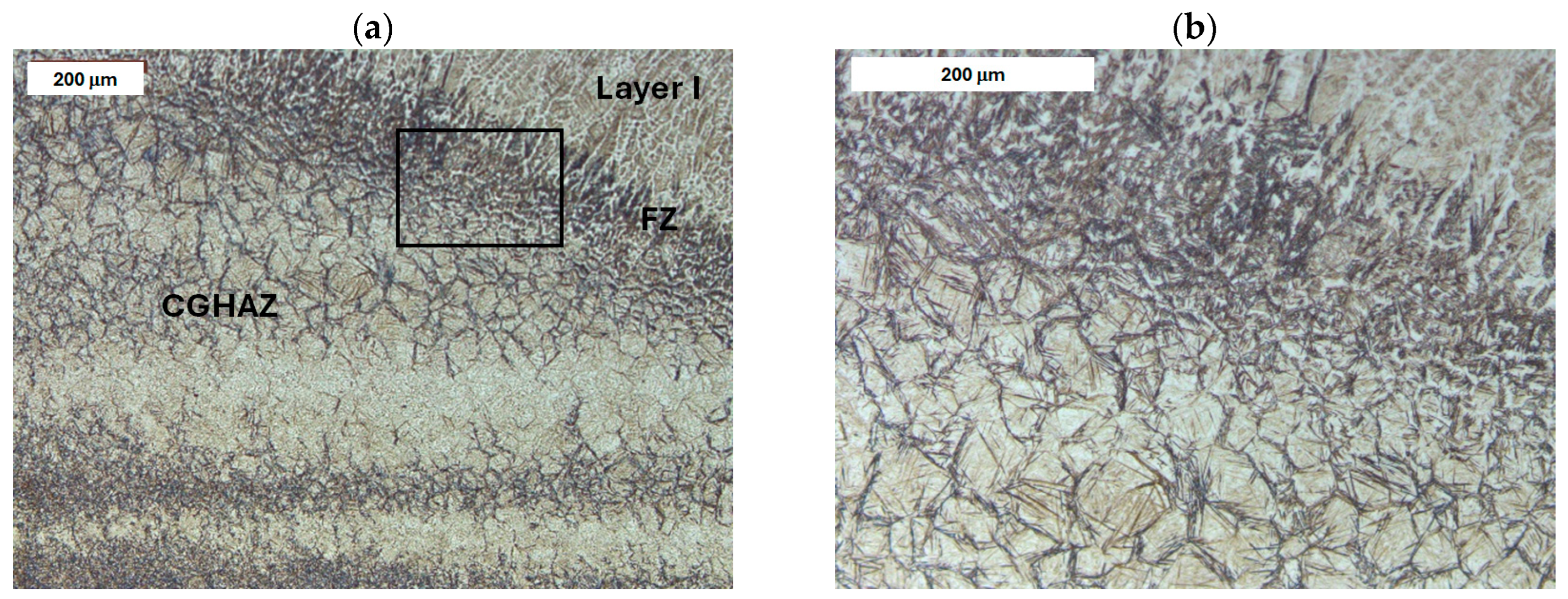
4.2. Examination of X37CrMoV5-1 Steel
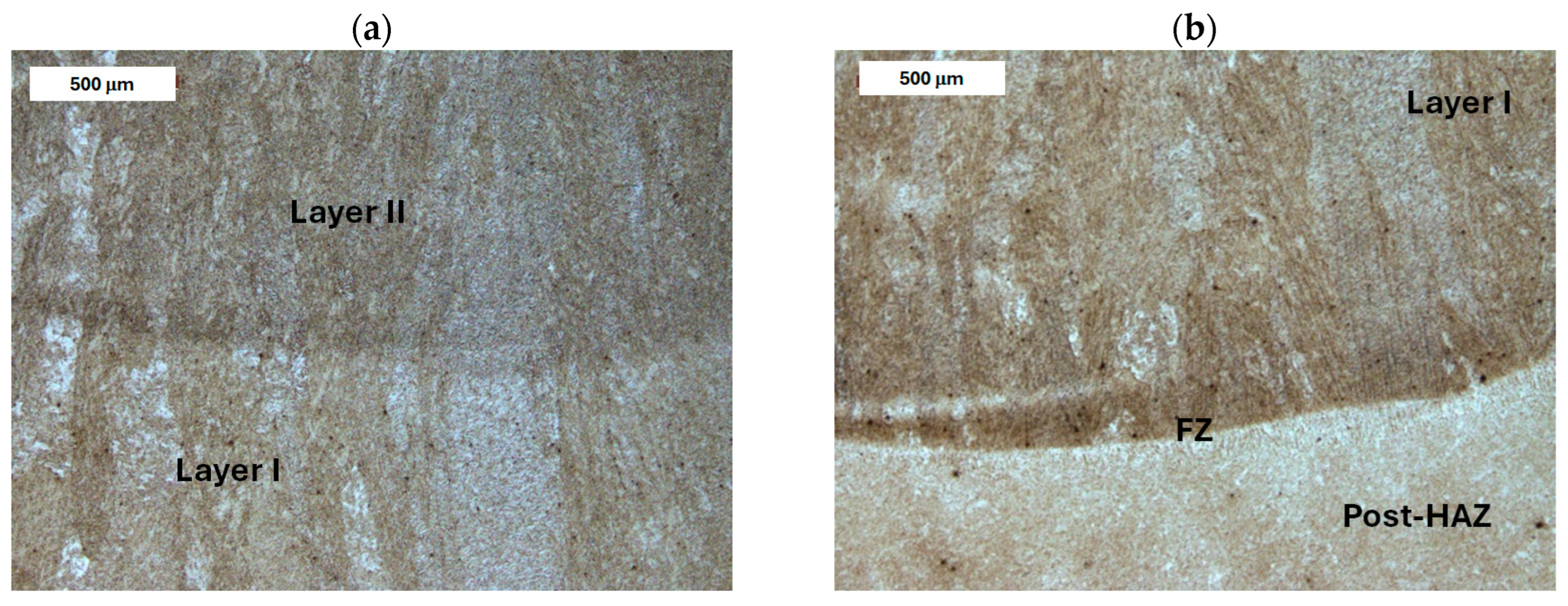
4.3. Examination of 55NiCrMoV7 Steel
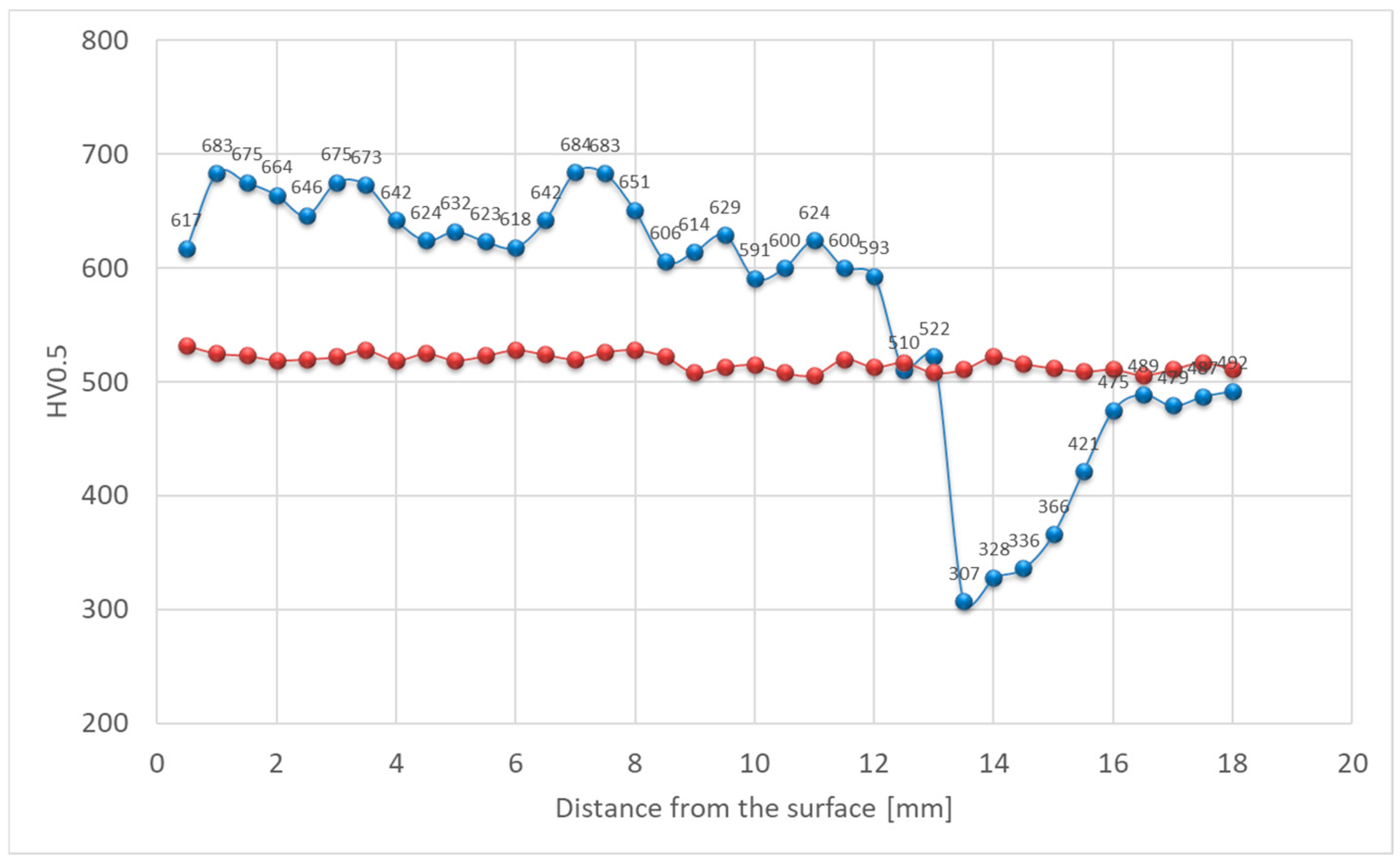
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mrzygłód, B.; Hawryluk, M.; Gronostajski, Z.; Opaliński, A.; Kaszuba, M.; Polak, S.; Widomski, P.; Ziemba, J.; Zwierzchowski, M. Durability analysis of forging tools after different variants of surface treatment using a decision-support system based on artificial neural networks. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2018, 18, 1079–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolik, J. Hard protective layers on forging dies—Development and applications. Coatings 2021, 11, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisiecka-Graca, P.; Lisiecki, Ł.; Zyguła, K.; Wojtaszek, M. Evaluation of cracking risk of 80MnSi8-6 nanobainitic steel during hot forging in the range of lower temperature limits. Mater. Sci. 2024, 42, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widomski, P.; Kaszuba, M.; Dobras, D.; Zindulka, O. Development of a method of increasing the wear resistance of forging dies in the aspect of tool material, thermo-chemical treatment and PVD coatings applied in a selected hot forging process. Wear 2021, 477, 203828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abachi, S.; Akkök, M.; Ilhan Gökler, M. Wear analysis of hot forging dies. Tribol. Int. 2010, 43, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widomski, P.; Gronostajski, Z. Comprehensive Review of Methods for Increasing the Durability of Hot Forging Tools. Procedia Manuf. 2020, 47, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gronostajski, Z.; Hawryluk, M.; Widomski, P.; Kaszuba, M.; Ziemba, J.; Smolik, J. Influence of the application of a PN+CrN hybrid layer on improvement of the lifetime of hot forging tools. Procedia Eng. 2017, 207, 514–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawryluk, M.; Gronostajski, Z.; Kaszuba, M.; Polak, S.; Widomski, P.; Ziemba, J.; Smolik, J. Application of selected surface engineering methods to improve the durability of tools used in precision forging. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 93, 2183–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zindulka, O.; Sochora, V. PVD Povlak CRNx–Když Tloušťka Není Na Závadu. Prumyslové Spektrum 2016, 9, 138–140. [Google Scholar]
- Panjan, P.; Cvahte, P.; Čekada, M.; Navinšek, B.; Urankar, I. PVD CrN coating for protection of extrusion dies. Vacuum 2001, 61, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munz, W.D.; Smith, I.J. Wear resistant PVD coatings for high temperature (950°) applications. In Proceedings of the Proceedings, Annual Technical Conference-Society of Vacuum Coaters, Chicago, IL, USA, 17–22 April 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Navinšek, B.; Panjan, P.; Gorenjak, F. Improvement of hot forging manufacturing with PVD and DUPLEX coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2001, 137, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubar, M.; Dubois, A.; Dubar, L. Wear analysis of tools in cold forging: PVD versus CVD TiN coatings. Wear 2005, 259, 1109–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fumiaki, H.; Ken, I.; Inoue, K.I. Development of novel multi-layer PVD coating for hot forging dies and punches. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Progress of Machining Technology, Matsue, Japan, 9 November 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Widomski, P.; Kaszuba, M.; Sokołowski, P.; Lange, A.; Walczak, M.; Długozima, M.; Gierek, M.; Chocyk, D.; Gładyszewski, G.; Boryczko, B. Nitriding of hardfaced layers as a method of improving wear resistance of hot forging tools. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2023, 23, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, G.; Fernández-Vicente, A.; Cid, J. Influence of the nitriding time in the wear behaviour of an AISI H13 steel during a crankshaft forging process. Wear 2007, 263, 1375–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaszuba, M.; Widomski, P.; Białucki, P.; Lange, A.; Boryczko, B.; Walczak, M. Laboratory tests of properties of the new-generation hybrid layers combining hardfacing and nitriding dedicated for improvement of forging tools’ durability. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2020, 20, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, M.; Belzunce, F.J. A comparative study of salt-bath nitrocarburizing and gas nitriding followed by post-oxidation used as surface treatments of H13 hot forging dies. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2016, 305, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widomski, P.; Gronostajski, Z.; Kaszuba, M.; Kowalska, J.; Pawełczyk, M. The laboratory tests of hybrid layers combining hardfacing and nitriding dedicated to increase the durability of forging tools in hot forging processes. Weld. Technol. Rev. 2019, 91, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Wu, Z.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, X. Effect of heat treatment and cooling rate on microstructure and properties of T92 welded joint. Mater. Sci. 2023, 41, 124–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saklakoglu, N.; Irizalp, S.G.; Dogan, S.; Ildas, G.; Saklakoglu, I.E. Performance of Fe-based hardfacings on hot forging die: Experimental, numerical and industrial studies. Met. Mater. 2018, 56, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashani, H.; Amadeh, A.; Vatanara, M.R. Improvement of wear resistance of hot working tool steel by hardfacing Part 2-Case study. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2008, 24, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashani, H.; Amadeh, A.; Farhani, M. Improvement of wear resistance of hot working tool steel by hardfacing Part 1-Effect of microstructure and hardness. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2007, 23, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouilland, L.; El Mansori, M.; Massaq, A. Friction-induced work hardening of cobalt-base hardfacing deposits for hot forging tools. J. Mater. Process Technol. 2009, 209, 3366–3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górnik, M.; Lachowicz, M.; Łatka, L. Corrosion resistance of PPTA Ni-based hardfacing layers. Mater. Sci. 2024, 42, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, Y.; Henckell, P.; Hildebrand, J.; Reimann, J.; Bergmann, J.; Barnikol-Oettler, S. Wire arc additive manufacturing of hot work tool steel with CMT process. J. Mater. Process Technol. 2019, 269, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noelke, C.; Luecke, M.; Kaierle, S.; Wesling, V.; Overmeyer, L.; Dorsch, F. Laser-dispersing of forging tools using AlN-ceramics. In High-Power Laser Materials Processing: Lasers, Beam Delivery, Diagnostics, and Applications III; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Q.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Z. The dynamics and deposition results of femtosecond laser-induced liquid film forward transfer. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Laser, Optics and Optoelectronic Technology (LOPET 2021), Xi’an, China, 28–30 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Herzog, D.; Asami, K.; Scholl, C.; Ohle, C.; Emmelmann, C.; Sharma, A.; Markovic, N.; Harris, A. Design guidelines for laser powder bed fusion in Inconel 718. J. Laser Appl. 2022, 34, 012015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrzański, L.A.; Bonek, M.; Piec, M.; Hajduczek, E.; Klimpel, A. Laser modification of hot-work tool steels gradient layers. In Proceedings of the 24th International Congress on Applications of Lasers and Electro-Optics, ICALEO 2005-Congress Proceedings, Miami, FL, USA, 31 October–3 November 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, C.; Gasser, A.; Backes, G.; Fu, J.; Schleifenbaum, J.H. Laser additive manufacturing of Inconel 718 at increased deposition rates. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 844, 143196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, J.; Cullen, C.; Fitzpatrick, S.; Payne, G.; Hall, L.; Marashi, J. Remanufacture of hot forging tools and dies using laser metal deposition with powder and a hard-facing alloy Stellite 21®. J. Remanufacturing 2019, 9, 189–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R. Weld Repair of Tools and Dies: 10 Popular Q&As; Postle Industries, Inc.: Cleveland, OH, USA, 2017; Available online: http://www.hardfacetechnologies.com/postle_hft_btsp/pdfs/forge-weld-repair-postle.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- Lazic, V.; Sedmak, A.; Aleksandrovic, S.; Milosavljevic, D.; Rajko, Č.; Grabulov, V. Reparation of the Damaged Forging Hammer Mallet by Hard Facing and Weld Cladding. Teh. Vjesn. 2009, 16, 107–113. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Chen, J.; Xue, L. Characteristics of H13 tool steel coatings by pulsed nd: Yag laser cladding. In Proceedings of the TMS 2013 142nd Annual Meeting and Exhibition, Annual Meeting, San Antonio, TX, USA, 3–7 March 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Corbin, S. Control of Laser Cladding Process. In Laser Cladding; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 15614-1:2017; Specification and Qualification of Welding Procedures for Metallic Materials—Welding Procedure Test. Part 1: Arc and Gas Welding of Steels and Arc Welding of Nickel and Nickel Alloys. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- Huang, Y.; Huang, T.; Zhang, S.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Zhan, Y.; Fan, K.; Xiong, J.; Yang, J.; Guo, Y.; et al. Effect of post weld heat treatment on microstructural and mechanical properties of martensitic heat-resistant steel weldments. Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip. 2024, 212, 105323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konat, Ł. Technological, Microstructural and Strength Aspects of Welding and Post-Weld Heat Treatment of Martensitic, Wear-Resistant Hardox 600 Steel. Materials 2021, 14, 4541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachowicz, M.M.; Sokołowski, P.; Kaszuba, M. The Influence of the Hot Working Tool Steel Substrate Material on the Element Distribution, Microstructure and Hardness of Gas Metal Arc Welding Hardfaced Layers. Adv. Sci. Technol. Res. J. 2024, 18, 320–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R. Stresses, shrinkage, and distortion in weldments. In Applied Welding Engineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 207–249. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Kannan, R.; Li, L. Characterization of as-welded microstructure of heat-affected zone in modified 9Cr–1Mo–V–Nb steel weldment. Mater. Charact. 2016, 118, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solgi, P.; Chenarani, M.; Eivani, A.R.; Ghosh, M.; Kumar, V.; Jafarian, H.R. Heat checking as a failure mechanism of dies exposed to thermal cycles: A review. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 26, 865–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burja, J.; Nagode, A.; Grabnar, K.; Medved, J.; Balaško, T. Effect of Nb, Ta, and Ti Microalloying on the Secondary Hardening of Mo-W Tool Steel. Mater. Tehnol. 2024, 58, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.; Lee, K.B.; Yang, H.R.; Lee, J.B.; Kim, Y.S. Secondary hardening and fracture behavior in alloy steels containing Mo, W, and Cr. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1997, 28, 775–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
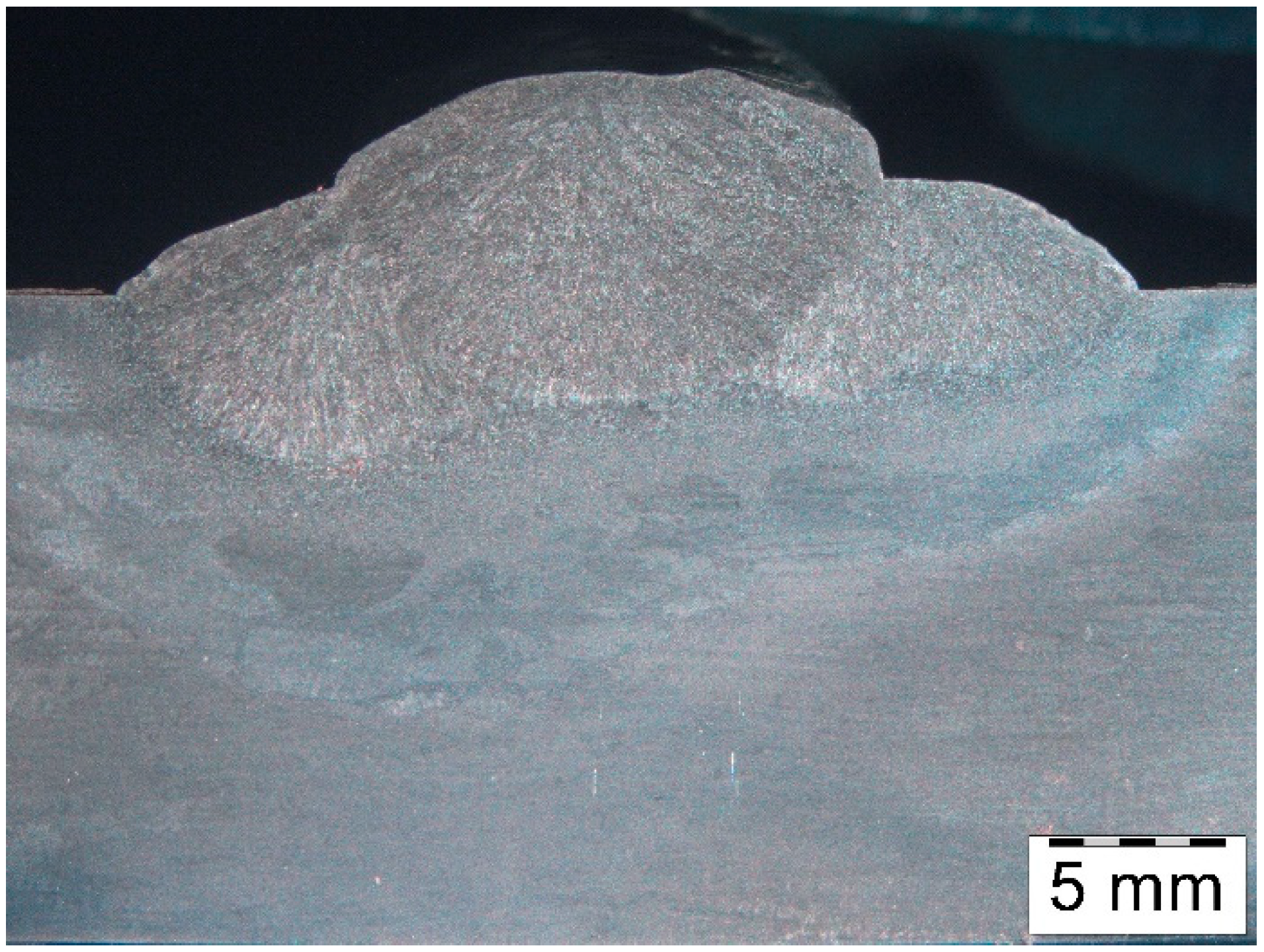
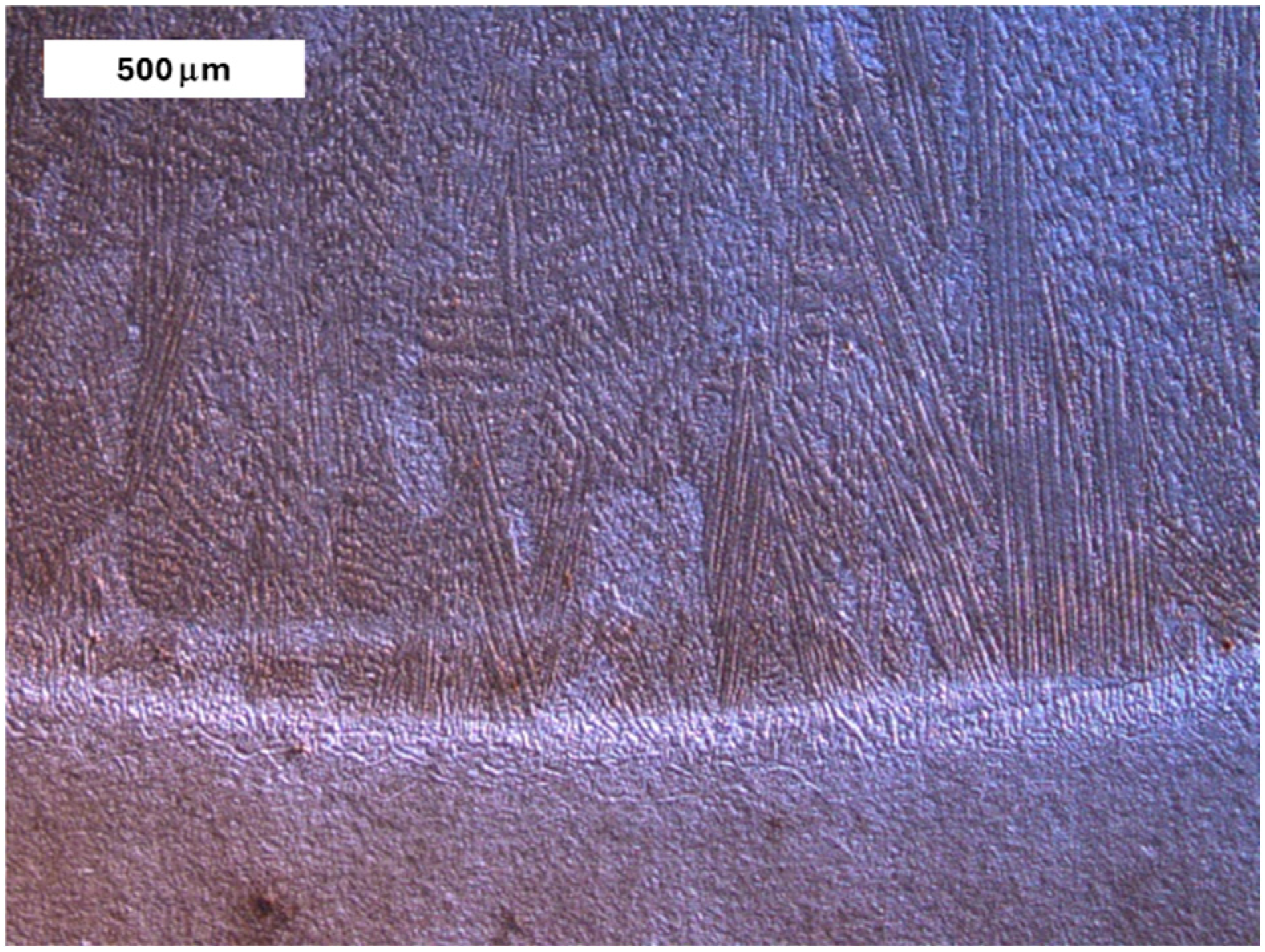


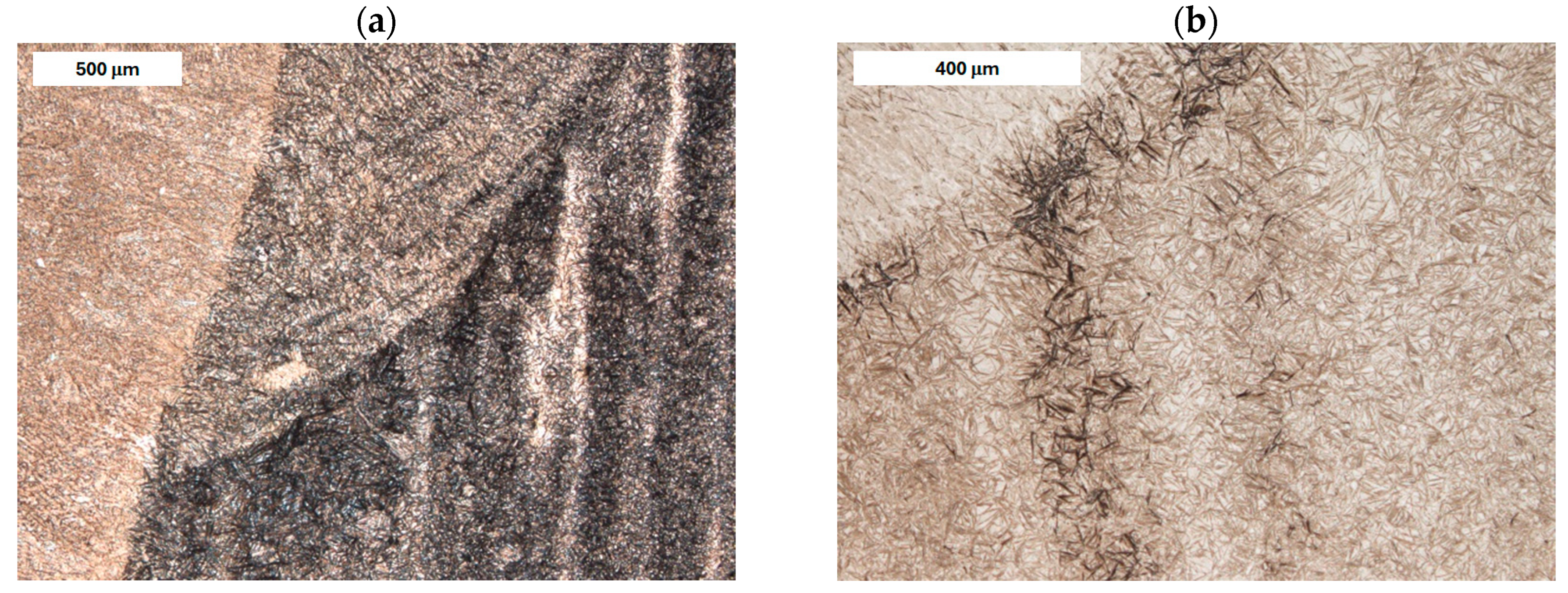
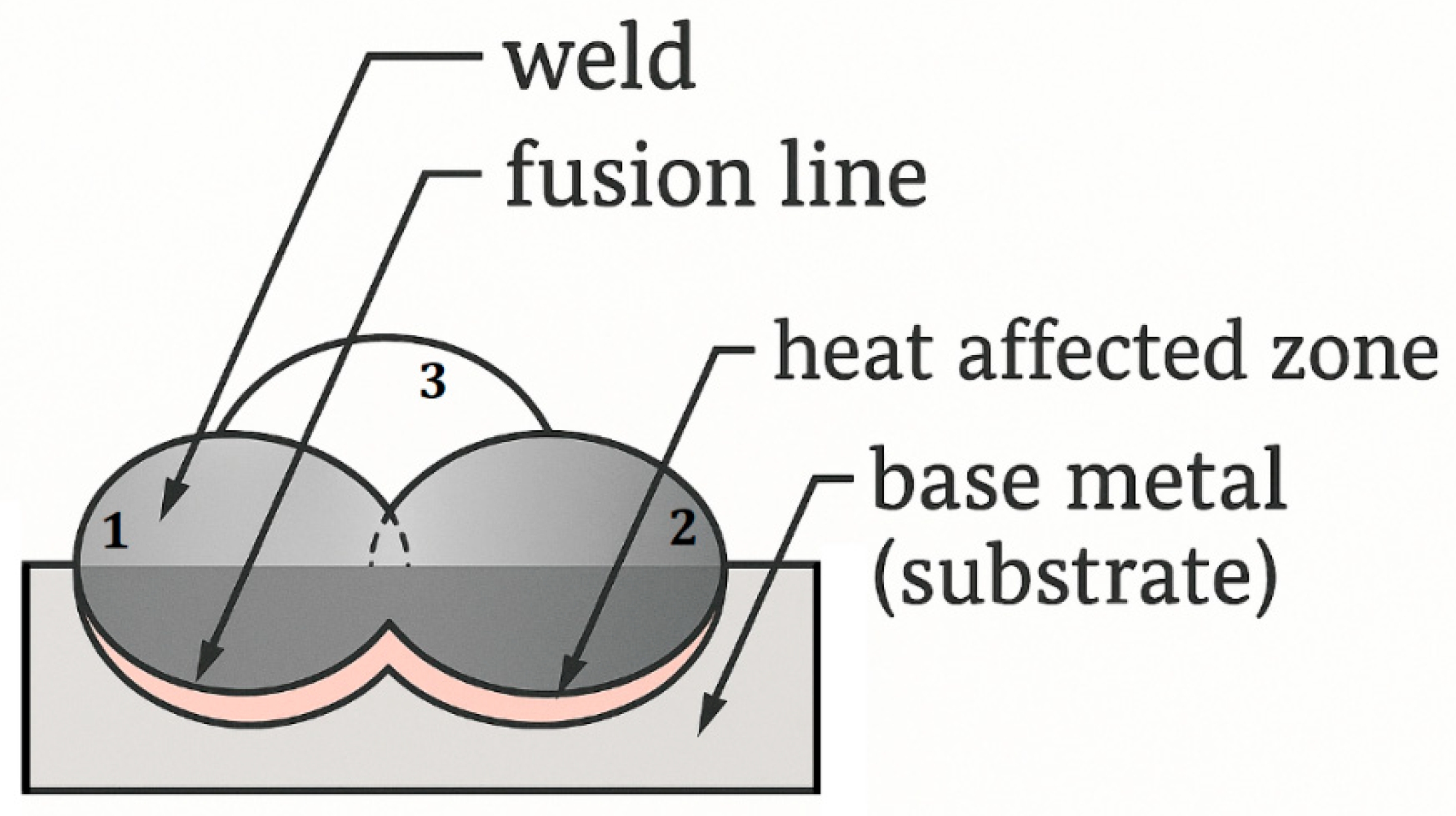
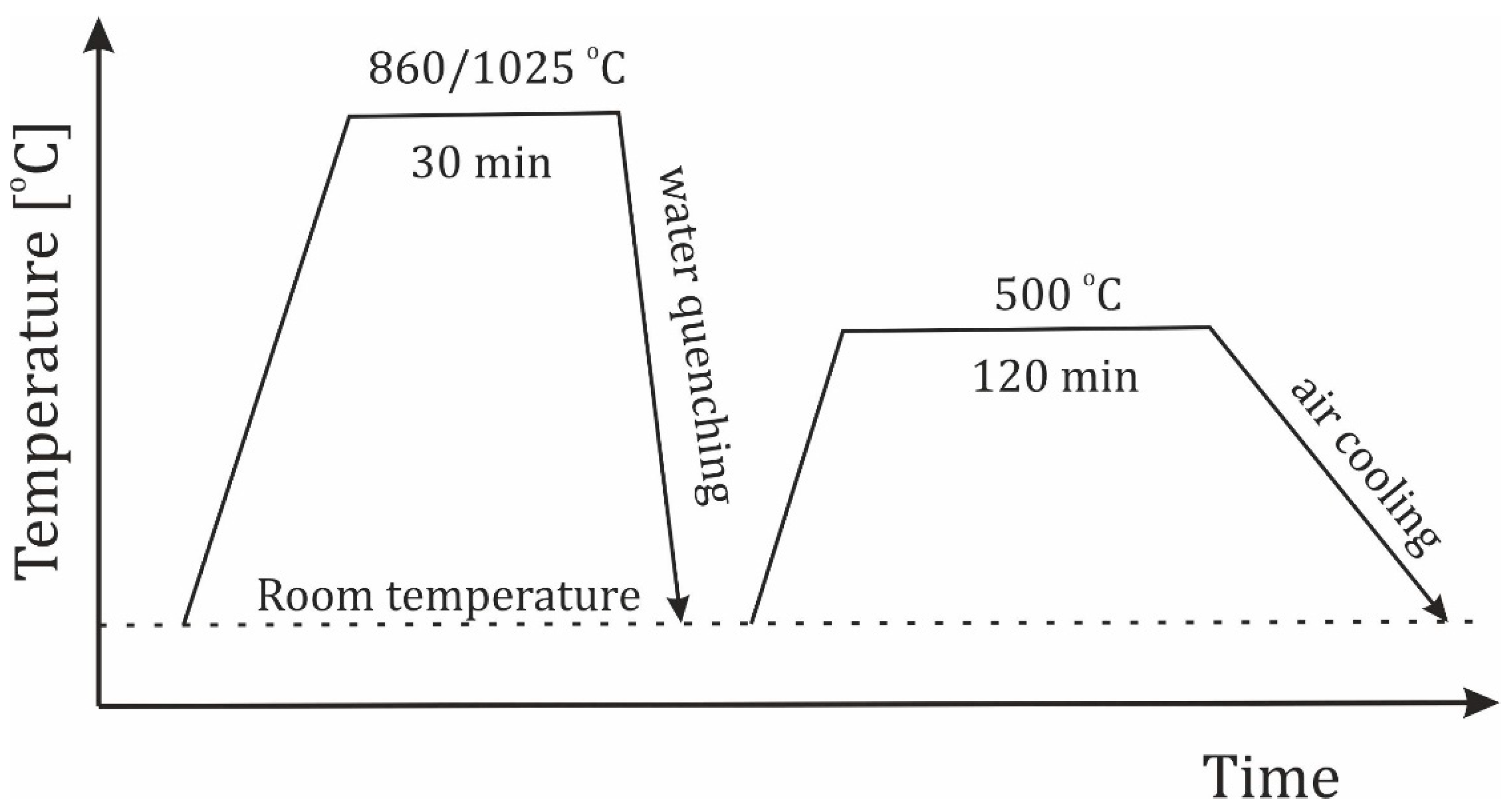
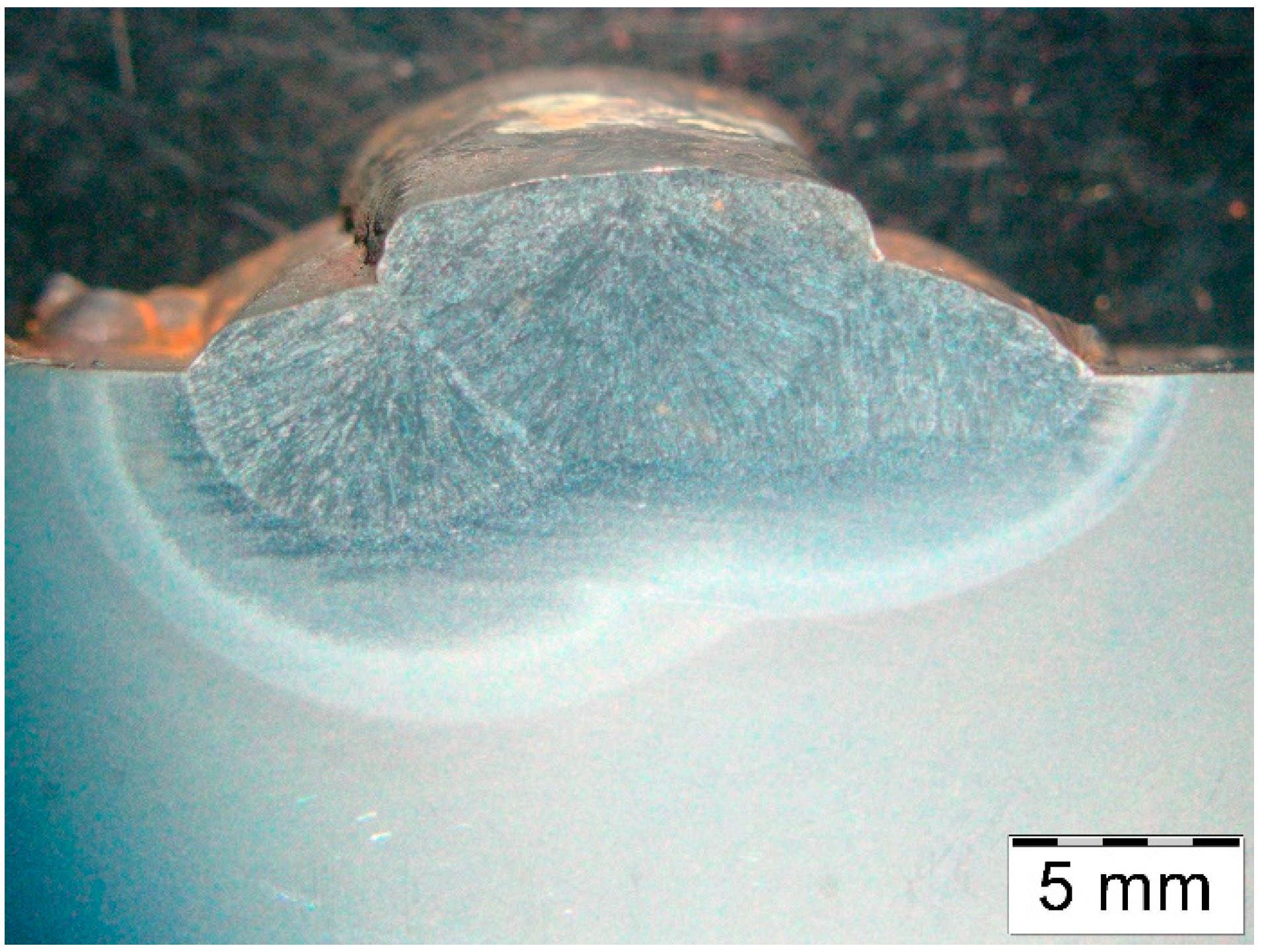
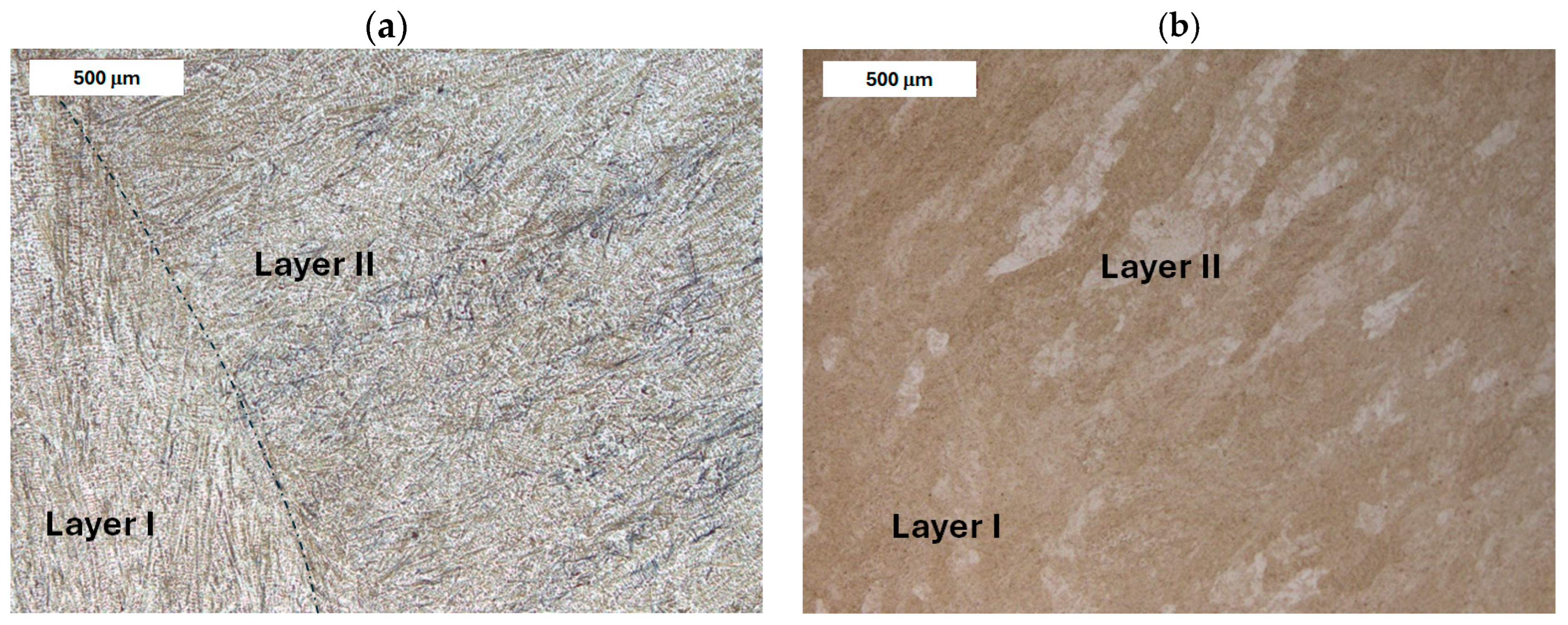

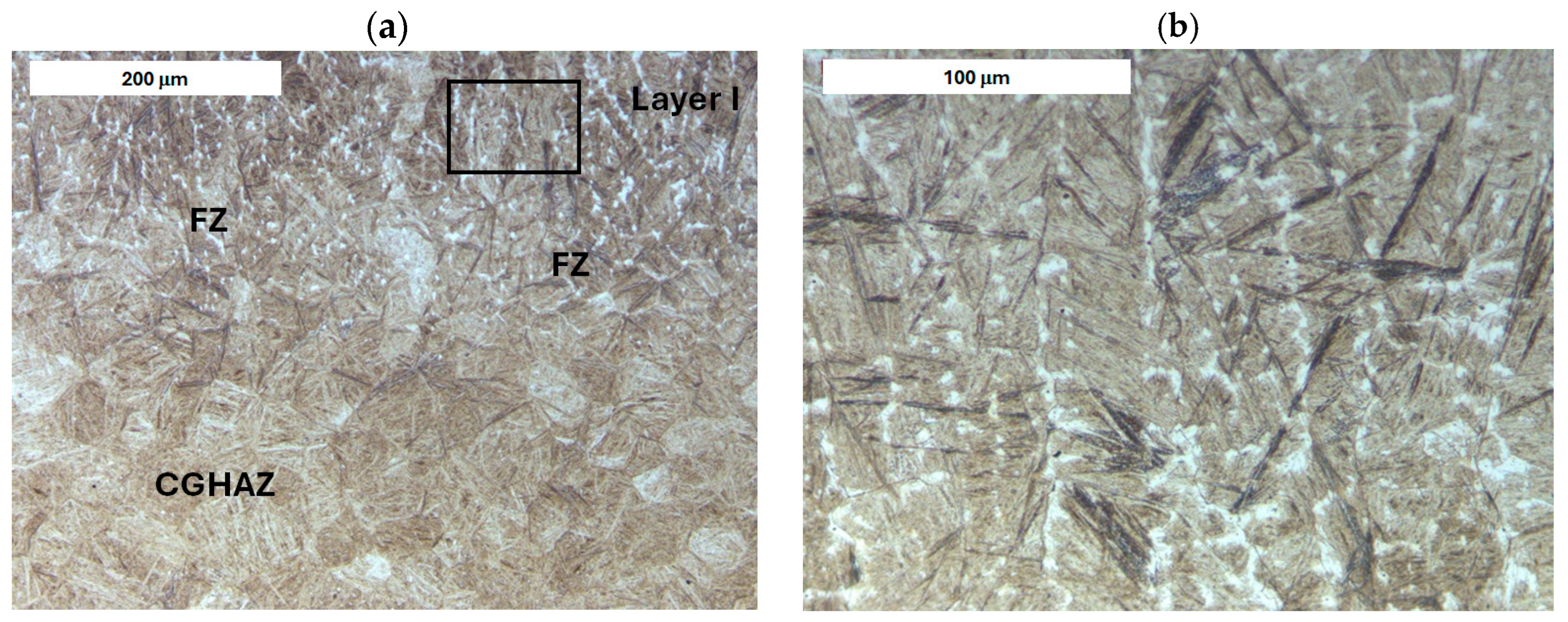
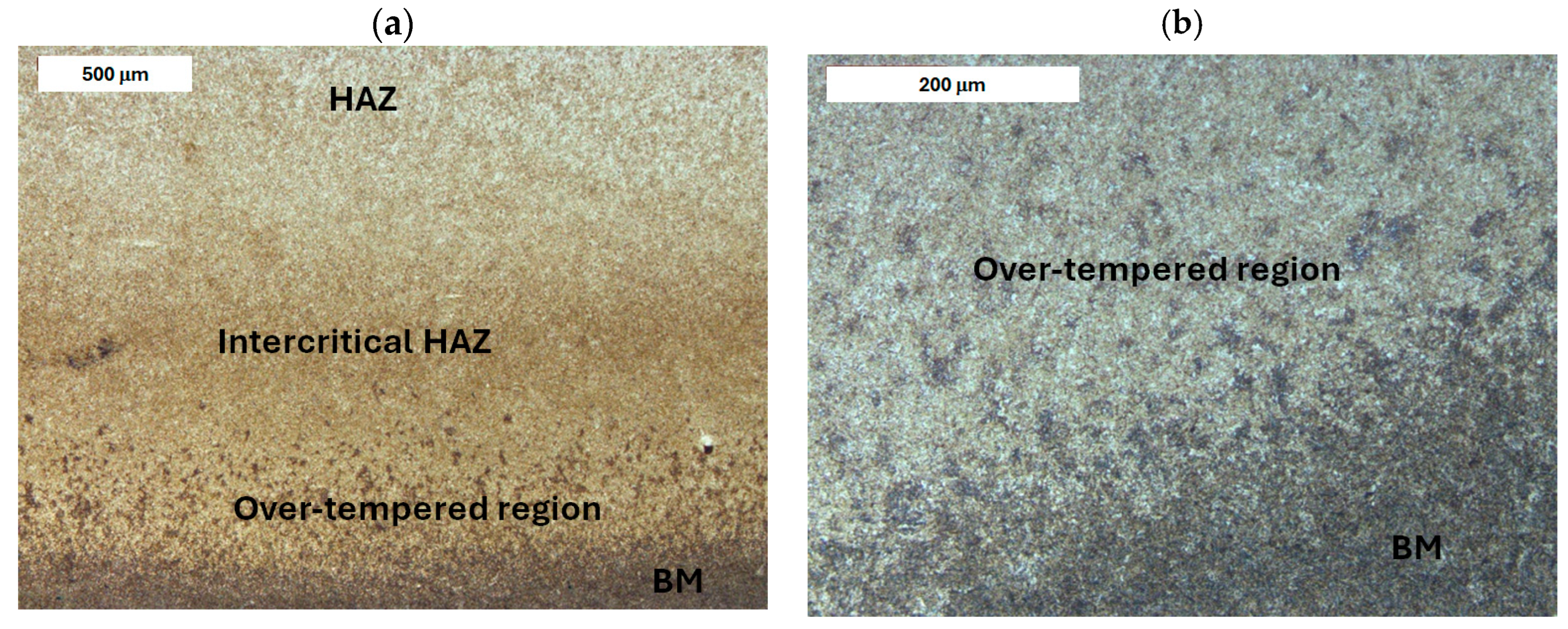
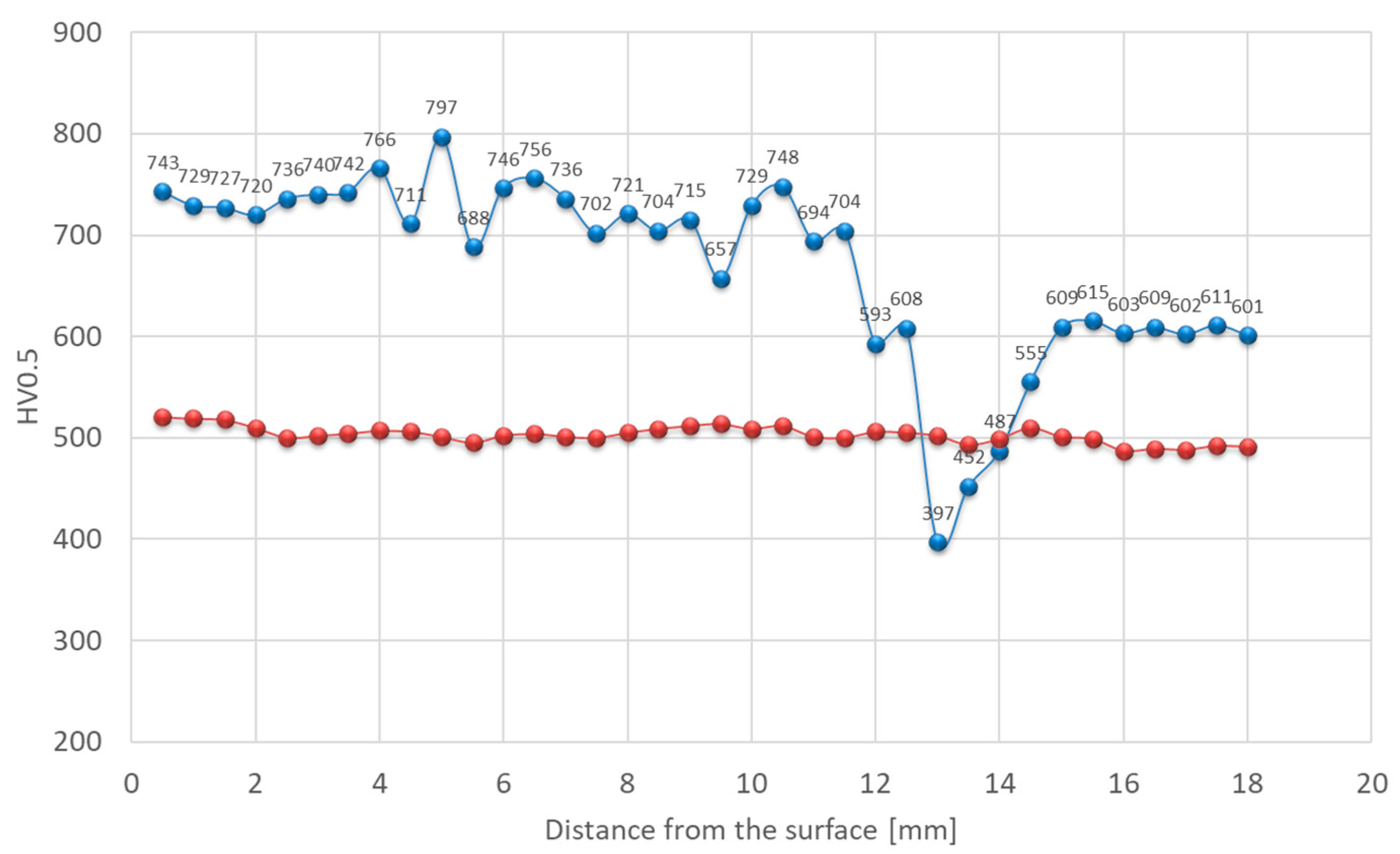




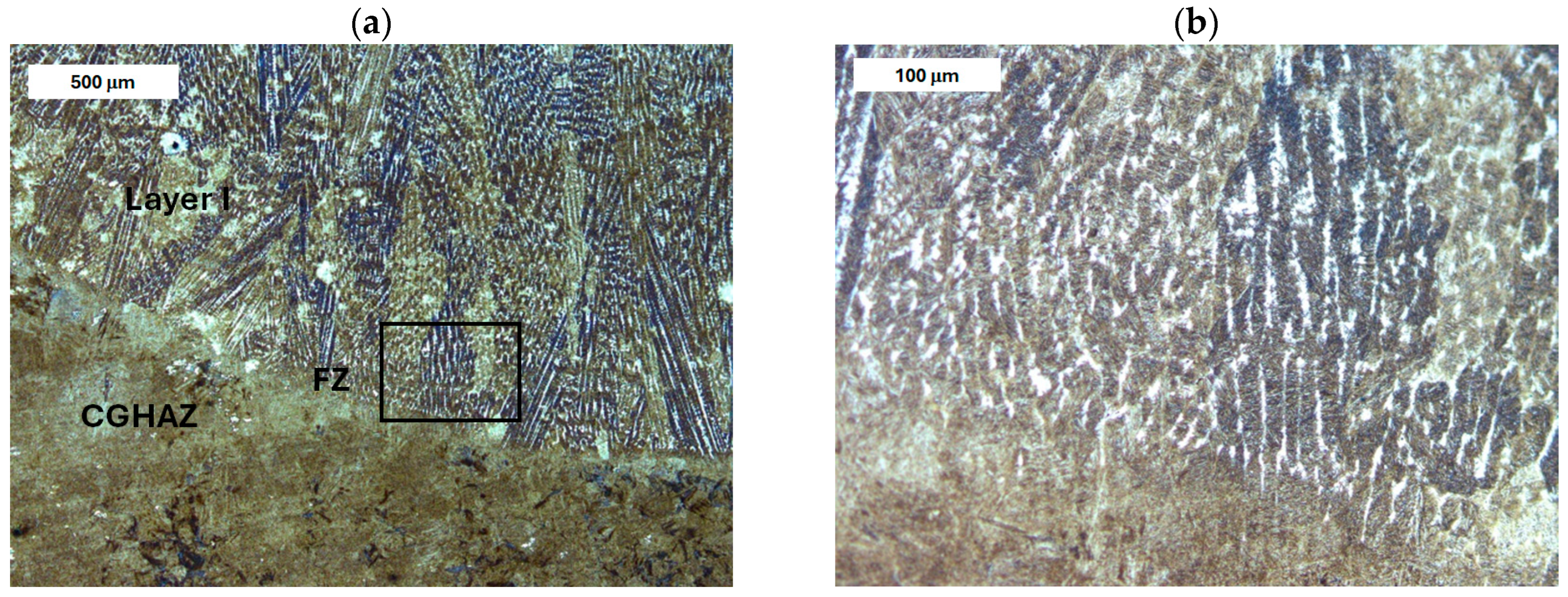

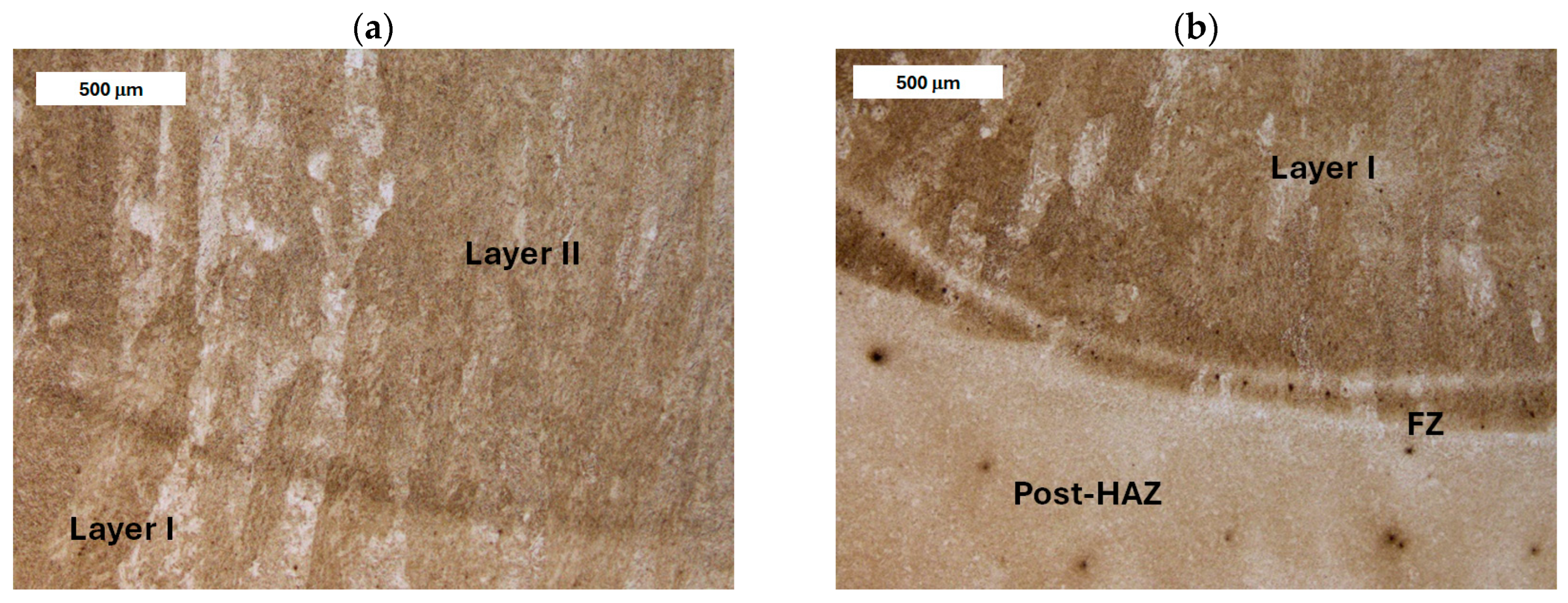
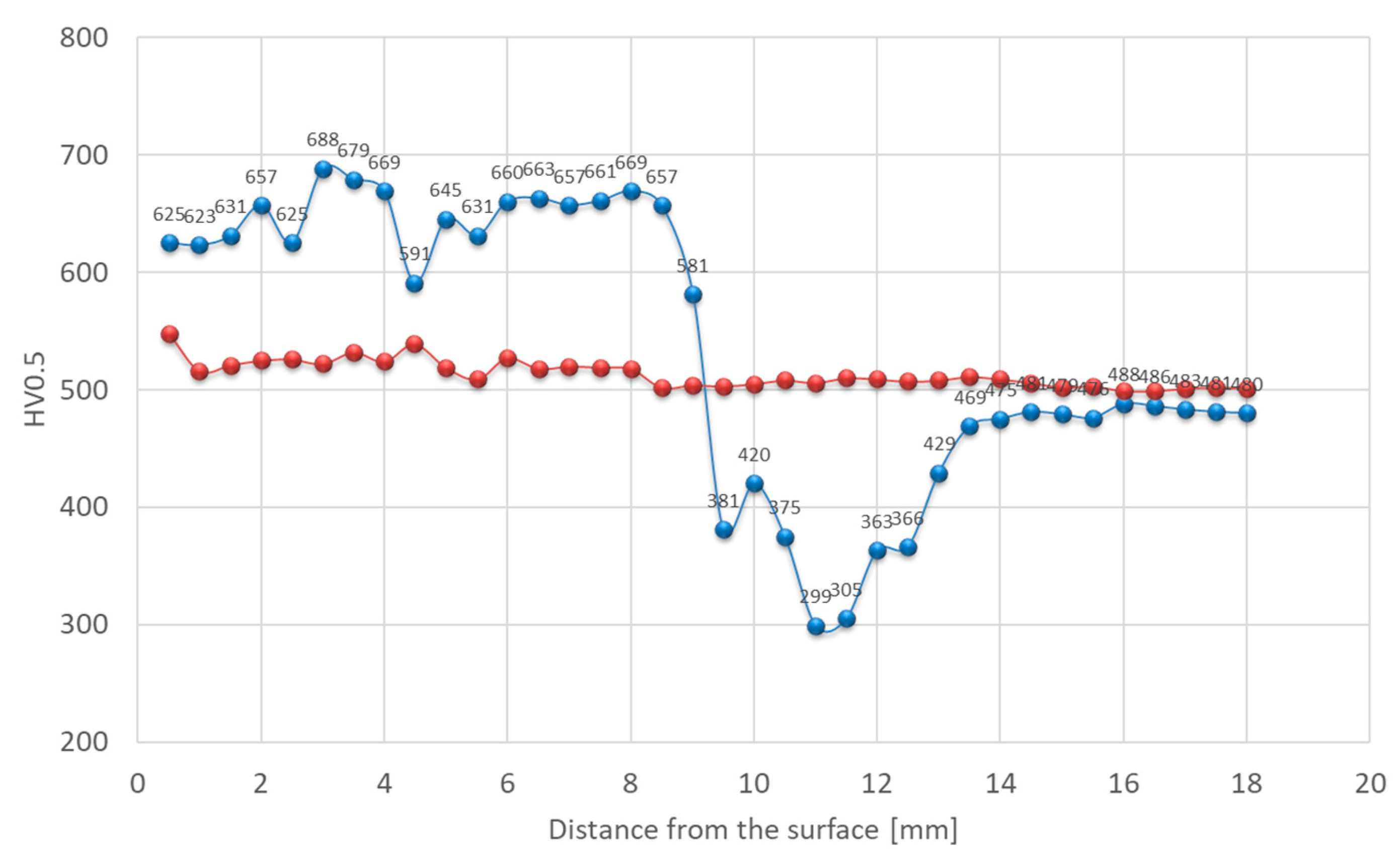

| Element, wt.% | C | Mn | Si | S | P | Cr | Mo | Ni | V | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.2714 (55NiCrMoV7, WNLV) | 0.60 | 0.72 | 0.23 | 0.005 | 0.009 | 0.97 | 0.43 | 1.71 | 0.08 | balance |
| 1.2343 (X37CrMoV5-1, WCL) | 0.38 | 0.33 | 0.86 | 0.003 | 0.011 | 4.80 | 1.13 | 0.10 | 0.33 | balance |
| Modified 1.2367, (X38CrMoV5-3) | 0.50 | 0.45 | 0.25 | - | 0.007 | 5.10 | 2.21 | 0.09 | 0.50 | balance |
| GMAW Parameter | Hardfacing Current, A | Hardfacing Voltage, V | Gun Speed, m/min | Gas Flow Rate, LPM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | 260 | 30 | 0.3 | 17–18 |
| Element, wt.% | C | Mn | Si | Cr | Mo | Ni | V | W | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hardfacing layer | 0.57 | 0.95 | 0.74 | 5.36 | 1.62 | 0.06 | 0.54 | 1.37 | Balance |
| Grade | Austenising | Tempering | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature [°C] | Time [min] | Temperature [°C] | Time [min] | |
| 1.2714 (55NiCrMoV7, WNLV) | 860 | 30 | 500 | 120 |
| 1.2343 (X37CrMoV5-1, WCL) | 1025 | 30 | 500 | 120 |
| Modified 1.2367, (X38CrMoV5-3) | 1025 | 30 | 500 | 120 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lachowicz, M.; Kaszuba, M.; Widomski, P.; Sokołowski, P. Effect of Post-Weld Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Hardness Evolution of the Martensitic Hardfacing Layers for Hot Forging Tools Repair. Materials 2025, 18, 4214. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18174214
Lachowicz M, Kaszuba M, Widomski P, Sokołowski P. Effect of Post-Weld Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Hardness Evolution of the Martensitic Hardfacing Layers for Hot Forging Tools Repair. Materials. 2025; 18(17):4214. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18174214
Chicago/Turabian StyleLachowicz, Marzena, Marcin Kaszuba, Paweł Widomski, and Paweł Sokołowski. 2025. "Effect of Post-Weld Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Hardness Evolution of the Martensitic Hardfacing Layers for Hot Forging Tools Repair" Materials 18, no. 17: 4214. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18174214
APA StyleLachowicz, M., Kaszuba, M., Widomski, P., & Sokołowski, P. (2025). Effect of Post-Weld Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Hardness Evolution of the Martensitic Hardfacing Layers for Hot Forging Tools Repair. Materials, 18(17), 4214. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18174214








