Optimizing Acoustic Performance of Semi-Dense Asphalt Mixtures Through Energy Dissipation Characterization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Material
2.1.1. Aggregate
2.1.2. Asphalt
2.1.3. Additive
2.2. Mix Design
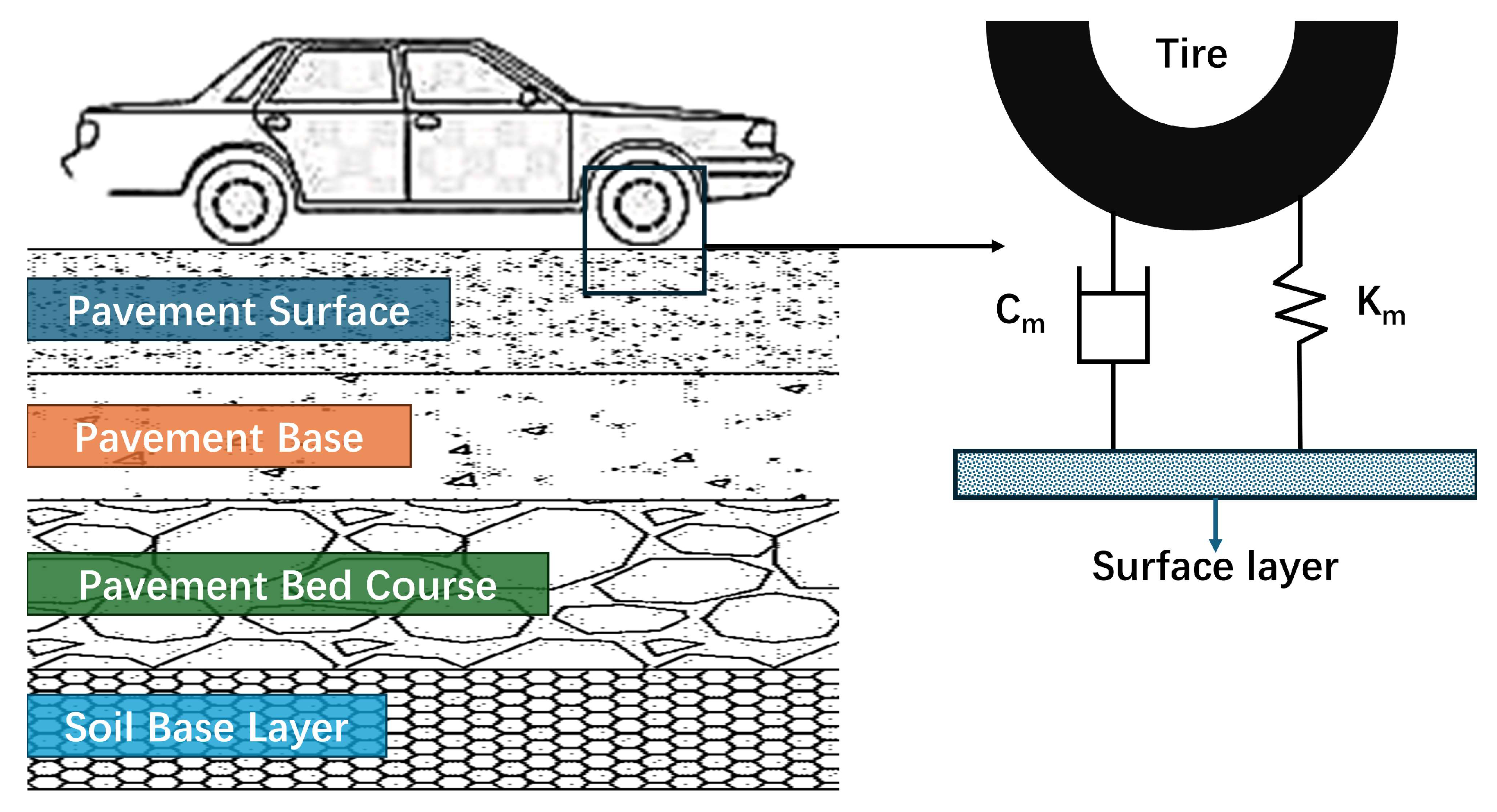
2.3. Pavement Performance
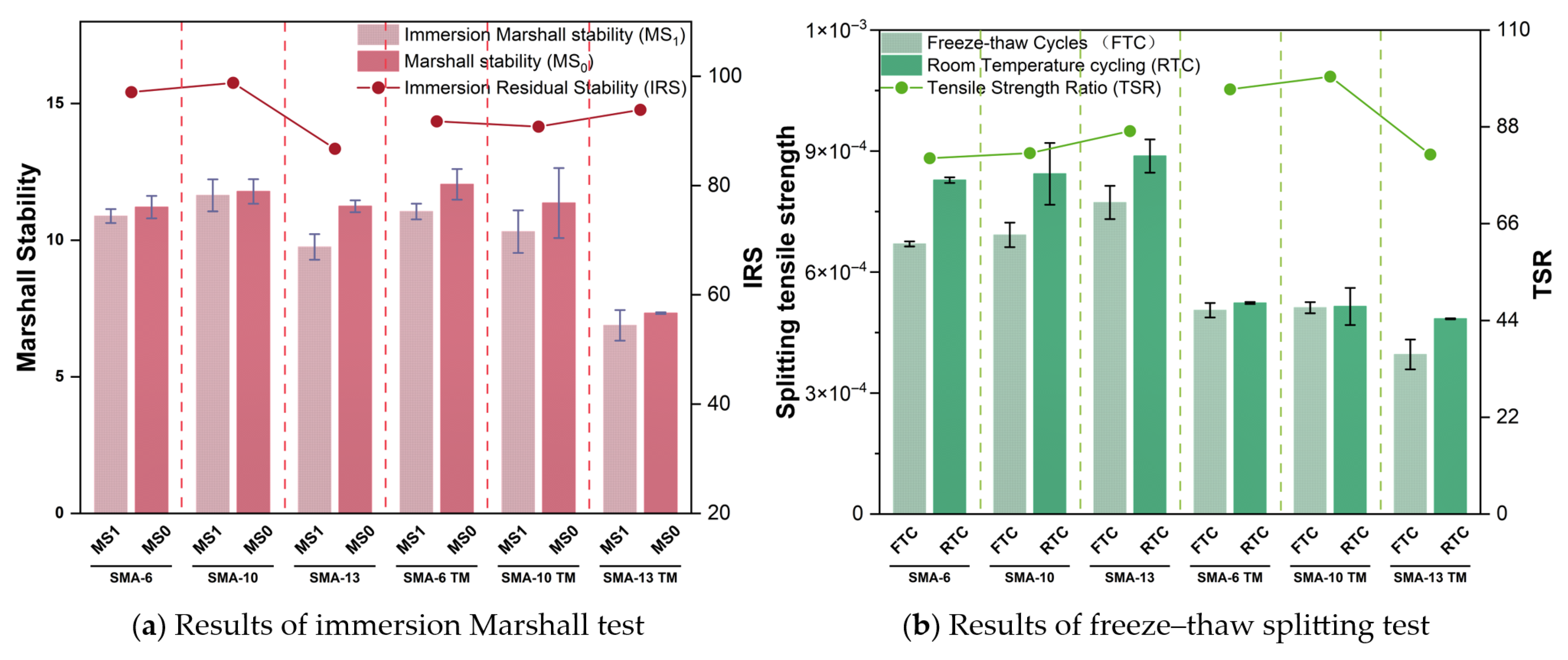
2.3.1. Water Stability
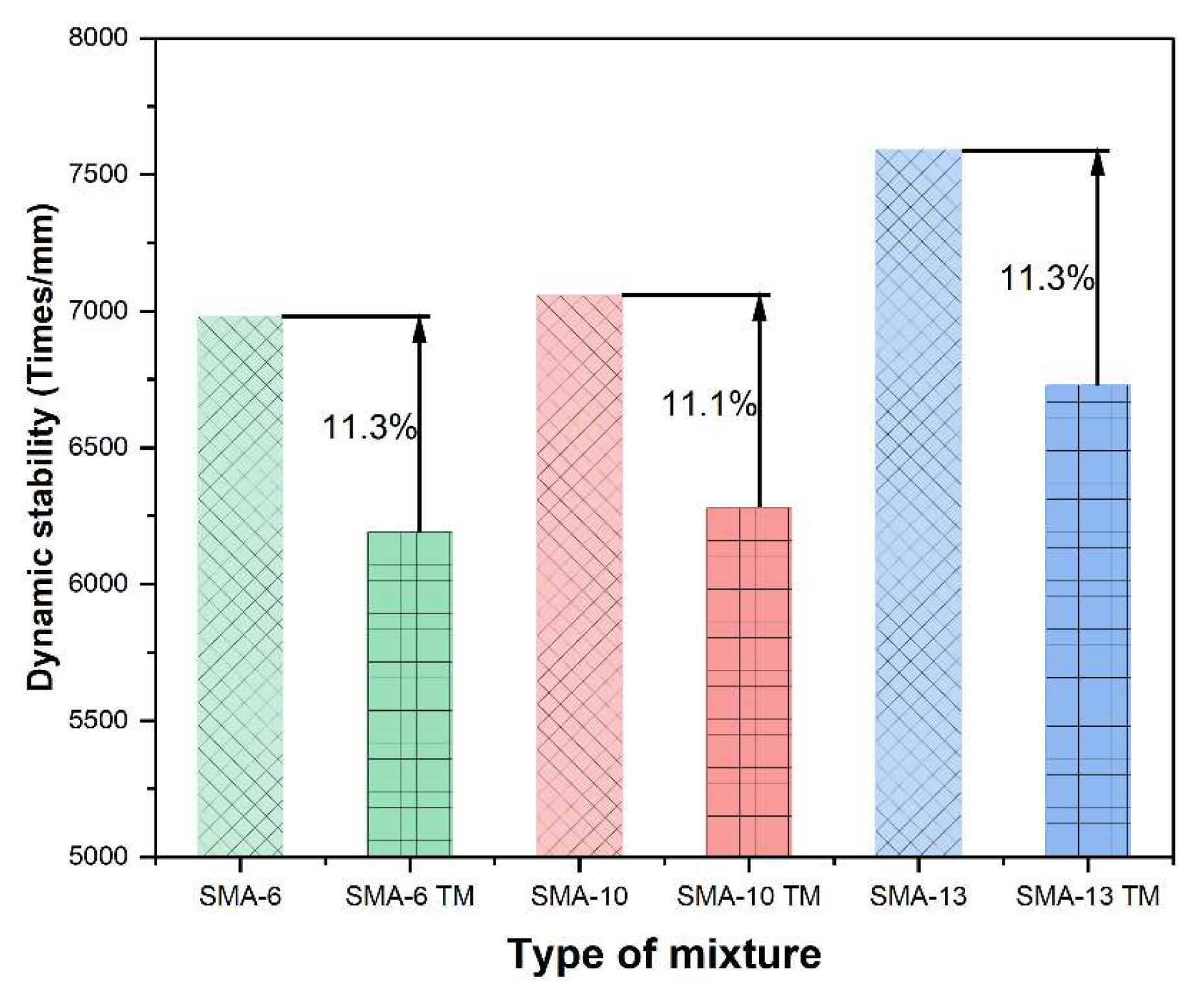
2.3.2. High-Temperature Performance
2.3.3. Low-Temperature Performance
2.4. Viscoelastic Characterization and Energy Dissipation Analysis
2.4.1. Dynamic Modulus Test
2.4.2. Master Curve Construction
2.4.3. Energy Dissipation Parameters
2.5. Damping Analysis
2.5.1. Damping Ratio
2.5.2. Energy Amplification Coefficient and Transfer Coefficient
2.6. Noise Testing
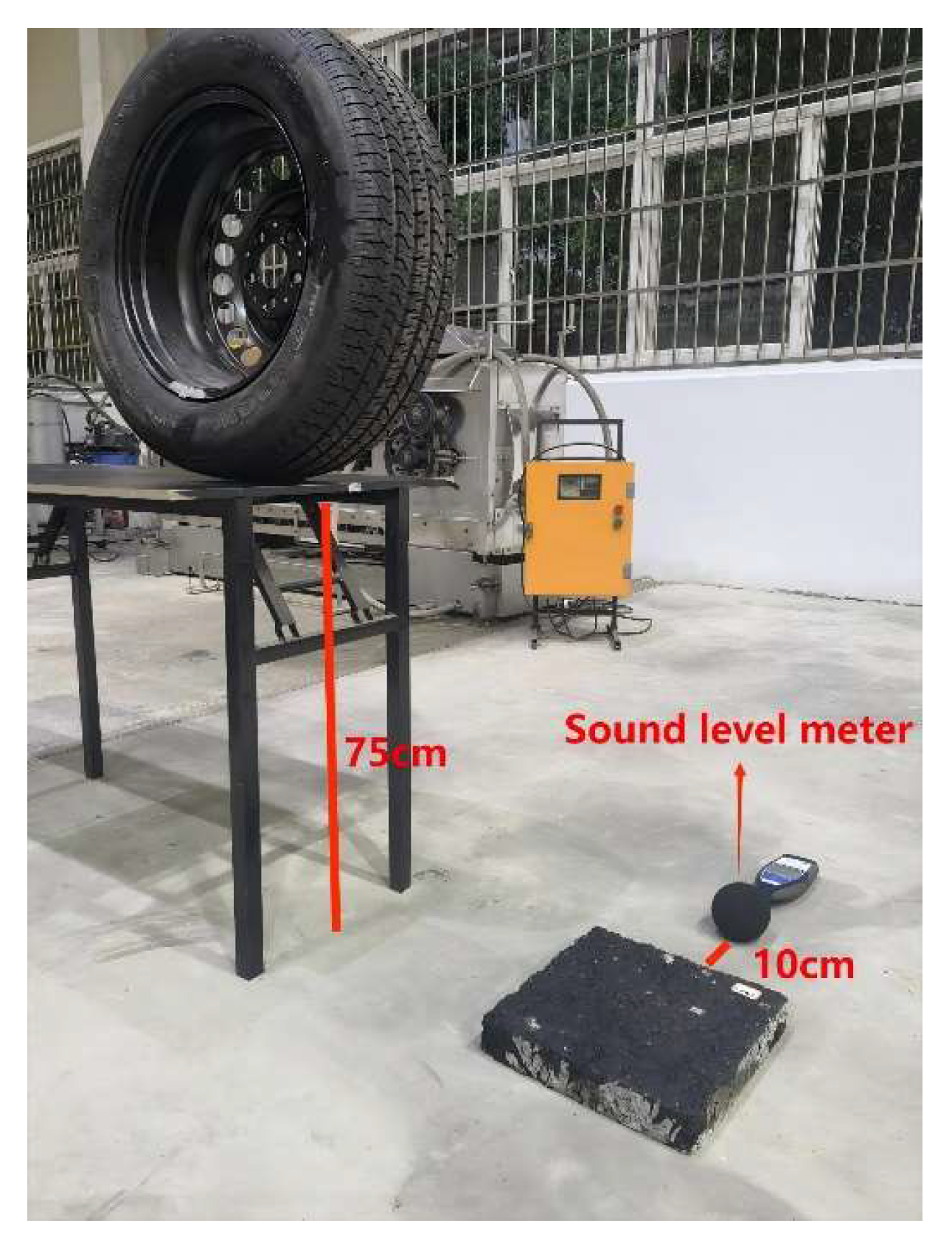
2.6.1. Tire Free Fall Test
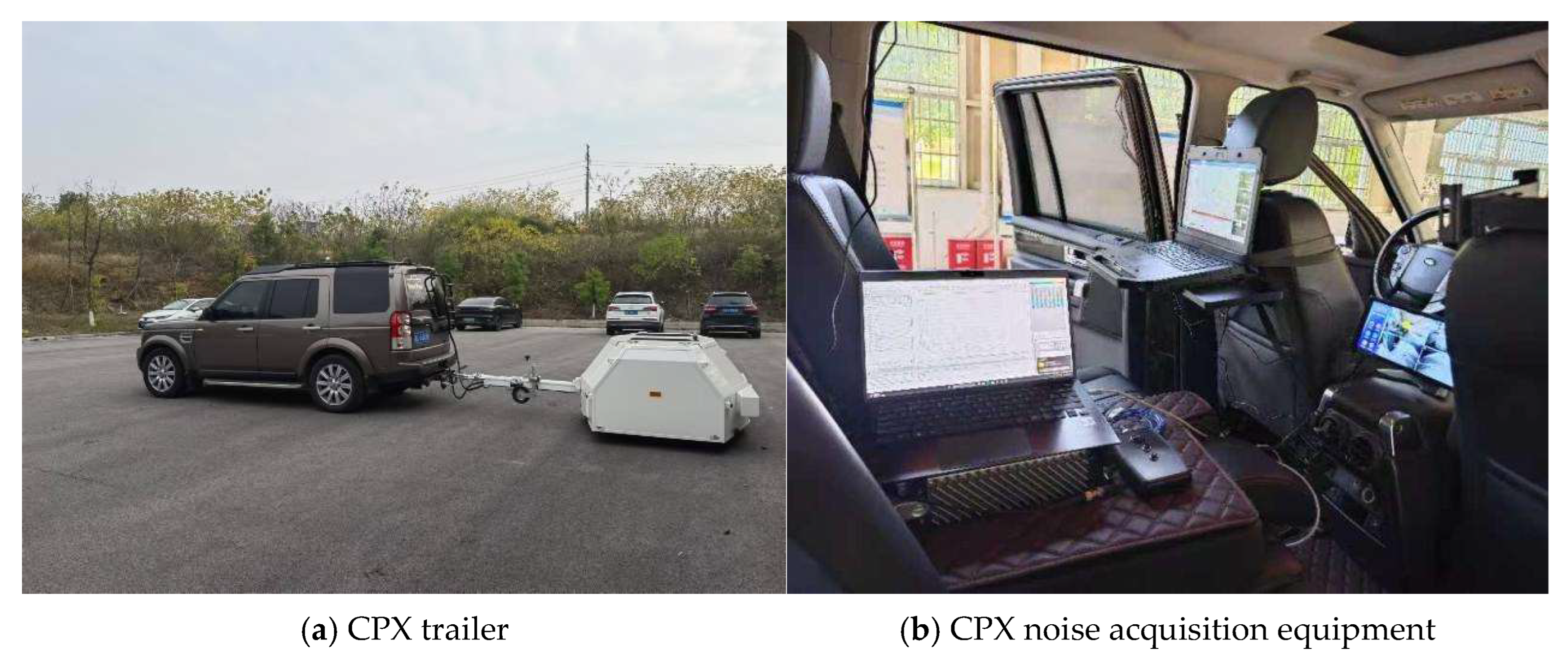
2.6.2. Actual Road Noise Testing
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Pavement Performance
3.1.1. Water Stability Performance
3.1.2. High-Temperature Performance
3.1.3. Low-Temperature Performance
3.2. Energy Dissipation Analysis
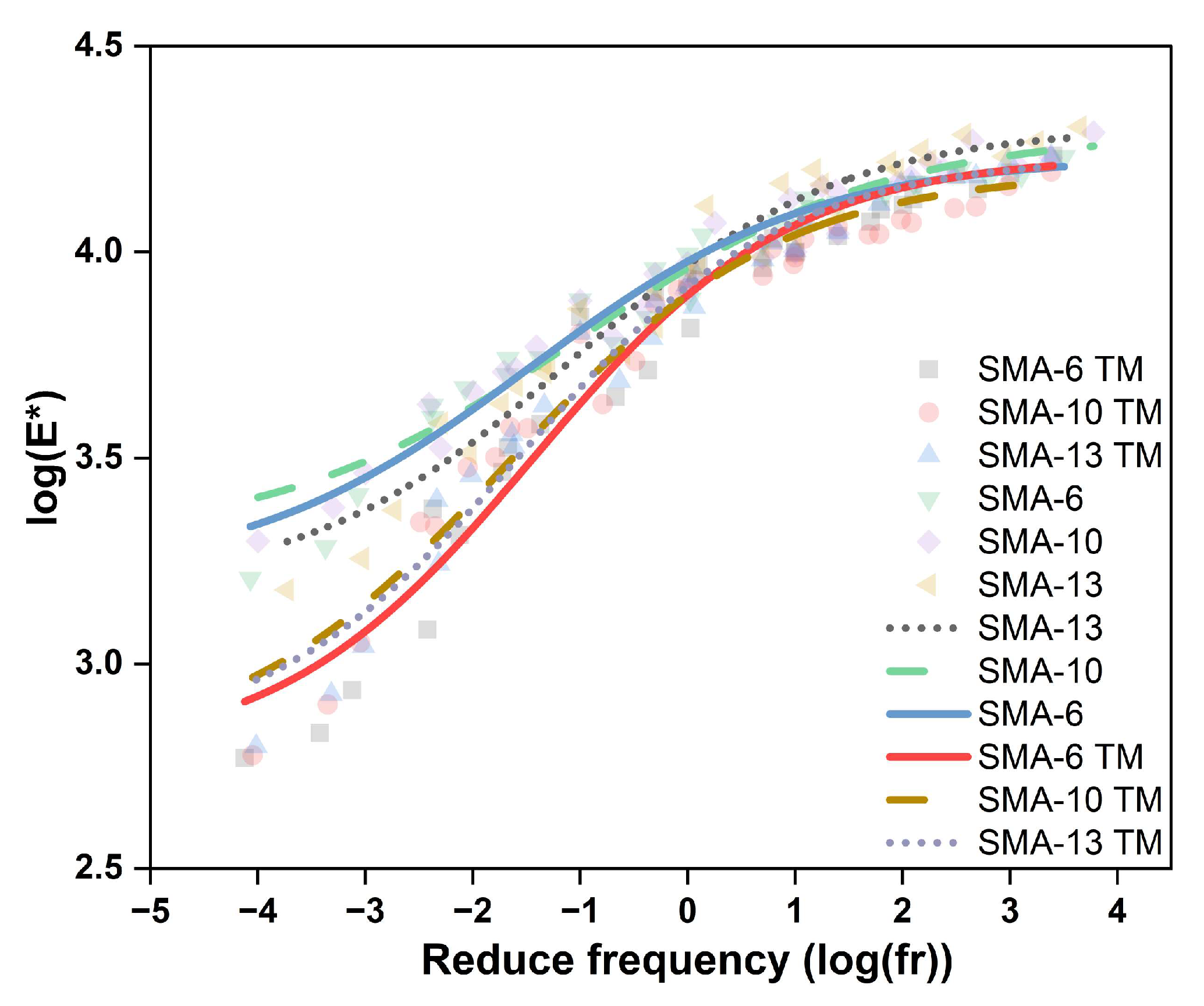
3.2.1. Main Curve Analysis
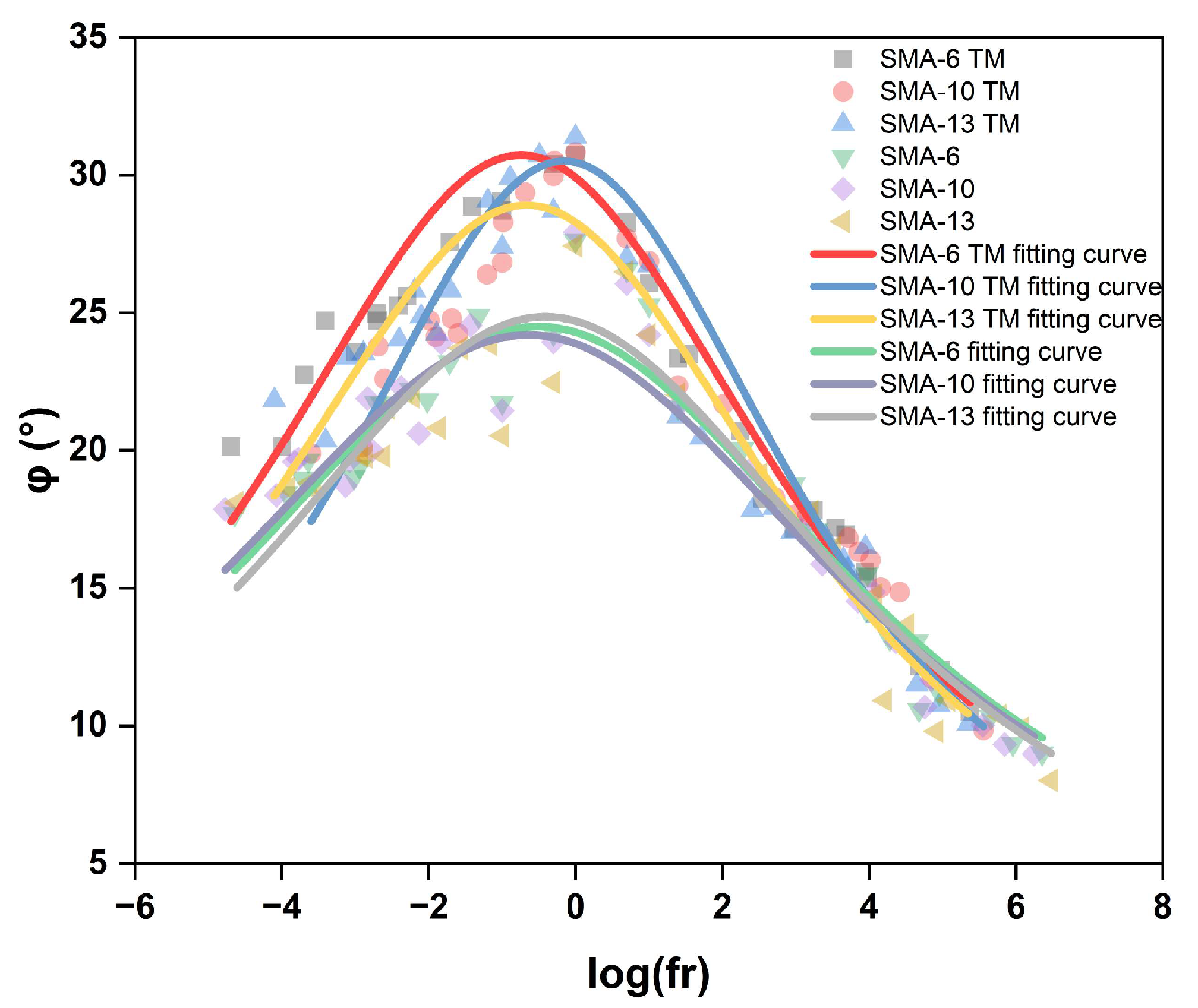
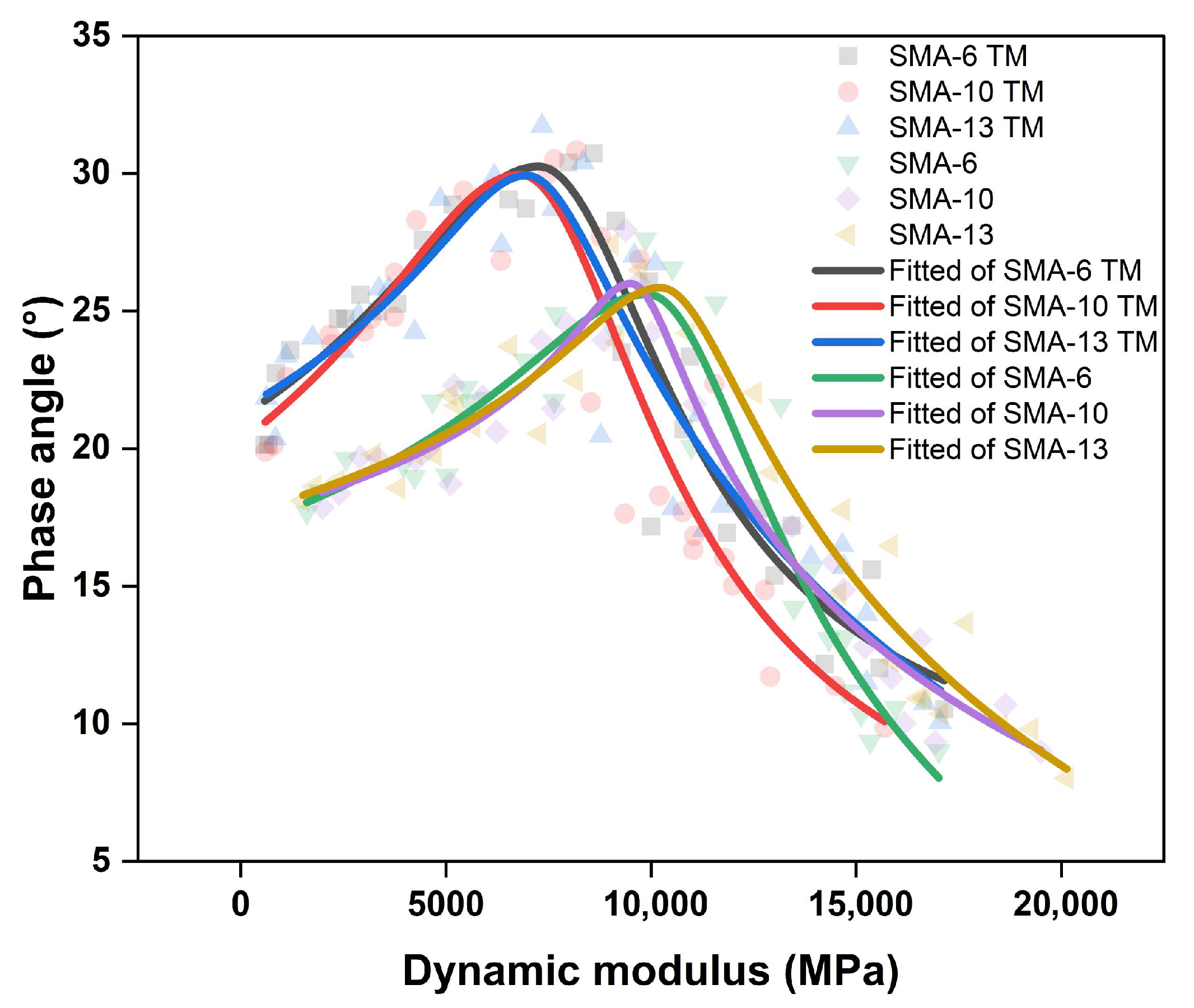
3.2.2. Correlation Analysis Between Dynamic Modulus and Phase Angle
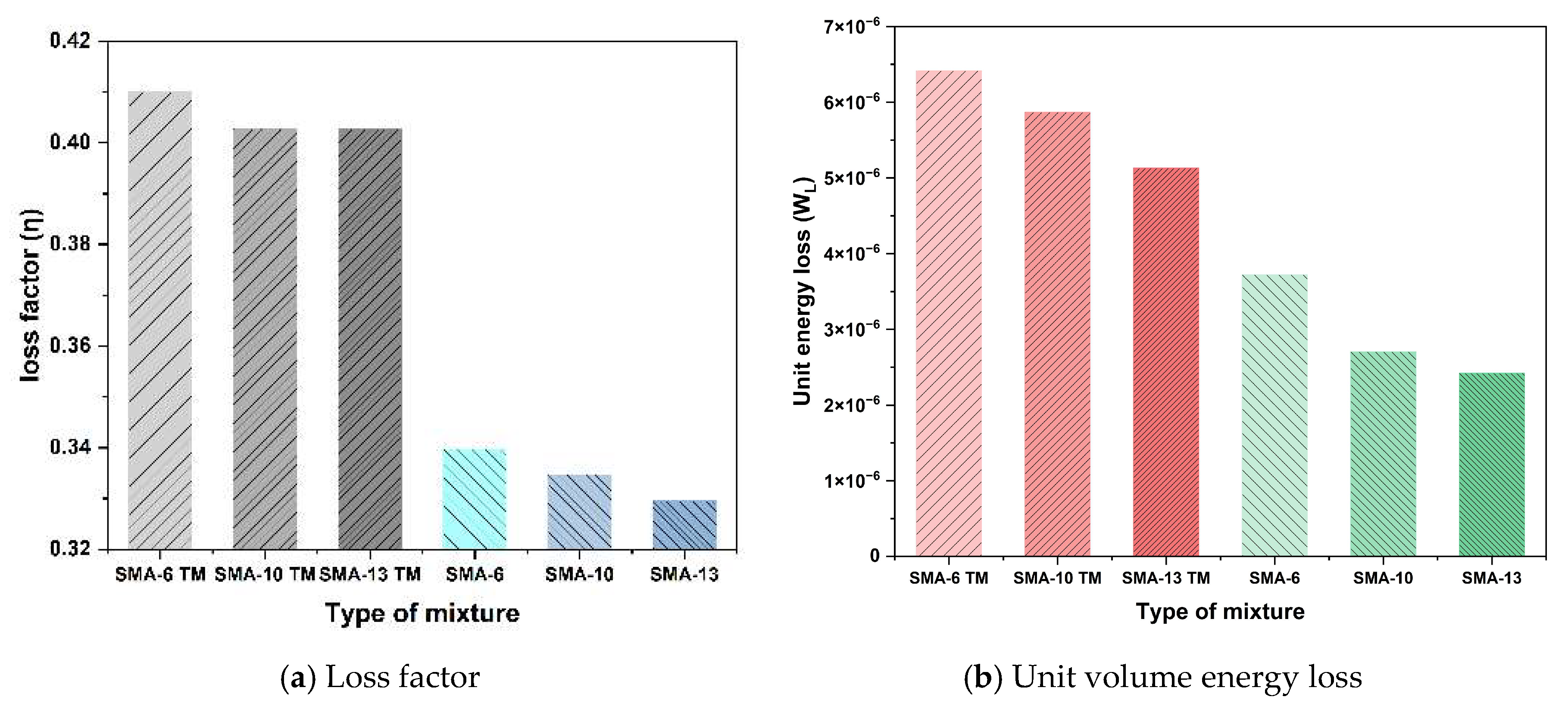
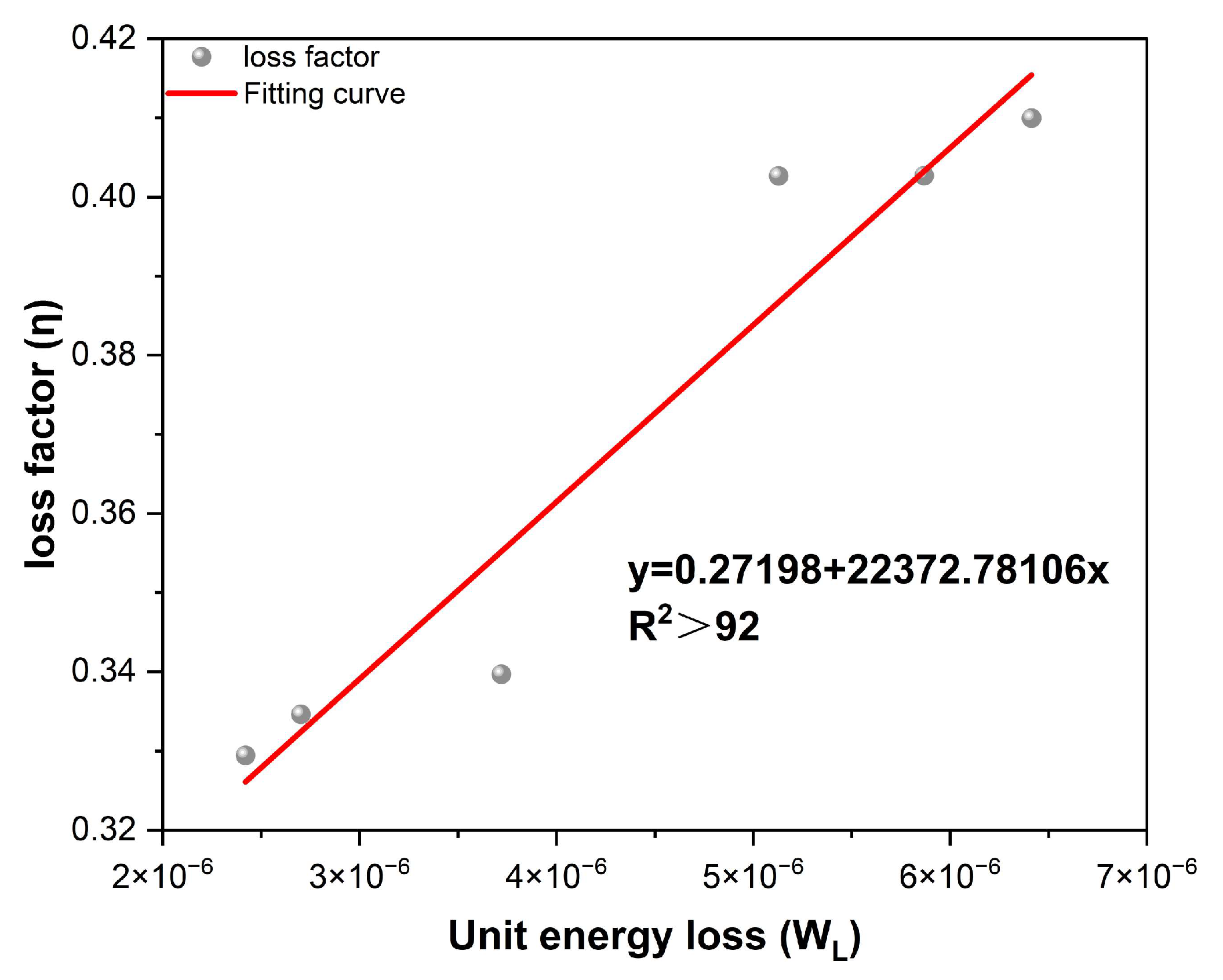
3.2.3. Macro Analysis of Energy Dissipation Characteristics
3.3. Damping Characteristic Analysis
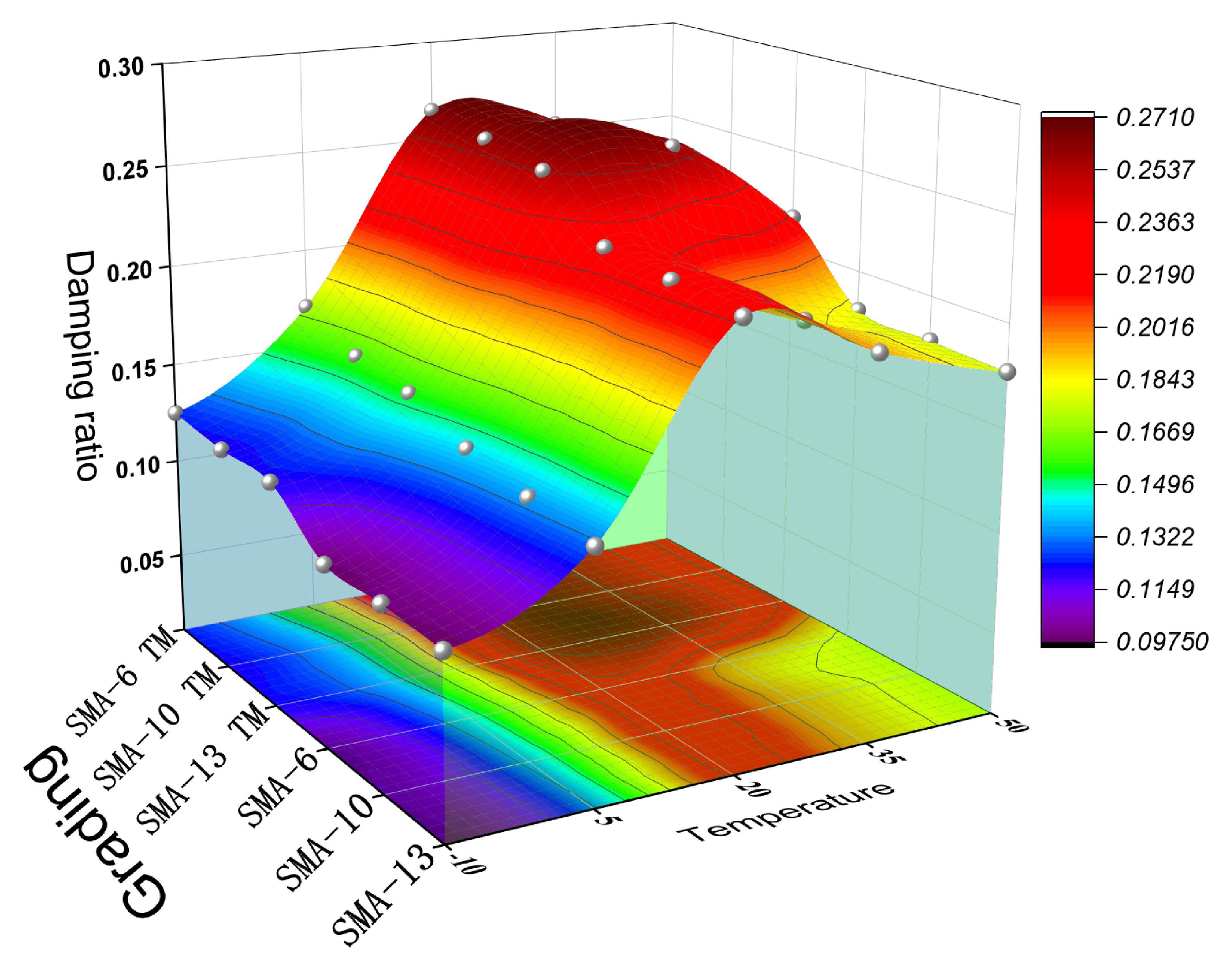
3.3.1. Damping Ratio
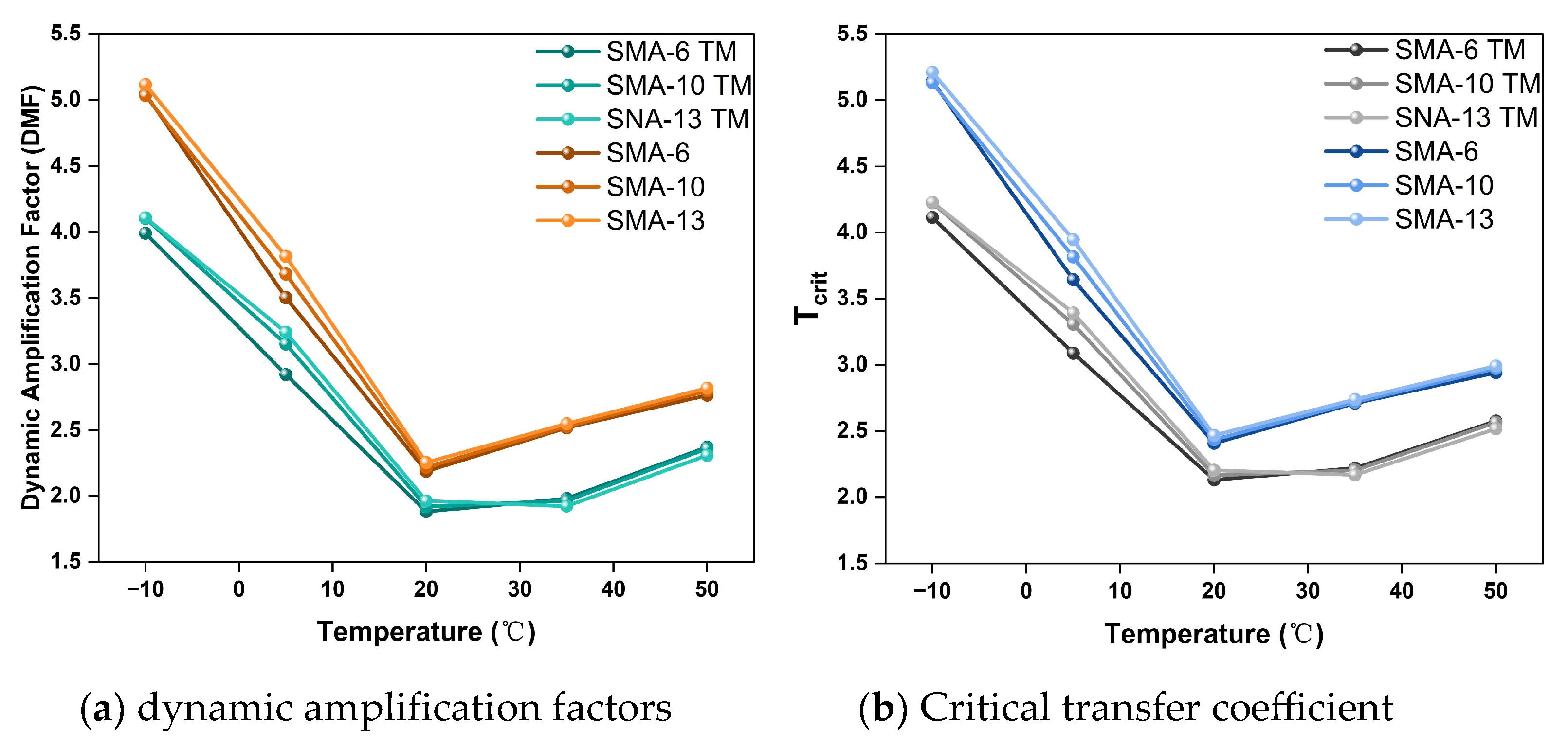
3.3.2. Analysis of Energy Amplification Coefficient and Transfer Coefficient
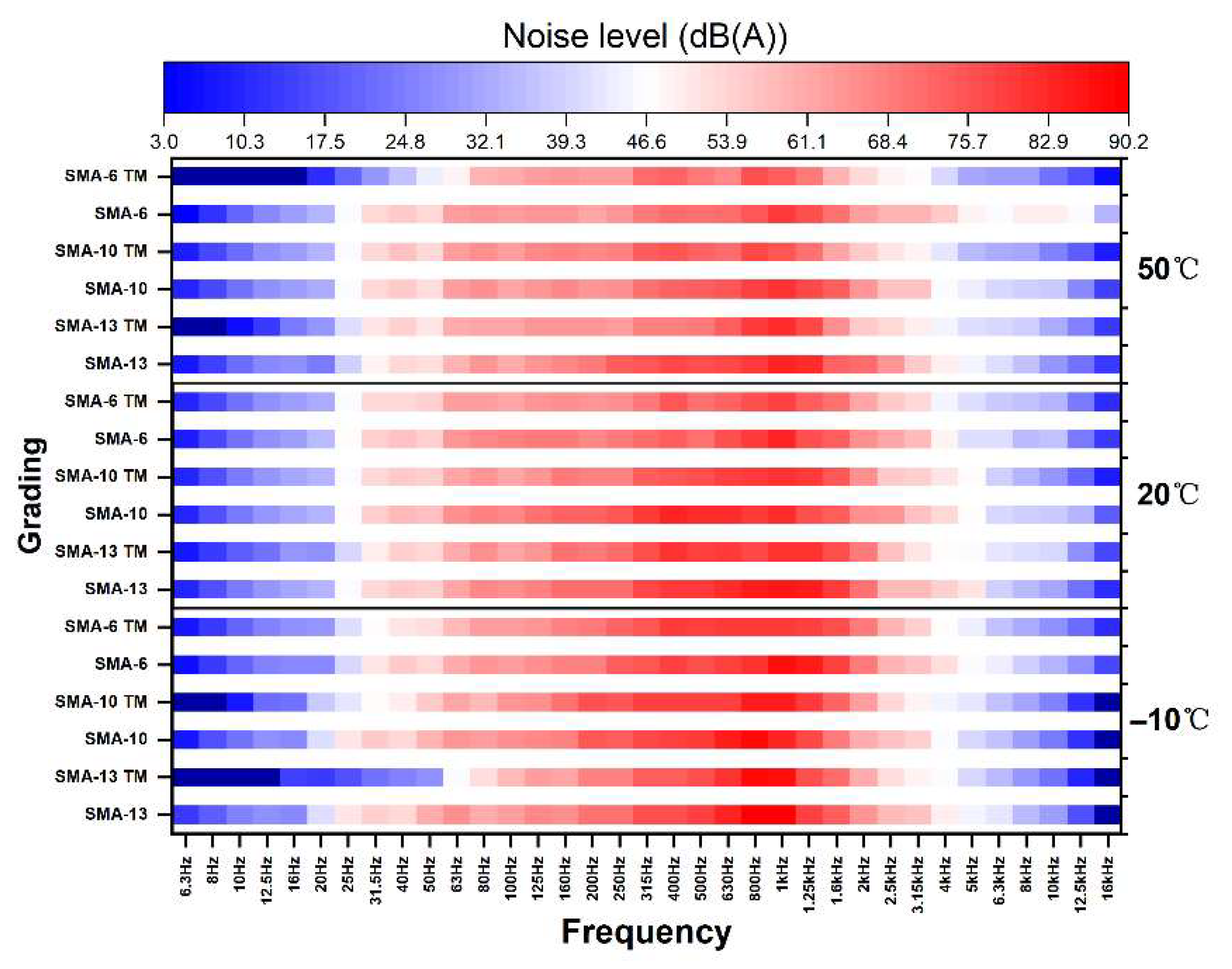
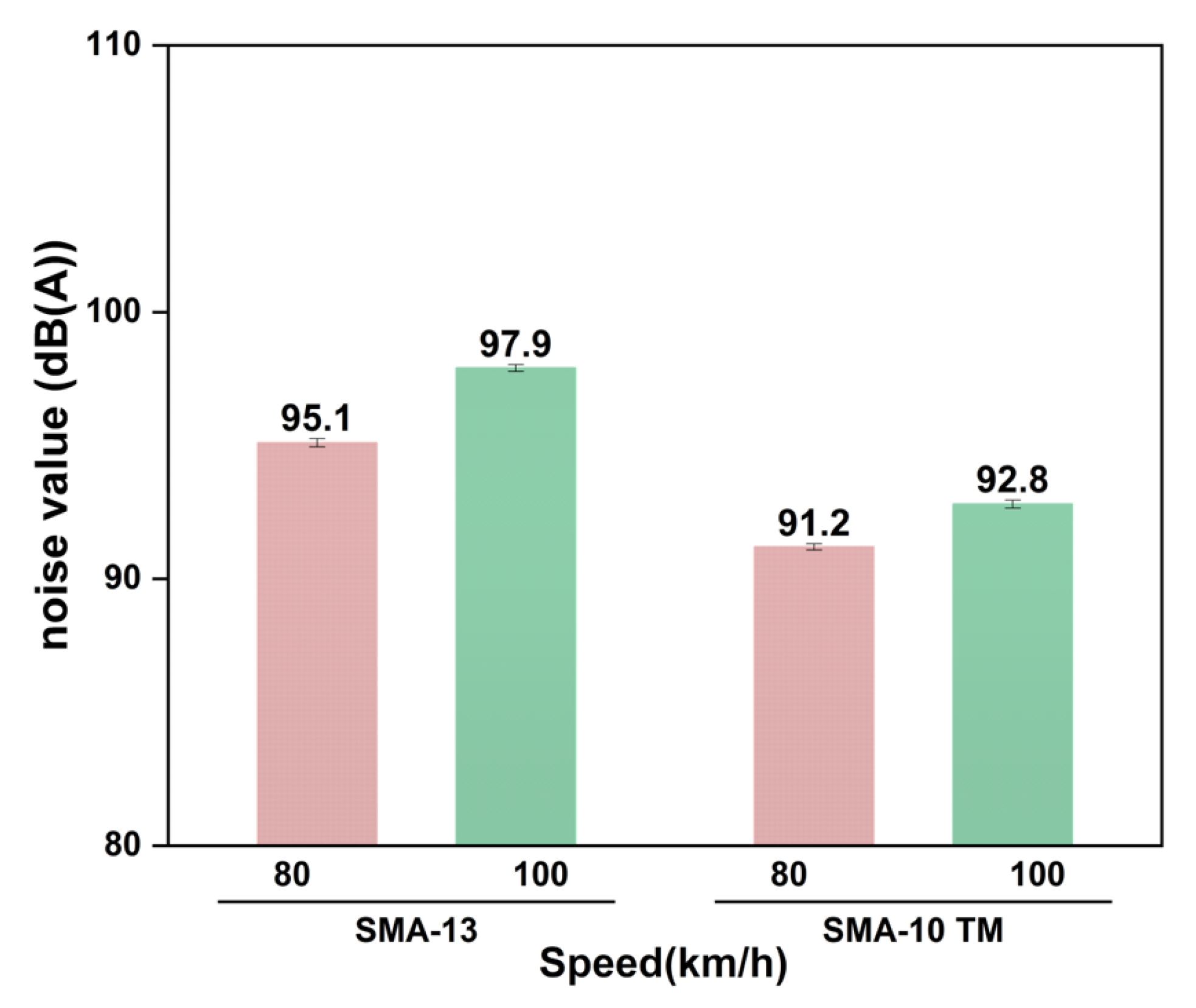
3.4. Analysis of Noise Reduction Effect
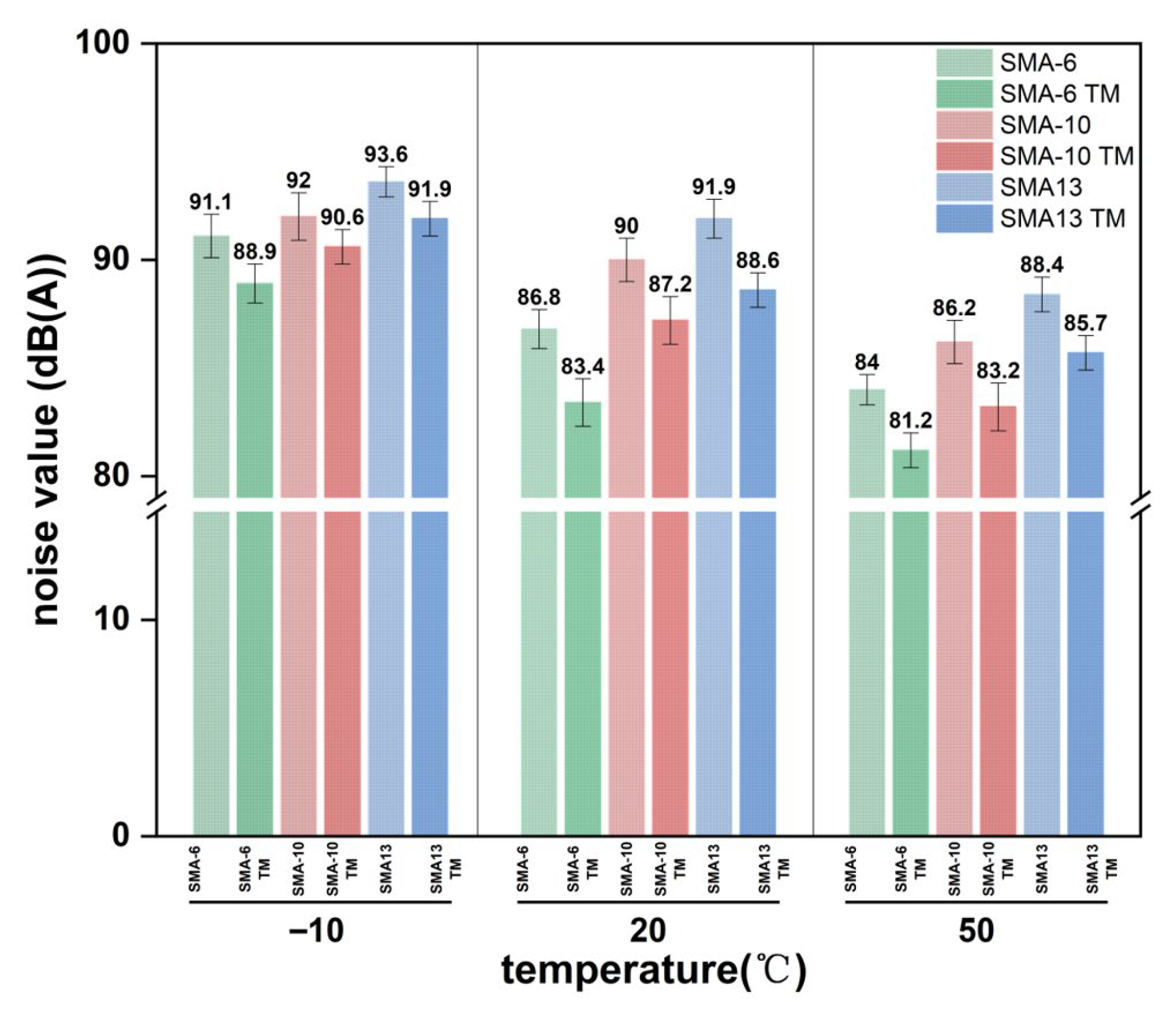
3.4.1. Indoor Damping and Noise Reduction Characteristics
3.4.2. Evaluation of Noise Reduction Effect on Tests Road
4. Conclusions
5. Limitations and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cui, L.; Zhang, Q. Discussion on the Current Situation and Related Issues of Noise Pollution Prevention and Control. Resour. Conserv. Environ. Prot. 2023, 3, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 2022 China Noise Pollution Prevention and Control Report. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/hjzl/sthjzk/hjzywr/202211/W020221116716100586404.pdf (accessed on 16 November 2022).
- Lu, D.; Kwan, M.-P. Influence pathways of noise exposure on people’s negative emotions and health across different activity contexts: A neural network-based double machine learning approach. Health Place 2025, 93, 103455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.S.; Park, Y.M. Presentation on Health Impact Assessment of Transportation Noise. J. Environ. Policy 2009, 8, 63–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aletta, F. Listening to cities: From noisy environments to positive soundscapes. In Frontiers 2022: Noise, Blazes and Mismatches; UN Environment Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 2022; pp. 7–22. [Google Scholar]
- Klompmaker, J.O.; Hoek, G.; Bloemsma, L.D.; Wijga, A.H.; van den Brink, C.; Brunekreef, B.; Lebret, E.; Gehring, U.; Janssen, N.A. Associations of combined exposures to surrounding green, air pollution and traffic noise on mental health. Environ. Int. 2019, 129, 525–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, E.; Silva, L.; Vuye, C. The influence of pavement degradation on population exposure to road traffic noise. Coatings 2019, 9, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fyhri, A.; Aasvang, G.M. Noise, sleep and poor health: Modeling the relationship between road traffic noise and cardiovascular problems. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 4935–4942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trojanová, M.; Játy, L. Noise Polution from Roundabut Traffic in the Outer Environment of Built-Up Areas of Towns. Int. Multidiscip. Sci. GeoConf. SGEM 2012, 4, 927–934. [Google Scholar]
- Ohiduzzaman, M.; Sirin, O.; Kassem, E.; Rochat, J.L. State-of-the-art review on sustainable design and construction of quieter pavements—Part 1: Traffic noise measurement and abatement techniques. Sustainability 2016, 8, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T. Literature review of tire-pavement interaction noise and reduction approaches. J. Vibroeng. 2018, 20, 2424–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berge, T.; Mioduszewski, P.; Ejsmont, J. Reduction of road traffic noise by source measures—Present and future strategies. Noise Control Eng. J. 2017, 65, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailenko, P.; Piao, Z.; Kakar, M.R.; Bueno, M.; Athari, S.; Pieren, R.; Heutschi, K.; Poulikakos, L. Low-Noise pavement technologies and evaluation techniques: A literature review. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2022, 23, 1911–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, A.E. Overview of noise control techniques and methods. In Noise Control; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Cao, K.; Zhou, J.; Li, A.; Sun, M. Laboratory investigation on influence of mixture parameters on noise reduction characteristics of porous asphalt concrete. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2023, 24, 2092619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, K.; Xiao, P.; Kang, A.; Wu, Z.; Dong, X. Effects of asphalt pavement characteristics on traffic noise reduction in different frequencies. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2022, 106, 103259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, H.; Yu, T.; Wu, G.; Jia, M. Influence of void content on noise reduction characteristics of different asphalt mixtures using meso-structural analysis. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 325, 126806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Castro-Fresno, D.; Lastra-Gonzalez, P.; Rodriguez-Hernandez, J. Selection of fibers to improve porous asphalt mixtures using multi-criteria analysis. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 266, 121198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiselev, A.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Z. The effect of two-phase mixing on the functional and mechanical properties of TPS/SBS-modified porous asphalt concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 270, 121841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Du, L.; Dai, W.; Zhang, K.; Wang, Y.; Guo, W. Study on the pore blocking characteristics and cleaning methods of permeable asphalt mixtures based on accelerated clogging simulation experiments. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 21, e03438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Li, K.; Li, C.; Wang, H.; Leng, Z.; Chen, X. Noise reduction performance and maintenance time of porous asphalt pavement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 452, 138913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhao, H.; Zhou, J.; Yao, T.; Guo, F.; Hu, Y. Investigation on sound absorption coefficients of porous asphalt concrete under different clogging conditions. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 428, 136081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Li, C.; Lu, W.; Lv, S.; Duan, H.; Lv, H.; Ding, L. Road performance and noise reduction characteristics of dense graded dry-process rubberised asphalt mixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 467, 140312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabani, M.; Tahami, S.A.; Hamedi, G.H. Performance evaluation of dry process crumb rubber-modified asphalt mixtures with nanomaterial. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2018, 19, 1241–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDaniel, R.; Shah, A.; Dare, T.; Bernhard, R. Hot Mix Asphalt Surface Characteristics Related to Ride, Texture, Friction, Noise and Durability; Institute for Safe, Quiet, and Durable Highways North Central Superpave Center Purdue University: West Lafayette, IN, USA, 2014; Volume 7. [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson, N.-A. Principles in the control of external tire/road noise. In Proceedings of the INTER-NOISE and NOISE-CON Congress and Conference Proceedings; Institute of Noise Control Engineering: Wakefield, MA, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Poulikakos, L.; Athari, S.; Mikhailenko, P.; Piao, Z.; Kakar, M.R.; Bueno, M.; Pieren, R.; Heutschi, K. Use of Waste and Marginal Materials for Silent Roads; Universitätsbibliothek der RWTH Aachen: Aachen, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Steiner, S.; Bühlmann, E.; Hammer, E. Milestones in establishing low-noise asphalts as a widely used, effective and durable noise abatement measure in Switzerland. In Proceedings of the Euronoise 2018, Crete, Greece, 27–31 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Piao, Z.; Heutschi, K.; Pieren, R.; Mikhailenko, P.; Poulikakos, L.D.; Hellweg, S. Environmental trade-offs for using low-noise pavements: Life cycle assessment with noise considerations. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 842, 156846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Ni, H.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, D.; Zheng, Y.; Hu, M. Porous asphalt mixture use asphalt rubber binders: Preparation and noise reduction evaluation. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 376, 134119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šernas, O.; Vaitkus, A.; Gražulytė, J.; Skrodenis, D.; Wasilewska, M.; Gierasimiuk, P. Development of low noise and durable semi-dense asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 293, 123413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angst, C.; Bürgisser, P.; Beckenbauer, T. Investigation machine for pavement acoustic durability; impact testing the durability of low noise road surface. In Proceedings of the 5th Eurasphalt & Eurobitume Congress, Istanbul, Turkey, 13–15 June 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Miljković, M.; Radenberg, M. Thin noise-reducing asphalt pavements for urban areas in Germany. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2012, 13, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardziejczyk, W.; Gierasimiuk, P.; Motylewicz, M. Noisiness of the surfaces on low-speed roads. Coatings 2016, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praticò, F.G.; Anfosso-Lédée, F. Trends and issues in mitigating traffic noise through quiet pavements. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2012, 53, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhard, R.; Wayson, R.L.; Haddock, J.; Neithalath, N.; El-Aassar, A.; Olek, J.; Pellinen, T.; Weiss, W.J. An Introduction to Tire/Pavement Noise of Asphalt Pavement; Institute of Safe, Quiet and Durable Highways, Purdue University: West Lafayette, IN, USA, 2005; Volume 26, p. 26. [Google Scholar]
- Caputo, P.; Miriello, D.; Bloise, A.; Baldino, N.; Mileti, O.; Ranieri, G.A. A comparison and correlation between bitumen adhesion evaluation test methods, boiling and contact angle tests. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2020, 102, 102680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caputo, P.; Rossi, C.O.; Calandra, P.; Policastro, D.; Giorno, E.; Godbert, N.; Aiello, I. Improving Bitumen Properties with Chitosan: A Sustainable Approach to Road Construction. Molecules 2025, 30, 1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, V.; Terán, F.; Paje, S. Dynamic stiffness of road pavements: Construction characteristics-based model and influence on tire/road noise. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 736, 139597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biligiri, K.P.; Kalman, B.; Samuelsson, A. Understanding the fundamental material properties of low-noise poroelastic road surfaces. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2013, 14, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biligiri, K.P. Effect of pavement materials’ damping properties on tyre/road noise characteristics. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 49, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Hangtian, N.; Yufeng, T.; Daquan, S.; Zhongbo, C.; Hao, J. Multi-scale analysis of damping characteristics of dry mixed rubberized porous asphalt mixtures for tire-pavement noise reduction. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 425, 138969. [Google Scholar]
- Vaitkus, A.; Čygas, D.; Vorobjovas, V.; Andriejauskas, T. Traffic/road noise mitigation under modified asphalt pavements. Transp. Res. Procedia 2016, 14, 2698–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JTG E42-2005; Test Methods of Aggregate for Highway Engineering. China National Standardization Administration: Beijing, China, 2005.
- JTG E20-2011; Specification for Tests of Asphalt and Asphalt Mixtures for Highway Engineering. China National Standardization Administration: Beijing, China, 2011.
- Lin, S.; Hung, W.; Leng, Z. Air pollutant emissions and acoustic performance of hot mix asphalts. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 129, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Birgisson, B.; Luo, X. A new dynamic modulus predictive model for asphalt mixtures based on the law of mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 255, 119348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, N.; Xiao, F.; Wang, J.; Amirkhanian, S. Precision analysis of sigmoidal master curve model for dynamic modulus of asphalt mixtures. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2018, 30, 04018290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arefin, M.S.; Quasem, T.; Nazzal, M.; Dessouky, S.; Abbas, A.R. Accuracy of MEPDG dynamic modulus predictions for short-term and long-term aged asphalt mixtures. J. Transp. Eng. Part B Pavements 2019, 145, 04019025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardziejczyk, W.; Jaskula, P.; Ejsmont, J.A.; Motylewicz, M.; Stienss, M.; Mioduszewski, P.; Gierasimiuk, P.; Zawadzki, M. Investigation of acoustic properties of poroelastic asphalt mixtures in laboratory and field conditions. Materials 2021, 14, 2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q. Research on the Vibration and Noise Reduction Performance of Double Layer Crushed Stone Seal Coating with Rubber Particles. Master’s Thesis, Chang’an University, Xi’an, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- JT/T 1465-2023; Proximity Test Method for the Effect of Road on Tire Noise. China National Standardization Administration: Beijing, China, 2023.
- Liu, Z.; Sun, L.; Li, J.; Liu, L. Effect of key design parameters on high temperature performance of asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 348, 128651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Bao, J. Micromechanical analysis of asphalt-mixture shear strength using the three-dimensional discrete element method. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2018, 30, 04018302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooley, L., Jr.; Brown, E.R.; Maghsoodloo, S. Developing critical field permeability and pavement density values for coarse-graded superpave pavements. Transp. Res. Rec. 2001, 1761, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, E.S.; Thives, L.P.; Ghisi, E.; Antunes, L.N. Analysis of permeability reduction in drainage asphalt mixtures due to decrease in void volume. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 248, 119292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nian, T.; Ge, J.; Li, P.; Wang, M.; Mao, Y. Improved discrete element numerical simulation and experiment on low-temperature anti-cracking performance of asphalt mixture based on PFC2D. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 283, 122792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Qian, G.; Yu, H.; He, Z.; Ge, J.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, H. Research on evolution of structural characteristics of force chain network during asphalt mixture compaction process. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2025, 22, e04468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, D.I.; James, R.S.; NeSmith, C. Tire/Pavement Noise Study; National Center for Asphalt Technology: Auburn, AL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]





| Aggregate Type | Test Items | Unit | Result | Specification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coarse aggregate | Crushing value | % | 12.4 | <18 |
| Los Angeles abrasion loss | % | 8.0 | <22 | |
| Apparent specific gravity | t/m3 | 2.926 | ≥2.6 | |
| Water absorption | % | 0.63 | ≤1.0 | |
| Fine aggregate | Apparent relative density | t/m3 | 2.728 | ≥2.6 |
| Soundness | % | 18 | >12 | |
| Sand equivalent | % | 67 | >65 | |
| Methylene blue value | g/kg | 1.3 | <2.5 | |
| Mineral powder | Apparent density | t/m3 | 2.757 | ≥2.5 |
| Moisture content | % | 0.6 | ≤1 | |
| Hydrophilicity coefficient | / | 0.82 | <1 | |
| Plasticity index | % | 2.4 | <4 |
| Indicator | Result | Requirement | Specification (JTG E20-2011) [45] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Penetration (25 °C, 5 s, 100 g) (0.1 mm) | 49.5 | 40–60 | T 0604 |
| Softening point (°C) | 97.9 | ≥60 | T 0604 |
| Ductility (5 °C, 5 cm/min) (cm) | 49.8 | ≥20 | T 0606 |
| 60 °C dynamic viscosity (Pa·s) | 507,881.5 | ≥200,000 | T 0605 |
| Test Parameters | Unit | Test Results | Technical Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ash content | % | 19.4 | 13~23 |
| pH value | - | 8.0 | 6.5~8.5 |
| Oil absorption rate | % | 6.1 | 5~9 |
| Moisture content | % | 3.7 | ≤5 |
| Mass loss (210 °C, 1 h) | % | 2.6, No combustion | ≤6, No combustion |
| Maximum length | mm | 3.8 | ≤6 |
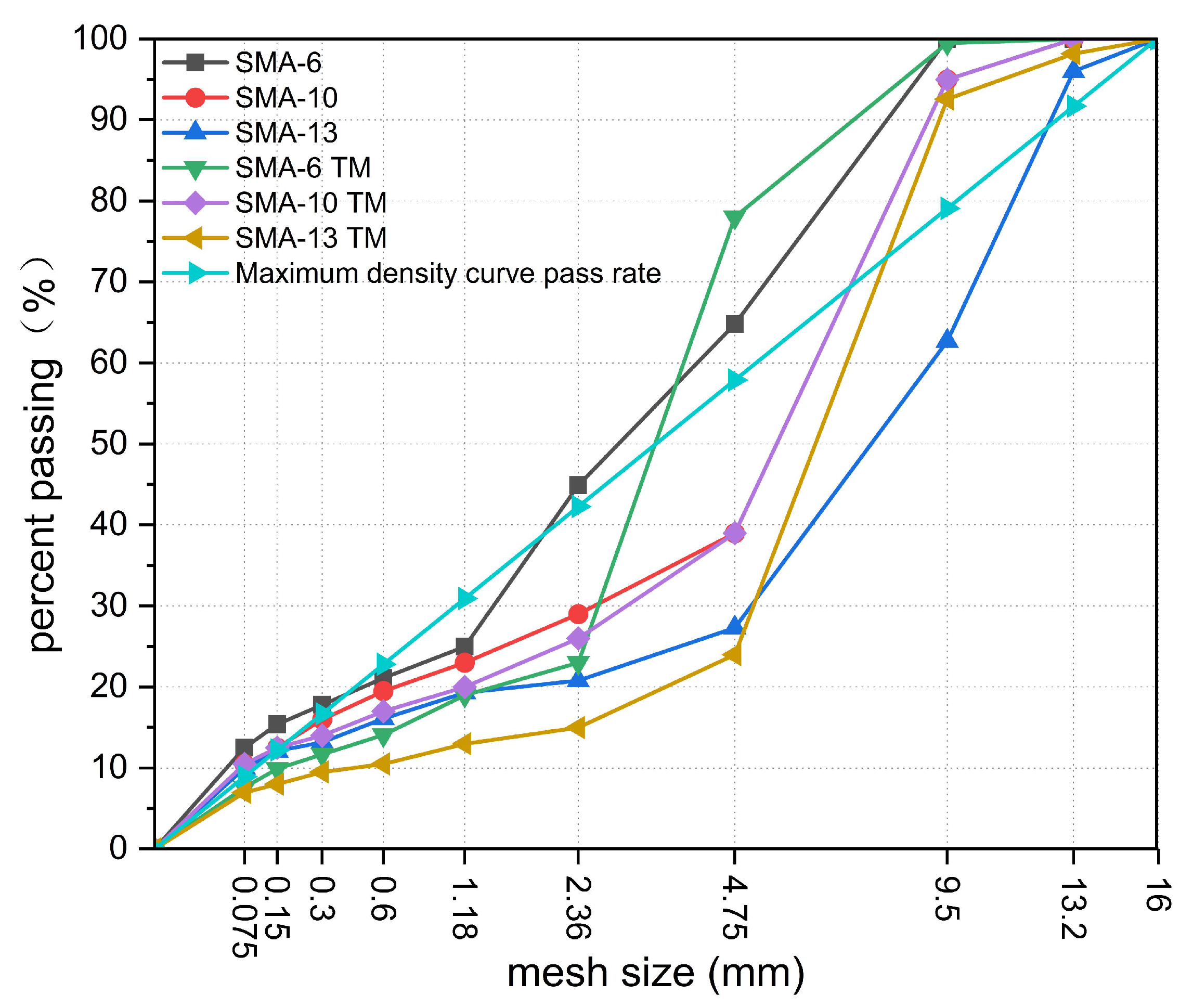
| Gradation Types | Target Porosity | Asphalt–Aggregate Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| SMA-6 | 4% | 6.32% |
| SMA-10 | 6.42% | |
| SMA-13 | 6.2% | |
| SMA-6 TM | 9% | 6.47% |
| SMA-10 TM | 6.26% | |
| SMA-13 TM | 6.44% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lv, H.; Xin, G.; Lu, W.; Duan, H.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Rao, C.; Jiang, R. Optimizing Acoustic Performance of Semi-Dense Asphalt Mixtures Through Energy Dissipation Characterization. Materials 2025, 18, 4086. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18174086
Lv H, Xin G, Lu W, Duan H, Wang J, Yang Y, Rao C, Jiang R. Optimizing Acoustic Performance of Semi-Dense Asphalt Mixtures Through Energy Dissipation Characterization. Materials. 2025; 18(17):4086. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18174086
Chicago/Turabian StyleLv, Huaqing, Gongfeng Xin, Weiwei Lu, Haihui Duan, Jinping Wang, Yi Yang, Chaoyue Rao, and Ruiyao Jiang. 2025. "Optimizing Acoustic Performance of Semi-Dense Asphalt Mixtures Through Energy Dissipation Characterization" Materials 18, no. 17: 4086. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18174086
APA StyleLv, H., Xin, G., Lu, W., Duan, H., Wang, J., Yang, Y., Rao, C., & Jiang, R. (2025). Optimizing Acoustic Performance of Semi-Dense Asphalt Mixtures Through Energy Dissipation Characterization. Materials, 18(17), 4086. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18174086





